
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Silk road
Silk road

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Genf
Genf
 Silk road
Silk road

日内瓦(法语:Genève,发音:[ʒənɛv] ( 聆听);法兰克-普罗旺斯语:Genèva [dzəˈnɛva] (
聆听);法兰克-普罗旺斯语:Genèva [dzəˈnɛva] ( 聆听); 德语:Genf,发音:[ɡɛnf] (
聆听); 德语:Genf,发音:[ɡɛnf] ( 聆听))是瑞士第二大城市,属于瑞士法语区,日内瓦州首府。建在日内瓦湖流入罗讷河之处。今天,日内瓦在国际上享有的高知名度主要得益于众多国际组织设立在此,包括联合国日内瓦办事处。
聆听))是瑞士第二大城市,属于瑞士法语区,日内瓦州首府。建在日内瓦湖流入罗讷河之处。今天,日内瓦在国际上享有的高知名度主要得益于众多国际组织设立在此,包括联合国日内瓦办事处。
日内瓦是一座著名的国际都市,在两次世界大战之间,国际联盟的总部就是设立在此地。今天仍然有许多国际组织在日内瓦设立总部或办事处,包括有国际红十字会的总部。属于联合国的组织有世界卫生组织等。
日内瓦得名于公元前凯尔特人在此建造的古城。罗马将领凯撒在《高卢战记》中提到日内瓦。
日内瓦第一次在拉丁语中出现是在凯撒的著作,在《高卢战记》中他对高卢战争的看法。这个名字最初有可能与位于利古里亚地区的Genua城相同(现热那亚),意思是“膝盖”,也就是指日内瓦的特殊地理位置在一个角落里;然而日内瓦这个名字的由来更有可能建立在gen-“诞生”著个字根上(Genawa位于河流的源头日内瓦湖上;也许日内瓦的意思便是“水的诞生”)。在被罗马征服后,日内瓦变成了“罗马行政区”(Provincia Romana)纳尔榜南西斯高卢的一部分。日内瓦的意大利语名为Ginevra。公元前58年,凯撒在日内瓦包围了西行的赫尔维蒂人。9世纪成为勃艮第首都。虽然日内瓦一直是勃艮第人、法兰克人和神圣罗马帝国争夺的对象,但在实际上日内瓦一直都是被其主教掌治著,直到宗教改革,成为日内瓦共和国。
由于喀尔文等人带领的宗教改革中,日内瓦常被喻为“新教的罗马”。16世纪日内瓦是喀尔文派的中心;老城区的日内瓦圣彼得大教堂便是喀尔文自己的教堂。英格兰玛丽一世因崇信天主教,大力迫害新教徒,因此大量新教学者逃向日内瓦,其中包括后来监督翻译《日内瓦圣经》的威廉·惠廷厄姆(William Whittingham)和他的合作者迈尔斯·科弗代尔(Miles Coverdale)、克里斯托弗·古德曼(Christopher Goodman)、安东尼·吉尔比(Anthony Gilby)、托马斯·桑普森(Thomas Sampson)和威廉·科尔(William Cole)。
Genf (schweizerdeutsch Gämf, Gänf, Genf; französisch Genève [ʒənɛv, ʒnɛv]; frankoprovenzalisch Geneva [ðəˈnɛva, ˈzɛnəva]; italienisch Ginevra; rätoromanisch  Genevra?/i) ist eine Stadt und politische Gemeinde sowie der Hauptort des Kantons Genf in der Schweiz.
Genevra?/i) ist eine Stadt und politische Gemeinde sowie der Hauptort des Kantons Genf in der Schweiz.
Die Stadt liegt am südwestlichen Zipfel der französischen Schweiz (Romandie) in der Genferseeregion am Ausfluss der Rhone aus dem Genfersee. Mit ihren 203'951 Einwohnern (31. Dezember 2019) ist Genf nach Zürich die zweitgrösste Stadt der Schweiz.[5] 47,9 Prozent[6] der Einwohner verfügen nicht über das Schweizer Bürgerrecht, womit Genf neben Basel und Lausanne zu den Schweizer Städten mit sehr hohem Ausländeranteil zählt.[7] Die statistische Bevölkerungsdichte hat mit 12'835 Einwohnern pro Quadratkilometer einen äusserst hohen Wert für Schweizer Verhältnisse. Die 1,2 Millionen Einwohner zählende Metropolregion Genf-Lausanne ist ein erweiterter Ballungsraum und ist der bedeutendste der französischen Schweiz.
Die Stadt Genf beheimatet neben New York City weltweit die meisten internationalen Organisationen, darunter UNO, CERN, IKRK, WHO, IAO, IOM, ISO, IEC, ITU, WIPO, WMO, WOSM und WTO. Zusammen mit Basel (Bank für Internationalen Zahlungsausgleich), New York City (UNO-Hauptquartier) und Strassburg (Europarat) zählt Genf zu den wenigen Städten der Welt, die als Sitz einer der gemeinhin als wichtigsten erachteten internationalen Organisationen fungieren, ohne die Hauptstadt eines Staates zu sein.[8] Zudem sind hier 175 Staaten diplomatisch vertreten, so unterhalten einige die diplomatische Repräsentanz in der Schweiz nicht in der Bundesstadt Bern, sondern in Genf.
Genf ist nach Zürich der zweitgrösste Finanzplatz der Schweiz, gefolgt von Lugano. In einer Rangliste der wichtigsten Finanzzentren weltweit belegt Genf im Jahr 2018 den 26. Platz.[9]
Seit Jahren wird Genf neben Zürich und Basel als Teil der zehn Städte mit der weltweit besten Lebensqualität[10] und zugleich mit den global höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten[11][12][13] gelistet. 2018 waren 18,6 Prozent der Bevölkerung Millionäre (gerechnet in US-Dollar). Genf ist damit, hinter Monaco, die Stadt mit der zweithöchsten Millionärsdichte weltweit.
ジュネーヴ(仏: Genève)は、スイス西部、レマン湖の南西岸に位置する都市(コミューヌ)。フランス語圏に属し、ジュネーヴ州の州都である。
人口は約19万人(2011年)、面積は15.93平方キロメートル、標高は375メートル。チューリッヒに次ぎスイス第2の都市[1]。金融業が発達しており、プライベードバンクの中心地である。
三日月形のレマン湖の南西側の角を取り囲むように広がり、サレーヴ山(Mont Salève)、ジュラ山脈等の山地に囲まれる。市内をアルヴ川、ローヌ川が流れる[2]。
『ジュネーヴ家族由来の著名人家系 -起こりから今日まで-』[3]という本が、土地の有力者とフランスのそれにまたがる閨閥の形成過程を17世紀から具体的に記している。第6巻まではインターネットアーカイブで見ることができる。最新巻は第7巻である。ピクテ銀行やロンバー・オディエ銀行等を営む各家系も登場する。そのような由緒あるプライベートバンクの本店がジュネーヴには集中している。
この世界都市にはロスチャイルド家のシャトー・ド・プレニーがあり、第二次世界大戦前には国際連盟の本部が置かれた。現在も国際連合の専門機関など多くの国際機関が所在し、条約の作成やさまざまな国際会議が行われている。
そのため、日本も特命全権大使を長とする在ジュネーブ国際機関日本政府代表部、及び、軍縮会議日本政府代表部を置いている。ただし、領事業務はこれらの代表部ではなく、在ジュネーブ領事事務所(旧・在ジュネーブ日本国総領事館)で行っている。
ジュネーヴでは、サロン・アンテルナショナル・ド・ロト(ジュネーヴ・モーターショー)、国際高級宝飾時計展(ジュネーヴ・サロン)をはじめとする様々な国際見本市が催される。日本の民間研究所が2016年に発表した「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界30位と評価された[4]。また、アメリカのシンクタンクが2016年に発表した世界都市ランキングでは世界36位と評価された[5]。
スイスの公用語は、ドイツ語、フランス語、イタリア語、ロマンシュ語の4言語であるが、フランス語圏のジュネーヴでは、ほとんどの場合フランス語が用いられる。世界都市であるため、基本的に英語も通用する。
Geneva (/dʒɪˈniːvə/ jin-EE-və;[4] French: Genève [ʒənɛv] ( listen); Arpitan: Genèva [dzəˈnɛva] (
listen); Arpitan: Genèva [dzəˈnɛva] ( listen); German: Genf [ɡɛnf] (
listen); German: Genf [ɡɛnf] ( listen); Italian: Ginevra [dʒiˈneːvra]; Romansh: Genevra) is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Republic and Canton of Geneva.
