
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Silk road
Silk road
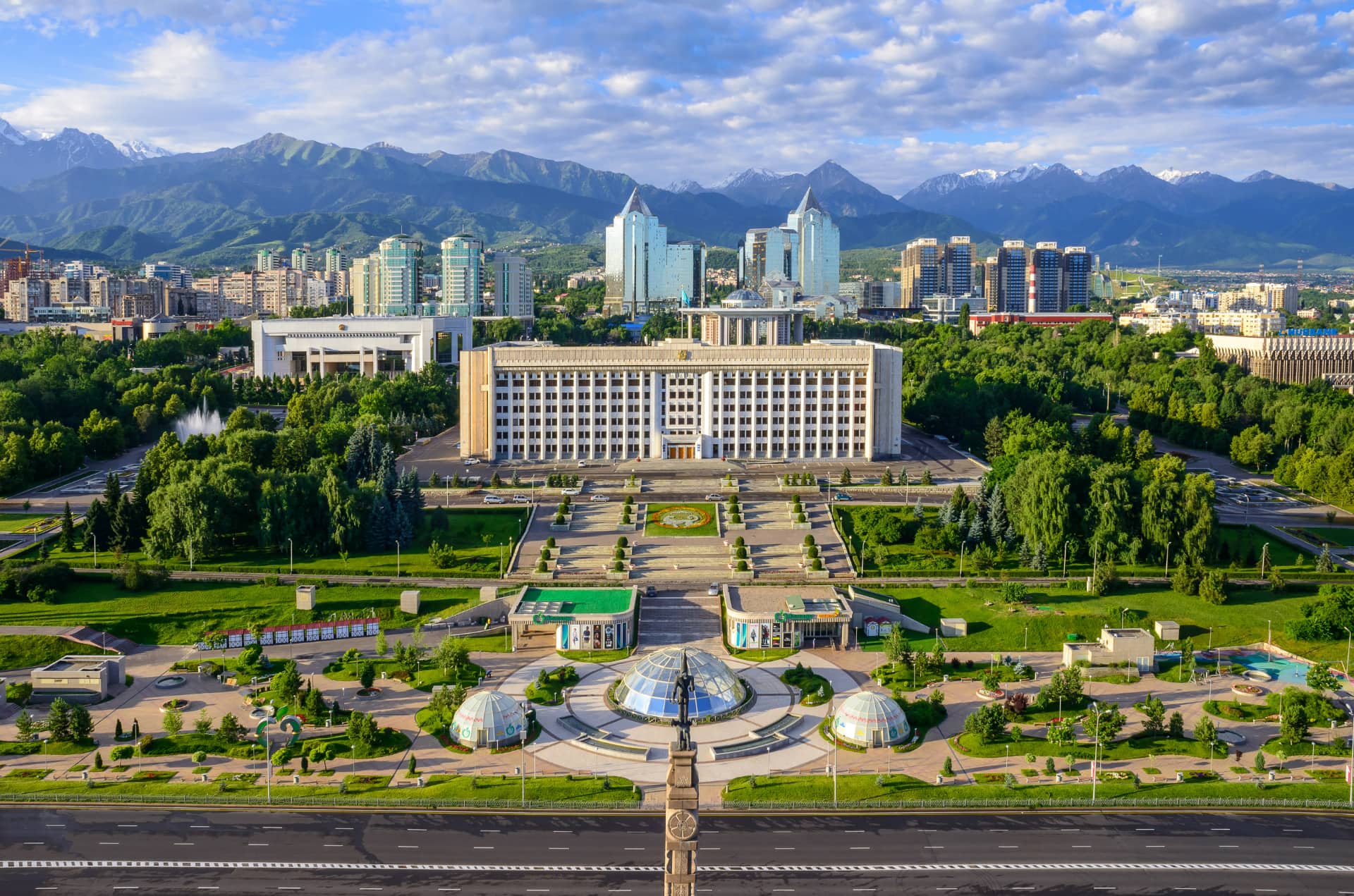
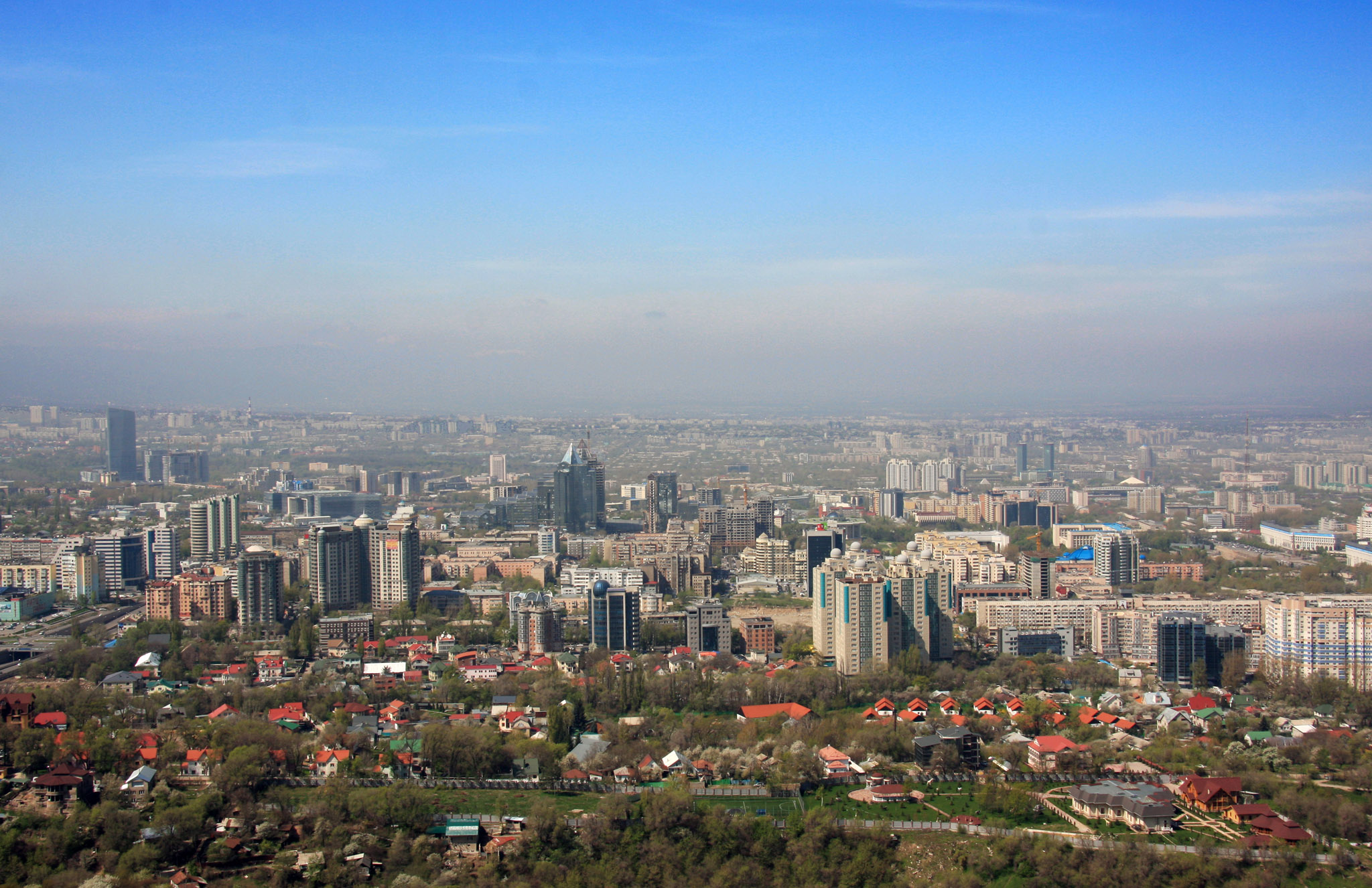



Almaty (kasachisch und russisch Алматы, bis 1993 Alma-Ata) ist mit rund zwei Millionen Einwohnern die größte Stadt Kasachstans. Sie liegt im Südosten des zentralasiatischen Staates unweit der Grenze zu Kirgisistan, war von 1936 bis 1991 Hauptstadt der Kasachischen SSR und nach dem Zerfall der Sowjetunion bis 1997 von Kasachstan.
Almaty ist neben der Hauptstadt Astana noch immer das kulturelle, wissenschaftliche und wirtschaftliche Zentrum des Landes mit Universitäten und zahlreichen Sakralbauten, Museen und Theatern. Zu den bekanntesten Sakralbauten gehören die Christi-Himmelfahrt- und die Nikolaus-Kathedrale. Der 1983 fertiggestellte 371,5 Meter hohe Fernsehturm Almaty auf dem Berg Kök-Töbe gehört zu den höchsten Bauwerken der Welt. Seit Anfang des 21. Jahrhunderts sind auch einige Wolkenkratzer in der Stadt entstanden. Die Stadt verfügt über zwei Bahnhöfe und zwei Flughäfen. Die am 1. Dezember 2011 eröffnete Metro Almaty sowie Oberleitungsbusse sorgen für den innerstädtischen Personentransport.
阿拉木图(哈萨克语:Алматы/Almaty,读作 [ɑlmɑˈtə] (ⓘ);俄语:Алма-Ата)是哈萨克斯坦的一座直辖市,是该国的第一大城市。坐落在哈萨克斯坦东南部的山区,邻近吉尔吉斯斯坦。阿拉木图早年盛产苹果,因此有“苹果城”之称。
阿拉木图(哈萨克语和俄语 Алматы,1993 年以前为阿拉木图)是哈萨克斯坦最大的城市,约有 200 万居民。它位于中亚国家的东南部,离吉尔吉斯斯坦边境不远。除首都阿斯塔纳外,阿拉木图仍是该国的文化、科学和经济中心,拥有多所大学和众多宗教建筑、博物馆和剧院。最著名的宗教建筑包括耶稣升天大教堂和圣尼古拉大教堂。
Die Altstadt von Damaskus gehört zum UNESCO-Welterbe in Syrien.
Wegen der günstigen Lage an der Kreuzung wichtiger Handelswege ist die Altstadt von Damaskus einer der ältesten kontinuierlich bewohnten Orte weltweit. Die Umayyaden machten Damaskus zur Hauptstadt ihres Kalifats. Außer den mittelalterlichen Bauten, die von dieser Blütezeit zeugen, sind im Stadtbild auch Elemente hellenistischer, römischer und byzantinischer Architektur erkennbar. Insgesamt präsentiert sich die historische Altstadt dem Besucher heute in der Form, die sie seit der ottomanischen Eroberung am Anfang des 16. Jahrhunderts erhielt. Wie alle syrischen Welterbestätten steht auch die Altstadt von Damaskus seit 2013 auf der Roten Liste des gefährdeten Welterbes.
