
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Geography
Geography


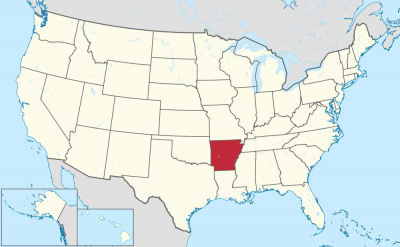


阿肯色州(英语:State of Arkansas /ˈɑːrkənsɔː/),是美国南部的一个州份,位处密西西比河中下游,北接密苏里州,西界俄克拉荷马州,南邻路易斯安那州,西南与得克萨斯州接壤,东隔密西西比河与田纳西州和密西西比州相望。其面积137,539平方公里,在五十个州内列第29位。2017年人口超过3百万,人口排名33。其首府是小石城。
该州的邮政缩写是AR。本州下辖共75个县,详见阿肯色州行政区划。
アーカンソー州(英: State of Arkansas [ˈɑrkənsɔː] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
地形的にはアメリカ内陸高原を構成するオザーク高原やワシタ山地(Ouachita Mountains)のある山岳地から、東部のミシシッピ川やアーカンソー・デルタのある低地まで多様である。
Arkansas (/ˈɑːrkənsɔː/)[c] is a state in the south central region of the United States, home to more than three million people as of 2018.[7][8] Its name is from the Osage language, of Siouan derivation; it denoted their related kin, the Quapaw people.[9] The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and the Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 33rd most populous of the 50 United States. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, located in the central portion of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, such as the Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area and Fort Smith metropolitan area, is a population, education, and economic center. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
The Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836.[10] Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and the state landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans as workers. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America during the Civil War.
On returning to the Union in 1868, the state continued to suffer due to its reliance on the large-scale plantation economy. Cotton continued as the leading commodity crop, although the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in terms of its economy and opportunities for residents.
White rural interests dominated the state's politics by disenfranchisement of African Americans and by refusal to reapportion the legislature. It was not until after the civil rights movement and federal intervention that more African Americans were able to vote. The Supreme Court overturned rural domination in the South and other states that had refused to reapportion their state legislatures, or retained rules based on geographic districts. In the landmark ruling of one man, one vote, it ruled that states had to organize both houses of their legislatures by districts that held approximately equal populations, and that these had to be redefined as necessary after each decade's census.
Following World War II, Arkansas began to diversify its economy. In the 21st century, its economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism; along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans and rice.
The culture of Arkansas is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state. Notable people from the state include politician and educational advocate William Fulbright; former president Bill Clinton, who also served as the 40th and 42nd governor of Arkansas; general Wesley Clark, former NATO Supreme Allied Commander; Walmart founder and magnate Sam Walton;[11] singer-songwriters Johnny Cash, Charlie Rich, Jimmy Driftwood, and Glen Campbell; actor-filmmaker Billy Bob Thornton; poet C. D. Wright; and physicist William L. McMillan, who was a pioneer in superconductor research.
L'Arkansas (prononcé : /aʁ.kɑ̃(n).sa(s)/3), les Arkansas (/aʁ.kɑ̃.sa/3), ou simplement les Arcs (/ɑɹk/4), (prononcé en anglais : /ˈɑɹkənsɔ/5), est un État du Sud des États-Unis. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Little Rock, située au centre du territoire. Avec une population de 2 915 918 habitants en 2010, estimée à 3 017 804 habitants en 2019, sur une superficie de 137 732 km2, l'État est le 32e plus peuplé et le 29e plus vaste du pays. L'Arkansas est entouré par six États : l'Oklahoma à l'ouest, le Missouri au nord, le Tennessee et le Mississippi à l'est, le Texas au sud-ouest et la Louisiane au sud. Il est divisé en 75 comtés. Surnommé The Natural State (« l'État naturel »), il présente des paysages variés : des chaînes montagneuses telles que les Monts Ozarks ou les Montagnes Ouachita ; au sud, des forêts denses nommées Timberlands de l'Arkansas (en) ; à l'est, les plaines du Mississippi et du delta de l'Arkansas (en).
Le nom de l'État provient du nom de la langue Sioux et désigne les Indiens Quapaw. Il forme un territoire dès 1819 et est admis dans l'Union le 15 juin 1836, dont il devient le 25e État. Esclavagiste, il repose sur l'économie de plantation (coton, riz) et se joint aux États confédérés durant la Guerre de Sécession (1861-1865). Après avoir réintégré l'Union, l'Arkansas connaît une crise due à l'effondrement des structures économiques et sociales antérieures. Les intérêts des Blancs ruraux dominent la vie politique locale jusqu'au Mouvement des droits civiques, au milieu du XXe siècle. L'État demeure ségrégationniste jusqu'à la fin des années 1960. Il est aujourd'hui un territoire populaire, conservateur, dont l'ancrage républicain se confirme depuis les années 2000. Néanmoins, l'État demeure de tradition démocrate au niveau local et beaucoup d'électeurs se considèrent toujours Dixiecrats. La tradition conservatrice de cet État s'illustre par l'application de la peine de mort par injection létale et l'interdiction du mariage homosexuel à la suite d'un référendum.
L'Arkansas demeure un État à dominante agricole. En plus des plantations traditionnelles, il produit du soja, et tend à se spécialiser dans l'arboriculture et l'élevage de poulets. Les ressources en hydrocarbures ont également permis une industrialisation durant l'après-guerre, avec la création de papeteries, de scieries, d'usines métallurgiques (aluminium) et textiles. Durant les dernières décennies, l'Arkansas voit son économie se diversifier dans les services, accueillant des sièges sociaux de grandes entreprises (Walmart, Tyson Foods), ainsi que des aciéries et des constructeurs aéronautiques. En outre, des personnalités comme le sénateur J. William Fulbright, le chanteur de country Johnny Cash ou l'ancien président Bill Clinton en sont originaires.
L'Arkansas (pronuncia italianizzata, AFI: /arˈkansas/[2]; in inglese , /ˈɑrkənsɔː/) è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, la cui capitale è Little Rock. Confina a nord con il Missouri, a est con il Tennessee e il Mississippi, a sud con la Louisiana e il Texas, e ad ovest con l'Oklahoma.
Il nome dello Stato deriva dalla parola Akansa (termine utilizzato dai nativi Algonchini per indicare i nativi Quapaw), modificata nella pronuncia attuale dai francesi del XVII secolo.[3]
Arkansas es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Little Rock.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Suroeste. Limita al norte con Misuri al este con el río Mississippi que lo separa de Tennessee y Mississippi, al sur con Louisiana, al suroeste con Texas y al oeste con Oklahoma. Fue admitido en la Unión el 15 de junio de 1836, como el estado número 25.
