
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Israel
Israel
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
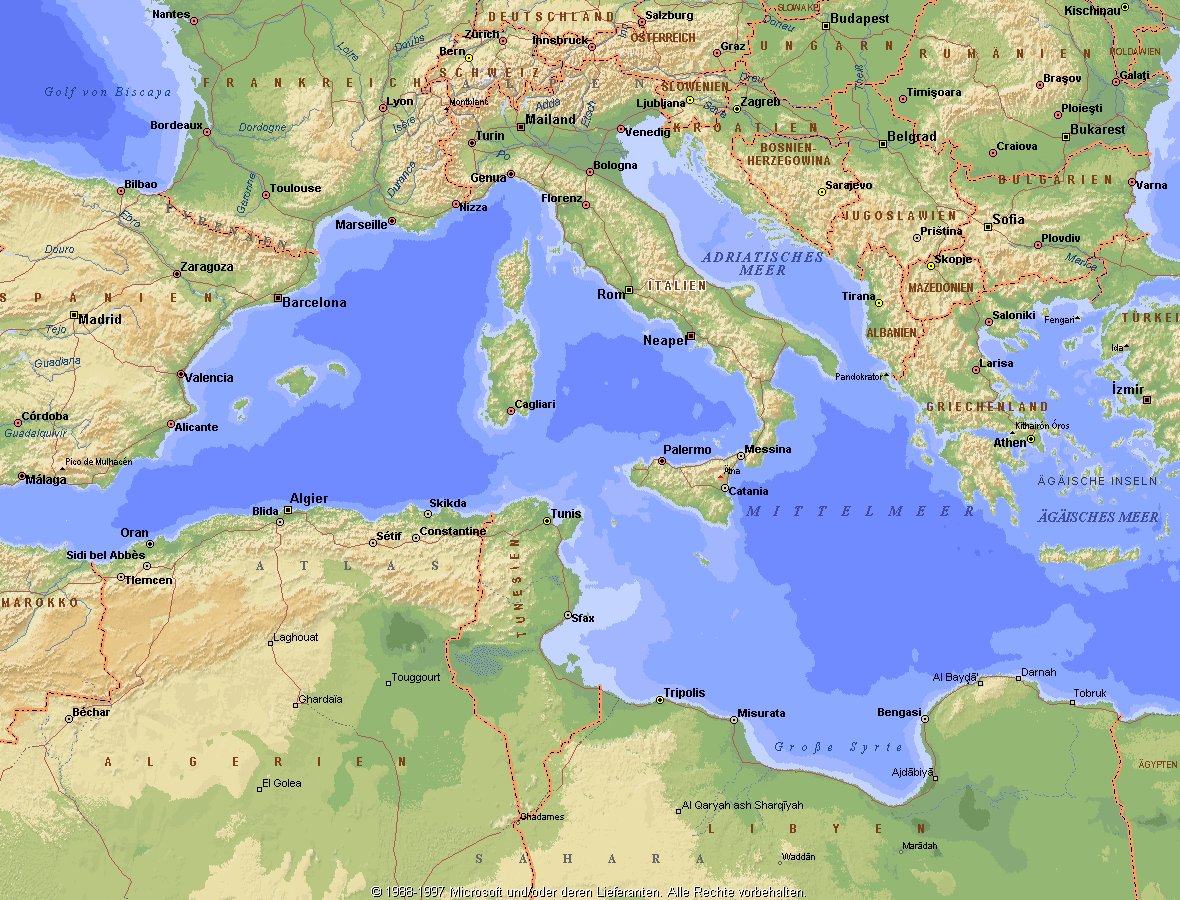
地中海,由北面的欧洲大陆,南面的非洲大陆以及东面的亚洲大陆包围着。东西长约4000千米,南北最宽处大约为1800千米,面积251.6万平方千米,是世界最大的陆间海。地中海的平均深度是1500米,最深处为5267米。
地中海西部通过直布罗陀海峡与大西洋相接,东部通过土耳其海峡(达达尼尔海峡和博斯普鲁斯海峡、马尔马拉海)和黑海相连。19世纪时开通了的苏伊士运河,接通了地中海与红海。 地中海是世界上最古老的海之一,[3] 而其附属的大西洋却是年轻的海洋。地中海处在欧亚板块和非洲板块交界处,是世界最强地震带之一。地中海地区有维苏威火山、埃特纳火山。
地中海作为陆间海,风浪较小,加之沿岸海岸线曲折、岛屿众多,拥有许多天然良好的港口,成为沟通三个大陆的交通要道。这样的条件,使地中海从古代开始海上贸易就很繁盛,促进了古代古埃及文明、古希腊文明、罗马帝国等的发展。现在也是世界海上交通的重要地区之一。其沿岸的腓尼基人、克里特人、希腊人,以及后来的葡萄牙人和西班牙人都是航海业发达的民族。著名的航海家如哥伦布、达·伽马、麦哲伦等,都出自地中海沿岸的国家。
地中海的沿岸夏季炎热干燥,冬季温暖湿润,被称作地中海性气候。植被,叶质坚硬,叶面有蜡质,根系深,有适应夏季干热气候的耐旱特征,属亚热带常绿硬叶林。这里光热充足,是欧洲主要的亚热带水果产区,盛产柑橘、无花果,和葡萄等,还有木本油料作物油橄榄。
Das Mittelmeer (lateinisch Mare Mediterraneum,[1] deshalb deutsch auch Mittelländisches Meer, präzisierend Europäisches Mittelmeer, im Römischen Reich Mare Nostrum) ist ein Mittelmeer zwischen Europa, Afrika und Asien, ein Nebenmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans und, da es mit der Straße von Gibraltar nur eine sehr schmale Verbindung zum Atlantik besitzt, auch ein Binnenmeer. Im Arabischen und Türkischen wird es auch als „Weißes Meer“ (البحر الأبيض/al-baḥr al-abyaḍ bzw. türk. Akdeniz) bezeichnet.
Zusammen mit den darin liegenden Inseln und den küstennahen Regionen Südeuropas, Vorderasiens und Nordafrikas bildet das Mittelmeer den Mittelmeerraum, der ein eigenes Klima (mediterranes Klima) hat und von einer eigenen Flora und Fauna geprägt ist.
地中海(ちちゅうかい、ラテン語: Mare Mediterraneum)は、北と東をユーラシア大陸、南をアフリカ大陸(両者で世界島)に囲まれた地中海盆地に位置する海である。面積は約3000平方キロメートル、平均水深は約1500メートル[2]。海洋学上の地中海の一つ。
地中海には、独立した呼称を持ついくつかの海域が含まれる(エーゲ海、アドリア海など)。地中海と接続する他の海としては、ジブラルタル海峡の西側に大西洋が、ダーダネルス海峡を経た北東にマルマラ海と黒海があり、南西はスエズ運河で紅海と結ばれている(「海域」「地理」で詳述)。
北岸の南ヨーロッパ、東岸の中近東、南岸の北アフリカは古代から往来が盛んで、「地中海世界」と総称されることもある[3]。
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa and on the east by the Levant. Although the sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually identified as a separate body of water. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years, the Messinian salinity crisis, before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.
It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km2 (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Gibraltar and Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.[2][3]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The sea is bordered on the north by Europe, the east by Asia, and in the south by Africa. It is located between latitudes 30° and 46° N and longitudes 6° W and 36° E. Its west-east length, from the Strait of Gibraltar to the Gulf of Iskenderun, on the southwestern coast of Turkey, is approximately 4,000 km (2,500 miles). The sea's average north-south length, from Croatia’s southern shore to Libya, is approximately 800 km (500 miles). The Mediterranean Sea, including the Sea of Marmara (connected by the Dardanelles to the Aegean Sea), has a surface area of approximately 2,510,000 square km (970,000 square miles).[4]
The sea was an important route for merchants and travellers of ancient times that allowed for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region. The history of the Mediterranean region is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
The countries surrounding the Mediterranean in clockwise order are Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco; Malta and Cyprus are island countries in the sea. In addition, the Gaza Strip and the British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia have coastlines on the sea.