 Belgium
Belgium

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port
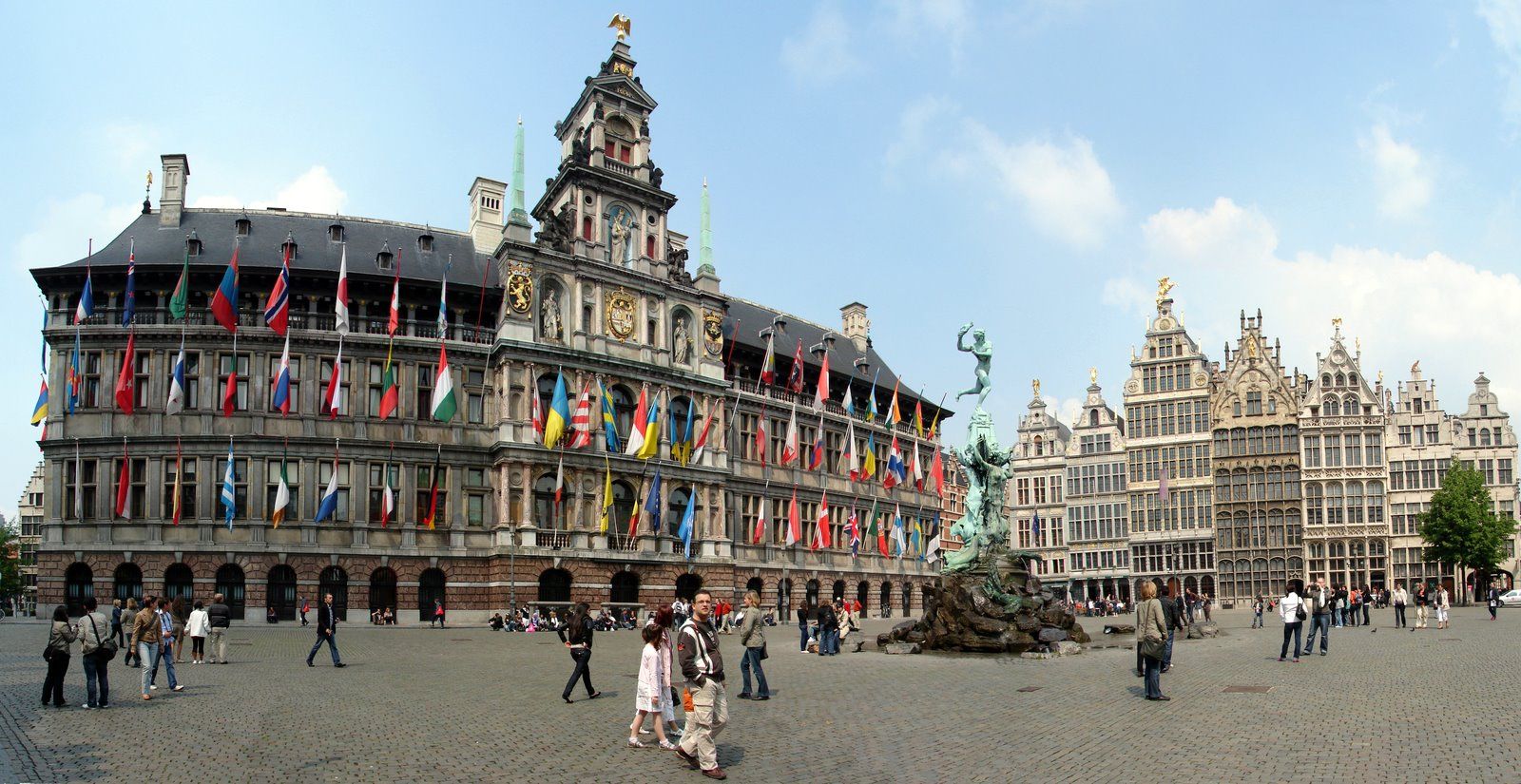

安特卫普位于比利时西北部斯海尔德河畔,是比利时最大港口和重要工业城市,面积140平方公里,人口45.7万人(2005年1月),居民大多使用荷兰地方方言,工商界主要使用法语。安特卫普是欧洲著名文化中心,是著名艺术大师罗宾斯和冯·狄克的诞生地,也是世界著名的游览城市。人们被其吸引的是它的三大看点:一是保存完好、充满中世纪情调的旧市区古老建筑;二是神秘的钻石加工和交易;三是有世界声誉的绘画艺术和众多的博物馆,建有罗宾斯故居博物馆、皇家艺术博物馆、国家海运博物馆以及钻石博物馆等。(Quelle:http://baike.baidu.com)
Antwerpen (veraltet deutsch Antorf oder Antorff, französisch Anvers) ist eine Hafenstadt in der Region Flandern in Belgien und die Hauptstadt der Provinz Antwerpen. Bezogen auf die Stadt als Verwaltungseinheit ist Antwerpen die größte Stadt des Landes. Die Agglomeration Antwerpen ist nach der Region Brüssel-Hauptstadt die zweitgrößte in Belgien.
Von großer internationaler Bedeutung ist Antwerpen durch seinen Seehafen, den zweitgrößten Europas, sowie als weltweit wichtigstes Zentrum für die Verarbeitung und den Handel von Diamanten.
Antwerpen war im 15. und 16. Jahrhundert eine der größten Städte der Welt, zeitweise die wichtigste Handelsmetropole Europas und als bedeutendes kulturelles Zentrum Wirkungsstätte von Künstlern wie Rubens. Antwerpen war Austragungsort der Olympischen Sommerspiele 1920 und Kulturhauptstadt Europas 1993. Das Druckereimuseum Plantin-Moretus, das Maison Guiette und der Turm der Liebfrauenkathedrale gehören zum UNESCO-Welterbe.
アントウェルペン(オランダ語: Antwerpen [ˈɑntʋɛrpə(n)] (![]() 音声ファイル), フランス語: Anvers [ɑ̃vɛʁ(s)], 英語: Antwerp [ˈæntwɜrp])は、ベルギーのフランデレン地域・アントウェルペン州の州都で、同国最大の都市(首都圏地域の人口を合わせればブリュッセル市が最大)。英語名に由来するアントワープや、フランス語名に由来するアンヴェルス(アンベルス)[1]も日本語の表記においてよく用いられる。2012年1月1日の総人口は502,604人。面積は204.51 km2, 人口密度は2,457.56人/km2である。
音声ファイル), フランス語: Anvers [ɑ̃vɛʁ(s)], 英語: Antwerp [ˈæntwɜrp])は、ベルギーのフランデレン地域・アントウェルペン州の州都で、同国最大の都市(首都圏地域の人口を合わせればブリュッセル市が最大)。英語名に由来するアントワープや、フランス語名に由来するアンヴェルス(アンベルス)[1]も日本語の表記においてよく用いられる。2012年1月1日の総人口は502,604人。面積は204.51 km2, 人口密度は2,457.56人/km2である。
Antwerp (/ˈæntwɜːrp/ (![]() listen), Dutch: Antwerpen [ˈɑntʋɛrpə(n)] (
listen), Dutch: Antwerpen [ˈɑntʋɛrpə(n)] (![]() listen), French: Anvers [ɑ̃vɛʁ(s)]) is a city in Belgium, and is the capital of Antwerp province in Flanders. With a population of 520,504,[2] it is the most populous city proper in Belgium. Its metropolitan area houses around 1,200,000 people, coming in second behind Brussels.[3][4]
listen), French: Anvers [ɑ̃vɛʁ(s)]) is a city in Belgium, and is the capital of Antwerp province in Flanders. With a population of 520,504,[2] it is the most populous city proper in Belgium. Its metropolitan area houses around 1,200,000 people, coming in second behind Brussels.[3][4]
Antwerp is on the River Scheldt, linked to the North Sea by the Westerschelde estuary. It is about 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Brussels, and about 15 kilometres (9 mi) from the Dutch border. The Port of Antwerp is one of the biggest in the world, ranking second in Europe[5][6] and within the top 20 globally.[7] Antwerp was also the place of the world's oldest stock exchange building, originally built in 1531 and re-built in 1872.[8]
Antwerp has long been an important city in the Low Countries, both economically and culturally, especially before the Spanish Fury (1576) in the Dutch Revolt. The inhabitants of Antwerp are nicknamed Sinjoren ([sɪnˈjoːˌrən]), after the Spanish honorific señor or French seigneur, "lord", referring to the Spanish noblemen who ruled the city in the 17th century.[9] Today Antwerp is a major trade and cultural centre. The city hosted the 1920 Summer Olympics.
Anvers (prononcé /ɑ̃.vɛʁs/1,2, ou /ɑ̃.vɛʁ/3, en néerlandais : Antwerpen) est une ville belge dans la Région flamande, chef-lieu de la province d'Anvers et de l'arrondissement administratif du même nom, située au cœur de la Dorsale européenne.
Au 1er avril 2017, la commune d’Anvers était la plus peuplée de Belgique, devant Gand et Charleroi, avec 521 216 habitants4, 259 740 hommes et 261 476 femmes, soit une densité de 1 270,06 habitants/km2. L’agglomération anversoise compte, elle, 1 250 000 habitants. C'est la deuxième plus peuplée de Belgique, après Bruxelles. C'est également la troisième commune et ville de Belgique pour ce qui est de la superficie, avec 204,51 km2, juste après Tournai et Couvin.
Archétype de la ville bourgeoise-marchande depuis le Bas Moyen Âge elle constitue alors, selon Fernand Braudel, le centre du commerce international et de la haute finance tout au long du XVIe siècle. Anvers abrite depuis 1931 le plus vieux et unique gratte-ciel d'Europe jusqu'en 1949, la Boerentoren, et dispute à Venise l'invention de la comptabilité en partie double. Anvers est connue pour abriter les plus prestigieux diamantaires de la Planète, avec Londres et Amsterdam, ainsi que la plus importante bourse de diamants de la Planète, la Antwerpse Diamantkring. Elle abrite également une grande concentration d'établissements d'audit et consulting. Enfin, le Port d'Anvers (deuxième port commercial d'Europe en termes d'activités et de tonnage, après celui voisin de Rotterdam) joue un rôle majeur dans la mondialisation des activités économiques européennes.
Les codes postaux vont de 2000 à 2600 à l’intérieur du district de la ville d’Anvers, située principalement sur la rive droite de l’Escaut et connue pour son port international de marchandises extrêmement développé, aujourd'hui le deuxième plus grand d'Europe en termes de volume de marchandises.
Les Anversois sont aussi appelés les Sinjoren, de l’espagnol señor, héritage de l'époque où elle faisait partie de l'Empire habsbourgeois de Charles Quint. La ville est souvent appelée ’t Stad (« La Ville ») et parfois de koekenstad (« la Ville des biscuits ») par allusion aux koffiekoeken (biscuits recouverts d'un fin glaçage au café) d’Anvers, réputées dans toute la Belgique.
Anversa (Antwerpen in olandese, Anvers in francese) è una città di 506.922 abitanti del Belgio settentrionale, la più importante nella regione delle Fiandre, una delle tre regioni dello Stato, e il capoluogo della provincia omonima.
Amberes (en neerlandés, Antwerpen ![]() [ˈɑntˌʋɛrpə(n)] (?·i), en francés, Anvers [ɑ̃ˈvɛʁ(s)]), antiguamente conocida como Antuerpia, es una ciudad situada en Bélgica que posee 521.600 habitantes en 2018. El área metropolitana cubre 1.449 km² (559 millas cuadradas) con un total de 2.190.769 habitantes, según el censo del 1 de enero de 2017.
[ˈɑntˌʋɛrpə(n)] (?·i), en francés, Anvers [ɑ̃ˈvɛʁ(s)]), antiguamente conocida como Antuerpia, es una ciudad situada en Bélgica que posee 521.600 habitantes en 2018. El área metropolitana cubre 1.449 km² (559 millas cuadradas) con un total de 2.190.769 habitantes, según el censo del 1 de enero de 2017.
Антве́рпен (нидерл. Antwerpen [ˈɑntˌʋɛrpə(n)], фр. Anvers [ɑ̃vɛʁs], з.-флам. Antwerpn) — город во Фламандском регионе Бельгии. Второй (после Брюсселя) город страны, самый большой город Фландрии. Административный центр провинции Антверпен. Город расположен на обоих берегах реки Шельды. Морской порт, входит в двадцатку крупнейших портов мира и является вторым в Европе после порта города Роттердама в Нидерландах[2].

Astana [astaˈna],[2] deutsch auch [asˈtaːna][3] (kasachisch und russisch Астана; Астана ist auch das kasachische Wort für Hauptstadt) ist seit dem 10. Dezember 1997 die Hauptstadt Kasachstans. Sie befindet sich im nördlichen Teil des Landes inmitten der Kasachischen Steppe am Ufer des Flusses Ischim. Mit 1.354.435 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2023) ist sie nach Almaty die zweitgrößte Stadt des Landes.
Die Stadt wurde 1830 als russische Festung gegründet. In den 1950er Jahren wurde der Ort zum Zentrum der sowjetischen Neulandkampagne zur Gewinnung von landwirtschaftlichen Anbauflächen. Dies führte dazu, dass sich das Stadtbild veränderte und die Entwicklung der Stadt vorangetrieben wurde. Nach der Unabhängigkeit Kasachstans von der Sowjetunion wurde eine Verlegung der Hauptstadt beschlossen und die Stadt somit am 10. Dezember 1997 zur Planhauptstadt. Im Süden der Stadt entstand daraufhin ein modernes Regierungsviertel mit markanten Bauwerken wie dem Bajterek-Turm, dem Khan Shatyr oder der Pyramide des Friedens und der Eintracht.