Aparte de la frontera este que forma el río Misisipi, por su territorio discurre en dirección este el río Arkansas. El nombre del estado deriva de la palabra kansas (el término con que los indios algonquinos designaban a los indios quapaw), tal como la pronunciaban los franceses en el siglo XVII.3 La geografía diversa del estado parte de las regiones montañosas del Ozark y las montañas de Ouachita, que componen las tierras altas del interior de los EE. UU., a la tierra densamente boscosa en el sur conocida como el Arkansas Timberlands, hasta las tierras bajas del este a lo largo del río Misssissippi y el delta de Arkansas. Conocido como «el estado natural», las diversas regiones de Arkansas ofrecen a los residentes y turistas una variedad de oportunidades de recreación al aire libre.
Арканза́с[1][2] (также Арка́нзас[3]; англ. Arkansas, [ˈɑːrkənsɔː] ![]() слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
Официальное прозвище — «Естественный штат» (англ. Natural State).
Слово «арканзас» является алгонкинским экзонимом сиуского племени куапо.

阿空加瓜山(西班牙语:Aconcagua,西班牙语发音:[akoŋˈkaɣwa]、奇楚瓦语:Aqunqhawaq),为南美洲最高峰,海拔6,961米,也是亚洲之外最高的山峰,亦为西、南半球最高峰。属于南美洲西边的安地斯山脉,座落在阿根廷门多萨省,距离该省省会门多萨西北112公里,距离智利边境15公里,为冰川山系。由安地斯山脉的造山运动形成,命名为阿空加瓜是因颜色Arauca(又称Aconca,在克丘亚语中写为Ackon Cahuak)。
阿空加瓜山峰顶较为平缓,东南侧雪线4,500米,厚约90米,发育有现代冰川,西侧无终年积雪,山麓多温泉。
Der Aconcagua (vollständig: Cerro Aconcagua) in den argentinischen Anden ist mit 6961 m[1] der höchste Berg Amerikas und der höchste außerhalb Asiens. Zugleich ist er nach dem Mount Everest der Berg mit der weitesten Dominanz (16.536 Kilometer) und der größten Schartenhöhe.


Ägypten (Aussprache [ɛˈɡʏptn̩] oder [ɛˈɡɪptn̩]; arabisch مصر Miṣr, offiziell Arabische Republik Ägypten) ist ein Staat im nordöstlichen Afrika mit über 100 Millionen Einwohnern[6] und einer Fläche von über einer Million Quadratkilometern. Die Megastadt Kairo ist ägyptische Hauptstadt und die größte Metropole Afrikas und Arabiens, der Ballungsraum „Greater Cairo“ ist eine der bevölkerungsreichsten Stadtregionen der Erde. Weitere Millionenstädte des Landes sind Alexandria und Gizeh. Hinsichtlich der Wirtschaftsleistung beim BIP pro Kopf liegt Ägypten auf Platz 94 von 190 Ländern (2016, PPP).
Das Alte Ägypten gilt als eine der frühen Hochkulturen der Welt. Ägypten wird seit der arabisch-islamischen Expansion zur Maschrek-Region des arabischen Raumes gezählt. Es hat als interkontinentaler Staat eine Landbrücke vom größeren afrikanischen Teil nach Asien, zur Sinai-Halbinsel. Durch die Revolution von 2011 änderten sich die gesellschaftlichen und politischen Verhältnisse im Land.
阿拉伯埃及共和国(阿拉伯语:جمهوريّة مصرالعربيّة,![]() 发音 帮助·信息),通称埃及,是东北非洲人口最多的国家,面积为1,001,450平方千米,2020年2月人口突破1亿[3]。原存在于当地的古埃及是世界文明古国之一,与两河流域文明有一定程度的交流,不过在希腊与罗马人的统治下,古埃及文明在公元前逐渐没落,后来被阿拉伯文化所取代。二战后,埃及于1953年由阿拉伯人建立共和国,地理上该国地跨二洲即亚洲和非洲,西奈半岛位于西南亚(西亚),而该国大部分国土位于北非地区。伊斯兰教为国教。埃及人大部分信仰伊斯兰教逊尼派,最大的宗教少数派为科普特正教。另外还有基督教其他教派和伊斯兰教什叶派;官方语言为阿拉伯语,通用英语和法语。埃及经济的多元化程度在中东地区名列前茅。
发音 帮助·信息),通称埃及,是东北非洲人口最多的国家,面积为1,001,450平方千米,2020年2月人口突破1亿[3]。原存在于当地的古埃及是世界文明古国之一,与两河流域文明有一定程度的交流,不过在希腊与罗马人的统治下,古埃及文明在公元前逐渐没落,后来被阿拉伯文化所取代。二战后,埃及于1953年由阿拉伯人建立共和国,地理上该国地跨二洲即亚洲和非洲,西奈半岛位于西南亚(西亚),而该国大部分国土位于北非地区。伊斯兰教为国教。埃及人大部分信仰伊斯兰教逊尼派,最大的宗教少数派为科普特正教。另外还有基督教其他教派和伊斯兰教什叶派;官方语言为阿拉伯语,通用英语和法语。埃及经济的多元化程度在中东地区名列前茅。
埃及也被认为是一个中等强国,各项重要产业如旅游业、农业、工业和服务业有着几乎同等的发展比重,埃及的苏伊士运河是亚洲与欧洲的桥梁。在地中海、中东和伊斯兰信仰地区尤其有广泛的影响力。
2015年埃及经济发展会议(EEDC),埃及计划于2019年底正式迁往新首都,缓解开罗人口压力。后该搬迁计划被推迟至2021年7月。
エジプト・アラブ共和国(エジプト・アラブきょうわこく、アラビア語: جمهورية مصر العربية)、通称:エジプト(アラビア語: مِصر)は、中東および北アフリカに位置する共和制国家。首都はカイロ。
アフリカ大陸では北東端に位置し、西にリビア、南にスーダン、北東のシナイ半島ではイスラエル、パレスチナ国・ガザ地区と国境を接する。北部は地中海、東部は紅海に面している。
エジプトは中東と北東アフリカの接点に存在し、古代文明が存在していた地域のひとつに数え上げられる。その歴史は紀元前の時代にまで遡るほど古い。
人口はアラブ諸国で最も多く、2020年2月に1億人を超えている[2]。同国地域には数千年前の古代都市の痕跡や幾多もの史跡がナイル川に沿う形で点在している。
また、水源が乏しい国の一つとしても知られており、南北に流れるナイル川の河谷とデルタ地帯(ナイル・デルタ)のほかは、国土の大部分の95%以上が砂漠である[3]。ナイル河口の東には地中海と紅海を結ぶスエズ運河がある。
同国は現在、MENA地域において2番目に人口密度の高い国と見做されており、中でもカイロは世界で最も人口密度の高い都市のひとつに当たる。
Egypt (/ˈiːdʒɪpt/ (![]() listen) EE-jipt; Arabic: مِصر, romanized: Miṣr), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip (Palestine) and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.
listen) EE-jipt; Arabic: مِصر, romanized: Miṣr), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip (Palestine) and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.
Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urbanisation, organised religion and central government.[14] Iconic monuments such as the Giza Necropolis and its Great Sphinx, as well the ruins of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak, and the Valley of the Kings, reflect this legacy and remain a significant focus of scientific and popular interest. Egypt's long and rich cultural heritage is an integral part of its national identity, which reflects its unique transcontinental location being all Mediterranean, Middle Eastern and North African.[15] Egypt was an early and important centre of Christianity, but was largely Islamised in the seventh century and remains a predominantly Muslim country, albeit with a significant Christian minority.
Modern Egypt dates back to 1922, when it gained independence from the British Empire as a monarchy. Following the 1952 revolution, Egypt declared itself a republic, and in 1958 it merged with Syria to form the United Arab Republic, which dissolved in 1961. Throughout the second half of the 20th century, Egypt endured social and religious strife and political instability, fighting several armed conflicts with Israel in 1948, 1956, 1967 and 1973, and occupying the Gaza Strip intermittently until 1967. In 1978, Egypt signed the Camp David Accords, officially withdrawing from the Gaza Strip and recognising Israel. The country continues to face challenges, from political unrest, including the recent 2011 revolution and its aftermath, to terrorism and economic underdevelopment. Egypt's current government, a semi-presidential republic has been described by a number of watchdogs as authoritarian or heading an authoritarian regime, responsible for perpetuating the country's problematic human rights record.
Islam is the official religion of Egypt and Arabic is its official language.[16] With over 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in North Africa, the Middle East, and the Arab world, the third-most populous in Africa (after Nigeria and Ethiopia), and the thirteenth-most populous in the world. The great majority of its people live near the banks of the Nile River, an area of about 40,000 square kilometres (15,000 sq mi), where the only arable land is found. The large regions of the Sahara desert, which constitute most of Egypt's territory, are sparsely inhabited. About half of Egypt's residents live in urban areas, with most spread across the densely populated centres of greater Cairo, Alexandria and other major cities in the Nile Delta.
Egypt is a developing country, ranking 116th on the Human Development Index. Politically, however, it is considered to be a regional power in North Africa, the Middle East and the Muslim world, and a middle power worldwide.[17] Egypt has a diversified economy, which is the second-largest in Africa, the 33rd-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the 20th-largest globally by PPP. Egypt is a founding member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Arab League, the African Union, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and the World Youth Forum.
L'Égypte Écouter (en arabe : مصر / miṣr ; en arabe égyptien : مصر / maṣr masˤɾ), en forme longue la république arabe d'Égypte (en arabe : جمهورية مصر العربية) / jumhuriyat misr al arabiya2, est un pays se trouvant en Afrique du Nord-Est et, pour la péninsule du Sinaï, en Asie de l'Ouest. Située sur la côte sud de la Méditerranée orientale, le bassin Levantin, l'actuelle Égypte occupe l'espace géographique qui fut autrefois celui de l'Égypte antique.
Avec plus de 106 millions d'habitants en 2021, l'Égypte est le troisième pays le plus peuplé d'Afrique derrière le Nigeria et l'Éthiopie. En très forte croissance, sa population a été multipliée par quatre en soixante ans.
Sa capitale est Le Caire et sa monnaie la livre égyptienne. La langue officielle du pays est l'arabe, utilisé dans tous les documents et dans l'éducation. En revanche, la langue parlée est l'arabe égyptien (arabe dialectal). Le siwi — tamazight (berbère) de l'ouest du pays — est parlé à Siwa. Le copte n'est utilisé que comme langue liturgique des chrétiens d'Égypte. Le nubien est parlé par les habitants de Haute-Égypte, au sud d'Assouan, qui fait partie du nord de la région de Nubie.
L'Egitto (in arabo: مصر, Miṣr), ufficialmente Repubblica Araba d'Egitto (in arabo: جمهورية مصر العربية, Ǧumhūriyya Miṣr al-ʿArabiyya), è un paese transcontinentale che attraversa l'angolo nord-est dell'Africa e l'angolo sud-ovest dell'Asia attraverso un ponte di terra formato dalla penisola del Sinai. La maggior parte del suo territorio di 1 001 000 chilometri quadrati si trova nel Nord Africa e confina con il mar Mediterraneo a nord, la striscia di Gaza e Israele a nord-est, il golfo di Aqaba e il mar Rosso ad est, il Sudan a sud e la Libia ad ovest. Dal 1958 al 31 dicembre 1971 era denominato Repubblica Araba Unita.
L'Egitto è uno dei paesi più popolati dell'Africa e del Medio Oriente, e il 14º più popolato al mondo. Buona parte dei suoi più di 100 milioni di abitanti[6] vive vicino alle rive del fiume Nilo, su una superficie di circa 10 000 chilometri quadrati, dove si trova l'unica terra arabile del paese. Le grandi regioni del deserto del Sahara, che costituiscono la maggior parte del territorio dell'Egitto, sono scarsamente abitate. Circa il 42% dei residenti in Egitto vive in aree urbane, con la maggior diffusione di tutti i centri densamente popolati al Cairo, Alessandria e altre grandi città del delta del Nilo, come Mansura.
L'Egitto ha una delle più lunghe storie di ogni Stato moderno, essendo stato continuamente abitato dal X millennio a.C.[7] I suoi monumenti, come la piramide di Giza e la Grande Sfinge, sono stati costruiti per la sua antica civiltà, che è stata una delle più avanzate del suo tempo. Le sue antiche rovine, come quelle di Menfi, Tebe, Karnak e la Valle dei Re, al di fuori di Luxor, sono un focus significativo di studi archeologici e di interesse popolare. La ricca eredità culturale dell'Egitto, così come l'attrazione della sua riviera del mar Rosso, hanno fatto del turismo una parte vitale dell'economia, che impiega circa il 34% della forza lavoro del paese.
L'economia dell'Egitto è una delle più diversificate del Vicino Oriente, con settori quali il turismo, l'agricoltura, l'industria e dei servizi a livelli di produzione senza uguali. L'Egitto è considerato una media potenza,[8] con una significativa influenza culturale, politica e militare in Nord Africa, Vicino Oriente e mondo musulmano.
Egipto (en árabe, مصر, Miṣr, pronunciado en dialecto egipcio: Maṣr; en copto, Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, khemi), oficialmente la República Árabe de Egipto (en árabe: جمهوريّة مصرالعربيّة Ŷumhūriyyat Miṣr Al-ʿArabiyyah7), es un país soberano transcontinental. Está ubicado mayoritariamente en el extremo noreste de África, mientras que en Asia se encuentra en la península del Sinaí. Limita con Sudán al sur, con Libia al oeste y con la Franja de Gaza (Palestina) e Israel al noreste. Al norte limita con el mar Mediterráneo y al sureste con el mar Rojo.
