
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Slovenia
Slovenia

 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea

 Abruzzo
Abruzzo
 Albania
Albania
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia

 Marche
Marche

 Molise
Molise
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 Puglia
Puglia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Veneto
Veneto
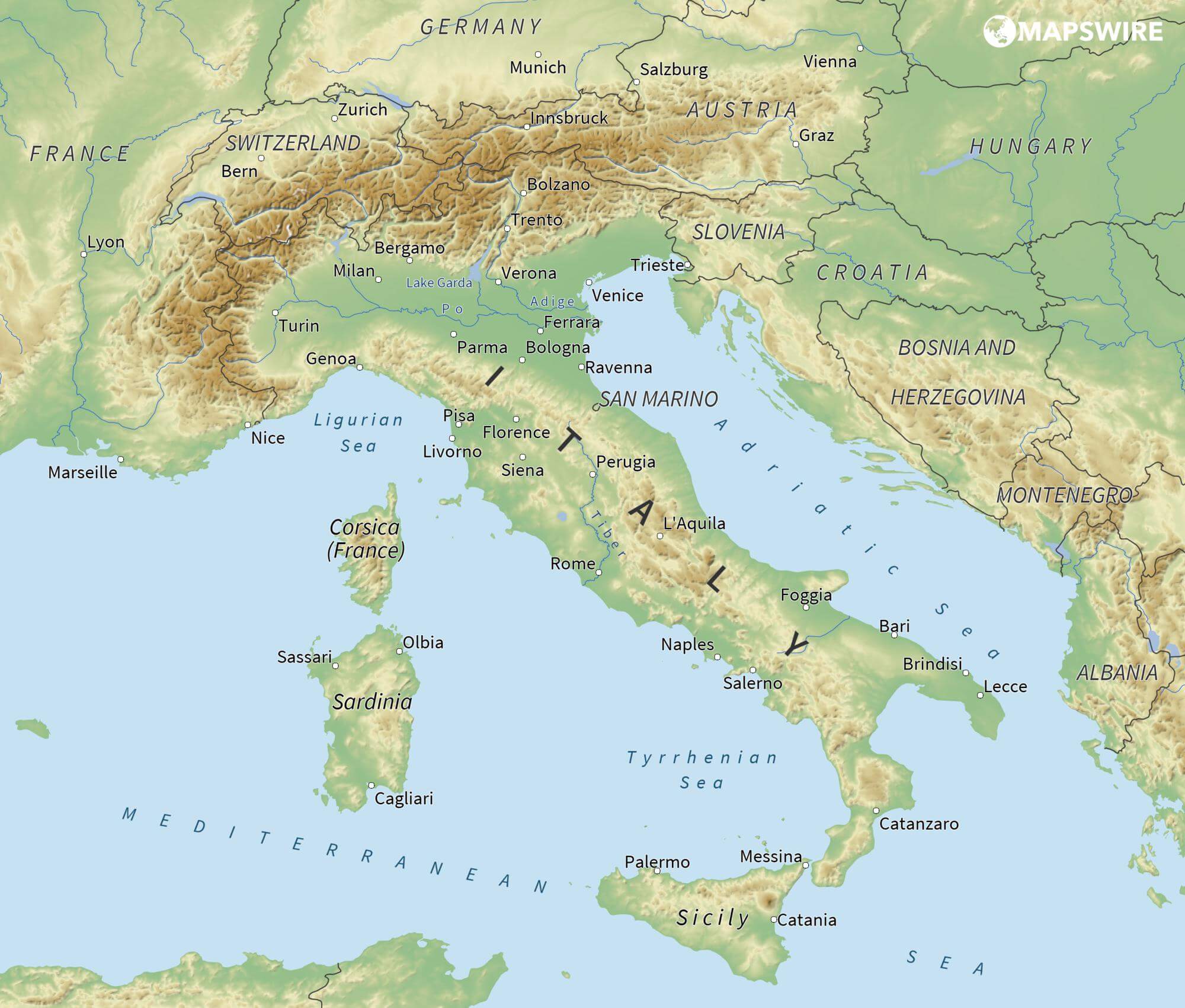
亚得里亚海(意大利语:Mar Adriatico,斯洛文尼亚语:Jadransko morje,克罗地亚语:Jadransko more,阿尔巴尼亚语:Deti Adriatik),是地中海的一部分水域,分隔了意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)和巴尔干半岛,也分隔了亚平宁山脉与狄那里克阿尔卑斯山脉及其临近地区。亚得里亚海西岸属于意大利,东岸则分别属于斯洛文尼亚、克罗地亚、波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那、黑山和阿尔巴尼亚。亚得里亚海透过位于其南部的奥特朗托海峡与爱奥尼亚海相连。波河、阿迪杰河、奥凡托河等河流流入亚得里亚海;海中有近1200个岛屿,其中只有69个有人居住。
Das Adriatische Meer, kurz auch die Adria (lateinisch Mare Adriaticum; italienisch Mare Adriatico; bosnisch, kroatisch und serbisch Jadransko more oder kurz Jadran; slowenisch Jadransko morje; albanisch Deti Adriatik oder kurz Adriatiku), ist das lang gestreckte nördliche Seitenbecken des Mittelmeeres zwischen der Apenninhalbinsel und Balkanhalbinsel. Es ist nach der Stadt Adria in Italien (Provinz Rovigo) benannt. Zum Adriatischen Meer wird alles gerechnet, was nördlich der Straße von Otranto liegt.
アドリア海(アドリアかい、英: Adriatic Sea ; イタリア語: Mar Adriatico ; クロアチア語: Jadransko more)は、地中海の海域の一つ。イタリア半島とバルカン半島に挟まれている。
The Adriatic Sea (/ˌeɪdriˈætɪk/) is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains over 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of 1,233 metres (4,045 ft). The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because the Adriatic collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures generally range from 30 °C (86 °F) in summer to 12 °C (54 °F) in winter, significantly moderating the Adriatic Basin's climate.
The Adriatic Sea sits on the Apulian or Adriatic Microplate, which separated from the African Plate in the Mesozoic era. The plate's movement contributed to the formation of the surrounding mountain chains and Apennine tectonic uplift after its collision with the Eurasian plate. In the Late Oligocene, the Apennine Peninsula first formed, separating the Adriatic Basin from the rest of the Mediterranean. All types of sediment are found in the Adriatic, with the bulk of the material transported by the Po and other rivers on the western coast. The western coast is alluvial or terraced, while the eastern coast is highly indented with pronounced karstification. There are dozens of marine protected areas in the Adriatic, designed to protect the sea's karst habitats and biodiversity. The sea is abundant in flora and fauna—more than 7,000 species are identified as native to the Adriatic, many of them endemic, rare and threatened ones.
The Adriatic's shores are populated by more than 3.5 million people; the largest cities are Bari, Venice, Trieste and Split. The earliest settlements on the Adriatic shores were Etruscan, Illyrian, and Greek. By the 2nd century BC, the shores were under Rome's control. In the Middle Ages, the Adriatic shores and the sea itself were controlled, to a varying extent, by a series of states—most notably the Byzantine Empire, the Croatian Kingdom, the Republic of Venice, the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The Napoleonic Wars resulted in the First French Empire gaining coastal control and the British effort to counter the French in the area, ultimately securing most of the eastern Adriatic shore and the Po Valley for Austria. Following Italian unification, the Kingdom of Italy started an eastward expansion that lasted until the 20th century. Following World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, the eastern coast's control passed to Yugoslavia and Albania. The former disintegrated during the 1990s, resulting in four new states on the Adriatic coast. Italy and Yugoslavia agreed on their maritime boundaries by 1975 and this boundary is recognised by Yugoslavia's successor states, but the maritime boundaries between Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Montenegro are still disputed. Italy and Albania agreed on their maritime boundary in 1992.
