
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 International cities
International cities






巴格达(阿拉伯语:بغداد,阿拉米语:ܒܓܕܐܕ),古称报达,《诸蕃志》称 白达,伊拉克首都,同时它也是伊拉克巴格达省的首府,为伊拉克最大城市及经济文化中心。位于美索不达米亚平原中部地区,底格里斯河流过巴格达市区,而距幼发拉底河约30千米[3]。巴格达人口约577万,在阿拉伯世界位于开罗之后列第二位。在历史上,巴格达曾是伊斯兰文明的政治、宗教、经济、商业、学术、交通中心。巴格达也是一座多民族多教派的城市。
阿拔斯王朝第二任哈里发曼苏尔于公元762年将阿拉伯帝国都城迁至此地。当时成为阿拉伯世界的政治、经济、宗教中心。[3]
10世纪后,因政治变动及战争而衰退[3]。随着阿拉伯王朝不复昔日光辉,巴格达先于1258年被蒙古人攻陷;1508年和1534年分别被波斯和土耳其人占领。1638年后巴格达长期受土耳其人的统治。1917年巴格达落入英军之手。直到1921年伊拉克独立后,巴格达被定为首都。巴格达位于美索不达米亚平原中部地区,底格里斯河流过巴格达市区,而距幼发拉底河约30千米,为两河相距最近之处;迪亚拉河流经城市郊区,并于巴格达东南方注入底格里斯河。
Bagdad (arabisch بغداد Baghdad, DMG Baġdād, kurdisch بەغدا Beẍda, von persisch „Geschenk des Herrn“ bzw. „Gottesgeschenk“, entsprechend baġ „Gott, Herr“ und dād „Gabe“)[1] ist die Hauptstadt des Iraks und des gleichnamigen Gouvernements. Sie ist mit ca. 6,7 Millionen Einwohnern (2018)[2] eine der größten Städte im Nahen Osten. In der Metropolregion, die weit über die Grenzen des Gouvernements hinausreicht, leben ca. 8,1 Millionen Menschen (2018), was knapp einem Viertel der Gesamtbevölkerung des Iraks entspricht.[2]
Die Stadt ist das politische, wirtschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum des Landes sowie Sitz der irakischen Regierung, des Parlaments, aller staatlichen und religiösen Zentralbehörden sowie zahlreicher diplomatischer Vertretungen. Bagdad ist der bedeutendste Verkehrsknotenpunkt Iraks und besitzt zahlreiche Universitäten, Hochschulen, Theater, Museen sowie Baudenkmäler.
バグダード(アラビア語: بغداد/ラテン文字表記: Baghdad, Baġdād)は、イラクの首都で同国最大の都市。また、バグダード県の県庁所在地でもある。アッバース朝によって建設された古都であり、イスラム世界における主要都市の1つ。2020年の人口はおよそ714.4万人[1]。日本語では多くの場合バグダッドと表記されるが、アラビア語の綴りと発音([bæɣˈdæːd])に近づけるとバグダードという表記になる。
Baghdad (/ˈbæɡdæd, bəɡˈdæd/; Arabic: بَغْدَاد [baɣˈdaːd] ( listen)) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient Akkadian city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
listen)) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient Akkadian city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million.[3] The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires. With the recognition of Iraq as an independent state (formerly the British Mandate of Mesopotamia) in 1932, Baghdad gradually regained some of its former prominence as a significant center of Arab culture, with a population variously estimated at 6 or over 7 million.[note 1] Compared to its large population, it has a small area at just 673 square kilometers (260 sq mi).
The city has faced severe infrastructural damage due to the Iraq War, which began with the United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003 and lasted until 2011, and the subsequent insurgency and renewed war that lasted until 2017, resulting in a substantial loss of cultural heritage and historical artifacts. During this period, Baghdad had one of the highest rates of terrorist attacks in the world. However, terrorist attacks are rare and have been declining since the territorial defeat of the Islamic State militant group in Iraq in 2017.
Bagdad ou Baghdad (en arabe : بغداد, baġdād, /baɣˈdaːd/ Écouter) est la capitale de l’Irak et de la province de Bagdad. Située au centre-est du pays, elle est traversée par le fleuve Tigre. Ses habitants sont appelés « Bagdadiens »1.