La mayor parte de su superficie la integra el desierto del Sahara. El río Nilo cruza el desierto de sur a norte, formando un estrecho valle y un gran delta en su desembocadura en el Mediterráneo. Estas tierras fértiles se hallan densamente pobladas, concentrando la mayor población nacional de África. Casi la mitad de los egipcios viven en áreas urbanas, sobre todo en los centros densamente poblados de El Cairo, su capital, y Alejandría.
Fue cuna de la antigua civilización egipcia, que junto con la mesopotámica fue el origen de la actual cultura occidental, influyendo decisivamente en la historia de la humanidad. Los restos de esta civilización jalonan el país, como las pirámides y la gran esfinge, o la ciudad meridional de Lúxor, que contiene un gran número de restos antiguos, tales como el templo de Karnak y el Valle de los Reyes. Egipto es actualmente un centro político y cultural importante del Oriente Próximo y se le considera una potencia regional. Su actual forma de gobierno es la república semipresidencialista. Entre 2013 y 2014 estuvo bajo gobierno interino, formado tras el golpe de Estado de 2013 que derrocó al primer presidente democrático del país, Mohamed Morsi.8
Еги́пет (араб. مصر Миср/Miṣr [misˤɾ], масри مصر Маср/Maṣr [ˈmɑsˤɾ], копт. Ⲭⲏⲙⲓ [kʰēmi]), официальное название — Ара́бская Респу́блика Еги́пет (араб. جمهورية مصر العربية Джумхурийят Миср аль-Арабийя, масри جمهورية مصر العربية Гумхурия Маср иль-Арабийя), — трансконтинентальное государство, расположенное в Северной Африке и на Ближнем Востоке (Синайский полуостров).
На северо-востоке граничит с Израилем и частично признанным государством Палестиной, на юге — с Суданом, на западе — с Ливией. На севере территория страны омывается водами Средиземного моря, на востоке — Красным морем, при этом оба моря соединены посредством искусственно сооружённого Суэцкого канала.
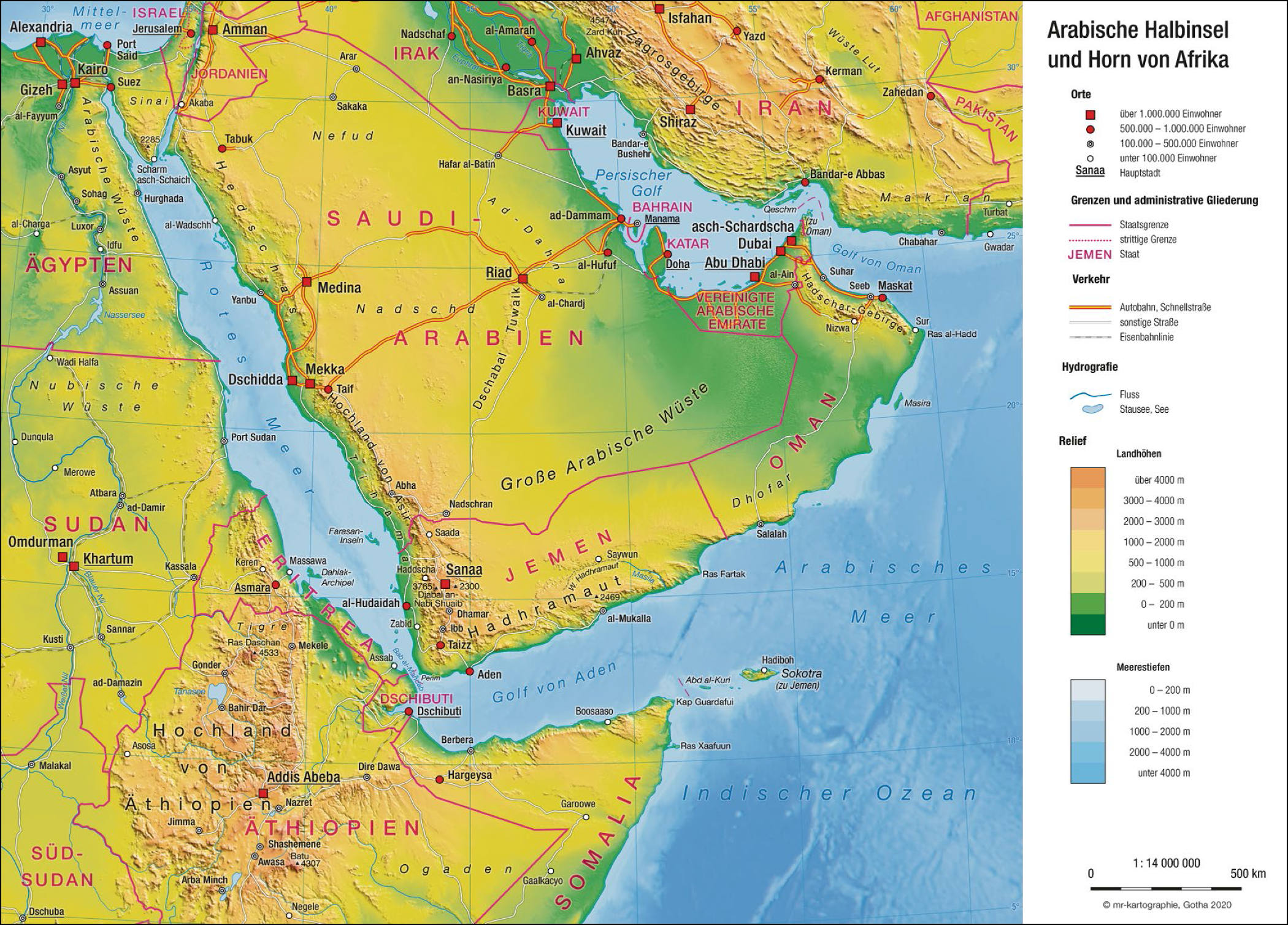
Die Arabische Halbinsel (arabisch جزيرة العرب, DMG Ǧazīrat al-ʿArab), auch Arabien, ist mit 2,73 Millionen km² Fläche die größte Halbinsel der Erde und liegt auf der Arabischen Platte in Vorderasien. Geologisch gehört sie zu Afrika, geographisch zu Asien. Der größte Staat auf der Halbinsel ist Saudi-Arabien. Die Halbinsel ist eine wichtige Region innerhalb der arabischen Welt.
Die Arabische Halbinsel wird begrenzt vom Golf von Akaba und dem Roten Meer im Westen und Südwesten, vom Arabischen Meer im Süden und Südosten sowie vom Persischen Golf im Nordosten. Die Arabische Halbinsel ist vor Westantarktika und Vorderindien die größte Halbinsel der Erde und wird zu Vorderasien gezählt; gleichwohl ist sie geologisch ein Teil Afrikas. Zusammen mit mehreren angrenzenden Staaten bildet sie den Nahen Osten.
