
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Mongolei
Mongolei

 Aljaksandr Lukaschenka
Aljaksandr Lukaschenka
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Belarus
Belarus
 China
China
 Emomali Rahmon
Emomali Rahmon
 India
India
 Iran
Iran
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Mohammad Mokhber
Mohammad Mokhber

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Qassym-Schomart Toqajew
Qassym-Schomart Toqajew
 Russia
Russia
 Sadyr Japarov
Sadyr Japarov
 Shavkat Mirziyoyev
Shavkat Mirziyoyev
 Shehbaz Sharif
Shehbaz Sharif
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
 Xi Jingping
Xi Jingping


The 2024 SCO summit was the 24th annual summit of heads of state of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation held between 3 and 4 July 2024 in Astana, Kazakhstan.
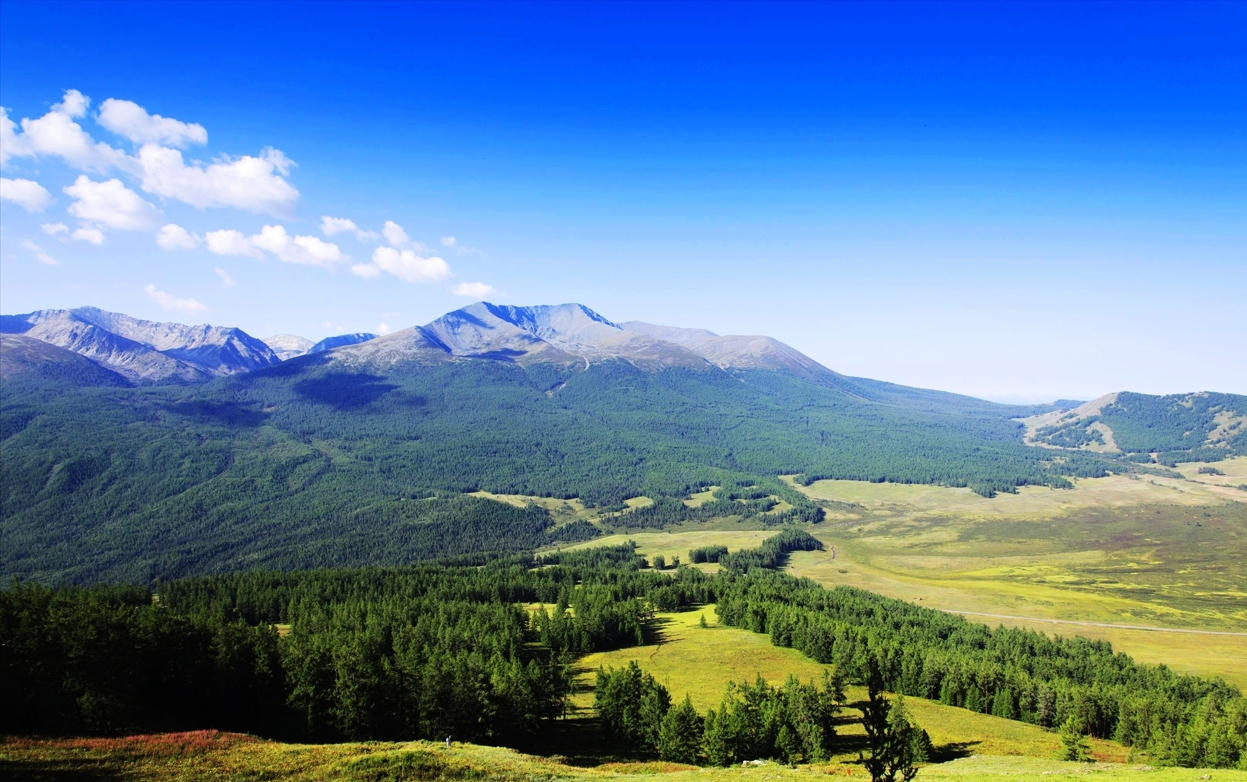