阿斯塔纳[3](哈萨克语:Астана/Astana,读作 [ɑstɑnɑ] (ⓘ))位于哈萨克斯坦中北部,是该国的首都、直辖市和第二大城市,四周与阿克莫拉州接壤。伊希姆河穿城而过,生态环境良好,是哈萨克斯坦工农业的主要生产基地、全国铁路交通枢纽。
现代的阿斯塔纳是一个新市镇,并遵循其他规划首都的进程进行城市规划。[4]自从成为哈萨克斯坦首都后,这座城市的面貌发生了巨大的变化。阿斯塔纳的总体规划是由日本建筑师黑川纪章设计的,并作为哈萨克斯坦政府、议会大厦、最高法院、阿克奥尔达总统府和众多政府部门和机构的所在地。目前城市也兴建一系列未来主义建筑,包括许多摩天大楼。
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 History
History
 Greece
Greece

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port
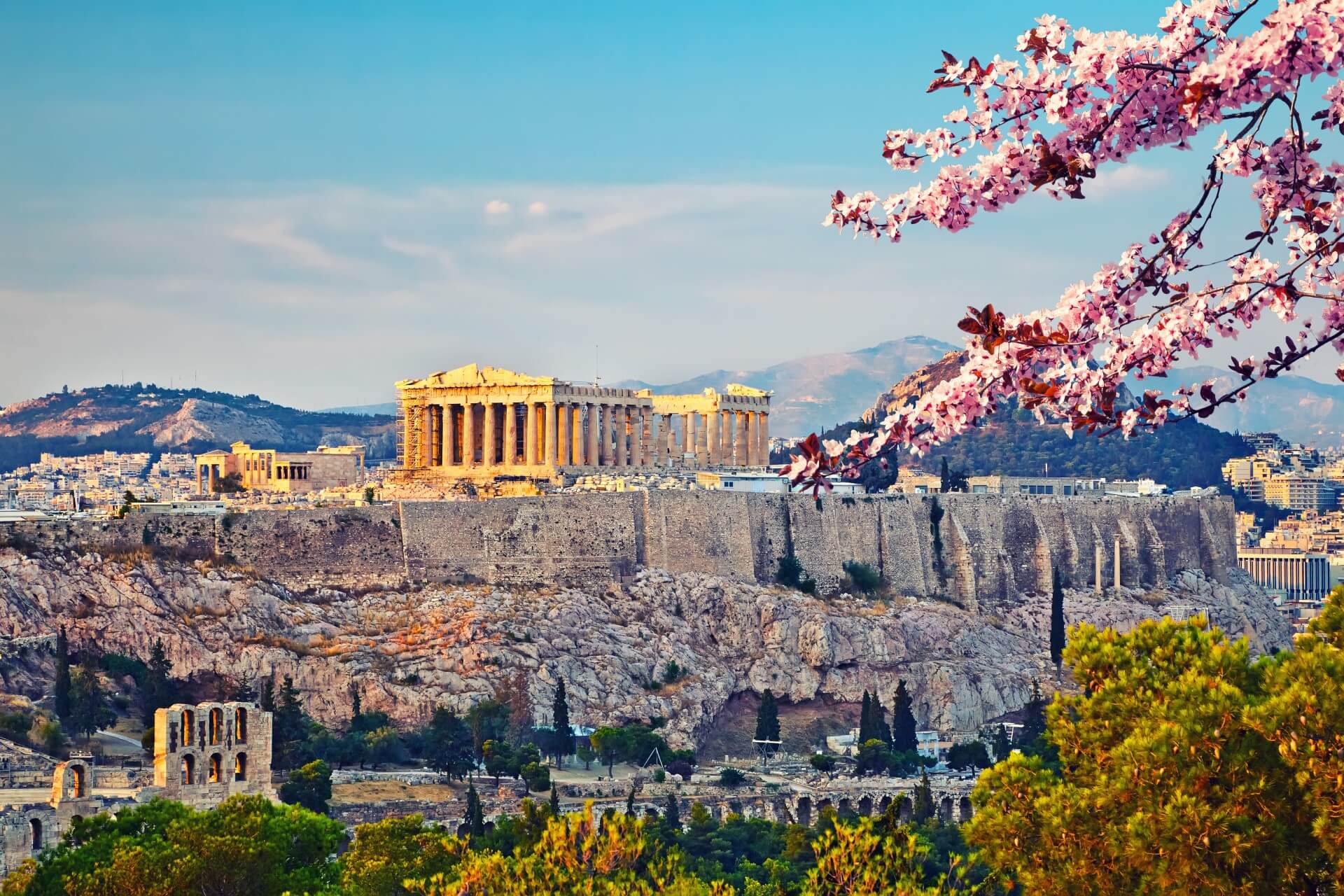

雅典建城至今已经有5000多年的历史,公元前8世纪,爱奥尼亚人建成的雅典是古希腊城邦的盟主。古代雅典是西方文化的源泉,雅典人对艺术、哲学、法律、科学作出了杰出的贡献。公元前5世纪为雅典的鼎盛时期,出现了许多不朽的大师。大悲剧家欧里庇德斯、大喜剧家阿里斯托芬、哲学家苏格拉底、柏拉图、亚里斯多德、历史学家希罗多德等都在这里诞生或居住过,这些光辉的名字照耀着人类文化的黎明。
雅典是希腊的古文物中心,至今仍保存着很多古代文化遗址,如今仍能显出当年的雄伟气概。雅典的博物馆世界驰名。
跨越时空两千五百年正是雅典给人的感觉,山丘上的卫城是西元前五百年的伟大艺术杰作,而山下的波拉卡区千年来就是一本希腊人的生活宝库,而身为希腊的首都及最大的城市,雅典的现代化建筑,拥挤的交通和空气污染严重,又和世界一般大都会无异。
现在雅典是全世界旅游爱好者的度假胜地。蔚蓝的爱琴海边涛声依旧,雅典的一砖一砾都闪烁着人类文明的光辉。 (Quelle:http://eur.bytravel.cn)
雅典(希腊语:Αθήνα,Athína,[aˈθina];古希腊语:Άθῆναι,转写:Athēnai)是希腊首都,也是希腊最大的城市。雅典位于巴尔干半岛南端,三面环山,一面傍海,西南距爱琴海法利龙湾8公里,属亚热带地中海气候。基菲索斯河和伊利索斯河穿城而过。市内多小山。
雅典是世界上最老的城市之一,有记载的历史就长达3000多年。现在雅典是欧洲第八大城市[1]。雅典是希腊经济、财政、工业、政治和文化中心。雅典也是欧盟商业中心之一。市区人口330万,加上郊区人口共有380万人口。城市的面积为39平方公里,加上郊区为412平方公里。[2]
古雅典是一个强大的城邦,是驰名世界的文化古城。希腊是西方哲学的摇篮,是柏拉图学院和亚里士多德的讲学场所的所在地。[3][4]苏格拉底、希罗多德、伯里克利、索福克勒斯、阿里斯托芬、欧里庇得斯、埃斯库罗斯和其他著名的哲学家、政治家和文学家都在雅典诞生或居住过[5],雅典也因此被称作“西方文明的摇篮”和民主的起源地。[6]公元前5世纪和4世纪在文化和政治上的成就对欧洲及世界文化产生重大影响。[7]
雅典至今仍保留了很多历史遗迹和大量的艺术作品,其中最著名的是雅典卫城的帕提农神庙,是西方文化的象征。
雅典是现代奥运会起源的地方。1896年曾举办过第一届夏季奥运会。2004年,第二十八届夏季奥林匹克运动会在雅典举行。Athen – neugriechisch Αθήνα [aˈθina] (f. sg.), Katharevousa und altgriechisch Ἀθῆναι Athênai (f. pl.) – ist die Hauptstadt Griechenlands. Athen ist die bevölkerungsreichste und flächengrößte Stadt des Landes. Die Gemeinde Athen im Zentrum des Ballungsraums Athen-Piräus ist dabei relativ klein. Athen im weiteren Sinne umfasst das Gebiet der Regionalbezirke Athen-Zentrum (87,3 km²), Athen-Nord (138,79 km²), Athen-Süd (68,9 km²), Athen-West (66,8 km²) und einiger umliegender Vororte mit zusammen 3,753 Mio. Einwohnern.[2]
Als kulturelles, historisches und wirtschaftliches Zentrum des Landes ist Athen auch die bedeutendste Metropole Griechenlands. Der Flughafen ist der wichtigste des Landes und der acht Kilometer vom Athener Zentrum entfernte Hafen Piräus der größte Griechenlands. Von hier und vom kleineren Rafina wird auch der Schiffsverkehr zu den zahlreichen griechischen Inseln abgefertigt. Im Schienenverkehr hat Athen nationale, jedoch keine internationale Bedeutung.
Die Stadt ist seit der Jungsteinzeit kontinuierlich besiedelt[3] und damit eine der ältesten Siedlungen und Städte Europas. 1985 wurde Athen erste Kulturhauptstadt Europas. In die Liste des Weltkulturerbes der UNESCO wurde 1987 die Akropolis und 1990 das Kloster Daphni aufgenommen.
Athen war in der klassischen Zeit Ort der attischen Polis. Die in dieser Zeit (5. Jahrhundert v. Chr.) entstandene attische Demokratie gilt als Begründerin einer auf dem Prinzip der Volkssouveränität gegründeten politischen Ordnung.
アテネ(現代ギリシア語: Αθήνα; Athína; IPA: [aˈθina]; カサレヴサ: Ἀθῆναι, Athinai; 古代ギリシア語: Ἀθῆναι, Athēnai)は、ギリシャ共和国の首都で同国最大の都市である。
アテネはアッティカ地方にあり、世界でももっとも古い都市の一つで約3,400年の歴史がある。古代のアテネであるアテナイは強力な都市国家であったことで知られる。芸術や学問、哲学の中心で、プラトンが創建したアカデメイアやアリストテレスのリュケイオン[1][2]があり、西洋文明の揺籃や民主主義の発祥地として広く言及されており[3][4]、その大部分は紀元前4-5世紀の文化的、政治的な功績により後の世紀にヨーロッパに大きな影響を与えたことは知られている。[5]今日の現代的なアテネは世界都市としてギリシャの経済、金融、産業、政治、文化生活の中心である。2008年にアテネは世界で32番目に富める都市に位置し[6]、UBSの調査では25番目に物価が高い都市[7]に位置している。
アテネ市の人口は655,780人[8](2004年は796,442人)[9]、市域面積は39 km2 (15 sq mi)[10]である。アテネの都市的地域(大アテネや大ピラエウス)は市域を超えて広がっており、人口は2011年現在3,074,160人に達し[11]、都市的地域の面積は412 km2 (159 sq mi)[10]である。ユーロスタットによれば大都市圏地域(Larger Urban Zones,LUZ) (en) の人口は欧州連合域内では7番目に大きい。
古典ギリシアの文化的遺産は今でもはっきりとしており、多くの古代遺跡や芸術作品が象徴している。もっとも有名で代表的なものにはパルテノン神殿があり初期の西洋文明の鍵となるランドマークと見なされる場合もある。アテネにはローマ帝国支配下のギリシャやビザンティンの遺跡もあり同様に少数のオスマン帝国の遺跡も残されているなど、何世紀にもわたる長い歴史を投影するモニュメントとなっている。アテネには2つのユネスコの世界遺産がありアテナイのアクロポリスと中世のダフニ修道院がそうである。現代のランドマークはギリシアが1833年に独立国となりアテネが首都に制定された時のもので、ギリシャ議会の議事堂や3部作(Trilogy )で構成されたギリシア国立図書館、アテネ大学、アテネアカデミーが含まれる。アテネは、最初の近代オリンピックであるアテネオリンピックと、その108年後に開催されたアテネオリンピック (2004年)の2度のオリンピックの舞台である。[12]アテネにはアテネ国立考古学博物館があり、世界最大の古代ギリシアの遺品の収蔵を特徴とし新しい2008年に完成したアクロポリス博物館もある。ギリシャ正教会の首長であるアテネ大主教が所在し、精神的な中心地でもある。(ギリシャ正教会は正教会に属し、クレタ島を除くギリシャ一国を管轄する。)正教会の定めるアテネの守護聖人は、ディオニシオス・オ・アレオパギティス、イェロテオス、フィロセイ。1985年には欧州文化首都に選ばれた。
Athens (/ˈæθɪnz/;[3] Greek: Αθήνα, Athína [aˈθina]; Ancient Greek: Ἀθῆναι, Athênai [a.tʰɛ̂ː.nai̯]) is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years[4] and its earliest human presence starting somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennium BC.[5]
Classical Athens was a powerful city-state that emerged in conjunction with the seagoing development of the port of Piraeus, which had been a distinct city prior to its 5th century BC incorporation with Athens. A centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum,[6][7] it is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy,[8][9] largely because of its cultural and political impact on the European continent, and in particular the Romans.[10] In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Greece. In 2012, Athens was ranked the world's 39th richest city by purchasing power[11] and the 67th most expensive[12] in a UBS study.