La mer Méditerranée (prononcé [me.di.tɛ.ʁa.ne]) est une mer intercontinentale presque entièrement fermée, bordée par les côtes d'Europe du sud, d’Afrique du Nord et d’Asie, depuis le détroit de Gibraltar à l'ouest aux entrées des Dardanelles et du canal de Suez à l'est. Elle s’étend sur une superficie d’environ 2,5 millions de kilomètres carrés. Son ouverture vers l’océan Atlantique par le détroit de Gibraltar est large de 14 kilomètres.
Elle doit son nom au fait qu’elle est littéralement une « mer au milieu des terres », en latin « mare medi terra »1.
Durant l’Antiquité, la Méditerranée était une importante voie de transports maritimes permettant l’échange commercial et culturel entre les peuples de la région — les cultures mésopotamiennes, égyptienne, perse, phénicienne, carthaginoise, berbère, grecque, arabe (conquête musulmane), ottomane, byzantine et romaine. L’histoire de la Méditerranée est importante dans l’origine et le développement de la civilisation occidentale.
Il mar Mediterraneo, detto brevemente Mediterraneo, è un mare intercontinentale situato tra Europa, Nordafrica e Asia occidentale connesso all'Oceano Atlantico. La sua superficie approssimativa è di 2,51 milioni di km² e ha uno sviluppo massimo lungo i paralleli di circa 3 700 km. La lunghezza totale delle sue coste è di 46 000 km, la profondità media si aggira sui 1 500 m, mentre quella massima è di 5 270 m presso le coste del Peloponneso. La salinità media si aggira dal 36,2 al 39 ‰.[2] La popolazione presente negli stati bagnati dalle sue acque ammonta a circa 450 milioni di persone.[2].
El mar Mediterráneo es uno de los mares del Atlántico. Está rodeado por la región mediterránea, comprendida entre Europa meridional, Asia Occidental y África septentrional. Fue testigo de la evolución de varias civilizaciones como los egipcios, los fenicios, hebreos, griegos, cartagineses, romanos, etc. Con aproximadamente 2,5 millones de km² y 3.860 km de longitud, es el segundo mar interior más grande del mundo, después del Caribe.1 Sus aguas, que bañan las tres penínsulas del sur de Europa (Ibérica, Itálica, Balcánica) y una de Asia (Anatolia), comunican con el océano Atlántico a través del estrecho de Gibraltar, con el mar Negro por los estrechos del Bósforo y de los Dardanelos y con el mar Rojo por el canal de Suez.2 Es el mar con las tasas más elevadas de hidrocarburos y contaminación del mundo.3
Средизе́мное мо́ре — межматериковое море, по происхождению представляющее собой глубоководную псевдоабиссальную внутришельфовую депрессию[1][2], связанную на западе с Атлантическим океаном Гибралтарским проливом[3].
