
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.


白宫新闻发言人(White House Press Secretary,香港称白宫发言人,台湾称白宫发言人或白宫新闻秘书)[1][2],是白宫中的一个高级别行政官员职位,主要职责是担任美国联邦政府行政部门的发言人,尤其与美国总统、高级行政官员和政策有关的事务。
白宫新闻发言人需要收集和发布与美国总统及其领导的联邦政府行政部门有关的新闻和信息,并且更重要的是要对于许多国内外的突发或关注度比较高的事件作出回应,其回应一般会被直接认为是美国总统所作出的官方回应。
白宫新闻发言人在日常工作中必须与新闻媒体保持高度互动,并且几乎每天都要直接与常驻白宫新闻办公厅的各大媒体组成的白宫记者团打交道并举行新闻发布会。
白宫新闻发言人由美国总统任命,无须经美国参议院同意;白宫新闻发言人经常主持新闻发布会,为非常重要的非内阁成员。
Der Pressesprecher des Weißen Hauses (englisch White House Press Secretary) ist eine hochrangige Funktion im Weißen Haus. Der Inhaber leitet das Office of the Press Secretary of the White House (dt.: Presseamt des Weißen Hauses) und hat die Aufgabe, Regierungserklärungen, insbesondere des Präsidenten, des Vizepräsidenten sowie weiterer hochrangiger Regierungspolitiker der Presse zuzuführen. Er ist vergleichbar mit dem Regierungssprecher bzw. dem Presse- und Informationsamt der Bundesregierung in Deutschland. Daneben gibt es auch die Position des Kommunikationsdirektors des Weißen Hauses, mit dem der Pressesprecher üblicherweise eng zusammenarbeitet.
Der Pressesprecher des Weißen Hauses ist für die Veröffentlichung von Regierungsinformationen an die Medien (hauptsächlich Journalisten) zuständig und hat täglich – meistens durch das „daily press briefing“ – mit den beim Weißen Haus akkreditierten Journalisten Kontakt.
| Image | Name | Start | End | Duration | President | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
George Akerson | March 4, 1929 | March 16, 1931 | 2 years, 12 days | Herbert Hoover | |
 |
Ted Joslin | March 16, 1931 | March 4, 1933 | 1 year, 353 days | ||
 |
Stephen Early | March 4, 1933 | March 29, 1945 | 12 years, 25 days | Franklin D. Roosevelt | |
 |
Jonathan Daniels | March 29, 1945 | May 15, 1945 | 47 days | ||
| Harry S. Truman | ||||||
 |
Charlie Ross | May 15, 1945 | December 5, 1950 | 5 years, 204 days | ||
 |
Stephen Early Acting |
December 5, 1950 | December 18, 1950 | 13 days | ||
 |
Joseph Short | December 18, 1950 | September 18, 1952 | 1 year, 288 days | ||
 |
Roger Tubby | September 18, 1952 | January 20, 1953 | 124 days | ||
 |
James Hagerty | January 20, 1953 | January 20, 1961 | 8 years, 0 days | Dwight D. Eisenhower | |
 |
Pierre Salinger | January 20, 1961 | March 19, 1964 | 3 years, 59 days | John F. Kennedy | |
| Lyndon B. Johnson | ||||||
 |
George Reedy | March 19, 1964 | July 8, 1965 | 1 year, 111 days | ||
 |
Bill Moyers | July 8, 1965 | February 1, 1967 | 1 year, 208 days | ||
 |
George Christian | February 1, 1967 | January 20, 1969 | 1 year, 354 days | ||
 |
Ron Ziegler | January 20, 1969 | August 9, 1974 | 5 years, 201 days | Richard Nixon | |
 |
Jerald terHorst | August 9, 1974 | September 9, 1974 | 31 days | Gerald Ford | |
 |
Ron Nessen | September 9, 1974 | January 20, 1977 | 2 years, 133 days | ||
 |
Jody Powell | January 20, 1977 | January 20, 1981 | 4 years, 0 days | Jimmy Carter | |
 |
Jim Brady[a] | January 20, 1981 | March 30, 1981 (de facto) January 20, 1989 (de jure) |
69 days/ 8 years, 0 days |
Ronald Reagan | |
 |
Larry Speakes[a] Acting |
March 30, 1981 | February 1, 1987 | 5 years, 308 days | ||
 |
Marlin Fitzwater[a] | February 1, 1987 Acting: February 1, 1987 – January 20, 1989 |
January 20, 1993 | 5 years, 354 days | ||
| George H. W. Bush | ||||||
 |
Dee Dee Myers | January 20, 1993 | December 22, 1994 | 1 year, 336 days | Bill Clinton | |
 |
George Stephanopoulos[b] De facto |
January 20, 1993 | June 7, 1993 | 138 days | ||
 |
Mike McCurry | December 22, 1994 | August 4, 1998 | 3 years, 225 days | ||
 |
Joe Lockhart | August 4, 1998 | September 29, 2000 | 2 years, 56 days | ||
 |
Jake Siewert | September 30, 2000 | January 20, 2001 | 112 days | ||
 |
Ari Fleischer | January 20, 2001 | July 15, 2003 | 2 years, 176 days | George W. Bush | |
 |
Scott McClellan | July 15, 2003 | May 10, 2006 | 2 years, 299 days | ||
 |
Tony Snow | May 10, 2006 | September 14, 2007 | 1 year, 127 days | ||
 |
Dana Perino | September 14, 2007 | January 20, 2009 | 1 year, 128 days | ||
 |
Robert Gibbs | January 20, 2009 | February 11, 2011 | 2 years, 22 days | Barack Obama | |
 |
Jay Carney | February 11, 2011 | June 20, 2014 | 3 years, 129 days | ||
 |
Josh Earnest | June 20, 2014 | January 20, 2017 | 2 years, 214 days | ||
 |
Sean Spicer | January 20, 2017 | July 21, 2017[29] | 182 days | Donald Trump | |
 |
Sarah Huckabee Sanders | July 21, 2017[30][31] | July 1, 2019 | 1 year, 345 days | ||
 |
Stephanie Grisham[c] | July 1, 2019 | April 7, 2020 | 281 days | ||
 |
Kayleigh McEnany | April 7, 2020 | January 20, 2021 | 288 days | ||
 |
Jen Psaki | January 20, 2021 | May 13, 2022 | 1 year, 113 days | Joe Biden | |
 |
Karine Jean-Pierre | May 13, 2022 | present | 1 year, 160 days | ||

