
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates


 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
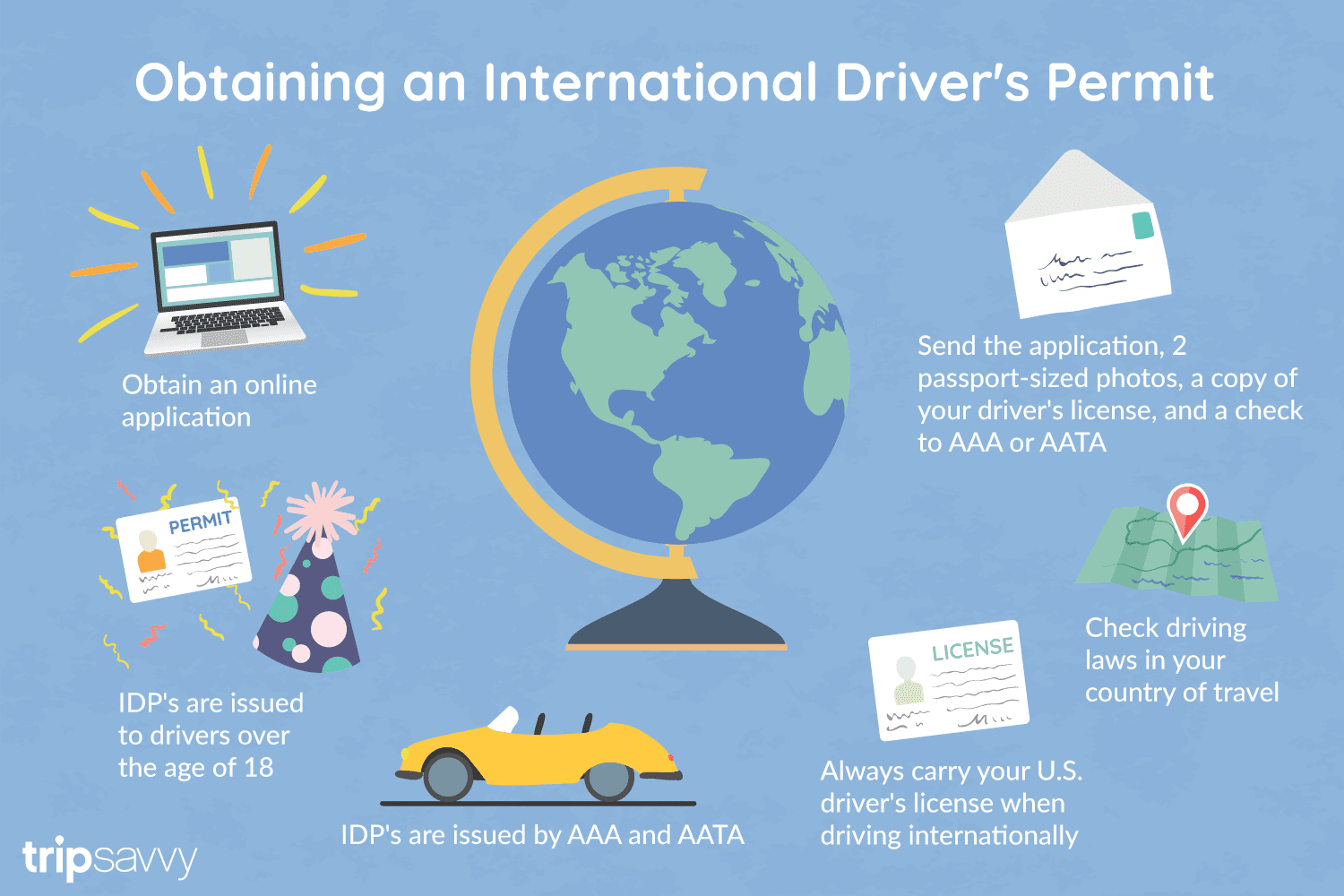
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)
 International Renewable Energy Agency,IRENA
International Renewable Energy Agency,IRENA
 Adnan Z. Amin
Adnan Z. Amin
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade


 Australia
Australia
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Bermuda
Bermuda




 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdul Rahman bin Hamad Al Attiyah
Abdul Rahman bin Hamad Al Attiyah
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdullah Yaccoub Bishara
Abdullah Yaccoub Bishara
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani
Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Fahim bin Sultan Al Qasimi
Fahim bin Sultan Al Qasimi
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Jamil Ibrahim Al-Hejailan
Jamil Ibrahim Al-Hejailan
 Katar
Katar
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Oman
Oman
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade

Der Kooperationsrat der Arabischen Staaten des Golfes (englisch Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, CCASG) (arabisch مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية, DMG Maǧlis at-taʿāwun li-duwal al-ḫalīǧ al-ʿarabiyya), auch als Golf-Kooperationsrat (englisch Gulf Cooperation Council, GCC) bekannt, ist ein Staatenbund, der sechs Staaten der Arabischen Halbinsel umfasst. Er wurde am 25. Mai 1981 in Abu Dhabi durch Kuwait, Bahrain, Saudi-Arabien, Katar, Vereinigte Arabische Emirate und Oman gegründet, um diese Staaten von den Auswirkungen der Islamischen Revolution im Iran im Jahr 1979 und des Ausbruch des Ersten Golfkriegs 1980 abzuschirmen.[1]
Die Organisation strebt die Zusammenarbeit ihrer Mitglieder in der Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik sowie die Förderung der wirtschaftlichen und gesellschaftlichen Beziehungen zwischen ihnen an, wozu 1982 im Rahmen des Unified Economic Agreement der Warenverkehr liberalisiert wurde. Für 2005 wurde eine Zollunion beschlossen, die schließlich auf das Jahr 2003 vorgezogen wurde. Bis 2010 war die Einführung einer gemeinsamen Währung vorgesehen. Unterschiedliche politische Ziele und eine Reihe trennender Fragen behindern jedoch die Integrationsbemühungen.
Die Mitglieder sind zu gegenseitigem Beistand im Verteidigungsfall verpflichtet. Der GCC unterhält eine gemeinsame Verteidigungstruppe, die 5.000 Mann umfasst. Der GCC kooperierte eng mit den Vereinigten Staaten, um gegen den Iran geschützt zu sein.
