Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 英格兰
英格兰



伦敦希思罗机场是世界上最繁忙的国际机场。我们的四个候机楼接待往返于世界 90 多个国家/地区 180 多个目的地的乘客。 无论您是入港、出港或转机,我们都提供必要的中文向导,让您的旅程轻松愉快。
伦敦希思罗机场(英语:London Heathrow Airport;IATA代码:LHR;ICAO代码:EGLL),通常简称为希思罗机场,是英国首都伦敦的主要国际机场,同时是英国航空与维珍航空的枢纽机场,位于大伦敦西侧的希灵登区,距离伦敦市中心约23千米(14英里),拥有2条平行的东西向跑道及4座航站楼,为全英国乃至全世界最繁忙的机场之一。运营机构为希思罗机场控股公司。
截至2016年,希思罗机场的总客运量在全球机场中排行第7,但因拥有众多的跨境航班,若仅计算跨境的客运流量,则为全球机场第二位,自2014年起仅次于迪拜国际机场。希思罗机场同时是全欧洲最繁忙的机场,相较巴黎戴高乐机场与法兰克福国际机场的客量还要高出31.5%,但航班数目则比该两个机场的总和少三分之一。这反映出由于航班数目限制下,航空公司多利用载客量高的广体客机(如空中客车A380、波音747、波音777)运营来往希思罗机场的航线。
Der Flughafen London Heathrow (IATA-Code: LHR, ICAO-Code: EGLL) ist der größte der sechs internationalen Verkehrsflughäfen der britischen Hauptstadt London. Er ist mit 78.047.278 Passagieren im Jahr 2017 der größte Flughafen Europas sowie der sechstgrößte weltweit. Heathrow dient als Drehkreuz für British Airways und Virgin Atlantic.
ロンドン・ヒースロー空港(ロンドン・ヒースローくうこう、英語: London Heathrow Airport)は、イギリスの首都ロンドンの西部にある最大規模の空港で、国際線利用者数では2013年まで世界一の空港だった[3]。所有・運営は、民間会社のイギリス空港会社 (BAA) である。空港コードはLHR (IATA) /EGLL (ICAO) 。ブリティッシュ・エアウェイズ、ヴァージン・アトランティック航空のハブ空港になっている。
Heathrow Airport (also known as London Heathrow)[2] (IATA: LHR, ICAO: EGLL) is a major international airport in London, United Kingdom. Heathrow is the second busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic, as well as the busiest airport in Europe by passenger traffic, and the seventh busiest airport in the world by total passenger traffic. It is one of six international airports serving Greater London. In 2017, it handled a record 78.0 million passengers, a 3.1% increase from 2016.[1]
Heathrow lies 14 miles (23 km) west of Central London,[3] and has two parallel east–west runways along with four operational terminals on a site that covers 12.27 square kilometres (4.74 sq mi). The airport is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings, which itself is owned by FGP TopCo Limited, an international consortium led by Ferrovial that also includes Qatar Holding LLC, Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec, GIC Private Limited, Alinda Capital Partners, China Investment Corporation and Universities Superannuation Scheme (USS).[4] London Heathrow is the primary hub for British Airways and the primary operating base for Virgin Atlantic.
In September 2012, the UK government established the Airports Commission, an independent commission chaired by Sir Howard Davies to examine various options for increasing capacity at UK airports. In July 2015, the commission backed a third runway at Heathrow, which the government approved in October 2016.[5][6][7]
L'aéroport International de Londres Heathrow (code AITA : LHR • code OACI : EGLL) est un aéroport situé dans la banlieue ouest de Londres au Royaume-Uni.
Il est le quatrième aéroport au niveau mondial selon le nombre total de passagers et le deuxième selon le nombre de passagers internationaux derrière Dubaï (chiffres provisoires 2014). C'est également le premier aéroport d'Europe en nombre de passagers1. En ce qui concerne le nombre de mouvements, l'aéroport ne se classe qu'au 13e rang mondial avec 476 197 décollages/atterrissages en 20111, mais est premier d'Europe devant Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle.
