
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Aerospace
Aerospace







 Automobile
Automobile



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology



 Automobile
Automobile
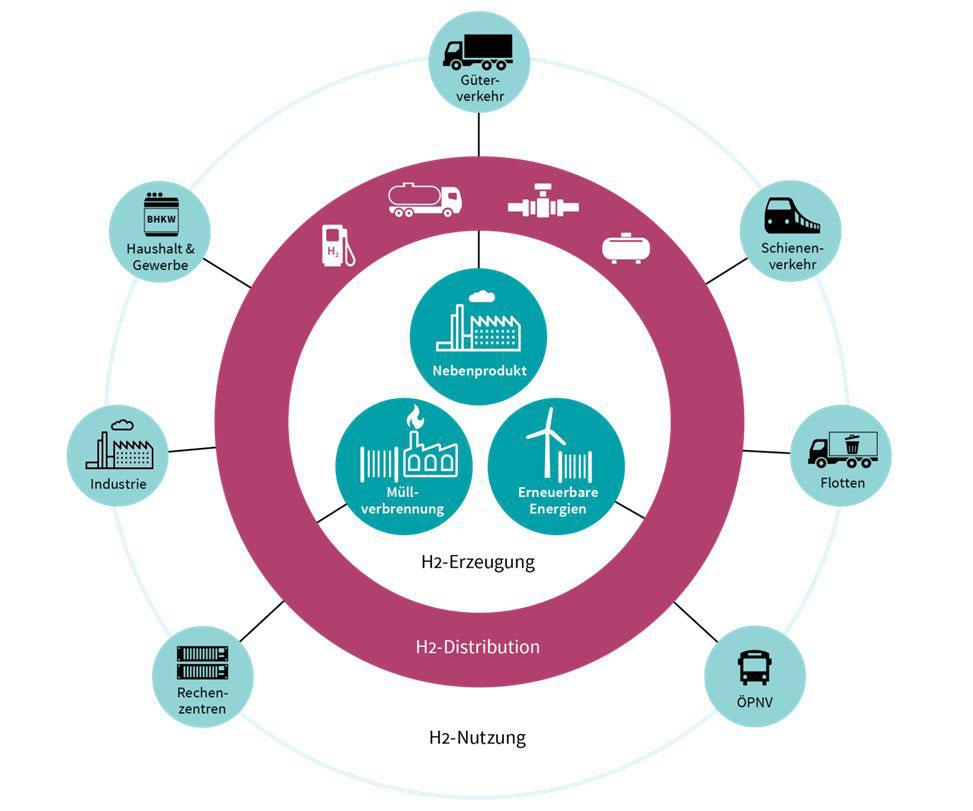
 *Hydrogen propulsion
*Hydrogen propulsion

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 ***Hydrogen Energy
***Hydrogen Energy



 Aerospace
Aerospace

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic





 Automobile
Automobile
 *Fuel cell vehicle
*Fuel cell vehicle



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Hydrogen propulsion
*Hydrogen propulsion

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 ***Hydrogen Energy
***Hydrogen Energy

