
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 China
China
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Legend
Legend
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
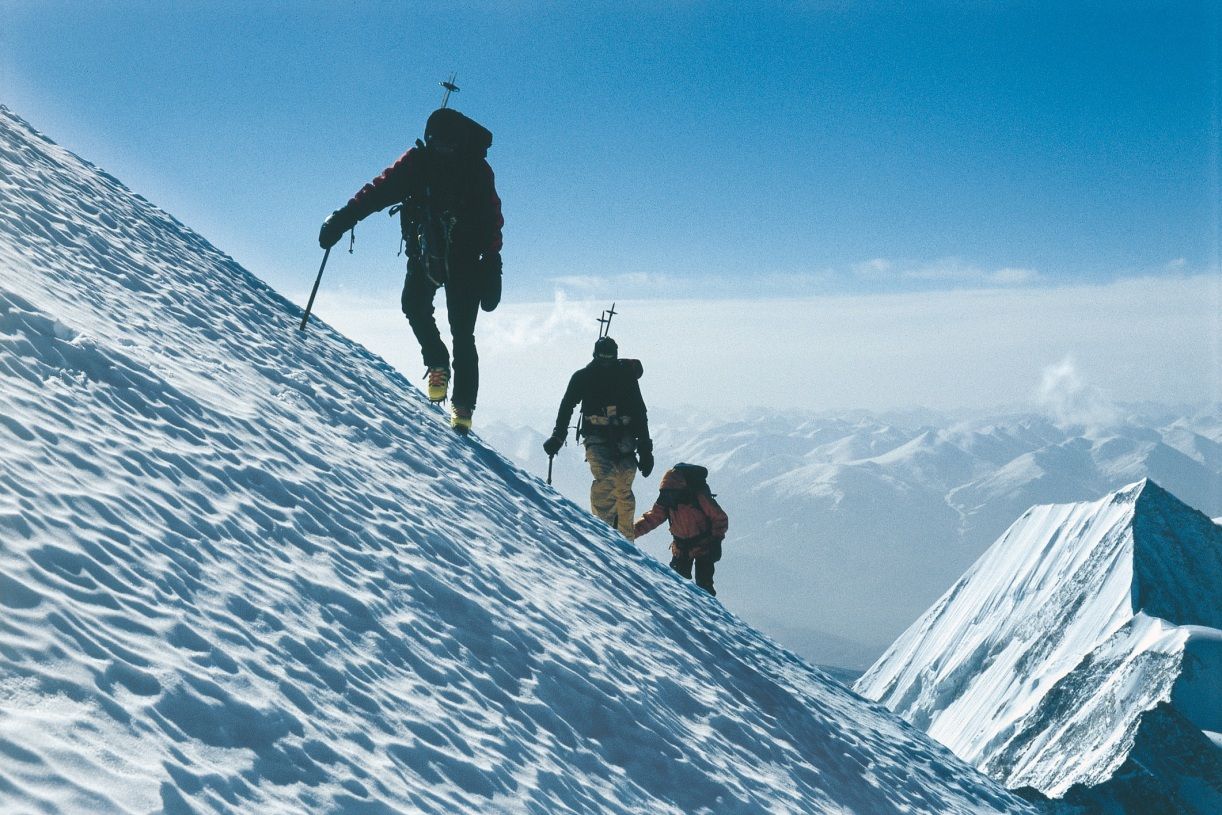



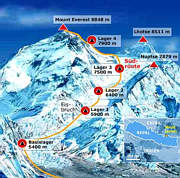


Der Mount Everest ist ein Berg im Himalaya und mit einer Höhe von 8848 m der höchste Berg der Erde. Er gehört zu den 14 Achttausendern und zu den Seven Summits. Der Mount Everest ist seit 1856 nach dem britischen Landvermesser George Everest benannt. Auf Nepali heißt der Berg Sagarmatha, auf Tibetisch Qomolangma (deutsche Aussprache „Tschomolangma“; englische Umschrift Chomolungma).
Der Mount Everest befindet sich im Mahalangur Himal in der Region Khumbu in Nepal an der Grenze zu China (Autonomes Gebiet Tibet); der westliche und südöstliche seiner drei Gipfelgrate bilden die Grenze. Auf nepalesischer Seite ist er Teil des Sagarmatha-Nationalparks, der zum UNESCO-Welterbe gehört. Auf der Nordseite gehört er zum Qomolangma National Nature Reserve, das mit dem von der UNESCO ausgewiesenen Qomolangma-Biosphärenreservat korrespondiert.[1]
Edmund Hillary und Tenzing Norgay gelang am 29. Mai 1953 die Erstbesteigung des „dritten Pols“. Am 8. Mai 1978 bestiegen Reinhold Messner und Peter Habeler den Gipfel erstmals ohne zusätzlichen Sauerstoff.