Avec une aire urbaine comprenant une population estimée à 10 millions d’habitants en 2012, c’est la plus grande ville d’Irak, ainsi que la deuxième ville la plus peuplée du monde arabe et du Moyen-Orient (derrière Le Caire, la capitale de l'Égypte). C'est un carrefour de communications aériennes, routières et ferroviaires d'une grande importance stratégique pour la république d'Irak.
Les origines de la ville actuelle remontent, au moins, au viiie siècle, avec, probablement, la présence de plusieurs petits foyers d'habitat antérieurs datant de la période préislamique. Elle fut la capitale de l'Empire abbasside à partir du viiie siècle et un centre de culture et de connaissance très important pendant des siècles, jusqu’au milieu du xiiie siècle. Bagdad a été, de 2003 à 2011, le centre d’un violent conflit en raison de la guerre d’Irak. Elle est devenue une ville d'enclaves fortifiées régies par les soldats de l'armée irakienne, les officiers de la police fédérale, les agents de police locaux et les agents de sécurité privés.
Baghdad (in arabo: بغداد, Baghdād, in età abbaside Madīnat al-Salām, "Città della pace", in italiano antico Baldacco, Baldacca o Baudac), o Bagdad[4], è la capitale dell'Iraq e dell'omonima provincia. È la seconda città più grande dell'Asia sud-occidentale, dopo Teheran: il calcolo della popolazione per il 2014 è di 7 665 292 abitanti[3]. Situata sul fiume Tigri a 33°20 nord e 44°26 est.
Bagdad3 (en árabe: بَغْدَاد Baġdād, en arameo: ܒܓܕܕ Baghdad) es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de Irak. Su número de habitantes es de 8 765 000 (est. 2016), lo que la convierte en la mayor ciudad del país y la segunda del mundo árabe, solo por detrás de El Cairo.
Ubicada a orillas del río Tigris, la ciudad fue fundada en el siglo viii y se convirtió en capital del Califato abasí. En poco tiempo se convirtió en un centro cultural, comercial e intelectual de gran relevancia del mundo islámico. Esto, y el hecho de ser sede de varias instituciones académicas relevantes, como la Casa de la sabiduría, le sirvieron a la ciudad para ganarse una reputación mundial de «Centro de Enseñanza».
Bagdad fue la ciudad más grande de la Edad Media durante gran parte del Califato abasí, cuando alcanzó un pico de un millón y medio de habitantes.4 Sin embargo, la urbe fue en gran parte destruida por las tropas del Imperio mongol en 1258, lo que resultó en un declive que se prolongaría por muchos siglos debido a frecuentes epidemias y la sucesión de varios imperios que dominaron la ciudad. Con el reconocimiento de Irak como estado independiente en 1938 tras la desaparición del Mandato Británico para Mesopotamia, Bagdad recuperó gradualmente parte de su pasada preeminencia como centro significante de la cultura musulmana.
En tiempos recientes la ciudad ha sufrido graves daños en sus infraestructuras, especialmente durante la invasión de Irak de 2003 y la consiguiente guerra de Irak que duró hasta diciembre de 2011. En los últimos años la capital ha sido objetivo de numerosos ataques de la guerrilla iraquí. Este conflicto militar también ha provocado una pérdida profunda e irreparable de la herencia cultural y de piezas históricas. Como resultado, Bagdad está considerado uno de los lugares menos hospitalarios del mundo en los que vivir y ofrece una calidad de vida muy baja.
Багда́д (араб. بغداد — «божий дар») — столица Ирака, административный центр мухафазы Багдад. С населением более 9 млн человек (2015)[3] он является одним из самых больших городов Ближнего Востока.
Багдад — политический, экономический и культурный центр Ирака. В нём находятся правительство, все центральные государственные и религиозные учреждения и множество дипломатических представительств. Город — важный транспортный узел. В нём также расположены многочисленные вузы, театры, музеи и памятники архитектуры.

