
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR




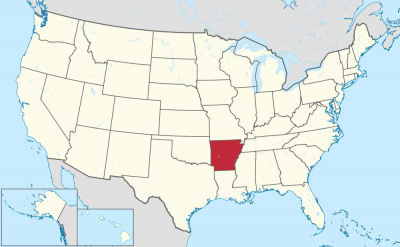


阿肯色州(英语:State of Arkansas /ˈɑːrkənsɔː/),是美国南部的一个州份,位处密西西比河中下游,北接密苏里州,西界俄克拉荷马州,南邻路易斯安那州,西南与得克萨斯州接壤,东隔密西西比河与田纳西州和密西西比州相望。其面积137,539平方公里,在五十个州内列第29位。2017年人口超过3百万,人口排名33。其首府是小石城。
该州的邮政缩写是AR。本州下辖共75个县,详见阿肯色州行政区划。
アーカンソー州(英: State of Arkansas [ˈɑrkənsɔː] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
地形的にはアメリカ内陸高原を構成するオザーク高原やワシタ山地(Ouachita Mountains)のある山岳地から、東部のミシシッピ川やアーカンソー・デルタのある低地まで多様である。
Arkansas (/ˈɑːrkənsɔː/)[c] is a state in the south central region of the United States, home to more than three million people as of 2018.[7][8] Its name is from the Osage language, of Siouan derivation; it denoted their related kin, the Quapaw people.[9] The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and the Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 33rd most populous of the 50 United States. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, located in the central portion of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, such as the Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area and Fort Smith metropolitan area, is a population, education, and economic center. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
The Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836.[10] Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and the state landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans as workers. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America during the Civil War.
On returning to the Union in 1868, the state continued to suffer due to its reliance on the large-scale plantation economy. Cotton continued as the leading commodity crop, although the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in terms of its economy and opportunities for residents.
White rural interests dominated the state's politics by disenfranchisement of African Americans and by refusal to reapportion the legislature. It was not until after the civil rights movement and federal intervention that more African Americans were able to vote. The Supreme Court overturned rural domination in the South and other states that had refused to reapportion their state legislatures, or retained rules based on geographic districts. In the landmark ruling of one man, one vote, it ruled that states had to organize both houses of their legislatures by districts that held approximately equal populations, and that these had to be redefined as necessary after each decade's census.
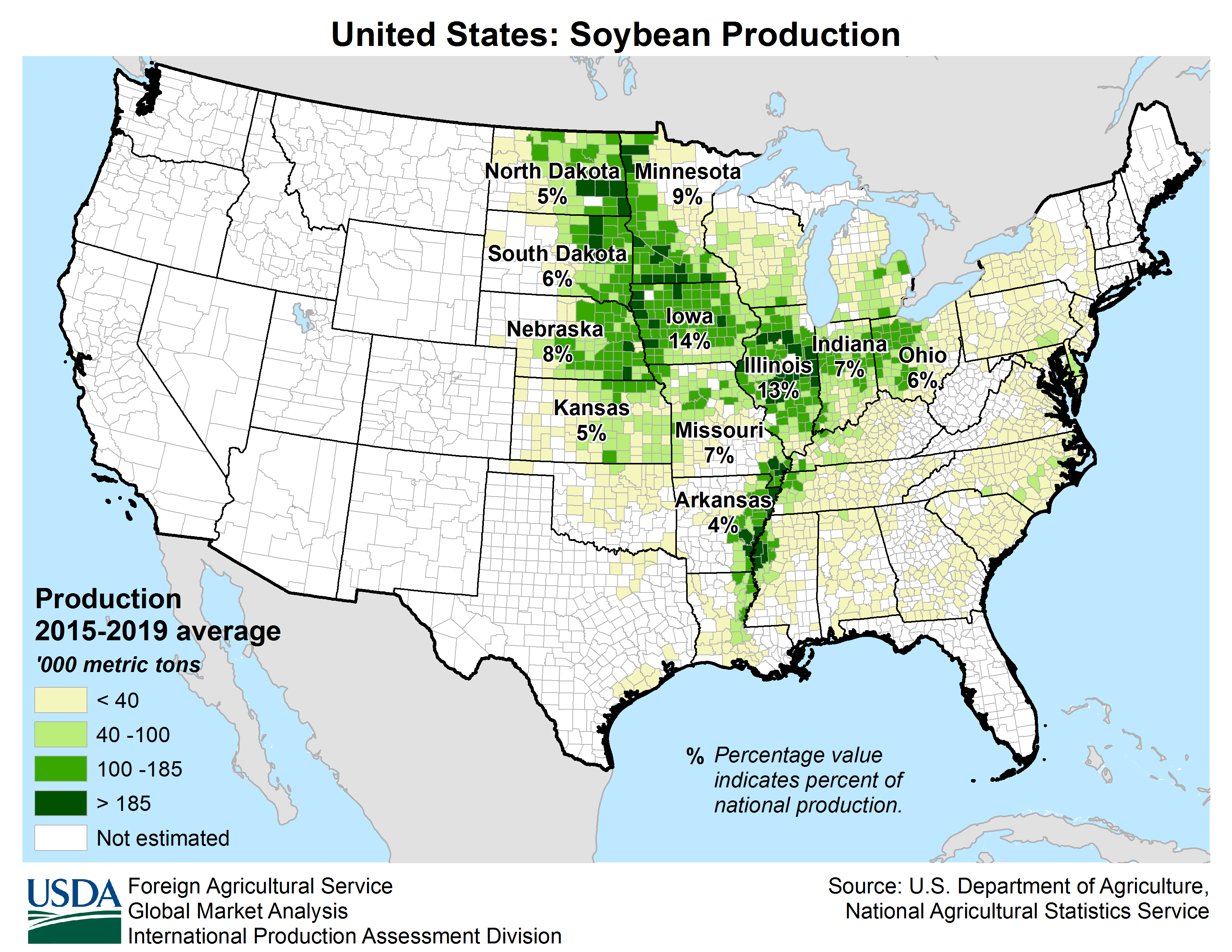
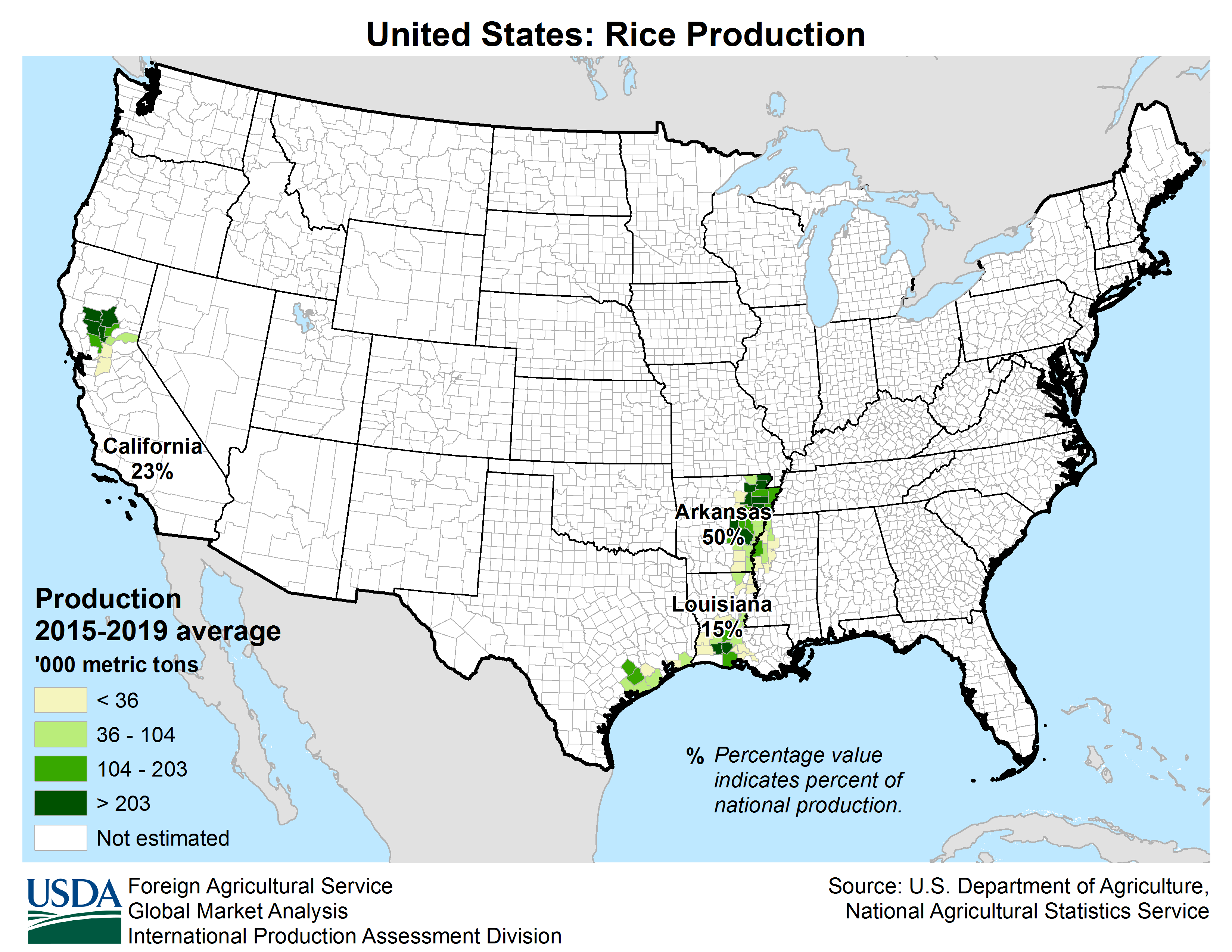
Following World War II, Arkansas began to diversify its economy. In the 21st century, its economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism; along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans and rice.
The culture of Arkansas is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state. Notable people from the state include politician and educational advocate William Fulbright; former president Bill Clinton, who also served as the 40th and 42nd governor of Arkansas; general Wesley Clark, former NATO Supreme Allied Commander; Walmart founder and magnate Sam Walton;[11] singer-songwriters Johnny Cash, Charlie Rich, Jimmy Driftwood, and Glen Campbell; actor-filmmaker Billy Bob Thornton; poet C. D. Wright; and physicist William L. McMillan, who was a pioneer in superconductor research.
L'Arkansas (prononcé : /aʁ.kɑ̃(n).sa(s)/3), les Arkansas (/aʁ.kɑ̃.sa/3), ou simplement les Arcs (/ɑɹk/4), (prononcé en anglais : /ˈɑɹkənsɔ/5), est un État du Sud des États-Unis. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Little Rock, située au centre du territoire. Avec une population de 2 915 918 habitants en 2010, estimée à 3 017 804 habitants en 2019, sur une superficie de 137 732 km2, l'État est le 32e plus peuplé et le 29e plus vaste du pays. L'Arkansas est entouré par six États : l'Oklahoma à l'ouest, le Missouri au nord, le Tennessee et le Mississippi à l'est, le Texas au sud-ouest et la Louisiane au sud. Il est divisé en 75 comtés. Surnommé The Natural State (« l'État naturel »), il présente des paysages variés : des chaînes montagneuses telles que les Monts Ozarks ou les Montagnes Ouachita ; au sud, des forêts denses nommées Timberlands de l'Arkansas (en) ; à l'est, les plaines du Mississippi et du delta de l'Arkansas (en).
Le nom de l'État provient du nom de la langue Sioux et désigne les Indiens Quapaw. Il forme un territoire dès 1819 et est admis dans l'Union le 15 juin 1836, dont il devient le 25e État. Esclavagiste, il repose sur l'économie de plantation (coton, riz) et se joint aux États confédérés durant la Guerre de Sécession (1861-1865). Après avoir réintégré l'Union, l'Arkansas connaît une crise due à l'effondrement des structures économiques et sociales antérieures. Les intérêts des Blancs ruraux dominent la vie politique locale jusqu'au Mouvement des droits civiques, au milieu du XXe siècle. L'État demeure ségrégationniste jusqu'à la fin des années 1960. Il est aujourd'hui un territoire populaire, conservateur, dont l'ancrage républicain se confirme depuis les années 2000. Néanmoins, l'État demeure de tradition démocrate au niveau local et beaucoup d'électeurs se considèrent toujours Dixiecrats. La tradition conservatrice de cet État s'illustre par l'application de la peine de mort par injection létale et l'interdiction du mariage homosexuel à la suite d'un référendum.