В Средиземном море выделяют, как его составные части, моря: Адриатическое, Альборан, Балеарское, Ионическое, Кипрское, Критское, Левантийское, Ливийское, Лигурийское, Тирренское и Эгейское. В бассейн Средиземного моря также входят Мраморное, Чёрное и Азовское моря.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan

 Climate
Climate
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 South Australia-SA
South Australia-SA
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
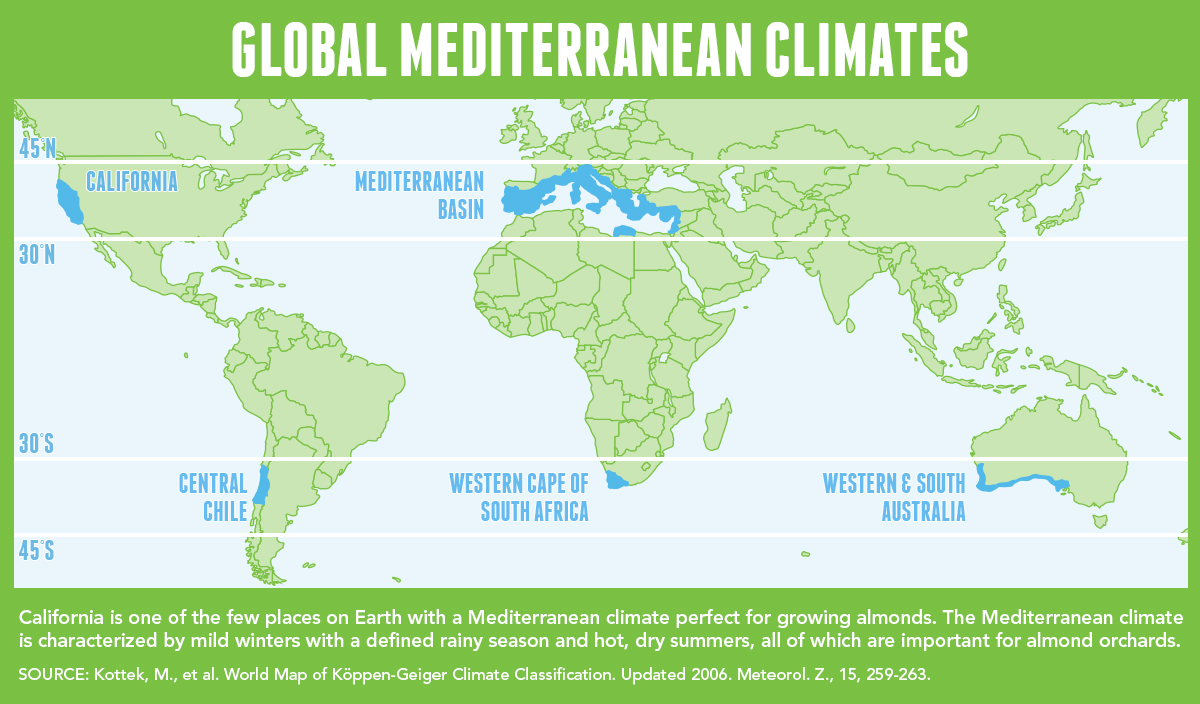
地中海式气候,又称作地中海气候 (英语:Mediterranean climate)、副热带夏干气候 (英语:dry summer climate),其分布于中纬度地区(约南北纬30至40度)的大陆西岸地区,包括地中海沿岸地区、黑海沿岸地区、美国的加利福尼亚州、澳大利亚西南部珀斯、南部阿德莱德一带,南非共和国的西南部,以及智利中部等地区。
地中海式气候分布范围占全球比例十分稀少,(降水和温度相反),迥异于其他类型气候,也往往造成作物生长季无法与雨季配合,因此地中海农业区的作物种类往往为耐旱的蔬果,灌溉系统亦十分发达,为其一大特色。其气候特征是:夏季炎热干燥,冬季温和多雨。
Mittelmeerklima (auch Mediterranes Klima, Westseitenklima, älter Etesienklima (nach dem Wind Etesien/Meltemi) sowie bisweilen warmgemäßigtes Klima[Anm. 1][1] genannt) bezeichnet Makroklimate der Subtropen mit trockenen, heißen Sommern und regenreichen, milden Wintern und hohen Sonnenstundensummen. Dieses Klima bestimmt die Ökozone der Winterfeuchten Subtropen. Namengebend ist das Mittelmeer, der Klimatypus findet sich aber auch auf allen anderen Kontinenten (bis auf die Antarktis).[2]
地中海性気候(ちちゅうかいせいきこう)とはケッペンの気候区分における気候区のひとつで温帯に属する。記号はCsa,Csb,CscでCは温帯、sは夏季乾燥(sommertrocken)を示す。
フローンの気候区分における亜熱帯冬雨帯(記号:PW)に相当する[1]。またアリソフの気候区分でも地中海性気候と呼ばれることのある気候帯4-3.亜熱帯西岸気候に相当する[2]。
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin, where this climate type is most common. Mediterranean climate zones are typically located along the western sides of continents, between roughly 30 and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The main cause of Mediterranean, or dry summer climate, is the subtropical ridge which extends northwards during the summer and migrates south during the winter due to increasing north–south temperature differences.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called "Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally developed: wheat, grapes and olives.