Athens is a global city and one of the biggest economic centres in southeastern Europe. It has a large financial sector, and its port Piraeus is both the largest passenger port in Europe,[13][14][15][16] and the second largest in the world.[17][dead link] The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens) had a population of 664,046 (in 2011)[2] within its administrative limits, and a land area of 38.96 km2 (15.04 sq mi).[18][19] The urban area of Athens (Greater Athens and Greater Piraeus) extends beyond its administrative municipal city limits, with a population of 3,090,508 (in 2011)[20] over an area of 412 km2 (159 sq mi).[19] According to Eurostat[21] in 2011, the functional urban area (FUA) of Athens was the 9th most populous FUA in the European Union (the 6th most populous capital city of the EU), with a population of 3.8 million people. Athens is also the southernmost capital on the European mainland.
The heritage of the classical era is still evident in the city, represented by ancient monuments and works of art, the most famous of all being the Parthenon, considered a key landmark of early Western civilization. The city also retains Roman and Byzantine monuments, as well as a smaller number of Ottoman monuments. Athens is home to two UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the Acropolis of Athens and the medieval Daphni Monastery. Landmarks of the modern era, dating back to the establishment of Athens as the capital of the independent Greek state in 1834, include the Hellenic Parliament and the so-called "architectural trilogy of Athens", consisting of the National Library of Greece, the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens and the Academy of Athens. Athens is also home to several museums and cultural institutions, such as the National Archeological Museum, featuring the world's largest collection of ancient Greek antiquities, the Acropolis Museum, the Museum of Cycladic Art, the Benaki Museum and the Byzantine and Christian Museum. Athens was the host city of the first modern-day Olympic Games in 1896, and 108 years later it welcomed home the 2004 Summer Olympics, making it one of only a handful of cities to have hosted the Olympics more than once.[22]
Athènes (en grec ancien Ἀθῆναι / Athễnai — le nom est toujours pluriel —, en grec moderne Αθήνα [a'θina] / Athína) est la capitale et la plus grande ville de la Grèce. En 2011, elle compte 664 046 habitants intra-muros sur une superficie de 39 km2. Son aire urbaine, le Grand Athènes, qui comprend notamment le port du Pirée, en compte plus de 3 millions. Berceau de la civilisation occidentale et dotée d'un riche passé, la ville est aujourd'hui le cœur politique, économique et culturel de la République hellénique, dont elle accueille la plupart des institutions, comme le Parlement, l'Áreios Págos (cour suprême) et le siège du Gouvernement.
Athènes est l'une des plus anciennes villes au monde, avec une présence humaine attestée dès le Néolithique. Fondée vers -800 autour de la colline de l'Acropole — par le héros Thésée, selon la légende —, la cité domine la Grèce au cours du Ier millénaire av. J.‑C.. Elle connaît son âge d'or au Ve siècle av. J.-C., sous la domination du stratège Périclès : principale puissance militaire de Grèce, à la tête d'une vaste alliance de cités, elle est également le cœur culturel de la Méditerranée. Première république de l'histoire, la démocratie athénienne connaît une vie intellectuelle importante, rassemblant des philosophes antiques (Socrate, Platon, Aristote), des auteurs de théâtre (Eschyle, Sophocle, Euripide, Aristophane) et l'historien Thucydide. De nombreux témoignages de cette période faste ont été conservés, comme le Parthénon, l'Agora (qui comprend notamment le temple d'Héphaïstos), l'Olympéion, le théâtre de Dionysos ou encore le Stade panathénaïque.
Intégrée au royaume de Macédoine, puis à l'Empire byzantin — période durant laquelle fut bâti le monastère de Daphni —, Athènes est conquise par l'Empire ottoman en 1456 et reste sous sa domination jusqu'en 1822, année de l'indépendance de la Grèce. Elle en devient la capitale et connaît une importante croissance urbaine. Occupée lors des deux guerres mondiales, la ville est ravagée par les destructions de la guerre civile grecque (1946 – 1949). Durant la seconde moitié du XXe siècle, Athènes devient le cœur économique et universitaire d'une Grèce en plein développement, dont les symboles sont les grandes avenues commerçantes telles que l'avenue Kifissias ou l'avenue Vasilissis Sofias. Frappée de plein fouet par la crise grecque depuis 2009, la ville a perdu plusieurs dizaines de milliers d'habitants et fait face à d'importantes difficultés économiques.
La ville s'étend sur la plaine d'Attique, sur les rives de la mer Égée. Elle est le chef-lieu du district régional d'Athènes-Centre et la capitale de la périphérie d'Attique, mais aussi celle du diocèse décentralisé du même nom. Le quartier le plus ancien, Pláka, est situé en contrebas de l'Acropole et comprend notamment la place Monastiráki. Kolonáki est le quartier huppé, à proximité de la place Syntagma. Enfin, Exárcheia est le quartier alternatif et branché de la ville, foyer de l'anarchisme en Grèce et de la contestation populaire depuis la crise. Grâce à son climat méditerranéen et ses nombreux musées, comme le musée de l'Acropole ou le musée national archéologique, Athènes est l'une des principales destinations touristiques d'Europe. Elle a également accueilli les Jeux olympiques d'été en 1896 et en 2004.
Atene (AFI: /aˈtɛne/[2]; in greco Αθήνα, traslitterato in Athína; in greco antico: Ἀθῆναι, Athḕnai)[3] è un comune greco di 655 780 abitanti,[1] capitale della Repubblica Ellenica, capoluogo dell'unità periferica di Atene Centrale e della periferia dell'Attica.
Il comune di Atene, stricto sensu, ha una superficie di 39 km², ma l'area metropolitana intesa come Grande Atene[4] ha un'estensione di 412 km² con 4 013 368 abitanti, ed è così la settima conurbazione più grande dell'Unione europea, e la quinta capitale più popolosa dell'Unione.[5]
Atene è una metropoli cosmopolita ed è il centro economico, finanziario, industriale e culturale della Grecia, e ha una notevole importanza a livello europeo, ma anche mondiale.[6] Nel 2012 è stata classificata come la 39ª città più ricca del mondo per potere d'acquisto[7] e come la 77ª più costosa[8] in una ricerca effettuata dalla società svizzera UBS.
È nota in tutto il mondo per la nascita della democrazia, per essere stata la sede dell'accademia di Platone e del liceo di Aristotele, oltre che aver dato i natali a Socrate, Pericle, Sofocle e molti altri filosofi e personaggi importanti dell'antichità. Tra le città più antiche del mondo,[9] è stata una fiorente polis ed è considerata la culla della civiltà occidentale.[10] Nel XXI secolo è stata al centro dell'attenzione di tutto il mondo per aver organizzato con successo i Giochi della XXVIII Olimpiade nel 2004 e per l'inaugurazione del Nuovo Museo dell'Acropoli nel 2009, che ha riaperto il dibattito riguardante i Marmi del Partenone.
Dall'aprile 2018 all'aprile 2019, Atene sarà capitale mondiale del libro.[11]
La città è anche la sede del Santo Sinodo della Chiesa di Grecia, presso il Monastero di Petraki.
Tradizionalmente la protettrice della città è la dea Atena, raffigurata sia sullo stemma che sulla bandiera della città.
Atenas (griego antiguo: Ἀθῆναι, romanización: Athēnai, griego moderno: Αθήνα, romanización: Athína) es la capital de Grecia y actualmente la ciudad más grande del país. La población del municipio de Atenas es de 664 046 (en 2011), pero su área metropolitana es mucho mayor y comprende una población de 3,8 millones (en 2011). Es el centro principal de la vida económica, cultural y política griega.
La historia de Atenas se extiende más de tres mil años, lo que la convierte en una de las ciudades habitadas más antiguas. Durante la época clásica de Grecia, fue una poderosa ciudad estado que nació junto con el desarrollo de la navegación marítima del puerto de El Pireo y que tuvo un papel fundamental en el desarrollo de la democracia. También fue un centro cultural donde vivieron muchos de los grandes artistas, escritores y filósofos de la Antigüedad. Estas contribuciones de Atenas al pensamiento de su época tuvieron una gran influencia en el desarrollo de Grecia, de Roma y de la cultura occidental.
Atenas es una ciudad rica en restos arqueológicos de extraordinaria importancia, de los cuales el más famoso es el Partenón en la Acrópolis. Además de construcciones de la época clásica griega, también se conservan monumentos romanos y bizantinos, así como varias construcciones modernas notables.
Афи́ны (греч. Αθήνα, МФА: [aˈθina]) — столица Греции. Располагается в исторической области Аттика и является экономическим, культурным и административным центром страны. Город назван в честь богини войны и мудрости Афины, которая была покровителем древнего полиса. Афины имеют богатую историю; в классический период (V век до н. э.) город-государство достигло вершины своего развития, определив многие тенденции развития позднейшей европейской культуры. Так, с городом связаны имена философов Сократа, Платона и Аристотеля, заложивших основы европейской философии, трагиков Эсхила, Софокла и Еврипида, стоявших у истоков драмы; политическим строем древних Афин была демократия.
Площадь территории городской агломерации — 412 км². Эта территория окружена горами: Эгалео, Парнис, Пенделикон и Имитос. Общая численность населения городской агломерации составляет 1/3 от общей численности населения Греции и составляет, в соответствии с переписью 2011 года, 3 090 508 человек. Таким образом плотность населения городской агломерации — 7500 человек на 1 км². Высота центра города над уровнем моря составляет 20 метров, в то время как рельеф территории города очень разнообразен, с равнинами и горами.

巴格达(阿拉伯语:بغداد,阿拉米语:ܒܓܕܐܕ),古称报达,《诸蕃志》称 白达,伊拉克首都,同时它也是伊拉克巴格达省的首府,为伊拉克最大城市及经济文化中心。位于美索不达米亚平原中部地区,底格里斯河流过巴格达市区,而距幼发拉底河约30千米[3]。巴格达人口约577万,在阿拉伯世界位于开罗之后列第二位。在历史上,巴格达曾是伊斯兰文明的政治、宗教、经济、商业、学术、交通中心。巴格达也是一座多民族多教派的城市。
阿拔斯王朝第二任哈里发曼苏尔于公元762年将阿拉伯帝国都城迁至此地。当时成为阿拉伯世界的政治、经济、宗教中心。[3]
10世纪后,因政治变动及战争而衰退[3]。随着阿拉伯王朝不复昔日光辉,巴格达先于1258年被蒙古人攻陷;1508年和1534年分别被波斯和土耳其人占领。1638年后巴格达长期受土耳其人的统治。1917年巴格达落入英军之手。直到1921年伊拉克独立后,巴格达被定为首都。巴格达位于美索不达米亚平原中部地区,底格里斯河流过巴格达市区,而距幼发拉底河约30千米,为两河相距最近之处;迪亚拉河流经城市郊区,并于巴格达东南方注入底格里斯河。
Bagdad (arabisch بغداد Baghdad, DMG Baġdād, kurdisch بەغدا Beẍda, von persisch „Geschenk des Herrn“ bzw. „Gottesgeschenk“, entsprechend baġ „Gott, Herr“ und dād „Gabe“)[1] ist die Hauptstadt des Iraks und des gleichnamigen Gouvernements. Sie ist mit ca. 6,7 Millionen Einwohnern (2018)[2] eine der größten Städte im Nahen Osten. In der Metropolregion, die weit über die Grenzen des Gouvernements hinausreicht, leben ca. 8,1 Millionen Menschen (2018), was knapp einem Viertel der Gesamtbevölkerung des Iraks entspricht.[2]
Die Stadt ist das politische, wirtschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum des Landes sowie Sitz der irakischen Regierung, des Parlaments, aller staatlichen und religiösen Zentralbehörden sowie zahlreicher diplomatischer Vertretungen. Bagdad ist der bedeutendste Verkehrsknotenpunkt Iraks und besitzt zahlreiche Universitäten, Hochschulen, Theater, Museen sowie Baudenkmäler.
バグダード(アラビア語: بغداد/ラテン文字表記: Baghdad, Baġdād)は、イラクの首都で同国最大の都市。また、バグダード県の県庁所在地でもある。アッバース朝によって建設された古都であり、イスラム世界における主要都市の1つ。2020年の人口はおよそ714.4万人[1]。日本語では多くの場合バグダッドと表記されるが、アラビア語の綴りと発音([bæɣˈdæːd])に近づけるとバグダードという表記になる。
Baghdad (/ˈbæɡdæd, bəɡˈdæd/; Arabic: بَغْدَاد [baɣˈdaːd] ( listen)) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient Akkadian city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
listen)) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient Akkadian city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million.[3] The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires. With the recognition of Iraq as an independent state (formerly the British Mandate of Mesopotamia) in 1932, Baghdad gradually regained some of its former prominence as a significant center of Arab culture, with a population variously estimated at 6 or over 7 million.[note 1] Compared to its large population, it has a small area at just 673 square kilometers (260 sq mi).
