
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Armenia
Armenia
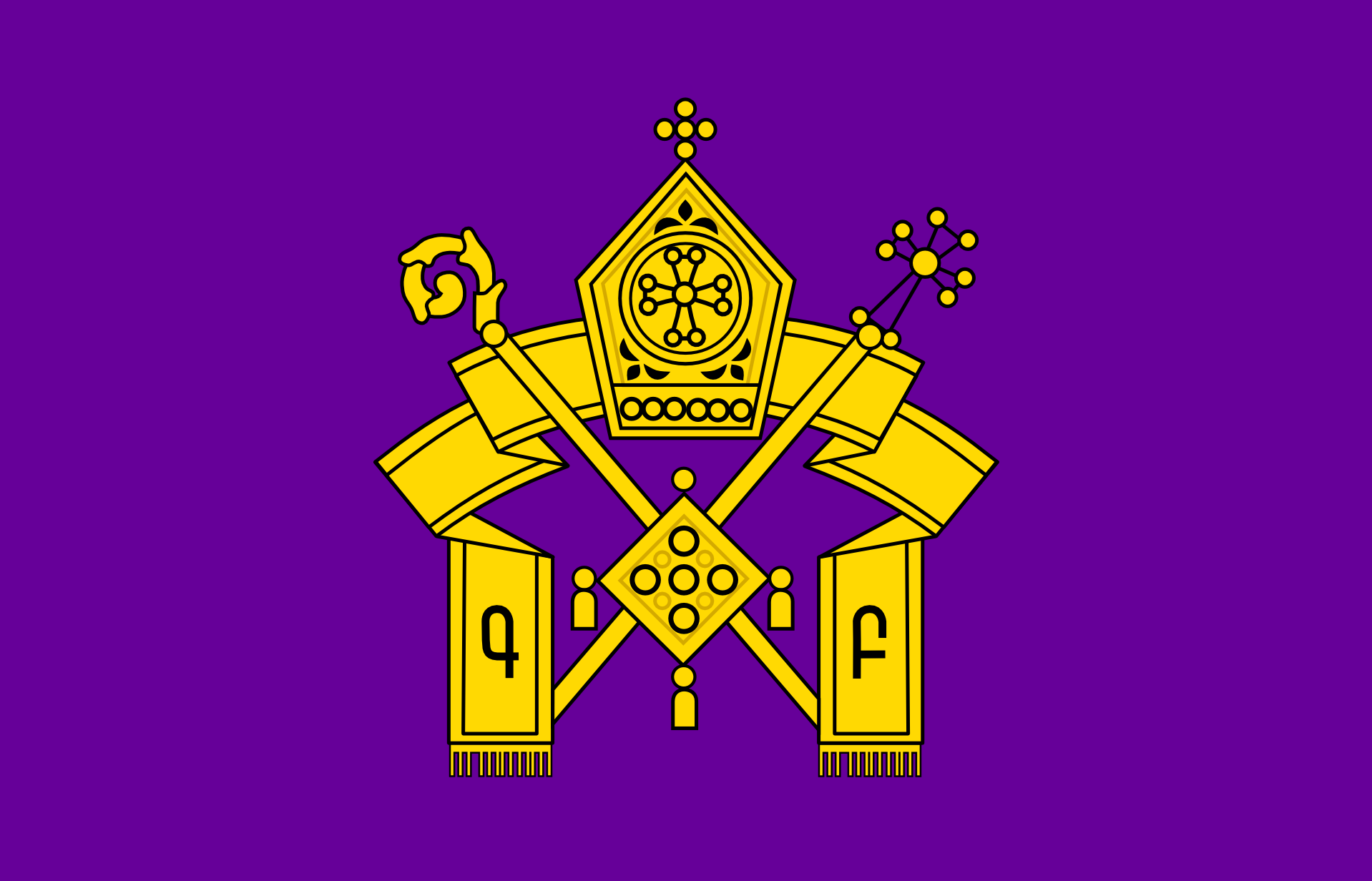

亚美尼亚使徒教会(亚美尼亚语:Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի,转写:Hay Arakelagan Yegeghetzi)是世界上最古老的国教会[1][2]以及最早被合法化的基督徒群体[3]。
Die Armenische Apostolische Kirche (armenisch Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի, Transkription ostarmenisch: Haj Arakelakan Jekeghezi; offizielle Bezeichnung auch: armenisch Հայաստանյայց Առաքելական Սուրբ Եկեղեցի, Transkription ostarmenisch: Hajastanjajz Arakelakan Surb Jekeghezi, Heilige Apostolische Kirche der Armenier) ist eine altorientalische Kirche mit heute neun[1] Millionen armenischen und türkischen Christen in zwei Katholikaten (Etschmiadsin, Sis), zwei Patriarchaten (Jerusalem, Konstantinopel) und rund 30 Diözesen, davon neun in Armenien.