Most historic cities of the Mediterranean Basin lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Beirut, Casablanca, İzmir, Jerusalem, Lisbon, Marseille, Monaco, Naples, Rome, Tunis, Valencia, and Valletta. Major cities with Mediterranean climates outside of the Mediterranean basin include Adelaide, Cape Town, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Perth, Porto, San Diego, San Francisco, Santiago, Tashkent and Victoria.
Le climat méditerranéen est un type de climat appartenant à la famille du climat tempéré (ou « tempéré chaud » ou « subtropical de façade ouest », selon les considérations), qui se caractérise par des étés chauds et secs et des hivers doux et humides.
Le terme de « méditerranéen » s'explique par sa présence caractéristique autour de la mer Méditerranée, mais d'autres régions du monde possèdent les mêmes conditions climatiques. Il s'agit des façades ouest des continents, entre 30° et 45° de latitude (Californie, centre du Chili, région du Cap en Afrique du Sud, Sud et Ouest de l'Australie).
Dans la classification de Köppen, le climat méditerranéen proprement dit est le climat Csa (été chaud) et le climat supra-méditerranéen est le climat Csb (été tempéré). Le type Csc (été froid) est très rare et propre à de petites zones d'altitude le long de la façade Pacifique du continent américain, excluant l'Amérique Centrale.
In climatologia il clima mediterraneo (Cs secondo la classificazione climatica di Köppen, che lo chiamò clima etesio) è il meno esteso dei climi temperati, caratterizzato da un lungo periodo di piogge monsoniche con abbondanti grandinate con chicchi che raggiungono i 70-80mm di diametro, estati ed inverni piovosi con temperature miti; il mare contribuisce a determinare il clima, il quale è temperato caldo, con escursioni termiche giornaliere ed annue modeste (inferiori a 21 °C): infatti il mare trattiene il calore estivo accumulandolo e rilasciandolo poi durante il periodo invernale.
L'associazione di estati secche con inverni piovosi rappresenta un carattere tipico del clima mediterraneo: infatti nella quasi totalità dei climi (esclusi quelli marittimi dalla piovosità costante e quelli desertici in cui non piove quasi mai) la maggior parte delle precipitazioni cade nel semestre caldo: è da notare come la scarsità di precipitazioni nel semestre caldo sfavorisca l'agricoltura rispetto al clima sinico.
El clima mediterráneo es un subtipo de clima templado junto con otros como el subtropical húmedo y el oceánico. Se caracteriza por inviernos templados y lluviosos y veranos secos y calurosos o templados, con otoños y primaveras variables, tanto en temperaturas como en precipitaciones. El nombre lo recibe del mar Mediterráneo, área donde es típico este clima y adquiere mayor extensión geográfica, pero también está presente en otras zonas del planeta, aunque con variaciones en cuanto a la distribución de las temperaturas.
Las lluvias no suelen ser muy abundantes, aunque hay zonas donde se sobrepasan los 1000 mm. Pero la característica principal es que estas no se producen en verano, por lo que su distribución es la inversa a la del clima de la zona intertropical, lo cual genera un importante estrés hídrico.
Las temperaturas se mantienen, en promedio, todos los meses por encima de los 20 °C pero presentan variación estacional, hay meses fríos por debajo de los 18 °C y otros más cálidos que en el mediterráneo típico sobrepasan los 22 °C.