Tektonisch gesehen bildet diese Halbinsel den größeren südlichen Teil der Arabischen Platte. Geologisch gehört die Halbinsel zur alten afrikanischen Kontinentalmasse, auch wenn sie durch den Grabenbruch des Roten Meeres getrennt ist. Die Halbinsel ist mit der Großen Nefud im Norden und der Rub al-Chali im Süden fast vollständig ein Wüstengebiet (eine sogenannte Wendekreiswüste); sie gehört zu den fünf größten Wüstengebieten der Erde.
阿拉伯半岛(/əˈreɪbiə/; 阿拉伯语:شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, shibhu l-jazīrati l-ʿarabiyyah, “阿拉伯半岛”或 جَزِيرَةُ الْعَرَب, jazīratu l-ʿarab,意为“阿拉伯人的岛”)[1]位于西亚,其西边和非洲接壤,它从中东向东南方伸入印度洋。面积3,237,500 km2(1,250,000 sq mi),是世界上最大的半岛[2][3][4][5][6]。向西它与非洲的边界是苏伊士运河、红海和曼德海峡。向南它伸入阿拉伯海和印度洋。向东它与伊朗隔波斯湾和阿曼湾相望。沙特阿拉伯、也门、阿曼、阿拉伯联合酋长国位于阿拉伯半岛上。其中以沙特阿拉伯的面积最大,占据大部分的阿拉伯半岛。
阿拉伯半岛常年受副高压带及信风带控制,非常干燥,几乎整个半岛都是热带沙漠气候区并有面积较大的无流区,缺乏天然淡水资源,本区有七个没有河流的国家。半岛沿波斯湾周围有大量石油储藏,自从20世纪陆续成功开采后,给阿拉伯半岛上临波斯湾的国家带来了巨大的财富。
阿拉伯半岛是伊斯兰教的诞生地。伊斯兰教的创教人穆罕默德在这里出生和生活。半岛上的麦加是伊斯兰教的圣地。以阿拉伯半岛为中心的阿拉伯帝国曾横跨欧亚非大陆。今天半岛上所有国家都以伊斯兰教为国教,并以逊尼派占多数。

Das Arabische Meer (arabisch بحر العرب, DMG Baḥr al-ʿArab, persisch دریای عرب, Urdu بحیرہ عرب, Hindi अरब सागर) ist ein Randmeer des Indischen Ozeans zwischen der Arabischen Halbinsel und Indien. Es hat eine Flächenausdehnung von 3,9 Millionen km². Seine größte Tiefe von 4481 Metern liegt im Süden.[1]
Im Nordwesten grenzt es an den Golf von Oman, der wiederum mit dem Persischen Golf verbunden ist. Im Südwesten verbindet der Golf von Aden das Arabische Meer mit dem Roten Meer. Im Südosten grenzt das Arabische Meer an die Lakkadivensee. Die meisten Ozeanographen betrachten die Lakkadivensee als Teil des Arabischen Meeres. Weiter im Osten grenzt diese, bzw. das Arabische Meer im erweiterten Sinn, an den Golf von Bengalen.[2]
Länder mit Küstenabschnitten am Arabischen Meer sind die Malediven, Indien, Pakistan, Oman, Jemen und Somalia.
Städte an der Küste sind unter anderem Mumbai (Bombay) und Karachi.
Der Indus ist der bedeutendste Strom zum Arabischen Meer. Weitere Flüsse sind Narmada und Tapti, die beide in den Golf von Khambhat münden.
Im Westen des Arabischen Meeres verläuft die Owen-Bruchzone.
阿拉伯海(阿拉伯语:بحر العرب)为印度洋的一部分。位于亚洲南部的阿拉伯半岛同印度半岛之间。北部为波斯湾和阿曼湾,西部经亚丁湾通红海。面积为386万平方公里。为世界性交通要道。
アラビア海(アラビアかい)は、インド洋の北西部、アラビア半島とインドとの間の海域。
面積約3,862,000 km2[1]、最大幅約2,400 km、最大水深4,652mである。インダス川が最大の流入河川。北側にオマーン湾があり、ホルムズ海峡を通じてペルシャ湾に繋がっている。西側にはアデン湾があり、紅海に通じる。アラビア海に面する国はインド、パキスタン、オマーン、イエメン、ソマリア、モルディブである。代表的な島にソコトラ島(イエメン)やマシーラ島(オマーン)がある。
紀元前数世紀から大航海時代にかけて重要な交易ルートであった。現在も、中東原油を運ぶタンカーや欧州との間の船舶が頻繁に往来し、ソマリア海賊を取り締まる海域でもある。
The Arabian Sea is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Peninsula, on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea,[1] on the southwest by the Somali Sea,[2] and on the east by India. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west, connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
The Arabian Sea has been crossed by important marine trade routes since the third or second millennium BCE. Major seaports include Kandla Port, Okha Port, Mumbai Port, Nhava Sheva Port (Navi Mumbai), Mormugão Port (Goa), New Mangalore Port and Kochi Port in India, the Port of Karachi, Port Qasim, and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan, Chabahar Port in Iran and the Port of Salalah in Oman. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Lakshadweep (India) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
La mer d’Arabie ou mer d'Oman, parfois appelée mer arabique (en arabe بحر العرب translittéré en Baḥr al-'Arab, en sanskrit सिन्धु सागर, translittéré en Sindhu Sagar), est une partie de l'océan Indien située entre la péninsule Arabique à l'ouest, le Pakistan au nord, le subcontinent indien au nord-est et à l'est, les îles Laquedives à l'est-sud-est et l'archipel des Maldives au sud-est. Elle est limitée au nord-ouest par le golfe d'Oman et à l'ouest par le golfe d'Aden. Sa surface est d'environ 3,6 millions de km², et sa profondeur maximale est de 5 800 mètres.
La mer est une voie de passage très fréquentée, en particulier pour le transport de pétrole venant du golfe Persique. Elle est également une zone de pêche pour les pays côtiers (sardine, maquereau, thon).
Il Mar Arabico (arabo: بحر العرب; translitterato: Bahr al-'Arab, latino: Mare Erythraeum) è la sezione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, stretto tra la penisola arabica a ovest, il corno d'Africa a sud-ovest, il sub-continente indiano ad est e la costa asiatica a nord.
Il mar Arabico copre approssimativamente una superficie di 3.686.000 km² ed ha una profondità massima di 5800 metri. Corrisponde alla porzione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, ed è delimitato ad oriente dalla costa occidentale della penisola indiana, a nord dalla costa pakistana e in parte da quella persiana, ad ovest dalla penisola arabica e a sud da una linea ideale che va dal capo Guardafui, la punta nord-est della Somalia, all'isola di Socotra e fino al Capo Comorin, punta meridionale della penisola del Deccan.
Il mar Arabico comunica tramite il golfo di Oman e lo stretto di Hormuz con il golfo Persico e tramite il golfo di Aden e lo stretto di Bab al Mandab con il mar Rosso. Altri golfi importanti che fanno parte del mar Arabico sono quelli di Cambay e di Kutch in prossimità della costa nord-occidentale indiana. Le isole principali che vi affiorano sono Socotra, prolungamento della costa africana, le isole Laccadive poste in prossimità alla costa sud-orientale dell'India e le isole di Masirah e Kuria Muria poste in prossimità della costa dell'Oman.