Fisheries and tourism are significant sources of income all along the Adriatic coast. Adriatic Croatia's tourism industry has grown faster economically than the rest of the Adriatic Basin's. Maritime transport is also a significant branch of the area's economy—there are 19 seaports in the Adriatic that each handle more than a million tonnes of cargo per year. The largest Adriatic seaport by annual cargo turnover is the Port of Trieste, while the Port of Split is the largest Adriatic seaport by passengers served per year.
La mer Adriatique (du latin : Mare Hadriaticum ou Mare Adriaticum) est une mer séparant la péninsule italienne de la péninsule balkanique. L'Adriatique est le bras de la Méditerranée situé le plus au nord en s'étendant du canal d'Otrante (où elle rejoint la mer Ionienne) jusqu'aux villes de Venise et de Trieste et à l'embouchure du Pô. Les pays côtiers sont l'Italie, la Slovénie, la Croatie, la Bosnie-Herzégovine, le Monténégro et l'Albanie, ainsi que la Grèce par l'île de Corfou.
Il mare Adriatico è l'articolazione del mar Mediterraneo orientale situata tra la penisola italiana e la penisola balcanica; suddiviso in Alto Adriatico, Medio Adriatico e Basso Adriatico, bagna sei Paesi: Italia, Slovenia, Croazia, Bosnia ed Erzegovina, Montenegro e Albania, confinando a sud-est con il Mar Ionio.
El mar Adriático (del latín, Mare Hadriaticum) es un golfo estrecho y alargado que forma parte del mar Mediterráneo. Se encuentra situado entre la península Itálica, al oeste, y la península de los Balcanes, al este, con una anchura máxima de unos 200 km, y una longitud de unos 800 km. Su extremo meridional limita con el mar Jónico, del que lo separa el canal de Otranto. Su superficie total es de, aproximadamente, 160 000 km².
Las costas occidental, septentrional, y parte de la oriental corresponden a Italia (60% de la longitud de costa del Adriático), mientras que el resto de la costa oriental corresponde a Croacia, Eslovenia, Bosnia y Herzegovina, Montenegro y Albania. Algunos de los ríos que desembocan en el Adriático son el Reno, el Po, el Adigio, el Brenta, el Piave y el Neretva.
La costa del Adriático concentra un gran número de centros turísticos, como Venecia, que recibe el nombre de «Reina del Adriático». Tras la división de Yugoslavia, la costa croata se ha convertido también en un destino turístico muy popular.
Sus aguas sostienen industria pesquera, y se llevan a cabo prospecciones petrolíferas en este mar. Durante los años 1990, varias investigaciones revelaron que sus niveles de contaminación son muy altos.
En las últimas décadas el gobierno de Italia ha intentado hacer de él una barrera contra la inmigración ilegal, en su mayor parte proveniente de Albania.
Адриати́ческое мо́ре (итал. mare Adriatico, эмил.-ром. Mèr Adriâtic, вен. Mar Adriàtico, неап. Mar Adriateco, словен. Jadransko morje, сербохорв. Jadransko more/Јадранско море, алб. Deti Adriatik, лат. mare Hadriaticum), также Адриатика — полузамкнутое море, часть Средиземного моря между Апеннинским и Балканским полуостровами. Омывает берега Италии (более 1000 км), Словении (47 км), Хорватии (1777 км), Боснии и Герцеговины (20 км), Черногории (200 км), Албании (472 км).


