
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Spain
Spain
 Audi Cup
Audi Cup
 Carlo Ancelotti
Carlo Ancelotti
 Fabio Capello
Fabio Capello
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 FIFA Club World Cup 2025
FIFA Club World Cup 2025
 Group H
Group H
 José Mourinho
José Mourinho
 Jupp Heynckes
Jupp Heynckes

 Madrid
Madrid
 Primera División
Primera División
 Primera División 2015/16
Primera División 2015/16
 Primera División 2016/17
Primera División 2016/17
 Primera División 2017/18
Primera División 2017/18
 Primera División 2018/19
Primera División 2018/19
 Rafael Benítez
Rafael Benítez
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Europa League
(F)UEFA Europa League
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 Group F
Group F
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 Group H
Group H
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 Group G
Group G
 UEFA Champions League 2019/20
UEFA Champions League 2019/20
 Group A
Group A
 UEFA Champions League 2025/26
UEFA Champions League 2025/26
 Vicente del Bosque
Vicente del Bosque
 Zinédine Zidane
Zinédine Zidane



























Die Jota (spanisch) ist eine populäre Lied- und Tanzgattung im Tripeltakt, die praktisch überall in Spanien beheimatet ist, wobei die aragonesischen und navarrensischen Jotas auch überregional die bekanntesten Varianten sind. In Valencia tanzte man früher die Jota bei Beerdigungen.
So vielfältig wie die Aufführungs- und Vortragsvarianten der Jota ist auch das Instrumentarium zur musikalischen Begleitung und zur Ausführung von oftmals virtuosen instrumentalen Einleitungen und Zwischenspielen. Neben der fast immer gegenwärtigen Gitarre kommen je nach Region auch Streich- und Blasinstrumente zum Einsatz, sowie in den nördlichen Provinzen auch Balginstrumente, wie die gaita gallega. Zur Kastagnettenbegleitung der Tanzenden gesellen sich meist weitere Perkussionsinstrumente, bei denen es sich auch um umfunktionierte Alltagsgegenstände, wie Mörser, Flaschen oder Viehglocken handeln kann.
Bei öffentlichen Aufführungen der Jota tragen Tänzer und Tänzerinnen meist die Tracht ihrer Region. Die Themen der Liedtexte sind weitgefächert und reichen vom Patriotismus über sexuelle Anspielungen bis hin zur Religion. Vorherrschend ist eine Textform in achtsilbigen Vierzeilern, mit Assonanz der ersten und dritten Verszeile.
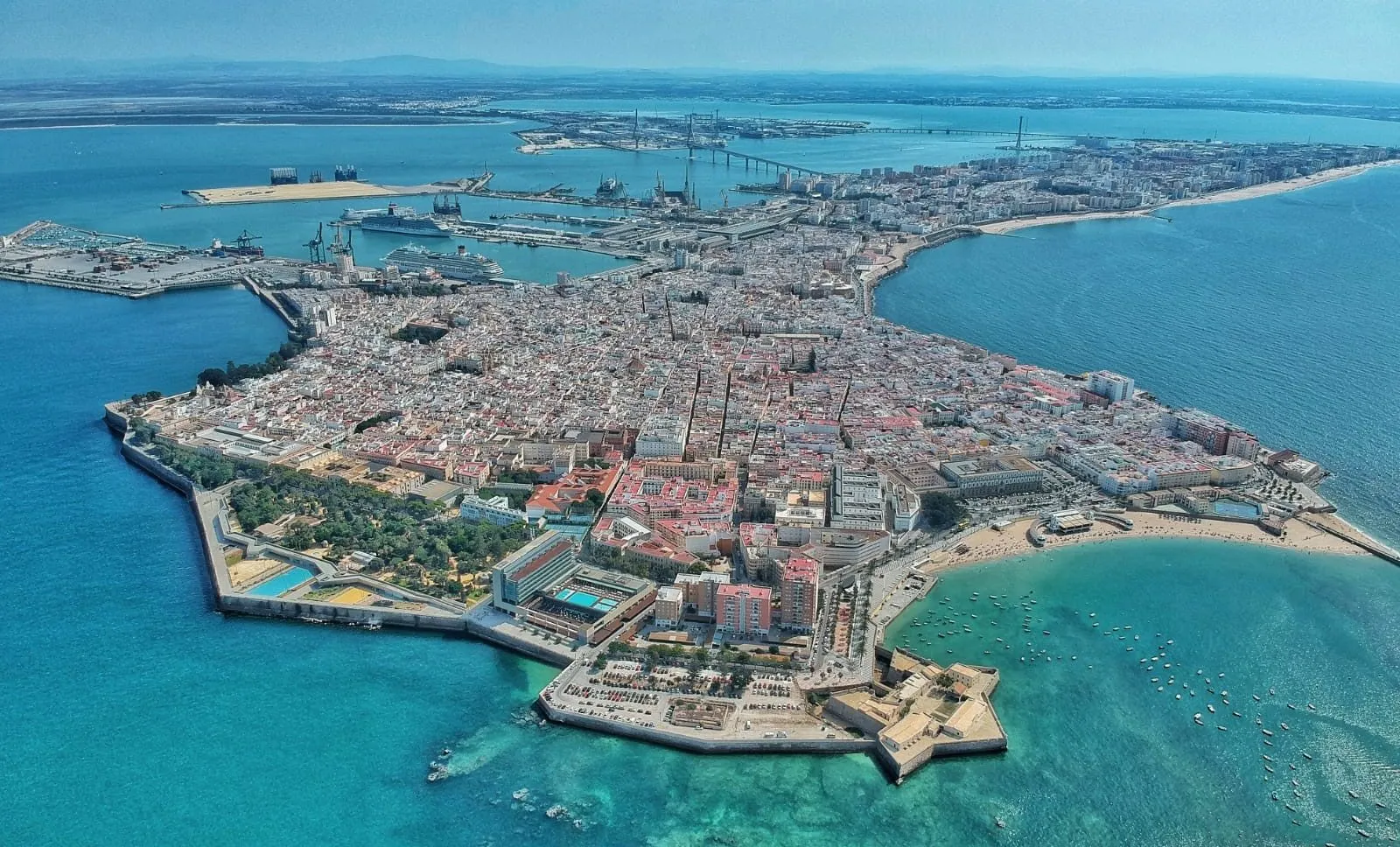
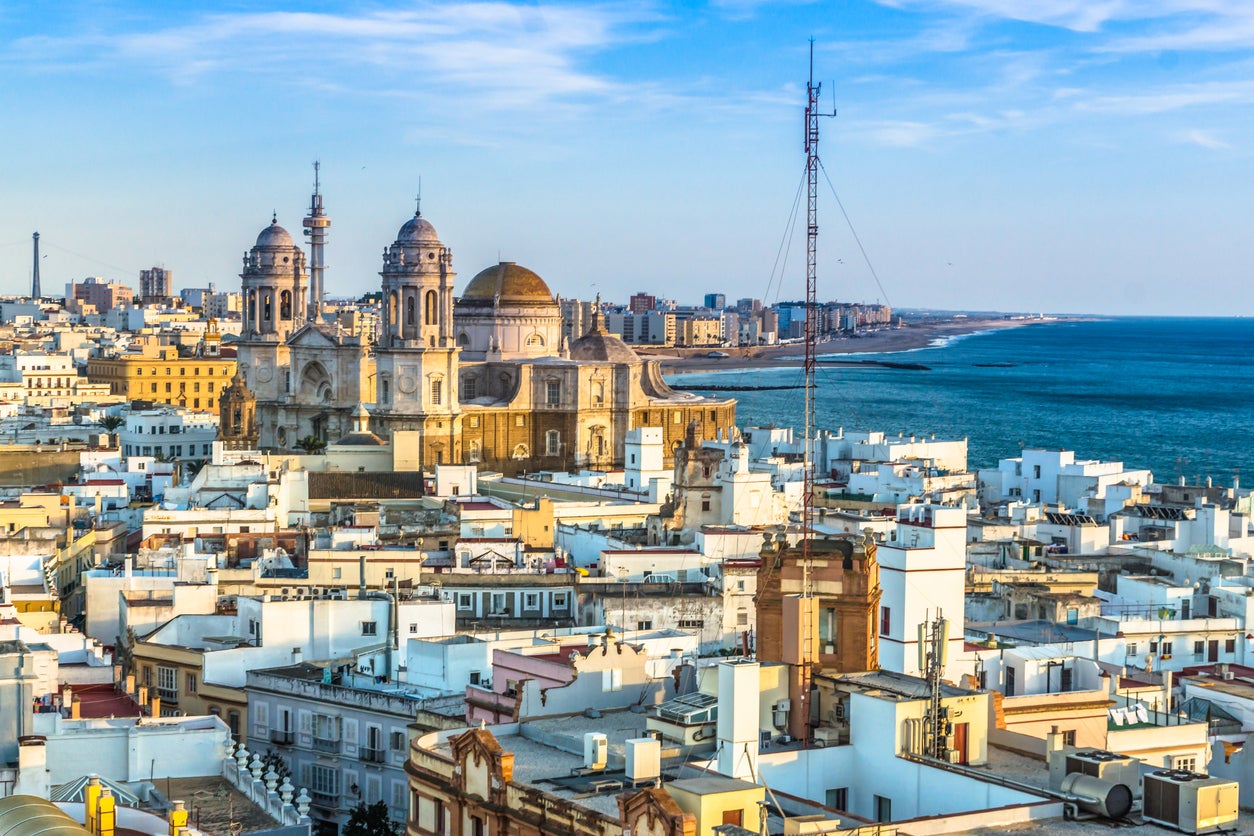



Cádiz [spanisch ˈkaðiθ, regional/lateinamerikanisch ˈkaðis, andalusisch Cái, latinisiert Gades] ist die Hauptstadt der Provinz Cádiz in der Autonomen Region Andalusien in Süd-Spanien mit 113.066 Einwohnern (1. Januar 2022). Die Stadt erhebt sich auf einer Landzunge, die in die Bucht von Cádiz vorspringt. Diese ist ein kleiner Teil des Golfs von Cádiz.
Die Altstadt mit den Vierteln (spanisch barrios) El Pópulo, La Viña und Santa María steht in starkem Kontrast zu den Hochhäusern der modernen Neustadt. Das Stadtbild wird durch viele kleine Plätze geprägt.
Die Einwohner von Cádiz werden Gaditanos genannt.
加的斯(西班牙语:Cádiz,西班牙语:[ˈkaðiθ];/kəˈdɪz/[1] )是西班牙西南部的一座滨海城市,属于安达卢西亚加的斯省,而且是加的斯省的省会。据2004年的统计加的斯共有133,242名居民,包括其郊区的居民数则为629,054人。2017年加的斯城区的总登记人口为118,048人。[2]城市面积12.30平方公里,位于一个伸入加的斯湾的半岛上。加的斯的地理位置是北纬36°30',西经6°20'。
加的斯拥有典型的安达鲁西亚特征,其老城(Casco Antiguo)分为数个不同的区(barrios)。这些区与新建的市区截然不同。老城区的小胡同一般通向其广场,而新区里则主要是宽广的大街和现代的建筑。此外市内点缀着许多公园和树木,有些巨树有可能是克里斯托弗·哥伦布带来的。此地也以雪莉酒闻名。







 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Chile
Chile
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].


 Dances
Dances
 International cities
International cities
 Andalusia
Andalusia
 History
History
 Animal world
Animal world
 Geography
Geography
 Canary Islands
Canary Islands
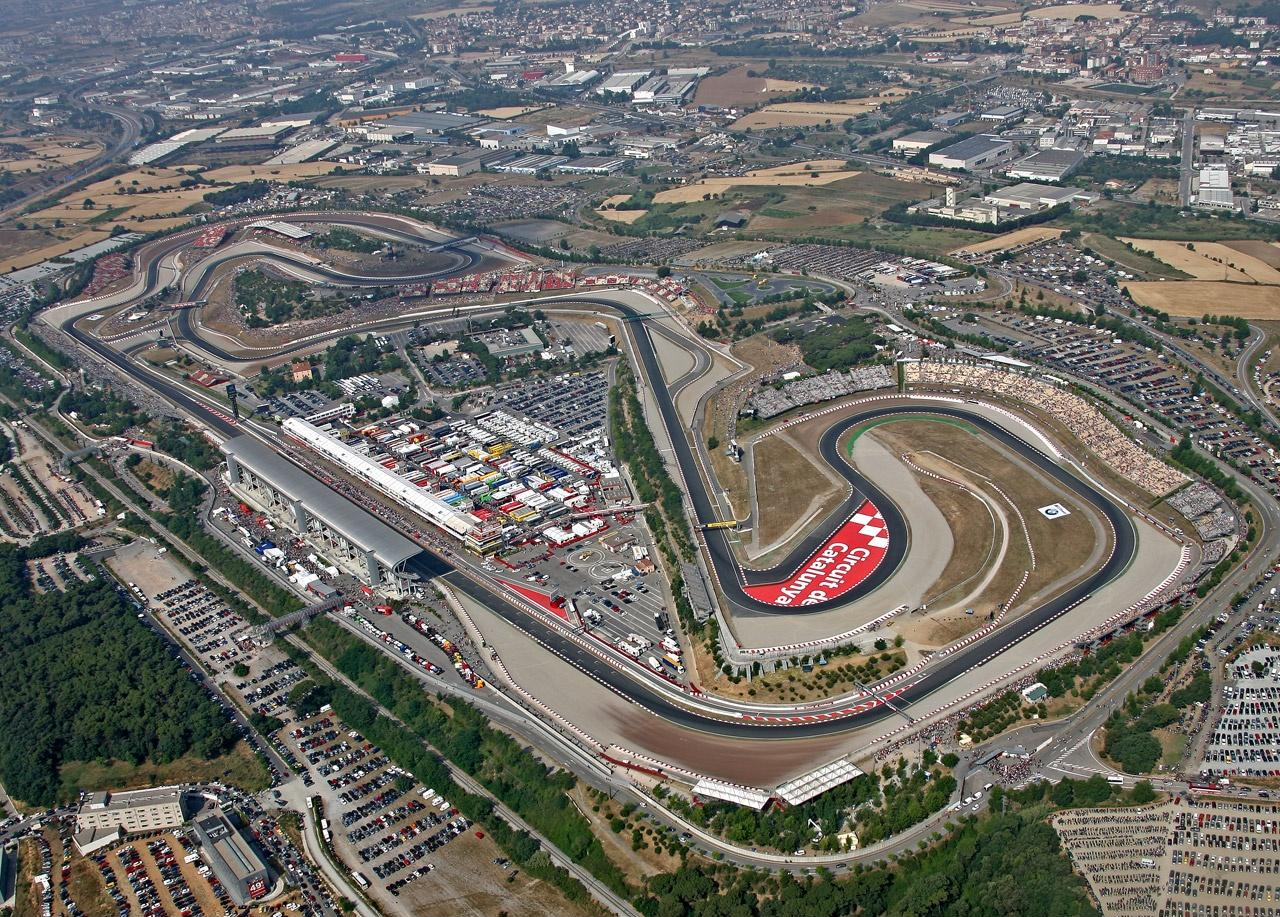
 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Galicia
Galicia
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 CESAER
CESAER
 Colleges and Universities in Europe
Colleges and Universities in Europe
 Music
Music
 Architecture
Architecture
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Castilla y León
Castilla y León
 Extremadura
Extremadura
 World Heritage
World Heritage