Il est l'un des six aéroports internationaux de Londres et il appartient à BAA Limited. L'aéroport de Londres Heathrow constitue la plate-forme de correspondance principale (hub) pour plusieurs compagnies aériennes britanniques, British Airways, bmi et Virgin Atlantic.
L'Aeroporto di Londra-Heathrow (IATA: LHR, ICAO: EGLL) (/hiːθˈroʊ/;[2] in inglese: London Heathrow Airport) è l'aeroporto principale di Londra con 72 367 054 passeggeri transitati nel 2013 rendendolo l'aeroporto più trafficato d'Europa e il settimo al mondo per passeggeri transitati, ma trasporta più passeggeri internazionali di ogni altro aeroporto al mondo.
L'aeroporto è situato a 31 km ad ovest dal centro di Londra e con due piste parallele in direzione est-ovest accanto ai terminal occupa una superficie di 12,14 km2. L'aeroporto è di proprietà, insieme ad altri tre aeroporti del Regno Unito, dell'Heathrow Airport Holdings, società partecipata principalmente dalla spagnola Ferrovial Group, dalla Cassa Depositi e Prestiti del Québec e da GIC Private Limited, un fondo d'investimenti di Singapore. Londra-Heathrow è hub di British Airways e Virgin Atlantic Airways.
Secondo l'Airport Commission, una commissione indipendente guidata da Howard Davis fondata nel settembre 2012 dal governo britannico, ha presentato due opzioni su una possibile espansione di Heathrow, insieme ad una terza opzione che mostrava invece come espandere Gatwick. Il rapporto finale verrà presentato nel corso dell'estate 2015 e mostrerà come Londra, l'Inghilterra e il Regno Unito manterranno il loro status di hub mondiale, in quanto Londra ha il sistema aeroportuale più trafficato al mondo.
El Aeropuerto de Londres Heathrow3 (código IATA: LHR, código OACI: EGLL), o simplemente Heathrow, es el aeropuerto con mayor actividad y conexiones en el Reino Unido.
En el año 2014, recibió más tráfico internacional de pasajeros que cualquier otro aeropuerto en el mundo. Además de que en ese mismo año fue el aeropuerto con mayor actividad en Europa respecto al tráfico total de pasajeros (un 31,5% más de pasajeros que el aeropuerto Charles de Gaulle de París o el aeropuerto de Fráncfort del Meno), pero estuvo en segundo lugar (tras el de Charles de Gaulle) respecto a los movimientos de aeronaves (un 10% menos que el aeropuerto francés) y fue tercero respecto al tráfico de carga.
El Aeropuerto de Heathrow se encuentra en Heathrow, en el distrito de Hillingdon, en el área oeste de Londres.
La nueva Terminal 5 es una de las terminales más modernas del mundo que fue expandida de 2012 a 2014. Lo más destacable de esta expansión es la construcción de un edificio de producción de frío para climatización, el cual es el de mayor complejidad y capacidad frigorífica de Europa, y para cuya construcción se ha destinado al mismo equipo de ingenieros que dirigió el montaje de las instalaciones del aeropuerto de Varsovia-Chopin.
Лондонский аэропорт Хи́троу (англ. London Heathrow Airport; IATA: LHR, ICAO: EGLL, FAA LID: EGLL) — крупнейший международный аэропорт города Лондона. Седьмой по загруженности пассажирский аэропорт в мире в 2016 году (75,7 млн человек)[1], и первый в Европе. Расположен в 24 км к западу от центрального Лондона. Включает 5 пассажирских терминалов и один грузовой. Последний, 5-й терминал, открыт 14 марта 2008 года королевой Елизаветой II.
 阿塞拜疆
阿塞拜疆
 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 巴林
巴林
 比利时
比利时
 巴西
巴西
 中国
中国
 联邦德国
联邦德国

 艾米利亚-罗马涅大区
艾米利亚-罗马涅大区
 英格兰
英格兰

 佛罗里达州
佛罗里达州
 2017年世界一级方程式锦标赛
2017年世界一级方程式锦标赛
 2018年世界一级方程式锦标赛
2018年世界一级方程式锦标赛

 2025年世界一级方程式锦标赛
2025年世界一级方程式锦标赛
 法国
法国
 印度
印度
 意大利
意大利
 日本
日本
 加拿大
加拿大
 卡塔尔
卡塔尔
 近畿地方
近畿地方

 伦巴第大区
伦巴第大区
 墨西哥
墨西哥
 摩纳哥
摩纳哥

 内华达州
内华达州
 奥地利
奥地利

 魁北克省
魁北克省
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 圣保罗州
圣保罗州
 沙特阿拉伯
沙特阿拉伯
 瑞士
瑞士
 上海市-沪
上海市-沪
 新加坡
新加坡
 西班牙
西班牙

 体育
体育

 施泰尔马克
施泰尔马克

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 阿拉伯联合酋长国
阿拉伯联合酋长国
 美国
美国
 英国
英国

 维多利亚州
维多利亚州

一级方程式赛车(英语:Formula One,也叫Formula 1或者F1)是由国际汽车联盟举办的最高等级的年度系列场地方程式赛车比赛,正式名称为“国际汽车联合会世界一级方程式锦标赛”。名称中“方程式”是指一组所有参赛车辆都必须遵守的规则[1]。F1赛季包括一系列的比赛,而这些所谓的“大奖赛”(Grand Prix,出自法语,本意Great Prizes)的场地是全封闭的专门赛道或者是临时封闭的普通公路。每场比赛的结果算入积分系统并以此确定两个年度世界冠军:一个给车手和另一个给制造商。F1的车手、制造商、组织者以及赛道都必须持有FIA超级驾驶执照,这是国际汽联颁发的最高级别执照。
一级方程式赛车通过产生大量的空气动力学下压力达到非常高的过弯速度,是风靡全球的赛车运动。发动机性能限制在每分钟最多15000转时,其比赛最高速度就可以超过360公里/小时。赛车过弯的横向加速度超过5个标准重力。F1赛车的性能非常依赖电子系统(牵引力控制系统和其他辅助驾驶装置自2008年已被禁止)、空气动力学、悬挂和轮胎。
Die Formel 1 ist eine vom Automobil-Dachverband Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA) festgelegte Formelserie. Hersteller konstruieren Autos, die den Formel-1-Regeln entsprechen. Diese Autos treten im Rahmen der Formel-1-Weltmeisterschaft zu Rennen in ungefähr 20 Orten pro Jahr an. Am Ende der Saison wird der Fahrer mit den meisten Punkten F1 Fahrerweltmeister und der Hersteller mit den meisten Punkten Konstrukteursweltmeister.
Die Formel 1 ist die höchstrangige von der FIA veranstaltete Rennserie des Formelsports. Sie wird als Königsklasse des Automobilsports bezeichnet, da sie den Anspruch erhebt, die höchsten technischen, fahrerischen, aber auch finanziellen Anforderungen aller Rennserien an Fahrer und Konstrukteure zu stellen. Sie wird auch kurz F1 genannt. Die F1 Weltmeisterschaft heißt offiziell FIA Formula One World Championship, bis 1980 hat sie Automobil-Weltmeisterschaft geheissen.
Formula One (also Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of single-seater auto racing sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) and owned by the Formula One Group. The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The "formula" in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants' cars must conform.[2] A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as Grands Prix (French for "grand prizes" or "great prizes"), which are held worldwide on purpose-built circuits and public roads.
The results of each race are evaluated using a points system to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Drivers must hold valid Super Licences, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA.[3] The races are required to be held on tracks graded "1" (formerly "A"), the highest grade rating issued by the FIA.[3] Most events are held in rural locations on purpose-built tracks, but there are several events in city centres throughout the world, with the Monaco Grand Prix being the most well-known.
Formula One cars are the fastest regulated road course racing cars in the world, owing to very high cornering speeds achieved through the generation of large amounts of aerodynamic downforce. The cars underwent major changes in 2017,[4] allowing wider front and rear wings, and wider tyres, resulting in cornering forces closing in on 8g and top speeds of up to approximately 375 km/h (230 mph).[5] The hybrid engines are currently limited in performance to a maximum of 15,000 rpm and the cars are very dependent on electronics—although traction control and other driving aids have been banned since 2008—and also on aerodynamics, suspension, and tyres.
While Europe is the sport's traditional base, the championship is truly global, with 11 of the 21 races in the 2018 season taking place outside Europe. With the annual cost of running a mid-tier team—designing, building, and maintaining cars, pay, transport—being US$120 million,[6] Formula One has a significant economic and job-creation effect, and its financial and political battles are widely reported. Its high profile and popularity have created a major merchandising environment, which has resulted in large investments from sponsors and budgets (in the hundreds of millions for the constructors). On 8 September 2016, it was announced that Liberty Media had agreed to buy Delta Topco, the company that controls Formula One, from private equity firm CVC Capital Partners for $4.4 billion in cash, stock, and convertible debt.[7] On 23 January 2017, it was confirmed that the acquisition had been completed, for $8 billion.[8]
La Formule 1, communément abrégée en F1, est une discipline de sport automobile considérée comme la catégorie reine de ce sport. Elle a pris au fil des ans une dimension mondiale et elle est, avec les Jeux olympiques et la Coupe du monde de football, l'un des événements sportifs les plus médiatisés.