珠穆朗玛峰是喜玛拉雅山脉的主峰,又称圣母峰,英文名Mt.Everest,海拔8848米,是地球上第一高峰,位于东经 86.9°,北纬27.9°。地处中尼边界东段,北坡在中华人民共和国西藏自治区的定曰县境内,南坡在尼泊尔王国境内,藏语称 “珠穆朗玛”[清康熙五十六年(公元 1717年)编绘的《皇舆全览图》中作“朱母朗马阿林”],意为“神女第三”。
珠 穆朗玛峰山体呈巨型金字塔状,威武雄壮昂首天外,地形极端险峻,环境异常复杂。雪线高度:北坡为5800—6200米,南坡为5500—6100米。东北 山脊、 东南山脊和西山山脊中间夹着三大陡壁(北壁、东壁和西南壁),在这些山脊 和峭壁之间又分布着548条大陆型冰川,总面积达1457.07平方公里,平均厚度达7260米。冰川的补给主要靠印度洋季风带两大降水带积雪变质形成。 冰川上 有千姿百态、瑰丽罕见的冰塔林,又有高达数十米的冰陡崖和步步陷井的明暗 冰裂隙,还有险象环生的冰崩雪崩区。(Quelle:http://news.xinhuanet.com)
珠穆朗玛峰(藏文:ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ;藏语拼音:qomolangma;威利:jo mo glang ma,香港称珠穆朗玛峰,台湾称圣母峰),中文简称珠峰,尼泊尔名萨加玛塔峰(尼泊尔语:सगरमाथा),英国名埃佛勒斯峰(英语:Mount Everest),为地球第一高峰,属于喜马拉雅山脉,位于中国西藏自治区与尼泊尔萨加玛塔专区边界上。2005年中国国家测绘局测量的岩面高为8,844.43米(29,017.2英尺),尼泊尔则使用传统的雪盖高8,848米(29,029英尺),BBC报道称2010年起两国官方互相承认对方的测量数据[5],中国国家测绘地理信息局则在2018年2月声明否认此说法,仍采用8,844.43米数据至今[6]。它除了是海拔最高的山峰之外,也是距离地心第五远的高峰。[7]它附近的高峰包括8,516米(27,940英尺)的洛子峰、7,855米(25,771英尺)的努子峰和7,580米(24,870英尺)的章子峰。
清朝经过测绘于1719年出版的全国地图上称此峰为“朱姆朗马阿林”,但没有标出高度或用经纬度标出其位置。1856年英属印度测量局首次公布此峰的经纬度及海拔高度,主张此峰8,840米(29,000英尺)是世界第一高峰。1865年英国皇家地理学会接受印度测量局局长安德鲁·史考特·华欧的建议,将此峰命名为“埃佛勒斯峰”,以纪念前任局长乔治·埃佛勒斯。1952年,中国采用“珠穆朗玛峰”为官方名称。
珠穆朗玛峰吸引了许多登山者。主要的攀登路线有两条,一条从尼泊尔东南部出发,经过与洛子峰之间的南坳登顶,称为“标准路线”;另一条则从西藏的北部出发,经过与章子峰之间的北坳登顶。从标准路线登顶对登山技术的挑战不算高,但这条路线的风险包括雪崩、摔落山谷、高山症、冻伤和通过昆布冰瀑的危险。到2016年为止,山上有超过200具尸体,其中一些成为地标。[8][9]
据气象记载,珠穆朗玛峰山顶最低温度为-60°C,最低月平均温度为-35°C,全年平均温度为-29°C,参照北极、南极,因此也被称为“世界第三极”。[10]
エベレスト、エヴェレスト(英: Everest)、またはチョモランマ(チベット語: ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ[1] Chomolungma, Qomolangma)、サガルマータ(ネパール語: सगरमाथा Sagarmāthā)は、ヒマラヤ山脈にある世界最高峰である。
エベレストはインド測量局(Survey of India)で長官を務めたジョージ・エベレストにちなんで命名された。
1920年代から長きにわたる挑戦の末、1953年にイギリス探検隊のメンバーでニュージーランド出身の登山家であるエドモンド・ヒラリーとネパール出身のシェルパであるテンジン・ノルゲイによって初登頂がなされた。
エベレストの標高については諸説あり、1954年にインド測量局が周辺12ヶ所で測定しその結果を平均して得られた8,848 mという数値が長年一般に認められてきた。1999年、全米地理学協会はGPSによる測定値が8,850mだったと発表した[2]。厳密には地殻変動などの影響によって標高は年々変動していると考えられている。
エベレストの南麓に位置するネパールのサガルマータ国立公園はユネスコの世界遺産に登録されている。
Mount Everest, known in Nepali as Sagarmatha (सगरमाथा) and in Tibetan as Chomolungma (ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ), is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The international border between Nepal (Province No. 1) and China (Tibet Autonomous Region) runs across its summit point.