Das Weiße Haus (englisch White House) in Washington, D.C., ist Amts- und offizieller Regierungssitz des Präsidenten der Vereinigten Staaten. Als Metonym ist es namensgebend für den Mitarbeiterstab des US-Präsidenten, das Executive Office of the President of the United States, ebenfalls meist als „Weißes Haus“ bezeichnet. Mitunter ist auch die ganze US-Regierung gemeint, vergleichbar den Begriffen 10 Downing Street oder historisch die Wilhelmstraße.[1]
Das Weiße Haus liegt an der Pennsylvania Avenue und hat die Hausnummer 1600. Seinen Namen erhielt es offiziell 1901 von Theodore Roosevelt aufgrund seines weißen Außenanstrichs; es wurde vermutlich schon zuvor umgangssprachlich als weißes Haus bezeichnet.[2] Die zumeist in den Medien abgebildete weiße Villa ist nur der mittlere Teil des Gebäudekomplexes White House Complex. Eine Galerie (englisch collonade) verbindet Haupthaus und Westflügel West Wing; eine weitere Haupthaus und Ostflügel East Wing. Westlich vom Westflügel liegt das Eisenhower Executive Office Building; dazwischen verläuft die West Executive Avenue.
白宫(英语:White House,也称白屋)是美国总统官邸与主要办公的地方,位于美国华盛顿哥伦比亚特区西北区,宾夕法尼亚大道1600号。自1800年美国第二任总统约翰·亚当斯入住以来,白宫就是美国历任总统在任时的居所。
白宫由爱尔兰裔建筑师詹姆斯·霍本设计[2],工程期为1792年至1800年,建材使用白色的阿维亚溪砂岩,风格则是新古典主义式样。第三任总统托马斯·杰佛逊于1801年搬入白宫后,他和建筑师本杰明·亨利·拉特罗布为了隐蔽白宫马厩与储藏室,而在白宫每侧增添少许列柱。到了1814年,英军在1812年战争中纵火摧毁华盛顿特区,白宫内部遭受火焚,外观也被烧黑。[3]待美军收复华盛顿后,美国政府便立刻重建白宫,第五任总统詹姆斯·门罗于1817年10月搬进部分重建完成的白宫行政官邸。其后白宫建筑工事仍持续进行,美国政府分别于1824年和1829年完成增建白宫南、北面的门廊。
随着美国政府逐渐扩大,白宫作为办公场所显得越来越拥挤。第二十六任总统西奥多·罗斯福于1901年要求白宫内所有办公室迁往新建成的白宫西厢办公室,八年后第二十七任总统威廉·霍华·塔虎脱扩建西厢办公室,并增建椭圆形办公室作为总统办公室之用。主建筑部分,三楼原本用作阁楼,也在1927年转为总统家庭的起居空间。至于与杰佛逊柱廊相连的白宫东厢办公室,落成后便一直用作处理白宫的社交事务,接待访客、民众与外宾,并于1946年改建扩大办公空间。1948年,美国政府发现白宫的外部承重墙与内部木梁并无效用。第三十三任总统哈瑞·S·杜鲁门任内便拆除白宫所有房间,以钢梁作为白宫新建筑结构的承重建材;此工程完工后,白宫所有房间才再度重建。
今日的白宫建筑群包括行政官邸、西厢、东厢、艾森豪威尔行政大楼与布莱尔宫等建物。行政官邸共有五层,包括地下室、大厅层、国家层、第二层与第三层。而一般语境下所称的“白宫”,通常是对“美国总统行政办公室”或总统行政与顾问团队的转喻,如“白宫宣布……”。此外,由于白宫是美国国家遗产,其产权属于美国国家公园管理局,是“总统公园”的一部分。2007年,白宫获美国建筑师学会评选为美国最喜爱的建筑第二名。
ホワイトハウス(英: White House)は、次の2つの意味で使用されている。
- アメリカ合衆国大統領が居住し、執務を行う官邸・公邸の建物。転じて、(日本語における「官邸」と同様に)そこで働くスタッフらを含めた政権の中枢を指す。
- アメリカ合衆国大統領行政府の中の一部局である「ホワイトハウス・オフィス」(資料によっては「ホワイトハウス事務局」との日本語表記も)。
また、前者の内、特に主要な4つの建物であるエグゼクティヴ・レジデンス、ウエストウイング(西棟)、イーストウイング(東棟)、アイゼンハワー行政府ビル、そして4つの庭であるローズ・ガーデン、ジャクリーン・ケネディ・ガーデン、北庭、南庭を指して「ホワイトハウス・コンプレックス」と総称する。
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. The term "White House" is often used as a metonym for the president and his advisers.
The residence was designed by Irish-born architect James Hoban[3] in the neoclassical style. Hoban modelled the building on Leinster House in Dublin, a building which today houses the Oireachtas, the Irish legislature. Construction took place between 1792 and 1800 using Aquia Creek sandstone painted white. When Thomas Jefferson moved into the house in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) added low colonnades on each wing that concealed stables and storage.[4] In 1814, during the War of 1812, the mansion was set ablaze by the British Army in the Burning of Washington, destroying the interior and charring much of the exterior. Reconstruction began almost immediately, and President James Monroe moved into the partially reconstructed Executive Residence in October 1817. Exterior construction continued with the addition of the semi-circular South portico in 1824 and the North portico in 1829.