 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italy
Italy
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein

 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Monaco
Monaco
 Austria
Austria

 Piemonte
Piemonte

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovenia
Slovenia

 Tyrol
Tyrol

 Trentino-Alto Adige
Trentino-Alto Adige

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta

 Veneto
Veneto

 Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg
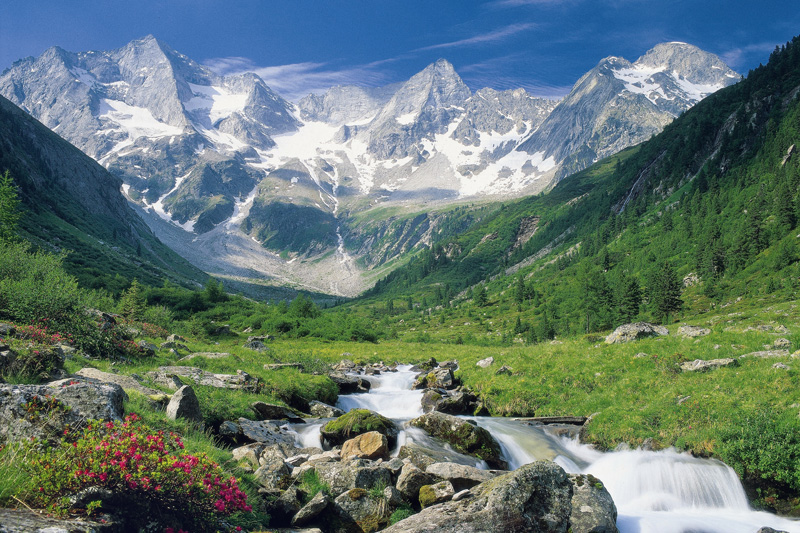