Chaque année depuis 1950, un championnat mondial des pilotes est organisé, complété depuis 1958 par un championnat mondial des constructeurs automobiles. La compétition est basée sur des Grands Prix, courses à bord de voitures monoplaces disputées sur circuits routiers fermés permanents mais parfois tracés en ville et temporaires, comme à Monaco, Valence, Singapour, et Bakou.
Cette discipline sportive, régie par la Fédération internationale de l'automobile (FIA), est gérée par la Formula One Administration (FOA) et un ensemble de sociétés satellites contrôlées par Liberty Media. Après l'ère des artisans des années 1960 et 1970, elle a peu à peu attiré les grands constructeurs automobiles mondiaux qui y investissent des sommes élevées, en espérant tirer profit des retombées médiatiques d'éventuels succès. La Formule 1 est considérée comme la vitrine technologique de l'industrie automobile qui y expérimente des nouveautés techniques, parfois issues de la technologie spatiale et susceptibles d'être adaptées ensuite sur les voitures de série.
Outre la compétition, le terme Formule 1 désigne l'ensemble des règles techniques des voitures monoplaces qui sont mises à jour tous les ans par la FIA. Ces règles sont très strictes sur les dimensions des voitures, la cylindrée des moteurs, les technologies mises en œuvre ; elles définissent également les mesures de sécurité des voitures pour assurer la protection du pilote. Les monoplaces de course répondant aux caractéristiques de la réglementation de la Formule 1 sont généralement désignées sous le terme générique de Formules 1.
La Formula 1 o Formula Uno,[1] in sigla F1, è la massima categoria (in termini prestazionali) di vetture monoposto a ruote scoperte da corsa su circuito definita dalla Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile (FIA).
La categoria è nata nel 1948 (in sostituzione della Formula A, a sua volta sorta solo qualche anno prima, nel 1946), diventando poi a carattere mondiale nella stagione 1950. Inizialmente definita dalla Commissione Sportiva Internazionale (CSI) dell'Associazione Internazionale degli Automobil Club Riconosciuti (AIACR), associazione antesignana della Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile, oggi la Formula Uno è regolata dal Consiglio Mondiale degli Sport Motoristici (in inglese: World Motor Sport Council, WMSC) della Federazione Internazionale dell'Automobile.
Il termine "formula", presente nel nome, fa riferimento a un insieme di regole alle quali tutti i partecipanti, le macchine e i piloti, devono adeguarsi; esse introducono un numero di restrizioni e specifiche nelle auto, al fine di evitare le eccessive disparità tecniche tra le auto, di porre dei limiti al loro sviluppo e di ridurre i rischi di incidenti. La formula ha avuto molti cambiamenti durante la sua storia. Ad esempio, ci sono stati differenti tipi di motori, con schemi da quattro fino a sedici cilindri e con cilindrate da 1,5 a 4,5 l.
La Fórmula 1, abreviada como F1 y también denominada la «categoría reina del automovilismo»1 o «la máxima categoría del automovilismo»,23 es la competición de automovilismo internacional más popular y prestigiosa, superando a categorías de automovilismo como la NASCAR, el Campeonato Mundial de Rally, el Campeonato Mundial de Turismos o la Fórmula E, entre otras.4 A cada carrera se le denomina Gran Premio y el torneo que las agrupa se denomina Campeonato Mundial de Fórmula 1. La entidad que la dirige es la Federación Internacional del Automóvil (FIA). El Formula One Group es controlado por la empresa estadounidense Liberty Media desde septiembre de 2016.5
Los automóviles utilizados son monoplazas con la última tecnología disponible, siempre limitadas por un reglamento técnico; algunas mejoras que fueron desarrolladas en la Fórmula 1 terminaron siendo utilizadas en automóviles comerciales, como el freno de disco.6 La mayoría de los circuitos de carreras donde se celebran los Grandes Premios son autódromos, aunque también se utilizan circuitos callejeros y anteriormente se utilizaron circuitos ruteros.
El inicio de la Fórmula 1 moderna se remonta al año 1950, en el que participaron escuderías como Ferrari, Alfa Romeo y Maserati. Algunas fueron reemplazadas por otras nuevas como McLaren, Williams, Red Bull y Renault, que se han alzado varias veces con el Campeonato Mundial de Constructores. Las escuderías tienen que planear sus fichajes y renovación de contratos 2 o 3 carreras antes del fin de la temporada. Por su parte, los pilotos deben contar con la superlicencia de la FIA para competir, que se obtiene sobre la base de resultados en otros campeonatos.