Because of crowding within the executive mansion itself, President Theodore Roosevelt had all work offices relocated to the newly constructed West Wing in 1901. Eight years later in 1909, President William Howard Taft expanded the West Wing and created the first Oval Office, which was eventually moved as the section was expanded. In the main mansion, the third-floor attic was converted to living quarters in 1927 by augmenting the existing hip roof with long shed dormers. A newly constructed East Wing was used as a reception area for social events; Jefferson's colonnades connected the new wings. East Wing alterations were completed in 1946, creating additional office space. By 1948, the residence's load-bearing exterior walls and internal wood beams were found to be close to failure. Under Harry S. Truman, the interior rooms were completely dismantled and a new internal load-bearing steel frame constructed inside the walls. Once this work was completed, the interior rooms were rebuilt.
The modern-day White House complex includes the Executive Residence, West Wing, East Wing, the Eisenhower Executive Office Building—the former State Department, which now houses offices for the president's staff and the vice president—and Blair House, a guest residence. The Executive Residence is made up of six stories—the Ground Floor, State Floor, Second Floor, and Third Floor, as well as a two-story basement. The property is a National Heritage Site owned by the National Park Service and is part of the President's Park. In 2007, it was ranked second[5] on the American Institute of Architects list of "America's Favorite Architecture".
La Maison-Blanche1 (en anglais : The White House) est la résidence officielle et le bureau du président des États-Unis. Elle se situe au 1600, Pennsylvania Avenue NW à Washington D.C. Le bâtiment en grès d'Aquia Creek et peint en blanc, construit entre 1792 et 1800, s'inspire du style georgien. Il est le lieu de résidence, de travail et de réception de tous les présidents américains depuis John Adams, deuxième président des États-Unis, qui y entre en 1800.
L'expression « Maison-Blanche » est souvent employée pour désigner, par métonymie, l'administration du président. Elle est le symbole du pouvoir exécutif et de la puissance politique américaine. Son actuel résident est Donald Trump, 45e président des États-Unis.
De son inauguration en 1800 à l'année 1942, la demeure subit de nombreuses modifications : des reconstructions à la suite d'incendies (1814 et 19292), de réaménagements fonctionnels par les présidents successifs ou d'extensions avec notamment la construction de l'aile ouest en 1901 et de l'aile est en 1942. À partir de cette date, si l'on excepte la modernisation des installations et la construction de quelques aménagements de sécurité ou de loisir (piscine, terrain de golf et jardins notamment), l'aspect de la Maison-Blanche n'évolue pratiquement plus. Son emprise au sol s'agrandit avec le temps avec l'adjonction, au sud, de jardins situés dans un espace autrefois public. Aujourd'hui le complexe de la Maison-Blanche comprend la résidence présidentielle (Executive Residence, le bâtiment central historique dans lequel la famille présidentielle réside et où se tiennent un certain nombre de réceptions officielles et quelques réunions), l'aile Ouest (où se trouvent