The current official elevation of 8,848 m (29,029 ft), recognized by China and Nepal, was established by a 1955 Indian survey and subsequently confirmed by a Chinese survey in 1975.[1] In 2005, China remeasured the rock height of the mountain, with a result of 8844.43 m. There followed an argument between China and Nepal as to whether the official height should be the rock height (8,844 m., China) or the snow height (8,848 m., Nepal). In 2010, an agreement was reached by both sides that the height of Everest is 8,848 m, and Nepal recognizes China's claim that the rock height of Everest is 8,844 m.[5]
In 1865, Everest was given its official English name by the Royal Geographical Society, upon a recommendation by Andrew Waugh, the British Surveyor General of India. As there appeared to be several different local names, Waugh chose to name the mountain after his predecessor in the post, Sir George Everest, despite George Everest's objections.[6]
Mount Everest attracts many climbers, some of them highly experienced mountaineers. There are two main climbing routes, one approaching the summit from the southeast in Nepal (known as the "standard route") and the other from the north in Tibet. While not posing substantial technical climbing challenges on the standard route, Everest presents dangers such as altitude sickness, weather, and wind, as well as significant hazards from avalanches and the Khumbu Icefall. As of 2017, nearly 300 people have died on Everest, many of whose bodies remain on the mountain.[7]
The first recorded efforts to reach Everest's summit were made by British mountaineers. As Nepal did not allow foreigners into the country at the time, the British made several attempts on the north ridge route from the Tibetan side. After the first reconnaissance expedition by the British in 1921 reached 7,000 m (22,970 ft) on the North Col, the 1922 expedition pushed the north ridge route up to 8,320 m (27,300 ft), marking the first time a human had climbed above 8,000 m (26,247 ft). Seven porters were killed in an avalanche on the descent from the North Col. The 1924 expedition resulted in one of the greatest mysteries on Everest to this day: George Mallory and Andrew Irvine made a final summit attempt on 8 June but never returned, sparking debate as to whether or not they were the first to reach the top. They had been spotted high on the mountain that day but disappeared in the clouds, never to be seen again, until Mallory's body was found in 1999 at 8,155 m (26,755 ft) on the north face. Tenzing Norgay and Edmund Hillary made the first official ascent of Everest in 1953, using the southeast ridge route. Norgay had reached 8,595 m (28,199 ft) the previous year as a member of the 1952 Swiss expedition. The Chinese mountaineering team of Wang Fuzhou, Gonpo, and Qu Yinhua made the first reported ascent of the peak from the north ridge on 25 May 1960.[8][9]
L’Everest, en tibétain ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ, Qomolangma ou encore Chomolungma, en népalais सगरमाथा, Sagarmāthā, aussi appelé mont Everest, est une montagne située dans la chaîne de l'Himalaya, à la frontière entre le Népal (province no 1 (en)) et la Chine (Tibet).
Il est aperçu par des Européens pour la première fois en 1847 puis, après quelques années d'observations et de calculs, son altitude est établie à 8 848 mètres et il est identifié comme le plus haut sommet du monde. Cette caractéristique lui vaut d'être baptisé de son nom actuel par les Occidentaux en 1865 et, dès les années 1920, de lui attirer l'intérêt des alpinistes qui se lancent à l'assaut de ses pentes. Plusieurs expéditions, en particulier britanniques, se succèdent depuis le versant nord au Tibet. Toutefois, les conditions climatiques extrêmes font leurs premières victimes, parmi lesquelles George Mallory et Andrew Irvine, en 1924, dont on ne saura probablement jamais avec certitude s'ils ont atteint le sommet. En 1950, le Népal autorise l'accès à la montagne depuis le sud offrant des possibilités d'ascension par l'arête Sud-Est, moins périlleuse. Finalement, trois ans plus tard, Edmund Hillary et Tensing Norgay réussissent à vaincre l'Everest. Dès lors, les exploits en tous genres s'enchaînent, alimentant les fantasmes populaires ; mais, en 1996, une série d'accidents mortels vient rappeler les dangers liés à la montagne, portant de nos jours à plus de 200 le nombre de victimes. Pourtant, le tourisme de masse se popularise, fragilisant le milieu naturel malgré les créations du parc national de Sagarmatha en 1976 et de la réserve naturelle du Qomolangma en 1988. Ainsi, plus de 14 000 alpinistes ont tenté l'ascension depuis 1922 et plus de 4 000 l'ont réussie, bien aidés, pour la majorité d'entre eux, par les porteurs sherpas.
Il monte Everest (pron. /ˈɛverest/[1]) è la vetta più alta del continente asiatico e della Terra con i suoi 8 848 m di altitudine s.l.m., situato nella catena dell'Himalaya assieme ad altri ottomila, al confine fra Cina e Nepal. Rientra dunque nelle cosiddette Sette Vette del Pianeta.
El monte Everest es la montaña más alta del planeta Tierra, con una altitud de 8.848 metros (29 029 pies) sobre el nivel del mar.1 Está localizada en el continente asiático, en la cordillera del Himalaya, concretamente en la subcordillera de Mahalangur Himal; marca la frontera entre China y Nepal, considerada como la frontera más alta del mundo.[cita requerida] El macizo incluye los picos vecinos Lhotse, 8516 m (27 940 pies); Nuptse, 7855 m (25 771 pies) y Changtse, 7580 m (24 870 pies).