The city has faced severe infrastructural damage due to the Iraq War, which began with the United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003 and lasted until 2011, and the subsequent insurgency and renewed war that lasted until 2017, resulting in a substantial loss of cultural heritage and historical artifacts. During this period, Baghdad had one of the highest rates of terrorist attacks in the world. However, terrorist attacks are rare and have been declining since the territorial defeat of the Islamic State militant group in Iraq in 2017.
Bagdad ou Baghdad (en arabe : بغداد, baġdād, /baɣˈdaːd/ Écouter) est la capitale de l’Irak et de la province de Bagdad. Située au centre-est du pays, elle est traversée par le fleuve Tigre. Ses habitants sont appelés « Bagdadiens »1.
Avec une aire urbaine comprenant une population estimée à 10 millions d’habitants en 2012, c’est la plus grande ville d’Irak, ainsi que la deuxième ville la plus peuplée du monde arabe et du Moyen-Orient (derrière Le Caire, la capitale de l'Égypte). C'est un carrefour de communications aériennes, routières et ferroviaires d'une grande importance stratégique pour la république d'Irak.
Les origines de la ville actuelle remontent, au moins, au viiie siècle, avec, probablement, la présence de plusieurs petits foyers d'habitat antérieurs datant de la période préislamique. Elle fut la capitale de l'Empire abbasside à partir du viiie siècle et un centre de culture et de connaissance très important pendant des siècles, jusqu’au milieu du xiiie siècle. Bagdad a été, de 2003 à 2011, le centre d’un violent conflit en raison de la guerre d’Irak. Elle est devenue une ville d'enclaves fortifiées régies par les soldats de l'armée irakienne, les officiers de la police fédérale, les agents de police locaux et les agents de sécurité privés.
Baghdad (in arabo: بغداد, Baghdād, in età abbaside Madīnat al-Salām, "Città della pace", in italiano antico Baldacco, Baldacca o Baudac), o Bagdad[4], è la capitale dell'Iraq e dell'omonima provincia. È la seconda città più grande dell'Asia sud-occidentale, dopo Teheran: il calcolo della popolazione per il 2014 è di 7 665 292 abitanti[3]. Situata sul fiume Tigri a 33°20 nord e 44°26 est.
Bagdad3 (en árabe: بَغْدَاد Baġdād, en arameo: ܒܓܕܕ Baghdad) es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de Irak. Su número de habitantes es de 8 765 000 (est. 2016), lo que la convierte en la mayor ciudad del país y la segunda del mundo árabe, solo por detrás de El Cairo.
Ubicada a orillas del río Tigris, la ciudad fue fundada en el siglo viii y se convirtió en capital del Califato abasí. En poco tiempo se convirtió en un centro cultural, comercial e intelectual de gran relevancia del mundo islámico. Esto, y el hecho de ser sede de varias instituciones académicas relevantes, como la Casa de la sabiduría, le sirvieron a la ciudad para ganarse una reputación mundial de «Centro de Enseñanza».
Bagdad fue la ciudad más grande de la Edad Media durante gran parte del Califato abasí, cuando alcanzó un pico de un millón y medio de habitantes.4 Sin embargo, la urbe fue en gran parte destruida por las tropas del Imperio mongol en 1258, lo que resultó en un declive que se prolongaría por muchos siglos debido a frecuentes epidemias y la sucesión de varios imperios que dominaron la ciudad. Con el reconocimiento de Irak como estado independiente en 1938 tras la desaparición del Mandato Británico para Mesopotamia, Bagdad recuperó gradualmente parte de su pasada preeminencia como centro significante de la cultura musulmana.
En tiempos recientes la ciudad ha sufrido graves daños en sus infraestructuras, especialmente durante la invasión de Irak de 2003 y la consiguiente guerra de Irak que duró hasta diciembre de 2011. En los últimos años la capital ha sido objetivo de numerosos ataques de la guerrilla iraquí. Este conflicto militar también ha provocado una pérdida profunda e irreparable de la herencia cultural y de piezas históricas. Como resultado, Bagdad está considerado uno de los lugares menos hospitalarios del mundo en los que vivir y ofrece una calidad de vida muy baja.
Багда́д (араб. بغداد — «божий дар») — столица Ирака, административный центр мухафазы Багдад. С населением более 9 млн человек (2015)[3] он является одним из самых больших городов Ближнего Востока.
Багдад — политический, экономический и культурный центр Ирака. В нём находятся правительство, все центральные государственные и религиозные учреждения и множество дипломатических представительств. Город — важный транспортный узел. В нём также расположены многочисленные вузы, театры, музеи и памятники архитектуры.
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage
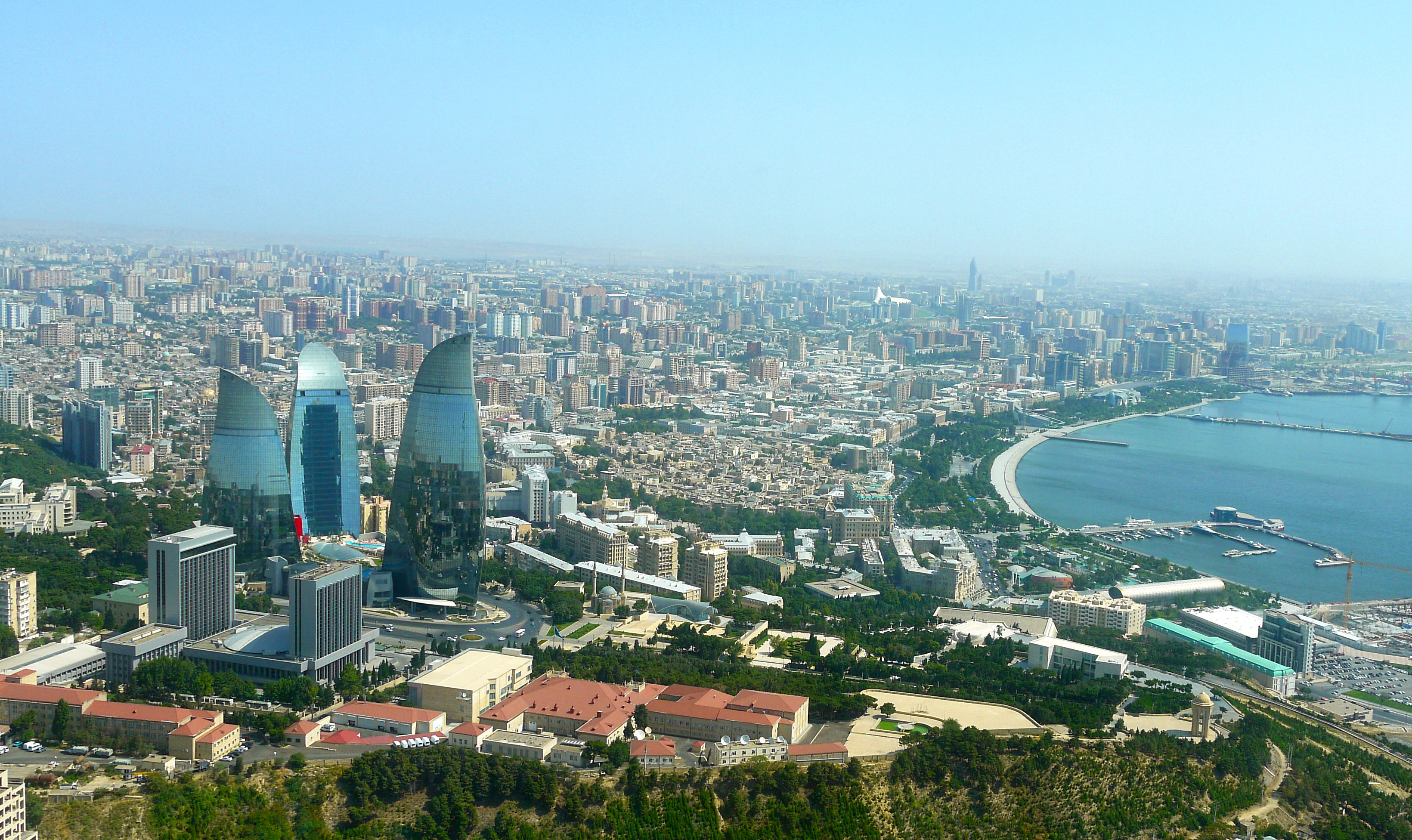

巴库(Baku, Баку)是阿塞拜疆首都和全国经济、文化中心。里海最大港口。位于阿普歇伦米岛南部,是石油工业中心,有“石油城”之誉。也是前苏联外高加索最大城市。 巴库由10个行政区和46个城镇组成,面积2200平方公里。人口182.88万。1月平均气温为4℃,7月平均气温为27.3℃。 在18世纪,巴库为巴库汗国都城。19世纪70年代开始工业性采油,19世纪末成为外高加索工业中心和石油基地,有22大炼油基地,其他工业多与石油有 关。1991年8月成为独立后阿塞拜疆的首都。城市西部的比比埃巴特区为老采油区。东部的基什雷区和邵武勉区为重要工业区。石油是巴库的经济命脉。石油开 采正向深处和外围海域发展。以石油、天然气开采和石油加工为主要工业,还有石油机械、电力和轻工 、食品工业。外高加索主要铁路枢纽,铁路通罗斯托夫、第比利斯和埃里温。有输油管道通黑海港口巴统。巴库是里海航运中心,可泊中等吨位船舶。城市中部为行 政、文化和居住区。建有科学院,大学和博物馆。里海最大港口,有“石油城”之誉。市内建有地铁,有阿塞拜疆科学学院、阿塞拜疆大学、石油化工学院等多所高 等院校。城市的中部是行政、文化区域,有历史博物馆和艺术博物馆。老城区以旧要塞为中心。 巴库是一座有着悠久历史的古城,城内有众多名胜古迹,如11世纪建造的瑟纳克一卡尔清真寺塔,12世纪的克孜一卡拉瑟塔楼,13世纪的巴伊洛夫石堡,15 世纪的希尔凡王宫及17世纪的汗王宫殿至今保存完好。2000年联合国教科文组织将巴库墙城及城内的希尔梵国王宫殿和少女塔作为文化遗产,列入《世界遗产 名录》。(Quelle:http://you.kuxun.cn)
巴库(阿塞拜疆语:Bakı,[bɑˈcɯ] (ⓘ))是阿塞拜疆的首都、经济文化中心。巴库同时也是里海最大港口,外高加索最大城市[4]。它的海拔是低于海平面28米(92英尺) ,使它成为世界上海拔最低的首都以及低于海平面的最大城市。面积2192平方公里,人口300万(2008年计算)[5]。巴库全市分为内城和新城两部分(亦有将苏联时期兴建区域分别划分的)。
在2007年,伊斯兰会议组织文化部长宣布巴库为2009年伊斯兰文化中心。为2015年第一届欧洲运动会主办国。巴库曾先后申办2016年夏季奥运会和2020年夏季奥运会,但皆因基础设施不完备没有入围。不过由于阿塞拜疆歌手艾尔与妮基在2011年欧洲歌唱大赛获得冠军,终使巴库获得举办2012年欧洲歌唱大赛的机会。
Baku (aserbaidschanisch Bakı / باکی; russisch Баку́ Baku) ist die Hauptstadt Aserbaidschans. Mit zwei Millionen Einwohnern in der Stadtprovinz ist Baku die bevölkerungsreichste und flächengrößte Stadt des Landes und des gesamten Kaukasus. Die Stadt an der Küste des Kaspischen Meeres ist Verkehrsknotenpunkt sowie Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum mit mehreren Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Durch die Lage innerhalb eines Erdölfördergebiets ist Baku der Knotenpunkt mehrerer Erdölleitungen und besitzt einen bedeutenden Erdölhafen. Baku kann aufgrund seiner günstigen Lage an mehreren historischen Handelswegen auf eine reiche Stadtgeschichte zurückblicken. In der Altstadt, die seit 2000 den Status eines UNESCO-Welterbes hat, sind zahlreiche Paläste, Moscheen und Festungsbauten erhalten geblieben.