共济会(英语:Freemasonry[注 1]),是一个会所遍布全球的兄弟会组织,由中世纪末欧洲地区的石匠行业协会演变而来,[注 2]现代的共济会起源于英格兰,英国共济联合总会(United Grand Lodge of England, UGLE) 成立于公元1717年,爱尔兰总会和苏格兰总会分别成立于1725年和1736年,这三个总会成为全球所有总会的起源。
英国共济联合总会建立后共济会的精神哲理迅速扩散至欧洲大陆和美洲,其成员在各个国家成立了自己的共济会总会,网罗了世界上无数的菁英,如杜鲁门等14位美国总统,如乔治华盛顿、加里波底、黎刹医生、穆斯塔法·凯末尔·阿塔图克、西蒙·玻利瓦尔等建国英雄,又如伏尔泰、孟德斯鸠等启蒙运动的哲学家,或是维克多·雨果、柯南·道尔等小说家,还有莫扎特、海顿等音乐家,再如鲁道夫·施泰纳、亚历山大·弗莱明等科学家,带领人们走出大战的丘吉尔、罗斯福等等杰出的人才都聚集在这个大家庭之中,目前全球约有400万以上的会员。[1]
共济会的会员等级制度至今仍带有浓厚的中世纪色彩[注 3],除了承袭石匠的建筑工艺之外也受到当时骑士精神和启蒙运动的影响,化为自己独特的仪式、标志、辨认方式和独特的教育系统。共济会组织其会员遍布众多国家和地区的学术界、艺术界、政界和商界。
共济会没有没有统一的中央组织主宰,加入者需与各地的共济会联系,获得两位共济会会员作为介绍人才可以提交申请。历史上大多数共济会会所只接受男性入会,直到20世纪开始,才开始有以共济会为名义成立并只接受女性入会的组织,例如:女子共济会的秩序(The Order of Women Freemasons)与Honourable Fraternity of Ancient Freemasons (HFAF) —— 古代共济会(HFAF – Freemasonry for Women (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆))[2]。[3]
于2024年6月,英国共济联合总会(UGLE)、女子共济会的秩序(OWF)和古代共济会(HFAF)这三个机构宣布成立历史性的共济会理事会(Council for Freemasonry in England and Wales),目的是以消除误解,解决面临的挑战,并促进包容等基本原则。尽管现仍有错误说法称共济会仅限男性加入,但女子共济会已经成为英国共济会一个世纪以来不可或缺的一部分。新成立的理事会将为合作提供一个正式的平台,促进各机构的社区服务目标,协调与其他组织的沟通和交流,并推动会员增长,尤其是女性会员。理事会将由每个大会的领袖组成,每届大会将严格轮流担任为期12个月的主席。理事会的成立是增进合作、消除误解,以及弘扬共济会价值观的关键一步。
Die Freimaurerei ist eine international verbreitete Bewegung von zumeist männlichen Initiationsgemeinschaften, die in sogenannten Logen organisiert sind. Die Mitglieder sind in Grade eingeteilt, von denen es je nach Lehrsystem drei bis 33 gibt. Sie treffen sich zu geselligen und ethisch-religiösen Zwecken und führen Zeremonien durch, die sogenannte Tempelarbeit.
Über die Vorgänge innerhalb der Versammlungen besteht Verschwiegenheitspflicht. Wegen dieses Arkanprinzips wird die Freimaurerei mitunter als Geheimbund bzw. Geheimgesellschaft bezeichnet, und viele Verschwörungstheorien sind über sie im Umlauf. Die Freimaurerei selbst versteht sich als Bund freier und gleicher Menschen mit der Überzeugung, dass die ständige Arbeit an sich selbst zu Selbsterkenntnis und einem menschlicheren Verhalten führe. Die fünf Grundideale der Freimaurerei sind Freiheit, Gleichheit, Brüderlichkeit, Toleranz und Humanität. Es gibt, je nach Quelle, weltweit 2,6 bis sieben Millionen Freimaurer.
Die Ursprünge der Freimaurerei liegen im Dunkeln. Sicher belegt ist die Gründung der ersten Großloge in London 1717. Deren Konstitution, die Alten Pflichten von 1723 bildet die Grundlage der heutigen Freimaurerei. Gemeinsam mit den Salons, den Lesegesellschaften und anderen Zusammenschlüssen der frühen Aufklärung bildeten die Logen in ganz Europa eine neue Form von Öffentlichkeit und trugen zur Verbreitung aufklärerischer Ideen bei. Zwei der bekanntesten freimaurerischen Symbole sind Winkel und Zirkel (in Amerika mit dem zentralen Buchstaben „G“, der oft für die allgegenwärtige Geometrie steht).