I fiumi principali che vi sfociano sono l'Indo, il Narmada, il Tapti ed il Mahi. Le principali città che si affacciano sul mar Arabico sono Aden in Yemen; Mascate in Oman; Gwadar e Karachi in Pakistan; Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut e Kochi (Cochin) in India. Le coste sono per la maggior parte rocciose ed accidentate, ma non mancano buoni approdi naturali che hanno favorito la nascita di importanti porti (Aden, Mascate, Bandar-e Abbas, Karachi, Bombay, Cochin, Colombo ecc.). Il clima è tropicale; la regione è interessata dai venti monsonici che la investono in maniera decrescente da est verso ovest.
El mar arábigo (también llamado mar de Arabia o mar de Omán) es un mar que forma parte del océano Índico y que está localizado en la costa suroccidental de Asia, entre la península arábiga y la península del Indostán.
Tienen costa al mar arábigo, desde oeste a este, Somalia, Yemen, Omán, Pakistán, India y las islas Maldivas. Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos no tienen costa a este mar, sino a uno de sus entrantes, el golfo de Omán, en el noroeste, que luego se estrecha hasta conectar con el golfo Pérsico o Arábico en el estrecho de Ormuz.
La máxima anchura del mar arábigo es de aproximadamente 2400 km, y su máxima profundidad es de 4652 m, cerca de la península arábiga, aproximadamente a la misma latitud que el extremo sur de India. El Indo es el único río de gran envergadura que fluye hacia este mar.
Entre sus principales ciudades costeras se encuentran Bombay en India y Karachi en Pakistán.
Арави́йское мо́ре (араб. بحر العرب, перс. دریای عرب, урду بحیرہ عرب, хинди अरब सागर, сомал. Bada Carbeed, англ. Arabian Sea) — окраинное море в северной части Индийского океана. Ограничено Аравийским полуостровом на западе и полуостровом Индостан на востоке.
Общая площадь моря — 3 862 000 км²[1]. Максимальная ширина — 2400 км. Максимальная глубина — 5803 м.[2] Крупнейшая река, впадающая в море — Инд.
Крупнейшими заливами являются: на западе Аденский залив, соединяющийся с Красным морем через Баб-эль-Мандебский пролив и на северо-западе Оманский залив, соединяющийся с Персидским заливом. На побережье Индии крупными являются Камбейский залив и залив Кач.
На берегах Аравийского моря расположены Сомали, Джибути, Йемен, Оман, Иран, Пакистан, Индия и Мальдивские острова. Крупнейшие города — Карачи, Аден, Маскат, Мумбаи, Коччи и др.



Die Vereinigten Arabischen Emirate (arabisch الإمارات العربية المتحدة, DMG al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida; amtlich: arabisch دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة, DMG Dawlat al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida ‚Staat der Vereinigten Arabischen Emirate‘), kurz VAE, sind eine Föderation von sieben Emiraten im Osten der Arabischen Halbinsel in Südwestasien. An der Küste des Persischen Golfs gelegen und mit Zugang zum Golf von Oman, grenzt das Land an Saudi-Arabien und Oman. Es besteht aus den Emiraten Abu Dhabi, Adschman, Dubai, Fudschaira, Ra’s al-Chaima, Schardscha und Umm al-Qaiwain.
Die Hauptstadt der VAE ist Abu Dhabi, als eine der fünf großen Städte des Landes neben Dubai, Schardscha, Adschman und Al-Ain ist es auch ein wichtiges Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum.[5]
Vor der Unabhängigkeit 1971 waren die VAE wegen der Protektoratsverträge, die die einheimischen Herrscher im 19. Jahrhundert mit dem Vereinigten Königreich abgeschlossen hatten, als „Vertragsküste“ oder „Vertragsstaaten“ bekannt. Das politische System gründet auf der Verfassung von 1971. Der Islam ist die offizielle Religion und Arabisch die offizielle Sprache. Das siebte Emirat Ra’s al-Chaima kam 1972 dazu.
Die VAE besitzen die siebtgrößten Ölvorkommen der Welt, sind die am weitesten entwickelten Volkswirtschaften des Nahen Ostens[6] und eines der reichsten Länder der Welt mit einem Pro-Kopf-Bruttoinlandsprodukt von $ 67.871 (Kaufkraftbereinigt).[7] Das Land steht beim Index der menschlichen Entwicklung auf dem 35. Platz (Stand 2019).[8][9] Der Internationale Währungsfonds klassifiziert die VAE als “high income developing economy”.
Das Land ist Gründungsmitglied des Golf-Kooperationsrates sowie Mitgliedsstaat der Arabischen Liga, der Vereinten Nationen, der Organisation für Islamische Zusammenarbeit, der OPEC und der Welthandelsorganisation.
阿拉伯联合酋长国或阿拉伯联合酋长国(阿拉伯语:دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة),通称阿联酋、阿联,是由阿布扎比、沙迦、迪拜、阿治曼、富查伊拉、乌姆盖万、哈伊马角七个酋长国组成的联邦制君主国。位于西南亚的阿拉伯半岛东南部,与阿曼和沙特阿拉伯接壤。首都阿布扎比,也是境内最大部族的酋长国领地,阿联酋的国家地区代码为UAE。
アラブ首長国連邦(アラブしゅちょうこくれんぽう、アラビア語: الإمارات العربية المتحدة、英: United Arab Emirates,UAE)は、西アジア・中東に位置し、7つの首長国からなる連邦制国家。首都はアブダビ市。
アラビア半島のペルシア湾(アラビア語圏ではアラビア湾と呼ぶ)に面した地域にある。東部ではオマーンと、南部および西部ではサウジアラビアと隣接する。カタールとは国境を接していないが、カタールとの間のサウジアラビアの一部地域の領有権をめぐる論争がある。
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; Arabic: الإمارات العربية المتحدة al-ʾImārāt al-ʿArabīyyah al-Muttaḥidah), sometimes simply called the Emirates (Arabic: الإمارات al-ʾImārāt), is a country in Western Asia at the northeast end of the Arabian Peninsula on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman to the east and Saudi Arabia to the south and west, as well as sharing maritime borders with Qatar to the west and Iran to the north. The sovereign constitutional monarchy is a federation of seven emirates consisting of Abu Dhabi (which serves as the capital), Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah and Umm Al Quwain. Their boundaries are complex, with numerous enclaves within the various emirates.[9] Each emirate is governed by a ruler; together, they jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the rulers serves as the President of the United Arab Emirates.[10] In 2013, the UAE's population was 9.2 million, of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million are expatriates.[11][12][13]
Human occupation of the present UAE has been traced back to the emergence of anatomically modern humans from Africa some 125,000 BCE through finds at the Faya-1 site in Mleiha, Sharjah. Burial sites dating back to the Neolithic Age and the Bronze Age include the oldest known such inland site at Jebel Buhais. Known as Magan to the Sumerians, the area was home to a prosperous Bronze Age trading culture during the Umm Al Nar period, which traded between the Indus Valley, Bahrain and Mesopotamia as well as Iran, Bactria and the Levant. The ensuing Wadi Suq period and three Iron Ages saw the emergence of nomadism as well as the development of water management and irrigation systems supporting human settlement in both the coast and interior. The Islamic age of the UAE dates back to the expulsion of the Sasanians and the subsequent Battle of Dibba. The UAE's long history of trade led to the emergence of Julfar, in the present-day emirate of Ras Al Khaimah, as a major regional trading and maritime hub in the area. The maritime dominance of the Persian Gulf by Emirati traders led to conflicts with European powers, including the Portuguese Empire and the British Empire.