Der Altai (russisch Алтай; in türkischer Lateinschrift Altay) ist ein bis zu 4506 m hohes mittelasiatisches Hochgebirge im Grenzgebiet von Kasachstan, Russland (Sibirien), der Mongolei und China.
Es erstreckt sich über rund 2100 km Länge vom Quellgebiet der Flüsse Irtysch und Ob in Südsibirien bis in die Trockenregionen Xinjiangs und zum ostmongolischen Hochplateau. Teile des Altai sind Weltnaturerbe der UNESCO.
Der Altai gliedert sich in drei Teile, den Russischen, den Mongolischen und den Gobi-Altai, deren höchste Gipfel über oder um 4000 m aufragen und große Gletscher tragen. Nördlich des Mongolischen Altai liegt der geografische Mittelpunkt Asiens in der Nähe der tuwinischen Hauptstadt Kysyl.
Das Gebirge ist durch die Schönheit seiner Landschaft und Flora (Naturschutzgebiet „Goldene Berge“) und die altaische Kultur ein Anziehungspunkt für Bergsteiger und Exkursionen. Bis in Höhen von 1800 m sind die Berghänge mit Zedern, Kiefern, Lärchen, Fichten und Birken bewachsen. Bis zur Schneegrenze (2400 bis 3000 m) liegen Hochgebirgsweiden und -steppen. Der Altai ist reich an Bodenschätzen wie Kohle, Blei und Zink, aber auch Edelmetallen und Eisenerz.
阿尔泰山脉(维吾尔语:ئالتاي تاغ تىزمىسى;俄语:Алтай;蒙古语:ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ ‧ Алтай或ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ
ᠶᠢᠨ
ᠨᠢᠷᠤᠭᠤ ‧ Алтайн нуруу;哈萨克语:Алтай таулары)位于中国新疆维吾尔自治区北部和蒙古西部一直延伸至俄罗斯境内与哈萨克东部,呈东南—西北走向。长约2000公里,海拔1000—3000米。北部的平均海拔2050米,南部的平均海拔2377米。[1]位于俄哈边境的北部,高峰有别卢哈山(4506米),友谊峰(4374米),中蒙俄交界的奎屯山(4082米)等。中国境内分布,主要是山脉中段,长500千米。森林、矿产资源丰富。
“阿尔泰”在蒙语中意味“金山”,从汉朝就开始开采金矿,至清朝在山中淘金的人曾多达5万多人。阿尔泰语系从阿尔泰山得名。
アルタイ山脈(アルタイさんみゃく)は西シベリアとモンゴルにまたがる山脈。漢字で阿爾泰山脈とも[1]。 東は、塩水湖のウヴス・ヌール、キヤールガス・ヌール、ドルゴン・ヌールや、淡水湖のen:Khar-Us Lake、en:Khar Lake (Khovd)、en:Airag Lakeなど、多くの湖が点在する北西モンゴル台地(Ubsunur Hollow、Great Lakes Depression)に接する。雪線はアルタイ山脈の東部分で1875m、西の方では北側約2010m、南側約2340mであり、雪線を越す峰は多い。アルタイ山脈の最高峰はベルーハ山(4506m)。
The Altai Mountains (/ɑːlˈtaɪ/; also spelled Altay Mountains; Altay: Алтай туулар, Altay tuular; Mongolian: ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ
ᠶᠢᠨ
ᠨᠢᠷᠤᠭᠤ, Altai-yin niruɣu (Chakhar) or Алтайн нуруу, Altain nuruu (Khalkha); Kazakh: Алтай таулары, Altai’ tay’lary, التاي تاۋلارى; Russian: Алтайские горы, Altajskije gory; Chinese: 阿尔泰山脉, Ā'ěrtài Shānmài, Xiao'erjing: اَعَرتَىْ شًامَىْ; Dungan: Артэ Шанмэ) are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan come together, and are where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The northwest end of the range is at 52° N and between 84° and 90° E (where it merges with the Sayan Mountains to the east), and extends southeast from there to about 45° N and 99° E, where it gradually becomes lower and merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert.
The name "Altai" means "Gold Mountain" in Mongolian; "alt" (gold) and "tai" (suffix – "with"; the mountain with gold) and also in its Chinese name, derived from the Mongol name (Chinese: 金山; literally: "Gold Mountain"). In Turkic languages altın means gold and dağ means mountain. The controversial Altaic language family takes its name from this mountain range.[1][2]
L'Altaï (en russe : Алтайские горы Altaïskie gory, en turc : Altağ ou Altay où Al signifie « or » et tağ « mont », en kazakh : Алтай таулары Altaï taoulary, en chinois : 阿尔泰山脉 ''Ā'ěrtài shānmài ; mongol : ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠢ ᠶᠢᠨ