 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage
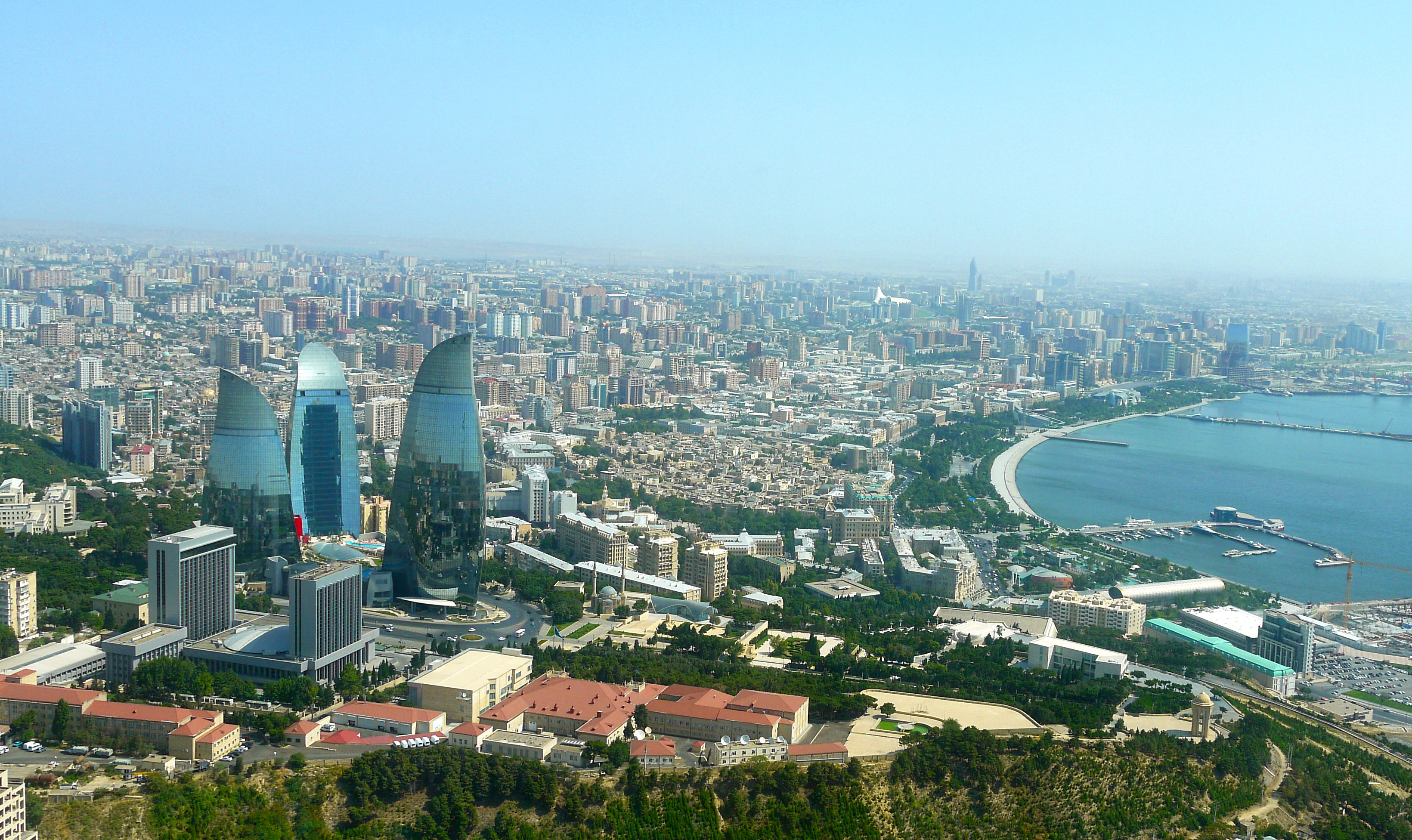

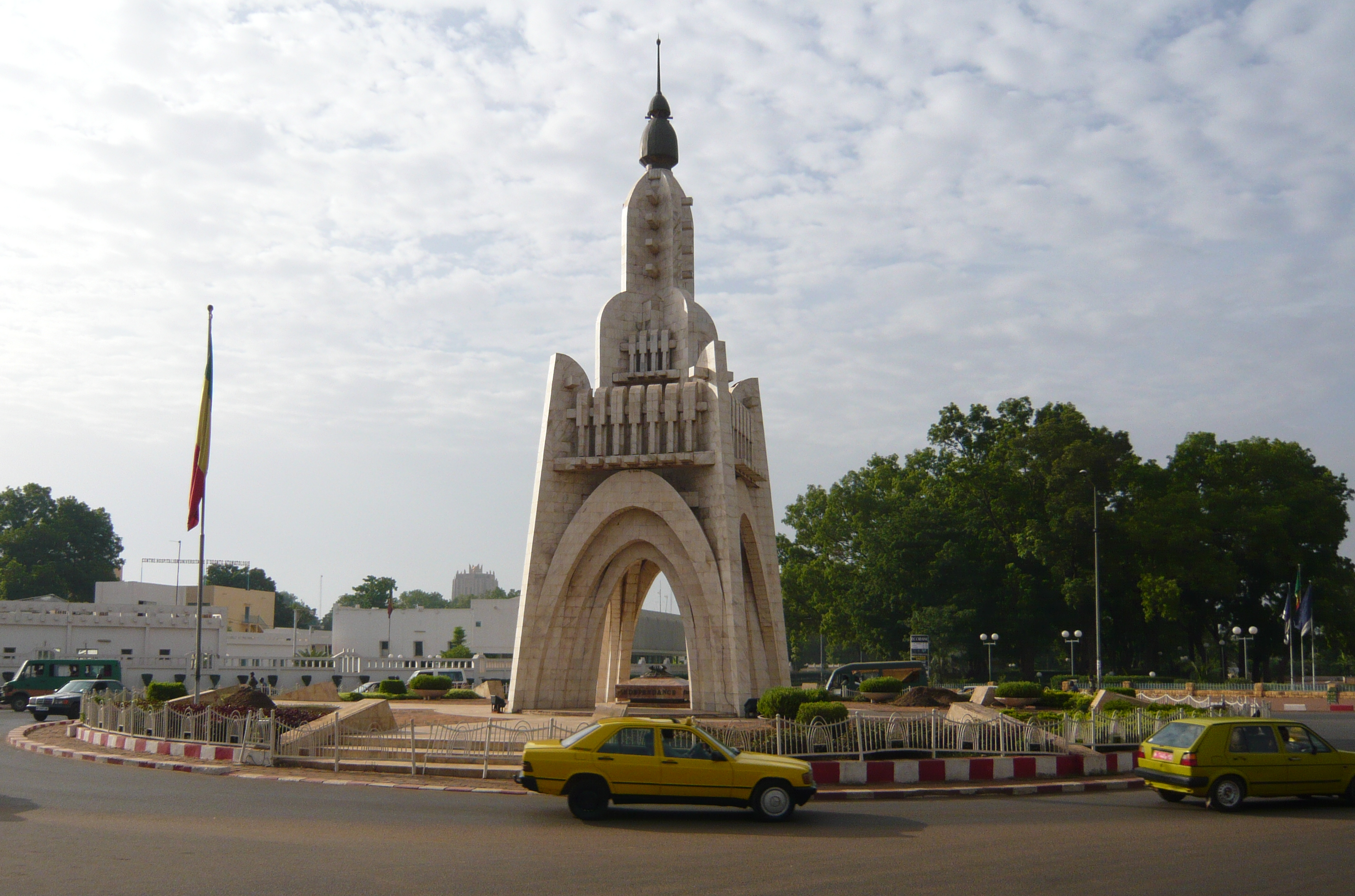
巴库(Baku, Баку)是阿塞拜疆首都和全国经济、文化中心。里海最大港口。位于阿普歇伦米岛南部,是石油工业中心,有“石油城”之誉。也是前苏联外高加索最大城市。 巴库由10个行政区和46个城镇组成,面积2200平方公里。人口182.88万。1月平均气温为4℃,7月平均气温为27.3℃。 在18世纪,巴库为巴库汗国都城。19世纪70年代开始工业性采油,19世纪末成为外高加索工业中心和石油基地,有22大炼油基地,其他工业多与石油有 关。1991年8月成为独立后阿塞拜疆的首都。城市西部的比比埃巴特区为老采油区。东部的基什雷区和邵武勉区为重要工业区。石油是巴库的经济命脉。石油开 采正向深处和外围海域发展。以石油、天然气开采和石油加工为主要工业,还有石油机械、电力和轻工 、食品工业。外高加索主要铁路枢纽,铁路通罗斯托夫、第比利斯和埃里温。有输油管道通黑海港口巴统。巴库是里海航运中心,可泊中等吨位船舶。城市中部为行 政、文化和居住区。建有科学院,大学和博物馆。里海最大港口,有“石油城”之誉。市内建有地铁,有阿塞拜疆科学学院、阿塞拜疆大学、石油化工学院等多所高 等院校。城市的中部是行政、文化区域,有历史博物馆和艺术博物馆。老城区以旧要塞为中心。 巴库是一座有着悠久历史的古城,城内有众多名胜古迹,如11世纪建造的瑟纳克一卡尔清真寺塔,12世纪的克孜一卡拉瑟塔楼,13世纪的巴伊洛夫石堡,15 世纪的希尔凡王宫及17世纪的汗王宫殿至今保存完好。2000年联合国教科文组织将巴库墙城及城内的希尔梵国王宫殿和少女塔作为文化遗产,列入《世界遗产 名录》。(Quelle:http://you.kuxun.cn)
巴库(阿塞拜疆语:Bakı)是阿塞拜疆的首都、经济文化中心。巴库同时也是里海最大港口,外高加索最大城市[3]。面积2192平方千米,人口300万(2008年计算)[1]。巴库全市分为内城和新城两部分(亦有将苏联时期兴建区域分别划分的)。
在2007年,伊斯兰会议组织文化部长宣布巴库为2009年伊斯兰文化中心。为2015年第一届欧洲运动会主办国。巴库曾先后申办2016年夏季奥运会和2020年夏季奥运会,但皆因基础设施不完备没有入围。不过由于阿塞拜疆歌手艾尔与妮基在2011年欧洲歌唱大赛获得冠军,终使巴库获得举办2012年欧洲歌唱大赛的机会。