欧洲南部高大的山脉。西起法国尼斯附近地中海海岸,呈弧形向北、东延伸,经意大利北部、瑞士南部、列支敦士登、德国西南部,东止奥地利的维也纳盆地。总面积约22万平方千米。长约1200千米,宽130~260千米,东宽西窄。平均海拔3000米左右。 山脉主干向西南方向延伸为比利牛斯山脉,向南延伸为亚平宁山脉,向东南方向延伸为迪纳拉山脉,向东延伸为喀尔巴阡山脉。阿尔卑斯山脉可分为3段。西段西阿尔卑斯山从地中海岸,经法国东南部和意大利的西北部,到瑞士边境的大圣伯纳德山口附近,为山系最窄部分,也是高峰最集中的山段。勃朗峰(4810米)是整个山脉的最高点,位于法国和意大利边界。中段中阿尔卑斯山,介于大圣伯纳德山口和博登湖之间,宽度最大。有马特峰(4479米)和蒙特罗莎峰( 4634米)。东段东阿尔卑斯山在博登湖以东,海拔低于西、中两段阿尔卑斯山。
阿尔卑斯山(德语:Alpen;法语:Alpes;意大利语:Alpi;斯洛文尼亚语:Alpe)是一座位于欧洲中心的山脉,它覆盖了意大利北部边界、法国东南部、瑞士、列支敦士登、奥地利、德国南部及斯洛文尼亚。它可以被细分为三个部分,从地中海到勃朗峰的西阿尔卑斯山,从瓦莱达奥斯塔到布伦纳山口(奥地利和意大利交界处)的中阿尔卑斯山,从布伦纳山口到斯洛文尼亚的东阿尔卑斯山。欧洲许多大河都发源于此,水力资源丰富,为旅游、度假、疗养胜地。
阿尔卑斯山共有128座海拔超过4000米的山峰,其中最高峰勃朗峰海拔4810.45米[1],位于法国和意大利的交界处。山脉呈弧形,长1200千米,宽130~260千米,平均海拔约3000米,总面积约22万平方千米[2]。阿尔卑斯山北边是水汽较多的气候,而南边则较为干燥,雨量很少。
Die Alpen sind das höchste Gebirge im Inneren Europas. Es erstreckt sich in einem 1200 Kilometer langen und zwischen 150 und 250 Kilometer[1] breiten Bogen vom Ligurischen Meer bis zum Pannonischen Becken.
Die gesamte Alpenregion nimmt eine Fläche von etwa 200.000 Quadratkilometern ein.[2] Sie dehnt sich etwa 750 km von West nach Ost und ca. 400 km von Süd nach Nord aus und wird vom Rhonetal, dem Schweizer Mittelland, dem Oberlauf der Donau, der Kleinen Ungarischen Tiefebene, der Po-Ebene und dem Golf von Genua umgrenzt.
Der Alpenbogen schließt im Südwesten am Golf von Genua an den Apennin an, umfasst die Po-Ebene, verzweigt sich zum Französischen und Schweizer Jura und endet fächerförmig im Osten vor dem westpannonischen Berg- und Hügelland. Im Nordosten an der Donau bei Wien sind die Alpen durch das Wiener Becken von den geologisch verwandten Karpaten getrennt, im Südosten gehen sie in das stark verkarstete Dinarische Gebirge über. Im Norden fallen die Alpen allmählich zum österreichischen und deutschen Alpenvorland ab. Im Süden ist der Abfall zur Po-Ebene steiler. Der Gebirgszug, zu dem die Alpen gehören, erstreckt sich vom afrikanischen Atlas bis nach Südostasien.[3]
Die Gipfelhöhen in den westlichen Gebirgsstöcken liegen meist zwischen 3000 und 4300 Meter über dem Meeresspiegel, in den Ostalpen sind die Berge etwas niedriger. Der höchste Gipfel der Alpen ist der Mont Blanc mit 4810 Metern. 128 Berge der Alpen sind Viertausender, etliche Berge mehr oder weniger vergletschert. Die Alpen sind in zahlreiche Gebirgsgruppen und -ketten gegliedert.
Die Alpen bilden im „Herzen Europas“[4] eine wichtige Klima- und Wasserscheide. Sie trennen den zentralen Mittelmeerraum mit dem Etesienklima vom atlantisch beeinflussten nördlichen Mitteleuropa und stehen am Ostrand unter kontinentalem Einfluss. Auch die Entwässerung folgt diesen Großrichtungen zu Mittelmeer, Nordsee und Schwarzem Meer.
Der Alpenraum umfasst Gebiete der acht Alpenstaaten Frankreich, Monaco, Italien, Schweiz, Liechtenstein, Deutschland, Österreich und Slowenien. Er bildet den Lebensraum von 13 Millionen Menschen und genießt europäische Bedeutung als Erholungsraum.[4] Ungarn hat Anteile an Mittelgebirgen, die zu den Alpen gezählt werden, beispielsweise an Günser und Ödenburger Gebirge, wird in der Regel jedoch nicht zum Alpenraum gezählt. Seit der Frühgeschichte stellen Alpentäler und -pässe auch wichtige transeuropäische Verkehrsverbindungen dar.
アルプス山脈(アルプスさんみゃく、羅: Alpes アルペース、仏: Alpes、伊: Alpi、独: Alpen、英: Alps)は、アルプス・ヒマラヤ造山帯に属し、ヨーロッパ中央部を東西に横切る「山脈」である。オーストリア、スロベニアを東端とし、イタリア、ドイツ、リヒテンシュタイン、スイス各国にまたがり、フランスを南西端とする多国にまたがっている。アルプ(スイスの高山山腹の夏季放牧場;英語: alp,フランス語: alpe,ドイツ語: Alpe)がいっぱいであるからアルプスであると考える説と、ケルト語の alp「岩山」を語源とし、ラテン語を経由したと考える説がある。最高峰のモンブランは標高4,810.9m(2007年)で、フランスとイタリアの国境をなし、ヨーロッパの最高峰[1]でもある。
アルプス山脈はヨーロッパの多数の河川の水源地となっており、ここからドナウ川、ライン川、ローヌ川、ポー川、といった大河川が流れ出て、それぞれ黒海、北海、地中海、アドリア海へと注ぐ。
The Alps (/ælps/; French: Alpes [alp]; German: Alpen [ˈalpn̩]; Italian: Alpi [ˈalpi]; Romansh: Alps; Slovene: Alpe [ˈáːlpɛ]) are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe,[2][note 1] stretching approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Monaco, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.[3] The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,810 m (15,781 ft) is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).