 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam
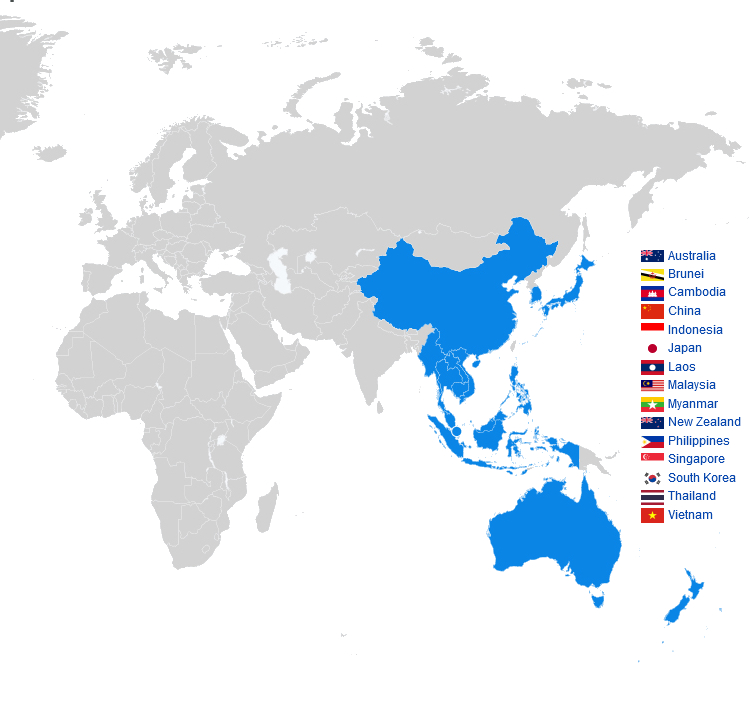
Die Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (kurz RCEP, deutsch Regionale, umfassende Wirtschaftspartnerschaft) ist ein seit 2020 bestehendes Freihandelsabkommen zwischen den zehn ASEAN-Mitgliedsstaaten und fünf weiteren Staaten in der Region Asien-Pazifik. Es ist die größte Freihandelszone der Welt.[1]
Das Projekt zur Gründung der RCEP entstand 2012, als die ASEAN-Staaten Verhandlungen mit der Volksrepublik China, Japan und Südkorea (ASEAN+3) sowie mit Indien, Australien und Neuseeland (ASEAN+6) aufgenommen hatten. Ursprünglich war die Einführung der Freihandelszone für 2017 geplant gewesen. Aufgrund von Bedenken verließ Indien 2019 die Verhandlungen. Am 15. November 2020, zum Abschluss des 37. ASEAN-Gipfeltreffens in der vietnamesischen Hauptstadt Hanoi, fand schließlich die Vertragsunterzeichnung statt.[2][3]
区域全面经济伙伴关系协定(英语:Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership,缩写为RCEP)是由东南亚国家联盟十国发起,由中国、日本、韩国、澳大利亚、新西兰等与东盟有自由贸易协议的五国共同参加,共计15个国家所构成的高级自由贸易协定。此协议也向其他外部经济体开放,比如中亚国家、南亚及大洋洲其他国家[2]。RCEP旨在通过削减关税及非关税壁垒,建立统一市场的自由贸易协定。经批准生效后,“各成员之间关税减让以立即降至零关税、10年内降至零关税的承诺为主”[3]。
東アジア地域包括的経済連携(ひがしアジアちいきほうかつてきけいざいれんけい、英語: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership; RCEP、アールセップ、域内包括的経済連携)とは、ASEAN加盟10カ国(ブルネイ、カンボジア、インドネシア、ラオス、マレーシア、ミャンマー、フィリピン、シンガポール、タイ、ベトナム)と、そのFTAパートナー5カ国(オーストラリア、中国、日本、ニュージーランド、韓国)の間で提案されている、アジア太平洋地域の自由貿易協定であり、世界の人口の3割、世界のGDPの3割を占める15カ国が交渉に参加している。交渉国15カ国は世界の人口の30%、GDPの30%弱を占めている[1]。
FTAパートナーであるインドは、交渉が開始された2011年からRCEP交渉に参加していたが、主に中国からの製造品やオーストラリアやニュージーランドからの農産物・乳製品のダンピング懸念を理由に、交渉の最終時点の2019年11月に交渉から離脱した[2]。2020年11月15日に第4回RCEP首脳会議の席上で協定は署名された[3]。
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP; /ˈɑːrsɛp/ AR-sep) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history.[1] It was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam, and will take effect within two years, after it has been ratified by the member countries.[2][3][4]
The trade pact, which includes a mix of high-income,[note 1] middle-income,[note 2] and low-income countries,[note 3] was conceived at the 2011 ASEAN Summit in Bali, Indonesia, while its negotiations were formally launched during the 2012 ASEAN Summit in Cambodia.[5][6][7] It was expected to eliminate about 90% of the tariffs on imports between its signatories within 20 years of coming into force, and establish common rules for e-commerce, trade, and intellectual property.[8]
The RCEP is the first free trade agreement between China, Japan, and South Korea, three of the four largest economies in Asia.[8] At the time it was signed, analysts predicted that it would help stimulate the economy amid the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as "pull the economic centre of gravity back towards Asia," and amplify the decline of the United States in economic and political affairs.[6][9][10]
Le partenariat régional économique global1, ou en anglais : Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), est un projet d'accord de libre-échange entre quinze pays autour de l'océan Pacifique. C'est l'accord commercial le plus important du monde2.