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD



 Aerospace
Aerospace

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Technology concepts
Technology concepts
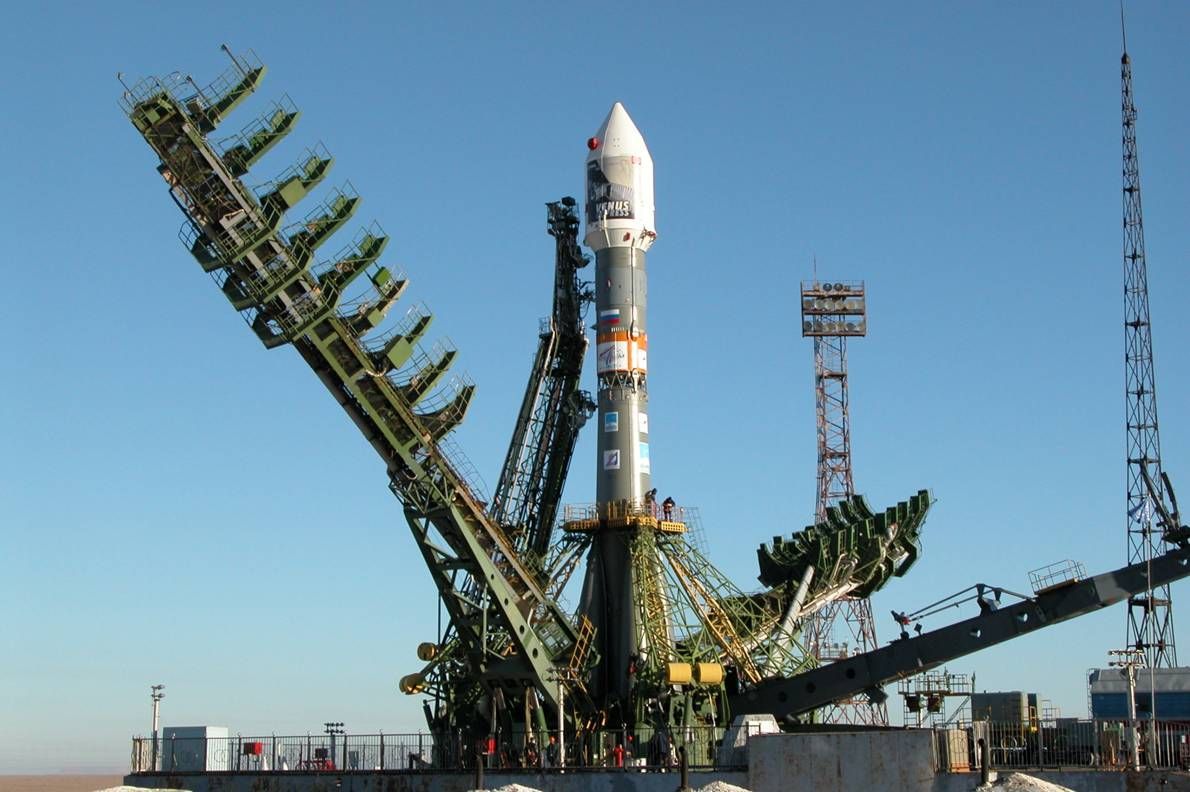
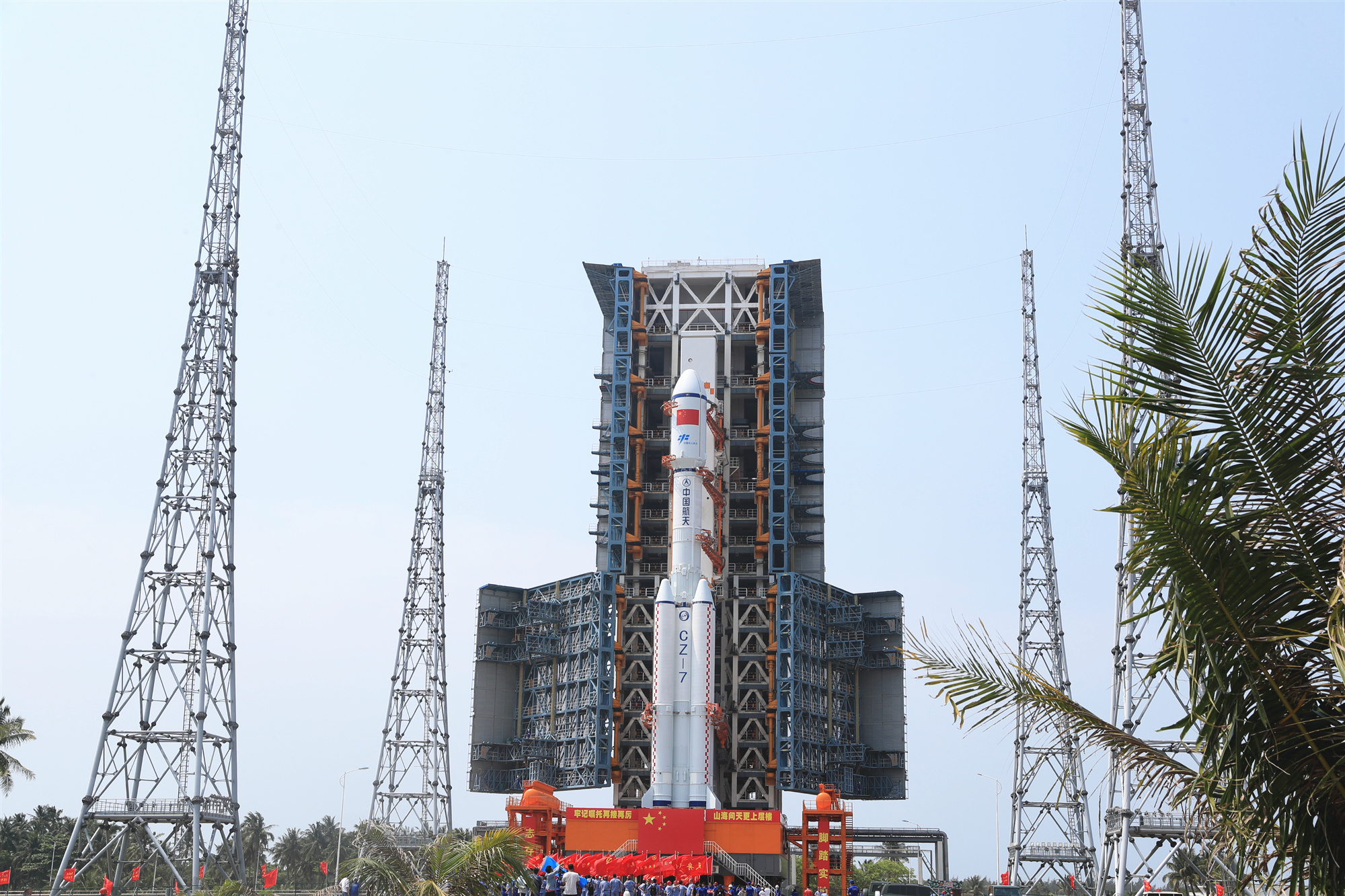