アルメニア使徒教会(アルメニア語: Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի, ラテン文字転写: Hay Arakelagan Yegeghetzi, 英語: Armenian Apostolic Church)は、アルメニア、ならびに世界各地にあるアルメニア人コミュニティで信仰されているキリスト教・非カルケドン派の教会。約500万人の信者を擁する。使徒教会の名は、伝承に十二使徒がアルメニアにキリスト教を伝えたとあることに由来する。アルメニア正教会(Armenian Orthodox Church)とも呼ばれる。なお、東方典礼カトリック教会であるアルメニア・カトリック教会 (Armenian Catholic Church) とは別組織である。
The Armenian Apostolic Church (Armenian: Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի, romanized: Hay Aṙak'elakan Yekeghetsi)[note 1] is the national church of the Armenian people. Part of Oriental Orthodoxy, it is one of the most ancient Christian communities.[4] The Kingdom of Armenia was the first state to adopt Christianity as its official religion under the rule of King Tiridates in the early 4th century.[5][6] According to tradition, the church originated in the missions of Apostles Bartholomew and Thaddeus in the 1st century.
It is sometimes referred to as the Armenian Orthodox Church or Gregorian Church. The latter is not preferred by the church itself, as it views the Apostles Bartholomew and Thaddeus as its founders, and St. Gregory the Illuminator as merely the first official governor of the church. It is also known simply as the Armenian Church.
L'Église apostolique arménienne (en arménien Հայաստանեայց Առաքելական Եկեղեցի, Hayastaneayc’ Aṙak’elakan Ekeġec’i) est une Église chrétienne autocéphale3. C'est une des Églises des trois conciles dites aussi « Églises antéchalcédoniennes »2.
Elle revendique son titre d'« apostolique » en faisant remonter ses origines aux apôtres Jude Thaddée et Barthélemy. Devenue religion officielle du royaume d'Arménie avec la conversion du roi Tiridate IV par saint Grégoire l'Illuminateur, elle développe son particularisme du VIe au début du VIIIe siècle, qui voit sa christologie se stabiliser selon la doctrine miaphysite.
Le « Patriarche suprême et Catholicos de tous les Arméniens » qui réside à Etchmiadzin près d'Erevan bénéficie d'une primauté d'honneur parmi les différents hiérarques ; le titulaire actuel est Sa Sainteté Garéguine II depuis le 27 octobre 1999.
La Chiesa apostolica armena (in lingua armena: Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի), a volte indicata come Chiesa ortodossa armena o Chiesa gregoriana o Chiesa Cattolica Ortodossa Gregoriana è tra le chiese più antiche della cristianità e una delle prime comunità cristiane nel mondo. È guidata da un cathólicos, in lingua armena կաթոլիքոս ("patriarca", plurale cathólicoi). Attualmente il Catholicos di tutti gli Armeni è Karekin II, che ha la sua sede a Echmiadzin, in Armenia.
La Chiesa apostolica armena è una delle Chiese ortodosse orientali.
Iglesia apostólica armenia, oficialmente Iglesia gregoriana apostólica armenia (en armenio, Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի), o también conocida como Iglesia ortodoxa armenia, es la Iglesia nacional más antigua del mundo;1234 no debe confundirse con la Iglesia católica armenia, que está en comunión con la Santa Sede.