Baku (aserbaidschanisch Bakı / باکی; russisch Баку́ Baku) ist die Hauptstadt Aserbaidschans. Mit zwei Millionen Einwohnern in der Stadtprovinz ist Baku die bevölkerungsreichste und flächengrößte Stadt des Landes und des gesamten Kaukasus. Die Stadt an der Küste des Kaspischen Meeres ist Verkehrsknotenpunkt sowie Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum mit mehreren Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Durch die Lage innerhalb eines Erdölfördergebiets ist Baku der Knotenpunkt mehrerer Erdölleitungen und besitzt einen bedeutenden Erdölhafen. Baku kann aufgrund seiner günstigen Lage an mehreren historischen Handelswegen auf eine reiche Stadtgeschichte zurückblicken. In der Altstadt, die seit 2000 den Status eines UNESCO-Welterbes hat, sind zahlreiche Paläste, Moscheen und Festungsbauten erhalten geblieben.バクー(Baku)は、アゼルバイジャン共和国の首都。カスピ海西岸に突き出したアブシェロン半島南岸に位置し、市街はバクー湾に面するように広がった港町である。行政的には11の行政区、48の町区に分割されており、2005年時点の総人口は2,045,815人[1]。アゼルバイジャン最大の都市であると同時に、南カフカース地域でも有数の大都市である。大規模な油田(バクー油田)をもち、帝政ロシア時代から石油の生産地として発展してきた。