L'Arkansas demeure un État à dominante agricole. En plus des plantations traditionnelles, il produit du soja, et tend à se spécialiser dans l'arboriculture et l'élevage de poulets. Les ressources en hydrocarbures ont également permis une industrialisation durant l'après-guerre, avec la création de papeteries, de scieries, d'usines métallurgiques (aluminium) et textiles. Durant les dernières décennies, l'Arkansas voit son économie se diversifier dans les services, accueillant des sièges sociaux de grandes entreprises (Walmart, Tyson Foods), ainsi que des aciéries et des constructeurs aéronautiques. En outre, des personnalités comme le sénateur J. William Fulbright, le chanteur de country Johnny Cash ou l'ancien président Bill Clinton en sont originaires.
L'Arkansas (pronuncia italianizzata, AFI: /arˈkansas/[2]; in inglese , /ˈɑrkənsɔː/) è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, la cui capitale è Little Rock. Confina a nord con il Missouri, a est con il Tennessee e il Mississippi, a sud con la Louisiana e il Texas, e ad ovest con l'Oklahoma.
Il nome dello Stato deriva dalla parola Akansa (termine utilizzato dai nativi Algonchini per indicare i nativi Quapaw), modificata nella pronuncia attuale dai francesi del XVII secolo.[3]
Arkansas es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Little Rock.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Suroeste. Limita al norte con Misuri al este con el río Mississippi que lo separa de Tennessee y Mississippi, al sur con Louisiana, al suroeste con Texas y al oeste con Oklahoma. Fue admitido en la Unión el 15 de junio de 1836, como el estado número 25.
Aparte de la frontera este que forma el río Misisipi, por su territorio discurre en dirección este el río Arkansas. El nombre del estado deriva de la palabra kansas (el término con que los indios algonquinos designaban a los indios quapaw), tal como la pronunciaban los franceses en el siglo XVII.3 La geografía diversa del estado parte de las regiones montañosas del Ozark y las montañas de Ouachita, que componen las tierras altas del interior de los EE. UU., a la tierra densamente boscosa en el sur conocida como el Arkansas Timberlands, hasta las tierras bajas del este a lo largo del río Misssissippi y el delta de Arkansas. Conocido como «el estado natural», las diversas regiones de Arkansas ofrecen a los residentes y turistas una variedad de oportunidades de recreación al aire libre.
Арканза́с[1][2] (также Арка́нзас[3]; англ. Arkansas, [ˈɑːrkənsɔː] ![]() слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
Официальное прозвище — «Естественный штат» (англ. Natural State).
Слово «арканзас» является алгонкинским экзонимом сиуского племени куапо.


 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
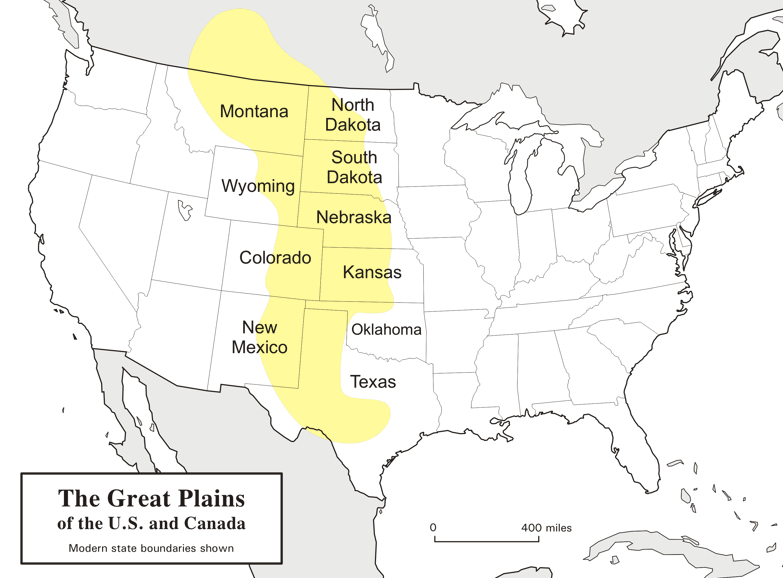
Die Great Plains (deutsch „Große Ebenen“) sind ein trockenes Gebiet östlich der Rocky Mountains in Nordamerika. Naturräumlich sind sie die klassischen Kurzgras-Prärien des amerikanischen Westens, heute werden sie intensiv landwirtschaftlich genutzt. Sie reichen von den kanadischen Prärieprovinzen (Alberta, Saskatchewan und Manitoba) bis nach Texas; manchmal wird auch ein kleiner Teil Mexikos dazu gezählt.