ᠨᠢᠷᠤᠭᠤ, VPMC : Altaiyin nuruɣu,cyrillique : Алтайн нуруу, MNS : Altain nuruu les « chaînes de montagnes d'or ») est une chaîne de montagne d'Asie dont l'appellation comprend diverses acceptions liées à la zone située entre la Russie, la Chine (province du Xinjiang), la Mongolie et le Kazakhstan et où les grands cours d'eau Irtych et Ob prennent leur source1.
I monti Altai (in russo: Алтай?, traslitterato: Altaj; mongolo: Алтайн нуруу [Altajn Nuruu]; cinese: 阿爾泰山脈T, 阿尔泰山脉S, Ā'ěrtài shānmàiP) sono un complesso sistema montuoso dell'Asia che si estende per circa 2000 km in direzione sud-est/nord-ovest dal deserto del Gobi al bassopiano della Siberia occidentale, attraverso Cina, Mongolia, Russia e Kazakistan. Questa frastagliata catena montuosa deve il nome al termine turco-mongolo altan, che significa «dorato».
Il sistema viene suddiviso in tre zone principali: l'Altai propriamente detto (noto in passato come Altai Sovietico o Grande Altai), l'Altai della Mongolia e l'Altai del Gobi. Un monte dell'Altai propriamente detto, il Belukha – che culmina a 4506 m – è la vetta più alta della catena. In passato queste montagne erano remote e scarsamente popolate, ma nel XX secolo esse si sono aperte a un estensivo sfruttamento minerario e gli antichi stili di vita delle popolazioni locali sono stati rapidamente trasformati.
Da questa catena montuosa prende il nome la speculata famiglia linguistica delle lingue altaiche.
El macizo de Altái (en ruso, Алтайские горы; en turco, Altağ o Altay, de Al, «oro» y tağ, «monte»; en mongol, Altain-ula, «montañas de oro») es una cordillera de Asia central, que ocupa territorios de Rusia, China, Mongolia y Kazajistán. En ella nacen los ríos Irtysh, Obi y Yeniséi. El término noroccidental de la cordillera se ubica en el 52º N y entre el 84º y 90º E (donde se fusiona con los montes Sayanes al este), y se extiende por el sudeste desde ese punto hasta aproximadamente  45°N 99°E, donde gradualmente pierde altura y se funde en el desierto de Gobi.
45°N 99°E, donde gradualmente pierde altura y se funde en el desierto de Gobi.
La cordillera es también conocida como el Ek-tagh. Las «Montañas Doradas de Altái» fueron declaradas Patrimonio de la Humanidad natural de la UNESCO en el año 1998 debido a que «representa un centro importante y original de biodiversidad de flora de montaña y especies animales en Asia septentrional, cierto número de ellas son raras y endémicas».1
Алтайские горы, или Алтай (монг. Алтайн нуруу, алт. Туулу Алтай — горная земля, южноалт. Алтай туулар,кирг. Алтай тоолору, каз. Алтай таулары, кит. упр. 阿尔泰山脉, пиньинь: Ā'ěrtài shānmài, палл.: Аэртай шаньмай) — горная система в Азии, на юге Сибири и в Центральной Азии, состоящая из высокогорных и среднегорных хребтов[2], разделённых глубокими долинами рек и обширными внутригорными и межгорными котловинами. Простирается с северо-запада на юго-восток более чем на 2000 км.
Горная система расположена на границе России (Алтайский край и Республика Алтай), Монголии (Баян-Ульгийский и Ховдский аймаки), Китая (Синцзян-Уйгурский автономный район) и Казахстана (Восточно-Казахстанская область).
Алтайский, Катунский заповедники и плоскогорье Укок в совокупности образуют объект Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО «Золотые горы Алтая».
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Pakistan
Pakistan