Für die Europäische Union ist die GCC-Region von strategischer Bedeutung. Der GCC ist der wichtigste Handelspartner der Union in der arabischen Welt. Auf ihn entfallen etwa die Hälfte des gesamten Handels mit den arabischen Staaten und etwa 4 Prozent der Gesamtausfuhr der Europäischen Union in Drittländer.
Waffenexporte Deutschlands in Länder des GCC hatten 2012 einen Wert von 1,42 Milliarden Euro (2011: 570 Millionen Euro). [2]
海湾阿拉伯国家合作委员会(阿拉伯语:مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسي),原名海湾合作委员会(阿拉伯语:مجلس التعاون الخليج الفارسي),中文简称海合会,是一个包括阿拉伯波斯湾地区的6个国家(即波斯湾六国)在内的政府国际组织和贸易集团,其目标主要针对经济和社会方面。
湾岸協力会議(わんがんきょうりょくかいぎ、英語:Gulf Cooperation Council、英略称:GCC、アラビア語:مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية)は、中東・アラビア湾岸地域における地域協力機構である。正式名称は「Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf(湾岸アラブ諸国協力会議、CCASG)」。日本政府での呼称は湾岸協力理事会(GCC)[1]。
1981年5月25日にアブダビで設立[2][3]。本部はリヤド。現在の事務局長はバーレーンのアブドゥッラティーフ・ビン・ラーシド・ザイヤーニー。
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (Arabic: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية), originally (and still colloquially) known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC, مجلس التعاون الخليجي), is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union consisting of all Arab states of the Persian Gulf except Iraq. Its member states are Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.[2][3] The Charter of the Gulf Cooperation Council was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.[4]
All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain),[5][6] two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen.[7][8]
A 2011 proposal to transform the GCC into a "Gulf Union" with tighter economic, political and military coordination has been advanced by Saudi Arabia, a move meant to counterbalance the Iranian influence in the region.[9][10] Objections have been raised against the proposal by other countries.[11][12] In 2014, Bahrain prime minister Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa said that current events in the region highlighted the importance of the proposal.[13]
In order to reduce their dependence on oil in the future, the GCC states are pursuing unprecedented economic structural reform initiatives.[14]
Le Conseil de coopération des États arabes du Golfe (arabe : مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية) ou Conseil de coopération du Golfe (CCG) (arabe :مجلس التعاون الخليج العربي) est une organisation régionale regroupant six monarchies arabes et musulmanes du golfe Persique : l'Arabie saoudite, Oman, le Koweït, Bahreïn, les Émirats arabes unis et le Qatar.
Il Consiglio di cooperazione del Golfo (in inglese Gulf Cooperation Council, GCC; in arabo: مجلس التعاون الخليج الفارسی, Majlis al-Taʿāwun al-Khalījī), il cui nome completo è Consiglio di cooperazione degli Stati del golfo Persico (in inglese Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, CCASG; in arabo: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسی, Majlis al-Taʿāwun li-duwal al-Khalīj al-Fārisī, è un'Organizzazione internazionale regionale che riunisce sei stati del golfo Persico.
El Consejo de Cooperación para los Estados Árabes del Golfo (en árabe: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسی – también conocida por sus siglas; CCEAG) es una organización regional formada por seis naciones del Próximo Oriente, antiguamente denominada como; Consejo de Cooperación del Golfo (مجلس التعاون الخليجي). Creada el 25 de mayo de 1981,12 el Consejo lo forman Baréin, Kuwait, Omán, Catar, Arabia Saudita y los Emiratos Árabes Unidos.34
La principal fuente de riqueza de los miembros del consejo es el petróleo. No obstante, se trata de una región vulnerable política y económicamente, fundamentalmente por su dependencia de una única fuente de riqueza, su escasa población, su gran superficie y su escasa capacidad militar.
Existe una unión aduanera entre todos los miembros del Consejo, los cuales pertenecen también a la Organización Mundial del Comercio. El Consejo se encuentra en la actualidad (2005) negociando un acuerdo de libre comercio con la Unión Europea.
Совет сотрудничества арабских государств Персидского залива (ССАГПЗ) (англ. Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf; араб. مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية) — региональная закрытая международная организация. В официальном названии организации слово Персидский отсутствует, поскольку арабские государства предпочитают называть этот залив Арабским.
Организация создана 25 мая 1981[1][2], её политика определена в Хартии, ратифицированной в 1982 году. Основная цель организации — координация, сотрудничество и интеграция во всех экономических, социальных и культурных делах. Относительное регулирование было осуществлено в экономических и финансовых вопросах; коммерции, таможне и коммуникациях; образовании и культуре; социальных проблемах и проблемах здравоохранения; СМИ и туризме; в законодательных и административных вопросах. Соглашение также должно стимулировать научный и технологический прогресс в промышленности, сельском хозяйстве и сохранении водных ресурсов. По условиям Объединённого экономического соглашения, тарифные барьеры между шестью государствами были упразднены, и народы Залива свободны в открытии производства и осуществлении контрактов в любом государстве на равных правах. Кроме того, в планах имеется создание объединённых сил обороны для быстрого развертывания. Органы Совета сотрудничества государств Персидского залива включают в себя Верховный совет глав государств, которые встречаются ежегодно, Совет министров, который заседает раз в три месяца. Генеральный секретариат находится в Эр-Рияде, Саудовская Аравия.
6 марта 2012 года шесть членов ССАГПЗ заявили, что Совет сотрудничества стран Залива будет развиваться от регионального блока в конфедерацию.

 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Architecture
Architecture
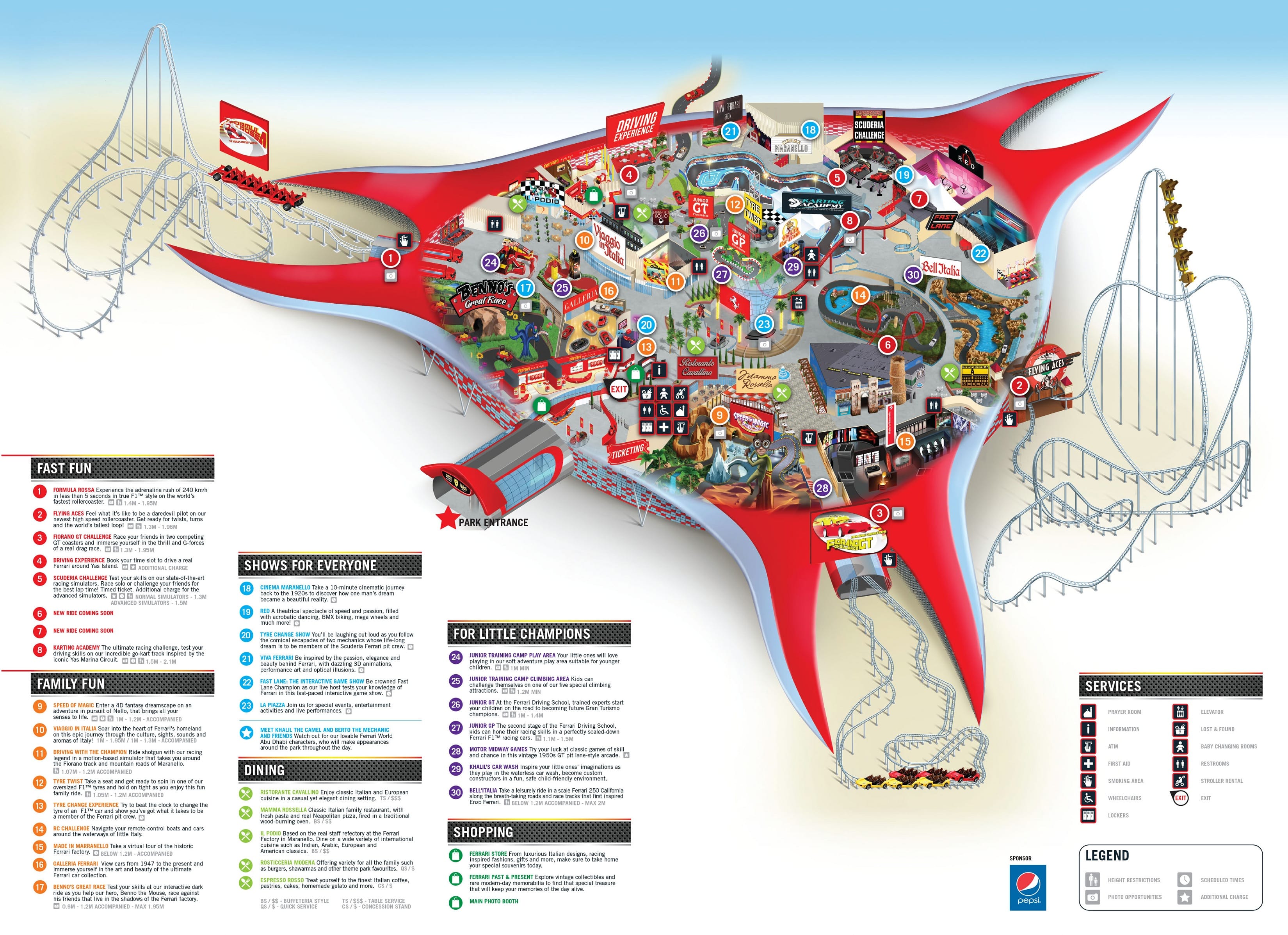
 Theme park
Theme park
 Sport
Sport
 Driving school
Driving school
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Companies
Companies
 Financial
Financial
 Geography
Geography