Армя́нская апо́стольская це́рковь[1] (арм. Հայ Առաքելական Եկեղեցի); традиционное, историческое название — Апостольская церковь Армении (арм. Հայաստանեայց Առաքելական Եկեղեցի) — одна из древнейших христианских церквей, имеющая ряд особенностей в догматике и обряде, отличающих её как от византийского православия, так и римского католицизма.
Относится к группе дохалкидонских Древневосточных православных церквей[2]. В богослужении используется армянский обряд.
Первыми проповедниками христианства в Армении и основателями церкви Армении считаются апостолы Фаддей и Варфоломей. Первым епископом в Армении, поставленным непосредственно апостолами, признан Закария (68—72). Традиционно считается, что крещение Армении произошло в 301 году. Некоторые современные исследователи склоняются к тому, что это, скорее, произошло позже, вероятно, в 314 году. Армения — первая страна, принявшая христианство в качестве государственной религии[3].

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].

Das Armenische Hochland (armenisch Հայկական լեռնաշխարհ oder Բարձր Հայք / Bardsr Hajk[1]), im Deutschen auch Armenisches Gebirge[2] oder Ararathochland genannt, bildet den zentralen Teil des nordanatolisch-nordiranischen Kettengebirges und umfasst im breiten Sinne auch den Kleinkaukasus.[3]
Je nach Definition ist das Armenische Hochland 300.000 bis 400.000 Quadratkilometer groß[4] und umfasst Gebiete der Türkei (vor allem die ehemaligen armenischen Provinzen des Osmanischen Reiches), des Iran, Georgiens, Aserbaidschans und fast vollständig die heutige Republik Armenien.
Viele Gebirge im Armenischen Hochland stellen eine Aneinanderreihung von Vulkanen dar. Zu diesen zählen das Dschawacheti-Gebirge, das Arsiani-Gebirge (Yalnızçam Dağları), das Geghamgebirge und der Haykakan Par (Ağri Dağları).[3] Die höchste Erhebung ist der 5137 m hohe Ararat, ein erloschener Vulkan. Große Seen sind der Vansee (Salzsee) und der Sewansee (Süßwassersee).
