Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 地理
地理


赤道通常指地球表面的点随地球自转产生的轨迹中周长最长的圆周线,长约40,000公里。如果把地球看做一个绝对的球体的话,赤道距离南北两极相等。它把地球分为南北两半球,其以北是北半球,以南是南半球,是划分纬度的基线,赤道的纬度为0°。赤道的78.7%被海洋覆盖,余下的21.3%为陆地。
赤道的纬度被定义为0°,与两条极圈及两条回归线——北回归线和南回归线组成地球表面五条重要的纬线,而赤道又是其中唯一一个大圆。地球赤道在天球上的投影则是天球赤道。
在太阳的季节性视运动中,每年经过赤道两次,分别在春分、秋分。此时太阳光在赤道处与地球表面垂直,即直射赤道。
由于太阳几乎全年都垂直地升落,赤道上看到的日出和日落是地球表面最快的。赤道上的昼长(日出到日落)也几乎全年保持不变[1];由于大气折射[2],以及日出日落是太阳的边缘而非中心触及地平线的缘故,每天的白昼都比夜晚长约14分钟。
Der Äquator eines Planeten oder sonstigen rotationsellipsoiden Himmelskörpers ist der auf seiner Oberfläche angenommene Großkreis, auf dessen Ebene (der Äquatorebene) die Rotationsachse senkrecht steht.[1] Die Erdoberfläche wird vom Äquator in eine Nord- und eine Südhälfte unterteilt, woher der lat. Name „Gleichmacher“ (veraltet „Gleicher“) stammt. Er ist Bezugskreis für die parallelen Kleinkreise, die zur Bemaßung der Erde in Nord-Süd-Richtung mit Hilfe von Breitenkreisen verwendet werden. Er selbst hat die geographische Breite 0°.
Der Schnitt der Äquatorebene der Erde mit der um die Erde gedachten Himmelskugel ist der Himmelsäquator.
In der Geometrie wird der Begriff Äquator allgemein auf die Kugel in Verbindung mit einer durch ihren Mittelpunkt festgelegten Achse angewendet.
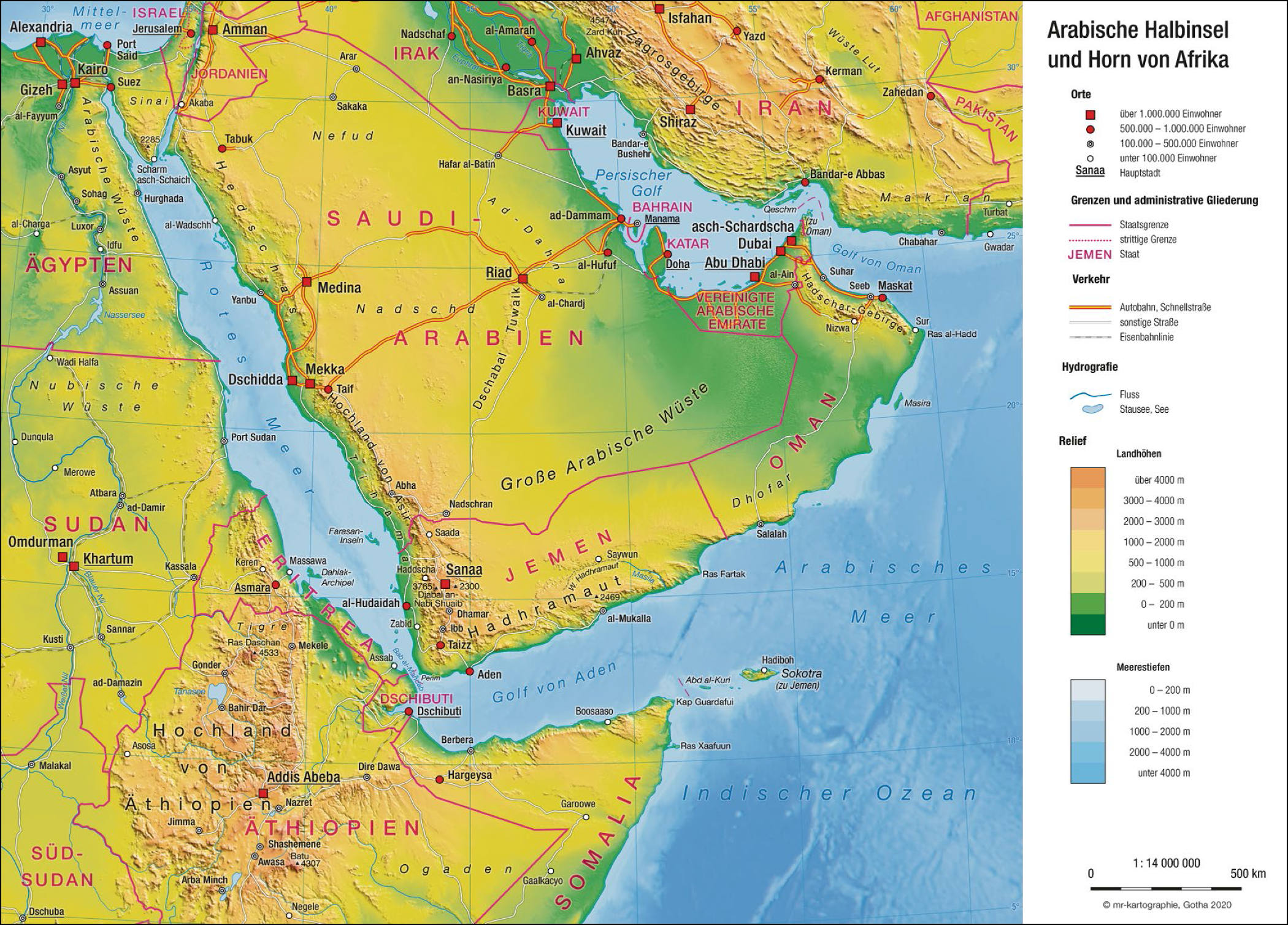
阿拉伯半岛(/əˈreɪbiə/; 阿拉伯语:شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, shibhu l-jazīrati l-ʿarabiyyah, “阿拉伯半岛”或 جَزِيرَةُ الْعَرَب, jazīratu l-ʿarab,意为“阿拉伯人的岛”)[1]位于西亚,其西边和非洲接壤,它从中东向东南方伸入印度洋。面积3,237,500 km2(1,250,000 sq mi),是世界上最大的半岛[2][3][4][5][6]。向西它与非洲的边界是苏伊士运河、红海和曼德海峡。向南它伸入阿拉伯海和印度洋。向东它与伊朗隔波斯湾和阿曼湾相望。沙特阿拉伯、也门、阿曼、阿拉伯联合酋长国位于阿拉伯半岛上。其中以沙特阿拉伯的面积最大,占据大部分的阿拉伯半岛。