Freshfields (bis Oktober 2024 Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer) ist eine international tätige Wirtschaftskanzlei mit Sitz in London. Die Kanzlei berät und vertritt nationale und internationale Unternehmen, Finanzinstitutionen und Regierungen. In Deutschland firmiert die Kanzlei unter dem Namen Freshfields PartG mbB.
富而德律师事务所(Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer)是全球最大的顶级跨国律师事务所,总部位于英国伦敦。
 阿塞拜疆
阿塞拜疆

 巴伐利亚州
巴伐利亚州
 比利时
比利时

 巴斯克自治区
巴斯克自治区
 丹麦
丹麦
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 英格兰
英格兰
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 B组
B组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 A组
A组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 C组
C组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 D组
D组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 E组
E组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 F组
F组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 G组
G组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 H组
H组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 I组
I组
 欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
欧洲足球锦标赛 2020
 J组
J组
 爱尔兰
爱尔兰
 意大利
意大利

 拉齐奥大区
拉齐奥大区
 荷兰
荷兰
 罗马尼亚
罗马尼亚
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 苏格兰
苏格兰
 西班牙
西班牙
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 英国
英国
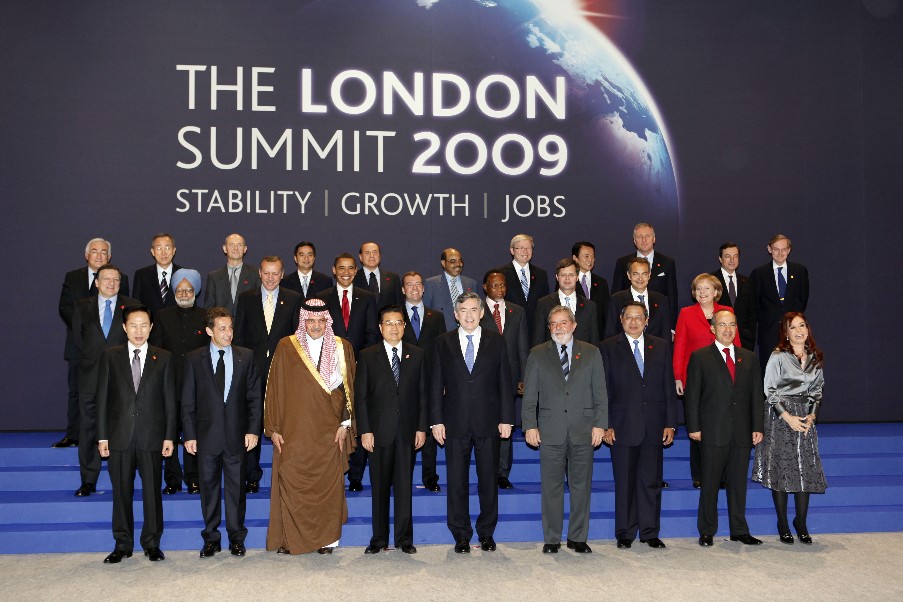
 阿卜杜拉·本·阿卜杜勒-阿齐兹
阿卜杜拉·本·阿卜杜勒-阿齐兹
 阿披实·威差奇瓦
阿披实·威差奇瓦
 安格娜·默克尔
安格娜·默克尔
 东南亚国家联盟
东南亚国家联盟
 素林·披苏旺
素林·披苏旺
 贝拉克·奥巴马
贝拉克·奥巴马
 克里斯蒂娜·费尔南德斯·德基什内尔
克里斯蒂娜·费尔南德斯·德基什内尔
 德米特里·阿纳托利耶维奇·梅德韦杰夫
德米特里·阿纳托利耶维奇·梅德韦杰夫
 英格兰
英格兰
 费利佩·卡尔德龙
费利佩·卡尔德龙
 金融稳定委员会
金融稳定委员会
 马里奥·德拉基
马里奥·德拉基

 财政金融
财政金融
 联合国秘书长
联合国秘书长
 潘基文
潘基文

 手拉手
手拉手
 胡锦涛
胡锦涛
 国际货币基金组织
国际货币基金组织
 多米尼克·斯特劳斯-卡恩
多米尼克·斯特劳斯-卡恩
 詹姆斯·戈登·布朗
詹姆斯·戈登·布朗
 扬·彼得·巴尔克嫩德
扬·彼得·巴尔克嫩德
 何塞·路易斯·罗德里格斯·萨帕特罗
何塞·路易斯·罗德里格斯·萨帕特罗
 若泽·曼努埃尔·巴罗佐
若泽·曼努埃尔·巴罗佐
 陆克文
陆克文
 卡莱马·莫特兰蒂
卡莱马·莫特兰蒂
 李明博
李明博
 李明博
李明博
 路易斯·伊纳西奥·卢拉·达席尔瓦
路易斯·伊纳西奥·卢拉·达席尔瓦
 曼莫汉·辛格
曼莫汉·辛格
 米雷克·托波拉内克
米雷克·托波拉内克
 非洲发展新伙伴计划
非洲发展新伙伴计划
 梅莱斯·泽纳维
梅莱斯·泽纳维
 尼古拉·萨科齐
尼古拉·萨科齐
 雷杰普·塔伊普·埃尔多安
雷杰普·塔伊普·埃尔多安
 西尔维奥·贝卢斯科尼
西尔维奥·贝卢斯科尼
 斯蒂芬·约瑟夫·哈珀
斯蒂芬·约瑟夫·哈珀
 苏西洛·班邦·尤多约诺
苏西洛·班邦·尤多约诺
 麻生太郎
麻生太郎
 英国
英国
 世界银行
世界银行
 罗伯特·佐利克
罗伯特·佐利克

 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
 世界贸易组织
世界贸易组织
 帕斯卡尔·拉米
帕斯卡尔·拉米
 运输和交通
运输和交通
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术


 航空航天
航空航天

 赛车,艇运动
赛车,艇运动
 企业
企业
 生活时尚
生活时尚
 往日岁月
往日岁月

 展览会
展览会

 船舶和航海学
船舶和航海学

 法律
法律



 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织