中国文昌航天发射场[2](China Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site),又称文昌航天城,位于中国海南省文昌市龙楼镇以南、中南水库以东,隶属中国西昌卫星发射中心,是西昌卫星发射中心下辖的两个发射场之一。[3][4][5]
该航天发射场于2009年9月14日开工建设,2014年10月中旬建成。由于此地点的纬度较低(约北纬19度),离赤道较近,地球自转造成的离心力可以让火箭在燃料不变的情况下携带更大的载荷。该中心可以用来发射大型长征五号系列火箭及中型长征七号系列火箭。
文昌衛星発射場(ぶんしょうえいせいはっしゃじょう、簡体字: 文昌卫星发射场、英語: Wenchang Satellite Launch Site)は、中華人民共和国海南省の文昌市郊外のロケット発射場、西昌衛星発射センターに所属。南シナ海に面した海南島の北東の海岸に位置する中国第4の発射場で、4つの発射場のうち最も南にあり、中国初となる海岸沿いの発射場。もとは弾道ロケットの試験場だった場所であるが、本格稼働に向け拡張工事が行われている。
Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site (文昌航天发射场[2][3]), located in Wenchang, Hainan, China. It is one of the two spacecraft launch sites of Xichang Satellite Launch Center (the other site is in Xichang).[4][5][6]
It is a former sub-orbital test center. It is China's fourth and southernmost space vehicle launch facility (spaceport). It has been specially selected for its low latitude, which is only 19 degrees north of the equator, which will allow for a substantial increase in payload, necessary for the future manned program, space station and deep space exploration program. Furthermore, it is capable of launching the new heavy-lift Long March 5 booster.[7]
Unlike the space centers on the mainland whose rail tracks are too narrow to transport the new five meter core boosters, Wenchang uses its sea port for deliveries. Initial launches of the CZ-5 booster from Wenchang were, as of early 2008, expected in 2014, one year after the intended commissioning of the Wenchang Launch Site.[8] They were later shifted to 2016.[9] The CZ-5B (max payload to LEO) variant will fly around 2018.[10] But CZ-5 carrier rocket was already shipped from North China's Tianjin port at 20 September 2015 for a rehearsal (some drills carried out on the launch pad that involves both the carrier rocket and a probe) of a scheduled Chang'e-5 lunar mission planned around 2019.[11]
The construction of the site was completed by October, 2014.[1] The first launch took place successfully at 20:00, June 25, 2016.[12]
La base de lancement de Wenchang est la quatrième base de lancement d'engins spatiaux de la République populaire de Chine. Elle est entrée en fonction le 25 juin 2016 avec le lancement du premier exemplaire du lanceur lourd Longue Marche 7. Elle est située à proximité de la ville de Wenchang sur la côte nord-est de l’île de Hainan. Utilisé jusque-là pour le tir de fusées-sondes, le site a été sélectionné en premier lieu pour sa faible latitude : situé sur le 19e parallèle nord, sa proximité avec l’équateur permet d’augmenter de manière importante la masse des charges utiles placées sur une orbite géostationnaire. La base est conçue pour permettre le tir des nouveaux lanceurs chinois en particulier le lanceur de moyenne puissance Longue Marche 7 qui doit assurer la majorité des lancements de satellites chinois à terme et le lanceur lourd Longue Marche 5 (charge utile de 25 tonnes en orbite basse) qui doit d'une part jouer un rôle central dans la réalisation du programme spatial habité en permettant la construction d’une station spatiale lourde d'autre part permettre l'envoi de sondes spatiales dans le système solaire.
Il centro spaziale di Wenchang (WSLC, Wenchang Satellite Launch Center) è uno spazioporto situato a Wenchang, sull'isola di Hainan, in Cina. In precedenza usato solo per voli suborbitali, il 25 giugno 2016 è stato utilizzato per la prima volta per un lancio orbitale. È il quarto centro di lancio cinese e quello situato più a sud (19° di latitudine), il che permette di aumentare il carico lanciato senza dover aumentare le dimensioni del lanciatore. Sarà utilizzato per future missioni umane, per la stazione spaziale cinese e per missioni nello spazio profondo. Sarà inoltre il sito di lancio per il futuro lanciatore spaziale cinese Lunga Marcia 5.
Il primo lancio è avvenuto alle ore 20.00 (ora locale) del 25 giugno 2016, quando un lanciatore Lunga Marcia 7 ha portato in orbita con successo alcuni satelliti.
El Centro de Lanzamiento de Satélites de Wenchang (WSLC), ubicado cerca de Wenchang, en la costa noreste de la isla de Hainan, es una base espacial china. Es la cuarta instalación de lanzamiento de vehículos espaciales, y situada más al sur, de la República Popular de China. Ha sido seleccionada especialmente por su baja latitud, que está a sólo 19 grados al norte del ecuador, lo que permitirá un aumento sustancial de la carga útil, necesaria para el futuro programa tripulado, la estación espacial y el programa de exploración del espacio profundo. Además, es el centro de lanzamiento de los nuevos vehículos Larga Marcha 5 (CZ-5).2
A diferencia de los centros espaciales en el continente cuyo ancho de vía es demasiado estrecho para transportar los nuevos vehículos de 5 metros, Wenchang hará uso de su puerto marítimo para las entregas. Los lanzamientos iniciales del CZ-5 se esperan para 2014, un año después de la prevista puesta en marcha del Centro de Wenchang.3
Китайский космодром Вэньчан (кит. трад. 中国文昌航天发射场, пиньинь: Zhōngguó wénchāng hángtiān fāshè chǎng, палл.: чжунго вэньчан хантянь фашэ чан, англ. China Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site, сокр. WSLC) — четвёртый китайский космодром. Прежнее (до ноября 2016 года) название: Центр запуска спутников Вэньчан[1]. Также известный, как Космический городок Вэньчан. Расположен на острове Хайнань (который ранее был известен курортами), на самом юге Китая. Космодром Вэньчан будет иметь ключевое значение для дальнейшей реализации амбициозной космической программы Китая. Его будут использовать для доставки на орбиту компонентов национальной космической станции и осуществления лунных миссий.