阿拉伯半岛常年受副高压带及信风带控制,非常干燥,几乎整个半岛都是热带沙漠气候区并有面积较大的无流区,缺乏天然淡水资源,本区有七个没有河流的国家。半岛沿波斯湾周围有大量石油储藏,自从20世纪陆续成功开采后,给阿拉伯半岛上临波斯湾的国家带来了巨大的财富。
阿拉伯半岛是伊斯兰教的诞生地。伊斯兰教的创教人穆罕默德在这里出生和生活。半岛上的麦加是伊斯兰教的圣地。以阿拉伯半岛为中心的阿拉伯帝国曾横跨欧亚非大陆。今天半岛上所有国家都以伊斯兰教为国教,并以逊尼派占多数。
Die Arabische Halbinsel (arabisch جزيرة العرب, DMG Ǧazīrat al-ʿArab), auch Arabien, ist mit 2,73 Millionen km² Fläche die größte Halbinsel der Erde und liegt auf der Arabischen Platte in Vorderasien. Geologisch gehört sie zu Afrika, geographisch zu Asien. Der größte Staat auf der Halbinsel ist Saudi-Arabien. Die Halbinsel ist eine wichtige Region innerhalb der arabischen Welt.
Die Arabische Halbinsel wird begrenzt vom Golf von Akaba und dem Roten Meer im Westen und Südwesten, vom Arabischen Meer im Süden und Südosten sowie vom Persischen Golf im Nordosten. Die Arabische Halbinsel ist vor Westantarktika und Vorderindien die größte Halbinsel der Erde und wird zu Vorderasien gezählt; gleichwohl ist sie geologisch ein Teil Afrikas. Zusammen mit mehreren angrenzenden Staaten bildet sie den Nahen Osten.
Tektonisch gesehen bildet diese Halbinsel den größeren südlichen Teil der Arabischen Platte. Geologisch gehört die Halbinsel zur alten afrikanischen Kontinentalmasse, auch wenn sie durch den Grabenbruch des Roten Meeres getrennt ist. Die Halbinsel ist mit der Großen Nefud im Norden und der Rub al-Chali im Süden fast vollständig ein Wüstengebiet (eine sogenannte Wendekreiswüste); sie gehört zu den fünf größten Wüstengebieten der Erde.