listen); Italian: Ginevra [dʒiˈneːvra]; Romansh: Genevra) is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Republic and Canton of Geneva.
The municipality (ville de Genève) has a population (as of December 2020) of 203,856, and the canton (essentially the city and its inner-ring suburbs) has 506,343 residents.[5] In 2014, the compact agglomération du Grand Genève had 946,000 inhabitants in 212 communities in both Switzerland and France.[6] Within Swiss territory, the commuter area named "Métropole lémanique" contains a population of 1.26 million.[7][8] This area is essentially spread east from Geneva towards the Riviera area (Vevey, Montreux) and north-east towards Yverdon-les-Bains, in the neighbouring canton of Vaud.
Geneva is a global city, a financial centre, and a worldwide centre for diplomacy due to the presence of numerous international organizations, including the headquarters of many agencies of the United Nations[9] and the Red Cross.[10] Geneva hosts the highest number of international organizations in the world.[11] It is also where the Geneva Conventions were signed, which chiefly concern the treatment of wartime non-combatants and prisoners of war. Together with, for instance, New York City (global headquarters of the UN), Basel (Bank for International Settlements), and Strasbourg (Council of Europe), Geneva is a city serving as the headquarters of one of the most important international organizations, without being the capital of a country.[12][13][14]
In 2021, Geneva was ranked as the world's ninth most important financial centre for competitiveness by the Global Financial Centres Index, fifth in Europe behind London, Zürich, Frankfurt and Luxembourg.[15] In 2019, Geneva was ranked among the ten most liveable cities in the world by Mercer together with Zürich and Basel.[16] The city has been referred to as the world's most compact metropolis[17] and the "Peace Capital".[18] In 2019, Mercer ranked Geneva as the thirteenth most expensive city in the world.[19] In a UBS ranking of global cities in 2018, Geneva was ranked first for gross earnings, second most expensive, and fourth in purchasing power.[20]
Genève est une ville suisse située à l’extrémité sud-ouest du Léman. Elle est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée de Suisse après Zurich. Elle est le chef-lieu et la commune la plus peuplée du canton de Genève (GE). Fin 2020, la ville comptait 205 007 habitants3. Son aire métropolitaine, ou aire urbaine, forme une agglomération transfrontalière : le « Grand Genève », qui s'étend sur le canton de Vaud et les départements français de l'Ain et de la Haute-Savoie, pour une population totale en décembre 2019 de 1 031 903 habitants (506 765 pour le canton de Genève4, 423 283 pour le pôle métropolitain du Genevois français5 et 101 855 pour le district de Nyon6). L'agglomération genevoise stricto sensu compte 608 620 habitants au 31 décembre 20197,4.
Genève est la ville qui accueille le plus d'organisations internationales au monde8. Le canton de Genève accueille 39 organisations internationales et 431 organisations non gouvernementales (ONG)9. Le siège européen des Nations unies, le Comité international de la Croix-Rouge (CICR), l'Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), l'Organisation mondiale de la santé (OMS), font partie de ces organisations internationales.
Genève et New York sont les deux centres de coopération internationale les plus importants du monde, Genève étant le plus important en nombre d'institutions, de réunions et de congrès10. L'Office des Nations unies à Genève (ONUG) est le centre de diplomatie multilatérale le plus actif au monde11 et il a été le théâtre de nombreuses négociations historiques. Avec notamment Bâle, New York et Strasbourg, Genève est le siège de plusieurs institutions internationales sans être capitale politique d’un État12.
Genève est la deuxième place financière du pays après Zurich. Elle est considérée comme la plus importante au monde en matière de gestion de fortune privée trans-nationale13 et s’impose entre autres comme la première place mondiale pour le négoce du pétrole devant Londres14. Du fait de son rôle à la fois politique et économique, elle fait partie des « villes mondiales ». Selon une étude de 2019 menée par Mercer Consulting15, Genève arrive (avec Zurich et Bâle) parmi les dix premières métropoles qui offrent la meilleure qualité de vie au monde. La ville est aussi connue comme une des plus coûteuses, se disputant chaque année la première place du classement des villes les plus chères du monde avec Zurich16,17, ce qui fait que les ménages genevois disposent en 201618, à revenu égal, du revenu disponible le plus bas de Suisse ; ceci est cependant très largement compensé par un revenu brut moyen (et médian) parmi les plus élevés de Suisse19,20.
La langue officielle de la ville est le français. Genève enregistre 3,23 millions de nuitées en 201821, ce qui contribue à sa caractéristique de « ville mondiale ». Le jet d'eau de Genève, culminant à 140 m, est depuis 1891 l'un des principaux attraits touristiques de la ville.
Ginevra (in francese e ufficialmente: Genève /ʒə.nɛv/; in tedesco: Genf /ˈgɛɱf/; in romancio: Genevra) è un comune svizzero di 201 818 abitanti del Canton Ginevra; ha lo status di città ed è la capitale del cantone. È la seconda città più popolata del paese dopo Zurigo e la terza piazza finanziaria più importante della Svizzera dopo Zurigo e Basilea.
È situata dove il Lago di Ginevra riconfluisce nel fiume Rodano.[1] Nel 2019 Ginevra è stata classificata da Mercer, insieme a Zurigo e Basilea, tra le dieci città più vivibili al mondo.[2]
Ginebra (en francés: Genève [ʒə.nɛv]; en arpitano: Genèva [dzəˈnɛva]; en alemán: Genf [ɡɛnf])2 es una ciudad y comuna de la Confederación Suiza, ubicada cerca de la frontera con Francia, capital del cantón de Ginebra. Es la ciudad más poblada de Romandía y la segunda de Suiza después de Zúrich. Se encuentra situada a la salida del Ródano del lago de Ginebra y es la capital de la República y Cantón de Ginebra.
En sí (la ville de Genève) tiene una población (en agosto de 2013) de 194 458 habitantes y el cantón (que incluye la ciudad) tiene 474 169 habitantes. En 2011, el área metropolitana (Grand Genève) tenía una población de 915 000 habitantes incluida la parte francesa. En territorio suizo, el área de tránsito (conocida como Métropole lémanique) tenía una población de 1,25 millones de habitantes. Esta zona se extiende al este de Ginebra hacia la zona de Riviera (Vevey, Montreux) y al noreste hacia Yverdon-les-Bains, en el vecino cantón de Vaud.