les bureaux de l'administration présidentielle dont le Bureau ovale, la Cabinet Room et la Roosevelt Room) et l'aile Est (où se trouvent le bureau de la First Lady et le secrétariat social de la Maison-Blanche), ainsi que le Old Executive Office Building, grand bâtiment situé juste en face de l'aile Ouest et qui abrite des bureaux de l'administration présidentielle et le bureau du vice-président des États-Unis. Le complexe inclut également un jardin au nord donnant sur Pennsylvania Avenue et un parc au sud dont la pelouse Sud, sur laquelle se pose l'hélicoptère présidentiel Marine One.
La Maison-Blanche et ses jardins font partie d'un plus grand ensemble, le parc du Président (President's Park) qui comprend aussi le Lafayette Square au nord, de l'autre côté de Pennsylvania Avenue, et l'Ellipse au sud (les deux ouverts au public) et géré par le National Park Service.
La Casa Bianca (in inglese White House) è la residenza e ufficio principale del presidente degli Stati Uniti d'America. Si trova a 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue a Washington, DC ed è stata la residenza di ogni presidente degli Stati Uniti da John Adams nel 1800. Il termine "Casa Bianca" è spesso usato come metonimo del presidente e dei suoi consiglieri.
Insieme alla Blair House, adibita a ospitare le delegazioni in visita di Stato, e al Number One Observatory Circle, che funge da residenza per il vicepresidente degli Stati Uniti, è una delle tre residenze ufficiali più importanti in Washington D.C.
La Casa Blanca (The White House, en inglés) es la residencia oficial y principal centro de trabajo del presidente de los Estados Unidos.
El proyecto fue ideado por George Washington y construido en 1790 bajo la dirección del arquitecto de origen irlandés James Hoban, en estilo Neoclásico.1 El presidente George Washington, junto con el arquitecto de la ciudad, Pierre Charles L'Enfant, escogió el sitio donde se construiría. Mediante un concurso se eligió al arquitecto, nativo de Dublín, que ganó la medalla de oro por la presentación del diseño que hoy conocemos.
El diseño de la Casa Blanca se vio inspirado por la Leinster House (Dublín), y Castletown House (Celbridge), ambas siguiendo el estilo del Palladianismo.
Como su nombre lo indica, es un edificio blanco localizado en Pennsylvania Avenue Nº 1600 (Avenida Pensilvania) al noroeste de Washington D. C.. Proyectada durante el primer mandato de George Washington, el edificio fue inaugurado por John Adams en 1800. Formalmente, el edificio recibió los nombres de Palacio Presidencial, la Mansión Ejecutiva, hasta que el presidente Theodore Roosevelt en 1902 propuso al Congreso que adoptara oficialmente el nombre de «La Casa Blanca».2
Бе́лый дом (англ. the White House) — официальная резиденция президента США, расположенная в Вашингтоне (округ Колумбия) по почтовому адресу: Пенсильвания-авеню, 1600 (англ. 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue).
Ирландский архитектор Джеймс Хобан спроектировал резиденцию[5] в неоклассическом стиле. С 1792 по 1800 год шло строительство. Использовался окрашенный в белый цвет песчаник Aquia Creek. В 1801 году Томас Джефферсон переехал в дом. Чтобы скрыть конюшни и хранилища, он вместе с архитектором Бенджамином Генри Латроубом добавил низкие колоннады на каждом крыле[6].
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.


 *American think tanks
*American think tanks
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

Die Gedenkstätte wurde am 28. Oktober 1986 vom Kongress der Vereinigten Staaten durch das Public Law 99-572 genehmigt. Die Planung und den Bau übernahmen[1] das Korean War Veterans Memorial Advisory Board und die American Battle Monuments Commission. Präsident George H. W. Bush nahm den ersten Spatenstich für das Denkmal am 14. Juni 1992, dem Flag Day, vor. Es wurde am 27. Juli 1995, dem 42. Jahrestag des Waffenstillstandes, von Präsident Bill Clinton und Kim Young-sam, dem Präsidenten von Südkorea, eröffnet und den Männern und Frauen gewidmet, die während des Krieges gedient hatten. Die Verwaltung der Gedenkstätte wurde der Abteilung National Mall and Memorial Parks des National Park Service übertragen. Die Gedenkstätte wurde am Tag ihrer Einweihung in das National Register of Historic Places eingetragen.
朝鲜战争老兵(阵亡将士)纪念碑(英语:Korean War Veterans Memorial)于1995年建于华盛顿特区,为纪念朝鲜战争中阵亡的美军和联合国军士兵。建立一个这样的“朝鲜战争老兵(阵亡将士)纪念碑”是在越战纪念墙完成以后就被提起的。美国国会授权美国战争纪念委员会建立这样一个纪念物来表彰那些曾经在朝鲜为国家服务过的美国男女公民(公法99-572于1986年10月28日立案)。当时的总统罗纳德·里根随即指定了一个朝鲜战争纪念墙顾问小组来帮助这项工作的推行。1988年9月,美国战争纪念委员会批准了计划中的纪念墙所在地华盛顿特区的国家广场的南侧,林肯纪念堂的西南侧。 老布什总统1992年6月14日为纪念园区奠基。1995年7月27日,朝鲜战争停战协定42周年日,克林顿总统和韩国总统金泳三出席揭幕。这是由“朝鲜战争的退伍军人纪念顾问委员会和美国战争纪念物委员会”设计管理的建筑。现在,该纪念馆的管理,移交给国家公园管理局,(国家广场和历史纪念公园组)。
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research




 Automobile
Automobile
 *Electric car engine
*Electric car engine


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Precision Instrument/Medical Equipment/Research Equipment
Precision Instrument/Medical Equipment/Research Equipment

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 Medical Equipment
Medical Equipment

 Medical equipment
Medical equipment
 In-Vitro-Diagnose
In-Vitro-Diagnose

 Medical equipment
Medical equipment
 Dental Equipment
Dental Equipment

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.


 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 England
England

 European Union
European Union
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Mexico
Mexico

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Queensland-QLD
Queensland-QLD
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Turkey
Turkey
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

Die G20 (Abkürzung für Gruppe der zwanzig wichtigsten Industrie- und Schwellenländer) ist ein seit 1999 bestehender informeller Zusammenschluss aus 19 Staaten und der Europäischen Union. Sie soll als Forum für die Kooperation und Konsultation in Fragen des internationalen Finanzsystems dienen.
An den Treffen der G20 nehmen die Staats- und Regierungschefs der G20 Länder, die Finanzminister und Zentralbankchefs der G8 und elf weiterer Staaten, darunter die O-5, sowie die EU-Präsidentschaft (wenn diese zu diesem Zeitpunkt nicht von einem G8-Staat geführt wird), der Präsident der Europäischen Zentralbank, der Geschäftsführende Direktor (Managing Director) des Internationalen Währungsfonds, der Vorsitzende des Internationalen Währungs- und Finanzausschusses (IMFC), der Präsident der Weltbank und der Vorsitzende des Development Committees von Weltbank und Internationalem Währungsfonds teil.
20国集团(G20)是一个国际经济合作论坛,于1999年9月25日由八国集团的财长在华盛顿宣布成立,属于布雷顿森林体系框架内非正式对话的一种机制,由原八国集团以及其余十二个重要经济体组成。该组织的宗旨是为推动已工业化的发达国家和新兴市场国家之间就实质性问题进行开放及有建设性的讨论和研究,以寻求合作并促进国际金融稳定和经济的持续增长,按照以往惯例,国际货币基金组织与世界银行列席该组织的会议。20国集团成员涵盖面广,代表性强,该集团的GDP占全球经济的90%,贸易额占全球的80%,因此已取代G8成为全球经济合作的主要论坛。 二十国集团(英语:Group of Twenty,缩写:G20)是一个国际经济合作论坛,于1999年12月16日在德国柏林成立,属于布雷顿森林体系框架内对话的一种机制,由七国集团(加拿大、美国、英国、法国、德国、意大利、日本),金砖五国(巴西、俄罗斯、印度、中国、南非),七个重要经济体(墨西哥、阿根廷、土耳其、沙特阿拉伯、韩国、印度尼西亚、澳大利亚),以及欧洲联盟组成。按照惯例,国际货币基金组织与世界银行列席该组织的会议。
G20(ジートゥエンティ)は、"Group of Twenty"の略で、主要国首脳会議(G7)に参加する7か国、EU、ロシア、および新興国11か国の計20か国・地域からなるグループである。
構成国・地域は、アメリカ合衆国、イギリス、フランス、ドイツ、日本、イタリア、カナダ、EU、ロシア、中華人民共和国、インド、ブラジル、メキシコ、南アフリカ共和国、オーストラリア、大韓民国、インドネシア、サウジアラビア、トルコ、アルゼンチンである。20か国・地域首脳会合(G20首脳会合)および20か国・地域財務大臣・中央銀行総裁会議(G20財務相・中央銀行総裁会議)を開催している。主要20か国・地域[1][2]とも言い、日本の放送局であるNHKでは、先進国会合であるG7と区別して、先進国に新興国を加えた主要20か国[3]と表現している。
The G20 (or Group of Twenty) is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability,[3] the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks[4], have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.[3]
Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank. Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 90%[5] of the gross world product (GWP), 80% of world trade (or, if excluding EU intra-trade, 75%), two-thirds of the world population,[2] and approximately half of the world land area.
With the G20 growing in stature[6] after its inaugural leaders' summit in 2008, its leaders announced on 25 September 2009 that the group would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.[7] Since its inception, the G20's membership policies have been criticized by some intellectuals,[8][9] and its summits have been a focus for major protests.[10][11]
The heads of the G20 nations held summits twice in 2009 and twice in 2010. Since the November 2011 Cannes summit, G20 summits have been held annually.[12]
Le Groupe des vingt (G20) est un groupe composé de dix-neuf pays et de l'Union européenne dont les ministres, les chefs des banques centrales et les chefs d'État se réunissent annuellement. Il a été créé en 1999, après la succession de crises financières dans les années 19901. Il vise à favoriser la concertation internationale, en intégrant le principe d'un dialogue élargi tenant compte du poids économique croissant pris par un certain nombre de pays. Le G20 représente 85 % du commerce mondial, les deux tiers de la population mondiale et plus de 90 % du produit mondial brut (somme des PIB de tous les pays du monde)1. Le 15 novembre 2008, pour la première fois de son histoire, les chefs d'État ou de gouvernement se sont réunis. Le G20 se décline sous trois formes : les G20 regroupant des chefs d'État et de gouvernement, les G20 finance regroupant les ministres des finances et les gouverneurs des banques centrales et, depuis les 20-21 avril 2010, des G20 sociaux, réunissant les ministres de l'emploi.
Il Gruppo dei 20 (o G20) è un forum dei leader, dei ministri delle finanze e dei governatori delle banche centrali, creato nel 1999, dopo una successione di crisi finanziarie per favorire l'internazionalità economica e la concertazione tenendo conto delle nuove economie in sviluppo. Di esso fanno parte i 19 paesi più industrializzati (quelli del G8 in primis) con l'eccezione di Spagna e Paesi Bassi (sono presenti invece Argentina e Sudafrica). È presente, inoltre, l'Unione europea.
Il G20 rappresenta i due terzi del commercio e della popolazione mondiale, oltre all'80% del PIL mondiale. Sono presenti anche alcune tra le maggiori organizzazioni internazionali.
El Grupo de los 20 (numerónimo: G-20) es un foro cuyos miembros permanentes son 19 países de todos los continentes (Alemania, Arabia Saudita, Argentina, Australia, Brasil, Canadá, China, Corea del Sur, Estados Unidos, Francia, India, Indonesia, Italia, Japón, México, Reino Unido, Rusia, Sudáfrica, Turquía y la Unión Europea).1
Es el principal espacio de deliberación política y económica del mundo.1 En conjunto las entidades políticas representadas en el G20 reúnen el 66 % de la población mundial y el 85 % del producto bruto mundial.1.
El G-20 cuenta además con 14 organizaciones internacionales socias, cuyas presidencias también integran el foro:2
- Mundiales (7): Naciones Unidas (ONU), Fondo Monetario Internacional (FMI), Banco Mundial, Consejo de Estabilidad Financiera (FSB), Organización Internacional del Trabajo (OIT), Organización Mundial de Comercio (OMC) y Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS)
- Regionales (7): Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN), Unión Africana, Nueva Alianza para el Desarrollo de África (NEPAD), Comunidad del Caribe (CARICOM), Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo (BID), Banco de Desarrollo de América Latina (CAF) y Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico (OCDE)
El G-20 surgió en dos etapas. Primero en 1999, como un grupo de segundo nivel de autoridades económicas y financieras, y luego como un grupo de primer nivel en 2008, como consecuencia de la crisis mundial que estalló ese año, al constituirse como Cumbre de Jefes de Estado, desplazando al G-8 y al G8+5 como foro de discusión de la economía mundial.3
La instancia más importante del G20 es la Cumbre de Jefes de Estado, denominada Cumbre de Líderes, que se reúne una vez por año.4 El G20 cuenta con dos instancias gubernamentales de segundo nivel, denominadas canales de trabajo: el Canal de Finanzas que reúne a los ministros de Finanzas y presidentes de bancos centrales y el Canal de Sherpas, para tratar los temas no económicos.4
Complementariamente el G-20 cuenta con grupos de participación de la sociedad civil, llamados grupos de afinidad: Business 20 (B20) para empresarios, Civil 20 (C20) para ONGs, Labour 20 (L20) para sindicatos, Science 20 (S20) para científicos, Think 20 (T20) para institutos de investigación, Women 20 (W20) para organizaciones feministas y Youth 20 (Y20) para organizaciones juveniles.4
En 2019 la cumbre se realizó en Osaka Japón, correspondiendo la presidencia del grupo a su primer ministro, Shinzō Abe.
Больша́я двадца́тка (также G20, G-20 , Группа двадцати; официально — англ. The Group of Twenty, major advanced and emerging economies[1]) — клуб правительств и глав центральных банков государств с наиболее развитой и развивающейся экономикой[2].
В совокупности, G20 представляет 85 % мирового валового национального продукта, 75 % мировой торговли (включая торговлю внутри ЕС) и две трети населения мира[2].
Европейский союз представлен председателем Европейской комиссии и председателем Европейского совета[3]. Кроме того, обычно на встречах G20 присутствуют представители различных международных организаций, среди которых Совет по финансовой стабильности, Международный валютный фонд, Всемирная торговая организация, Африканский Союз, АСЕАН, Организация Объединённых Наций и Всемирный банк[2].
Группа 20 была создана в ответ на азиатский финансовый кризис конца 1990-х[2] и растущее сознание того, что страны с развивающейся рыночной экономикой не были адекватно представлены в мировых экономических обсуждениях и принятии решений. Переход от «большой семёрки» к формату G20 был ускорен из опасения катастрофы глобальной экономики в общемировой экономический кризис 2008 года[4]. До 2008 года группа не проводила саммитов на высшем уровне, её основной формой деятельности были ежегодные встречи на уровне министров финансов и глав центробанков. На сегодняшний день саммиты G20 являются глобальным форумом для сотрудничества и консультаций по вопросам, относящимся к международной финансово-экономической систе.


 Architecture
Architecture
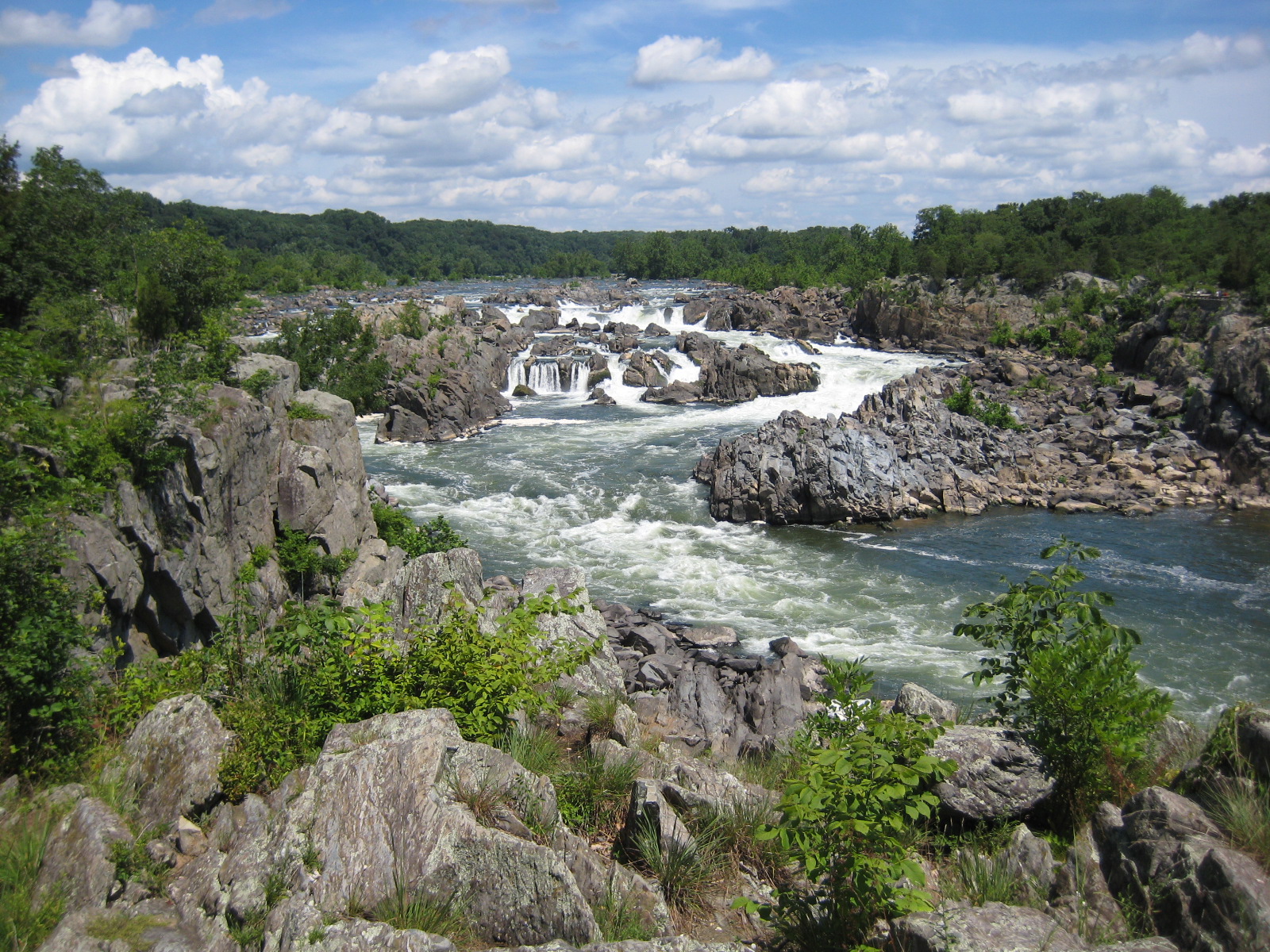
 Geography
Geography
 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD
 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA
 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
 Art
Art
 Companies
Companies