The altitude and size of the range affects the climate in Europe; in the mountains precipitation levels vary greatly and climatic conditions consist of distinct zones. Wildlife such as ibex live in the higher peaks to elevations of 3,400 m (11,155 ft), and plants such as Edelweiss grow in rocky areas in lower elevations as well as in higher elevations. Evidence of human habitation in the Alps goes back to the Palaeolithic era. A mummified man, determined to be 5,000 years old, was discovered on a glacier at the Austrian–Italian border in 1991.
By the 6th century BC, the Celtic La Tène culture was well established. Hannibal famously crossed the Alps with a herd of elephants, and the Romans had settlements in the region. In 1800, Napoleon crossed one of the mountain passes with an army of 40,000. The 18th and 19th centuries saw an influx of naturalists, writers, and artists, in particular, the Romantics, followed by the golden age of alpinism as mountaineers began to ascend the peaks.
The Alpine region has a strong cultural identity. The traditional culture of farming, cheesemaking, and woodworking still exists in Alpine villages, although the tourist industry began to grow early in the 20th century and expanded greatly after World War II to become the dominant industry by the end of the century. The Winter Olympic Games have been hosted in the Swiss, French, Italian, Austrian and German Alps. At present, the region is home to 14 million people and has 120 million annual visitors.[4]
Les Alpes (prononcé [alp]) sont une chaîne de montagnes qui s'étend en Europe, recouvrant la frontière nord de l'Italie, le Sud-Est de la France, Monaco, la Suisse, le Liechtenstein, l'Autriche, le Sud de l'Allemagne et la Slovénie.
Les Alpes culminent à 4 809 mètres, au sommet du mont Blanc. On recense 82 sommets majeurs de plus de 4 000 m d'altitude (Suisse : 48, Italie : 38, France : 24). Les cols de montagne reliant les vallées ou les pays dépassent souvent les 2 000 m d'altitude. Les Alpes forment une barrière de 1 200 km entre la Méditerranée et le Danube.
Le Alpi sono la catena montuosa più importante d'Europa, situate nell'Europa centrale a cavallo dei confini di Italia, Francia, Svizzera, Liechtenstein, Germania, Austria, Slovenia e Ungheria, separando l'Europa settentrionale da quella meridionale con lo stivale italiano. Suddivise in varie sezioni e svariati sottogruppi racchiudono in sé le vette più alte del continente centrale europeo, rivestendo anche un'importanza storica, naturalistica, idrografica e turistico-economica per i rispettivi paesi.
Los Alpes son una importante cadena de montañas situada en la Europa Central. Su cumbre más alta es el Mont Blanc, con 4.810 metros de altitud. Alrededor de los Alpes, favorecidos por ríos importantes de caudal uniforme y ricas tierras de cultivo, se ubicaron desde la prehistoria diversos pueblos, principalmente celtas, como los borgoñones, leucos, lombardos, helvecios, y posteriormente germánicos en el noreste y pueblos itálicos después de la conquista de la Galia Cisalpina por Julio César. Actualmente viven unos 14 millones de personas en la región de los Alpes.
А́льпы (фр. Alpes, нем. Alpen, итал. Alpi, романш. Alps, словен. Alpe) — самый высокий и протяжённый горный хребет среди систем, целиком лежащих в Европе. При этом Кавказские горы выше, а Уральские — протяжённей, но они лежат также и на территории Азии (в зависимости от выбранного определения границы между Европой и Азией).
Альпы представляют собой сложную систему хребтов и массивов, протянувшуюся выпуклой к северо-западу дугой от Лигурийского моря до Среднедунайской низменности. Альпы располагаются на территории 8 стран: Франции, Монако, Италии, Швейцарии, Германии, Австрии, Лихтенштейна и Словении. Общая длина альпийской дуги составляет около 1200 км (по внутреннему краю дуги — около 750 км), ширина — до 260 км. Самой высокой вершиной Альп является гора Монблан высотой 4810 метров над уровнем моря, расположенная на границе Франции и Италии[1]. Всего в Альпах сосредоточено около 100 вершин-четырёхтысячников[2].
Альпы являются международным центром альпинизма, горнолыжного спорта и туризма. Туризм в Альпах начал активно развиваться в XX веке и получил большой толчок после окончания Второй мировой войны, став одним из главных направлений в конце столетия. Пять стран из восьми (Швейцария, Франция, Италия, Австрия и Германия) были хозяйками Зимних Олимпийских игр, которые проводились в альпийских объектах[3]. Несмотря на активное развитие туризма, в альпийском регионе по-прежнему существует самобытная традиционная культура, включая сельское хозяйство, деревообработку и сыроварение.
Благодаря расположению в центре Западной Европы, Альпы являются одной из наиболее изученных горных систем. Многие понятия названы по имени Альп, в частности, альпийский климатический пояс, период альпийской складчатости, альпийский тип рельефа, альпийские луга, альпинизм.
 Albania
Albania
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Greece
Greece
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Croatia
Croatia
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Romania
Romania
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Turkey
Turkey
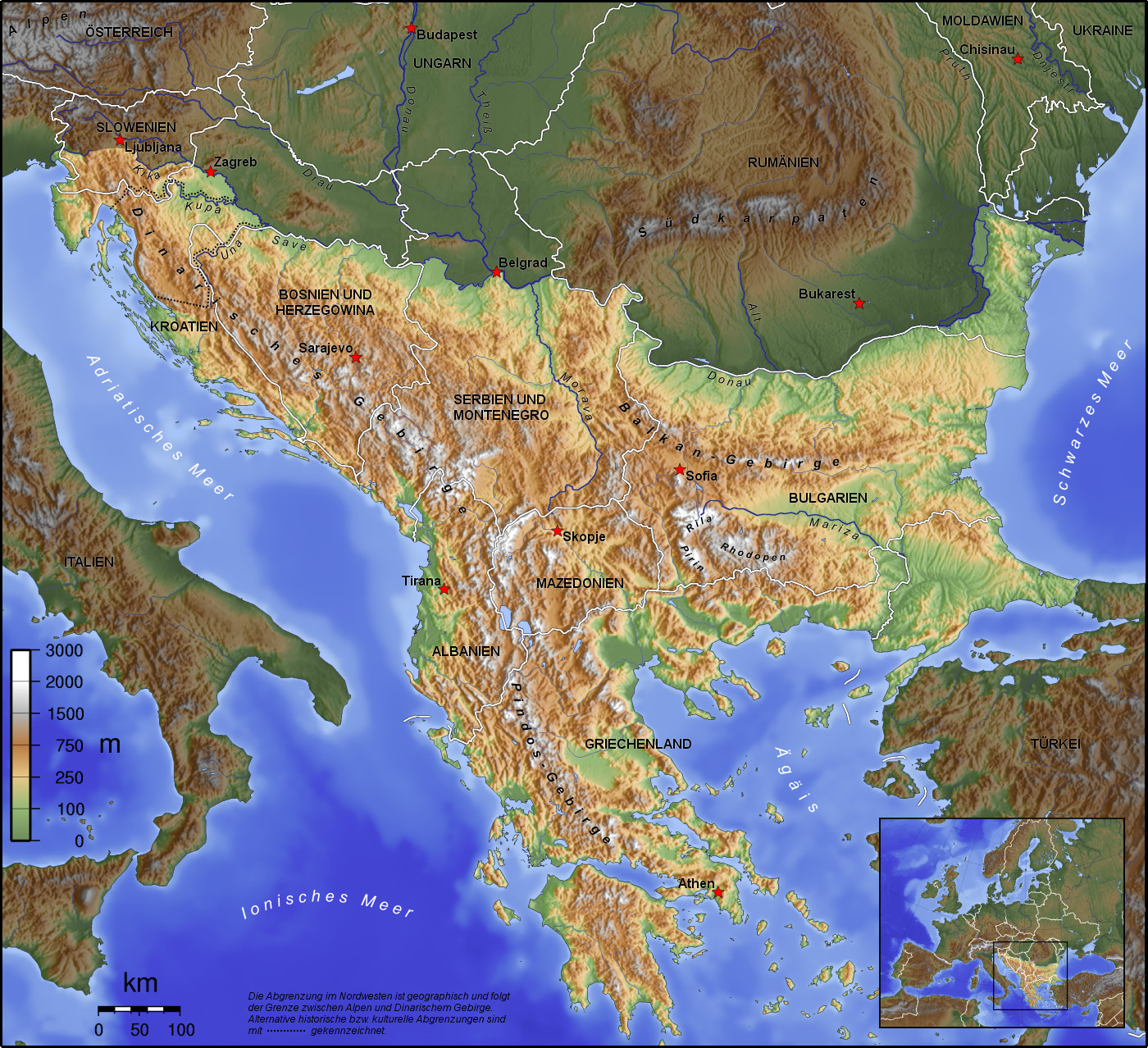
巴尔干半岛(Balkans),是一个地理名词,用以描述欧洲的东南隅位于亚得里亚海和黑海之间的陆地,详细的范围依照定义不同有许多种说法。该地约有55万平方公里和近5500万人口。在古希腊时代,巴尔干半岛被称为哈伊莫司半岛。该地区的名称来自于一条通过保加利亚中心到东塞尔维亚的巴尔干山脉。[1]
巴尔干地区向来存在诸多矛盾,其中既有宗教矛盾,也有领土争端。由于半岛的地缘政治重要性,由此而来的列强干涉致使这一地区的矛盾频繁被放大为战争,因此又有欧洲火药库之称。不过近年巴尔干半岛(南斯拉夫内战后至今)已实现停火与和平,只是偶然间在领土主权上有些纠纷,例如科索沃主权问题。第一次世界大战的触发点之——萨拉热窝事件亦是发生在巴尔干半岛上。
目前,巴尔干半岛共有11个国家,共有面积是47.6万平方公里,人口1.3亿。
南欧相邻地中海的三大半岛,从东向西分别为巴尔干半岛、意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)、伊比利亚半岛。
半岛地处欧、亚、非三大陆之间,是欧、亚联系的陆桥,南临地中海重要航线,东有博斯普鲁斯海峡和达达尼尔海峡扼黑海的咽喉,地理位置极为重要。地形以山地为主,喀尔巴阡山以南多为山丘及石灰岩地形,以北多以为平原为主。半岛西部有迪纳拉-品都斯山脉,中东部有喀尔巴阡-老山(巴尔干)山脉。老山山脉是阿尔卑斯、喀尔巴阡山的延伸,经南斯拉夫东部,横贯保加利亚中部,直临黑海。东西两列山脉之间是古老的罗多彼山脉和马其顿山丛,最高峰穆萨拉峰,海拔2925米。半岛上平原分布零散,仅萨瓦河、多瑙河、马里查河谷较宽广。 巴尔干半岛位于欧洲东南部,三面被水环绕:西邻亚德里亚海、南面是地中海(包括爱奥尼亚海和爱琴海)和马尔马拉海、东边是黑海。其北部边界通常被定为多瑙河、萨瓦河和库帕河。[2] [3]巴尔干半岛包括49万平方公里土地。
Die Balkanhalbinsel (auch kurz Balkan, oft synonym mit Südosteuropa verwendet) ist eine geographisch nicht eindeutig definierte Halbinsel im Südosten Europas. Sie ragt in das Mittelmeer und ist nach dem Balkangebirge benannt. Der größte Staat auf der Halbinsel ist Griechenland, gefolgt von Bulgarien (in dem sich der Großteil des Balkangebirges befindet), Serbien, Bosnien und Herzegowina, Albanien, Nordmazedonien, Montenegro und dem Kosovo. Die Staatsgebiete von Serbien, Kroatien, Rumänien, Slowenien und der Türkei, die durch ihre thrakischen Provinzen Anteil am Balkan hat, reichen über die Grenzen der Balkanhalbinsel hinaus.
Ungeachtet der Herleitung des geographischen Namens sind das dominierende Gebirge des Balkans die Dinariden im westlichen Teil der Halbinsel; ihr höchster Gipfel Jezerca (2694 m) liegt in Albanien. Die höchste Erhebung des Balkans ist der Gipfel Musala (2925 m) im Rila-Gebirge. Das Balkangebirge erreicht 2376 m maximale Gipfelhöhe.
バルカン半島(バルカンはんとう、Balkan Peninsula)、またはバルカン(Balkans)は東南ヨーロッパにある地理的領域であり、地理的・歴史的に様々な意味合いと定義付け[1][2]の下で使用される概念である[3]。名称はバルカン山脈からきている。この山脈はセルビアとブルガリアの国境から黒海沿岸まで、ブルガリア全土を横断している。バルカン半島は北西をアドリア海に、南西をイオニア海に、南と南東をエーゲ海に、そして東と北東を黒海によって区切られている[4]。北側の境界は論者と文脈によって様々に定義されていて不定である。バルカン半島の最高地点はリラ山地にあるムサラ山(2925メートル)である。
バルカン半島という概念はドイツの地理学者アウグスト・ツォイネによって1808年に創り出された[5][6]。彼はバルカン山脈がディナル・アルプス山脈と共にアドリア海から黒海まで東南ヨーロッパを区分していると誤認していた[5]。この地域はかつてオスマン帝国の属領であり、バルカン半島という用語は19世紀にはヨーロッパ・トルコ(European Turkey)の同義語であった[7]。バルカン半島という言葉は地理学的というよりもむしろ地政学的定義を持っており、この傾向は20世紀初頭にユーゴスラヴィア王国が成立するとさらに増した。バルカン半島を定義する自然境界が「半島」の学術的定義と一致していないため、現代の地理学者は「バルカン半島」という考え方を拒絶しており、通常はバルカンを「地域」として議論を行っている。この言葉には徐々に、特に1990年代以降、バルカニゼーション(バルカン化)のプロセスと関連して汚名と侮蔑的意味合いが与えられており[4][8]、それ故に東南ヨーロッパ(南東ヨーロッパ)という別の用語が使用されている。
The Balkans (/ˈbɔːlkənz/ BAWL-kənz), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographic area in Southeast Europe with various geographical and historical definitions.[2][3][4] The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined.[5] The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.
The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808,[6] who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of Southeast Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. The term Balkan Peninsula was a synonym for Rumelia in the 19th century, the European provinces of the Ottoman Empire. It had a geopolitical rather than a geographical definition, which was further promoted during the creation of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the early 20th century. The definition of the Balkan Peninsula's natural borders do not coincide with the technical definition of a peninsula; hence modern geographers reject the idea of a Balkan peninsula, while historical scholars usually discuss the Balkans as a region. The term has acquired a stigmatized and pejorative meaning related to the process of Balkanization,[5][7] and hence the preferred alternative term used for the region is Southeast Europe.