 Party and government
Party and government
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Vietnam
Vietnam

ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム(博鰲アジアフォーラム、Boao Forum for Asia、略称BFA、中国語:博鳌亚洲论坛、ピンイン:Bóáo Yàzhōu Lùntán)は、中華人民共和国に本拠を置く国際非営利組織。
スイスのダボスで開催されている世界の政治家・財界人・知識人が集まる国際会議(ダボス会議)を主催する世界経済フォーラムにならい、そのアジア版を目指して、中国政府の全面的支援を受けて構想された。2001年2月27日の設立にはアジアの25カ国とオーストラリアの計26カ国が参加している。
ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム主催の最初の国際会議は2002年4月12日・4月13日に開催され、日本からは小泉純一郎内閣総理大臣が出席して演説を行った[1]。国際会議の会場は、2001年の発足会議以来、中国・海南省の海浜リゾート地・ボアオ(博鰲、海南島東海岸の瓊海市)に固定されている。会議は毎年行われ、各国首脳や大企業経営者、学者、NGO代表など政府・民間のハイレベルの人材が集い、アジアや世界の経済動向、金融政策、経済統合、経済投資、国際協力、社会問題、環境問題などに関する討議が行われる。また多くの経済人や政治家、社会運動家らが直接話し合い、国家間協力や企業提携などのトップ会談が持たれる。
過去の議題には中国の世界貿易機関(WTO)への加入問題、90年代後半のアジア金融危機問題などが取り上げられ、2004年には中国の地政学的な「和平崛起」(平和的台頭)戦略の可否が議題となった。
The Boao Forum for Asia (BFA; Chinese: 博鳌亚洲论坛; pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán) is a non-profit organisation that hosts high-level forums for leaders from government, business and academia in Asia and other continents to share their vision on the most pressing issues in this dynamic region and the world at large. BFA is modelled on the World Economic Forum held annually in Davos, Switzerland. Its fixed address is in Bo'ao, Hainan province, China, although the Secretariat is based in Beijing. The forum, sometimes known as the “Asian Davos”, takes its name from the town of Boao, located in China’s southern Hainan province, which has been the permanent venue for its annual conference since 2002.[1]
The Forum is committed to promoting regional economic integration and bringing Asian countries even closer to their development goals. Initiated in 1998 by Fidel V. Ramos, former President of the Philippines, Bob Hawke, former Prime Minister of Australia, and Morihiro Hosokawa, former Prime Minister of Japan, the Boao Forum for Asia was formally inaugurated in February 2001. The founding of the BFA was driven by the People's Republic of China and founded by 26 Asian and Australasian states on 27 February 2001. The organisation held its first meeting from 12–13 April 2002.
Discussions at the BFA focus on economics, integration, cooperation, society and the environment. In the past the forum also addressed China's entry into the World Trade Organization, as well as Southeast Asia's economic crisis during the 1990s. The geopolitical strategy 'China's peaceful rise' was a topic of discussion for the forum in 2004. In addition to its annual meeting, the BFA also sponsors other forums and meetings related to Asian issues.
El Foro de Boao para Asia (en chino: 博鳌亚洲论坛, pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán), conocida también por sus siglas en inglés BFA, es una organización no lucrativa que organiza foros de alto nivel para líderes del gobierno, los negocios y la academia en Asia y otros continentes para compartir su visión sobre los asuntos más apremiantes en esta región y en el mundo entero. El Foro Boao es el modelo del Foro Económico Mundial que se celebra anualmente en Davos, Suiza. Tiene su sede en Bo'ao, Hainan, China, aunque la Secretaría se encuentra en Pekín.
El Foro tiene como objetivos promover la integración económica regional y acercar a los países asiáticos hacia sus metas de desarrollo.1 Fue creado en 1998 por Fidel V. Ramos, expresidente de Filipinas, Bob Hawke, ex primer ministro de Autralia y Morihiro Hosokawa, ex primer ministro de Japón.2 El Foro de Boao para Asia fue formalmente inaugurado en febrero de 2001. La creación del foro fue liderado por la República Popular de China y fundada por 26 países de Asia y Australasia el 27 de febrero de 2001. La organización tuvo su primera reunión el 12 y 13 de abril de 2002.
Las discusiones del Foro Boao se centran en economía, cooperación, sociedad y medio ambiente. En e pasado el foro también abordaba el ingreso de China en la Organización Mundial del Comercio, así como la crisis financiera asiática de los años noventa. Además de su reunión anual, el foro también patrocina otros foros y reuniones relacionados con temas asiáticos.
Боаоский Азиатский Форум, БАФ (кит: 博鳌亚洲论坛; пиньинь: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán, англ: Boao Forum for Asia, аббр: BFA), также известен как «Восточный Давос» — неправительственная и некоммерческая международная организация, имеющая своей целью поддержку и развитие экономического обмена, взаимодействия и сотрудничества как в Азии, так и за её пределами путём проведения ежегодных встреч высокого уровня с участием представителей правительственных, деловых, промышленных и научных кругов и обсуждения актуальных экономических, социальных, экологических и др. проблем.
Учреждён в 2001 году. Ежегодные конференции в Боао проводятся с 2002 года.
Главный офис организации находится в г. Боао, пров. Хайнань, КНР.
В 2018 году Боаоский азиатский форум /БАФ/ пройдет 8-11 апреля. Главными темами мероприятия станут реформы, открытость, инновации и "Пояс и путь"[1].
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Belarus
Belarus
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Cuba
Cuba
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine

 Party and government
Party and government
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations


Afghanistan Ägypten Algerien Angola Antigua und Barbuda Äquatorialguinea Äthiopien Aserbaidschan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesch Barbados Belarus Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivien Botswana Brunei Burkina Faso Burundi Chile Demokratische Republik Kongo Dominica Dominikanische Republik Dschibuti Ecuador Elfenbeinküste Eritrea Eswatini Fidschi Gabun Gambia Ghana Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Indien Indonesien Irak Iran Jamaika Jemen Jordanien Kambodscha Kamerun Kap Verde Katar Kenia Kolumbien Komoren Kuba Kuwait Laos Lesotho Libanon Liberia Libyen Madagaskar Malawi Malaysia Malediven Mali Marokko Mauretanien Mauritius Mongolei Mosambik Myanmar Namibia Nepal Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Nordkorea Oman Osttimor Pakistan Palästina Panama Papua-Neuguinea Peru Philippinen Republik Kongo Ruanda Saint Lucia Sambia São Tomé und Príncipe Saudi-Arabien Senegal Seychellen Sierra Leone Simbabwe Singapur Somalia Sri Lanka St. Kitts und Nevis St. Vincent und die Grenadinen Südafrika Sudan Suriname Syrien Tansania Thailand Togo Trinidad und Tobago Tschad Tunesien Turkmenistan Uganda Usbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vereinigte Arabische Emirate Vietnam Zentralafrikanische Republik
Die Bewegung der Blockfreien Staaten (kurz Bewegung der Blockfreien oder Blockfreien-Bewegung, englisch Non-Aligned Movement) ist eine Internationale Organisation von Staaten, deren erklärtes Ziel es war, sich im Ost-West-Konflikt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg neutral zu verhalten und keinem der beiden Militärblöcke anzugehören. Die Gründung der Organisation ging auf eine Initiative des jugoslawischen Präsidenten Josip Broz Tito, des ägyptischen Staatschefs Nasser, des indischen Premiers Nehru sowie des indonesischen Präsidenten Sukarno zurück. Die Organisation konstituierte sich 1961 auf ihrer ersten Sitzung in Belgrad.[1] Ihr traten viele ehemalige afrikanische und asiatische Kolonien bei, die sich soeben erst als Staaten konstituiert hatten oder noch um ihre Unabhängigkeit rangen.[2]
Die Organisation verurteilte die Blockbildung in der Zeit des Ost-West-Konfliktes wegen der Gefahr eines Dritten Weltkrieges und setzte sich für die friedliche Koexistenz und Abrüstung ein. Die steigende Zahl der Mitglieder machte es der Organisation jedoch zunehmend schwer, sich auf eine gemeinsame Politik zu einigen. Mit der Auflösung des Warschauer Paktes Anfang der 1990er Jahre verlor sie an Bedeutung. Die heterogene Zusammensetzung der Bewegung machte es schwer, gemeinsame Ziele zu definieren und zu verfolgen.[3] Die Staaten der Blockfreien-Bewegung vertreten 55 Prozent der Weltbevölkerung und halten nahezu zwei Drittel der Sitze in der UN-Generalversammlung.
Das Ziel der Organisation ist die Gleichberechtigung zwischen den Staaten und eine positive wirtschaftliche Entwicklung der Mitgliedstaaten.
不结盟运动(英语:Non-Aligned Movement, NAM)是一个拥有120个成员国和17个观察员国的松散国际组织[3]。它成立于冷战时期,其成员国奉行独立自主的外交政策,不与美苏两个超级大国中的任何一个结盟。联合国中有三分之二的会员是该组织的成员国,全球约55%的人口也生活在不结盟运动国家。不结盟运动定期举行首脑会议,到目前为止已经在前南斯拉夫、埃及、赞比亚、阿尔及利亚、斯里兰卡、古巴、印度、津巴布韦、印尼、哥伦比亚、南非、马来西亚、塞尔维亚、委内瑞拉、阿塞拜疆和乌干达[4]举行会议。

 Architecture
Architecture
 Bhutan
Bhutan

 History
History
 K 500 - 1000 AD
K 500 - 1000 AD
 Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh

 Art
Art

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Nepal
Nepal
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH

 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN



 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Guam
Guam
 China
China
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Japan
Japan
 Kinki
Kinki
 Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ

 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
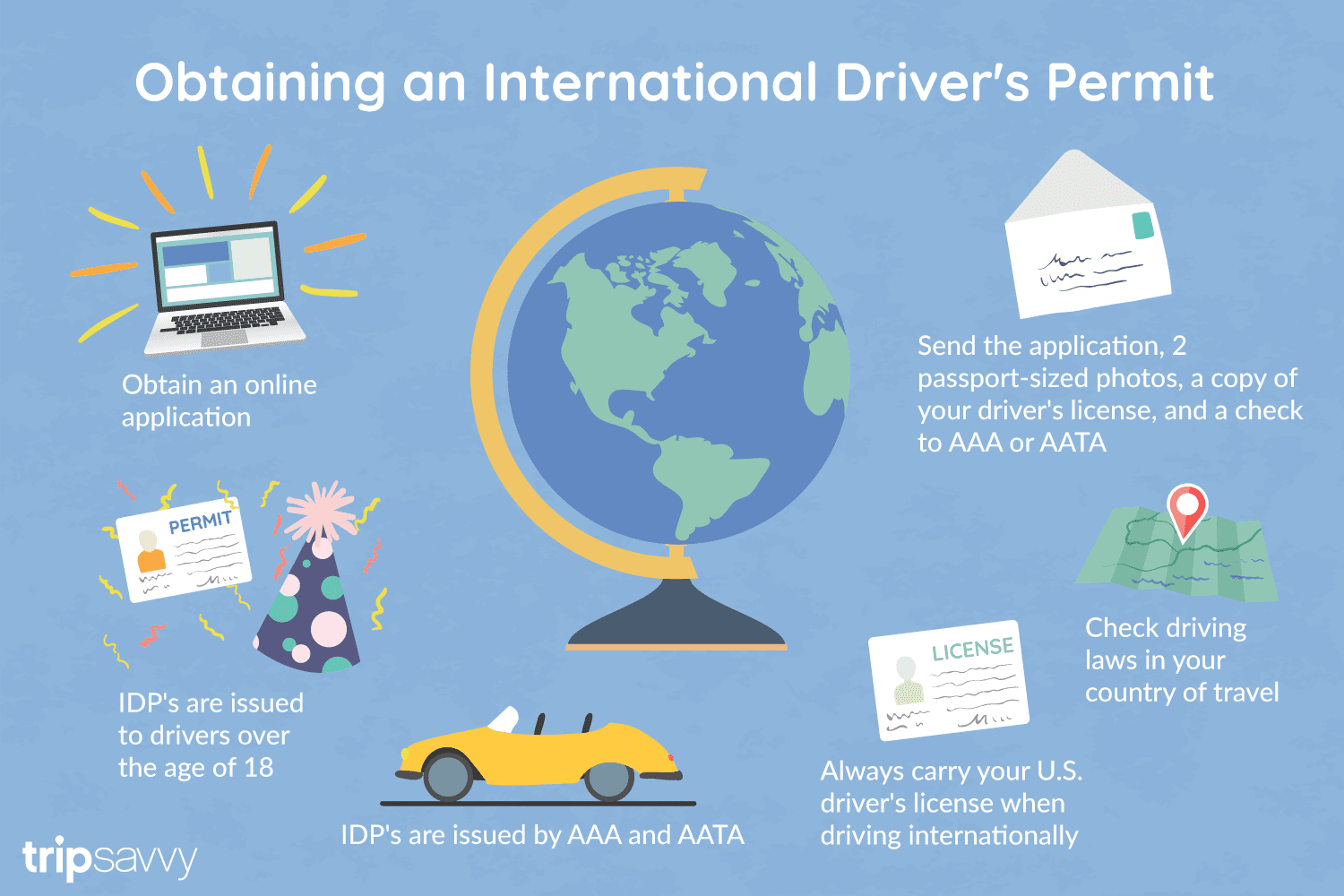
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)

 China
China
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN

Die Khata, auch Khatag, Katakh, Khatak, Khadag, Haddak oder chinesisch Hada (哈达) ist ein traditioneller Begrüßungsschal, der in Tibet meist aus weißer Seide[1] – als Symbol für das reine Herz des Überreichenden – und in der Mongolei in hellem Blau – das den Himmel symbolisiert – angefertigt wird.
Er steht für Glück, Wohlwollen und Mitgefühl.
 Geography
Geography
 Religion
Religion
 Sport
Sport
 Driving school
Driving school