日本語名のバクーはキリル文字綴りによるロシア語綴り・アゼルバイジャン語(アゼリー語)旧綴り Баку (Baku) に基づくが、アゼルバイジャン語の発音では母音の前で子音 k が軟音化するためカタカナ表記するならば「バキュ」に近く、現在アゼルバイジャンで使われているアゼルバイジャン語のラテン文字正書法では Bakı と綴る。バクーという名前の由来には諸説あるが、最も一般的なものは、ペルシャ語で「風が吹きつけた」という意味の "bād-kūbe"(バード・クーベ)から来ているとする説が一般的である。
気候は晴天が多く、乾燥している。寒気と暖気がぶつかることで起きる強風が時折吹き付け、先述した語源の根拠となっている。海岸は美しく、市街近郊には温泉や鉱泉がある。
市街の中心はその南西部にあり、イチェリ・シェヘル (İçəri Şəhər) すなわち「内城」と呼ばれる城壁に囲まれた旧市街と、帝政ロシア時代にその周囲に築かれた新市街とに分かれる。その周囲、北から東にかけての平地から丘陵の斜面一帯にソビエト連邦時代につくられた市街が広がっている。近年は豊富なオイルマネーをもとに近未来的な巨大建築物が出現し、「第二のドバイ」「第二のシンガポール」とも呼ばれている[2]。
Baku (/bəˈkuː/ bə-KOO, /ˈbɑːkuː/ BAH-koo; Azerbaijani: Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region, with a population of 2,262,600 (January 1, 2018). Baku is located 28 metres (92 ft) below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world and also the largest city in the world located below sea level. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, alongside the Bay of Baku. At the beginning of 2009, Baku's urban population was estimated at just over two million people.[5] Officially, about 25 percent of all inhabitants of the country live in Baku's metropolitan area. Baku is the sole metropolis in Azerbaijan.