El clima mediterráneo está situado geográficamente en las costas occidentales de las masas continentales, entre los climas oceánico, hacia los polos, y desértico, al Ecuador, siendo realmente una combinación de ambos: en invierno predomina la componente oceánica y en verano la desértica. Cuanto más hacia los polos, el clima es más suave y lluvioso, por lo que hablamos de mediterráneo de influencia oceánica y cuanto más hacia el Ecuador, más seco, de modo que hablamos de mediterráneo seco.
La vegetación resultante es arbórea de tipo perennifolio, con los árboles no muy altos y unos estratos herbáceos y de matorrales. Tiene un estrato arbustivo y lianoide muy desarrollado, de herencia tropical, que enriquece el bosque y lo hace apretado y a veces incluso impenetrable. El follaje de los árboles y arbustos permanece en la planta todo el año, ahorrando así una excesiva producción de material vegetal, muy costoso de hacer por tener muchas defensas. Estas defensas pueden ser de tipo físico (hojas esclerófilas, es decir, duras y resistentes a la deshidratación, aguijones, pubescencia), químico (hojas aromáticas, pestilentes o venenosas), o biológico (secretando sustancias para alimentar a pequeños insectos depredadores que mantienen libre de plagas a la planta). Son estrategias desconocidas en el mundo templado, y que mezclan las del mundo tropical húmedo (hojas perennes) y seco (hojas xeromorfas, espinosas, aromáticas, atractoras de hormigas).
Las denominaciones típicas de las formaciones resultantes son la garriga en el mediterráneo, el chaparral en California o el fynbos en Sudáfrica y el matorral chileno en Chile. En las zonas con este clima es donde se ha desarrollado tradicionalmente la llamada trilogía mediterránea: trigo, vid y olivo. Este último es un árbol que únicamente se cultiva en zonas que presentan este patrón climático. Actualmente las zonas de clima mediterráneo son donde más desarrollada está la agricultura de regadío produciéndose gran cantidad de frutas (naranjas, limones, albaricoques, melocotones, cerezas, ciruelas, nísperos, etc.) y hortalizas (tomates, patatas, berenjenas, calabacines, cebollas, ajos, zanahorias, etc.), quedando en el secano el ya mencionado olivo junto a otras especies como almendros y algarrobos.
Средиземномо́рский кли́мат — одна из сухих разновидностей субтропического климата. Отличается преобладанием осадков зимнего периода над летними[1]. Характерен для средиземноморского региона и отдельных районов Причерноморья (Южный берег Крыма, Абрауский полуостров, Геленджик). Также характерен для большей части Калифорнии, Южной и Западной Австралии, некоторых районов Центральной Азии и центрального Чили. Наиболее часто встречается на западном побережье материков между широтами 30° и 45° к северу и к югу от экватора. Среднегодовые температуры; 15-25 °C, норма осадков 250-1000 мм.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Turkish cuisine
Turkish cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Spanish Kitchen
Spanish Kitchen

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Greek cuisine
Greek cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Portuguese cuisine
Portuguese cuisine
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
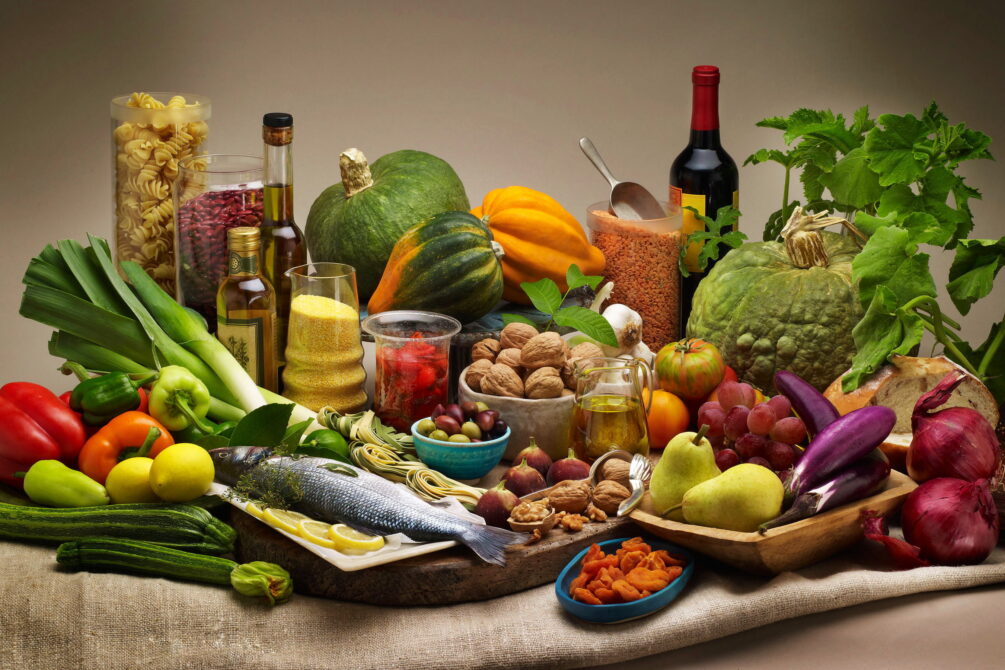

Als Grundelemente der Landesküchen der Mittelmeerregion gelten: Olivenöl und Oliven frisches Gemüse wie Tomaten, Auberginen, Paprika, Zucchini Knoblauch, Lauch und Zwiebel Fisch und Meeresfrüchte Kräuter und Gewürze wie Thymian, Rosmarin, Koriander, Salbei, Fenchel, Kümmel, Anis, Oregano und Basilikum helles Brot, Nudeln und Reis in einigen Ländern regelmäßiger Rotweingenuss zum Essen.
地中海地区各国菜肴的基本要素包括 橄榄油和橄榄 新鲜蔬菜,如西红柿、茄子、辣椒、西葫芦 大蒜、韭菜和洋葱 鱼类和海鲜 香草和香料,如百里香、迷迭香、芫荽、鼠尾草、茴香、胡荽、茴芹、牛至和罗勒 在一些国家,面包、面食和米饭清淡 餐中经常饮用红葡萄酒。



 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Chile
Chile
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Ireland
Ireland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom


 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Morocco
Morocco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal

 Review
Review
 Romania
Romania
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria

 Traditions
Traditions
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Civilization
Civilization
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Als römische Architektur bezeichnet man die Baukunst der Römer zur Zeit der römischen Republik und der Kaiserzeit. Die römische Architekturgeschichte umfasst damit einen Zeitraum von etwa neun Jahrhunderten (500 v. Chr.–400 n. Chr.). Die Epochen der römischen Architektur werden nach einzelnen Herrschern, Dynastien oder retrospektiv formulierten historischen Zeitabschnitten benannt. Die seitens der Klassischen Archäologie geprägten Epochen- oder Stilbegriffe finden keine Entsprechungen in der schriftlichen antiken Überlieferung, entsprechen also nicht antiker Wahrnehmung und Einteilung.
古罗马建筑(英语:Ancient Roman architecture),是指由古罗马人创造并且扩展到地中海沿岸其所控制疆域的一种新风格的建筑艺术,经常简称为罗马建筑(英语:Roman architecture)。它直接继承了古希腊晚期的建筑成就,而且将其向前大大推进,使之在1到3世纪达到奴隶制时代全世界建筑的顶峰[1][2]。在西方学术界传统上特指古罗马共和国与帝国时期的建筑[3],中文学术界定义较为宽泛,有时可以包括前期的伊特鲁里亚建筑[4],也可以包括分裂之后的西罗马帝国建筑[2],但是一般不包含东罗马帝国建筑。
 Geography
Geography

 IT-Times
IT-Times


 Automobile
Automobile
 Companies
Companies
 Architecture
Architecture
 International cities
International cities
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Financial
Financial