バクー(Baku)は、アゼルバイジャン共和国の首都。カスピ海西岸に突き出したアブシェロン半島南岸に位置し、市街はバクー湾に面するように広がった港町である。行政的には11の行政区、48の町区に分割されており、2005年時点の総人口は2,045,815人[1]。アゼルバイジャン最大の都市であると同時に、南カフカース地域でも有数の大都市である。大規模な油田(バクー油田)をもち、帝政ロシア時代から石油の生産地として発展してきた。
日本語名のバクーはキリル文字綴りによるロシア語綴り・アゼルバイジャン語(アゼリー語)旧綴り Баку (Baku) に基づくが、アゼルバイジャン語の発音では母音の前で子音 k が軟音化するためカタカナ表記するならば「バキュ」に近く、現在アゼルバイジャンで使われているアゼルバイジャン語のラテン文字正書法では Bakı と綴る。バクーという名前の由来には諸説あるが、最も一般的なものは、ペルシャ語で「風が吹きつけた」という意味の "bād-kūbe"(バード・クーベ)から来ているとする説が一般的である。
気候は晴天が多く、乾燥している。寒気と暖気がぶつかることで起きる強風が時折吹き付け、先述した語源の根拠となっている。海岸は美しく、市街近郊には温泉や鉱泉がある。
市街の中心はその南西部にあり、イチェリ・シェヘル (İçəri Şəhər) すなわち「内城」と呼ばれる城壁に囲まれた旧市街と、帝政ロシア時代にその周囲に築かれた新市街とに分かれる。その周囲、北から東にかけての平地から丘陵の斜面一帯にソビエト連邦時代につくられた市街が広がっている。近年は豊富なオイルマネーをもとに近未来的な巨大建築物が出現し、「第二のドバイ」「第二のシンガポール」とも呼ばれている[2]。
Baku (/bəˈkuː/ bə-KOO, /ˈbɑːkuː/ BAH-koo; Azerbaijani: Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region, with a population of 2,262,600 (January 1, 2018). Baku is located 28 metres (92 ft) below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world and also the largest city in the world located below sea level. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, alongside the Bay of Baku. At the beginning of 2009, Baku's urban population was estimated at just over two million people.[5] Officially, about 25 percent of all inhabitants of the country live in Baku's metropolitan area. Baku is the sole metropolis in Azerbaijan.
Baku is divided into twelve administrative districts (raions) and 48 townships. Among these are the townships on the islands of the Baku Archipelago, and the town of Oil Rocks built on stilts in the Caspian Sea, 60 kilometres (37 miles) away from Baku. The Inner City of Baku, along with the Shirvanshah's Palace and Maiden Tower, were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2000. According to the Lonely Planet's ranking, Baku is also among the world's top ten destinations for urban nightlife.[6]
The city is the scientific, cultural, and industrial center of Azerbaijan. Many sizeable Azerbaijani institutions have their headquarters there. The Baku International Sea Trade Port is capable of handling two million tons of general and dry bulk cargoes per year.[7] In recent years, Baku has become an important venue for international events. It hosted the 57th Eurovision Song Contest in 2012, the 2015 European Games, 4th Islamic Solidarity Games, the F1 Azerbaijan Grand Prix since 2016, and will host UEFA Euro 2020. The city is bidding for Expo 2025 against Yekaterinburg, Russia and Osaka, Japan.
La ville de Bakou (azéri : Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) est la capitale de l'Azerbaïdjan. Elle se trouve dans l'est du pays, sur la rive sud de la péninsule d'Abşeron, au bord de la mer Caspienne. Son histoire débute au Ier millénaire avant Jésus-Christ, mais les traces écrites les plus anciennes ne datent que du Ve siècle.
En 2011, sa population est estimée à 2 045 815 habitants1 et 3 millions de personnes environ vivent dans l'agglomération.
Baku (pron. bakù[2]; in azero: Bakı?; in russo: Баку?), conosciuta anche come Baqy, Baky o Baki, in italiano Bacù[2], è la capitale, la più grande città e il più grande porto dell'Azerbaigian e di tutto il Caucaso.
È considerata una delle più antiche e più grandi città dell'Oriente. Situata sulla costa meridionale della penisola di Abşeron, la città si compone di tre parti principali: il centro, la vecchia Città Murata estesa sul territorio di 21,5 ettari e la parte della città costruita nell'epoca sovietica. La sua popolazione nel 2014 era stimata in 2.122.300 di abitanti.
Bakú (en azerí, Bakı, [bɑˈkɯ]) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Azerbaiyán, del mar Caspio y del Cáucaso. Está situada en la costa sur de la península de Absheron, que se proyecta en el Caspio. La ciudad se compone de dos partes principales: el centro y la ciudad vieja interior. En enero de 2018 Bakú tenía una población de 2.262.600 habitantes,3 de los cuales 153.400 eran desplazados internos y 143.400 refugiados de la guerra de Nagorno Karabaj.
Bakú se divide en once distritos administrativos (raiones) y 48 municipios. Entre estos se encuentran los municipios de las islas de la bahía de Bakú y Neft Daşları construidas sobre pilotes en el mar Caspio, a 60 km de Bakú. El centro urbano de la ciudad, con el Palacio de los Shirvanshah y la Torre de la Doncella, fue inscrito por la Unesco como Patrimonio de la Humanidad en 2000. De acuerdo con la clasificación de Lonely Planet, Bakú también se encuentra entre los diez mejores destinos de vida nocturna urbana del mundo.4
La ciudad fue uno de los mayores centros petrolíferos de la antigua Unión Soviética y actualmente es el centro científico, cultural e industrial de Azerbaiyán. Muchas instituciones importantes de Azerbaiyán tienen su sede allí, incluyendo SOCAR, una de las cien principales empresas del mundo, entre otras.5 El Puerto de Comercio Marítimo Internacional de Bakú, protegido por las islas del archipiélago Bakú hacia el este y la península de Absheron al norte, es capaz de transportar dos millones de toneladas de carga general y seca a granel por año.6 La ciudad acogió el 57.º Festival de Eurovisión en 2012 y fue la sede de los Juegos Europeos 2015, es la sede del Gran Premio de Azerbaiyán de Fórmula 1 desde 2016 y será la sede del Campeonato Mundial de Ciclismo BMX en 2018 y de la EURO 2020.7
Баку́ (азерб. Bakı, МФА (азерб.): [bɑˈcɯ]) — столица Азербайджанской Республики, крупнейший промышленный, экономический и научно-технический центр Закавказья, а также самый крупный порт на Каспийском море и самый большой город на Кавказе[9][10].
Площадь территории, которая административно управляется Баку, составляет 2150 км²[1]; население данной территории — 2 181,8 тыс. жителей (на 1 января 2014 года). Баку расположен на южном берегу Апшеронского полуострова. Город по своей древности, величине территории и численности населения является одним из старинных и крупнейших городов Востока. Население всего Апшеронского полуострова (Бакинской агломерации) составляет 2 673,7 тыс. жителей[7]. Баку удостоен в 2010 году Программой ООН по окружающей среде (UNEP) звания одного из главных городов по проведению Всемирного дня окружающей среды. Подобные города избираются ежегодно. В 2010 году, наряду с Баку, этих званий были удостоены также Генуя (Италия) и Женева (Швейцария)[11].



曼谷(法语:Bangkok),官方名字功特玛哈那空[2](泰语:กรุงเทพมหานคร,转写:krung deːb mahaː nagara,皇家拉丁音译:Krung Thep Maha Nakhon,国际音标:[krūŋ tʰêːp mahǎː nákʰɔ̄ːn] 聆听 帮助·信息),泰国口语简称功特[2](泰语:กรุงเทพ,皇家拉丁音译:Krung Thep,国际音标:[krūŋ tʰêːp],
聆听 帮助·信息),泰国口语简称功特[2](泰语:กรุงเทพ,皇家拉丁音译:Krung Thep,国际音标:[krūŋ tʰêːp], 聆听 帮助·信息),是泰国首都与最大城市,在当地华人社区亦作泰京,为泰国政治、经济、贸易、交通、文化、科技、教育与各方面中心。位于昭披耶河东岸,近泰国湾。
聆听 帮助·信息),是泰国首都与最大城市,在当地华人社区亦作泰京,为泰国政治、经济、贸易、交通、文化、科技、教育与各方面中心。位于昭披耶河东岸,近泰国湾。
Bangkok (thailändisch กรุงเทพมหานคร, Krung Thep Maha Nakhon, [kruŋ tʰêːp máʔhǎː náʔkʰɔːn],  anhören?/i; kurz กรุงเทพฯ, Krung Thep, [kruŋ tʰêːp]; historische Schreibung zum Teil auch Bankok[2]) ist seit 1782 die Hauptstadt des Königreichs Thailand. Sie hat einen Sonderverwaltungsstatus und wird von einem Gouverneur regiert. Die Hauptstadt hat 8,249 Millionen Einwohner (Volkszählung 2010) und ist die mit Abstand größte Stadt des Landes. In der Bangkok Metropolitan Region (BMR), der größten Metropolregion in Thailand, leben insgesamt 14,566 Millionen Menschen (Volkszählung 2010).[1]
anhören?/i; kurz กรุงเทพฯ, Krung Thep, [kruŋ tʰêːp]; historische Schreibung zum Teil auch Bankok[2]) ist seit 1782 die Hauptstadt des Königreichs Thailand. Sie hat einen Sonderverwaltungsstatus und wird von einem Gouverneur regiert. Die Hauptstadt hat 8,249 Millionen Einwohner (Volkszählung 2010) und ist die mit Abstand größte Stadt des Landes. In der Bangkok Metropolitan Region (BMR), der größten Metropolregion in Thailand, leben insgesamt 14,566 Millionen Menschen (Volkszählung 2010).[1]
Die Stadt ist das politische, wirtschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum Thailands mit Universitäten, Hochschulen, Palästen und über 400 Wats (buddhistische Tempelanlagen und Klöster) sowie wichtigster Verkehrsknotenpunkt des Landes. In Bangkok ist auch die Wirtschafts- und Sozialkommission für Asien und den Pazifik (UNESCAP) beheimatet. Mit mehr als 17 Millionen ausländischen Touristen war Bangkok im Jahr 2013 die meistbesuchte Stadt der Welt, bevor sie 2014 wieder von London abgelöst wurde und seither auf Platz 2 rangiert.[3] Seit 2016 steht Bangkok mit über 20 Millionen Touristen jährlich auf Platz 1 der meistbesuchten Städte der Welt.
バンコク都(バンコクと、フランス語: Bangkok,[bāːŋ kɔ̀ːk], 聴く[ヘルプ/ファイル])正式名称クルンテープマハーナコーン(กรุงเทพมหานคร,[krūŋ tʰêːp mahǎː nákʰɔ̄ːn])は[1]、タイ王国の首都。タイでは、クルンテープ(กรุงเทพ,[krūŋ tʰêːp],
聴く[ヘルプ/ファイル])正式名称クルンテープマハーナコーン(กรุงเทพมหานคร,[krūŋ tʰêːp mahǎː nákʰɔ̄ːn])は[1]、タイ王国の首都。タイでは、クルンテープ(กรุงเทพ,[krūŋ tʰêːp], 聴く[ヘルプ/ファイル])の通称で呼ばれている[2]。
聴く[ヘルプ/ファイル])の通称で呼ばれている[2]。
人口8,249,117人(2010年)、面積1568.737 km2。都市圏人口は2018年時点で1600万人を超えており、世界有数の大都市圏を形成している[3]。ASEAN経済の中心地で、東南アジア屈指の世界都市でもある。
タイの王宮や政治の中枢機関が集中しているだけでなく、交通と宿泊施設の整ったバンコクは多くの各国要人を招き、アジアで2番目に多くの国際会議が開かれる都市であり[4]、政治的に多大な影響力を持つ。
Bangkok,[a] officially known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon[b] and colloquially as Krung Thep,[c] is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies 1,568.7 square kilometres (605.7 sq mi) in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estimated population of 10.539 million as of 2020, 15.3 percent of the country's population. Over 14 million people (22.2 percent) lived within the surrounding Bangkok Metropolitan Region at the 2010 census, making Bangkok an extreme primate city, dwarfing Thailand's other urban centres in both size and importance to the national economy.
Bangkok traces its roots to a small trading post during the Ayutthaya Kingdom in the 15th century, which eventually grew and became the site of two capital cities, Thonburi in 1768 and Rattanakosin in 1782. Bangkok was at the heart of the modernization of Siam, later renamed Thailand, during the late-19th century, as the country faced pressures from the West. The city was at the centre of Thailand's political struggles throughout the 20th century, as the country abolished absolute monarchy, adopted constitutional rule, and underwent numerous coups and several uprisings. The city, incorporated as a special administrative area under the Bangkok Metropolitan Administration in 1972, grew rapidly during the 1960s through the 1980s and now exerts a significant impact on Thailand's politics, economy, education, media and modern society.