Il inclut les dix pays membres de l'ASEAN, à savoir : la Birmanie, Brunei, le Cambodge, l'Indonésie, le Laos, la Malaisie, les Philippines, Singapour, la Thaïlande et le Vietnam ; ainsi que cinq autres pays qui possèdent déjà un accord de libre-échange bilatéral avec l'ASEAN, à savoir : l'Australie, la Chine, le Japon, la Corée du Sud et la Nouvelle-Zélande.
Il Partenariato Economico Globale Regionale (in lingua inglese Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) è un accordo di libero scambio nella regione dell'Asia Pacifica tra i dieci stati dell'ASEAN (cioè Brunei, Cambogia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Filippine, Singapore, Thailandia e Vietnam) e cinque dei loro partner di libero scambio: Australia, Cina, Giappone, Nuova Zelanda e Corea del Sud. I 15 paesi membri rappresentano circa il 30% della popolazione mondiale e del PIL, rendendolo il più grande blocco commerciale.[1] È stato firmato al vertice dell'ASEAN virtuale ospitato in Vietnam il 15 novembre 2020,[2][3] e dovrebbe entrare in vigore entro due anni, dopo che sarà stato ratificato dai paesi membri.[4]
Il patto commerciale, che comprende un mix di alto reddito, reddito medio, e paesi a basso reddito, è stato concepito al vertice dell'ASEAN del 2011 a Bali,[5] mentre i negoziati sono stati avviati ufficialmente nel corso del vertice dell'ASEAN del 2012 in Cambogia.[6]
L'RCEP è il primo accordo di libero scambio tra Cina, Giappone e Corea del Sud (tre delle quattro maggiori economie asiatiche) ed è il primo accordo multilaterale di libero scambio a includere la Cina.[7] Al momento della firma, gli analisti prevedevano che avrebbe aiutato a stimolare l'economia durante la pandemia di COVID-19, e "avrebbe attirato il centro di gravità economico verso l'Asia".
La Asociación Económica Integral Regional (abreviado RCEP por sus siglas en inglés) es un acuerdo de libre comercio (TLC) entre los diez estados miembros de la Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN) (Brunéi, Camboya, Indonesia, Laos, Malasia, Myanmar, Filipinas, Singapur, Tailandia , Vietnam) y cinco estados de Asia-Pacífico con los que la ASEAN tiene acuerdos de libre comercio existentes (Australia, China, Japón, Corea del Sur y Nueva Zelanda). El tratado fue firmado en la Cumbre de la ASEAN del 15 de noviembre de 202012 y se espera que entre en vigor en un plazo inferior a dos años, después de que sea ratificado por todos los estados miembros.
Incluye estados con PIBs muy diversos,3 conformando entre los 15 países en torno al 30% de la población mundial y el 30% del Producto Mundial Bruto.
Las negociaciones se iniciaron formalmente en noviembre de 2012 en la Cumbre de la ASEAN en Camboya.4 El RCEP se considera una alternativa al Acuerdo de Asociación Transpacífico (TPP, por sus siglas en inglés), un acuerdo comercial propuesto que incluye varias naciones de Asia y América, pero excluye a China y la India.5 Tras la salida de Estados Unidos durante la presidencia de Donald Trump del TPP se retomaron con más fuerza las negociaciones en el RCEP y se firmó el acuerdo en noviembre de 2020 por las naciones de la ASEAN, incluida China.6 El pacto entrará en vigor cuando los países que lo han firmado procedan a tramitar su ratificación a nivel nacional.7
El tratado RCEP es el primer tratado de libre comercio entre China, Japón y Corea del sur (tres de las cuatro grandes economías asiáticas), y es el primer tratado multilateral que incluye a China.8 En el momento de la firma, los analistas predijeron que ayudaría en la recuperación de la economía tras la pandemia de COVID-19, así como a empujar el centro de gravedad de la economía mundial hacia Asia.9
Всесторо́ннее региона́льное экономи́ческое партне́рство, сокращенно ВРЭП (англ. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) — это соглашение о «зоне свободной торговли плюс» («ЗСТ +»), охватывающее 10 государств-членов Ассоциации государств Юго-Восточной Азии (АСЕАН) (Бруней, Вьетнам, Индонезия, Камбоджа, Лаос, Малайзия, Мьянма, Сингапур, Таиланд, Филиппины) и 6 государств, с которыми у АСЕАН уже подписаны соглашения о свободной торговле (Австралия, Индия, КНР, Новая Зеландия, Республика Корея и Япония). ВРЭП охватывает 4 развитые и 12 развивающихся государств. Начало переговоров было положено 20 ноября 2012 г. на саммите АСЕАН в Камбодже[1].