Ginebra es una ciudad global, centro financiero y mundial de la diplomacia debido a la presencia de numerosas organizaciones internacionales, entre ellas la sede de muchos de los organismos de las Naciones Unidas3 y la Cruz Roja.4 De hecho, Ginebra es la ciudad que alberga el mayor número de organizaciones internacionales del mundo.5 Es también el lugar donde se firmaron los Convenios de Ginebra, que principalmente se refieren al tratamiento, en situaciones bélicas, de los no combatientes y los prisioneros de guerra.
Junto con Nueva York, Basilea y Estrasburgo, Ginebra es una de las pocas ciudades del mundo que es sede de varias instituciones internacionales sin ser la capital política de un estado.6
Ginebra fue posicionada como el noveno centro mundial financiero más importante en cuanto a competitividad en el Índice Global de Centros Financieros, por delante de Fráncfort, y el tercero en Europa después de Londres y Zúrich.7 La ciudad ha sido conocida como la metrópolis más compacta del mundo y la "capital de la paz".8 Sin embargo, entre 2009 y 2011, Ginebra apareció como la cuarta y quinta ciudad, respectivamente, más cara del mundo.9 En 2019 Ginebra, fue clasificada entre las diez ciudades más habitables del mundo por Mercer junto con Zúrich y Basilea.10
Жене́ва (фр. Genève [ʒəˈnɛv], франкопров. Geneva, нем. Genf, итал. Ginevra, романш. Genevra) — город на юго-западе Швейцарии. Столица одноимённого франкоязычного кантона и административный центр одноимённой коммуны.
С населением в 201 тыс. человек (2017 год) Женева является вторым по величине городом страны. Иностранные граждане составляют 48 % населения. В пределах трансграничной агломерации «Большая Женева» проживает 915 тыс. человек. Расположена на берегах Женевского озера при выходе из него реки Роны, у границы с Францией. В 2014 году была названа лучшим городом для проживания[4].
В городе расположены штаб-квартиры многочисленных международных организаций, в том числе Европейского отделения ООН, Красного Креста, ВТО, ВОЗ, ЦЕРН, до 1946 года — Лиги Наций. Женева также является мировым финансовым центром. Вблизи города расположен Большой адронный коллайдер. Наряду с Базелем, Нью-Йорком и Страсбургом, Женева является одним из немногих городов мира, в котором находится одна из влиятельных международных организаций и который при этом не является столицей какой-либо страны.
Река Рона делит город на две части. На левом берегу Роны исторический центр с собором Святого Петра и готической ратушей, на правом берегу — Дворец Наций и железнодорожный вокзал. Главная достопримечательность — фонтан высотой 147 метров.
Впервые упоминается Юлием Цезарем как кельтское поселение Генава в I веке до н. э. В средние века была под властью различных европейских государств. В XVI веке проведена Реформация, на рубеже XVIII—XIX веков находилась в составе наполеоновской Франции. В 1815 году на правах кантона вошла в состав Швейцарии.
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990

 History
History

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Italy
Italy

 Liguria
Liguria
 Genua
Genua
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port

热那亚(意大利语:Genova,英语:Genoa),意大利最大商港和重要工业中心,利古里亚大区和同名省热那亚省的首府。位于意大利西北部,利古里亚海热那亚湾北岸。热那亚历史悠久,曾是海洋霸主热那亚共和国的首都,2004年热那亚被选为当年的“欧洲文化首都”。热那亚还是著名航海家克里斯托弗·哥伦布和小提琴大师尼科罗·帕格尼尼的家乡。热那亚及其所在的利古里亚海岸沿岸为著名旅游胜地。
Genua (italienisch Genova [ˈdʒɛːnova], im Ligurischen Zena) ist die Hauptstadt der italienischen Region Ligurien. Das im Nordwesten des Landes am Ligurischen Meer gelegene ehemalige Zentrum der im Mittelalter bedeutenden Republik Genua ist heute Verwaltungssitz einer gleichnamigen Metropolitanstadt. Die Stadt ist mit circa 590.000 Einwohnern die sechstgrößte Italiens.[2] In der Agglomeration hat Genua rund 800.000 Einwohner und 1,5 Millionen in der Metropolregion.[3] Die Prachtstraßen Le Strade Nuove mit den Renaissance- und Barockbauten der Palazzi dei Rolli im Zentrum der Altstadt wurden im Jahre 2006 von der UNESCO zum Welterbe erklärt.
ジェノヴァ(伊: Genova (![]() 音声ファイル))は、イタリアの北西部にある都市。その周辺地域を含む人口約58万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。リグーリア州の州都であり、ジェノヴァ県の県都である。ジェノバとも表記する。
音声ファイル))は、イタリアの北西部にある都市。その周辺地域を含む人口約58万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。リグーリア州の州都であり、ジェノヴァ県の県都である。ジェノバとも表記する。
リグリア海に面した港湾都市で、中世には海洋国家(ジェノヴァ共和国)として栄え、商工業・金融業の中心地としての長い歴史を持つ。現代においてもミラノ、トリノなど北イタリアの産業都市を背後に持つジェノヴァ港はイタリア最大の貿易港であり、地中海有数のコンテナ取扱高を誇っている。
Genoa (/ˈdʒɛnoʊ.ə/ JEN-oh-ə; Italian: Genova [ˈdʒɛːnova] (![]() listen); Ligurian: Zêna [ˈzeːna]; English, historically, and Latin: Genua) is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits.[1] As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Genoa, which in 2015 became the Metropolitan City of Genoa,[2] counted 855,834 resident persons.[3] Over 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera.[4]
listen); Ligurian: Zêna [ˈzeːna]; English, historically, and Latin: Genua) is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits.[1] As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Genoa, which in 2015 became the Metropolitan City of Genoa,[2] counted 855,834 resident persons.[3] Over 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera.[4]
Located on the Gulf of Genoa in the Ligurian Sea, Genoa has historically been one of the most important ports on the Mediterranean: it is currently the busiest in Italy and in the Mediterranean Sea and twelfth-busiest in the European Union.[5][6] Genoa has been nicknamed la Superba ("the proud one") due to its glorious past and impressive landmarks.[7] Part of the old town of Genoa was inscribed on the World Heritage List (UNESCO) in 2006 as Genoa: Le Strade Nuove and the system of the Palazzi dei Rolli. The city's rich cultural history in art, music and cuisine allowed it to become the 2004 European Capital of Culture. It is the birthplace of Christopher Columbus, Andrea Doria, Niccolò Paganini, Giuseppe Mazzini, Renzo Piano and Grimaldo Canella, founder of the House of Grimaldi, among others.
Genoa, which forms the southern corner of the Milan-Turin-Genoa industrial triangle of Northwest Italy, is one of the country's major economic centers.[8][9] The city has hosted massive shipyards and steelworks since the 19th century, and its solid financial sector dates back to the Middle Ages. The Bank of Saint George, founded in 1407, is among the oldest in the world and has played an important role in the city's prosperity since the middle of the 15th century.[10][11] Today a number of leading Italian companies are based in the city, including Fincantieri, Selex ES,[12] Ansaldo Energia,[13] Ansaldo STS, Edoardo Raffinerie Garrone, Piaggio Aerospace, Mediterranean Shipping Company and Costa Cruises.
Gênes (italien : Genova, en ligurien : Zena) est une ville italienne, située dans le Golfe de Gênes en face de la Mer de Ligurie, capitale de la Ligurie. Il s'agit de l'un des principaux ports italiens et de l'un des plus grands ports de la mer Méditerranée. En 2017, elle compte 580 112 habitants et 846 363 au sein de son agglomération. Sa zone urbaine compte environ 1 540 000 habitants.