The Asian investment boom in the 1980s and 1990s led many multinational corporations to locate their regional headquarters in Bangkok. The city is now a regional force in finance and business. It is an international hub for transport and health care, and has emerged as a centre for the arts, fashion, and entertainment. The city is known for its street life and cultural landmarks, as well as its red-light districts. The Grand Palace and Buddhist temples including Wat Arun and Wat Pho stand in contrast with other tourist attractions such as the nightlife scenes of Khaosan Road and Patpong. Bangkok is among the world's top tourist destinations, and has been named the world's most visited city consistently in several international rankings.
Bangkok's rapid growth coupled with little urban planning has resulted in a haphazard cityscape and inadequate infrastructure. Despite an extensive expressway network, an inadequate road network and substantial private car usage have led to chronic and crippling traffic congestion, which caused severe air pollution in the 1990s. The city has since turned to public transport in an attempt to solve the problem, operating five rapid transit lines and building other public transit, but congestion still remains a prevalent issue. The city faces long-term environmental threats such as sea level rise due to climate change.
Bangkok (thaï : กรุงเทพมหานคร, Krungthep Mahanakhon) est la capitale de la Thaïlande. La ville a également le statut de province.
La ville occupe une superficie de 1 569 km2 dans le delta du fleuve Chao Phraya en Thaïlande centrale et son nombre d’habitants est supérieur à 9 millions, plus de 19 millions de personnes habitent l’aire métropolitaine de la capitale, soit plus que tous les autres centres urbains du pays.
Les racines de Bangkok remontent à un petit comptoir commercial créé durant le Royaume d’Ayutthaya au xve siècle au bord du fleuve Chao Phraya qui prend de l’importance avant de devenir le site d’une première capitale, Thonburi, en 1768. Mais la date officielle de sa fondation par Rama Ier, premier roi de la dynastie Chakri, est le 6 avril 1782, sur l’autre rive du fleuve. Bangkok s’inscrit au xixe siècle au cœur du mouvement de modernisation du royaume de Siam, alors que le pays subit la pression des nations colonisatrices européennes. La ville est ensuite au xxe siècle le théâtre de l’évolution politique de la Thaïlande, notamment avec l’abolition de la monarchie absolue, l’adoption d’une constitution, et plusieurs soubresauts politiques parfois violents. La ville a connu une formidable croissance à partir des années 1960 et exerce aujourd’hui une influence centrale sur la vie politique, économique, culturelle, universitaire et médiatique de la Thaïlande1.
Le boom économique asiatique des années 1980 et 1990 a amené beaucoup d’entreprises multinationales à installer leur siège régional à Bangkok. La ville est un important pôle d’affaires. C’est également une plateforme internationale pour les transports et la santé, tout comme pour les arts, la mode, les spectacles et le tourisme. Bangkok fait partie des villes les plus visitées au monde.
Bangkok (in thailandese: บางกอก?), in thai ufficialmente denominata Krung Thep Maha Nakhon o Krung Thep (in thailandese: กรุงเทพมหานคร?, กรุงเทพฯ; pronuncia[?·info]), è la capitale e la città più estesa e popolosa della Thailandia, situata lungo il fiume Chao Phraya, nei pressi del golfo della Thailandia. Secondo il censimento del 2010, aveva una popolazione di oltre 8,3 milioni di abitanti, pari al 12,6% del totale del paese, mentre erano oltre 14,6 milioni (22,2%) quelli che vivevano nella regione metropolitana, che comprende anche le province circostanti.[1] Tra le città più popolose e trafficate del mondo,[2] nonché una delle destinazioni preferite del turismo mondiale, a partire dalla seconda metà del XX secolo ha conosciuto un rapidissimo sviluppo industriale, rappresentando una delle città economicamente più dinamiche del sud-est asiatico.
Bangkok u oficialmente Krung Thep Mahanakhon ([bāːŋ kɔ̀ːk] en tailandés, กรุงเทพมหานคร o กรุงเทพ  [krūŋ tʰêːp mahǎː nákʰɔ̄ːn] (?·i), RTGS: Krung Thep Mahanakhon traducido como «La ciudad de los ángeles»)1 es la capital y ciudad principal de Tailandia.2 Aunque el nombre oficial de la capital no es Bangkok, es comúnmente empleado internacionalmente para referirse a la ciudad.3
[krūŋ tʰêːp mahǎː nákʰɔ̄ːn] (?·i), RTGS: Krung Thep Mahanakhon traducido como «La ciudad de los ángeles»)1 es la capital y ciudad principal de Tailandia.2 Aunque el nombre oficial de la capital no es Bangkok, es comúnmente empleado internacionalmente para referirse a la ciudad.3
Bangkok significa «aldea de la ciruela silvestre» y es el nombre de una parte del lado del río Thon Buri. Así pues, Bangkok es conocida como Krung Thep Mahanakhon. Fue un pequeño puesto de comercio en la desembocadura del río Chao Phraya durante el reino de Ayutthaya. Llegó al primer plano de Siam, cuando recibió el estatus de ciudad capital en 1768 después de la quema de Ayutthaya.4 Sin embargo el actual reino Rattanakosin no comenzó hasta 1782 cuando Rama I trasladó la capital a la isla de Rattanakosin, después de la muerte del rey Taksin. La capital de Rattanakosin es ahora formalmente llamada "Phra Nakhon" (en tailandés: พระนคร), perteneciente a los antiguos límites en el núcleo de la metrópolis y el nombre de Bangkok incorpora la acumulación urbana desde el siglo XVIII, con su propia administración pública y gobernador.
Durante los últimos doscientos años Bangkok ha crecido hasta llegar a ser el centro político, social y económico de Tailandia ampliando su pujanza hacia Indochina y el Sudeste asiático. Su influencia en el arte, la política, moda, educación y entretenimiento, así como en los negocios, le ha proporcionado a Bangkok el estatus de ciudad global. En 2016, según un informe elaborado por MasterCard, fue reconocida como la ciudad más visitada por turistas extranjeros con 21,47 millones superando a Londres.5
La ciudad tenía una población de alrededor de 8.5 millones de habitantes, mientras que el área de gran Bangkok posee 11.971.000 habitantes (a enero de 2008).6 Esto, a su vez, ha cambiado el país ya que ha pasado de ser una población tailandesa homogénea a una heterogénea donde se incluye ciudadanos de procedencia occidental, con grupos de India o China, otorgando a la ciudad un estatus cosmopolita.
Бангко́к[6], в Таиланде используется название Крунгте́п[7] (тайск. กรุงเทพฯ, Крунгтхеп[8], или กรุงเทพมหานคร, Крунг Тхеп Маха Накхон[9]) — столица и самый крупный город Таиланда с населением 5,6 млн чел. (2011). Имя, данное городу при основании, попало в Книгу рекордов Гиннесса как самое длинное название города в мире. Бангкок раскинулся на восточном берегу реки Чаупхраи, недалеко от её впадения в Сиамский залив.
Один из наиболее быстрорастущих (в том числе экономически) городов Юго-Восточной Азии. Занимает площадь свыше 1,5 тыс. км². Местные жители считают свой город зарождающимся новым региональным центром, способным соперничать с такими городами, как Сингапур и Гонконг. Бангкок является также одним из наиболее привлекательных для туристов городов мира[10].
Столичный округ и пять соседних провинций (Нонтхабури, Самутпракан, Патхумтхани, Самутсакхон и Накхонпатхом) образуют агломерацию Большой Бангкок.

这座城市在展示通俗文化的同时,也没有忘记根深蒂固的传统。比如说,梅尔塞节还有在格拉西亚区、桑斯区或波布雷诺区举办的节庆活动,都向游客提供着不可多得的认识巴塞罗那的欢庆一面的机会。
以蔬果,新鲜水产香肠和橄榄油为基本原料,传统与现代相融合的烹饪手艺可以烹制出具有革新性又富有想象力的美食。于此,手工糖果和泡沫葡萄酒只能浅浅地触摸到巴塞罗那饮食文化的精髓。
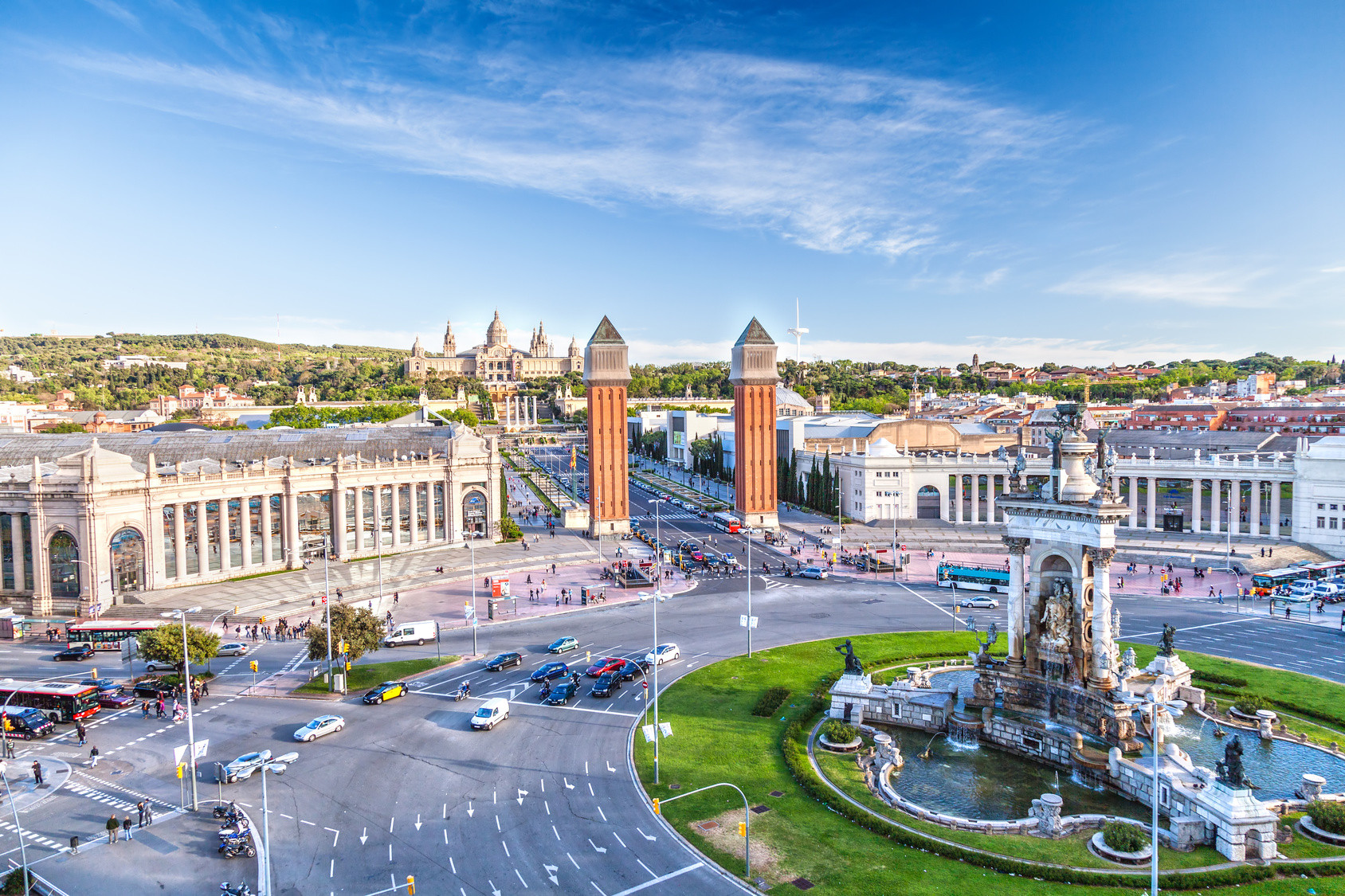
巴塞罗那(加泰罗尼亚语:Barcelona,西班牙语:Barcelona)是西班牙加泰罗尼亚首府和巴塞罗那省省会,位于伊比利亚半岛的东北面,濒临地中海,全市人口约160万,都会区人口则约500万,为加泰罗尼亚第一大城。加泰罗尼亚的议会、行政机构、高等法院等政府中枢机构,以及最高首长均驻设于此。1999年,巴塞罗那由美国《国家地理杂志》评选为50个人生必游景点之一。
相传巴塞罗那由迦太基将领、汉尼拔的父亲哈米尔卡·巴卡所兴建,在其漫长的历史上还曾作为巴塞罗那伯爵领地和阿拉贡王国的都城。巴塞罗那因其众多历史建筑和文化景点成为众多旅游者的目的地,其中之代表是被列入联合国世界遗产的安东尼·高第和路易·多门内克·蒙塔内的建筑作品。安东尼·高第一直在巴塞罗那生活和工作,在这里有他很多的作品,其中最著名的包括桂尔宫、桂尔公园和圣家堂。巴塞罗那尚有两个知名的足球俱乐部:巴塞罗那和皇家西班牙人,其中巴塞罗那是世界最著名的足球俱乐部之一。
Barcelona (katalanisch [bəɾsəˈɫonə]; spanisch [baɾθeˈlona]; deutsch [baɐ̯səˈloːna] oder [baɐ̯t͡səˈloːna]) ist die Hauptstadt Kataloniens und nach Madrid die zweitgrößte Stadt Spaniens. Sie liegt am Mittelmeer, circa 120 Kilometer südlich der Pyrenäen und der Grenze zu Frankreich. Barcelona ist Verwaltungssitz der gleichnamigen Provinz und der Comarca Barcelonès.