亚美尼亚高原(Armenian Highlands,亚美尼亚语:Հայկական լեռնաշխարհ,罗马化:Haykakan leṙnašxarh,英文名称另有Armenian Upland, Armenian plateau,或是Armenian tableland,[1])是组成西亚北部的三个高原中,位居中央,高度最高的一座。[1]亚美尼亚高原从西方,顺着时钟方向,受安纳托利亚高原、高加索、库拉-阿拉斯低地、伊朗高原、美索不达米亚所包围。亚美尼亚高原受到亚拉拉特平原(其中有亚拉拉特山)所分隔,而分成东西两个区域。所谓西亚美尼亚就是今日所称的东部安那托利亚地区,而所谓的东亚美尼亚即为今日的小高加索山脉,也称Caucasus Minor,或是古代所称的Anti-Caucasus,[2][3]即“在高加索对面”的意思。
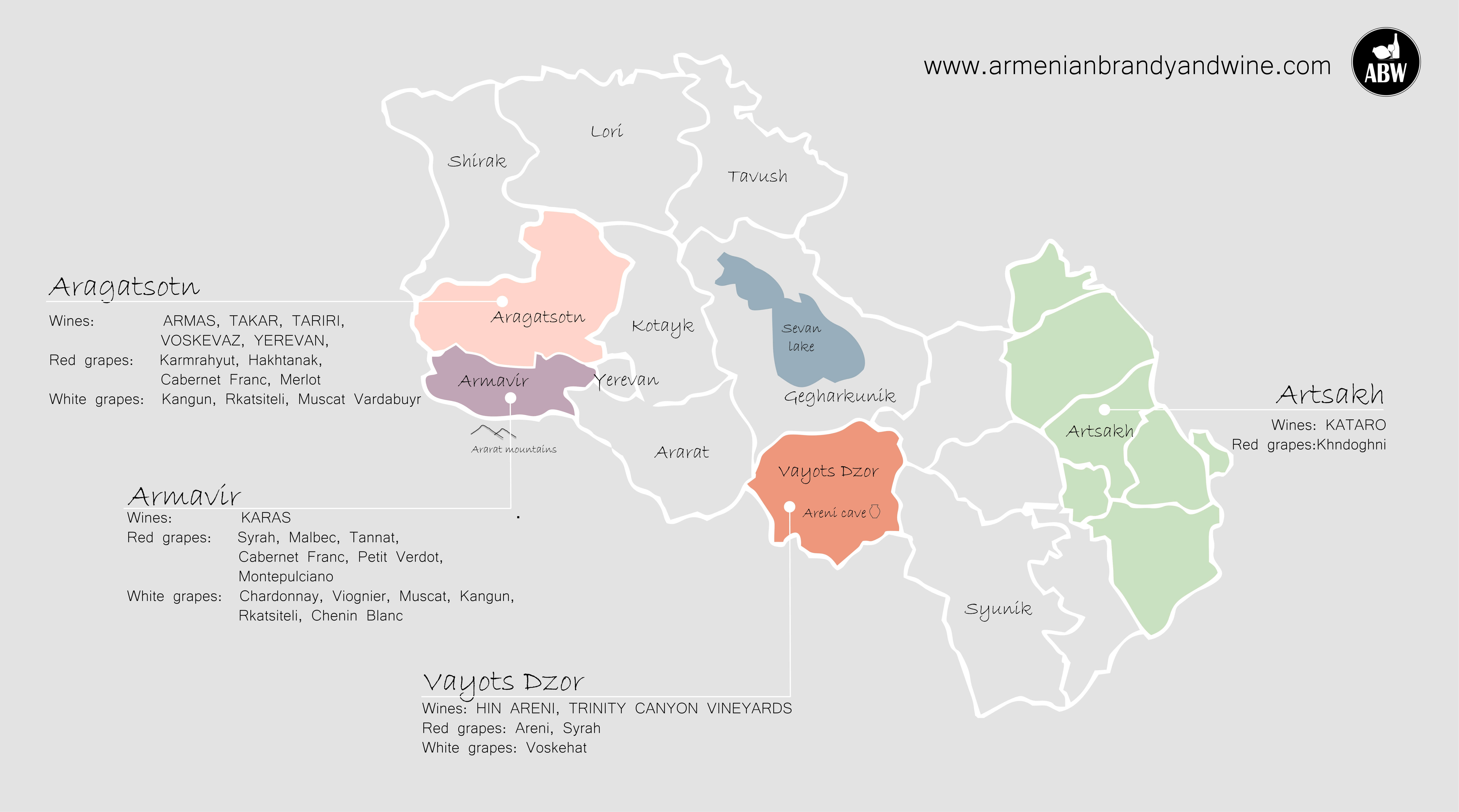
亚美尼亚共和国(亚美尼亚语:Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն,罗马化:Hayastani Hanrapetutyun),通称亚美尼亚,是一个位于西亚外高加索地区的共和制国家,有时也会被视为是东欧的一部分[4][5][6]。行政疆界上,亚美尼亚位于黑海与里海之间,属内陆国家,西邻土耳其,北邻格鲁吉亚,东为阿塞拜疆,南接伊朗和阿塞拜疆的飞地纳希切万自治共和国,以埃里温为首都。亚美尼亚曾经是苏联的加盟共和国之一,1991年苏联解体时独立。在亚美尼亚语中,亚美尼亚被称为“哈亚斯坦”(亚美尼亚语:Հայաստան,ISO 9985转写:Hayastan)。
在4世纪早期(公元301年),亚美尼亚是世界上第一个将基督教视为官方宗教的国家[7][8]。因此,亚美尼亚经常被指为“第一个基督教国家” [9][10][注 1]。绝大部分国民信奉基督教的东方正统教会(与埃塞俄比亚和埃及的科普特正教会同宗,非东正教),但因为周围被伊斯兰国家所包围着,再加上与邻国之间的国界争议问题,成为高加索地区动荡不安的火药库地带。
目前,亚美尼亚与邻国阿塞拜疆之间存在纳戈尔诺-卡拉巴赫的领土争议问题,1988年以来一直宣称阿塞拜疆西南部的纳戈尔诺-卡拉巴赫(境内大多数居民为信奉基督教的亚美尼亚人)是亚美尼亚领土的一部分,并且支持当地的武装与阿塞拜疆政府对抗,支持在1991年宣布独立但为未被普遍承认的国家的阿尔察赫共和国,曾在1990年代双方因此问题在边境发生军事对抗,并于2020年10月再次爆发。亚美尼亚也因为1915年奥斯曼帝国土耳其民族主义者发动的亚美尼亚种族大屠杀的历史认知问题与土耳其之间有外交上和对大屠杀事件承认问题上存在争议,但是近年亚土双方已透过元首互访等方式逐渐修复关系、重建沟通对话。亚美尼亚是欧洲委员会和集体安全条约组织一员。
アルメニア共和国(アルメニアきょうわこく、アルメニア語: Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն)、通称アルメニアは、ユーラシア大陸の南コーカサスの内陸国である。西アジアのアルメニア高原に位置し[3] [4]、西にトルコ、北にジョージア、東に事実上の独立した共和国アルツァフ共和国とアゼルバイジャン、南ではイランとアゼルバイジャンの飛び地ナヒチェヴァンに国境を接する[5]。
アルメニアは、古代の文化遺産を持つ、単一・多政党制・民主主義の国民国家である。同国は発展途上国であり、人間開発指数(2018年)では81位にランクされている[6]。その経済は、主に工業生産と鉱物抽出に基づいている。ユーラシア経済連合、欧州評議会、集団安全保障条約機構に加盟している。
一方で、1991年に宣言された事実上の独立国であるアルツァフを支持している。また、世界最古の国教会であるアルメニア使徒教会を国内の主要な宗教施設として認めている[7]。アルメニア語のユニークなアルファベットは、西暦405年にメスロプ・マシュトツによって作成された。