Соглашение о создании ВРЭП было подписано в Ханое 15 ноября 2020 года. Его вступление в силу создаст крупнейшую в мире зону свободной торговли с примерно 2,2 млрд потребителями и объемом ВВП в $28 трлн, что составляет более 32% от общего мирового объема ВВП.[2].

 Australia
Australia
 England
England
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Ireland
Ireland
 Canada
Canada
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Schottland
Schottland
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Wales
Wales


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Angola
Angola
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Australia
Australia
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belize
Belize
 Benin
Benin
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brazil
Brazil
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Cuba
Cuba
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Germany
Germany
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia
 Georgia
Georgia
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Japan
Japan
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liberia
Liberia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mexico
Mexico
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Panama
Panama
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Genf
Genf
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Togo
Togo
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tschad
Tschad
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uganda
Uganda
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Roberto Azevêdo
Roberto Azevêdo
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Mike Moore
Mike Moore
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Pascal Lamy
Pascal Lamy
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Peter Sutherland
Peter Sutherland
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Renato Ruggiero
Renato Ruggiero
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Supachai Panitchpakdi
Supachai Panitchpakdi
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic
 Cyprus
Cyprus


世界贸易组织(简称世贸组织或世贸;英语:World Trade Organization,缩写为 WTO;法语:Organisation Mondiale du Commerce,缩写为 OMC;西班牙语:Organización Mundial del Comercio,缩写为 OMC)是负责监督成员经济体之间各种贸易协议得到执行的一个国际组织,前身是1948年起实施的关税及贸易总协定的秘书处。
世贸总部位于瑞士日内瓦,现任总干事是罗伯托·阿泽维多。截至2016年7月29日,世界贸易组织共有164个成员。[5]世界贸易组织的职能是调解纷争,加入WTO不算签订一种多边贸易协议,但其设置的入会门槛可以做为愿意降低关税、法政上配合、参与国际贸易的门票,它是贸易体制的组织基础和法律基础,是众多贸易协定的管理者,是各成员贸易立法的监督者,是就贸易提供解决争端和进行谈判的场所。该机构是当代最重要的国际经济组织之一,其成员间的贸易额占世界贸易额的绝大多数,被称为“经济联合国”。
世界貿易機関(せかいぼうえききかん、英: World Trade Organization、略称:WTO)は、自由貿易促進を主たる目的として創設された国際機関である。常設事務局がスイスのジュネーブに置かれている。
GATT(ガット)ウルグアイ・ラウンドにおける合意によって、世界貿易機関を設立するマラケシュ協定(WTO設立協定)に基づいて1995年1月1日にGATTを発展解消させて成立した。
本来GATTは、第二次世界大戦後の安定を見据え、国際通貨基金および国際復興開発銀行とともに設立が予定されていた国際貿易機関(ITO)の設立準備の際に、暫定協定として結ばれたものであった。国際貿易機関の設立が廃案となり、GATTがその代替として発展強化されていくうちに、再びこの分野の常設機関が求められ、WTOが設立されることとなった。発展解消であるため、GATTの事務局及び事務局長もWTOへと引き継がれることとなった[4]。
WTOはGATTを継承したものであるが、GATTが協定(Agreement)に留まったのに対し、WTOは機関(Organization)であるのが根本的な違いである。
を基本原則としている。また、物品貿易だけでなく金融、情報通信、知的財産権やサービス貿易も含めた包括的な国際通商ルールを協議する場である。
対抗処置の発動では、紛争処理機関(パネル)の提訴に対し全加盟国による反対がなければ採択されるというネガティブ・コンセンサス方式(逆コンセンサス方式)を採用した強力な紛争処理能力を持つ。これは国際組織としては稀な例であり、コンセンサス方式を採っていたGATTとの大きな違いで、WTOの特徴の一つといえる。
新多角的貿易交渉(新ラウンド)は、2001年11月にカタールのドーハで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議で開始を決定し、ドーハ・ラウンドと呼ばれていた。2002年2月1日の貿易交渉委員会で新ラウンドがスタートした。しかし9年に及ぶ交渉は先進国と、急速に台頭してきたBRICsなど新興国との対立によって中断と再開を繰り返した末、ジュネーブで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議(2011年12月17日)で「交渉を継続していくことを確認するものの、近い将来の妥結を断念する」(議長総括)となり事実上停止状態になった。
その後、2013年のバリ島における閣僚会議で、貿易円滑化協定を含む合意が成立し、2014年7月まで貿易円滑化協定をWTO協定に加える(附属書1Aに追加)するための文書を一般理事会で採択すべきとされた[5]。しかしインドが合意を蒸し返す状態で反対したため期限までに採択できなかった[6]。その後食糧備蓄への補助金の問題で先進国側が譲歩することでようやくインドが合意し、2014年11月27日の一般理事会で貿易円滑化協定が採択された[6]。WTO加盟国の3分の2が改正を受諾した日に発効することになっており、2017年2月22日にこの要件を満たし、協定が発効した。
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 124 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. It is the largest international economic organization in the world.[5][6]