Les Balkans sont une des trois « péninsules » de l'Europe du Sud, mais cette appellation traditionnelle est parfois contestée en l'absence d'un isthme : les géographes préfèrent le terme de « région ». Elle est bordée par des mers sur trois côtés : la mer Adriatique et la mer Ionienne à l'ouest, la mer Égée au sud et la mer de Marmara et la mer Noire à l'est. Au nord, on la délimite généralement par les cours du Danube, de la Save et de la Kupa. Cette région couvre une aire totale de plus de 550 000 km2 et regroupe une population de près de 53 millions d’habitants.
La penisola balcanica, nota anche come Balcani (dalla forma abbreviata di Monti Balcani, sistema montuoso tra Bulgaria e Serbia; dal turco balkan ‘monteʼ[2]), è una penisola dell'Europa orientale; è delimitata a ovest dal mare Adriatico, a sud-ovest dal mar Ionio, a est dal mar Nero, a sud-est dal mar di Marmara, e a sud dal mar Egeo.
Come spesso accade per le penisole, incerta è la definizione del suo confine sulla terraferma, aggravato dal fatto che si tratta di uno dei suoi confini più estesi. Non aiuta inoltre la definizione di questa linea di demarcazione il fatto che il territorio presenta al suo interno grandi differenze e frammentazioni per storia, nazionalità, lingua, cultura e religione delle popolazioni che vi abitano.
Solitamente se ne stabilisce il confine sul Danubio e sul suo affluente Sava. In questo modo si include in tale area anche parte della Slovenia e della Romania (paese di lingua romanza orientale), che però storicamente hanno avuto a che fare con i Balcani solo dopo la dissoluzione dell'Impero asburgico. Secondo il geografo Vittorio Vialli, la delimitazione a nord è rappresentata dalla linea geografica Istria-Odessa. Esclude dalla regione la Slovenia l'interpretazione del confine che include il fiume Kupa, facendolo partire dalla città di Fiume e raggiungendo le foci del Danubio.[3] In tal modo confina a ovest con la cosiddetta regione geografica italiana,[4][5] che include anche territori non facenti parte della Repubblica Italiana. La definizione politica di Balcani venne in uso nel XIX secolo per designare i paesi europei interessati dall'espansione e dalla successiva dissoluzione dell'Impero ottomano.[6]
Del resto le caratteristiche del territorio, solcato da catene montuose parallele che ostacolarono il movimento in direzione nord-sud e una colonizzazione uniforme già ai tempi dell'espansione greco-romana, e la sua stessa collocazione geografica contribuiscono a spiegare le tormentate vicende storiche che hanno caratterizzato la penisola.[7]
Fino al 1975 la penisola era attraversata dal Balkan Express, un treno con partenza da Vienna e arrivo a Istanbul. Il clima è continentale nel nord e nell’est del territorio (con estati calde e inverni molto rigidi), mentre l’area occidentale e la Grecia hanno un clima mediterraneo.
La península balcánica o península de los Balcanes es una de las tres grandes penínsulas del sur de Europa, continente al que está unida por los montes Balcanes al este (cordilleras que han dado nombre a la península) y los Alpes Dináricos, al oeste.
Балка́нский полуо́стров (хорв. Balkanski poluotok, словен. Balkanski polotok, серб. Балканско полуострво, рум. Peninsula Balcanică, болг. и макед. Балкански полуостров, алб. Gadishulli Ballkanik, греч. Βαλκανική χερσόνησος, тур. Balkan Yarımadası, босн. Balkansko poluostrvo, черног. Balkansko poluostrvo) расположен на юго-востоке Европы. Площадь — около 467 тыс. км².
С юга, юго-запада и юго-востока омывается: Адриатическим, Ионическим, Мраморным, Критским, Эгейским и Чёрным морями.
Северной границей полуострова считается условная линия, проведённая от устья Дуная, по рекам Дунай, Сава и Купа (Колпа), а от истока последней в Горском Котаре (Хорватия) — до залива Кварнер с портом Риека (Хорватия).
Рельеф преимущественно гористый (Стара-Планина, Родопы, Динарское нагорье, Пинд). По размерам в Европе уступает только Скандинавскому и Пиренейскому полуостровам.
 Albania
Albania
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Greece
Greece
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Croatia
Croatia
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Romania
Romania
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Turkey
Turkey