Armenia (/ɑːrˈmiːniə/ (![]() listen);[14] Armenian: Հայաստան, romanized: Hayastan, IPA: [hɑjɑsˈtɑn]), officially the Republic of Armenia,[a] is a landlocked country located in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.[15] It is a part of the Caucasus region; and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the Lachin corridor under a Russian peacekeeping force,[16] and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south.[17] Yerevan is the capital and largest city.
listen);[14] Armenian: Հայաստան, romanized: Hayastan, IPA: [hɑjɑsˈtɑn]), officially the Republic of Armenia,[a] is a landlocked country located in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.[15] It is a part of the Caucasus region; and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the Lachin corridor under a Russian peacekeeping force,[16] and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south.[17] Yerevan is the capital and largest city.
Armenia is a unitary, multi-party, democratic nation-state with an ancient cultural heritage. The first Armenian state of Urartu was established in 860 BC, and by the 6th century BC it was replaced by the Satrapy of Armenia. The Kingdom of Armenia reached its height under Tigranes the Great in the 1st century BC and became the first state in the world to adopt Christianity as its official religion in the late 3rd or early 4th century AD.[18][19][20] The official date of state adoption of Christianity is 301.[21] The ancient Armenian kingdom was split between the Byzantine and Sasanian Empires around the early 5th century. Under the Bagratuni dynasty, the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia was restored in the 9th century. Declining due to the wars against the Byzantines, the kingdom fell in 1045 and Armenia was soon after invaded by the Seljuk Turks. An Armenian principality and later a kingdom Cilician Armenia was located on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea between the 11th and 14th centuries.
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, the traditional Armenian homeland composed of Eastern Armenia and Western Armenia came under the rule of the Ottoman and Persian empires, repeatedly ruled by either of the two over the centuries. By the 19th century, Eastern Armenia had been conquered by the Russian Empire, while most of the western parts of the traditional Armenian homeland remained under Ottoman rule. During World War I, 1.5 million Armenians living in their ancestral lands in the Ottoman Empire were systematically exterminated in the Armenian genocide. In 1918, following the Russian Revolution, all non-Russian countries declared their independence after the Russian Empire ceased to exist, leading to the establishment of the First Republic of Armenia. By 1920, the state was incorporated into the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic, and in 1922 became a founding member of the Soviet Union. In 1936, the Transcaucasian state was dissolved, transforming its constituent states, including the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, into full Union republics. The modern Republic of Armenia became independent in 1991 during the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Armenia is a developing country and ranks 81st on the Human Development Index (2018).[22] Its economy is primarily based on industrial output and mineral extraction. While Armenia is geographically located in the South Caucasus, it is generally considered geopolitically European. Since Armenia aligns itself in many respects geopolitically with Europe, the country is a member of numerous European organizations including the Council of Europe, the Eastern Partnership, Eurocontrol, the Assembly of European Regions, and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. Armenia is also a member of certain regional groups throughout Eurasia, including the Asian Development Bank, the Collective Security Treaty Organization, the Eurasian Union, and the Eurasian Development Bank. Armenia supports the de facto independent Artsakh, which was proclaimed in 1991. Armenia also recognises the Armenian Apostolic Church, the world's oldest National church, as the country's primary religious establishment.[23][4] The unique Armenian alphabet was created by Mesrop Mashtots in 405 AD.
L’Arménie (en arménien Hayastan, Հայաստան), en forme longue la république d'Arménie (en arménien Hayastani Hanrapetut’yun, Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն), est un pays situé dans la région du Petit Caucase en Asie occidentale4. Cette ancienne république socialiste soviétique a des frontières terrestres avec la Turquie à l'ouest, la Géorgie au nord-nord-ouest, l'Azerbaïdjan à l'est et l'Iran au sud-est.
Bien que géographiquement située en Asie5,6,7, l'Arménie est considérée comme faisant culturellement, historiquement et politiquement parlant, partie de l'Europe, voire, géographiquement8, à sa lisière9,10. Le pays est d'ailleurs considéré comme un berceau du christianisme et des civilisations indo-européennes. Il a joué un rôle historique dans leur diffusion. L'Arménie est membre de plus de trente-cinq organisations internationales, comme l'ONU, le Conseil de l'Europe, la Communauté des États indépendants, etc. En 2015, un nouvel accord de partenariat avec l'Union européenne a été initié 11.
L'Arménie est un État-nation unitaire, démocratique et multipartite doté d'un riche héritage culturel. Héritière d'une des plus anciennes civilisations au monde, Urartu, son territoire représente seulement un dixième de l'Arménie historique12. L'arrivée des Armens, peuplade indo-européenne, marque la constitution de la satrapie d'Arménie au VIe siècle av. J.-C. Au Ier siècle av. J.-C., le royaume d'Arménie sous Tigrane le Grand atteint son apogée.
L'Arménie fut la première nation à adopter le christianisme comme religion d'État en 30113,14. Bien que l'Arménie actuelle soit un pays constitutionnellement séculier, la religion chrétienne y tient une place importante.
Au IXe siècle, le royaume d'Arménie est rétabli par la dynastie bagratide. Les guerres contre les Byzantins l'affaiblirent jusqu'à sa chute en 1045 puis l'invasion des Turcs seldjoukides s'ensuivit. La principauté et ensuite le royaume arménien de Cilicie a perduré sur la côte méditerranéenne entre les XIe et XIVe siècles.
Entre les XVIe et XIXe siècles, le plateau arménien composé de l'Arménie occidentale et de l'Arménie orientale était sous contrôle des empires ottoman et iranien respectivement. Au XIXe siècle, l'Arménie orientale fut conquise par l'empire russe et la partie occidentale demeura sous l'empire ottoman. Peu après le début de la Première Guerre mondiale, les Arméniens vivant sur leurs terres ancestrales dans l'empire ottoman furent soumis à une extermination systématique, le génocide arménien.
En 1918, après la révolution russe, les pays non russes déclarèrent leur indépendance ce qui entraîne l'établissement de la république démocratique d'Arménie. En 1920, le pays fut incorporé dans la république démocratique fédérative de Transcaucasie qui devint un membre fondateur de l'Union soviétique. En 1936, la république transcaucasienne fut dissoute ce qui entraîna l'émergence de la république socialiste soviétique d'Arménie. La république d'Arménie devint indépendante en 1991 lorsque l'Union soviétique s'est désintégrée.
L'Armenia (in armeno: Հայաստան?, traslitterato: Hayastan), ufficialmente Repubblica di Armenia (in armeno: Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն?, traslitterato: Hayastani Hanrapetut’yun), è uno Stato asiatico[3][4][5][6] indipendente del Caucaso meridionale con capitale Erevan.