The WTO deals with regulation of trade in goods, services and intellectual property between participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a dispute resolution process aimed at enforcing participants' adherence to WTO agreements, which are signed by representatives of member governments[7]:fol.9–10 and ratified by their parliaments.[8] The WTO prohibits discrimination between trading partners, but provides exceptions for environmental protection, national security, and other important goals.[9] Trade-related disputes are resolved by independent judges at the WTO through a dispute resolution process.[9]
The WTO's current Director-General is Roberto Azevêdo,[10][11] who leads a staff of over 600 people in Geneva, Switzerland.[12] A trade facilitation agreement, part of the Bali Package of decisions, was agreed by all members on 7 December 2013, the first comprehensive agreement in the organization's history.[13][14] On 23 January 2017, the amendment to the WTO Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement marks the first time since the organization opened in 1995 that WTO accords have been amended, and this change should secure for developing countries a legal pathway to access affordable remedies under WTO rules.[15]
Studies show that the WTO boosted trade,[16][17][9] and that barriers to trade would be higher in the absence of the WTO.[18] The WTO has highly influenced the text of trade agreements, as "nearly all recent [preferential trade agreements (PTAs)] reference the WTO explicitly, often dozens of times across multiple chapters... in many of these same PTAs we find that substantial portions of treaty language—sometime the majority of a chapter—is copied verbatim from a WTO agreement."[19]
L'Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC ; en anglais : World Trade Organization, WTO, en espagnol : Organización Mundial del Comercio, OMC) est une organisation internationale qui s'occupe des règles régissant le commerce international entre les pays. Au cœur de l'organisation se trouvent les accords de l'OMC, négociés et signés en avril 1994 à Marrakech1 par la majeure partie des puissances commerciales du monde2 et ratifiés par leurs assemblées parlementaires. L'OMC a pour but principal de favoriser l'ouverture commerciale. Pour cela, elle tâche de réduire les obstacles au libre-échange, d'aider les gouvernements à régler leurs différends commerciaux et d'assister les exportateurs, les importateurs et les producteurs de marchandises et de services dans leurs activités.
Depuis 2001, le cycle de négociation mené par l'OMC est le Cycle de Doha3. Bien que l'OMC ne soit pas une agence spécialisée de l'ONU, elle entretient des liens avec cette dernière4. Le siège de l'OMC est au Centre William-Rappard, à Genève. Depuis le 1er septembre 2013, l'organisation est présidée par le Brésilien Roberto Azevêdo qui a été élu directeur général.
L'Organizzazione mondiale del commercio, abbreviato in OMC (in inglese: World Trade Organization, WTO), è un'organizzazione internazionale creata allo scopo di supervisionare numerosi accordi commerciali tra gli stati membri. Vi aderiscono[3] 164 Paesi, a cui se ne aggiungono altri 22 con ruolo di osservatori,[4] comprendendo così oltre il 95% del commercio mondiale di beni e servizi.[5]
La sede dell'OMC si trova, dal 1995, presso il Centro William Rappard a Ginevra, Svizzera.[6]
La Organización Mundial del Comercio (OMC) fue establecida en 1995. Tiene su sede en Ginebra, Suiza, y sus idiomas oficiales son el inglés, el francés y el español. La OMC no forma parte del sistema de las Naciones Unidas, y tampoco de los organismos de Bretton Woods como el Banco Mundial o el FMI.Nota 1
Всеми́рная торго́вая организа́ция (ВТО; англ. World Trade Organization (WTO), фр. Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), исп. Organización Mundial del Comercio) — международная организация, созданная 1 января 1995 года с целью либерализации международной торговли и регулирования торгово-политических отношений государств-членов. ВТО образована на основе Генерального соглашения по тарифам и торговле (ГАТТ), заключенного в 1947 году и на протяжении почти 50 лет фактически выполнявшего функции международной организации, но не являвшегося тем не менее международной организацией в юридическом смысле.