Innerhalb des Stadtgebietes leben etwa 1,65 Millionen Menschen. Damit ist Barcelona die elftgrößte Gemeinde der Europäischen Union, nach Hamburg die zweitgrößte, die nicht die Hauptstadt eines Mitgliedstaates ist, und nach Paris die am zweitdichtesten besiedelte Millionenstadt Europas. Zusammen mit den in der Àrea Metropolitana de Barcelona zusammengeschlossenen Gemeinden der Agglomeration beträgt die Einwohnerzahl 3,16 Millionen. Im weiteren Einzugsbereich der Metropolregion (Àmbit Metropolità de Barcelona) leben insgesamt 4,86 Millionen Menschen. Mit jährlich mehr als sieben Millionen Touristen aus dem Ausland zählt Barcelona überdies zu den drei meistbesuchten Städten Europas.[2]
Barcelona (/ˌbɑːrsəˈloʊnə/ BAR-sə-LOH-nə, Catalan: [bəɾsəˈlonə], Spanish: [baɾθeˈlona]) is a city in Spain. It is the capital and largest city of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within city limits,[5] its urban area extends to numerous neighbouring municipalities within the Province of Barcelona and is home to around 4.8 million people,[3][7] making it the sixth most populous urban area in the European Union after Paris, London, Madrid, the Ruhr area and Milan.[3] It is the largest metropolis on the Mediterranean Sea, located on the coast between the mouths of the rivers Llobregat and Besòs, and bounded to the west by the Serra de Collserola mountain range, the tallest peak of which is 512 metres (1,680 feet) high.
Founded as a Roman city, in the Middle Ages Barcelona became the capital of the County of Barcelona. After merging with the Kingdom of Aragon, Barcelona continued to be an important city in the Crown of Aragon as an economic and administrative centre of this Crown and the capital of the Principality of Catalonia. Barcelona has a rich cultural heritage and is today an important cultural centre and a major tourist destination. Particularly renowned are the architectural works of Antoni Gaudí and Lluís Domènech i Montaner, which have been designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The headquarters of the Union for the Mediterranean are located in Barcelona. The city is known for hosting the 1992 Summer Olympics as well as world-class conferences and expositions and also many international sport tournaments.
Barcelona is one of the world's leading tourist, economic, trade fair and cultural centres, and its influence in commerce, education, entertainment, media, fashion, science, and the arts all contribute to its status as one of the world's major global cities.[8][9] It is a major cultural and economic centre in southwestern Europe, 24th in the world (before Zürich, after Frankfurt)[10] and a financial centre. In 2008 it was the fourth most economically powerful city by GDP in the European Union and 35th in the world with GDP amounting to €177 billion.[11] In 2012 Barcelona had a GDP of $170 billion; and it was leading Spain in employment rate in that moment.[12]
In 2009 the city was ranked Europe's third and one of the world's most successful as a city brand.[13] In the same year the city was ranked Europe's fourth best city for business and fastest improving European city, with growth improved by 17% per year,[14] and the city has been experiencing strong and renewed growth for the past three years. Since 2011 Barcelona has been a leading smart city in Europe.[15] Barcelona is a transport hub, with the Port of Barcelona being one of Europe's principal seaports and busiest European passenger port,[16] an international airport, Barcelona–El Prat Airport, which handles over 40 million passengers per year,[17] an extensive motorway network, and a high-speed rail line with a link to France and the rest of Europe.[18]
Barcelone (Barcelona en catalan, prononcé /bəɾsəˈlonə/, et en espagnol, prononcé /baɾθeˈlona/) est la capitale administrative et économique de la Catalogne, de la province de Barcelone, de la comarque du Barcelonès ainsi que de son aire et de sa région métropolitaines, en Espagne.
Barcelone est la deuxième ville d'Espagne en termes de population, d'économie et d'activités, la onzième ville la plus peuplée de l'Union européenne et la sixième en incluant sa banlieue4: 4,84 millions de personnes vivent dans l'agglomération barcelonaise5. La majeure partie des municipalités adjacentes sont en outre rassemblées dans l'Aire métropolitaine de Barcelone.
Située sur le littoral méditerranéen, elle est traversée par les fleuves Llobregat et Besòs et bordée à l'ouest par la serra de Collserola qui culmine à 512 mètres (sommet : Tibidabo). Elle est considérée comme ville mondiale en raison de son importance dans les domaines de la finance, du commerce international, de l'édition, des arts, du divertissement et des médias. Barcelone est donc un centre économique majeur qui jouit de surcroît d'un des principaux ports méditerranéens et du deuxième aéroport espagnol derrière celui de Madrid-Barajas. Elle est aussi la ville qui possède le plus grand parc métropolitain du monde, le parc Collserola, devant Central Park à New York. Ayant été fondée par les Romains, la ville devint la capitale des comtes de Barcelone puis l'une des villes majeures de la Couronne d'Aragon et, après, la capitale de la principauté de Catalogne. Redessinée plusieurs fois pendant son histoire, elle est une destination touristique majeure et jouit d'un patrimoine culturel unique. Le palais Güell (en 1984), la Casa Milà, le parc Güell, le palais de la musique catalane et l'hôpital de Sant Pau figurent d'ailleurs sur la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO. En outre, la ville est également connue pour avoir accueilli les Jeux olympiques en 1992 et, plus récemment, le siège de l'union pour la Méditerranée. Chaque année, les visiteurs arrivent par milliers et le nombre augmente de plus en plus. En 2015, un total de 8 988 038 touristes ont visité Barcelone6.
Barcellona (AFI: /barʧelˈlona/[1]; in catalano e spagnolo Barcelona) è una città di 1.620.809 abitanti (area metropolitana istituzionale: 3.239.337 abitanti) della Spagna, capoluogo della Catalogna, una comunità autonoma della parte nord-orientale dello Stato, oltre che dell'omonima provincia e della comarca del Barcelonès. Soprannominata Ciutat Comtal o Ciudad Condal (Città dei Conti), è la seconda città della Spagna per numero di abitanti dopo la capitale Madrid.
Nel 1992 fu sede dei Giochi Olimpici estivi. Nel 2004 vi si è tenuto per la prima volta assoluta il Forum Universale delle Culture, la città ha ospitato l'Esposizione internazionale del 1888 e quella del 1929, ed è la sede fissa del Mobile World Congress e dell'Unione per il Mediterraneo. Forte del turismo, del porto e della vicinanza alla Francia (160 km da Le Perthus), la città è il secondo maggior centro industriale e finanziario della Spagna dopo Madrid, nonché il maggior porto commerciale e turistico e uno dei maggiori d'Europa.
Barcelona es una ciudad española, capital de la comunidad autónoma de Cataluña, de la comarca del Barcelonés y de la provincia homónima.
Con una población de 1 620 809 habitantes en 2017,6 es la segunda ciudad más poblada de España después de Madrid, y la undécima de la Unión Europea. El área metropolitana de Barcelona, incluida en el ámbito metropolitano de Barcelona, cuenta con 5 029 181 habitantes (2011), siendo así la sexta ciudad de mayor población de la Unión Europea.78
Se ubica a orillas del mar Mediterráneo, a unos 120 km al sur de la cadena montañosa de los Pirineos y de la frontera con Francia, en un pequeño llano litoral limitado por el mar al este, la sierra de Collserola al oeste, el río Llobregat al sur y el río Besós al norte. Por haber sido capital del condado de Barcelona, se suele aludir a ella con la denominación antonomástica de Ciudad Condal.
La historia de Barcelona se extiende a lo largo de 4000 años, desde finales del Neolítico, con los primeros restos hallados en el territorio de la ciudad, hasta la actualidad. El sustrato de sus habitantes aúna a los pueblos íberos, romanos, judíos, visigodos, musulmanes y cristianos. Como capital de Cataluña y segunda ciudad en importancia de España, la Ciudad Condal ha forjado su relevancia con el tiempo, desde ser una pequeña colonia romana hasta convertirse en una ciudad valorada internacionalmente por aspectos como su economía, su patrimonio artístico, su cultura, su deporte y su vida social.
Barcelona ha sido escenario de diversos acontecimientos internacionales que han contribuido a consolidarla, desarrollarla y darle proyección mundial. Los más relevantes han sido la Exposición Universal de 1888, la Exposición Internacional de 1929, los Juegos Olímpicos de 1992 y el Fórum Universal de las Culturas 2004. Es también sede del secretariado de la Unión para el Mediterráneo.9
En la actualidad, Barcelona está reconocida como una ciudad global por su importancia cultural, financiera, comercial y turística. Posee uno de los puertos más importantes del Mediterráneo y es también un importante punto de comunicaciones entre España y Francia, debido a las conexiones por autopista y alta velocidad ferroviaria. El aeropuerto de Barcelona-El Prat, situado a 15 km del centro de la ciudad, fue utilizado por más de 47,2 millones de pasajeros en 2017.10

北海市(邮政式拼音:Pakhoi)是中华人民共和国广西壮族自治区下辖的地级市,位于广西南部,北部湾沿岸。南流江由北向西南流入海。市境东与玉林市及广东省湛江市毗邻,北与钦州市相接,西面与南面临北部湾。全市总面积3,989平方公里,人口162.57万,市人民政府驻海城区。北海市是沿海开放城市,国家历史文化名城。
北海地处广西壮族自治区南端,北部湾东北岸。位于东经108°50′45″~109°47′28″,北纬20°26′~21°55′34″之间,西北距自治区首府南宁206公里,东距湛江198公里,东南距海口市147海里。市区南北西三面环海,有涠洲(24.74平方公里)、斜阳(1.8平方公里)两个海岛,涠洲距市区大约20.2海里。北海地区海岸线总长达500多公里。
北海,别名“珠城”,是广西壮族自治区地级市,民国15年(1926年)成立北海市,建国后依次隶属广东省钦廉专区(先驻北海市后驻钦州镇)、广西省钦州专区(治所在钦州镇和廉州镇)、广东省合浦专区(治所在廉州镇)、广西壮族自治区钦州地区(治所在钦州镇)。 地处广西壮族自治区南端,北部湾东北岸。北海是我国最早的对外通商口岸和海上“丝绸之路”起点之一,历史上是云贵、川、桂、湘、鄂等省与海外贸易的主要商品集散地之一。 西北距首府南宁206公里,东距广东湛江198公里,东南距海南海口市147海里。地势总体呈北高南低,地形平坦开阔;气候属海洋性季风气候,具有典型的亚热带特色;下辖3个区、1个县,总面积3337平方千米 。根据第七次人口普查数据,截至2020年11月1日零时,北海市常住人口为1853227人。
北海是古代“海上丝绸之路”的重要始发港,是国家历史文化名城、广西北部湾经济区重要组成城市,是中国西部地区唯一列入全国首批14个进一步对外开放的沿海城市,也是中国西部唯一同时拥有深水海港、全天候机场、高速铁路和高速公路的城市。
2018年11月,入选中国城市全面小康指数前100名。 2020年入选“2020中国最宜置业百佳县市”。 北海是中国网红城市,2020年入选“2020网红城市百强榜单”。 2020年~2021年度获得2020年中国十大秀美之城。 2021年北海市生产总值为1504.4亿元,同比增长8.8%。
 Architecture
Architecture
 Civilization
Civilization

 Geography
Geography
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans