
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen


 Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft der Frauen 2015
Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft der Frauen 2015
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Kanada
Kanada
 Olympische Sommerspiele
Olympische Sommerspiele

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen

蒙特利尔(法语:Montréal,[mɔ̃ʁeal] ![]() 聆听;英语:Montreal,/ˌmʌntriːˈɒl/ (
聆听;英语:Montreal,/ˌmʌntriːˈɒl/ (![]() 聆听)),蒙特利尔,港澳称为满地可,台湾称为蒙特娄[5][6]、蒙特利尔[6],是一座位于加拿大魁北克省西南部的城市,主要位于圣劳伦斯河和渥太华河汇合处的蒙特利尔岛及周边小岛上。根据2011年人口普查,蒙特利尔人口约为342万[9],是魁北克省内最大城市、加拿大第二大城市及北美第十五大城市。“蒙特利尔”一词来源于中古法语“Mont Royal”,意思为“皇家山”,至今蒙特利尔城中心的地标皇家山仍以此命名。法语是蒙特利尔的官方语言,也是城市里最常用的语言,使用人口占城市总人口的60.5%,使得蒙特利尔成为世界上仅次于巴黎的第二大法语城市。
聆听)),蒙特利尔,港澳称为满地可,台湾称为蒙特娄[5][6]、蒙特利尔[6],是一座位于加拿大魁北克省西南部的城市,主要位于圣劳伦斯河和渥太华河汇合处的蒙特利尔岛及周边小岛上。根据2011年人口普查,蒙特利尔人口约为342万[9],是魁北克省内最大城市、加拿大第二大城市及北美第十五大城市。“蒙特利尔”一词来源于中古法语“Mont Royal”,意思为“皇家山”,至今蒙特利尔城中心的地标皇家山仍以此命名。法语是蒙特利尔的官方语言,也是城市里最常用的语言,使用人口占城市总人口的60.5%,使得蒙特利尔成为世界上仅次于巴黎的第二大法语城市。
蒙特利尔曾经是加拿大经济首都,拥有最多的人口及最发达的经济,但是在1976年蒙特利尔奥运会后被安大略省的多伦多超过。今天蒙特利尔仍然是加拿大最重要的经济中心之一,航空工业、金融、设计、电影工业等行业发达。蒙特利尔被认为是世界最佳宜居城市,并被联合国教育、科学及文化组织认定为设计之城。1999年第35届国际技能竞赛在这里举行。
Montreal (deutsch [mɔntʁeˈa:l]) bzw. Montréal (französisch [mɔ̃ʁeˈal], englisch [ˌmʌntɹiːˈɒl]) ist eine Millionenstadt in Kanada. Sie liegt im Südwesten der Provinz Québec auf der Île de Montréal, der größten Insel im Hochelaga-Archipel, die vom Sankt-Lorenz-Strom und von Mündungsarmen des Ottawa umflossen wird. Die Nachbarprovinz Ontario liegt knapp 60 Kilometer westlich, die Grenze zu den USA etwas mehr als 50 Kilometer südlich. Das Stadtbild wird vom Mont Royal geprägt, einem 233 Meter hohen Hügelzug vulkanischen Ursprungs im Zentrum der Insel, von dem sich der Name der Stadt ableitet.
Als der französische Seefahrer Jacques Cartier im Jahr 1535 als erster Europäer die Gegend erforschte, lebten Sankt-Lorenz-Irokesen auf der Insel. 1642 gründeten Paul Chomedey de Maisonneuve und Jeanne Mance das Fort Ville-Marie, eine katholische Missionsstation. Daraus entwickelte sich in der Folge die Siedlung Montreal, die 1760 unter britische Herrschaft kam. Montreal erhielt 1832 die Stadtrechte. Die Stadt wuchs rasch und entwickelte sich zum wirtschaftlichen und kulturellen Zentrum des Landes, verlor aber im letzten Viertel des 20. Jahrhunderts diese führende Rolle an Toronto. Bedeutende Ereignisse von weltweiter Ausstrahlung waren die Weltausstellung Expo 67 und die Olympischen Sommerspiele 1976.
Die Wirtschaft Montreals ist stark diversifiziert. Wichtige Pfeiler des Dienstleistungssektors sind Finanzdienstleistungen, Medien, Handel und Design. Von großer Bedeutung ist auch der Tourismus, dies aufgrund der Sehenswürdigkeiten und des vielfältigen kulturellen Angebots, das neben Museen auch zahlreiche Festivals in den Bereichen Film, Theater und Musik umfasst. Mehr als 60 internationale Organisationen haben ihren Sitz in Montreal. Im Industriesektor sind Luftfahrt-, Pharma- und Spitzentechnologieunternehmen vorherrschend. Mit vier Universitäten und mehreren weiteren Hochschulen ist Montreal ein bedeutender Bildungsstandort. Außerdem ist die Stadt ein Knotenpunkt im Schienen- und Straßennetz und verfügt darüber hinaus über den größten Binnenhafen auf dem amerikanischen Kontinent.
Mit einer Bevölkerungszahl von 1.649.519 Einwohnern (Stand: 2011)[1] ist Montreal die zweitgrößte Stadt Kanadas nach Toronto und die größte der Provinz Québec. Die Verwaltungsregion, die alle Gemeinden auf der Insel umfasst, zählt 1.886.481 Einwohner (2011).[2] Der Ballungsraum Communauté métropolitaine de Montréal, der urbane Gebiete im näheren Umkreis miteinbezieht, zählt 3.824.221 Einwohner (2011).[3] Französisch ist Montreals Amtssprache und die Hauptsprache von 56,9 % der Bevölkerung, während 18,6 % hauptsächlich Englisch sprechen. Der Rest entfällt auf verschiedene Sprachen von Einwanderern, womit Montreal eine multikulturelle Bevölkerung besitzt.[4]
Montreal ist die zweitgrößte Stadt der Welt nach Paris, in der Französisch als Muttersprache gesprochen wird.[5][6][7][8] Montreal gehört auch weltweit zu den größten Städten, in denen Französisch die offizielle Sprache ist. Die Stadt stand früher an zweiter Stelle nach Paris, hat aber diesen Rang in den letzten Jahren an Kinshasa[9] und Abidjan[10] abgegeben.
モントリオール(英語: Montreal [ˌmɒntrɪˈɔːl] (![]() 音声ファイル))、モンレアル(フランス語: Montréal[mɔ̃ʁeal] (
音声ファイル))、モンレアル(フランス語: Montréal[mɔ̃ʁeal] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、カナダ・ケベック州の都市。セントローレンス川沿いに位置し、アメリカ合衆国との国境や、カナダのオンタリオ州との州境に近い。
音声ファイル))は、カナダ・ケベック州の都市。セントローレンス川沿いに位置し、アメリカ合衆国との国境や、カナダのオンタリオ州との州境に近い。
モントリオール市は、カナダではオンタリオ州のトロントに次ぎ人口・経済規模で第二の都市である[5]。ケベック州では最大の都市である。2015年、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス・人材・文化・政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第24位の都市と評価された[6]。
住民の大半がフランス系カナダ人を中心にしたヨーロッパ系だが、市内の人口の31.7%は非白人と世界各地からの移民も多い多民族都市である。
周辺地域を含むモントリオール大都市圏の人口は約380万人であり、これは北米で15番目、世界でも第77位の規模。面積は約4千km2。モントリオール大都市圏の住民の7割弱が第一言語をフランス語とし、フランス語圏ではパリとキンシャサ[7]に次ぐ規模である。
フランス文化の薫り高い異国的な雰囲気、美食の町、石造りの住宅街、街中にある数多くの教会、石畳のヨーロッパ調の旧市街の街並みなどから観光客向けに「北米のパリ」と宣伝される。一方では、都市圏の住民の1割強の第一言語は英語であり、19世紀の終わりから20世紀の始めにかけて英国系移民によって街が発展してきたことからヴィクトリア朝の建物が多いなど英国文化も色濃く残り、北米文化と混合している側面も持つ。
Montreal (/ˌmʌntriˈɔːl/ ( listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] (
listen) MUN-tree-AWL;[14] French: [mɔ̃ʁeal] ( listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
listen); officially Montréal) is the most populous municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec and the second-most populous municipality in Canada. Originally called Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary",[15] it is named after Mount Royal,[16] the triple-peaked hill in the heart of the city. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which took its name from the same source as the city,[17][18] and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. It has a distinct four-season continental climate with warm to hot summers and cold, snowy winters.[19]
In 2016, the city had a population of 1,704,694,[9] with a population of 1,942,044 in the urban agglomeration, including all of the other municipalities on the Island of Montreal.[9] The broader metropolitan area had a population of 4,098,927.[11] French is the city's official language[20][21] and is the language spoken at home by 49.8% of the population of the city, followed by English at 22.8% and 18.3% other languages (in the 2016 census, not including multi-language responses).[9] In the larger Montreal Census Metropolitan Area, 65.8% of the population speaks French at home, compared to 15.3% who speak English.[11] The agglomeration Montreal is one of the most bilingual cities in Quebec and Canada, with over 59% of the population able to speak both English and French.[9] Montreal is the second-largest primarily French-speaking city in the world, after Paris.[22][23][24][25] It is situated 258 kilometres (160 mi) south-west of Quebec City.
Historically the commercial capital of Canada, Montreal was surpassed in population and in economic strength by Toronto in the 1970s.[26] It remains an important centre of commerce, aerospace, transport, finance, pharmaceuticals, technology, design, education, art, culture, tourism, food, fashion, gaming, film, and world affairs. Montreal has the second-highest number of consulates in North America,[27] serves as the location of the headquarters of the International Civil Aviation Organization, and was named a UNESCO City of Design in 2006.[28][29] In 2017, Montreal was ranked the 12th most liveable city in the world by the Economist Intelligence Unit in its annual Global Liveability Ranking,[30] and the best city in the world to be a university student in the QS World University Rankings.[31]
Montreal has hosted multiple international conferences and events, including the 1967 International and Universal Exposition and the 1976 Summer Olympics.[32][33] It is the only Canadian city to have held the Summer Olympics. In 2018, Montreal was ranked as an Alpha− world city.[34] As of 2016 the city hosts the Canadian Grand Prix of Formula One,[35] the Montreal International Jazz Festival[36] and the Just for Laughs festival.[37]
Montréal [ˈmɔ̃ˌʁeal]3 Écouter est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée du Canada. Elle se situe principalement sur l’île fluviale de Montréal, sur le fleuve Saint-Laurent (entre Québec et le lac Ontario) dans le Sud de la province de Québec, dont elle est la métropole4.
En 2016, la ville comptait 1 704 694 habitants1 et son aire urbaine (appelée Région métropolitaine de Montréal) plus de 4 millions, soit environ la moitié de la population du Québec5. Montréal est ainsi la 19e agglomération la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord6 et la 122e ville la plus peuplée du monde7.
Ville francophone la plus peuplée d'Amérique8, Montréal est considérée comme ayant la deuxième population francophone au monde après ParisNote 1,9,10. En 2011, environ 50 % de la population de Montréal était de langue maternelle française, 13 % était de langue anglaise et 33 % était d'une autre langue11, ce qui fait d'elle l'une des villes les plus cosmopolites du monde12.
Montréal est le 3e plus grand centre financier d'Amérique du Nord et le 12e au monde13. Cœur économique du Québec, Montréal est aussi la seconde place financière du Canada et possède une économie fortement diversifiée14 par le commerce, l’éducation, les technologies de l'information et les industries aérospatiale, pharmaceutique, du tourisme et du cinéma. La ville est la 3e en importance dans l'industrie mondiale du jeu vidéo15. Classée ville mondiale en 2012, Montréal est la deuxième ville consulaire d'Amérique du Nord, abrite le siège de l'Organisation de l'aviation civile internationale et est le siège de plus de 65 organisations internationales gouvernementales et non gouvernementales16, ce qui fait d'elle la 3e ville en importance en Amérique du Nord pour ce qui est du nombre de siège sociaux d'organisations internationales, derrière New York et Washington17. De plus, la ville est la première d'Amérique du Nord pour le nombre de congrès internationaux18. En 2017, Montréal est consacrée « meilleure ville étudiante » au monde19 et est considérée comme la « Métropole universitaire du Canada, avec six universités et 450 centres de recherche »20.
Montréal a accueilli plusieurs événements internationaux d'envergure, dont l'Exposition universelle de 1967 et les Jeux olympiques d'été de 1976. Hôte du Grand Prix de Formule 1 du Canada, elle accueille annuellement de nombreux festivals, tels le Festival international de jazz de Montréal, les FrancoFolies, et le festival Juste pour rire. Le club de hockey des Canadiens de Montréal y a élu domicile dès sa création en 1909.
Montréal (in francese, pronuncia: /mɔ̃ʁeal/ ascolta[?·info]) o Montreal (pronuncia: [ˈmɔntreal][2]; in inglese: /mʌntriːˈɒl/ ascolta[?·info]), in italiano Monreale, è una città del Canada. È il centro più popoloso della provincia del Québec e il suo più importante polo economico, oltre a essere la seconda città più popolosa del Canada. Montréal è anche la seconda agglomerazione urbana del paese dopo quella di Toronto. In francese viene detta la Métropole e la sua area metropolitana conta all'incirca 4 milioni di abitanti[3]. Il centro storico di Montréal è il Vieux-Montréal (Vecchia Montréal).
Montreal (Montréal1 en la grafía oficial de la ciudad, en francés; pronunciación en francés: /mɔ̃.ʀe.al/ (![]() escuchar), pronunciación en inglés: /ˌmʌn.tɹiˈɒːl/ (
escuchar), pronunciación en inglés: /ˌmʌn.tɹiˈɒːl/ (![]() escuchar)) es la mayor ciudad de la provincia de Quebec, en Canadá y la segunda más poblada del país.2 Es también una región administrativa de Quebec. Se sitúa en la isla del mismo nombre entre el río San Lorenzo y la Rivière des Prairies. Es uno de los principales centros industriales, comerciales y culturales de Norteamérica.
escuchar)) es la mayor ciudad de la provincia de Quebec, en Canadá y la segunda más poblada del país.2 Es también una región administrativa de Quebec. Se sitúa en la isla del mismo nombre entre el río San Lorenzo y la Rivière des Prairies. Es uno de los principales centros industriales, comerciales y culturales de Norteamérica.
Montreal es la cuarta ciudad francófona más poblada del mundo, detrás de París, Kinshasa y Abiyán.34 Sin embargo, Montreal también tiene una considerable comunidad anglófona,5 y un creciente número de personas cuyo idioma materno no es ni el francés ni el inglés.
La palabra «Montreal» es la versión arcaica, en francés antiguo, de «Mont-Royal» (cuando «royal» se decía y se escribía «real» sin acento, como en castellano), un monte localizado en la ciudad, en el centro de la isla.67 Montreal es uno de los centros culturales más importantes de Canadá, puesto que acoge varios acontecimientos nacionales e internacionales. Entre ellos, podemos citar el festival Juste pour Rire, uno de los mayores festivales de humor del mundo, el Festival de Jazz de Montréal, uno de los mayores festivales de jazz del mundo, y el Grand Prix de Montréal. La ciudad, en total, acoge más de 70 eventos internacionales al año.
La población de Montreal es de las mejor formadas del mundo, poseyendo la mayor concentración de estudiantes universitarios per cápita de toda Norte América. La ciudad posee cuatro universidades —dos francófonas y dos anglófonas— y doce facultades. Es un centro de la industria de alta tecnología, especialmente en el área de medicina y de la industria aeroespacial.8
Fundada en 1642, Montreal fue una de las primeras ciudades de Canadá. Desde entonces, y hasta la década de 1960, fue el principal centro financiero e industrial de Canadá, así como la mayor ciudad del país. Considerada hasta entonces la capital económica de Canadá, también era considerada una de las ciudades más importantes del mundo. Sin embargo, durante la década de 1970, la anglófona Toronto le arrebató el puesto de capital financiera e industrial del país. En 2001, los 27 municipios de la isla de Montreal fueron fusionados con la ciudad de Montreal. En 2004, tras los resultados de un referéndum, 15 de estos municipios nuevamente volvieron a ser ciudades independientes.
Монреа́ль (фр. Montréal, [mɔ̃ʁeˈal], англ. Montreal) — самый крупный город в провинции Квебек и второй по величине город в Канаде. Первоначально назывался Вилль-Мари — город Марии. Название Монреаль произошло от горы Мон-Руаяль (Королевская гора)[2], находящейся в центре города[3][4], форма Монреаль возникла под влиянием окситанского языка части первых поселенцев.
По данным 2016 года, население Большого Монреаля составляло 4 098 927 человек[5]. Население самого города Монреаль составляет в 1 704 694 человек[6].
Единственный официальный язык в городе — французский, для 59,8 % жителей города этот язык является родным, затем по количеству носителей следует английский язык — 19,4 %[7][8]. В Большом Монреале доля носителей французского составляет 67,9 % от населения, второе место занимает английский — 16,5 %[9]. Больше половины населения города владеет в той или иной степени обоими языками[10]. До 2014 года Монреаль был вторым по населению франкоязычным городом мира после Парижа, но к 2015 году на 3-ю позицию его сместил африканский Абиджан[11]. Также в мире есть и другие крупные франкоязычные города — африканские Киншаса, Касабланка, Алжир, но в этих городах французский используется преимущественно в письменном виде или же в качестве второго языка[12][13].
Монреаль обыкновенно занимает самые высокие места в рейтинге самых удобных для жизни городов в мире. Журнал Monocle Magazine назвал город «культурной столицей Канады», а недавно ЮНЕСКО назвало Монреаль городом дизайна[14][15]. Уступив в середине 70-х титул экономической столицы Торонто, Монреаль остается важным деловым, промышленным и культурным центром Канады. В числе наиболее значимых отраслей: аэрокосмическая, биотехнологическая, фармацевтическая, отрасль информационных технологий, туризм, киноиндустрия, а также развитая индустрия компьютерных игр[16][нет в источнике].

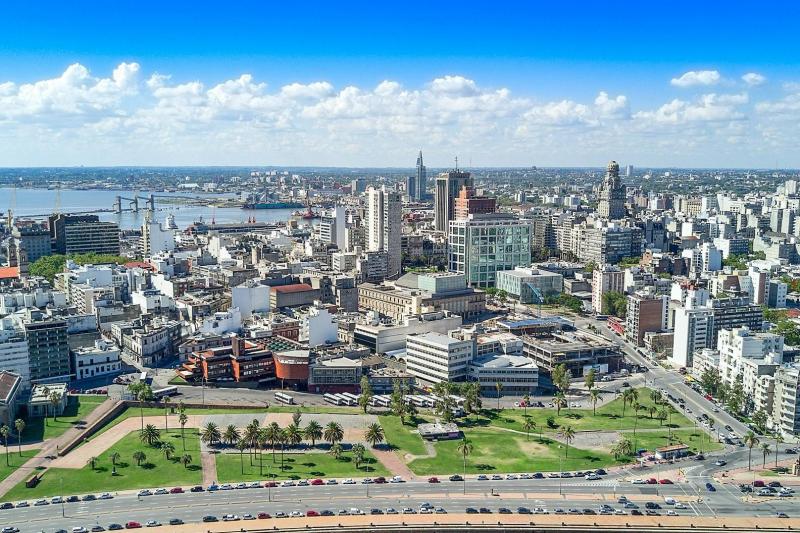
印度西岸大城市和全国最大海港。是印度马哈拉施特拉邦的首府。在孟买岛上,距海岸16公里,有桥梁与堤道相连。1534年为葡萄牙所占, 1661年转属英国,为重要的贸易中心。
孟买位于马哈拉施特拉邦西海岸外的撒尔塞特岛,面临阿拉伯海。孟买港是一个天然深水良港,承担印度超过一半的客运量,货物吞吐量相当大。
孟 买是印度的商业和娱乐业之都,拥有重要的金融机构--诸如印度储备银行、孟买证券交易所、印度国家证券交易所和许多印度公司的总部。该市是印度印地语影视 业(称为宝莱坞)的大本营。由于其广阔的商业机会,和相对较高的生活水准,孟买吸引了来自印度各地的移民,使得该市成为各种社会群体和文化的大杂烩。孟买 拥有贾特拉帕蒂·希瓦吉终点站和象岛石窟等数项世界文化遗产,还是非常罕见的在市界以内拥有国家公园(桑贾伊·甘地国家公园)的城市。
孟买(英语:Mumbai,印地语:मुम्बई;马拉提语:मुंबई, Muṃbaī /mumbəi/;也称为Bombay,马拉地语为बॉम्बे,是1995年前的正式名称),是印度马哈拉施特拉邦首府。2018年,孟买市人口为1998万人。[7]都会区已达2364万,是印度人口最多的城市,也是世界人口最多的城市之一。包括邻近郊区的孟买大都会区(MMR)人口为2500万,是世界第七大城市。孟买是排名世界第八位的大都会区。2015年,孟买大都会区的人口排名上升到世界第四位[8]。孟买位于马哈拉施特拉邦西海岸外的撒尔塞特岛。 孟买港是深水良港。[9]孟买拥有重要的金融机构,诸如印度储备银行、孟买证券交易所、印度国家证券交易所和许多印度公司的总部。由于其相对较高的生活水准,使其成为文化的大杂烩。孟买拥有贾特拉帕蒂·希瓦吉终点站和象岛石窟及该市独特的英式建筑群等数项世界遗产,市内拥有桑贾伊·甘地国家公园。
组成孟买的七岛最初是马拉地语族科里人的家园,这些人起源于古吉拉特邦。几世纪以来,这些群岛一直由原住民控制,后来割让给葡萄牙帝国,英王查理二世时割让给不列颠东印度公司。
随著主要道路和铁路的建设,1845年完成的填海工程将孟买转变为阿拉伯海的主要海港。19世纪的孟买以经济和教育发展为特征。在20世纪初期,它是印度独立运动的坚实基础。
孟买是印度的金融,商业和娱乐之都,它是世界十大商业中心之一。其占印度GDP的6.16%,印度工业总产值的25%,印度海洋贸易的70%(尼赫鲁港)。该市拥有重要的金融机构以及众多印度公司和跨国公司的公司总部。它也是印度一些主要的科学和核研究所的所在地。该市是印地语影视(宝莱坞)和马拉地语电影业的荷里活。
Mumbai (Marathi मुंबई IAST Mumbaī [ˈmumbəi]), bis 1995 offiziell Bombay (englisches Kolonialtoponym), ist die Hauptstadt des indischen Bundesstaates Maharashtra und die wichtigste Hafenstadt des Subkontinents. Sie liegt auf der Insel Salsette vor der Westküste Maharashtras. Das Stadtzentrum befindet sich auf einem schmalen Landstreifen, der von der sumpfigen Küste in das Arabische Meer hineinragt. Die Stadt ist das wirtschaftliche Zentrum Indiens. Sie ist Verkehrsknoten und Kulturzentrum mit Universitäten, Theatern, Museen und Galerien.
Mumbai ist mit 20,5 Millionen Einwohnern in der eigentlichen Stadt (das heißt ohne Vorortgürtel) die größte Stadt in Indien und eine der bevölkerungsreichsten Städte der Welt. Mit 28,4 Millionen Einwohnern in der Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR), die auch die nördlichen Gebiete mit der Stadt Thane einschließt, gehört Mumbai auch zu den größten Metropolregionen der Welt (Zahlen jeweils Volkszählung 2011).
Zahlreiche Gebäude im Zentrum Mumbais sind in einer regionalen Variation des Historismus erbaut worden, die teilweise britisch inspiriert und teilweise eine britische Interpretation des Mogul-Baustils ist. Mehrere Baudenkmäler der Stadt, darunter der Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus, die Höhle von Elephanta und die viktorianisch-gotischen und Art-déco-Gebäudeensembles im Stadtzentrum stehen auf der UNESCO-Liste des Weltkulturerbes.

名古屋为爱知县首府,是仅次于东京、大阪和横滨的第四大城市。位于本州中南部浓尾平原,濒临伊势湾,为中部日本的政治、工业、经济、文化和交通中心。早在12世纪就见于史书记载,古称那古野、那古屋、名 护屋,1889年设市。二次世界大战期间,城区大部分被炸毁,战后按原来式样重建,形成一个半径达40公里的“大名古屋”。
名古屋面积为376平方公里,人口215万。是一个充满了活力的城市,它有众多的娱乐中心、购物中心、博物馆,也是著名的会展中心。
全市划分为14个行政区。中区、热田区及其毗邻地带是市中心,有宽100米的大街贯穿其间。市中心的名古屋城建于庆长15年(公元1610年),1959年重建,为名古屋市象征。其他古迹有:热 田刘宫、大须观音寺(即真福寺)。(Quelle: http://trip.sotrip.com/tour/newsotrip/sotrip_dest/destination_home/japan/riben/mingguwu/index.html )
名古屋市(日语:名古屋市/なごやし Nagoya shi */?)是位于日本爱知县西部(尾张地方)的都市,为爱知县首府,同时是中部地方与东海地方的中枢都市、以及爱知县唯一的政令指定都市,人口约230万,在日本各都市中排名第四,仅次于东京、横滨及大阪,也是日本三大都市圈之一中京圈的核心城市。由于位于东京与京都之间,因此又被称为“中京”[1]。全市划分为16个区。
名古屋是东海地方在政治、经济、文化、交通等领域的中枢,市中心的名驿(名古屋站商圈)、荣、锦三、大须、金山是全市主要的商业区,其中前两地拥有大规模的地下街廓。2008年,名古屋市和神户市一起被联合国教科文组织认可为“创意都市”[2]。2017年,名古屋的城区人口约有1,007万人,在世界排名第37位[3]。此外,在美国智库AT Kearney颁布的全球城市排名中,名古屋市被评为世界第69位的都市[4]。
名古屋的市徽由圆形中置一“八”字而成,取自江户时代在此当家的尾张德川家的印记“丸八印”[5]。
Nagoya ist mit 2,1 Mio Einwohnern nach Tokio, Yokohama und Osaka viertgrößtes japanisches Industriezentrum und sportlich hauptsächlich durch den Baseballverein Chūnichi Dragons und den Fußballverein Nagoya Grampus Eight bekannt. In der Agglomeration von Nagoya befindet sich der Hauptsitz des Automobilkonzerns Toyota.
Die Stadt war schon im Mittelalter als Handelszentrum und Hauptort der Provinz Owari bekannt. Oda Nobunaga wurde 1534 in der Burg Nagono, Vorgängerin der Burg Nagoya, geboren. 1555 zog er in die Burg von Kiyosu um und verlagerte damit das Machtzentrum in Zentraljapan nach Kiyosu. 1610 wurde die Burg von Nagoya von Tokugawa Ieyasu wieder aufgebaut. Anschließend wurde Nagoya wieder zum eindeutigen Zentrum Owaris. Nachdem die Familie Tokugawa ihre Macht als Shōgun gesichert hatte, gab der erste Shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu die Stadt Nagoya an seinen Sohn weiter. Von den historischen Bauten überstanden nur wenige den Krieg. Die meisten wurden im Zweiten Weltkrieg am 14./17. Mai 1945 völlig zerstört. Die Burg wurde 1959 wieder aufgebaut. Der Kulturschatz der Tokugawa-Familie wird heute im Tokugawa-Museum ausgestellt.(Quelle: http://www.mexpedia-japan.de/Staedte.php)
Nagoya (jap. 名古屋市, -shi) ist eine Großstadt, Hafenstadt und Verwaltungssitz der japanischen Präfektur Aichi auf Honshū am Pazifik (Japan).
Nagoya ist mit 2,3 Mio. Einwohnern nach Tokio, Yokohama und Osaka viertgrößtes japanisches Industriezentrum und sportlich hauptsächlich durch den Baseballverein Chūnichi Dragons und den Fußballverein Nagoya Grampus Eight bekannt.
東京特別区部を除くと横浜市・大阪市に次ぐ全国第3位の人口を有する市[3]。中部地方における行政・経済・文化の中枢で、東日本と西日本を結ぶ交通の要所となっている。
古くは三種の神器のひとつである草薙剣(くさなぎのつるぎ)を祀る[4]熱田神宮がある鳥居前町であり、江戸時代は尾張徳川家の治める城下町として繁栄した歴史を持つ。また、タイ王国から寄贈された真舎利(釈迦の遺骨・お骨)を安置するために創建された日本唯一の寺[5]である覚王山日泰寺がある。
名古屋市を中心として中京圏を形成し、愛知県内や岐阜県南部、三重県北部に多くの衛星都市を持ち、日本の三大都市圏の1つに数えられる。2019年の都市的地域の人口は約1,024万人と推計される[6]。中京圏の域内総生産は約3,637億ドルであり、これは国内で3番目、世界で第22番目の規模である[7]。
アメリカ合衆国のシンクタンクが2019年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界70位の都市であると評価された[8]。ユネスコの創造都市に認定されている[9]。市章は、尾張徳川家の合印に由来する「㊇」である[10]。
Nagoya (名古屋市, Nagoya-shi) is the largest city in the Chūbu region of Japan. It is Japan's fourth-largest incorporated city and the third most populous urban area. Located on the Pacific coast on central Honshu, it is the capital of Aichi Prefecture and is one of Japan's major ports along with those of Tokyo, Osaka, Kobe, Yokohama, and Chiba. It is also the center of Japan's third-largest metropolitan region, known as the Chūkyō metropolitan area. As of 1 October 2019, 2,327,557 people lived in the city, part of Chūkyō metropolitan Area's 10.11 million people,[4] making it one of the 50 largest urban areas in the world.
In 1610, the warlord Tokugawa Ieyasu, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, moved the capital of Owari Province from Kiyosu to Nagoya. This period saw the renovation of Nagoya Castle. Nagoya was proclaimed a city in 1889, during the Meiji Restoration; it became a major industrial hub for Japan. The traditional manufactures of timepieces, bicycles, and sewing machines were followed by the production of special steels, chemicals, oil, and petrochemicals, as the area’s automobile, aviation, and shipbuilding industries flourished.[5] Nagoya was impacted by bombing from US air raids during World War II.
After the war, Nagoya developed into a major port and transport center. The Shinkansen high-speed line connecting Tokyo and Osaka converges on Nagoya. Nagoya is served by two airports: Chubu Centrair International Airport in nearby Tokoname, and Nagoya Airfield, home to Mitsubishi Aircraft Corporation. Nagoya remains an important center for the automotive, aviation, and ceramic industries, hosting the headquarters of Brother Industries, Ibanez, Lexus, and Toyota Tsusho, among others.
Nagoya is home to Nagoya University, the Nagoya Institute of Technology, and Nagoya City University. It is also the location of numerous cultural institutions, including the Tokugawa Art Museum, Atsuta Shrine, Higashiyama Zoo and Botanical Gardens, Aichi Arts Center, and Misono-za. Nagoya TV Tower is the oldest TV tower in Japan.
Nagoya (名古屋市, Nagoya-shi?) est la troisième ville du Japon par sa superficie et la quatrième par la population, derrière Tokyo, Yokohama et Osaka. Située sur la côte Pacifique, au bord de la baie d'Ise dans la région du Chūbu, au centre de Honshū, c'est la capitale de la préfecture d'Aichi. Le pachinko, né à Nagoya, y a son musée.
L'agglomération de Nagoya, qui compte environ neuf millions d'habitants, est la troisième du pays.
Nagoya è una città della regione di Chūbu nell'isola di Honshū in Giappone, con un porto sull'oceano Pacifico. È il capoluogo della prefettura di Aichi, la quarta maggiore città del Giappone e la terza città sul piano economico. Dispone di due aeroporti, tra cui il nuovo Aeroporto Internazionale di Chūbu-Centrair, aperto il 17 febbraio 2005.
Nagoya (名古屋市 Nagoya-shi?) es la cuarta ciudad más grande de Japón. Localizada en la costa del Pacífico en la región de Chūbu, en el centro de la isla de Honshū, es la capital de la prefectura de Aichi.
Наго́я (яп. 名古屋市 Нагоя-си, букв. «именной (фамильный) старый дом»[1]) — город, определённый указом правительства, четвёртый по количеству населения город в Японии. Один из крупнейших портов Японии и административный центр префектуры Айти. Ядро экономического района Токай
 *Changjiang|Yangtze Fluß
*Changjiang|Yangtze Fluß
 *Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone
*Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone
 China
China
 Chinese Super League 2019
Chinese Super League 2019

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Seidenstraße
Seidenstraße

 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe

 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen
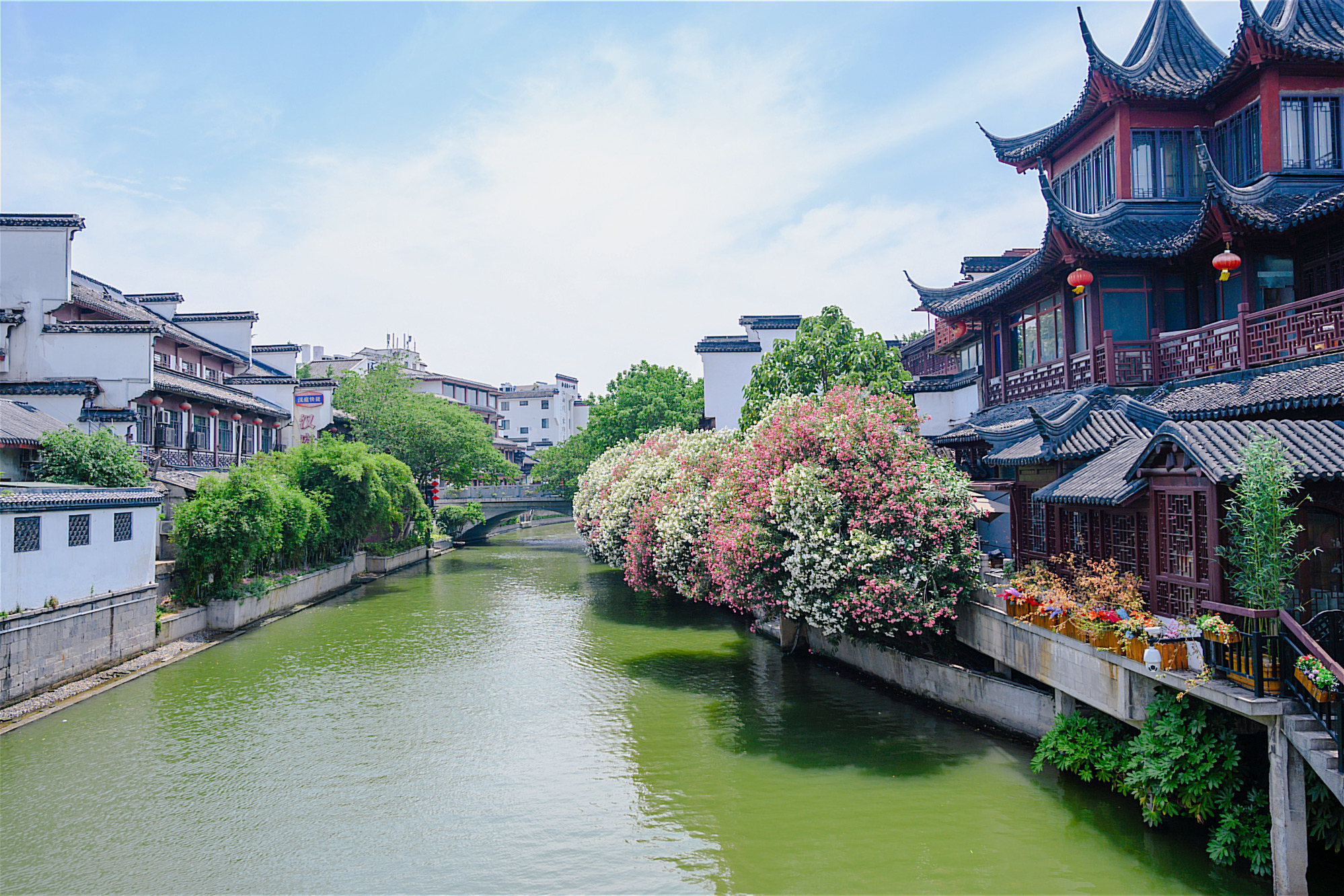





南京市(英文:Nanjing,邮政式拼音:Nanking),简称“宁”,别称金陵,是中华人民共和国江苏省省会、副省级城市和特大城市[7],华东地区区域中心城市。地处长江下游沿岸,位于江苏省西南部。是长江下游和长三角地区重要产业城市、长三角的副中心城市和中国东部暨江苏省的政治、经济、科教、文化、信息中心[8][9],也是全国综合性交通和通信枢纽城市以及科教中心城市之一[10]。
全市下辖11个区[11],总面积6582.31平方千米[4],2016年底常住人口827.05万,其中城镇人口678.14万人[12]。
南京有2500多年建城史和前后近500年建都史[13],先后有东吴、东晋、南朝宋、齐、梁、陈、南唐、明朝、太平天国、中华民国等十个朝代及政权定都南京[注 2],有“六朝古都”、“十朝都会”之称[注 3],历史上长期是中国南方的政治文化中心,亦被视为中华之正朔所在,是国家首批国家历史文化名城。
南京是全国重要科教文化中心,有八所大学列入全国百所重点建设大学,居各大城市第三位。根据自然出版集团发布的2016年自然指数,位居国内科研领先城市前三[14]。技术研发经费支出、发明专利数量名列前茅。新兴产业蓬勃,例如,软件与信息服务业居全国第四,新型显示产业居全国第二,智慧电网产业居全国首位,设有南京软件谷、智慧电网谷、生物医药谷、卫星应用产业园等多个产业园区[15]。有中国三大图书馆之一的南京图书馆[16]、三大博物馆之一的南京博物院[17]等。
南京,简称“宁”,古称金陵、建康,是江苏省会、副省级市、南京都市圈核心城市,国务院批复确定的中国东部地区重要的中心城市、全国重要的科研教育基地和综合交通枢纽 。全市下辖11个区,总面积6587km²,2017年建成区面积1398.69km²,常住人口833.5万人,城镇人口685.89万人,城镇化率82.3%,是长三角及华东唯一的特大城市。
南京地处中国东部、长江下游、濒江近海,是中国东部战区司令部驻地 ,长江国际航运物流中心 ,长三角辐射带动中西部地区发展的国家重要门户城市,也是东部沿海经济带与长江经济带战略交汇的重要节点城市。
南京是中国四大古都、首批国家历史文化名城 ,是中华文明的重要发祥地 ,历史上曾数次庇佑华夏之正朔 ,是四大古都中唯一未做过异族政权首都的古都 ,长期是中国南方的政治、经济、文化中心 。南京早在100-120万年前就有古人类活动,35-60万年前已有南京猿人在汤山生活,有着7000多年文明史、近2600年建城史和近500年的建都史,有“六朝古都”、“十朝都会”之称。
南京是国家重要的科教中心,自古以来就是一座崇文重教的城市,有“天下文枢”、“东南第一学”的美誉,明清时期中国一半以上的状元均出自南京江南贡院。截至2016年,南京各类高等院校74所,其中111计划高校9所及学科25个,仅次于北京;211高校8所、双一流高校12所,仅次于北京上海;两院院士82人、千人计划特聘专家87人,均居中国第三。
Nanjing (chinesisch 南京, Pinyin Nánjīng ‚Südliche Hauptstadt‘,  Anhören?/i) ist eine bezirksfreie Stadt in der Volksrepublik China. Neben die Schreibung nach der offiziellen Pinyin-Transkription Nanjing sieht man heute vielfach noch die ältere deutsche Schreibweise nach Stange Nanking (mit Diakritikum: Nank’ing).[2] Nanjing ist Hauptstadt und Metropole der Provinz Jiangsu. Zudem war es Ende des 14. und Anfang des 15. Jahrhunderts Hauptstadt der Ming-Dynastie sowie 1927–49 Hauptstadt der Republik China, gehört damit zu den vier großen historischen Hauptstädten Chinas. Nanjings Kurzbezeichnung lautet Ning (寧 / 宁, Níngjīng ‚friedlich, ruhig‘), sie ist geschichtlich auch unter der Bezeichnung Jinling (金陵, Jīnlíng ‚goldener Hügel‘) bekannt. Die Stadt ist ein politisch kulturelles Zentrum Chinas mit einer langen Geschichte. Daher hat Nanjing im Chinesischen auch die Bezeichnung "Antikes Kapitol der sechs Dynastien" (六朝古都, Liù Cháo Gǔdū) bzw. "Metropole der zehn Dynastien" (十朝都會 / 十朝都会, Shí Cháo Dūhuì). Nanjing zählt 5.827.888 Einwohner im urbanen Stadtgebiet (Stand 2010) und 8.270.000 in der Agglomeration (Stand 2016). Somit ist Nanjing – hinter Shanghai – die zweitgrößte Stadt in Ostchina.
Anhören?/i) ist eine bezirksfreie Stadt in der Volksrepublik China. Neben die Schreibung nach der offiziellen Pinyin-Transkription Nanjing sieht man heute vielfach noch die ältere deutsche Schreibweise nach Stange Nanking (mit Diakritikum: Nank’ing).[2] Nanjing ist Hauptstadt und Metropole der Provinz Jiangsu. Zudem war es Ende des 14. und Anfang des 15. Jahrhunderts Hauptstadt der Ming-Dynastie sowie 1927–49 Hauptstadt der Republik China, gehört damit zu den vier großen historischen Hauptstädten Chinas. Nanjings Kurzbezeichnung lautet Ning (寧 / 宁, Níngjīng ‚friedlich, ruhig‘), sie ist geschichtlich auch unter der Bezeichnung Jinling (金陵, Jīnlíng ‚goldener Hügel‘) bekannt. Die Stadt ist ein politisch kulturelles Zentrum Chinas mit einer langen Geschichte. Daher hat Nanjing im Chinesischen auch die Bezeichnung "Antikes Kapitol der sechs Dynastien" (六朝古都, Liù Cháo Gǔdū) bzw. "Metropole der zehn Dynastien" (十朝都會 / 十朝都会, Shí Cháo Dūhuì). Nanjing zählt 5.827.888 Einwohner im urbanen Stadtgebiet (Stand 2010) und 8.270.000 in der Agglomeration (Stand 2016). Somit ist Nanjing – hinter Shanghai – die zweitgrößte Stadt in Ostchina.
南京市(ナンキンし、中国語: 南京市、拼音: Nánjīng ( 聞く)、英語: Nanjing)は、中華人民共和国の副省級市で、江蘇省の省都。古くから長江流域・華南の中心地で、かつては三国・呉、東晋、南朝の宋・斉・梁・陳(以上の6朝を総称して六朝)、十国の南唐や明といった王朝や南京国民政府の首都であった。中国四大古都の一つ。14世紀から15世紀にかけて、世界最大の都市であった[1]。2016年の都市的地域の人口は678.14万人であり、総人口は827万人である[2]。
聞く)、英語: Nanjing)は、中華人民共和国の副省級市で、江蘇省の省都。古くから長江流域・華南の中心地で、かつては三国・呉、東晋、南朝の宋・斉・梁・陳(以上の6朝を総称して六朝)、十国の南唐や明といった王朝や南京国民政府の首都であった。中国四大古都の一つ。14世紀から15世紀にかけて、世界最大の都市であった[1]。2016年の都市的地域の人口は678.14万人であり、総人口は827万人である[2]。
金陵(きんりょう)は南京の別名である。また清朝のころには江寧(こうねい、簡体字:江宁)と呼ばれたことから略称は「寧(簡体字:宁)」である。夏はとても暑く、重慶、武漢と並ぶ中国三大ボイラー(三大火炉)の一つと言われている。
南京の歴史は春秋時代に呉がこの地に城を築いたことに始まる。戦国時代に呉を征服した楚は金陵邑を設置。その後秦朝による統一事業が達成され、始皇帝がこの地に巡幸してきた際に、「この地に王者の気がある」と言われ、それに怒って地形を無理やり変えてこの地の気を絶とうとした。また名前も金から秣(まぐさ)の秣陵県と改称している。
三国時代になると呉の孫権が229年に石頭城という要塞を築いて建業と称してこの地に都を置いた。西晋にて一旦、建業とされた後に司馬鄴(愍帝)を避諱して建康と改められ、東晋及びその後の四王朝(宋、斉、梁、陳)の都となった。呉を含めた六国が全て同じ地に都を置いたことから六朝時代の名がある。
隋代には江寧県、唐代には金陵県、白下県、上元県と改称されている。隋唐代には新たに開削された大運河により、長江対岸の揚州が物資の集積地となり、この地域の中心地としての地位を奪われた恰好となり、往時の都としての繁栄は見られなくなった。唐崩壊後の五代十国時代には、南唐の都城である金陵府が置かれ、後に改名されて西都と称する。
明の太祖朱元璋(洪武帝)は1356年、集慶路と呼ばれていたこの地を征服し、以後ここを根拠地として全土を統一するに至った。1368年、応天府と改められ、首都とする。1421年には、靖難の役で皇位を簒奪した永楽帝により首都が北京(順天府)へ遷都され、「南京」と改められる。なお、この遷都に批判的であった息子の洪熙帝は即位後直ちに都を南京に戻そうとしたが、在位1年に満たずに急死したため計画は中止となる。このため、北京が国都として確定したものの、洪武帝の陵墓(明孝陵)のある南京もまた明朝創業の地として重要視されて副都としての扱いを受けた。明一代に於いて首都北京周辺の北直隷に対して副都南京周辺は南直隷とされ、南京には首都北京に異常があった際に備えて北京に置かれた朝廷を縮小したもの(南京六部(中国語版))が置かれていた。1644年に北京が李自成の順軍によって陥落させられて明が滅びると、南京の官僚たちによって南京を首都とした亡命政権・南明が建てられたが翌年には清によって滅ぼされた。明代の南京の紫禁城は現在の故宮公園であり皇城の中に宮城があり、現在の故宮公園はかつての宮城の一部であり、門や主要建築物の石壇が残っている。ちなみに北京の紫禁城(故宮)も明の北京遷都の際、南京の紫禁城を模して建てたものであった(南京の紫禁城は靖難の役のとき攻城のあげく、焼却されてがれきとなった)。
清代に入ると江寧と呼ばれるようになった。太平天国の乱では占領され、天京とされた。また1858年の天津条約・1860年の北京条約に於いて西欧に対して開港した。
辛亥革命により中華民国が成立すると、1912年には一時的に臨時政府が置かれ、1927年4月には国民政府の首都となった。日中戦争(支那事変)中の1937年12月には日本軍によって占領された。
1940年3月に汪兆銘政権(南京国民政府)の首都となった。
1949年1月16日には国共内戦の結果、中華民国の中央政府は撤退し、4月23日には中国人民解放軍により占領された。同年10月1日に中華人民共和国が建国されると直轄地になるが、1953年に江蘇省の発足とともに同省の省都となった。1994年には副省級市になっている。なお、現在も中華民国は南京を「公式な首都」としている(詳細は「中華民国#首都」を参照)。
Nanjing ( listen), formerly romanized as Nanking and Nankin,[4] is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China and the second largest city in the East China region,[b] with an administrative area of 6,600 km2 (2,500 sq mi) and a total population of 8,270,500 as of 2016.[5] The inner area of Nanjing enclosed by the city wall is Nanjing City (南京城), with an area of 55 km2 (21 sq mi), while the Nanjing Metropolitan Region includes surrounding cities and areas, covering over 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi), with a population of over 30 million.
listen), formerly romanized as Nanking and Nankin,[4] is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China and the second largest city in the East China region,[b] with an administrative area of 6,600 km2 (2,500 sq mi) and a total population of 8,270,500 as of 2016.[5] The inner area of Nanjing enclosed by the city wall is Nanjing City (南京城), with an area of 55 km2 (21 sq mi), while the Nanjing Metropolitan Region includes surrounding cities and areas, covering over 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi), with a population of over 30 million.
Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949,[6] and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure,[7] enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province.[8] Nanjing has been ranked seventh in the evaluation of "Cities with Strongest Comprehensive Strength" issued by the National Statistics Bureau, and second in the evaluation of cities with most sustainable development potential in the Yangtze River Delta. It has also been awarded the title of 2008 Habitat Scroll of Honor of China, Special UN Habitat Scroll of Honor Award and National Civilized City.[9] Nanjing boasts many high-quality universities and research institutes, with the number of universities listed in 100 National Key Universities ranking third, including Nanjing University which has a long history and is among the world top 10 universities ranked by Nature Index.[10] The ratio of college students to total population ranks No.1 among large cities nationwide. Nanjing is one of the top three Chinese scientific research centers, according to the Nature Index,[11] especially strong in the chemical sciences, and also strong in many other areas, for instance, it hosts the nation's best computer software laboratory and wireless communication laboratory in the IT field, as well as the state key laboratory for pharmaceutical biotechnology.
Nanjing, one of the nation's most important cities for over a thousand years, is recognized as one of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. It has been one of the world's largest cities, enjoying peace and prosperity despite wars and disasters.[12][13][14][15] Nanjing served as the capital of Eastern Wu (229–280), one of the three major states in the Three Kingdoms period ; the Eastern Jin and each of the Southern Dynasties (Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang and Chen), which successively ruled southern China from 317–589; the Southern Tang(937–75), one of the Ten Kingdoms ; the Ming dynasty when, for the first time, all of China was ruled from the city (1368–1421);[16] and the Republic of China (1927–37, 1946–49) prior to its flight to Taiwan during the Chinese Civil War.[17] The city also served as the seat of the rebel Taiping Heavenly Kingdom (1853–64) and the Japanese puppet regime of Wang Jingwei (1940–45) during the Second Sino-Japanese War. It suffered severe atrocities in both conflicts, including the Nanjing Massacre.
Nanjing has served as the capital city of Jiangsu province since the establishment of the People's Republic of China. It boasts many important heritage sites, including the Presidential Palace and Sun Yat-sen Mausoleum. Nanjing is famous for human historical landscapes, mountains and waters such as Fuzimiao, Ming Palace, Chaotian Palace, Porcelain Tower, Drum Tower, Stone City, City Wall, Qinhuai River, Xuanwu Lake and Purple Mountain. Key cultural facilities include Nanjing Library, Nanjing Museum and Nanjing Art Museum.
Nankin ou Nanjing ([Écoutez] chinois : 南京 ; pinyin : nánjīng ; EFEO : Nanking ; zhuyin : ㄋㄢˊ ㄐㄧㄥ ; littéralement : « capitale du Sud », à mettre en rapport à Pékin, 北京, běijīng, « capitale du Nord »), immédiatement en amont du delta du Yangzi Jiang, le premier fleuve chinois, est la capitale de la province chinoise du Jiangsu. La ville compte aujourd'hui plus de huit millions d'habitants. Elle a joué un rôle considérable dans l'histoire chinoise. La prise de la ville par les Japonais en 1937 s'accompagna d'un massacre dont l'ampleur n'est pas connue avec certitude.
Nankin a le statut administratif de ville sous-provinciale. L'abréviation chinoise du nom de la ville est níng (寧).
Nanchino (AFI: /nanˈkino/[1]; in cinese 南京S, NánjīngP, Nan-chingW, letteralmente "capitale [京, jīng] del sud [南, nán]") è un importante capoluogo della provincia dello Jiangsu in Cina, soprattutto se inserito nel contesto della storia e della cultura cinese, essendo stata, per lungo tempo, la capitale della Cina.
Situata nei pressi del bacino di drenaggio del fiume Azzurro e nella zona economica del delta, Nanchino è da millenni una delle più importanti città cinesi. È stata riconosciuta come una delle quattro grandi antiche capitali della Cina. Fu capitale del regno di Wu durante il periodo dei tre regni, e capitale ufficiale della Repubblica di Cina, anche se la capitale provvisoria di quest'ultima è Taipei, essendo Nanchino situata nella Repubblica Popolare Cinese. La città è anche una delle 15 località sub-provinciali della Repubblica Popolare Cinese, godendo di autonomia politica ed economica seconda solo a quella della provincia. Nanchino è un importantissimo centro nell'educazione, nella ricerca, nei trasporti, e nel turismo. La città ha ospitato i II Giochi olimpici giovanili estivi.
Con una popolazione urbana di oltre 8 milioni di abitanti (2010), Nanchino è il secondo polo commerciale della Cina orientale dopo Shanghai. È stata classificata seconda tra le "città con il maggior sviluppo sostenibile" secondo uno studio redatto dall'Istituto nazionale di statistica della Cina, e seconda tra le città con maggior sviluppo sostenibile potenziale del delta del fiume Azzurro. Ha anche vinto il premio d'onore della Cina e il premio d'onore delle Nazioni Unite[2].
Nankín1 (en chino: 南京市, pinyin: Nánjīng, transcripción antigua: Nanking, pronunciado [ nǎn.tɕíŋ](![]() escuchar), literalmente: la capital del sur) es una ciudad-subprovincia y la capital de la provincia de Jiangsu en la República Popular China, situada cerca del río Yangtsé. Es la segunda ciudad más grande de la región, después de Shanghái.
escuchar), literalmente: la capital del sur) es una ciudad-subprovincia y la capital de la provincia de Jiangsu en la República Popular China, situada cerca del río Yangtsé. Es la segunda ciudad más grande de la región, después de Shanghái.
Nankín, también es conocida como la "Capital de la Educación, la Ciencia, la Cultura, el Arte y el Turismo". Durante la Rebelión Taiping fue conocida como "La capital del cielo" Tianjing. Es una de las Cuatro capitales antiguas de China y fue la capital para diez dinastías o reinos. Ha sido el centro económico y político del sureste de China durante más de 1000 años. En la actualidad, es un importante centro turístico. Su población en 2012 era más de ocho millones de habitantes.
Нанки́н (кит. 南京, пиньинь: Nánjīng, палл.: Наньцзин [Слушать (инф.)], буквально — «южная столица») — бывшая столица Китая, порт в низовьях реки Янцзы, столица провинции Цзянсу.
Расположен в восточной части страны, в 260 км к северо-западу от Шанхая.Крупный промышленный и культурный центр. Население — 8 187 800 человек (2013)[1].
Время основания достоверно не известно. Согласно легенде, цитируемой художником Чен И, жившим во времена династии Мин, правитель царства У, Фучай, основал форт Ечэн в районе современного Нанкина в 495 году до н. э.[2] Позднее, в 473 году до н. э. царство Юэ завоевало У и возвело форт Юэчэн на окраине сегодняшних Врат Китая[zh].
Город несколько раз менял названия (см. Цзянькан), столица Восточной Цзинь, 316—420).
В середине XIV века Нанкин был очагом восстания против монгольской империи Юань. Он стал столицей одного из лидеров повстанцев, Чжу Юаньчжана, который в 1368 году провозгласил здесь новую империю Мин, а сам стал её первым императором (девиз правления Хунъу). В 1368—1421 годах служил столицей Хунъу и его преемников Цзяньвэня и Юнлэ. В царствие Хунъу Нанкин был обнесён мощной крепостной стеной; для самого же императора был сооружён грандиозный мавзолейный комплекс Сяолин у подножия Горы пурпурного золота (Цзыцзиньшань) к востоку от города.
Уже в 1403 году, в самом начале царствия Юнлэ на судоверфи Лунцзян («Драконовая река»), расположенной под стенами Нанкина, на реке Циньхуай[zh] близ её впадения в Янцзы, развернулось строительство огромных кораблей для экспедиций Чжэн Хэ в Индийский океан[3].
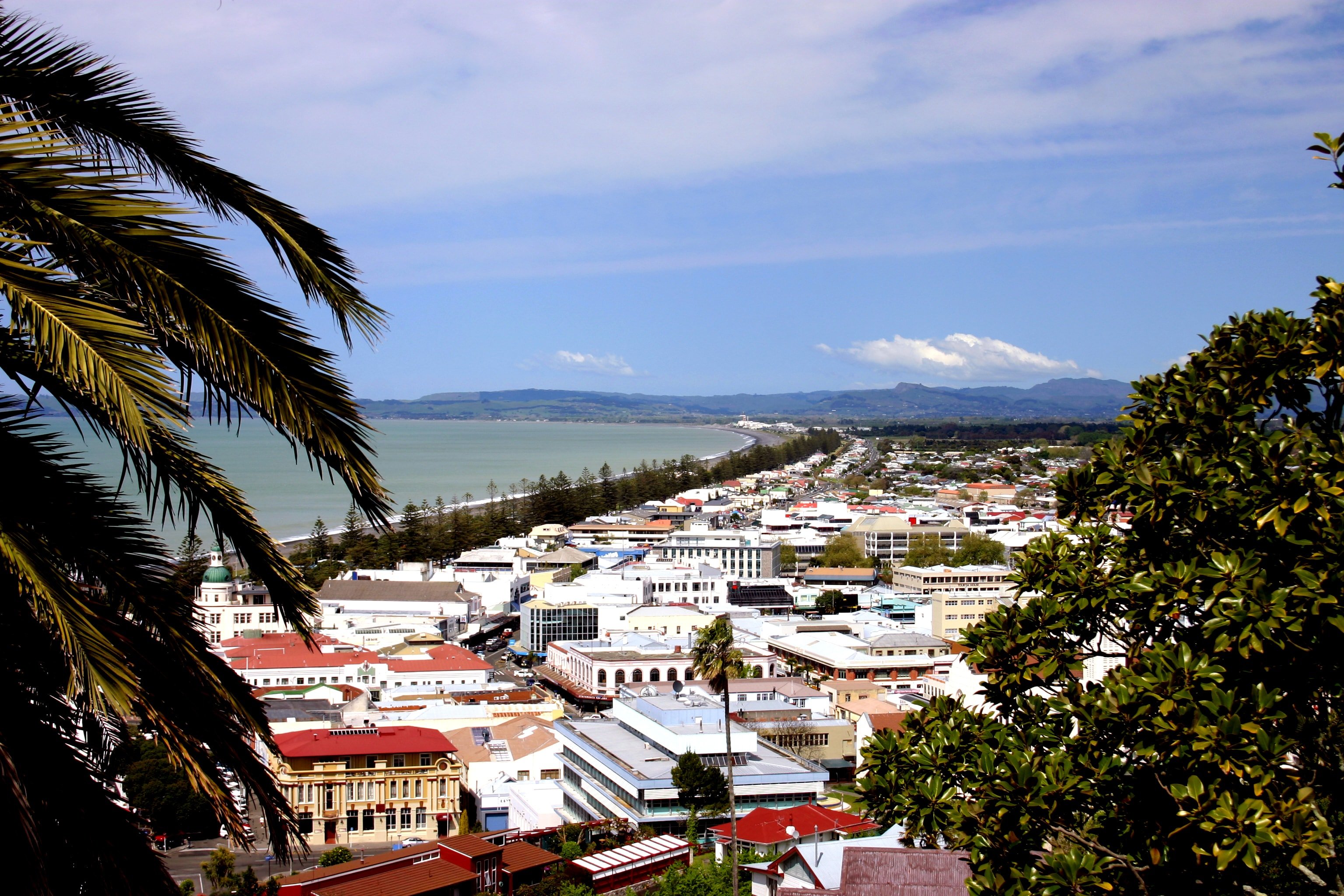



Napier ist eine Küstenstadt an der Hawke Bay auf der Nordinsel von Neuseeland. Die mit über 56.000 Einwohnern 14.-größte Stadt Neuseelands ist die Hauptstadt der Region Hawke’s Bay und wird als eigenständiger Stadt-Distrikt verwaltet. Zusammen mit dem etwa zehn Kilometer südlicheren Hastings bildet sie den fünftgrößten Ballungsraum Neuseelands, der im Englischen oft als the Twin Cities bezeichnet wird.
 Campania
Campania
 Neapel
Neapel
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990

 Geschichte
Geschichte

 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 Italien
Italien
 Seidenstraße
Seidenstraße

 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe

 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen
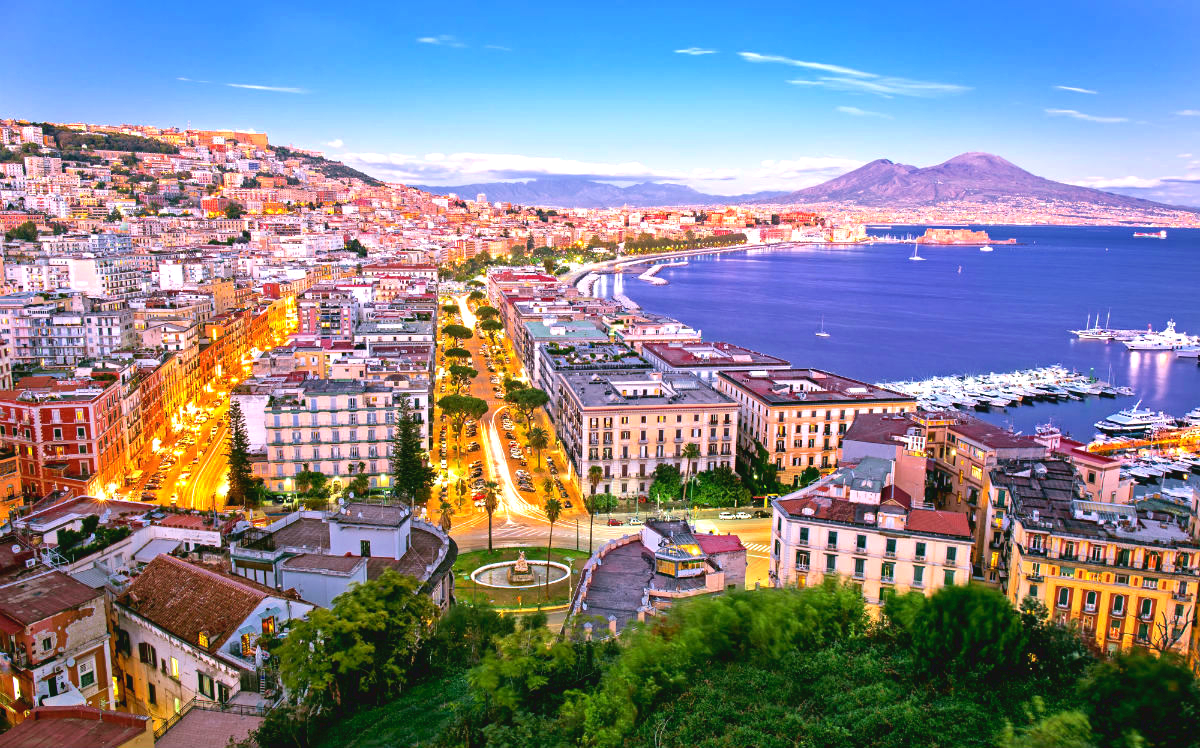


那不勒斯(意大利语:Napoli;那不勒斯语:Nàpule)是意大利南部的第一大城市,坎帕尼亚大区以及那不勒斯省的首府。城市面积117平方公里,人口略低于100万。那不勒斯都会区有大约380万人口,是仅次于米兰和罗马的意大利第三大都会区[3]和欧洲第15大都会区[3]。那不勒斯地区也是意大利人口最稠密的地方之一。
那不勒斯位于那不勒斯湾的北岸,其东西两侧分别是两个火山区域:维苏威火山和坎皮佛莱格瑞火山区。因此,该市自古至今不断受到火山活动和地震的威胁。
那不勒斯始于前600年[4],以其丰富的历史、文化、艺术和美食而著称,那不勒斯历史中心被联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产。比萨饼起源于那不勒斯。音乐是那不勒斯文化中产生了广泛影响的的一个重要组成部分,包括发明了浪漫吉他和曼陀林,以及对歌剧和拿波里民谣的重大贡献。
Neapel (Italienisch Napoli, Neapolitanisch Napule, altgriechisch: Νεάπολις („neue Stadt“)) ist mit knapp einer Million Einwohnern die drittgrößte Stadt Italiens. Die Hauptstadt der Region Kampanien sowie der Metropolitanstadt Neapel ist ein wirtschaftliches und kulturelles Zentrum Süditaliens. Die Metropolregion hat bis zu 4,4 Millionen Einwohner. Viele Neapolitaner sprechen das stark vom Standarditalienischen abweichende Neapolitanisch.
Die ursprüngliche griechische Siedlung trug den Namen Neapolis („Neustadt“). Später geriet sie unter römische Herrschaft. Vom Spätmittelalter bis zum 18. Jahrhundert gehörte Neapel zu den größten Städten Europas. Seine politische Geschichte ist über weite Strecken von Fremdherrschaft geprägt, zudem war es die Hauptstadt süditalienischer Reiche.
ナポリ(伊: Napoli (![]() 音声ファイル) ; ナポリ語: Napule)は、イタリア南部にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約98万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。カンパニア州の州都であり、ナポリ県の県都でもある。ローマ、ミラノに次ぐイタリア第三の都市で、南イタリア最大の都市である。都市圏人口は約300万人。
音声ファイル) ; ナポリ語: Napule)は、イタリア南部にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約98万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。カンパニア州の州都であり、ナポリ県の県都でもある。ローマ、ミラノに次ぐイタリア第三の都市で、南イタリア最大の都市である。都市圏人口は約300万人。
ナポリ湾に面した港湾都市・工業都市である[4]。古代ギリシア人によって建設された植民市に起源を持ち、13世紀以降はナポリ王国の首都として南イタリアの政治・経済の中心地となった[4]。ヴェスヴィオ火山を背景とする風光明媚な景観[4]で知られる観光都市であり、「ナポリを見てから死ね (vedi Napoli e poi muori)」[注釈 1]と謳われる[4]。旧市街地は「ナポリ歴史地区」として世界遺産に登録されている。ナポリ周辺にも、ヴェスヴィオ火山やポンペイの遺跡、カプリ島などの観光地を有する。
Naples (/ˈneɪpəlz/; Italian: Napoli [ˈnaːpoli ] (![]() listen), Neapolitan: Napule [ˈnɑːpələ] or [ˈnɑːpulə]; Latin: Neapolis; Ancient Greek: Νεάπολις, lit. 'new city') is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest municipality in Italy after Rome and Milan. In 2017, around 967,069 people lived within the city's administrative limits while its province-level municipality has a population of 3,115,320 residents. Its continuously built-up metropolitan area (that stretches beyond the boundaries of the Metropolitan City of Naples) is the second or third largest metropolitan area in Italy.
listen), Neapolitan: Napule [ˈnɑːpələ] or [ˈnɑːpulə]; Latin: Neapolis; Ancient Greek: Νεάπολις, lit. 'new city') is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest municipality in Italy after Rome and Milan. In 2017, around 967,069 people lived within the city's administrative limits while its province-level municipality has a population of 3,115,320 residents. Its continuously built-up metropolitan area (that stretches beyond the boundaries of the Metropolitan City of Naples) is the second or third largest metropolitan area in Italy.
First settled by Greeks in the second millennium BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world.[3] In the ninth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope or Παρθενόπη was established on the Island of Megaride,[4] later refounded as Neápolis in the sixth century BC.[5] The city was an important part of Magna Graecia, played a major role in the merging of Greek and Roman society and a significant cultural centre under the Romans.[6] It was capital of the Duchy of Naples (661-1139), then the Kingdom of Naples (1282 and 1816) and finally the Two Sicilies until the unification of Italy in 1861.
Between 1925 and 1936, Naples was expanded and upgraded by Benito Mussolini's government but severely damaged by Allied bombing during World War II, leading to extensive post-1945 reconstruction work.[7] Naples has experienced significant economic growth in recent decades, helped by the construction of the Centro Direzionale business district and an advanced transportation network, which includes the Alta Velocità high-speed rail link to Rome and Salerno and an expanded subway network. Naples is the third-largest urban economy in Italy, after Milan and Rome[8]. The Port of Naples is one of the most important in Europe and home of the Allied Joint Force Command Naples, the NATO body that oversees North Africa, the Sahel and Middle East.[9]
Naples' historic city centre is the largest in Europe and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, with a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the Palace of Caserta and the Roman ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Naples is also known for its natural beauties such as Posillipo, Phlegraean Fields, Nisida, and Vesuvius.[10]
Neapolitan cuisine is synonymous with pizza, which originated in the city but it includes many other less well-known dishes and is the Italian city with the highest number of accredited stars from the Michelin Guide.[11]
The best known sports team in Naples is the Serie A club S.S.C. Napoli, two-time Italian champions who play at the San Paolo Stadium in the southwest of the city.
Naples (en italien Napoli /ˈnapoli/, en napolitain Napule) est une ville d'Italie, capitale de la région de Campanie. Elle est la troisième ville d'Italie par sa population et la dix-huitième de l'Union européenne ainsi que respectivement la deuxième (devant Rome) et la neuvième en incluant sa banlieue2. C'est aussi la deuxième plus grande cité méditerranéenne en Europe, après Barcelone.
L'histoire de Naples s'étend sur plus de vingt-huit siècles. Sous le nom de Parthénope, elle fut fondée durant l'Antiquité par la cité voisine de Cumes. Elle s'étend ensuite rapidement jusqu'à devenir un des principaux centres commerciaux, culturels, philosophiques et politiques de la Grande-Grèce puis de l'Empire romain. Après avoir été brièvement dépendante de l'Empire byzantin, elle devient autonome au sein du duché de Naples. Dès le XIIIe siècle et pour ensuite plus de 600 ans, elle devient la capitale du Royaume de Naples puis successivement du Royaume des Deux-Siciles. Elle reste alors un des principaux centres de développement économiques et technologiques d'Europe jusqu'à son annexion au Royaume d’Italie en 1860, date à laquelle elle entame un relatif déclin socio-économique.
Au cours des siècles, Naples a aussi été un des grands centres universitaires internationaux. L'Université de Naples «Frédéric-II» est la plus ancienne université laïque du monde et la 6e plus ancienne en général. Elle compte également l'Université de Naples «L'Orientale», un des plus anciens instituts de langues orientales, ainsi que l'École militaire Nunziatella, une des plus renommées d'Italie. Elle est aussi un des hauts-lieux de la musique (avec l'école napolitaine de musique, à l'origine de l'Opéra bouffe, ou la chanson napolitaine), de l'art et de l'architecture (le Baroque napolitain, l'École du Pausilippe, le Liberty napolitain, le Théâtre napolitain et la Manufacture de Capodimonte) ou encore la cuisine napolitaine (avec les pâtes et surtout la pizza napolitaine comme icône, Naples étant la ville italienne la plus étoilée au Guide Michelin3).
La ville est aussi célèbre pour son patrimoine et ses monuments. Le centre historique de Naples (avec ses fontaines, vestiges antiques, palais et plus de 1 000 églises) est ainsi le plus grand centre-ville inscrit au patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO tandis que le parc national du Vésuve et le Miglio d'oro ont été reconnus réserve de biosphère. De plus, Naples est connue pour ses nombreuses beautés naturelles (Posillipo, Champs Phlégréens, Nisida, Vésuve, etc.), comparables à ceux de Rio de Janeiro4.
Enfin, elle abrite également la Villa Rosebery (l'une des trois résidences officielles du président de la République italienne), le siège d'un commandement interalliés et interarmées de l'OTAN, la Apple Developer Academy ainsi qu'un vaste patrimoine archéologique avec notamment la Naples souterraine ou, à proximité, la ville d'Herculanum, une ancienne banlieue5.
Napoli (AFI: /ˈnapoli/[4] ; Nàpule in napoletano, pronuncia [ˈnɑːpulə] o [ˈnɑːpələ]) è un comune italiano di 964 004 abitanti[2], capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana e della regione Campania.
Terzo comune in Italia per popolazione, Napoli è tra le più popolose e densamente popolate aree metropolitane dell'Unione europea.[N 1]
Fondata dai Cumani nell'VIII secolo a.C., fu tra le città più importanti della Magna Græcia[5][6], grazie al rapporto privilegiato con Atene[7], ed esercitò una notevole influenza commerciale, culturale e religiosa sulle popolazioni italiche circostanti[8] tanto da diventare sede della scuola epicurea di Filodemo di Gadara e Sirone. Dopo il crollo dell'Impero romano, nell'VIII secolo la città formò un ducato autonomo indipendente dall'Impero bizantino; in seguito, dal XIII secolo e per circa seicento anni, fu capitale del Regno di Napoli; con la Restaurazione divenne capitale del Regno delle Due Sicilie sotto i Borbone fino all'Unità d'Italia. Per motivi culturali, politici, storici e sociali è stata, dall'evo antico sino ai giorni nostri, una delle città cardine dell'Occidente.[9]
Sede della Federico II, la più antica università statale d'Europa,[10] ospita altresì l'Orientale, la più antica università di studi sinologici ed orientalistici del continente[11] e la Nunziatella, una delle più antiche accademie militari al mondo, eletta patrimonio storico e culturale dei Paesi del Mediterraneo da parte dell'Assemblea parlamentare del Mediterraneo.[12] Luogo d'origine della lingua napoletana, ha esercitato ed esercita un forte ruolo in numerosi campi del sapere, della cultura e dell'immaginario collettivo a livello nazionale ed internazionale.
Centro della filosofia naturalistica del rinascimento[13] e centro illuminista di livello europeo[14], è stata a lungo un punto di riferimento globale per la musica classica e l'opera attraverso la scuola musicale napoletana[15], dando tra l'altro origine all'opera buffa.[16]
Città dall'imponente tradizione nel campo delle arti figurative, che affonda le proprie radici nell'età classica, ha dato luogo a movimenti architettonici e pittorici originali, quali il rinascimento napoletano[17] e il barocco napoletano,[18] il caravaggismo,[19] la scuola di Posillipo[20] ed il Liberty napoletano,[21] nonché ad arti minori ma di rilevanza internazionale, quali la porcellana di Capodimonte[22] ed il presepe napoletano.[23]
È all'origine di una forma distintiva di teatro,[24] di una canzone di fama mondiale[25] e di una peculiare tradizione culinaria[26] che comprende alimenti che assumono il ruolo di icone globali, come la pizza napoletana,[27] e l'arte dei suoi pizzaioli che è stata dichiarata dall'UNESCO patrimonio immateriale dell'umanità.[28]
Nel 1995 il centro storico di Napoli è stato riconosciuto dall'UNESCO come patrimonio mondiale dell'umanità, per i suoi eccezionali monumenti, che testimoniano la successione di culture del Mediterraneo e dell'Europa[29]. Nel 1997 l'apparato vulcanico Somma-Vesuvio è stato eletto dalla stessa agenzia internazionale (con il vicino Miglio d'Oro, in cui ricadono anche i quartieri orientali della città) tra le riserve mondiali della biosfera.[30]
Nápoles (en italiano Napoli, en napolitano Napule) es la ciudad más poblada del sur de Italia, capital de la región de Campania y de la Ciudad metropolitana de Nápoles de más de 6 millones de habitantes. La ciudad de Nápoles administrativa tiene algo menos de un millón de habitantes,2 que, unidos a los de su área metropolitana, se elevan a 3,7 millones. Sus habitantes reciben el gentilicio de napolitanos. Está situada a medio camino entre el monte Vesubio y otra área volcánica, los Campos Flégreos. Da nombre al Golfo de Nápoles.
Tiene una gran riqueza histórica, artística, cultural y gastronómica, lo que llevó a la Unesco a declarar su centro histórico Patrimonio de la Humanidad.3 Griegos, romanos, bizantinos, normandos, franceses y españoles han dejado su huella en Nápoles. Estuvo brevemente bajo dominación austríaca en las primeras décadas del siglo XVIII, tras la cual se convirtió en el centro político del reino independiente de Nápoles y, posteriormente, de las Dos Sicilias, gobernado por los Borbones. En el año 1861 pasó a formar parte del Reino de Italia. En el siglo XX, durante el fascismo y en la reconstrucción subsiguiente a la Segunda Guerra Mundial se edificó gran parte de la periferia. En las últimas décadas, Nápoles se ha dotado de un distrito financiero con rascacielos (CDN) e infraestructuras como el TAV, hacia Roma y Salerno, o una red de metro en proceso de expansión. Por otra parte, también le acucian grandes problemas como el crimen organizado, muy presente en la vida de una parte de sus habitantes y que constituye un freno al desarrollo económico y social; o de otra naturaleza, las fuerzas telúricas: la ciudad ha sufrido grandes terremotos y la actividad volcánica es vigilada constantemente.
Неа́поль (др.-греч. Νεάπολις, от др.-греч. νέα πόλις букв. — новый город; лат. Neapolis, итал. Napoli, неап. Napule) — город в Италии. Административный центр области Кампания и провинции Неаполь. Расположен в бухте Неаполитанского залива.
Неаполь — третий по величине город Италии (после Рима и Милана) и самый большой город Южной Италии с населением около миллиона человек (с пригородами — около трёх миллионов). Крупный транспортный узел (международный аэропорт, морской порт). Наряду с официальным итальянским языком в просторечии местных жителей распространён неаполитанский диалект. Святой покровитель города — св. Януарий, день памяти которого 19 сентября отмечается как праздник города.
Находится в сейсмоопасной зоне (историческая часть — на западном склоне Везувия). Последнее извержение Везувия произошло в 1944 году. Последнее катастрофическое землетрясение случилось в Неаполе в 1980 году.


Neu-Delhi (englisch New Delhi; Hindi नई दिल्ली IAST Naī Dillī; Urdu نئی دہلی; Panjabi ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ) ist die Hauptstadt Indiens, Sitz der indischen Regierung, des Parlaments und der obersten Gerichte. Neu-Delhi ist ein relativ kleiner Teil der Megastadt Delhi, der mit 31,87 Millionen Einwohnern drittgrößten Metropolregion der Welt (Stand 2021),[2] und verfügt innerhalb des Nationalen Hauptstadtterritoriums Delhi über eine eigene Kommunalverwaltung, die 2011 ein Gebiet mit rund 250.000 Einwohnern umfasste.
Der Grundstein Neu-Delhis wurde während der Kolonialzeit am 15. Dezember 1911 südlich des damaligen Stadtzentrums Shahjahanabad gelegt, um Calcutta als Hauptstadt Britisch-Indiens abzulösen.[3]
Das Verhältnis zwischen den Namen Delhi und Neu-Delhi ist komplex. Neu-Delhi ist ein Teil der Metropole Delhi, die als National Capital Territory of Delhi („Nationales Hauptstadtterritorium Delhi“) von der indischen Zentralregierung mitverwaltet wird. Im engeren Sinn bezeichnet Neu-Delhi nur das während der britischen Kolonialzeit planmäßig angelegte Regierungsviertel, welches lediglich einen sehr kleinen Teil des Hauptstadtterritoriums umfasst und im Wesentlichen mit den Grenzen der kommunalen Verwaltungseinheit Neu-Delhi übereinstimmt. Mit dem davon zu unterscheidenden Distrikt Neu-Delhi besteht aber noch eine weitere administrative Einheit gleichen Namens mit anderer Grenzziehung.
Im alltäglichen Sprachgebrauch wird Neu-Delhi oft erheblich weiter gefasst. Als Neu-Delhi gegründet wurde, bestand Delhi in erster Linie aus der ummauerten Altstadt von Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi, Alt-Delhi). Durch das rasante Bevölkerungswachstum wurden nach der indischen Unabhängigkeit nach und nach auch die umliegenden, einstmals ländlichen Gebiete urbanisiert. Diese „neuen“ Teile Delhis werden entsprechend auch häufig zu Neu-Delhi gezählt. Heute wird die Bezeichnung Neu-Delhi somit oft komplementär zu Alt-Delhi für alle Gebiete Delhis außerhalb von Shahjahanabad benutzt. Vielfach sind die Namen Delhi und Neu-Delhi aber auch gänzlich austauschbar.
新德里(又译纽德里,印地语:नई दिल्ली;英语:New Delhi)是印度的首都,印度联邦政府所在地,也是印度大都市区德里的一个区。它位于印度西北部,座落在恒河支流亚穆纳河西岸,东北紧连旧德里(沙贾汉纳巴德)。整个德里国家首都辖区面积1,482平方公里,人口1,637万(2011年);其中新德里人口1,337万。2013年4月“世界城市区域研究”(Demographia World Urban Areas)发布第9届调查报告,世界大都市依照人口数排名第4,约2,282万人。[4]新德里是全国的政治、经济和文化中心。新德里是典型的放射型城市,城市以姆拉斯广场为中心,城市街道成辐射状、蛛网式地伸向四面八方。宏伟的建筑群大多集中于市中心。政府主要机构集中在市区从总统府到印度门之间绵延几公里的宽阔大道两旁。国会大厦为大圆盘式建筑,四周绕以白色大理石高大圆柱,是中亚式的建筑,屋檐和柱头的雕饰又为印度风格。总统府屋顶为巨大的半球形结构,带有莫卧儿王朝的遗风。城市西端的康瑙特市场建筑新巧,呈圆盘形,是新德里的最大商业中心。新德里还是全国交通的中心,有5条国家级公路、6条铁路与各地相通,还建有两座机场。新德里的奠基石是乔治五世在1911年德里杜尔巴期间奠定的。它由英国建筑师埃德温·鲁琴斯爵士和赫伯特·贝克爵士设计。新首都于1931年2月13日由印度总督艾文勋爵揭幕。

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Finanz
Finanz
 ***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center
***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus
N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus
M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus

 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 ***Globale wirtschaftliche Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der Städte
***Globale wirtschaftliche Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der Städte

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Seidenstraße
Seidenstraße
 Vereinigte Staaten
Vereinigte Staaten

 Wichtiger Hafen
Wichtiger Hafen
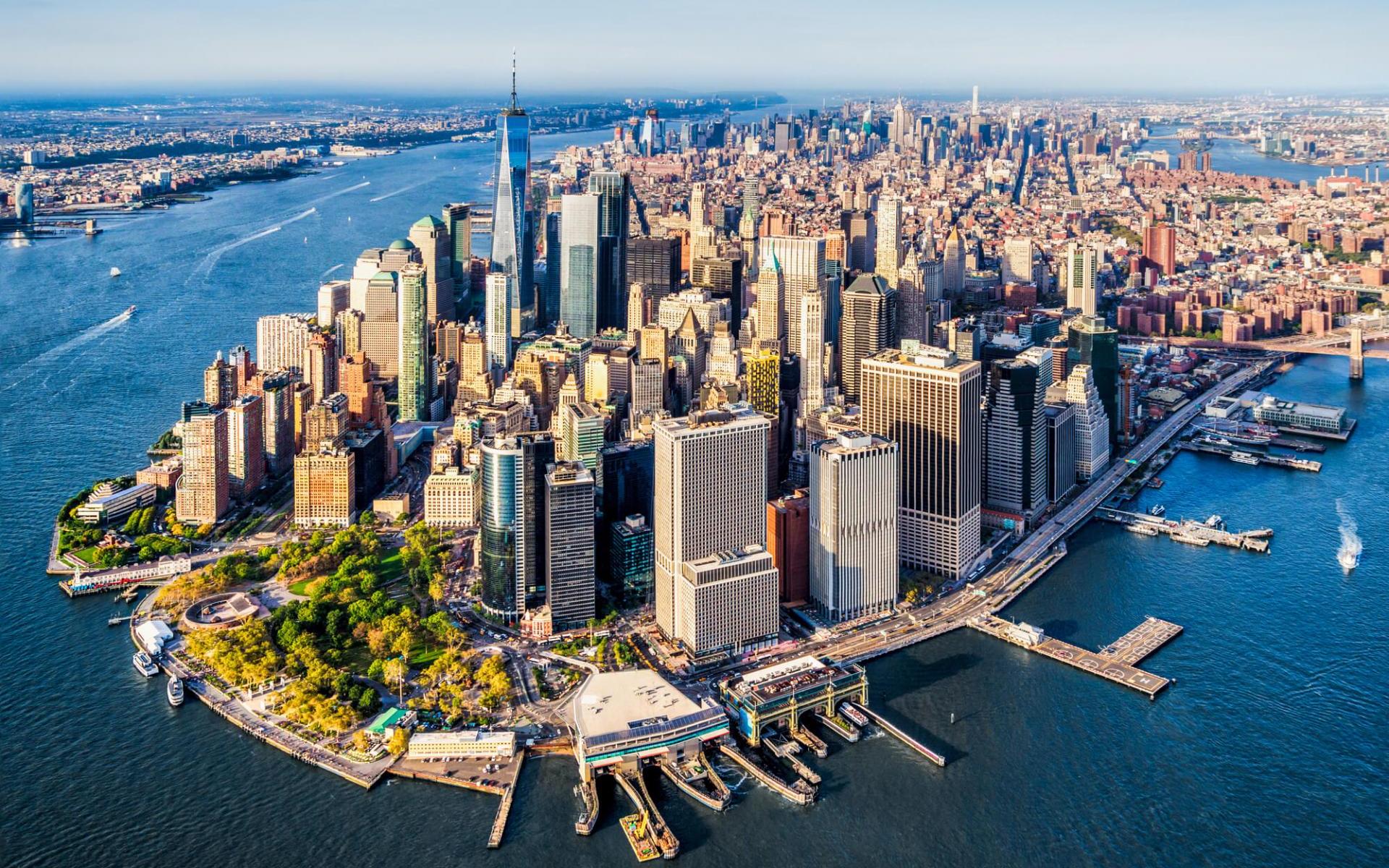

美国纽约(NewYork)是美国乃至美洲最大的城市,全市由由五个区组成:曼哈顿(Manhattan)、布鲁克林(Brooklyn)、皇 后区(Queens)、布郎克斯(Bronxs)和斯塔滕岛(Staten Island)。光是一个曼哈顿(Manhattan)就超过旧金山的大小,曼哈顿区是纽约市的精华所在,分成上中下城的曼哈顿区,拥有最流行最金融和最 颓废的风情。美国最大的500家公司中,有三分之一以上把总部设在曼哈顿。这里还能领略到著名的自由女神像、联合国总部、时代广场、大都会艺术博物馆、中央公园、苏活(soho)商业区、小意大利、第五大道商业区、格林威治村、华尔街、洛克菲勒中心、百老汇剧院区、唐人街等等人们印象中的纽约。
纽约是美国文化、艺术、音乐和出版中心,有众多的博物馆、美术馆、图书馆、科学研究机构和艺术中心,美国三大广播电视网和一些有影响的报刊、通讯社的总部都设在这里。(Quelle:http://www.ghl.com.cn)
纽约市(英语:New York City,简写为NYC),通称纽约,是位于美国纽约州的城市,为美国人口最多的城市、纽约都会区的核心、以及世界最大的城市之一,是对全球的经济、商业、金融、媒体、政治、教育和娱乐具有极大影响力的国际大都会。纽约还是联合国总部所在地[5],因此也被认为是世界外交的中心[6]。纽约还被称为“世界文化之都”[7][8],名列世界三大国际都会“纽伦港”之一。[9]
纽约位于东北部,濒临大西洋海岸,坐拥世界上最大的天然港口之一的纽约港[10]。纽约市共有曼哈顿区、皇后区、布鲁克林区、布朗克斯区、斯塔滕岛区等5个行政区,每一个行政区也各自是纽约州的一个县[11]。1898年,五个行政区被合并为现在的纽约市[12]。纽约也是全美国人口最密集的主要城市[13],2012年约有8,336,697人[14]居住于302.64平方英里(783.8平方千米)的土地上[15]。纽约都市区在全美的都会区中也高居第一,人口达到1980万[16],同时也是全美最大的联合统计区的一部分,在大区中人口达到2340万[17]。纽约也是语言和人口族群最为多元化的城市[18][19],在此使用的语言达到800种[20][21],而在2005年,全市有36%的人口是非美国出生的。
纽约的历史可以追溯至1624年,荷兰殖民者在这时候在此地建立贸易站,名为新阿姆斯特丹[22]。1664年,纽约及其周边地区为英国所占[22][23][24]。美国建国后,纽约在1785年至1790年为首都[25],1790年,纽约取代费城成为美国第一大城市[26]。纽约市的标志自由女神像在19世纪末20世纪初迎接了数百万移民的到来[27],它同时也是美国及其民主制度的象征[28]。
每年来到纽约的游客达到近5500万[29],许多区域和地标为人们所熟知。纽约还被不同媒体选为世界上被拍照最多的城市[30][31][32]。时报广场位于百老汇剧院区枢纽[33],被称作“世界的十字路口”[34],是世界上行人来往最密集的步行地段之一[35][36]和世界娱乐产业的中心之一[37]。城中的许多桥梁、高楼[38]和公园世界闻名。纽约的金融区,以曼哈顿下城的华尔街为龙头,被称为世界的金融中心[39][40],世界上最大的证券交易所(按上市公司市值)纽约证券交易所也位于此地[41]。曼哈顿的房地产是世界上最为昂贵的之一[42],其唐人街是西半球最为密集的华人聚居地[43][44]。纽约地铁是世界上最为发达的城市交通系统之一,提供24小时不间断的服务[45]。纽约同时还是许多高等学府的所在地[46],其中包括哥伦比亚大学、纽约大学和洛克菲勒大学等排名位于世界前35的学校[47]。
New York City (AE: [nuːˈjɔɹk ˈsɪɾi], kurz: New York, deutsch veraltet: Neuyork,[1] Abk.: NYC) ist eine Weltstadt an der Ostküste der Vereinigten Staaten. Sie liegt im Bundesstaat New York und ist mit rund 8,5 Millionen Einwohnern die bevölkerungsreichste Stadt der Vereinigten Staaten.[2]
Die Metropolregion New York mit 18,9 Mio. Einwohnern[3] ist einer der bedeutendsten Wirtschaftsräume und Handelsplätze der Welt, Sitz vieler internationaler Konzerne und Organisationen wie der Vereinten Nationen sowie wichtiger See- und Binnenhafen an der amerikanischen Ostküste und dem Hudson. Die Stadt genießt mit ihrer großen Anzahl an Sehenswürdigkeiten, den 500 Galerien, etwa 200 Museen, mehr als 150 Theatern und mehr als 18.000 Restaurants Weltruf auch in den Bereichen Kunst und Kultur und verzeichnet jedes Jahr etwa 50 Mio. Besucher, davon knapp 12 Mio. aus dem Ausland.[4][5] Laut Forbes Magazine ist New York City die Stadt mit den höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten in den Vereinigten Staaten sowie eine der teuersten Städte weltweit.[6]
Nachdem 1524 Giovanni da Verrazano und 1609 Henry Hudson die Gegend des heutigen New Yorks erforscht hatten, siedelten ab 1610 niederländische Kaufleute an der Südspitze der Insel Manna-Hatta und bald darauf an der Westspitze von Long Island, dem heutigen Brooklyn. Erst 1626 kaufte Peter Minuit den Einheimischen, wahrscheinlich Lenni-Lenape-Indianern, die Insel „Manna-hatta“ für Waren im Wert von 60 Gulden ab. Die damit begründete Siedlung erhielt danach den Namen Nieuw Amsterdam und war zunächst Hauptstadt der Kolonie Nieuw Nederland, bis sie 1664 von den Briten erobert wurde und die Stadt den seither gültigen Namen bekam.[7] Ihr Aufstieg zur Weltstadt begann 1825 mit der Fertigstellung des Eriekanals.
Die Metropolregion New York erbrachte 2016 eine Wirtschaftsleistung von 1,657 Billionen US-Dollar. Unter den Städten der Welt belegt es damit den zweiten Rang hinter Tokio und wäre als eigener Staat gezählt unter den 20 größten Volkswirtschaften der Welt.[8]
ニューヨーク市(英: New York City)は、アメリカ合衆国ニューヨーク州にある都市。
1790年以来、同国最大の都市であり[4]、市域人口は800万人を超え、都市圏人口では定義にもよるが2000万人以上である[2][5]。2015年の市内総生産は6625億ドルであり[6]、全米最大、東京に続き世界2位である。
ロンドンと並ぶ世界トップクラスの世界都市[7]、金融センターであり[8]、国際連合の本部所在地でもあり、世界の政治、経済、文化、ファッション、エンターテインメントなどに多大な影響を及ぼしている。
The City of New York, often called New York City (NYC) or simply New York, is the most populous city in the United States.[9] With an estimated 2017 population of 8,622,698[7] distributed over a land area of about 302.6 square miles (784 km2),[10][11] New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the United States.[12] Located at the southern tip of the state of New York, the city is the center of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass[13] and one of the world's most populous megacities,[14][15] with an estimated 20,320,876 people in its 2017 metropolitan statistical area and 23,876,155 residents in its combined statistical area.[4][5] A global power city,[16] New York City has been described uniquely[17] as the cultural,[18][19][20][21] financial,[22][23] and media capital of the world,[24][25] and exerts a significant impact upon commerce,[23] entertainment, research, technology, education, politics, tourism, art, fashion, and sports. The city's fast pace[26][27] has inspired the term New York minute.[28] Home to the headquarters of the United Nations,[29] New York is an important center for international diplomacy.[30][31]
Situated on one of the world's largest natural harbors,[32][33] New York City consists of five boroughs, each of which is a separate county of the State of New York.[34] The five boroughs – Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, The Bronx, and Staten Island – were consolidated into a single city in 1898.[35] The city and its metropolitan area constitute the premier gateway for legal immigration to the United States.[36] As many as 800 languages are spoken in New York,[37][38][39] making it the most linguistically diverse city in the world.[38][40][41] New York City is home to more than 3.2 million residents born outside the United States,[42] the largest foreign-born population of any city in the world.[43] In 2017, the New York metropolitan area produced a gross metropolitan product (GMP) of US$1.73 trillion.[44] If greater New York City were a sovereign state, it would have the 12th highest GDP in the world.[45]
New York City traces its origins to a trading post founded by colonists from the Dutch Republic in 1624 on Lower Manhattan; the post was named New Amsterdam in 1626.[46] The city and its surroundings came under English control in 1664[46] and were renamed New York after King Charles II of England granted the lands to his brother, the Duke of York.[47] New York served as the capital of the United States from 1785 until 1790.[48] It has been the country's largest city since 1790.[49] The Statue of Liberty greeted millions of immigrants as they came to the Americas by ship in the late 19th and early 20th centuries[50] and is a world symbol of the United States and its ideals of liberty and peace.[51] In the 21st century, New York has emerged as a global node of creativity and entrepreneurship,[52] social tolerance,[53] and environmental sustainability,[54][55] and as a symbol of freedom and cultural diversity.[56]
Many districts and landmarks in New York City are well known, with the city having three of the world's ten most visited tourist attractions in 2013[57] and receiving a record 62.8 million tourists in 2017.[58] Several sources have ranked New York the most photographed city in the world.[59][60] Times Square, iconic as the world's "heart"[61] and its "Crossroads",[62] is the brightly illuminated hub of the Broadway Theater District,[63] one of the world's busiest pedestrian intersections,[64][65] and a major center of the world's entertainment industry.[66] The names of many of the city's landmarks, skyscrapers,[67] and parks are known around the world. Manhattan's real estate market is among the most expensive in the world.[68][69] New York is home to the largest ethnic Chinese population outside of Asia,[70][71] with multiple signature Chinatowns developing across the city.[72][73][74] Providing continuous 24/7 service,[75] the New York City Subway is the largest single-operator rapid transit system worldwide, with 472 rail stations.[76][77][78] Over 120 colleges and universities are located in New York City, including Columbia University, New York University, and Rockefeller University, which have been ranked among the top universities in the world.[79][80] Anchored by Wall Street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan, it has been called both the most economically powerful city and the leading financial center of the world,[23][81][82][83] and the city is home to the world's two largest stock exchanges by total market capitalization, the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ.[84][85]
New Yorka (prononciation en anglais américain /nuːˈjɔɹk/ ; Écouter), officiellement nommée City of New York, connue également sous les noms et abréviations de New York City ou NYC, est la plus grande ville des États-Unis en termes d'habitants et l'une des plus importantes du continent américain. Elle se situe dans le Nord-Est des États-Unis, sur la côte atlantique, à l'extrémité sud-est de l'État de New York. La ville de New York se compose de cinq arrondissements appelés boroughs : Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, le Bronx et Staten Island. Ses habitants s'appellent les New-Yorkais (en anglais : New Yorkers).
New York exerce un impact significatif sur le commerce mondial, la finance, les médias, l'art, la mode, la recherche, la technologie, l'éducation et le divertissement. Regroupant l'ensemble des caractéristiques d'une ville mondiale, elle est parfois considérée comme « la capitale du monde ». Si elle n'est plus la capitale fédérale des États-Unis depuis plus de deux siècles (elle occupe cette fonction de 1785 à 17902), New York alimente pendant quelques décennies une rivalité financière et politique avec Philadelphie.
Il n'en reste pas moins que New York est la ville la plus peuplée du pays depuis 1790, avec 8 550 405 habitants selon le Bureau du recensement des États-Unis (estimations de 20153,4). Elle est aussi la troisième plus grande ville du continent américain derrière Mexico et São Paulo. Située au cœur de la mégalopole du BosWashb, l'agglomération new-yorkaise (20 182 305 habitants5) s'étend sur plusieurs comtés de l'État de New York (banlieues est et nord) et empiète sur deux États limitrophes. En effet, l'État du New Jersey comprend ses banlieues ouest et sud, et celui du Connecticut comprend ses banlieues nord-est. Son aire urbaine quant à elle comptait 24 millions d'habitants en 20156.
New York accueille quelque 50 millions de visiteurs annuellement7,8,9. Times Square, « The Crossroads of the World »10,11,12, est l'une des intersections les plus populaires du monde13, et le quartier des théâtres de Broadway14 est la plaque tournante du spectacle dans le pays tout entier et un centre majeur de l'industrie du divertissement dans le monde15. La ville abrite un grand nombre de ponts et tunnels (78916 en 2012), gratte-ciel et parcs de renommée mondiale17.
New York se place en tête dans la triade des grands centres financiers mondiaux avec Londres et Hong Kong, ces trois villes étant appelées par les médias anglophones « Nylonkong »18. Le quartier financier de New York, ancré par Wall Street dans le Lower Manhattan, fonctionne ainsi comme la « capitale financière du monde »19,20,21,22,23,24 et est le foyer du New York Stock Exchange (Bourse de New York)25, tandis que le nouveau One World Trade Center est le plus haut gratte-ciel d'Amérique du Nord. De plus, le marché immobilier de Manhattan est parmi les plus chers dans le monde26.
New York est frappée le 11 septembre 2001 par le plus grave attentat ayant jamais touché les États-Unis, deux avions de ligne détournés par des terroristes membres d'Al-Qaïda percutèrent les tours jumelles du World Trade Center et les détruisirent entièrement. En 2018, le quartier est toujours en reconstruction. New York est l'une des villes les plus cosmopolites du monde, par ses nombreux quartiers ethniques. Les plus connus sont Little Italy, ou encore Chinatown qui intègre la plus forte concentration de population chinoise des Amériques27,28,29,30. Enfin, New York accueille des institutions d'importance mondiale. On peut notamment citer le siège de l'ONU, mais aussi de nombreux sièges de multinationales31 et des centres culturels tels que le Metropolitan Museum of Art, le Brooklyn Museum, le Museum of Modern Art, le Lincoln Center. De nombreuses universités réputées sont situées à New York, notamment l'université de la ville de New York, l'université Columbia, l'université de New York, et l'université Rockefeller, qui sont classées dans le top 50 des universités dans le monde32.
New York (AFI: /njuˈjɔrk/[6], in inglese americano [nuː ˈjɔɹk], in italiano conosciuta anche come Nuova York) è una città degli Stati Uniti d'America. Viene detta New York City per distinguerla dall'omonimo Stato federato.
Conosciuta nel mondo anche come "grande mela" (Big Apple), un paragone le cui origini risalgono al libro The Wayfarer in New York scritto da Edward S. Martin nel 1909,[7][8] è situata nello Stato omonimo e sorge su un'area di circa 785 km² alla foce del fiume Hudson, sull'oceano Atlantico, mentre l'area metropolitana comprende anche località situate nei due adiacenti stati del New Jersey e del Connecticut.
È la città più popolosa degli Stati Uniti (tanto che la sua popolazione di 8,5 milioni di abitanti supera il doppio dei 4 milioni di Los Angeles, seconda città nazionale), nonché uno dei centri economici più importanti del mondo, riconosciuta come città globale. L'agglomerato urbano conta 18.223.567 abitanti,[9] quello metropolitano è di 23.019.036 abitanti, che la rendono, secondo le stime, dalla terza alla sesta area urbana più popolata del mondo, e tra le prime tre dell'emisfero boreale e del continente americano (in concorrenza con Città del Messico e San Paolo). New York è anche stimata come diciottesima città più popolata al mondo, tra le città africane di Kinshasa e Lagos, nonché la più popolosa città anglofona del mondo.
Situata sulla cosiddetta baia di New York (New York Bay), in parte sul continente e in parte su isole, è amministrativamente divisa in cinque distretti (borough): Manhattan, The Bronx, Queens, Brooklyn e Staten Island. Di essi, uno è nel continente (il Bronx, situato a nord di Manhattan), tre si trovano su isole: (Staten Island, di fronte al New Jersey; Queens e Brooklyn, rispettivamente nell'estremità nord-occidentale e sud-occidentale dell'isola di Long Island) e uno, Manhattan, sull'appendice inferiore della penisola su cui si trova anche il Bronx e che da esso è separato dall'Harlem River, fiume-canale che collega l'Hudson all'East River. I cinque distretti sono sedi di contea metropolitana: la contea di New York propriamente detta occupa il territorio di Manhattan, quella di Kings il territorio di Brooklyn e quella di Richmond il territorio di Staten Island; le altre due contee (Bronx e Queens) sono omonime dei distretti e si sovrappongono al loro territorio amministrativo. New York è inoltre riconosciuta come una delle città con i panorami urbani più impressionanti del mondo.
Non appartengono a New York, né fanno parte della sua area metropolitana, ma gravitano intorno ad essa per ragioni economiche e culturali, alcune città del confinante Stato del New Jersey, come Jersey City, Newark e Hoboken, situate sulla riva occidentale dell'Hudson, di fronte a Manhattan. La citata Newark è tra l'altro sede di uno degli aeroporti internazionali che servono New York, il Newark-Liberty, situato a 24 km da Manhattan.
Uno dei suoi simboli più famosi è la Statua della Libertà, nonostante non appartenga al suo territorio.
Nueva York2 (en inglés: New York City) es la ciudad más poblada del estado homónimo y de los Estados Unidos de América, y la segunda mayor concentración urbana del continente americano, después de la Ciudad de México. La ciudad de Nueva York está entre las aglomeraciones urbanas más grandes y pobladas del mundo.4
Desde finales del siglo XIX es uno de los principales centros de comercio y finanzas del mundo. Nueva York está considerada como ciudad global, por sus influencias a nivel mundial en los medios de comunicación, en la política, en la educación, en el entretenimiento, las artes y la moda.5 La influencia artística y cultural de la ciudad es de las más fuertes del mundo. En esta ciudad se encuentra la sede central de la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, lo que también la convierte en un importante punto de las relaciones internacionales. La enorme relevancia de la ciudad a todos los niveles la convierte, juntamente con Londres, Tokio y París, en una de las ciudades más destacadas e influyentes del planeta.6
La ciudad se compone de cinco boroughs (a veces traducido como 'condado', 'distrito' o 'comuna') cada uno de los cuales coincide con un condado: Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, y Staten Island. Con más de 8,4 millones de neoyorquinos en un área urbana de 830 kilómetros cuadrados (320 mi²), Nueva York es la segunda ciudad con más densidad de población de los Estados Unidos, detrás de Union City, Nueva Jersey, localizada al otro lado del río Hudson.7
La ciudad tiene muchos lugares y edificios reconocidos por todo el mundo. Por ejemplo, la estatua de la Libertad, ubicada en la isla homónima, y la isla de Ellis, que recibió a millones de inmigrantes que llegaban a Estados Unidos a finales del siglo XIX y comienzos del XX. Wall Street ha sido uno de los principales centros mundiales de finanzas desde la Segunda Guerra Mundial y es la sede de la Bolsa de Nueva York. La ciudad también ha concentrado a muchos de los edificios más altos del mundo, entre los que se encuentran el edificio Empire State y las torres gemelas del World Trade Center, que fueron derribadas en los atentados del 11 de septiembre de 2001.
La ciudad también es la cuna de muchos movimientos culturales estadounidenses, como por ejemplo el renacimiento de Harlem en literatura y artes visuales, el expresionismo abstracto (también conocido como Escuela de Nueva York) en pintura, y hip hop,8 punk y Tin Pan Alley en música. En 2005, se hablaban casi 170 idiomas en la ciudad, y el 36 % de su población había nacido fuera de los Estados Unidos.910 Con su metro en funcionamiento las 24 horas del día, el movimiento de tráfico y gente es constante.
Нью-Йо́рк (англ. New York City, МФА: New York  слушать, [nuː ˈjɔɹk ˈsɪtɪ] или [njuː ˈjɔːk ˈsɪti]) — крупнейший город США[2][3], входящий в одну из крупнейших агломераций мира[4][5][6]. Население города составляет 8 405 837 человек[1], агломерации — 20,63 млн (оценка на 2015 год). Нью-Йорк расположен на берегу Атлантического океана в юго-восточной части штата Нью-Йорк. Город был основан в начале XVII века голландскими колонистами и до 1664 года назывался Новый Амстердам[7].
слушать, [nuː ˈjɔɹk ˈsɪtɪ] или [njuː ˈjɔːk ˈsɪti]) — крупнейший город США[2][3], входящий в одну из крупнейших агломераций мира[4][5][6]. Население города составляет 8 405 837 человек[1], агломерации — 20,63 млн (оценка на 2015 год). Нью-Йорк расположен на берегу Атлантического океана в юго-восточной части штата Нью-Йорк. Город был основан в начале XVII века голландскими колонистами и до 1664 года назывался Новый Амстердам[7].
Нью-Йорк включает пять административных округов (районов, боро): Бронкс, Бруклин, Куинс, Манхэттен и Статен-Айленд. Основные достопримечательности расположены в боро Манхэттен. Среди них: исторические небоскрёбы (Эмпайр-стейт-билдинг, Крайслер-билдинг), Рокфеллеровский центр, Вулворт-билдинг, художественный Метрополитен-музей, Метрополитен-опера, Музей Соломона Гуггенхайма (живопись), Американский музей естественной истории (скелеты динозавров и планетарий), легендарный отель «Челси», штаб-квартира ООН, Гарлем.
Нью-Йорк — важный мировой финансовый, политический, экономический и культурный центр[8].