Following decades of maritime conflict, the coastal emirates became known as the Trucial States with the signing of the General Maritime Treaty with the British in 1820 (ratified in 1853 and again in 1892), which established the Trucial States as a British Protectorate. This arrangement ended with independence and the establishment of the United Arab Emirates on 2 December 1971, immediately following the British withdrawal from its treaty obligations. Six emirates joined the UAE in 1971, the seventh, Ras Al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972.[14]
Islam is the official religion and Arabic is the official language of the UAE. The UAE's oil reserves are the sixth-largest in the world while its natural gas reserves are the world's seventh-largest.[15][16] Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure.[17] The UAE's economy is the most diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, while its most populous city of Dubai is an important global city and international aviation and maritime trade hub.[18][19] Consequently, the country is much less reliant on oil and gas than in previous years and is economically focusing on tourism and business. The UAE government does not levy income tax although there is a system of corporate tax in place and Value Added Tax at 5% was established in 2018.[20]
The UAE's rising international profile has led to it being recognised as a regional and a middle power.[21][22] It is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, OPEC, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
Les Émirats arabes unis Écouter (abrégés en EAU ou Émirats ; en arabe : الإمارات العربية المتحدة (al-imārāt al-ʿarabiyyat al-muttaḥida) دولة الإمارات العربيّة المتّحدة (dawlat al-imārāt al-ʿarabiyyat al-muttaḥida)) sont un État fédéral, créé en 1971, situé au Moyen-Orient entre le golfe Persique et le golfe d'Oman. Il est composé de sept émirats : Abou Dabi, Ajman, Charjah, Dubaï, Fujaïrah, Ras el Khaïmah et Oumm al Qaïwaïn4. Sa capitale fédérale est la ville d'Abou Dabi.
Les Émirats arabes unis comptent parmi les plus importants producteurs et exportateurs de pétrole.
En 2018, il comptent 9 701 315 habitants. L'ONU estime que 90 % de la population est constituée d'immigrants2.
Les principales réserves gazières et pétrolières sont dans l'émirat d'Abou Dabi, déjà membre de l'Organisation des pays exportateurs de pétrole avant la création de la fédération. Les sept Émirats ne sont pas égaux entre eux en ce qui concerne les ressources pétrolières.
L'émirat de Dubaï s'est tourné depuis quelques années vers de nouvelles ressources telles que les ports francs, les nouvelles technologies mais surtout le tourisme de luxe. La ville de Dubaï est d'ailleurs devenue la capitale économique de la fédération.
Gli Emirati Arabi Uniti (in arabo: دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة, Dawlat al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida, «Stato degli Emirati Arabi Uniti») sono uno Stato nel sud-est della Penisola araba, nell'Asia sud-occidentale. Esso è composto da sette emirati: Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujaira, Ras al-Khaima, Sharja e Umm al-Qaywayn. Prima del 1971, erano noti come gli Stati della tregua (Trucial States), con riferimento a una tregua imposta nel XIX secolo dai britannici ad alcuni sceicchi arabi che non contrastavano, e anzi foraggiavano, attività piratesche miranti a colpire il naviglio transitante nel tratto di mare di loro competenza. La nazione confina con l'Oman a sud-est, con l'Arabia Saudita a sud-Ovest ed è bagnata dal Golfo Persico a nord.
Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos (en árabe, دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة Dawlat Al-Imārāt al-‘Arabīya al-Muttaḥida) —o simplemente conocido como EAU— es un país soberano constituido en monarquía federal5 de Oriente Medio, situado en la península de Arabia. Está compuesto por siete emiratos:6 Abu Dabi, Ajmán, Dubái, Fuyaira, Ras al-Jaima, Sarja y Umm al-Qaywayn. Limita con Omán al sureste, con el golfo Pérsico al norte y con Arabia Saudita al oeste y sur.
El petróleo es la principal fuente de ingresos y el componente esencial de su PIB.7 Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos son la 30ª economía por volumen de PIB y en cuanto al índice de desarrollo humano elaborado por Naciones Unidas fueron situados en el puesto n.º 42 de entre de 188 países en 2016.8
Los primeros asentamientos importantes en la región datan de la Edad del Bronce.9 En el siglo VII d.C. se vio la llegada del Islam y durante el siglo XVI, el territorio cayó bajo la influencia de las potencias coloniales europeas, asentándose finalmente el dominio británico. Tras el fin del protectorado del Reino Unido en diciembre de 1971, seis jeques formaron la unión suscribiendo la Constitución de 1971, a la cual se unió Ras al-Jaima unos meses después.10 Cada emirato conserva una considerable autonomía política, judicial y económica.11
Объединённые Ара́бские Эмира́ты (араб. الإمارات العربية المتحدة [аль-Имара́т аль-Араби́я аль-Мутта́хида], англ. United Arab Emirates), аббр. ОАЭ (сокращённо — Арабские Эмираты или просто Эмираты) — федеративное государство на Ближнем Востоке, состоящее из семи эмиратов (араб. إمارات [имара́т], ед.ч. إمارة [има́ра]), каждый из которых представляет собой государство — абсолютную монархию: Абу-Даби, Аджман, Дубай, Рас-аль-Хайма, Умм-эль-Кайвайн, Фуджейра и Шарджа. Некоторые из перечисленных эмиратов попадают под определение карликового государства.
Государство возглавляется президентом Объединённых Арабских Эмиратов, которым является эмир крупнейшего эмирата Абу-Даби. Столицей Объединённых Арабских Эмиратов также является одноимённая столица этого эмирата.
Такая ключевая роль эмирата Абу-Даби, крупнейшего и наиболее богатого из эмиратов, во многом связана с тем, что административное устройство ОАЭ опирается на право каждого эмирата распоряжаться запасами углеводородов на своей территории. Таким образом, фактически, в соответствии с запасами нефти распределяется влияние тех или иных эмиратов в определении общей политики страны. Например, эмир Дубая является главой правительства ОАЭ.
Государство ОАЭ расположено в юго-западной части Азии, восточной части Аравийского полуострова. Граничит с Саудовской Аравией на западе и юге, с Оманом — на юго-востоке и на северо-востоке (оманский полуанклав губернаторство Мусандам и его полный анклав, вилайет Мусандама Мадха). Омывается водами Персидского и Оманского заливов.


 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Bahrain
Bahrain

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Gambia
Gambia

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institute of Culture and Language
Institute of Culture and Language
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Katar
Katar
 Comoros
Comoros
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Literature
Literature
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Oman
Oman
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Republik Südsudan
Republik Südsudan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Senegal
Senegal
 Somalia
Somalia
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 United Nations
United Nations
 Official languages
Official languages
 Cyprus
Cyprus
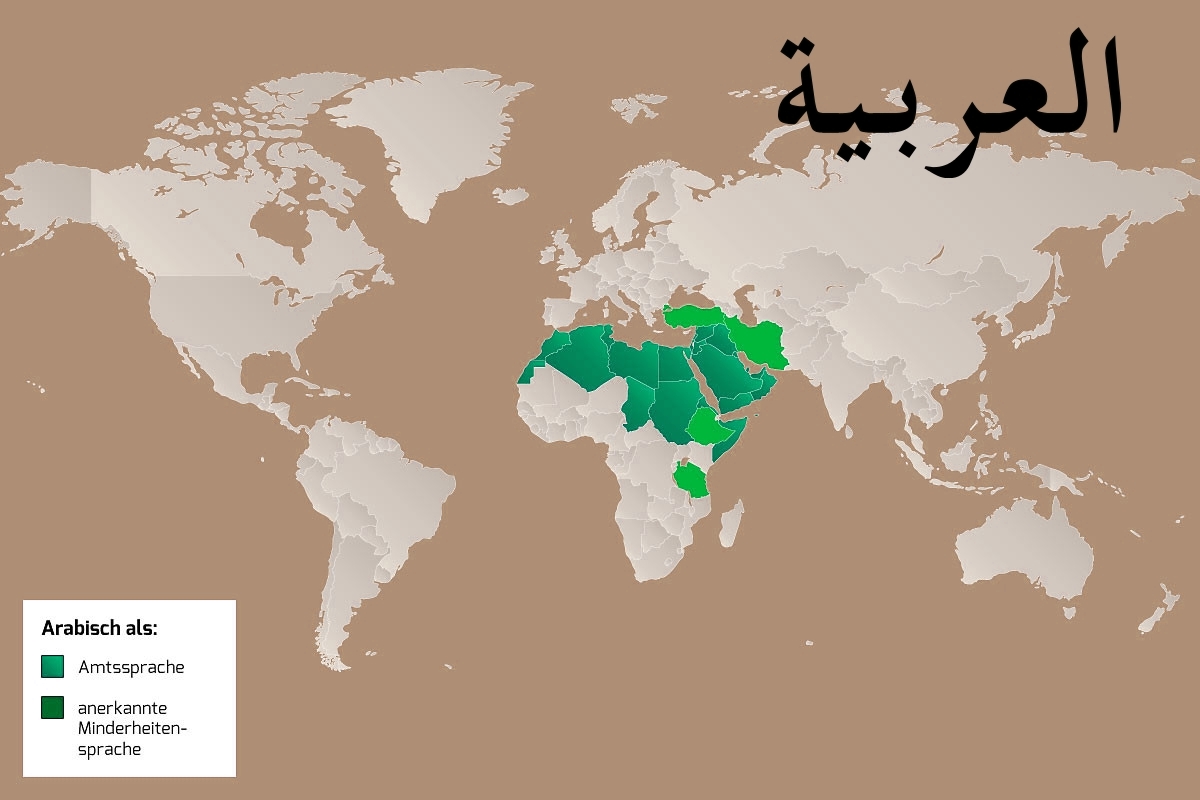
Die arabische Sprache (kurz Arabisch; Eigenbezeichnung اَللُّغَةُ اَلْعَرَبِيَّة, DMG al-luġatu l-ʿarabiyya ‚die arabische Sprache‘, kurz العربية, DMG al-ʿarabiyya ‚das Arabische‘, Ausspracheⓘ/?) ist die am weitesten verbreitete Sprache des semitischen Zweigs der afroasiatischen Sprachfamilie und in ihrer Hochsprachform الفصحى / al-Fuṣḥā eine der sechs Amtssprachen der Vereinten Nationen. Schätzungsweise wird Arabisch von 313 Millionen Menschen als Muttersprache und von weiteren 424 Millionen als Zweit- oder Fremdsprache gesprochen.[2][3] Auch durch seine Rolle als Sakralsprache entwickelte sich das Arabische zur Weltsprache.[4] Die moderne arabische Standardsprache beruht auf dem klassischen Arabischen, der Sprache des Korans und der Dichtung, und unterscheidet sich stark von den gesprochenen Varianten des Arabischen.
Aus dem klassischen Arabisch hat sich in den letzten anderthalb Jahrtausenden eine Vielzahl von Dialekten entwickelt. Für alle Sprecher dieser Sprache, außer den Sprechern des Maltesischen, ist Hocharabisch Schrift- und Dachsprache. Das Maltesische ist mit den maghrebinisch-arabischen Dialekten stark verwandt, wurde jedoch im Gegensatz zu den anderen gesprochenen Formen des Arabischen zu einer eigenständigen Standardsprache ausgebaut. Ob Hocharabisch als moderne Standardsprache zu betrachten ist, ist umstritten (siehe auch Ausbausprache). Es fehlt oft an einem einheitlichen Wortschatz für viele Begriffe der modernen Welt sowie am Fachwortschatz in vielen Bereichen moderner Wissenschaften. Darüber hinaus ist Hocharabisch innerhalb der einzelnen arabischen Länder relativ selten ein Mittel zur mündlichen Kommunikation.
Die einzelnen arabischen Dialekte in den verschiedenen Ländern unterscheiden sich teilweise sehr stark voneinander, wenn auch meist nur in der Aussprache, und sind bei vorliegender geographischer Distanz gegenseitig nicht oder nur schwer verständlich. So werden beispielsweise algerische Filme, die im dortigen Dialekt gedreht worden sind, zum Teil hocharabisch untertitelt, wenn sie in den Golfstaaten ausgestrahlt werden.
阿拉伯语(اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ,al-ʿarabiyyah [al ʕaraˈbijːa] (ⓘ)或者 عربي/عربى,ʿarabīy [ˈʕarabiː] (ⓘ)或 [ʕaraˈbij]),书写形式也称阿拉伯文,是除了英语和法语之外最多国家使用的官方语言。阿拉伯语源自公元6世纪的古典阿拉伯语。它包括书面语及流通于中东、北非和非洲之角(即索马里半岛)的各种口语。阿拉伯语属于亚非语系。
 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR
 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS
 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK
 Party and government
Party and government
 States of Asia
States of Asia