Baku is divided into twelve administrative districts (raions) and 48 townships. Among these are the townships on the islands of the Baku Archipelago, and the town of Oil Rocks built on stilts in the Caspian Sea, 60 kilometres (37 miles) away from Baku. The Inner City of Baku, along with the Shirvanshah's Palace and Maiden Tower, were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2000. According to the Lonely Planet's ranking, Baku is also among the world's top ten destinations for urban nightlife.[6]
The city is the scientific, cultural, and industrial center of Azerbaijan. Many sizeable Azerbaijani institutions have their headquarters there. The Baku International Sea Trade Port is capable of handling two million tons of general and dry bulk cargoes per year.[7] In recent years, Baku has become an important venue for international events. It hosted the 57th Eurovision Song Contest in 2012, the 2015 European Games, 4th Islamic Solidarity Games, the F1 Azerbaijan Grand Prix since 2016, and will host UEFA Euro 2020. The city is bidding for Expo 2025 against Yekaterinburg, Russia and Osaka, Japan.
La ville de Bakou (azéri : Bakı, IPA: [bɑˈcɯ]) est la capitale de l'Azerbaïdjan. Elle se trouve dans l'est du pays, sur la rive sud de la péninsule d'Abşeron, au bord de la mer Caspienne. Son histoire débute au Ier millénaire avant Jésus-Christ, mais les traces écrites les plus anciennes ne datent que du Ve siècle.
En 2011, sa population est estimée à 2 045 815 habitants1 et 3 millions de personnes environ vivent dans l'agglomération.
Baku (pron. bakù[2]; in azero: Bakı?; in russo: Баку?), conosciuta anche come Baqy, Baky o Baki, in italiano Bacù[2], è la capitale, la più grande città e il più grande porto dell'Azerbaigian e di tutto il Caucaso.
È considerata una delle più antiche e più grandi città dell'Oriente. Situata sulla costa meridionale della penisola di Abşeron, la città si compone di tre parti principali: il centro, la vecchia Città Murata estesa sul territorio di 21,5 ettari e la parte della città costruita nell'epoca sovietica. La sua popolazione nel 2014 era stimata in 2.122.300 di abitanti.
Bakú (en azerí, Bakı, [bɑˈkɯ]) es la capital y ciudad más poblada de Azerbaiyán, del mar Caspio y del Cáucaso. Está situada en la costa sur de la península de Absheron, que se proyecta en el Caspio. La ciudad se compone de dos partes principales: el centro y la ciudad vieja interior. En enero de 2018 Bakú tenía una población de 2.262.600 habitantes,3 de los cuales 153.400 eran desplazados internos y 143.400 refugiados de la guerra de Nagorno Karabaj.