 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary

琥珀之路(英语:Amber Road)是一条古代运输琥珀的贸易道路,这条水路和陆路结合而成的通商道路,从欧洲北部的北海和波罗的海通往欧洲南部的地中海,连结了欧洲的多个重要城市,维持了多个世纪。
在公元前后的很长一段时间,琥珀作为装饰品中的重要组成部分,被从北海和波罗的海海岸的产地,经由维斯瓦河和第聂伯河运输到意大利、希腊、黑海和埃及。琥珀之路连结了琥珀的产地和在欧洲、中东地区和远东地区的消费地,并经由另一条通商道路丝绸之路继续通往亚洲。
Als Bernsteinstraße werden verschiedene Handelswege des Altertums (Altstraßen) bezeichnet, auf denen (unter anderem) Bernstein von der Nord- und Ostsee nach Süden in den Mittelmeerraum gelangte. Genau genommen handelt es sich nicht um eine Straße, sondern um unabhängige Handelswege, die für verschiedene Handelsgüter genutzt wurden. Die Bezeichnung „Bernsteinstraße“ tritt etwa ab dem Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts auf und hat in antiken Quellen keine Entsprechung.




迪纳拉山脉(克罗地亚语:Dinarsko gorje;塞尔维亚语:Динарски Алпи;英语:Dinaric Alps)是欧洲东南部的一条主要山脉,西起阿尔卑斯山脉,沿亚得里亚海海岸向东南延伸约645千米,东隔多瑙河流域与喀尔巴阡山脉相望,向南延伸为希腊境内诸山脉和爱琴海诸岛。
迪纳拉山脉是欧洲第四大山脉,仅次于高加索山脉、斯堪的纳维亚山脉和阿尔卑斯山脉,跨斯洛文尼亚、克罗地亚、波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那、塞尔维亚、黑山、阿尔巴尼亚和科索沃,最高点为阿尔巴尼亚境内的湖泊峰,海拔2692米。
Das Dinarische Gebirge (auch als Dinarische Alpen oder Dinariden bezeichnet) gehört zu den jungalpidischen Faltengebirgen in Südosteuropa und ist ein Teilabschnitt des den Mittelmeerraum umspannenden Faltungsgürtels. Es erstreckt sich über 600 Kilometer entlang des Ostufers der Adria von den Julischen Alpen in Nordostitalien und Slowenien über Nordwest-Kroatien, Bosnien-Herzegowina, Südwest-Serbien und Montenegro bis nach Nordalbanien, wo es im Querriegel des Prokletije (Albanische Alpen) abschließt.
Das großteils verkarstete Gebirge zeigt alle Typformen des außertropischen Karstformenschatzes. Aufgrund starker (neo-)tektonischer Aktivität der adriatischen Mikroplatte verfügt es wegen seiner treppenartig angeordneten Relieffolge und tektonisch angelegter Groß-Poljen – sogenannten Poljentreppe – über eines der komplexesten Karstreliefs der Erde.[1] Aus den in den dinarischen Ländern gebräuchlichen regionalen Landschafts- und Relief-Toponymen hat sich ein Großteil der geologischen und geomorphologischen Begriffe zur Karstterminologie entlehnt.
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 San Marino
San Marino
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Cyprus
Cyprus

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Geography
Geography
 European Union
European Union
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Financial
Financial
 History
History
 Architecture
Architecture