Die Great Plains umfassen (je nach Grenzziehung) eine Fläche von knapp 2 Millionen Quadratkilometern und erstrecken sich insgesamt etwa auf einer maximalen Breite von über 750 km und einer Länge von fast 3000 km. Während sie an den Rocky Mountains noch über 1800 m hoch sind, fallen sie nach Osten auf ca. 500 m ab. Damit sind sie insgesamt als Hochebene zu betrachten, die sich als „Piedmont-Plateau“, zum Teil in Schichtstufen ansteigend, vor dem Gebirge ausbreitet.
Man kann die Great Plains in zwei klimatische Regionen unterteilen, da man westlich des 100. Längengrades einen spärlichen Niederschlagsdurchschnitt vorfindet (weniger als 500 mm pro Jahr), wohingegen die östliche Region ein vergleichsweise humides Klima hat. Entsprechend dominiert im Westen die Viehwirtschaft und im Osten der Getreideanbau.
大平原(英语:Great Plains),多称北美大平原、北美大草原,是北美洲中部一块广袤的平原地区,大致位于密西西比河以西、洛基山脉以东、格兰德河以北。自然植被以草为主。
大平原东西长800千米,南北长3,200千米。另根据内布拉斯加-林肯大学大平原研究中心的定义,其总面积约130万平方千米。大平原主要包括了美国的科罗拉多州、堪萨斯州、蒙大拿州、内布拉斯加州、新墨西哥州 、北达科他州、俄克拉荷马州、南达科他州、得克萨斯州和怀俄明州,以及加拿大的草原三省(艾伯塔省、曼尼托巴省和萨斯喀彻温省)还有墨西哥的一小部分。



 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

Der Louisiana Purchase (Louisiana-Kauf; im Französischen vente de la Louisiane, d. h. Verkauf von Louisiana) war der Kauf von 2.144.476 km² Land, das die USA 1803 von Frankreich erwarben. Der Kaufpreis betrug damals 15 Millionen US-Dollar oder 80 Millionen französische Francs (7 US-Dollar pro km²). Gemessen an der Kaufkraft entspricht das einem heutigen Wert von circa 251 Millionen US-Dollar oder knapp 117 Dollar pro km² (Stand 2018).[1]
Verkauft wurde das Gebiet der ehemaligen Kolonie Louisiana, das westlich des Mississippi River lag. Dieses Gebiet ist viel größer als der heutige Staat Louisiana: Es umfasst außer Teilen des heutigen Louisiana auch die heutigen Staaten Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas und Nebraska sowie Teile von Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, außerdem noch Randgebiete der kanadischen Provinzen Manitoba, Saskatchewan und Alberta.
Der Louisiana Purchase war das größte Grundstücksgeschäft der Geschichte. Das gekaufte Land verdoppelte damals das Territorium der Vereinigten Staaten und macht fast ein Viertel des heutigen Staatsgebiets aus.
路易斯安那购地(英语:Louisiana Purchase;法语:Vente de la Louisiane)是美国于1803年以每英亩三美分向法国购买超过529,911,680英亩(2,144,476平方公里)土地的交易案,该交易的总价为1500万美元或相当于8000万法郎;若计算通货膨胀等因素,此数额在今日相当于3亿100万美元。如以国内生产总值相对比例计算,此数额在2004年相当于4,178亿美元。而土地上所有后续条约和财务结算的总成本,估计约为26亿美元。[1]。
法属路易斯安那的版图远超今日美国的路易斯安那州。从南至北,该属地范围包括了现今美国路易斯安那州密西西比河两岸(包括新奥尔良市)、阿肯色州、奥克拉荷马州、德克萨斯州北部边界地带、新墨西哥州东北角、密苏里州、堪萨斯州、科罗拉多州洛基山脉以东、爱荷华州、内布拉斯加州、怀俄明州大部(落基山脉以东)、明尼苏达州密西西比河以西、南达科他州、北达科他州大部、蒙大拿州大部(除西端),以及现今加拿大马尼托巴、萨斯喀彻温、艾伯塔各省之密苏里河流域地区(也即南部边境地带)。购地所涉土地面积是今日美国国土的22.3%,与当时美国原有国土面积大致相当,因此使得当时美国的国土翻倍。

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 California-CA
California-CA

 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Universities and colleges in the United States of America
Universities and colleges in the United States of America

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History