美国航天科学家。生于德国。早年就读于瑞士苏黎世技术学校。 1932年毕业于柏林工学院。1934年获柏林大学物理学博士学位。1932年起在德国陆军军械部从事火箭研究。第二次世界大战期间,他到美国陆军装备设 计研究局工作。1950年到红石兵工厂研制弹道导弹。1958年任美国航空航天局的领导成员。1960-1970年任马歇尔航天中心主任。1961年任 J·F·肯尼迪总统的空间事务科学顾问,分管“阿波罗”工程,领导“土星”号运载火箭的研制工作。1969年7月,用他领导设计的世界上最大的火箭(“土 星”5号火箭)第一次把人送上了月球。1970年他担任美国国家航空航天局主管计划的副局长。1972年辞去副局长职务,担任费尔柴德工业公司的技术发展 副经理。著有《火星计划》、《高层大气物理学和医学》等。
韦恩赫尔·冯·布劳恩(德语:Wernher von Braun,1912年3月23日—1977年6月16日),全称韦恩赫尔·马格努斯·马克西米利安,布劳恩男爵(德语:Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun),德国出身的美国火箭专家,二十世纪航天事业的先驱之一[2]。曾是纳粹德国著名的V2火箭的总设计师[3],二战结束后,美国将他和他的设计小组带到美国。移居美国后,冯·布劳恩任美国国家航空航天局的空间研究开发项目的主设计师,主持设计了阿波罗4号的运载火箭土星5号。NASA用以下的话来形容冯·布劳恩:“无庸置疑的,他是史上最伟大的火箭科学家。他最大成就是在担任NASA马歇尔空间飞行中心总指挥时,主持土星5号的研发,成功地在1969年7月首次达成人类登陆月球的壮举。”
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun (* 23. März 1912 in Wirsitz, Provinz Posen, Deutsches Reich; † 16. Juni 1977 in Alexandria, Virginia, USA) war als deutscher und später US-amerikanischer Raketentechniker ein Wegbereiter der Raketenwaffen und der Raumfahrt.
Er wurde wegen seiner Pionierleistungen als führender Konstrukteur der ersten funktionstüchtigen und leistungsstarken Flüssigkeitsrakete Aggregat 4 („V2“) in der Zeit des Nationalsozialismus sowie der späteren leitenden Tätigkeit beim Bau von Trägerraketen für die NASA-Missionen berühmt. Seine Mitverantwortung für den Tod von mindestens 12.000 Zwangsarbeitern und weiterer 8.000 Menschen durch die Herstellung und den Einsatz der V2 hat in Deutschland eine einseitige positive Würdigung von Brauns beendet.
 Algerian Navy
Algerian Navy
 Argentine Navy
Argentine Navy
 Brazilian Navy
Brazilian Navy
 British Army
British Army
 Deutsche Marine
Deutsche Marine
 Französische Marine
Französische Marine

 Königlich Omanische Luftwaffe
Königlich Omanische Luftwaffe
 Königlich-Thailändische Marine
Königlich-Thailändische Marine
 Koninklijke Marine
Koninklijke Marine



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Helicopter
Helicopter
 Malaysische Marine
Malaysische Marine
 Marine der Islamischen Republik Pakistan
Marine der Islamischen Republik Pakistan
 Marinha Portuguesa
Marinha Portuguesa
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 Westland Lynx
Westland Lynx
 Nigerianische Marine
Nigerianische Marine
 Norwegische Luftstreitkräfte
Norwegische Luftstreitkräfte
 Republic of Korea Navy
Republic of Korea Navy
 Royal Navy
Royal Navy
 South African Air Force
South African Air Force



威廉·爱德华·波音(英语:William Edward Boeing,1881年10月1日—1956年9月28日)是波音公司的创始人。
William Edward Boeing, geboren als Wilhelm Eduard Böing (* 1. Oktober 1881 in Detroit; † 28. September 1956 auf dem Puget Sound) war ein US-amerikanischer Flugzeugkonstrukteur und Begründer der Boeing-Flugzeugwerke.
威廉·艾梅尔·“威利”· 梅塞施密特(Wilhelm Emil "Willy" Messerschmitt,1898年6月26日 – 1978年9月15日)是一位著名的德国飞机设计家和制造家。梅塞施密特出生在德国法兰克福,生父是一位酒商。他的继父是一位任教于慕尼黑艺术学院的美国教授-卡尔·冯·马尔。
梅塞施密特最出名的设计大概就是属于与华特·雷特尔共同研发的Bf 109战斗机了。Bf 109战斗机在二次世界大战中成为德国空军最重要的战斗机。直至今日,它仍然是产量最多的战斗机,大约有35,000架。另一架梅塞施密特所设计的飞机-Me 209战斗机,则打破了活塞螺桨飞机平飞速度的世界绝对记录。他的公司-梅塞施密特(Messerschmitt AG)也制造了世界第一种服役的喷射战斗机,虽然梅塞施密特本人并没有亲自参与设计。
Wilhelm „Willy“ Emil Messerschmitt (* 26. Juni 1898 in Frankfurt am Main; † 15. September 1978 in München) war ein deutscher Flugzeugkonstrukteur und Vorstandsvorsitzender der Messerschmitt AG. Er gilt als ein Pionier der Luftfahrt.
 Astronomy
Astronomy



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