阿拉伯埃及共和国(阿拉伯语:جمهوريّة مصرالعربيّة,![]() 发音 帮助·信息),通称埃及,是东北非洲人口最多的国家,面积为1,001,450平方千米,2020年2月人口突破1亿[3]。原存在于当地的古埃及是世界文明古国之一,与两河流域文明有一定程度的交流,不过在希腊与罗马人的统治下,古埃及文明在公元前逐渐没落,后来被阿拉伯文化所取代。二战后,埃及于1953年由阿拉伯人建立共和国,地理上该国地跨二洲即亚洲和非洲,西奈半岛位于西南亚(西亚),而该国大部分国土位于北非地区。伊斯兰教为国教。埃及人大部分信仰伊斯兰教逊尼派,最大的宗教少数派为科普特正教。另外还有基督教其他教派和伊斯兰教什叶派;官方语言为阿拉伯语,通用英语和法语。埃及经济的多元化程度在中东地区名列前茅。
发音 帮助·信息),通称埃及,是东北非洲人口最多的国家,面积为1,001,450平方千米,2020年2月人口突破1亿[3]。原存在于当地的古埃及是世界文明古国之一,与两河流域文明有一定程度的交流,不过在希腊与罗马人的统治下,古埃及文明在公元前逐渐没落,后来被阿拉伯文化所取代。二战后,埃及于1953年由阿拉伯人建立共和国,地理上该国地跨二洲即亚洲和非洲,西奈半岛位于西南亚(西亚),而该国大部分国土位于北非地区。伊斯兰教为国教。埃及人大部分信仰伊斯兰教逊尼派,最大的宗教少数派为科普特正教。另外还有基督教其他教派和伊斯兰教什叶派;官方语言为阿拉伯语,通用英语和法语。埃及经济的多元化程度在中东地区名列前茅。
埃及也被认为是一个中等强国,各项重要产业如旅游业、农业、工业和服务业有着几乎同等的发展比重,埃及的苏伊士运河是亚洲与欧洲的桥梁。在地中海、中东和伊斯兰信仰地区尤其有广泛的影响力。
2015年埃及经济发展会议(EEDC),埃及计划于2019年底正式迁往新首都,缓解开罗人口压力。后该搬迁计划被推迟至2021年7月。
Ägypten (Aussprache [ɛˈɡʏptn̩] oder [ɛˈɡɪptn̩]; arabisch مصر Miṣr, offiziell Arabische Republik Ägypten) ist ein Staat im nordöstlichen Afrika mit über 100 Millionen Einwohnern[6] und einer Fläche von über einer Million Quadratkilometern. Die Megastadt Kairo ist ägyptische Hauptstadt und die größte Metropole Afrikas und Arabiens, der Ballungsraum „Greater Cairo“ ist eine der bevölkerungsreichsten Stadtregionen der Erde. Weitere Millionenstädte des Landes sind Alexandria und Gizeh. Hinsichtlich der Wirtschaftsleistung beim BIP pro Kopf liegt Ägypten auf Platz 94 von 190 Ländern (2016, PPP).
Das Alte Ägypten gilt als eine der frühen Hochkulturen der Welt. Ägypten wird seit der arabisch-islamischen Expansion zur Maschrek-Region des arabischen Raumes gezählt. Es hat als interkontinentaler Staat eine Landbrücke vom größeren afrikanischen Teil nach Asien, zur Sinai-Halbinsel. Durch die Revolution von 2011 änderten sich die gesellschaftlichen und politischen Verhältnisse im Land.
エジプト・アラブ共和国(エジプト・アラブきょうわこく、アラビア語: جمهورية مصر العربية)、通称:エジプト(アラビア語: مِصر)は、中東および北アフリカに位置する共和制国家。首都はカイロ。
アフリカ大陸では北東端に位置し、西にリビア、南にスーダン、北東のシナイ半島ではイスラエル、パレスチナ国・ガザ地区と国境を接する。北部は地中海、東部は紅海に面している。
エジプトは中東と北東アフリカの接点に存在し、古代文明が存在していた地域のひとつに数え上げられる。その歴史は紀元前の時代にまで遡るほど古い。
人口はアラブ諸国で最も多く、2020年2月に1億人を超えている[2]。同国地域には数千年前の古代都市の痕跡や幾多もの史跡がナイル川に沿う形で点在している。
また、水源が乏しい国の一つとしても知られており、南北に流れるナイル川の河谷とデルタ地帯(ナイル・デルタ)のほかは、国土の大部分の95%以上が砂漠である[3]。ナイル河口の東には地中海と紅海を結ぶスエズ運河がある。
同国は現在、MENA地域において2番目に人口密度の高い国と見做されており、中でもカイロは世界で最も人口密度の高い都市のひとつに当たる。
Egypt (/ˈiːdʒɪpt/ (![]() listen) EE-jipt; Arabic: مِصر, romanized: Miṣr), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip (Palestine) and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.
listen) EE-jipt; Arabic: مِصر, romanized: Miṣr), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip (Palestine) and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.
Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urbanisation, organised religion and central government.[14] Iconic monuments such as the Giza Necropolis and its Great Sphinx, as well the ruins of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak, and the Valley of the Kings, reflect this legacy and remain a significant focus of scientific and popular interest. Egypt's long and rich cultural heritage is an integral part of its national identity, which reflects its unique transcontinental location being all Mediterranean, Middle Eastern and North African.[15] Egypt was an early and important centre of Christianity, but was largely Islamised in the seventh century and remains a predominantly Muslim country, albeit with a significant Christian minority.
Modern Egypt dates back to 1922, when it gained independence from the British Empire as a monarchy. Following the 1952 revolution, Egypt declared itself a republic, and in 1958 it merged with Syria to form the United Arab Republic, which dissolved in 1961. Throughout the second half of the 20th century, Egypt endured social and religious strife and political instability, fighting several armed conflicts with Israel in 1948, 1956, 1967 and 1973, and occupying the Gaza Strip intermittently until 1967. In 1978, Egypt signed the Camp David Accords, officially withdrawing from the Gaza Strip and recognising Israel. The country continues to face challenges, from political unrest, including the recent 2011 revolution and its aftermath, to terrorism and economic underdevelopment. Egypt's current government, a semi-presidential republic has been described by a number of watchdogs as authoritarian or heading an authoritarian regime, responsible for perpetuating the country's problematic human rights record.
Islam is the official religion of Egypt and Arabic is its official language.[16] With over 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in North Africa, the Middle East, and the Arab world, the third-most populous in Africa (after Nigeria and Ethiopia), and the thirteenth-most populous in the world. The great majority of its people live near the banks of the Nile River, an area of about 40,000 square kilometres (15,000 sq mi), where the only arable land is found. The large regions of the Sahara desert, which constitute most of Egypt's territory, are sparsely inhabited. About half of Egypt's residents live in urban areas, with most spread across the densely populated centres of greater Cairo, Alexandria and other major cities in the Nile Delta.
Egypt is a developing country, ranking 116th on the Human Development Index. Politically, however, it is considered to be a regional power in North Africa, the Middle East and the Muslim world, and a middle power worldwide.[17] Egypt has a diversified economy, which is the second-largest in Africa, the 33rd-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the 20th-largest globally by PPP. Egypt is a founding member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Arab League, the African Union, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and the World Youth Forum.
L'Égypte Écouter (en arabe : مصر / miṣr ; en arabe égyptien : مصر / maṣr masˤɾ), en forme longue la république arabe d'Égypte (en arabe : جمهورية مصر العربية) / jumhuriyat misr al arabiya2, est un pays se trouvant en Afrique du Nord-Est et, pour la péninsule du Sinaï, en Asie de l'Ouest. Située sur la côte sud de la Méditerranée orientale, le bassin Levantin, l'actuelle Égypte occupe l'espace géographique qui fut autrefois celui de l'Égypte antique.
Avec plus de 106 millions d'habitants en 2021, l'Égypte est le troisième pays le plus peuplé d'Afrique derrière le Nigeria et l'Éthiopie. En très forte croissance, sa population a été multipliée par quatre en soixante ans.
Sa capitale est Le Caire et sa monnaie la livre égyptienne. La langue officielle du pays est l'arabe, utilisé dans tous les documents et dans l'éducation. En revanche, la langue parlée est l'arabe égyptien (arabe dialectal). Le siwi — tamazight (berbère) de l'ouest du pays — est parlé à Siwa. Le copte n'est utilisé que comme langue liturgique des chrétiens d'Égypte. Le nubien est parlé par les habitants de Haute-Égypte, au sud d'Assouan, qui fait partie du nord de la région de Nubie.
L'Egitto (in arabo: مصر, Miṣr), ufficialmente Repubblica Araba d'Egitto (in arabo: جمهورية مصر العربية, Ǧumhūriyya Miṣr al-ʿArabiyya), è un paese transcontinentale che attraversa l'angolo nord-est dell'Africa e l'angolo sud-ovest dell'Asia attraverso un ponte di terra formato dalla penisola del Sinai. La maggior parte del suo territorio di 1 001 000 chilometri quadrati si trova nel Nord Africa e confina con il mar Mediterraneo a nord, la striscia di Gaza e Israele a nord-est, il golfo di Aqaba e il mar Rosso ad est, il Sudan a sud e la Libia ad ovest. Dal 1958 al 31 dicembre 1971 era denominato Repubblica Araba Unita.
L'Egitto è uno dei paesi più popolati dell'Africa e del Medio Oriente, e il 14º più popolato al mondo. Buona parte dei suoi più di 100 milioni di abitanti[6] vive vicino alle rive del fiume Nilo, su una superficie di circa 10 000 chilometri quadrati, dove si trova l'unica terra arabile del paese. Le grandi regioni del deserto del Sahara, che costituiscono la maggior parte del territorio dell'Egitto, sono scarsamente abitate. Circa il 42% dei residenti in Egitto vive in aree urbane, con la maggior diffusione di tutti i centri densamente popolati al Cairo, Alessandria e altre grandi città del delta del Nilo, come Mansura.
L'Egitto ha una delle più lunghe storie di ogni Stato moderno, essendo stato continuamente abitato dal X millennio a.C.[7] I suoi monumenti, come la piramide di Giza e la Grande Sfinge, sono stati costruiti per la sua antica civiltà, che è stata una delle più avanzate del suo tempo. Le sue antiche rovine, come quelle di Menfi, Tebe, Karnak e la Valle dei Re, al di fuori di Luxor, sono un focus significativo di studi archeologici e di interesse popolare. La ricca eredità culturale dell'Egitto, così come l'attrazione della sua riviera del mar Rosso, hanno fatto del turismo una parte vitale dell'economia, che impiega circa il 34% della forza lavoro del paese.
L'economia dell'Egitto è una delle più diversificate del Vicino Oriente, con settori quali il turismo, l'agricoltura, l'industria e dei servizi a livelli di produzione senza uguali. L'Egitto è considerato una media potenza,[8] con una significativa influenza culturale, politica e militare in Nord Africa, Vicino Oriente e mondo musulmano.
Egipto (en árabe, مصر, Miṣr, pronunciado en dialecto egipcio: Maṣr; en copto, Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, khemi), oficialmente la República Árabe de Egipto (en árabe: جمهوريّة مصرالعربيّة Ŷumhūriyyat Miṣr Al-ʿArabiyyah7), es un país soberano transcontinental. Está ubicado mayoritariamente en el extremo noreste de África, mientras que en Asia se encuentra en la península del Sinaí. Limita con Sudán al sur, con Libia al oeste y con la Franja de Gaza (Palestina) e Israel al noreste. Al norte limita con el mar Mediterráneo y al sureste con el mar Rojo.
La mayor parte de su superficie la integra el desierto del Sahara. El río Nilo cruza el desierto de sur a norte, formando un estrecho valle y un gran delta en su desembocadura en el Mediterráneo. Estas tierras fértiles se hallan densamente pobladas, concentrando la mayor población nacional de África. Casi la mitad de los egipcios viven en áreas urbanas, sobre todo en los centros densamente poblados de El Cairo, su capital, y Alejandría.
Fue cuna de la antigua civilización egipcia, que junto con la mesopotámica fue el origen de la actual cultura occidental, influyendo decisivamente en la historia de la humanidad. Los restos de esta civilización jalonan el país, como las pirámides y la gran esfinge, o la ciudad meridional de Lúxor, que contiene un gran número de restos antiguos, tales como el templo de Karnak y el Valle de los Reyes. Egipto es actualmente un centro político y cultural importante del Oriente Próximo y se le considera una potencia regional. Su actual forma de gobierno es la república semipresidencialista. Entre 2013 y 2014 estuvo bajo gobierno interino, formado tras el golpe de Estado de 2013 que derrocó al primer presidente democrático del país, Mohamed Morsi.8
Еги́пет (араб. مصر Миср/Miṣr [misˤɾ], масри مصر Маср/Maṣr [ˈmɑsˤɾ], копт. Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ [kʰēmi]), официальное название — Ара́бская Респу́блика Еги́пет (араб. جمهورية مصر العربية Джумхурийят Миср аль-Арабийя, масри جمهورية مصر العربية Гумхурия Маср иль-Арабийя), — трансконтинентальное государство, расположенное в Северной Африке и на Ближнем Востоке (Синайский полуостров).