ВТО отвечает за разработку и внедрение новых торговых соглашений, а также следит за соблюдением членами организации всех соглашений, подписанных большинством стран мира и ратифицированных их парламентами. ВТО строит свою деятельность, исходя из решений, принятых в 1986—1994 годах в рамках Уругвайского раунда и более ранних договоренностей ГАТТ. Обсуждения проблем и принятие решений по глобальным проблемам либерализации и перспективам дальнейшего развития мировой торговли проходят в рамках многосторонних торговых переговоров (раунды). К настоящему времени проведено 8 раундов таких переговоров, включая Уругвайский, а в 2001 году стартовал девятый в Дохе, Катар. Организация пытается завершить переговоры по Дохийскому раунду переговоров, который был начат с явным акцентом на удовлетворение потребностей развивающихся стран. По состоянию на декабрь 2012 года будущее раунда переговоров в Дохе остаётся неопределённым: программа работы состоит из 21 части, а первоначально установленный окончательный срок 1 января 2005 года был давно пропущен[3]. В ходе переговоров возник конфликт между стремлением к свободной торговле и стремлением множества стран к протекционизму, особенно в плане сельскохозяйственных субсидий. До сих пор эти препятствия остаются главными и мешают любому прогрессу для запуска новых переговоров в рамках Дохийского раунда. По состоянию на июль 2012 года, существуют различные группы переговоров в системе ВТО для решения текущих вопросов в плане сельского хозяйства, что приводит к застою в самих переговорах[4].
Штаб-квартира ВТО расположена в Женеве, Швейцария. Глава ВТО (генеральный директор) — Роберту Карвалью ди Азеведу, в штате самой организации около 600 человек[5].
На 26 апреля 2015 года в ВТО состояли 162 страны[6].
Правила ВТО предусматривают ряд льгот для развивающихся стран. В настоящее время развивающиеся страны — члены ВТО имеют (в среднем) более высокий относительный уровень таможенно-тарифной защиты своих рынков по сравнению с развитыми. Тем не менее, в абсолютном выражении общий размер таможенно-тарифных санкций в развитых странах гораздо выше, вследствие чего доступ на рынки высокопередельной продукции из развивающихся стран серьёзно ограничен[7].
Правила ВТО регулируют только торгово-экономические вопросы. Попытки США и ряда европейских стран начать дискуссию об условиях труда (что позволило бы считать недостаточную законодательную защиту работников конкурентным преимуществом) были отвергнуты из-за протестов развивающихся стран, которые утверждали, что такие меры только ухудшат благосостояние работников в связи с сокращением числа рабочих мест, снижением доходов и уровня конкурентоспособности[7].
Mitglieder der WTO
| Staat | Beitrittsdatum |
|---|---|
| 30. Juni 1995 | |
| 29. Juli 2016 | |
| 8. September 2000 | |
| 23. November 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 5. Februar 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 12. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Dezember 1996 | |
| 3. Juni 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 21. Januar 1996 | |
| 7. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. November 1999 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 14. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Oktober 1996 | |
| 14. Juni 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Juli 1995 | |
| 25. Oktober 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 26. Juni 2014 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. April 2000 | |
| 13. Oktober 2004 | |
| 13. Dezember 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 2008 | |
| 30. November 2015 | |
| 13. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 20. Dezember 1998 | |
| 30. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1997 | |
| 27. März 1997 | |
| 30. November 2000 | |
| 20. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. Februar 2013 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 10. Februar 1999 | |
| 14. Juli 2016 | |
| 1. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 17. November 1995 | |
| 29. April 2012 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 4. April 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. Juli 2001 | |
| 29. Januar 1997 | |
| 26. August 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. April 2004 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 3. September 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. Dezember 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. November 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 6. September 1997 | |
| 9. Juni 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Mai 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. August 2012 | |
| 26. Juli 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2005 | |
| 10. Mai 2012 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. April 2015 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 5. März 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. März 2013 | |
| 1. Januar 2002 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 27. Juli 2007 | |
| 1. März 1995 | |
| 19. Oktober 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 29. März 1995 | |
| 26. März 1995[2] | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 16. Mai 2008 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 10. April 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 24. August 2012 | |
| 11. Januar 2007 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 |

 Australia
Australia
 Cookinseln
Cookinseln
 Fidschi
Fidschi
 Föderierte Staaten von Mikronesien
Föderierte Staaten von Mikronesien
 Französisch-Polynesien
Französisch-Polynesien
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Nauru
Nauru
 Neukaledonien
Neukaledonien
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Niue
Niue
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Republik Palau
Republik Palau
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Samoa
Samoa
 Tonga
Tonga
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu



Tauranga (deutsch: Ankerplatz oder Rastplatz ) ist eine über 114.789 Einwohner (2013)[1] zählende Hafenstadt im Nordosten der Nordinsel von Neuseeland. Sie ist die größte und aus ökonomischer Sicht wichtigste Stadt der Region Bay of Plenty und zudem die größte neuseeländische Agglomeration, die offiziell einen Māori-Namen führt. Tauranga überschritt 2004 die 100.000 Einwohner-Marke, wurde zum Stadtdistrikt mit einem eigenen City Council (Stadtrat) und ist zugleich Verwaltungssitz des Western-Bay-of-Plenty District.[2]

 Australia
Australia
 Australia
Australia
 England
England
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa
 South Africa
South Africa
 South Africa
South Africa
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Sport
Sport
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Religion
Religion



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Animal world
Animal world
 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Important port
Important port