Gênes, avec Milan et Turin, délimite le « triangle industriel », zone la plus industrialisée d'Italie. En outre à Gênes se trouve la quatrième meilleure université du pays. La ville est un centre important pour les sciences, la technologie, la mode et le sport, considérée comme le berceau du football italien. Une partie importante du centre historique est sous la protection de l'UNESCO.
Gênes est l'une des plus grandes villes de Méditerranée et la principale de la mer de Ligurie.
Genova (IPA: /ˈʤɛnova/, Zena /ˈzeːna/ in ligure[3]) è un comune italiano di 578 924 abitanti[1] , capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana[4] e della regione Liguria, sesto comune italiano e terzo del Nord Italia[5] per popolazione, quinto per movimento economico, parte del triangolo industriale Milano-Torino-Genova. La città che appartiene ad un agglomerato urbano di 862.885 abitanti[6], ed è cuore di una vasta area metropolitana di oltre 1.510.000 abitanti[7][8][9][10], è il più grande comune della Liguria.
Affacciata sul Mar Ligure, la sua storia è legata alla marineria e al commercio. È nota, tra l'altro, per aver dato i natali a Cristoforo Colombo, Giuseppe Mazzini, Goffredo Mameli e Niccolò Paganini. Il suo porto è uno dei più importanti italiani ed europei.[11][12][13]. Simbolo "fisico" della città è il suo faro, conosciuto come la Lanterna, mentre viene tradizionalmente rappresentata dalla Croce di San Giorgio, negli stemmi sorretta da due grifoni. Per oltre otto secoli capitale dell'omonima repubblica, Genova è stata citata con gli appellativi di "La Superba" e "La Dominante".[14]
Génova (en italiano, Genova, pronunciado ![]() [dʒɛːnova] (?·i); Zena en el dialecto genovés del idioma ligur) es la sexta ciudad italiana y la tercera del Norte de Italia por población, ya que cuenta con 609 746 habitantes y la cuarta ciudad por movimiento económico. Es la capital de la provincia homónima y de la región de Liguria. El área urbana cuenta con 850 000 habitantes y el "Área Metropolitana Genovese" cuenta con 1 510 000 habitantes.2
[dʒɛːnova] (?·i); Zena en el dialecto genovés del idioma ligur) es la sexta ciudad italiana y la tercera del Norte de Italia por población, ya que cuenta con 609 746 habitantes y la cuarta ciudad por movimiento económico. Es la capital de la provincia homónima y de la región de Liguria. El área urbana cuenta con 850 000 habitantes y el "Área Metropolitana Genovese" cuenta con 1 510 000 habitantes.2
En el último siglo, Génova ha crecido absorbiendo a 25 municipios del litoral y de los valles; actualmente está dividida en 25 circunscripciones y 71 unidades urbanas. Hacia el oeste de Sampierdarena conserva algunas villas de los siglos XVI y XVII.
Génova también posee el segundo acuario más grande de la Unión Europea, tras el Oceanográfico de Valencia.34
La vida de la ciudad, desde sus orígenes, estuvo unida a su puerto y a las actividades marineras que fueron el punto de referencia constante de toda su historia política y cultural durante su famosa República de Génova.
Ге́нуя (итал. Genova [ˈdʒɛːnova], лиг. Zena [ˈzeːna], лат. Genua, Ianua) — город на севере Италии. Административный центр региона Лигурия и одноимённой провинции Генуя.
Население — около 580 тыс. человек (2017 год)[2], шестой по величине город страны. Образует агломерацию Большая Генуя с населением свыше 1,5 миллиона человек. Расположен на северо-западе Италии, на берегу Генуэзского залива Лигурийского моря. Вытянулся узкой полосой более чем на 30 км и ограничен с двух сторон морем и Апеннинскими горами. Центр Лигурийской Ривьеры.
Является крупнейшим морским портом Италии. Также в городе расположены международный аэропорт имени Христофора Колумба и метрополитен. Исторический центр примыкает к старому порту. Дворцы знати Палацци-деи-Ролли, находятся под охраной ЮНЕСКО.
В древности — поселение лигуров, завоёванное римлянами в III веке до н. э. С XI века вела активную торговлю в Средиземном море; благодаря участию в крестовых походах превратилась в могущественную Генуэзскую республику с многочисленными заморскими колониями. После поражения в войне с Венецией и смещения торговых путей в Атлантический океан в XIV—XVI веках пришла в упадок, потеряв независимость в 1797 году. Родина Христофора Колумба.

哥德堡(瑞典语:Göteborg, 发音:[jœtɛˈbɔrj] ![]() 聆听)是瑞典的第二大城市,仅次于首都斯德哥尔摩。哥德堡近邻挪威,也是瑞典经济最发达的城市之一。哥德堡是瑞典享誉全球的汽车制造厂沃尔沃汽车之创厂地,而瑞典超级足球联赛中的哥登堡足球会则是一支以哥德堡为主场的球队。同时它也拥有在斯堪的纳维亚地区最多学生的哥德堡大学(Göteborgs universitet)。
聆听)是瑞典的第二大城市,仅次于首都斯德哥尔摩。哥德堡近邻挪威,也是瑞典经济最发达的城市之一。哥德堡是瑞典享誉全球的汽车制造厂沃尔沃汽车之创厂地,而瑞典超级足球联赛中的哥登堡足球会则是一支以哥德堡为主场的球队。同时它也拥有在斯堪的纳维亚地区最多学生的哥德堡大学(Göteborgs universitet)。
约塔河在哥德堡流入卡特加特海湾,将城市分成了两个部分。约塔河的入海口很适合作为港口,因此哥德堡也是北欧国家里最大的港口城市之一。
(schwedisch [ˌʝøtəˈbɔrj]; deutsch veraltet Gotenburg oder Gothenburg; lateinisch Gothoburgum, englisch Gothenburg, dänisch Gøteborg) ist eine Großstadt in den schwedischen Provinzen Västra Götalands län, deren Residenzstadt sie ist, und Hallands län sowie den historischen Provinzen Västergötland, Bohuslän und Halland.
Göteborg ist nach Stockholm und vor Malmö die zweitgrößte Stadt Schwedens; denselben Rang nimmt auch die Storgöteborg („Groß-Göteborg“) genannte, 13 Gemeinden umfassende Metropolregion mit 993.453 Einwohnern (Stand 30. September 2016) ein.[2] Die Stadt gliedert sich in zehn Stadtbezirke.
Gothenburg (/ˈɡɒθənbɜːrɡ/ (![]() listen);[5] abbreviated Gbg;[6][7] Swedish: Göteborg [jœtɛˈbɔrj] (
listen);[5] abbreviated Gbg;[6][7] Swedish: Göteborg [jœtɛˈbɔrj] (![]() listen)) is the second-largest city in Sweden and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and part of Västra Götaland County. It is situated by Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 570,000 in the city center and about 1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area.[1]
listen)) is the second-largest city in Sweden and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and part of Västra Götaland County. It is situated by Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 570,000 in the city center and about 1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area.[1]
Gothenburg was founded as a heavily fortified, primarily Dutch, trading colony, by royal charter in 1621 by King Gustavus Adolphus. In addition to the generous privileges (e.g. tax relaxation) given to his Dutch allies from the then-ongoing Thirty Years' War, the king also attracted significant numbers of his German and Scottish allies to populate his only town on the western coast. At a key strategic location at the mouth of the Göta älv, where Scandinavia's largest drainage basin enters the sea, the Port of Gothenburg is now the largest port in the Nordic countries.[8]
Gothenburg is home to many students, as the city includes the University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology. Volvo was founded in Gothenburg in 1927.[9] The original parent Volvo Group and the now separate Volvo Car Corporation are still headquartered on the island of Hisingen in the city. Other key companies are SKF and Astra Zeneca.
Gothenburg is served by Göteborg Landvetter Airport 30 km (19 mi) southeast of the city center. The smaller Göteborg City Airport, 15 km (9.3 mi) from the city center, was closed to regular airline traffic in 2015.
The city hosts some of the largest annual events in Scandinavia. The Gothenburg Film Festival, held in January since 1979, is the leading Scandinavian film festival with over 155,000 visitors each year.[10] In summer, a wide variety of music festivals are held in the city, such as Way Out West and Metaltown.
Göteborg (en suédois /ˌʝøːtəˈbɔrʲ/ Écouter mais aussi utilisé en français), ou Gothembourg (nom français mais peu usité), est la cinquième ville des pays nordiques et la plus grande qui ne soit pas une capitale. Göteborg est la deuxième localité de la Suède par l'importance de son poids démographique ainsi que par son industrie et ses activités économiques. La ville est située à mi-chemin entre Oslo et Copenhague, sur le fleuve Göta älv à quelques kilomètres de son embouchure dans le Cattégat, dégagé des glaces pendant l'hiver.
La commune de Göteborg (en suédois Göteborgs kommun) compte, en 2010, 522 259 habitants (appelés les Gothembourgeois). L’agglomération, qui couvre également des communes immédiatement environnantes, compte 549 839 habitants et l’aire urbaine appelée Stor-Göteborg (Grand Göteborg), élargie à encore d’autres communes, comprend 905 729 habitants. Göteborg est le chef-lieu du comté de Västra Götaland (Västra Götalands län), siège d'une cour d'appel, d'une université, d'une école polytechnique et d'un évêché. C'est aussi un centre culturel important (musée des beaux-arts, opéra, orchestre symphonique) et le principal port de Scandinavie.
Göteborg (en suédois /ˌʝøːtəˈbɔrʲ/ Écouter mais aussi utilisé en français), ou Gothembourg (nom français mais peu usité), est la cinquième ville des pays nordiques et la plus grande qui ne soit pas une capitale. Göteborg est la deuxième localité de la Suède par l'importance de son poids démographique ainsi que par son industrie et ses activités économiques. La ville est située à mi-chemin entre Oslo et Copenhague, sur le fleuve Göta älv à quelques kilomètres de son embouchure dans le Cattégat, dégagé des glaces pendant l'hiver.
La commune de Göteborg (en suédois Göteborgs kommun) compte, en 2010, 522 259 habitants (appelés les Gothembourgeois). L’agglomération, qui couvre également des communes immédiatement environnantes, compte 549 839 habitants et l’aire urbaine appelée Stor-Göteborg (Grand Göteborg), élargie à encore d’autres communes, comprend 905 729 habitants. Göteborg est le chef-lieu du comté de Västra Götaland (Västra Götalands län), siège d'une cour d'appel, d'une université, d'une école polytechnique et d'un évêché. C'est aussi un centre culturel important (musée des beaux-arts, opéra, orchestre symphonique) et le principal port de Scandinavie.
Göteborg (pronuncia svedese [jœtəˈbɔrj][2] ), in italiano Gotemburgo[3], è una città della Svezia meridionale, situata nella contea di Västra Götaland e collocata nella provincia storica del Västergötland, sebbene alcuni sobborghi cittadini si estendano nella provincia di Bohuslän. Fu fondata nel 1621 dal re Gustavo II Adolfo.
Göteborg ha circa mezzo milione di abitanti, è la seconda città più popolosa della Svezia dopo Stoccolma e la quinta del Nord Europa. Se si considera l'intera area metropolitana, gli abitanti diventano più di 940.000.
Gotemburgo1 (en sueco, Göteborg ![]() [jœteˈbɔrj] (?·i)) es la segunda ciudad en importancia y tamaño de Suecia, después de la capital, Estocolmo. Ubicada en la provincia de Västra Götaland en la costa oeste del país, en la desembocadura del río Göta älv en el estrecho de Kattegat. Es la sede administrativa y arzobispal de la provincia.
[jœteˈbɔrj] (?·i)) es la segunda ciudad en importancia y tamaño de Suecia, después de la capital, Estocolmo. Ubicada en la provincia de Västra Götaland en la costa oeste del país, en la desembocadura del río Göta älv en el estrecho de Kattegat. Es la sede administrativa y arzobispal de la provincia.
Su puerto es el más grande entre los países nórdicos ya que tiene sus aguas descongeladas durante todo el año. Es el lugar de tránsito de la mayor parte de las exportaciones e importaciones de Suecia.
Grandes industrias como SKF y AB Volvo tienen sus oficinas principales en esta ciudad. Sede de dos establecimientos universitarios, tiene la población universitaria más numerosa de Escandinavia. En las últimas décadas se ha desarrollado el turismo y los eventos culturales.
Fue fundada y fortificada en 1621 por el rey Gustavo II Adolfo, después de varios intentos fallidos de fundación debido a los ataques de daneses y noruegos.
Гётеборг, Йётеборг[2] (швед. Göteborg, (Göteborg , /jœte'bɔrj/)) — город на юго-западе Швеции в лене Вестра-Гёталанд. Является вторым по величине городом Швеции после Стокгольма. Площадь города примерно — 450 км².
Расположен на берегу пролива Каттегат в устье реки Гёта-Эльв[3].
 China
China
 Chinese Super League 2019
Chinese Super League 2019
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1991
Women's Soccer World Cup 1991

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race

 Important port
Important port

广州,简称穗,别称羊城、花城,广东省省会,位于广东省中南部,东江、西江、北江交汇处,珠江三角洲北缘,濒临中国南海。
广州对外贸易发达,得益于良好的地理位置,广州自秦汉至明清,一直是中国对外贸易的重要港口城市。汉武帝时期,即有中国船队从广州出发,远航至东南亚和南亚诸国通商贸易。到明清时期,广州更是特殊开放的口岸,较长时间内曾是全国唯一的对外贸易港口城市。
每年春秋两季专门在广州举办的“中国进出口商品交易会”(即“广交会”),与世界200多个国家和地区建立经贸联系,吸引了大量的客商及投资者。
广州(英语:Canton,拼音:Guǎngzhōu,注音:ㄍㄨㄤˇ ㄓㄡ,粤拼:gwong2 zau1),简称穗或广,别称羊城,为广东省省会。广州于1921年正式设市,开创中国市政建制,现在是副省级市。广州是国家中心城市、华南地区的经济、文化、科技和教育中心及交通枢纽,也是中国人民解放军南部战区联合作战指挥部所在地[9]。2010年亚洲运动会在广州举行。
广州拥有2200年以上历史,古代广州水网密布,水城历史悠久于威尼斯,河道在清代后由于城建变迁而逐渐泯没[10]。为中国首批历史文化名城之一,是中国南方最大、历史最悠久的对外通商口岸,也是全国首批对外开放的14个沿海城市之一,世界著名的港口城市之一。广州港是中国大陆第五大港口,世界第八大港口[11]。由于经济水平发达、发展程度优秀,广州与北京、上海、深圳并称为中国内地四大一线城市。据联合国《2016年中国城市可持续发展报告》显示,广州人类发展指数蝉联中国大陆35个主要城市第一[8]。
广州地处华南,广东省的东南部,珠江三角洲中北缘,西江、北江、东江三江汇合处,濒临南海,东连东莞市和惠州市博罗、龙门两县,西邻佛山市的三水、南海和顺德三区,北靠清远市的市区和佛冈县及韶关市的新丰县,南接中山市,毗邻香港、澳门特别行政区,地理位置优越,是“海上丝绸之路”的起点之一[12],被称为中国的“南大门”[13]。
Guangzhou, die Hauptstadt der Provinz Guangdong, liegt im nördlichen Teil des Deltas des Perflusses. Sie hat eine Gesamtfläche von 7400 km². Sie ist eine der bekanntesten Kulturstädte Chinas. Heutzutage ist sie die größte Industrie- und Handelsstadt und der größte Außenhandelshafen in Südchina. Die fünf Ziegenstatuen im Yuexiu-Park sind das Stadtwappen der Stadt Guangzhou. Daher wird Guangzhou auch „Ziegenstadt" genannt. Guangzhous wichtige Sehenswürdigkeiten und historische Stätten sind das Zhenghai-Gebäude, der Tempel für fünf Unsterblichen, der Ahnentempel der Familie Chen, das Mausoleum des Königs des Südlichen Yue-Reiches und die Gedächtnishalle für Dr. Sun Yat-sen. Traditionelle und moderne Bauwerke stehen harmonisch nebeneinander und bieten zusammen mit der Lokaloper und dem ausgeprägten Brauchtum einen schönen und faszinierenden Anblick. Dank des subtropischen Monsunklimas sind die Bäume und Rasen das ganze Jahr hindurch grün und die Blumen blühen. Daher wird Guangzhou auch als „Blumenstadt" bezeichnet. Sie liegt verkehrsgünstig und ist malerisch. Guangzhous gastfreundliche Bevölkerung heißt alle ihre Gäste herzlich willkommen. (Quelle: http://www.deviko.de/china/reiseziele/guangzhou.php)
Guangzhou (Exonym: Kanton bzw. Canton, chinesisch 廣州市 / 广州市, Pinyin Guǎngzhōu Shì, IPA (hochchinesisch) [kwɑŋ21ʈʂɔw5], Jyutping Gwong2zau1Si5, Abk.: 穗, Suì) ist eine Stadt im Süden der Volksrepublik China mit 11.114.200 Einwohnern im geographischen Stadtgebiet und 14.043.500 Einwohnern im administrativen Stadtgebiet (Stand Jahresende 2011 bzw. 2016[1][2]). Sie ist Hauptstadt der Provinz Guangdong sowie ein bedeutender Industrie- und Handelsstandort. Die Region wird auch als „Fabrik der Welt“ bezeichnet.
Guangzhou ist die größte Stadt im Perlflussdelta, einer der größten zusammenhängenden Stadtlandschaften (Megalopolen) weltweit. Zum Perlfluss-Delta gehören neben Guangzhou unter anderem die Millionenstädte Hongkong, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan, Jiangmen, Huizhou, Zhongshan und Zhuhai. Insgesamt wohnen hier auf einer Fläche, die in etwa der von Baden-Württemberg entspricht, über 100 Millionen Menschen.
Die im Deutschen (und ähnlich in anderen westlichen Sprachen) verwendete Bezeichnung Kanton geht auf den Namen der Provinz Guangdong zurück. In China wird Guangzhou auch 穗城, Suìchéng ‚Stadt der Ähren‘ oder 羊城, Yángchéng ‚Stadt der Ziegen‘ genannt. Das Wahrzeichen der Stadt ist eine Statue mit fünf Ziegen. Die Nähe zu Hongkong hat – wie im gesamten Perlflussdelta – einen positiven Einfluss auf die wirtschaftliche Entwicklung gehabt. In Guangzhou findet zweimal jährlich – im Frühjahr und im Herbst – die Canton Fair, Chinas größte Import- und Exportmesse, statt. Im Oktober 2010 wurde hier der damals höchste Fernsehturm der Welt (Canton Tower, 600 m) eröffnet, 2012 ging dieser Rekord an den Tokyo Skytree.
広州市(こうしゅうし、繁体字: 廣州市、簡体字: 广州市、拼音: Guǎngzhōu、英語: Canton/Kwangchow/Guangzhou)は、中華人民共和国広東省に位置する副省級市で、広東省人民政府が置かれる省都。
広東省のみならず、華南地域全体の経済、文化、教育、交通などの中心都市の一つであり、国務院により、国家中心都市の一つに指定されている。2010年の常住人口は1,270万人、市内総生産は1兆0604億元(約13兆円)[1]であり、昔から羊城と愛称され、花城、穂城の名もあり、穂(拼音: Suì)と略称される。地下鉄、高速道路網が発達している。
一般に北京市、上海市と共に、中国本土の三大都市の一つに数えられる。また、深圳市を含めた4都市は「一線都市」に分類されており、「北上広深」として四大都市に数えられることもある[2]。アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界56位の都市と評価された[3]。中国本土では北京市、上海市に次ぐ3位である。
古代の百越の地。秦の始皇帝が中国を統一して現在の広州に南海郡番禺県を設置したのが始まり。秦帝国の崩壊後、趙佗が南越国を樹立して自立したが、前漢の武帝によって滅ぼされた。漢代には交州に属し、三国呉が広州を分置した。古代から中国の南海貿易の中心地として発展し、唐代半ばの741年には最初の市舶司が設置され、多数のイスラム教徒やユダヤ人やゾロアスター教徒が訪れ、外国人居留区である蕃坊もおかれたが、アブー・ザイド(Abu Zayd Hasan As-Sirafi)の『東邦誌』によると878年の広州大虐殺(英語版)でコミュニティーが消滅した。唐末の黄巣の乱に際して襲撃を受けて多大な打撃を受けたが復興し、五代十国時代には南漢王国の首都となった。海禁政策を取った明代でも広州は南海諸国の朝貢船入港地となり、清代半ばの1757年からは広州のみが対外開放されて欧米諸国と広東貿易が行われた。この構図は近代に入り西欧列強の圧力に屈するまで続く。
阿片戦争中の1841年には一時イギリス軍に占領され、1911年には孫文が広州蜂起を行い、辛亥革命の先駆けとなった。袁世凱の没落後、孫文は1921年に越秀山南麓で広州中華民国政府(中国語版)非常(時期)大総統に就任した。1924年には軍閥割拠の中国を統一するため国共合作を行い、黄埔軍官学校を設立、蒋介石が校長となり、周恩来が政治部主任を務めた。この時期には毛沢東も農民運動講習会をこの地で開催している。孫文没後、蒋介石の国民党は共産党と決裂し、1927年共産党は広州コミューンを樹立したが、間もなく国民党軍の攻撃を受けた(広州起義)。蒋介石は1928年に首都を南京に移転している。1938年日本軍が占領。終戦まで占領状態が維持される。
中華人民共和国成立後も香港に近い広州は中国の対外貿易港として機能し、毎年春秋には広州交易会(カントン・フェアー)が開催され続けている。1979年、鄧小平が対外経済開放政策を取ると、深圳・珠海の経済特区を経済圏に収める広州は経済的に急速に発展を遂げた。しかし、多数の人口が農村から流入し、治安の悪化が社会問題となっている。
Guangzhou (Cantonese pronunciation: [kʷɔ̌ːŋ.tsɐ́u], Chinese: 广州), also known as Canton,[6] is the capital and most populous city of the province of Guangdong.[7] Located in southern China on the Pearl River about 120 km (75 mi) north-northwest of Hong Kong and 145 km (90 mi) north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road[8] and continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub today, as well as one of China's three largest cities.[9]
Guangzhou is situated at the heart of the most-populous built-up metropolitan area in mainland China, an area that extends into the neighboring cities of Foshan, Dongguan, Zhongshan and Shenzhen, forming one of the largest urban agglomerations on the planet. Administratively, the city holds sub-provincial status;[10] and is one of China's nine National Central Cities.[11] In 2015 the city's administrative area was estimated to have a population of 13,501,100.[12] Guangzhou is ranked as an Alpha- Global city.[13] In recent years, there has been a rapidly increasing number of foreign residents and immigrants from Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and especially from Africa.[14] This has led to it being dubbed the "Capital of the Third World".[15][16] The migrant population from other provinces of China in Guangzhou was 40 percent of the city's total population in 2008. Together with Shanghai, Beijing and Shenzhen, Guangzhou has one of the most expensive real estate markets in China.[17]
Guangzhou has a comparatively recent history of two centuries related to its importance for foreign trade. Long the only Chinese port accessible to most foreign traders, the city fell to the British during the First Opium War. No longer enjoying a monopoly after the war, it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong (which is close by) and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major entrepôt. In modern commerce, Guangzhou is best known for its annual Canton Fair, the oldest and largest trade fair in China. For the three consecutive years 2013–2015, Forbes ranked Guangzhou as the best commercial city on the Chinese mainland.[18]
Canton2 (du portugais Cantão) ou Guangzhou (chinois simplifié : 广州市 ; chinois traditionnel : 廣州市 ; pinyin : guǎngzhōu shì ; cantonais Jyutping : gwong²zau¹ si⁵ Écouter la prononciation en mandarin, Écouter la prononciation en cantonais) est la capitale de la province du Guangdong dans le sud de la Chine. Elle a le statut administratif de ville sous-provinciale de la République populaire de Chine. Avec près de 12,7 millions d'habitants (dont 11 070 000 résidents urbains sur un territoire de 3 843 km2)3, c'est la troisième ville la plus peuplée du pays derrière Shanghai et Pékin, et la première du Sud de la Chine. Avec les villes de Shenzhen, Foshan, Dongguan, Zhongshan, et Jiangmen, elle forme la mégalopole chinoise du delta de la Rivière des Perles, grande agglomération s'étirant sur près de 20 000 km2 et rassemblant plus de 50 millions d'habitants. Elle a accueilli les Jeux asiatiques de 2010.
Canton (AFI: /kanˈtɔn/[2][3]; dal portoghese Cantão; in cinese 廣州T, 广州S, GuǎngzhōuP) è la più grande città costiera del sud della Cina, capoluogo della provincia del Guangdong (广东). La parola Canton deriva da una traslitterazione in lingua francese di Guangdong. Conta circa 12 700 000 abitanti ed è la terza città della Cina per abitanti e importanza dopo Shanghai e Pechino. Situata non lontano da Hong Kong, Canton è inoltre al centro della Pearl River Delta Mega City, "megacittà del delta del Fiume delle Perle", la più grande conurbazione metropolitana del mondo che conta 46,5 milioni di abitanti.
Cantón2 o Guangzhou (chino simplificado: 广州, chino tradicional: 廣州, pinyin: Guǎngzhōu, Jyutping: Gwong² zau1, pronunciado: ["Kuán-Chóu"](![]() escuchar), literalmente: «prefectura ancha») es una ciudad del sur de la República Popular China, capital de la provincia de Cantón o Guandong. Su población es de 3 152 825 habitantes en la zona urbana, alcanzando los 13 080 500 habitantes en toda el área metropolitana (2014).3 Actualmente es la conurbación más grande de la Tierra, con 46 900 000 habitantes, si se cuenta junto a su área metropolitana, a los suburbios de la zona del Delta del río de las Perlas. Dispone de un aeropuerto internacional y se comunica con la vecina Hong Kong (a una distancia de 120 km) mediante trenes, autobuses y un servicio de ferry.
escuchar), literalmente: «prefectura ancha») es una ciudad del sur de la República Popular China, capital de la provincia de Cantón o Guandong. Su población es de 3 152 825 habitantes en la zona urbana, alcanzando los 13 080 500 habitantes en toda el área metropolitana (2014).3 Actualmente es la conurbación más grande de la Tierra, con 46 900 000 habitantes, si se cuenta junto a su área metropolitana, a los suburbios de la zona del Delta del río de las Perlas. Dispone de un aeropuerto internacional y se comunica con la vecina Hong Kong (a una distancia de 120 km) mediante trenes, autobuses y un servicio de ferry.
Cantón es la tercera ciudad más grande de China, detrás de Pekín y Shanghái. Tiene un estado administrativo subprovincial y es una de las seis ciudades centrales nacionales de China.4 Cantón es considerada como una ciudad global y en los últimos años ha aumentado rápidamente el número de residentes extranjeros y de inmigrantes ilegales procedentes de Oriente Medio, Europa del este y el Sudeste Asiático, así como de África.5 Esto ha llevado a que se conozca a la ciudad como la «Capital del Tercer Mundo».6 La población migrante de otras provincias de China en Cantón era el 40 por ciento de la población total de la ciudad en 2008. La mayoría de ellos son migrantes rurales que hablan sólo mandarín y han asumido muchos empleos que los ciudadanos locales no estaban dispuestos a hacer.7
La ciudad fue, durante mucho tiempo, el único puerto chino permitido para la mayoría de los comerciantes extranjeros. Cantón cayó a manos británicas y fue abierta por la Primera Guerra del Opio. Perdió importancia en el comercio frente a otros puertos nacionales como Hong Kong y Shanghai, pero siguió sirviendo como un entrepôt importante. En el comercio moderno, Guangzhou es más conocido por su Feria de Cantón, la feria más antigua, de más alto nivel, más grande y más completa en China. Durante tres años consecutivos (2013-2015), Forbes clasificó Cantón como la mejor ciudad comercial en el continente chino.8 Otro de sus elementos más característicos es su gastronomía local, pues la cantonesa es una de las cocinas regionales más famosas y populares de China en todo el mundo.
Гуанчжо́у (кант. трад. 廣州, упр. 广州, ютпхин: Gwong2jau1, йель: Gwong2zau1, кант.-рус.: Куончау, пиньинь: Guǎngzhōu, палл.: Гуанчжоу), ранее был известен как Канто́н[2]) — город субпровинциального значения Китайской Народной Республики, столица провинции Гуандун, политический, экономический, научно-технический, образовательный, культурный и транспортный центр всего южного Китая. Гуанчжоу с населением свыше 10 млн человек является третьим по величине городом Китая, уступая Шанхаю и Пекину. Площадь города 7434,4 км² на суше и 744 км² на море. ВВП составляет 411 млрд юаней, или 47 053 юаня на душу населения.





海南島が中原の影響下に入ったのは前漢の時代である。前110年、武帝は郡を広西より派遣し海南島の瓊北烈楼港(現在の海口鎮海)に上陸し、儋耳及び珠崖郡を設置したのが始まりである。
宋代の1071年(熙寧4年)に海口浦が設置され、海口の地名が誕生した。宋代には政争に敗れた蘇軾が昌化郡(現在の儋州一帯)に左遷された際に海口の金粟庵(現在の五公祠)に投宿し、また罪を赦されて都に戻る際にも投宿し『洞酌亭並引』を残している。また元により都である臨安が陥落した際、趙昺を擁立した勢力が海口で交戦し、元軍に敗れている。
元代になると海口には瓊州郡民按撫舶司が設置され、海南島における貿易活動の監督に当たっていた。漢代より海南島は広西の帰属であったが、明代の1370年より広東の帰属と改編されている。
清末の1858年(咸豊8年)、清朝と英仏政府との間で天津条約が締結されると、瓊州は開港地に指定され、両国(後に独奥西白丹も)の領事館が設立されることとなり、欧米への門戸が開かれることとなり、1873年には日本海口領事館も開設されている(領事は香港領事による兼任)。
中華民国成立後の1926年、それまで瓊山県に属していた海口を独立させ海口市が成立、広東省の直轄とし、1949年には海南特別行政区を設置し広東省から独立させている。1950年に人民解放軍の海南島上陸作戦によって中華人民共和国の統治下に入った後は1956年地級市に昇格、1988年の海南省成立にともない省都となった。2002年行政区画が再編され瓊山市を併合した。
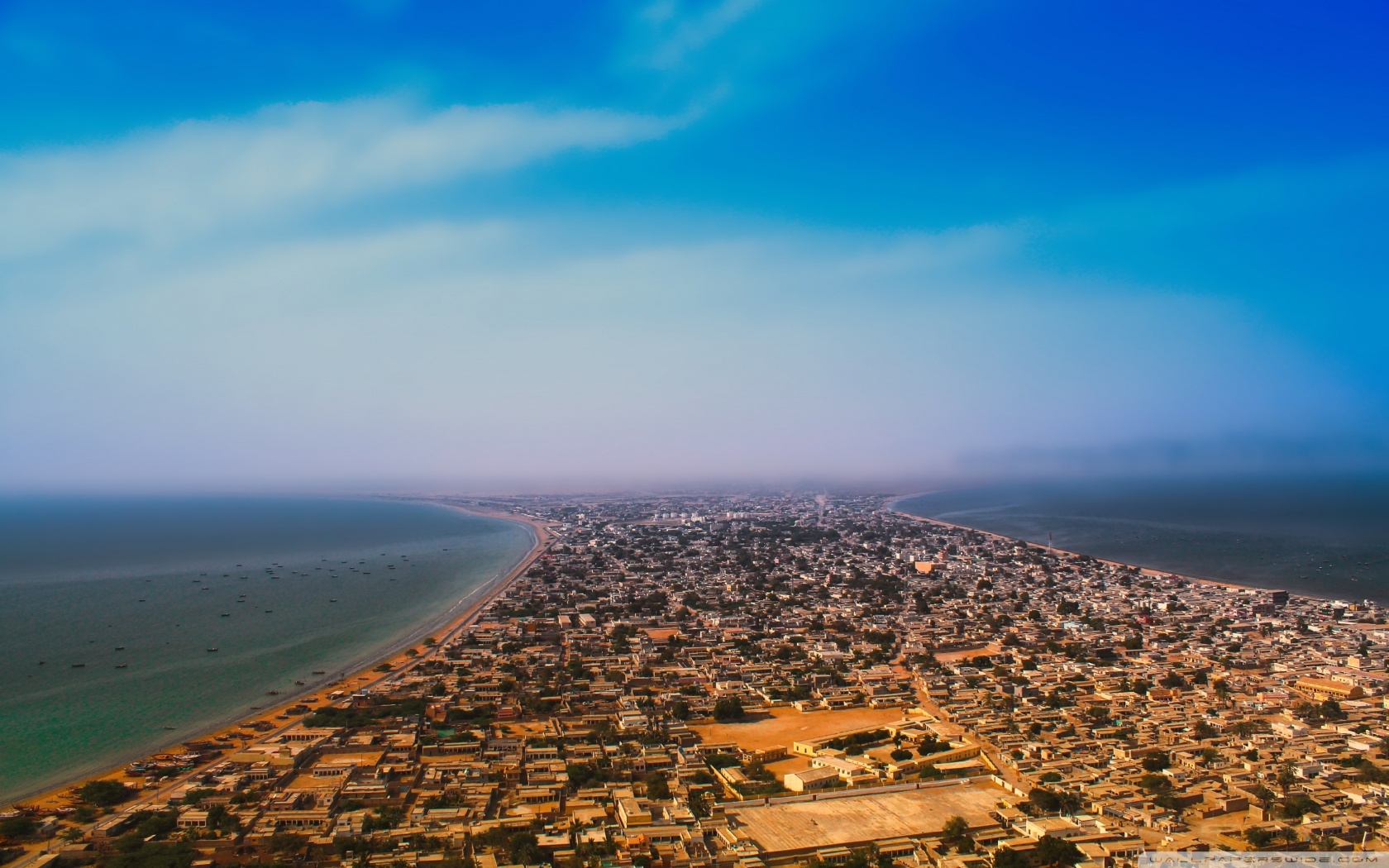
Hǎikǒu (Chinese: 海口; pinyin: Hǎikǒu) is the capital and most populous city of Hainan province, China.[3] It is situated on the northern coast of Hainan, by the mouth of the Nandu River. The northern part of the city is the district of Haidian Island, which is separated from the main part of Haikou by the Haidian River, a branch of the Nandu.
Administratively, Haikou is a prefecture-level city, comprising four districts, and covering 2,280 square kilometres (880 sq mi). There are 2,046,189 inhabitants in the built up area all living within the 4 urban districts of the city.[4]
Haikou was originally a port city. Today, more than half of the island's total trade still goes through its ports. The city is home to Hainan University, which has its main campus on Haidian Island.
Haikou (chinois : 海口市 ; pinyin : ) est la capitale de la province insulaire chinoise de Hainan. La ville-préfecture de Haikou a une superficie de 2 304,84 km2. Haikou occupe la côte nord de l'île de Hainan et fait face à la péninsule de Leizhou située à l'extrémité sud-ouest de la province du Guangdong. Le détroit de Qiongzhou large d'une vingtaine de kilomètres sépare Haikou de la péninsule.
Haikou (cinese: 海口, pinyin: Hǎikǒu) è una città della Cina, situata all'estremo Nord dell'isola di Hainan. Nel 2010 aveva una popolazione stimata in 1,8 milioni, risultando quindi la città di gran lunga più abitata dell'isola.[1]
Haikou léase Jái-Kóu (chino: 海口市, pinyin: Hǎikǒu shì,conocida como ciudad coco) es la capital de la provincia de Hainan, en la República Popular China. La ciudad está situada en el norte de la isla de Hainan, en el canal de Qiongzhou. Haikóu significa "boca del mar". Tiene un población de poco más de 2 millones de habitantes (2010) que ocupan un área de 244,55 km². La mayoría de sus habitantes son de etnia han, que conviven con Li, Miao y Hui.
Хайкоу (кит. 海口) — городской округ на острове Хайнань, место пребывания властей одноимённой провинции Китая. Расположен на севере острова, напротив полуострова Лэйчжоубаньдао, от которого его отделяет 15-километровый Хайнаньский пролив. В городском округе расположен международный аэропорт Хайкоу Мэйлань. Население — 830 192 жителей (2006).
В древности на месте Хайкоу находилась гавань островной столицы Цюншань (ныне — южная часть современного городского округа). С XIII века в этих местах размещался китайский гарнизон; это поселение было укреплено при империи Мин.
Торговое значение города сильно выросло после заключения Тяньцзиньского трактата 1876 году, а к 1930-м годам Хайкоу стал самым большим городом острова. Во время Второй японо-китайской войны оккупанты не скупились на развитие Хайкоу в качестве порта для сырьевых материалов. При создании провинции Хайнань в 1988 году Хайкоу стал местом размещения её властей.