Bakú se divide en once distritos administrativos (raiones) y 48 municipios. Entre estos se encuentran los municipios de las islas de la bahía de Bakú y Neft Daşları construidas sobre pilotes en el mar Caspio, a 60 km de Bakú. El centro urbano de la ciudad, con el Palacio de los Shirvanshah y la Torre de la Doncella, fue inscrito por la Unesco como Patrimonio de la Humanidad en 2000. De acuerdo con la clasificación de Lonely Planet, Bakú también se encuentra entre los diez mejores destinos de vida nocturna urbana del mundo.4
La ciudad fue uno de los mayores centros petrolíferos de la antigua Unión Soviética y actualmente es el centro científico, cultural e industrial de Azerbaiyán. Muchas instituciones importantes de Azerbaiyán tienen su sede allí, incluyendo SOCAR, una de las cien principales empresas del mundo, entre otras.5 El Puerto de Comercio Marítimo Internacional de Bakú, protegido por las islas del archipiélago Bakú hacia el este y la península de Absheron al norte, es capaz de transportar dos millones de toneladas de carga general y seca a granel por año.6 La ciudad acogió el 57.º Festival de Eurovisión en 2012 y fue la sede de los Juegos Europeos 2015, es la sede del Gran Premio de Azerbaiyán de Fórmula 1 desde 2016 y será la sede del Campeonato Mundial de Ciclismo BMX en 2018 y de la EURO 2020.7
Баку́ (азерб. Bakı, МФА (азерб.): [bɑˈcɯ]) — столица Азербайджанской Республики, крупнейший промышленный, экономический и научно-технический центр Закавказья, а также самый крупный порт на Каспийском море и самый большой город на Кавказе[9][10].
Площадь территории, которая административно управляется Баку, составляет 2150 км²[1]; население данной территории — 2 181,8 тыс. жителей (на 1 января 2014 года). Баку расположен на южном берегу Апшеронского полуострова. Город по своей древности, величине территории и численности населения является одним из старинных и крупнейших городов Востока. Население всего Апшеронского полуострова (Бакинской агломерации) составляет 2 673,7 тыс. жителей[7]. Баку удостоен в 2010 году Программой ООН по окружающей среде (UNEP) звания одного из главных городов по проведению Всемирного дня окружающей среды. Подобные города избираются ежегодно. В 2010 году, наряду с Баку, этих званий были удостоены также Генуя (Италия) и Женева (Швейцария)[11].

巴拉瑞特(英语:Ballarat,/ˈbæləˌræt/),早期中文亦称“孖辣”,位于澳大利亚维多利亚州中部高地,是距离墨尔本西北方105千米(65英里)的一座内陆观光城市,人口105,471(2018年)[2],以特有的采矿史和历史遗产闻名于世。亚罗威河流经此城市。
Ballarat ist eine Stadt mit etwa 94.000 Einwohnern[1] im Bundesstaat Victoria in Australien, 120 Kilometer westnordwestlich von Melbourne. Sie ist die drittgrößte Stadt des Staates und eine der größten nicht an der Küste gelegenen Städte in Australien. Die Stadt ist Zentrum der Local Government Area Ballarat City. Der Name Ballarat ist abgeleitet vom Aborigine-Ausdruck für „Ruheplatz“.



班贝格(德语:Bamberg),也译作班堡、班贝克或巴姆贝格,是德国巴伐利亚州的直辖市,位于巴伐利亚北部,隶属于上弗兰肯行政区,也是班贝格县的首府。班贝格是一座大学城和行政城市,是天主教班贝格总教区的驻地,也是上弗兰肯地区的重要中心。班贝格老城是德国最大的一座未受战争毁坏的历史城区,1993年入选联合国教科文组织的世界文化遗产名录。班贝格还以多种特产啤酒而出名。
Bamberg (mittelalterlich: Babenberg, bambergisch: „Bambärch“) ist eine kreisfreie Stadt im bayerischen Regierungsbezirk Oberfranken und Standort des Landratsamtes Bamberg. Sie ist die größte Mittelstadt Bayerns, Universitäts-, Schul- und Verwaltungsstadt, wichtiges Wirtschaftszentrum Oberfrankens sowie Sitz des gleichnamigen Erzbistums. Das bekannteste Bauwerk ist der viertürmige Bamberger Dom, einer der früheren Kaiserdome.
Die Stadt ist in der Landesplanung als Oberzentrum des westlichen Oberfrankens ausgewiesen und zählt zur Metropolregion Nürnberg. Bamberg hat etwa 77.000 Einwohner und ist damit die größte Stadt Oberfrankens, die Agglomeration hat rund 112.000 Einwohner.[2]
Die Altstadt ist der größte unversehrt erhaltene historische Stadtkern in Deutschland und seit 1993 als Weltkulturerbe in die Liste der UNESCO eingetragen.[3] Darüber hinaus ist Bamberg überregional bekannt für seine vielfältige Biertradition.