Da un punto di vista storico-culturale, il paese è tuttavia a volte considerato europeo[7][8] ed è un membro del Consiglio d'Europa.
L'Armenia confina con la Turchia a ovest, la Georgia a nord, l'Azerbaigian e la repubblica de facto dell'Artsakh (già Nagorno Karabakh) a est, l'Iran e l'exclave azera del Naxçıvan a sud. È quindi uno Stato senza sbocco al mare.
Armenia (en armenio, Հայաստան, Hayastan), conocida oficialmente como República de Armenia, es un país del Cáucaso Sur y sin salida al mar localizado entre Europa y Asia. Comparte frontera al oeste con Turquía, al norte con Georgia, al este con Azerbaiyán y al sur con Irán y el exclave azerbaiyano de Najicheván.
Armenia es una antigua república soviética y un Estado unitario, multipartidista y en un proceso de democratización4 que tiene sus raíces en una de las más antiguas civilizaciones del mundo. Dotada de un rico patrimonio cultural, se destacó como la primera nación en adoptar el cristianismo como religión oficial5 en los primeros años del siglo IV (la fecha tradicional es 301).65 Aunque Armenia es un Estado constitucional secular, la fe cristiana desempeña un papel primordial en su historia y en la identidad del pueblo armenio.
Cultural, histórica y políticamente, Armenia se considera como parte de Europa.78 Sin embargo, su localización en el Cáucaso meridional la sitúa en una supuesta frontera imaginaria entre Europa y Asia: en realidad se trata de un país transcontinental, a medio camino entre los dos ámbitos geográficos.9 Estas clasificaciones son arbitrarias, pues no hay diferencia geográfica fácilmente definible entre Asia y Europa.10
Armenia es actualmente miembro de más de 35 organizaciones internacionales, incluyendo las Naciones Unidas, el Consejo de Europa, el Banco Asiático de Desarrollo, la Comunidad de Estados Independientes, la Organización Mundial del Comercio y la Organización de Cooperación Económica del Mar Negro. Es uno de los integrantes de la Asociación para la Paz de la Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte, así como de la alianza militar Organización del Tratado de la Seguridad Colectiva (OTSC). Es también miembro observador de la Comunidad Económica Eurasiática, de la Francofonía y del Movimiento de Países No Alineados.
Арме́ния (арм. Հայաստան [hɑjɑsˈtɑn]), официальное название — Респу́блика Арме́ния (арм. Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն [hɑjɑstɑˈni hɑnɾɑpɛtuˈtʰjun]) — государство в Закавказье.
Государство расположено на севере Передней Азии, на северо-востоке Армянского нагорья. Выхода к морю не имеет. Граничит с Азербайджаном на востоке; на юго-западе — с Нахичеванской АР, входящей в состав Азербайджана; с Ираном на юге, с Турцией на западе и с Грузией на севере. Имеет транспортную связь с непризнанной Нагорно-Карабахской Республикой[10] (Республика Арцах), осуществляемую с 10 ноября 2020 года через Лачинский коридор, находящегося под контролем российских миротворческих сил[11]. Армения контролирует часть территории, оспариваемой Азербайджаном (анклавы Кярки, Бархударлы, Софулу, Верхняя Аскипара), Азербайджан контролирует часть территории, оспариваемой Арменией (эксклав Арцвашен).
Население Армении на 2017 год составило 2 986 100 человек[12], территория — 29 743 км²[6]. По некоторым данным, занимает сто тридцать шестое место в мире по численности населения и сто тридцать восьмое по территории.
Столица — Ереван. Государственный язык — армянский.
Унитарное государство с парламентской формой правления[13]. С 9 апреля 2018 года президентом Армении является Армен Саркисян. Подразделяется на 10 областей и город Ереван.
Почти 95 % населения исповедует христианство; большинство христиан принадлежит к Армянской апостольской церкви, являющейся одной из Древневосточных церквей[14].
Индустриально-аграрная страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. В структуре ВВП приходится: на сельское хозяйство — 31,1 %, промышленность — 21,8 %, торговлю — 8,7 %, строительство — 8, 5 %, транспорт — 5,1 %, другие сферы — 24,9 %[15]. Объём номинального ВВП за 2018 год составил $ 12,4 млрд (около $ 4238 на душу населения). Денежная единица — армянский драм (усреднённый курс за 2019 год — 475 драмов за $ 1).
28 мая 1918 года была провозглашена независимая Первая Республика Армении. 29 ноября 1920 года в Армении была установлена советская власть и образована


Mutter Armenien (armenisch Մայր Հայաստան Majr Hajastan, russisch Мать-Армения) ist ein Monument im Siegespark der armenischen Hauptstadt Jerewan. Es besteht unter anderem aus einem Militärmuseum, einem Grabmal des unbekannten Soldaten sowie einer Statue.
亚美尼亚之母(亚美尼亚语:Մայր Հայաստան)是位于亚美尼亚首都埃里温胜利公园内的一座雕像,俯瞰整个埃里温。亚美尼亚之母高22米,包含底座在内的话高51米。

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Haruhiko Kuroda
Haruhiko Kuroda
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Kimimasa Tarumizu
Kimimasa Tarumizu
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masao Fujioka
Masao Fujioka
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masatsugu Asakawa
Masatsugu Asakawa
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Mitsuo Sato
Mitsuo Sato
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Shiro Inoue
Shiro Inoue
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Tadao Chino
Tadao Chino
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takeshi Watanabe
Takeshi Watanabe
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Taroichi Yoshida
Taroichi Yoshida
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sweden
Sweden
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tonga
Tonga
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


亚洲开发银行(英语:Asian Development Bank,缩写:ADB,简称亚银、亚行、亚开行),香港旧译亚洲发展银行,属于亚太地区的政府之间金融机构,其目的是为了促进亚洲经济与社会的发展。1966年12月19日成立,有31个创始会员国,目前有68个成员体,其中亚太有49个。总部设置于菲律宾马尼拉并在世界各地拥有31个办事处。亚洲开发银行仿照世界银行的股权制度,依照成员体的资本比例,得到相应比例的投票权。2014年以来,亚洲开发银行发布亚太创意生产指数年度报告。[3][4]亚洲开发银行为联合国观察员。
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966,[4] which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world[5] to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries.[6] From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public.[7] The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. Upon completion of their study programs, scholars are expected to contribute to the economic and social development of their home countries.[8] ADB is an official United Nations Observer.[9]
El Banco Asiático de Desarrollo (BAsD) es una organización financiera para el desarrollo económico de Asia y el Pacífico. Su objetivo principal es la erradicación de la pobreza y facilitar ayudas para mejorar el nivel de vida de la población de la región a través de préstamos y colaboración técnica.
Creado en 1966 por 31 países. Hoy cuenta con 67 miembros (48 regionales y 19 no regionales). Estados Unidos y Japón son sus principales accionistas, con el 15,6% del capital cada uno.
El Banco tiene como su principal objetivo la lucha contra la pobreza. Para ello busca promover el crecimiento económico y la cooperación en la región de Asia-Pacífico, y acelerar el proceso de desarrollo económico de sus países miembros. Las dos terceras partes de personas pobres del mundo (aquellos que viven con menos de dos dólares diarios por persona), cerca de 1.800 millones de pobres, viven en esta región. El BAsD aprobó una nueva Estrategia a Largo Plazo (2008-2020) centrada en un crecimiento económico, medioambientalmente sostenible e integración regional.
Азиа́тский банк разви́тия (англ. Asian Development Bank) — банк, основанный в 1966 году, его главной задачей является стимулировать рост экономики в Азии и на Дальнем Востоке, направляя в эти регионы прямые займы и оказывая техническое содействие.
Штаб-квартира в Маниле (Филиппины). Президентом АБР с 28 апреля 2013 года является японец Такэхико Накао. 17 января 2020 года президентом станет Масацугу Асакава, избранный 2 декабря 2019 года[1].
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 History
History
 Religion
Religion
 Architecture
Architecture
 Geography
Geography
 States of Asia
States of Asia


 Art
Art