На северо-востоке граничит с Израилем и частично признанным государством Палестиной, на юге — с Суданом, на западе — с Ливией. На севере территория страны омывается водами Средиземного моря, на востоке — Красным морем, при этом оба моря соединены посредством искусственно сооружённого Суэцкого канала.

Das Arabische Meer (arabisch بحر العرب, DMG Baḥr al-ʿArab, persisch دریای عرب, Urdu بحیرہ عرب, Hindi अरब सागर) ist ein Randmeer des Indischen Ozeans zwischen der Arabischen Halbinsel und Indien. Es hat eine Flächenausdehnung von 3,9 Millionen km². Seine größte Tiefe von 4481 Metern liegt im Süden.[1]
Im Nordwesten grenzt es an den Golf von Oman, der wiederum mit dem Persischen Golf verbunden ist. Im Südwesten verbindet der Golf von Aden das Arabische Meer mit dem Roten Meer. Im Südosten grenzt das Arabische Meer an die Lakkadivensee. Die meisten Ozeanographen betrachten die Lakkadivensee als Teil des Arabischen Meeres. Weiter im Osten grenzt diese, bzw. das Arabische Meer im erweiterten Sinn, an den Golf von Bengalen.[2]
Länder mit Küstenabschnitten am Arabischen Meer sind die Malediven, Indien, Pakistan, Oman, Jemen und Somalia.
Städte an der Küste sind unter anderem Mumbai (Bombay) und Karachi.
Der Indus ist der bedeutendste Strom zum Arabischen Meer. Weitere Flüsse sind Narmada und Tapti, die beide in den Golf von Khambhat münden.
Im Westen des Arabischen Meeres verläuft die Owen-Bruchzone.
阿拉伯海(阿拉伯语:بحر العرب)为印度洋的一部分。位于亚洲南部的阿拉伯半岛同印度半岛之间。北部为波斯湾和阿曼湾,西部经亚丁湾通红海。面积为386万平方公里。为世界性交通要道。
アラビア海(アラビアかい)は、インド洋の北西部、アラビア半島とインドとの間の海域。
面積約3,862,000 km2[1]、最大幅約2,400 km、最大水深4,652mである。インダス川が最大の流入河川。北側にオマーン湾があり、ホルムズ海峡を通じてペルシャ湾に繋がっている。西側にはアデン湾があり、紅海に通じる。アラビア海に面する国はインド、パキスタン、オマーン、イエメン、ソマリア、モルディブである。代表的な島にソコトラ島(イエメン)やマシーラ島(オマーン)がある。
紀元前数世紀から大航海時代にかけて重要な交易ルートであった。現在も、中東原油を運ぶタンカーや欧州との間の船舶が頻繁に往来し、ソマリア海賊を取り締まる海域でもある。
The Arabian Sea is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Peninsula, on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea,[1] on the southwest by the Somali Sea,[2] and on the east by India. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west, connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
The Arabian Sea has been crossed by important marine trade routes since the third or second millennium BCE. Major seaports include Kandla Port, Okha Port, Mumbai Port, Nhava Sheva Port (Navi Mumbai), Mormugão Port (Goa), New Mangalore Port and Kochi Port in India, the Port of Karachi, Port Qasim, and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan, Chabahar Port in Iran and the Port of Salalah in Oman. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Lakshadweep (India) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
La mer d’Arabie ou mer d'Oman, parfois appelée mer arabique (en arabe بحر العرب translittéré en Baḥr al-'Arab, en sanskrit सिन्धु सागर, translittéré en Sindhu Sagar), est une partie de l'océan Indien située entre la péninsule Arabique à l'ouest, le Pakistan au nord, le subcontinent indien au nord-est et à l'est, les îles Laquedives à l'est-sud-est et l'archipel des Maldives au sud-est. Elle est limitée au nord-ouest par le golfe d'Oman et à l'ouest par le golfe d'Aden. Sa surface est d'environ 3,6 millions de km², et sa profondeur maximale est de 5 800 mètres.
La mer est une voie de passage très fréquentée, en particulier pour le transport de pétrole venant du golfe Persique. Elle est également une zone de pêche pour les pays côtiers (sardine, maquereau, thon).
Il Mar Arabico (arabo: بحر العرب; translitterato: Bahr al-'Arab, latino: Mare Erythraeum) è la sezione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, stretto tra la penisola arabica a ovest, il corno d'Africa a sud-ovest, il sub-continente indiano ad est e la costa asiatica a nord.
Il mar Arabico copre approssimativamente una superficie di 3.686.000 km² ed ha una profondità massima di 5800 metri. Corrisponde alla porzione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, ed è delimitato ad oriente dalla costa occidentale della penisola indiana, a nord dalla costa pakistana e in parte da quella persiana, ad ovest dalla penisola arabica e a sud da una linea ideale che va dal capo Guardafui, la punta nord-est della Somalia, all'isola di Socotra e fino al Capo Comorin, punta meridionale della penisola del Deccan.
Il mar Arabico comunica tramite il golfo di Oman e lo stretto di Hormuz con il golfo Persico e tramite il golfo di Aden e lo stretto di Bab al Mandab con il mar Rosso. Altri golfi importanti che fanno parte del mar Arabico sono quelli di Cambay e di Kutch in prossimità della costa nord-occidentale indiana. Le isole principali che vi affiorano sono Socotra, prolungamento della costa africana, le isole Laccadive poste in prossimità alla costa sud-orientale dell'India e le isole di Masirah e Kuria Muria poste in prossimità della costa dell'Oman.
I fiumi principali che vi sfociano sono l'Indo, il Narmada, il Tapti ed il Mahi. Le principali città che si affacciano sul mar Arabico sono Aden in Yemen; Mascate in Oman; Gwadar e Karachi in Pakistan; Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut e Kochi (Cochin) in India. Le coste sono per la maggior parte rocciose ed accidentate, ma non mancano buoni approdi naturali che hanno favorito la nascita di importanti porti (Aden, Mascate, Bandar-e Abbas, Karachi, Bombay, Cochin, Colombo ecc.). Il clima è tropicale; la regione è interessata dai venti monsonici che la investono in maniera decrescente da est verso ovest.
El mar arábigo (también llamado mar de Arabia o mar de Omán) es un mar que forma parte del océano Índico y que está localizado en la costa suroccidental de Asia, entre la península arábiga y la península del Indostán.
Tienen costa al mar arábigo, desde oeste a este, Somalia, Yemen, Omán, Pakistán, India y las islas Maldivas. Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos no tienen costa a este mar, sino a uno de sus entrantes, el golfo de Omán, en el noroeste, que luego se estrecha hasta conectar con el golfo Pérsico o Arábico en el estrecho de Ormuz.
La máxima anchura del mar arábigo es de aproximadamente 2400 km, y su máxima profundidad es de 4652 m, cerca de la península arábiga, aproximadamente a la misma latitud que el extremo sur de India. El Indo es el único río de gran envergadura que fluye hacia este mar.
Entre sus principales ciudades costeras se encuentran Bombay en India y Karachi en Pakistán.
Арави́йское мо́ре (араб. بحر العرب, перс. دریای عرب, урду بحیرہ عرب, хинди अरब सागर, сомал. Bada Carbeed, англ. Arabian Sea) — окраинное море в северной части Индийского океана. Ограничено Аравийским полуостровом на западе и полуостровом Индостан на востоке.
Общая площадь моря — 3 862 000 км²[1]. Максимальная ширина — 2400 км. Максимальная глубина — 5803 м.[2] Крупнейшая река, впадающая в море — Инд.
Крупнейшими заливами являются: на западе Аденский залив, соединяющийся с Красным морем через Баб-эль-Мандебский пролив и на северо-западе Оманский залив, соединяющийся с Персидским заливом. На побережье Индии крупными являются Камбейский залив и залив Кач.
На берегах Аравийского моря расположены Сомали, Джибути, Йемен, Оман, Иран, Пакистан, Индия и Мальдивские острова. Крупнейшие города — Карачи, Аден, Маскат, Мумбаи, Коччи и др.
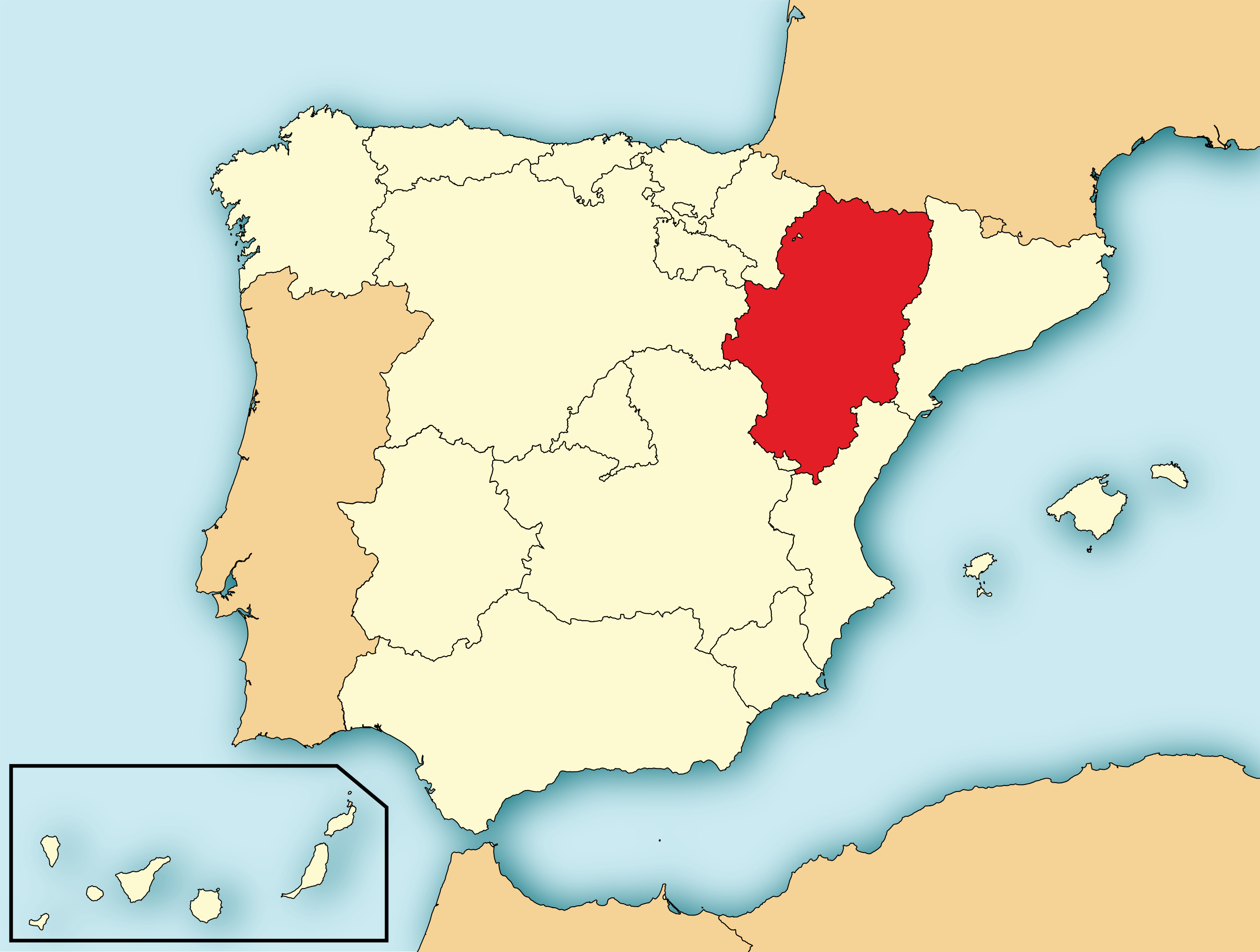


Aragonien oder Aragon (spanisch und aragonesisch Aragón, katalanisch Aragó) ist eine autonome Gemeinschaft im Nordosten Spaniens. Sie grenzt im Norden auf dem Hauptkamm der Pyrenäen an Frankreich, im Osten an Katalonien, im Südosten an Valencia und im Westen an Kastilien-La Mancha, Kastilien und León, La Rioja sowie Navarra. Hauptstadt ist Saragossa.
Das Gebiet der heutigen autonomen Gemeinschaft entspricht dem früheren Königreich Aragonien im engeren Sinne, das seinen Namen wiederum dem Fluss Aragón verdankte.
阿拉贡(西班牙语:Aragón;加泰罗尼亚语:Aragó;阿拉贡语:Aragón)是西班牙东北部的一个自治区,面积47,719平方公里,人口1,277,471(2003年)。
阿拉贡向北与法国相邻,向东是加泰罗尼亚,向南是巴伦西亚省,向西是卡斯蒂利亚-拉曼恰、卡斯蒂利亚-莱昂、拉里奥哈和纳瓦拉。萨拉戈萨省、韦斯卡省和特鲁埃尔省属于阿拉贡自治地区。阿拉贡的首府是萨拉戈萨。



 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织
 亚洲国家
亚洲国家



 阿拉贡自治区
阿拉贡自治区