Bamberg (German pronunciation: [ˈbambɛɐ̯k]) is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. A large part of the town has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1993.
Bamberg Écouter (parfois orthographié Babenberg ; Bambärch en bambergeois (de)) est une ville allemande, située dans le sud du pays, dans le nord du Land de Bavière et la région de Haute-Franconie. Elle est le chef-lieu de l'arrondissement de Bamberg et le centre urbain (de) de l'ouest de la région. Elle dépend de la région métropolitaine de Nuremberg (de).
Ville de taille moyenne, elle abrite une université, un archidiocèse et est un centre économique pour la région.
Depuis le début de XIXe siècle, Bamberg a été rattachée à la Bavière. Ville épiscopale, troisième site historique, Bamberg abrite 2 200 monuments historiques. Les églises médiévales côtoient des maisons bourgeoises de style baroque et des édifices monumentaux. Le monument le plus réputé de cette ville est la cathédrale Saint-Pierre et Saint-Georges, dont les quatre tours s'élèvent par-dessus la ville, et qui est l'une des plus anciennes cathédrales de l'Empire.
Bâtie sur sept collines, la ville est née au Moyen Âge et a été transformée aux XVIIe et XVIIIe siècles en cité baroque par les princes-évêques.
En 1007 avec sa femme Cunégonde, Henri II choisit Bamberg comme capitale et évêché. En 1014, il est sacré Empereur du Saint-Empire. L'ancien hôtel de ville du XIVe siècle est bâti sur une île artificielle de la rivière Regnitz.
Sous le règne des princes-évêques Lothaire-François de Schönborn (1693-1729) et Frédéric-Charles de Schönborn-Buchheim (1729-1745), la ville connut, à l'époque baroque, une floraison culturelle.
C'est un important centre économique et culturel de la Franconie (en allemand Franken). Les destructions que connurent la majorité des villes allemandes durant la Seconde Guerre mondiale furent épargnées à Bamberg qui n'était alors pas industrialisée.
« Ville de rêve » (« Traumstadt »), Bamberg est inscrite au patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO depuis 1993 et son cœur historique figure parmi les mieux préservés d'Allemagne.
La ville compte aujourd'hui environ 75 000 habitants, et jusqu'à 112 000 en tenant compte de l'agglomération.
Bamberga (in tedesco Bamberg, in francone orientale Bambärch) è una città extracircondariale della Baviera, in Germania. È situata nell'Alta Franconia sul fiume Regnitz, vicino alla confluenza col fiume Meno. La sua popolazione è di 69.989 abitanti (2008).[1]
Bamberga è nota anche per la sua intensa produzione di birra ed in particolare per il birrificio Schlenkerla, che risale all'epoca medioevale, e produce la caratteristica ed unica Rauchbier.
La città sorge su sette colli: Domberg, Michaelsberg, Kaulberg/Obere Pfarre, Stefansberg, Jakobsberg, Altenburg e Abtsberg.
Bamberg o Bamberga (en alemán: Bamberg) es una ciudad en la región de Baviera, en Alemania, a orillas del río Regnitz.
Бамберг (нем. и бав. Bamberg, в Средневековье Babenberg, в.-франк. Bambärch) — город окружного подчинения в Верхней Франконии, земля Бавария, Германия. Расположен у реки Регниц. Город является центром городского самоуправления. В городе находится Университет Отто-Фридриха, работают государственные учреждения. Бамберг, как и Рим, расположен на семи горах. В Средние века Бамберг называли «немецким Римом». В соборе Бамберга погребён Климент II (папа римский) — единственный папа, похороненный севернее Альп.
Бамберг — один из немногих старинных городов Германии, уцелевших во время Второй мировой войны и составляющих её историческое наследие. В 1993 году город Бамберг был включен в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
В период 1945 — 2014 гг. в Бамберге базировались американские военные. Они покинули город в сентябре 2014 года.


 Hessen
Hessen
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Lower Austria
Lower Austria
 Victoria-VIC
Victoria-VIC
 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD