
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Samoa
Samoa





 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Angola
Angola
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Australia
Australia
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belize
Belize
 Benin
Benin
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brazil
Brazil
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Cuba
Cuba
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Germany
Germany
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia
 Georgia
Georgia
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Japan
Japan
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liberia
Liberia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mexico
Mexico
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Panama
Panama
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Genf
Genf
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Togo
Togo
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tschad
Tschad
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uganda
Uganda
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Roberto Azevêdo
Roberto Azevêdo
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Mike Moore
Mike Moore
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Pascal Lamy
Pascal Lamy
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Peter Sutherland
Peter Sutherland
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Renato Ruggiero
Renato Ruggiero
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Supachai Panitchpakdi
Supachai Panitchpakdi
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic
 Cyprus
Cyprus


世界贸易组织(简称世贸组织或世贸;英语:World Trade Organization,缩写为 WTO;法语:Organisation Mondiale du Commerce,缩写为 OMC;西班牙语:Organización Mundial del Comercio,缩写为 OMC)是负责监督成员经济体之间各种贸易协议得到执行的一个国际组织,前身是1948年起实施的关税及贸易总协定的秘书处。
世贸总部位于瑞士日内瓦,现任总干事是罗伯托·阿泽维多。截至2016年7月29日,世界贸易组织共有164个成员。[5]世界贸易组织的职能是调解纷争,加入WTO不算签订一种多边贸易协议,但其设置的入会门槛可以做为愿意降低关税、法政上配合、参与国际贸易的门票,它是贸易体制的组织基础和法律基础,是众多贸易协定的管理者,是各成员贸易立法的监督者,是就贸易提供解决争端和进行谈判的场所。该机构是当代最重要的国际经济组织之一,其成员间的贸易额占世界贸易额的绝大多数,被称为“经济联合国”。
世界貿易機関(せかいぼうえききかん、英: World Trade Organization、略称:WTO)は、自由貿易促進を主たる目的として創設された国際機関である。常設事務局がスイスのジュネーブに置かれている。
GATT(ガット)ウルグアイ・ラウンドにおける合意によって、世界貿易機関を設立するマラケシュ協定(WTO設立協定)に基づいて1995年1月1日にGATTを発展解消させて成立した。
本来GATTは、第二次世界大戦後の安定を見据え、国際通貨基金および国際復興開発銀行とともに設立が予定されていた国際貿易機関(ITO)の設立準備の際に、暫定協定として結ばれたものであった。国際貿易機関の設立が廃案となり、GATTがその代替として発展強化されていくうちに、再びこの分野の常設機関が求められ、WTOが設立されることとなった。発展解消であるため、GATTの事務局及び事務局長もWTOへと引き継がれることとなった[4]。
WTOはGATTを継承したものであるが、GATTが協定(Agreement)に留まったのに対し、WTOは機関(Organization)であるのが根本的な違いである。
を基本原則としている。また、物品貿易だけでなく金融、情報通信、知的財産権やサービス貿易も含めた包括的な国際通商ルールを協議する場である。
対抗処置の発動では、紛争処理機関(パネル)の提訴に対し全加盟国による反対がなければ採択されるというネガティブ・コンセンサス方式(逆コンセンサス方式)を採用した強力な紛争処理能力を持つ。これは国際組織としては稀な例であり、コンセンサス方式を採っていたGATTとの大きな違いで、WTOの特徴の一つといえる。
新多角的貿易交渉(新ラウンド)は、2001年11月にカタールのドーハで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議で開始を決定し、ドーハ・ラウンドと呼ばれていた。2002年2月1日の貿易交渉委員会で新ラウンドがスタートした。しかし9年に及ぶ交渉は先進国と、急速に台頭してきたBRICsなど新興国との対立によって中断と再開を繰り返した末、ジュネーブで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議(2011年12月17日)で「交渉を継続していくことを確認するものの、近い将来の妥結を断念する」(議長総括)となり事実上停止状態になった。
その後、2013年のバリ島における閣僚会議で、貿易円滑化協定を含む合意が成立し、2014年7月まで貿易円滑化協定をWTO協定に加える(附属書1Aに追加)するための文書を一般理事会で採択すべきとされた[5]。しかしインドが合意を蒸し返す状態で反対したため期限までに採択できなかった[6]。その後食糧備蓄への補助金の問題で先進国側が譲歩することでようやくインドが合意し、2014年11月27日の一般理事会で貿易円滑化協定が採択された[6]。WTO加盟国の3分の2が改正を受諾した日に発効することになっており、2017年2月22日にこの要件を満たし、協定が発効した。
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 124 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. It is the largest international economic organization in the world.[5][6]
The WTO deals with regulation of trade in goods, services and intellectual property between participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a dispute resolution process aimed at enforcing participants' adherence to WTO agreements, which are signed by representatives of member governments[7]:fol.9–10 and ratified by their parliaments.[8] The WTO prohibits discrimination between trading partners, but provides exceptions for environmental protection, national security, and other important goals.[9] Trade-related disputes are resolved by independent judges at the WTO through a dispute resolution process.[9]
The WTO's current Director-General is Roberto Azevêdo,[10][11] who leads a staff of over 600 people in Geneva, Switzerland.[12] A trade facilitation agreement, part of the Bali Package of decisions, was agreed by all members on 7 December 2013, the first comprehensive agreement in the organization's history.[13][14] On 23 January 2017, the amendment to the WTO Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement marks the first time since the organization opened in 1995 that WTO accords have been amended, and this change should secure for developing countries a legal pathway to access affordable remedies under WTO rules.[15]
Studies show that the WTO boosted trade,[16][17][9] and that barriers to trade would be higher in the absence of the WTO.[18] The WTO has highly influenced the text of trade agreements, as "nearly all recent [preferential trade agreements (PTAs)] reference the WTO explicitly, often dozens of times across multiple chapters... in many of these same PTAs we find that substantial portions of treaty language—sometime the majority of a chapter—is copied verbatim from a WTO agreement."[19]
L'Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC ; en anglais : World Trade Organization, WTO, en espagnol : Organización Mundial del Comercio, OMC) est une organisation internationale qui s'occupe des règles régissant le commerce international entre les pays. Au cœur de l'organisation se trouvent les accords de l'OMC, négociés et signés en avril 1994 à Marrakech1 par la majeure partie des puissances commerciales du monde2 et ratifiés par leurs assemblées parlementaires. L'OMC a pour but principal de favoriser l'ouverture commerciale. Pour cela, elle tâche de réduire les obstacles au libre-échange, d'aider les gouvernements à régler leurs différends commerciaux et d'assister les exportateurs, les importateurs et les producteurs de marchandises et de services dans leurs activités.
Depuis 2001, le cycle de négociation mené par l'OMC est le Cycle de Doha3. Bien que l'OMC ne soit pas une agence spécialisée de l'ONU, elle entretient des liens avec cette dernière4. Le siège de l'OMC est au Centre William-Rappard, à Genève. Depuis le 1er septembre 2013, l'organisation est présidée par le Brésilien Roberto Azevêdo qui a été élu directeur général.
L'Organizzazione mondiale del commercio, abbreviato in OMC (in inglese: World Trade Organization, WTO), è un'organizzazione internazionale creata allo scopo di supervisionare numerosi accordi commerciali tra gli stati membri. Vi aderiscono[3] 164 Paesi, a cui se ne aggiungono altri 22 con ruolo di osservatori,[4] comprendendo così oltre il 95% del commercio mondiale di beni e servizi.[5]
La sede dell'OMC si trova, dal 1995, presso il Centro William Rappard a Ginevra, Svizzera.[6]
La Organización Mundial del Comercio (OMC) fue establecida en 1995. Tiene su sede en Ginebra, Suiza, y sus idiomas oficiales son el inglés, el francés y el español. La OMC no forma parte del sistema de las Naciones Unidas, y tampoco de los organismos de Bretton Woods como el Banco Mundial o el FMI.Nota 1
Всеми́рная торго́вая организа́ция (ВТО; англ. World Trade Organization (WTO), фр. Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), исп. Organización Mundial del Comercio) — международная организация, созданная 1 января 1995 года с целью либерализации международной торговли и регулирования торгово-политических отношений государств-членов. ВТО образована на основе Генерального соглашения по тарифам и торговле (ГАТТ), заключенного в 1947 году и на протяжении почти 50 лет фактически выполнявшего функции международной организации, но не являвшегося тем не менее международной организацией в юридическом смысле.
ВТО отвечает за разработку и внедрение новых торговых соглашений, а также следит за соблюдением членами организации всех соглашений, подписанных большинством стран мира и ратифицированных их парламентами. ВТО строит свою деятельность, исходя из решений, принятых в 1986—1994 годах в рамках Уругвайского раунда и более ранних договоренностей ГАТТ. Обсуждения проблем и принятие решений по глобальным проблемам либерализации и перспективам дальнейшего развития мировой торговли проходят в рамках многосторонних торговых переговоров (раунды). К настоящему времени проведено 8 раундов таких переговоров, включая Уругвайский, а в 2001 году стартовал девятый в Дохе, Катар. Организация пытается завершить переговоры по Дохийскому раунду переговоров, который был начат с явным акцентом на удовлетворение потребностей развивающихся стран. По состоянию на декабрь 2012 года будущее раунда переговоров в Дохе остаётся неопределённым: программа работы состоит из 21 части, а первоначально установленный окончательный срок 1 января 2005 года был давно пропущен[3]. В ходе переговоров возник конфликт между стремлением к свободной торговле и стремлением множества стран к протекционизму, особенно в плане сельскохозяйственных субсидий. До сих пор эти препятствия остаются главными и мешают любому прогрессу для запуска новых переговоров в рамках Дохийского раунда. По состоянию на июль 2012 года, существуют различные группы переговоров в системе ВТО для решения текущих вопросов в плане сельского хозяйства, что приводит к застою в самих переговорах[4].
Штаб-квартира ВТО расположена в Женеве, Швейцария. Глава ВТО (генеральный директор) — Роберту Карвалью ди Азеведу, в штате самой организации около 600 человек[5].
На 26 апреля 2015 года в ВТО состояли 162 страны[6].
Правила ВТО предусматривают ряд льгот для развивающихся стран. В настоящее время развивающиеся страны — члены ВТО имеют (в среднем) более высокий относительный уровень таможенно-тарифной защиты своих рынков по сравнению с развитыми. Тем не менее, в абсолютном выражении общий размер таможенно-тарифных санкций в развитых странах гораздо выше, вследствие чего доступ на рынки высокопередельной продукции из развивающихся стран серьёзно ограничен[7].
Правила ВТО регулируют только торгово-экономические вопросы. Попытки США и ряда европейских стран начать дискуссию об условиях труда (что позволило бы считать недостаточную законодательную защиту работников конкурентным преимуществом) были отвергнуты из-за протестов развивающихся стран, которые утверждали, что такие меры только ухудшат благосостояние работников в связи с сокращением числа рабочих мест, снижением доходов и уровня конкурентоспособности[7].
Mitglieder der WTO
| Staat | Beitrittsdatum |
|---|---|
| 30. Juni 1995 | |
| 29. Juli 2016 | |
| 8. September 2000 | |
| 23. November 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 5. Februar 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 12. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Dezember 1996 | |
| 3. Juni 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 21. Januar 1996 | |
| 7. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. November 1999 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 14. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Oktober 1996 | |
| 14. Juni 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Juli 1995 | |
| 25. Oktober 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 26. Juni 2014 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. April 2000 | |
| 13. Oktober 2004 | |
| 13. Dezember 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 2008 | |
| 30. November 2015 | |
| 13. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 20. Dezember 1998 | |
| 30. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1997 | |
| 27. März 1997 | |
| 30. November 2000 | |
| 20. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. Februar 2013 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 10. Februar 1999 | |
| 14. Juli 2016 | |
| 1. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 17. November 1995 | |
| 29. April 2012 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 4. April 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. Juli 2001 | |
| 29. Januar 1997 | |
| 26. August 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. April 2004 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 3. September 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. Dezember 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. November 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 6. September 1997 | |
| 9. Juni 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Mai 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. August 2012 | |
| 26. Juli 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2005 | |
| 10. Mai 2012 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. April 2015 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 5. März 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. März 2013 | |
| 1. Januar 2002 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 27. Juli 2007 | |
| 1. März 1995 | |
| 19. Oktober 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 29. März 1995 | |
| 26. März 1995[2] | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 16. Mai 2008 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 10. April 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 24. August 2012 | |
| 11. Januar 2007 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 |
 Australia
Australia
 Cookinseln
Cookinseln
 Fidschi
Fidschi
 Föderierte Staaten von Mikronesien
Föderierte Staaten von Mikronesien
 Französisch-Polynesien
Französisch-Polynesien
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Nauru
Nauru
 Neukaledonien
Neukaledonien
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Niue
Niue
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Republik Palau
Republik Palau
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Samoa
Samoa
 Tonga
Tonga
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Australia
Australia
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Dominica
Dominica
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 India
India
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nauru
Nauru
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Uganda
Uganda
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 Cyprus
Cyprus

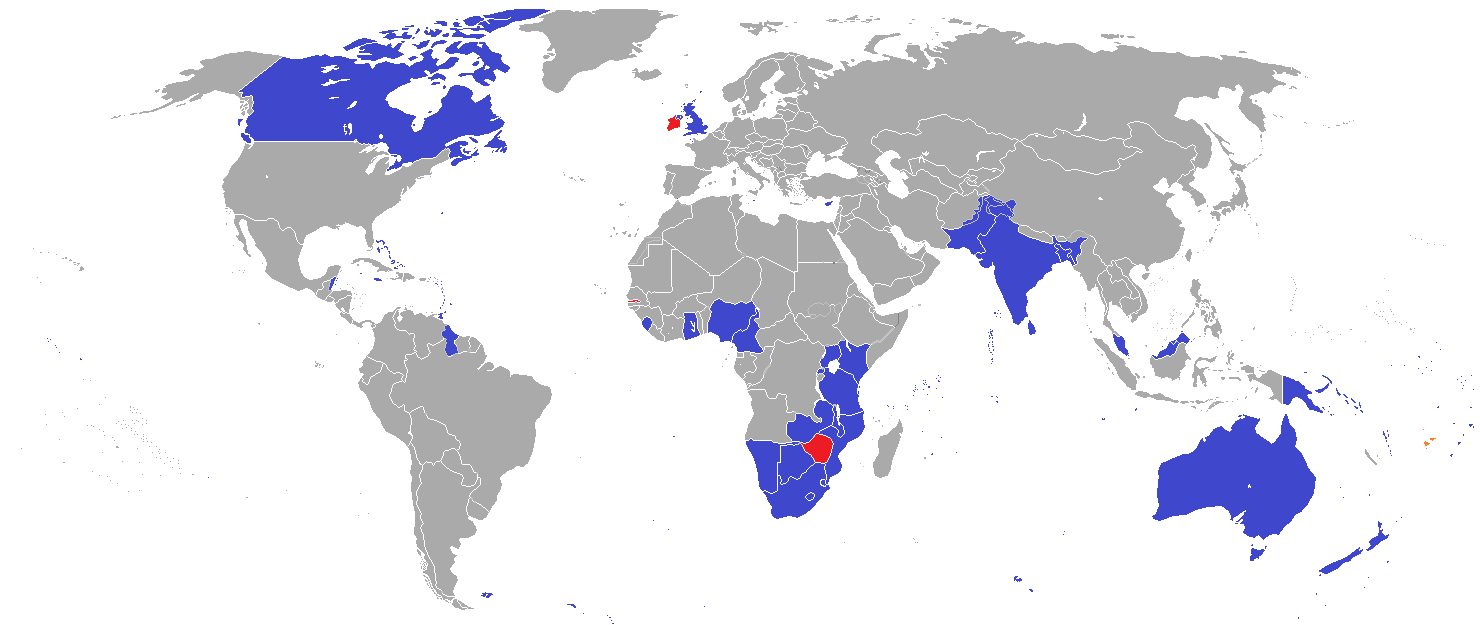
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].
 International cities
International cities
 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand