
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 India
India

 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Pakistan
Pakistan

 Party and government
Party and government
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Vietnam
Vietnam

ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム(博鰲アジアフォーラム、Boao Forum for Asia、略称BFA、中国語:博鳌亚洲论坛、ピンイン:Bóáo Yàzhōu Lùntán)は、中華人民共和国に本拠を置く国際非営利組織。
スイスのダボスで開催されている世界の政治家・財界人・知識人が集まる国際会議(ダボス会議)を主催する世界経済フォーラムにならい、そのアジア版を目指して、中国政府の全面的支援を受けて構想された。2001年2月27日の設立にはアジアの25カ国とオーストラリアの計26カ国が参加している。
ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム主催の最初の国際会議は2002年4月12日・4月13日に開催され、日本からは小泉純一郎内閣総理大臣が出席して演説を行った[1]。国際会議の会場は、2001年の発足会議以来、中国・海南省の海浜リゾート地・ボアオ(博鰲、海南島東海岸の瓊海市)に固定されている。会議は毎年行われ、各国首脳や大企業経営者、学者、NGO代表など政府・民間のハイレベルの人材が集い、アジアや世界の経済動向、金融政策、経済統合、経済投資、国際協力、社会問題、環境問題などに関する討議が行われる。また多くの経済人や政治家、社会運動家らが直接話し合い、国家間協力や企業提携などのトップ会談が持たれる。
過去の議題には中国の世界貿易機関(WTO)への加入問題、90年代後半のアジア金融危機問題などが取り上げられ、2004年には中国の地政学的な「和平崛起」(平和的台頭)戦略の可否が議題となった。
The Boao Forum for Asia (BFA; Chinese: 博鳌亚洲论坛; pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán) is a non-profit organisation that hosts high-level forums for leaders from government, business and academia in Asia and other continents to share their vision on the most pressing issues in this dynamic region and the world at large. BFA is modelled on the World Economic Forum held annually in Davos, Switzerland. Its fixed address is in Bo'ao, Hainan province, China, although the Secretariat is based in Beijing. The forum, sometimes known as the “Asian Davos”, takes its name from the town of Boao, located in China’s southern Hainan province, which has been the permanent venue for its annual conference since 2002.[1]
The Forum is committed to promoting regional economic integration and bringing Asian countries even closer to their development goals. Initiated in 1998 by Fidel V. Ramos, former President of the Philippines, Bob Hawke, former Prime Minister of Australia, and Morihiro Hosokawa, former Prime Minister of Japan, the Boao Forum for Asia was formally inaugurated in February 2001. The founding of the BFA was driven by the People's Republic of China and founded by 26 Asian and Australasian states on 27 February 2001. The organisation held its first meeting from 12–13 April 2002.
Discussions at the BFA focus on economics, integration, cooperation, society and the environment. In the past the forum also addressed China's entry into the World Trade Organization, as well as Southeast Asia's economic crisis during the 1990s. The geopolitical strategy 'China's peaceful rise' was a topic of discussion for the forum in 2004. In addition to its annual meeting, the BFA also sponsors other forums and meetings related to Asian issues.
El Foro de Boao para Asia (en chino: 博鳌亚洲论坛, pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán), conocida también por sus siglas en inglés BFA, es una organización no lucrativa que organiza foros de alto nivel para líderes del gobierno, los negocios y la academia en Asia y otros continentes para compartir su visión sobre los asuntos más apremiantes en esta región y en el mundo entero. El Foro Boao es el modelo del Foro Económico Mundial que se celebra anualmente en Davos, Suiza. Tiene su sede en Bo'ao, Hainan, China, aunque la Secretaría se encuentra en Pekín.
El Foro tiene como objetivos promover la integración económica regional y acercar a los países asiáticos hacia sus metas de desarrollo.1 Fue creado en 1998 por Fidel V. Ramos, expresidente de Filipinas, Bob Hawke, ex primer ministro de Autralia y Morihiro Hosokawa, ex primer ministro de Japón.2 El Foro de Boao para Asia fue formalmente inaugurado en febrero de 2001. La creación del foro fue liderado por la República Popular de China y fundada por 26 países de Asia y Australasia el 27 de febrero de 2001. La organización tuvo su primera reunión el 12 y 13 de abril de 2002.
Las discusiones del Foro Boao se centran en economía, cooperación, sociedad y medio ambiente. En e pasado el foro también abordaba el ingreso de China en la Organización Mundial del Comercio, así como la crisis financiera asiática de los años noventa. Además de su reunión anual, el foro también patrocina otros foros y reuniones relacionados con temas asiáticos.
Боаоский Азиатский Форум, БАФ (кит: 博鳌亚洲论坛; пиньинь: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán, англ: Boao Forum for Asia, аббр: BFA), также известен как «Восточный Давос» — неправительственная и некоммерческая международная организация, имеющая своей целью поддержку и развитие экономического обмена, взаимодействия и сотрудничества как в Азии, так и за её пределами путём проведения ежегодных встреч высокого уровня с участием представителей правительственных, деловых, промышленных и научных кругов и обсуждения актуальных экономических, социальных, экологических и др. проблем.
Учреждён в 2001 году. Ежегодные конференции в Боао проводятся с 2002 года.
Главный офис организации находится в г. Боао, пров. Хайнань, КНР.
В 2018 году Боаоский азиатский форум /БАФ/ пройдет 8-11 апреля. Главными темами мероприятия станут реформы, открытость, инновации и "Пояс и путь"[1].
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Belarus
Belarus
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Cuba
Cuba
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine

 Party and government
Party and government
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations


Afghanistan Ägypten Algerien Angola Antigua und Barbuda Äquatorialguinea Äthiopien Aserbaidschan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesch Barbados Belarus Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivien Botswana Brunei Burkina Faso Burundi Chile Demokratische Republik Kongo Dominica Dominikanische Republik Dschibuti Ecuador Elfenbeinküste Eritrea Eswatini Fidschi Gabun Gambia Ghana Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Indien Indonesien Irak Iran Jamaika Jemen Jordanien Kambodscha Kamerun Kap Verde Katar Kenia Kolumbien Komoren Kuba Kuwait Laos Lesotho Libanon Liberia Libyen Madagaskar Malawi Malaysia Malediven Mali Marokko Mauretanien Mauritius Mongolei Mosambik Myanmar Namibia Nepal Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Nordkorea Oman Osttimor Pakistan Palästina Panama Papua-Neuguinea Peru Philippinen Republik Kongo Ruanda Saint Lucia Sambia São Tomé und Príncipe Saudi-Arabien Senegal Seychellen Sierra Leone Simbabwe Singapur Somalia Sri Lanka St. Kitts und Nevis St. Vincent und die Grenadinen Südafrika Sudan Suriname Syrien Tansania Thailand Togo Trinidad und Tobago Tschad Tunesien Turkmenistan Uganda Usbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vereinigte Arabische Emirate Vietnam Zentralafrikanische Republik
Die Bewegung der Blockfreien Staaten (kurz Bewegung der Blockfreien oder Blockfreien-Bewegung, englisch Non-Aligned Movement) ist eine Internationale Organisation von Staaten, deren erklärtes Ziel es war, sich im Ost-West-Konflikt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg neutral zu verhalten und keinem der beiden Militärblöcke anzugehören. Die Gründung der Organisation ging auf eine Initiative des jugoslawischen Präsidenten Josip Broz Tito, des ägyptischen Staatschefs Nasser, des indischen Premiers Nehru sowie des indonesischen Präsidenten Sukarno zurück. Die Organisation konstituierte sich 1961 auf ihrer ersten Sitzung in Belgrad.[1] Ihr traten viele ehemalige afrikanische und asiatische Kolonien bei, die sich soeben erst als Staaten konstituiert hatten oder noch um ihre Unabhängigkeit rangen.[2]
Die Organisation verurteilte die Blockbildung in der Zeit des Ost-West-Konfliktes wegen der Gefahr eines Dritten Weltkrieges und setzte sich für die friedliche Koexistenz und Abrüstung ein. Die steigende Zahl der Mitglieder machte es der Organisation jedoch zunehmend schwer, sich auf eine gemeinsame Politik zu einigen. Mit der Auflösung des Warschauer Paktes Anfang der 1990er Jahre verlor sie an Bedeutung. Die heterogene Zusammensetzung der Bewegung machte es schwer, gemeinsame Ziele zu definieren und zu verfolgen.[3] Die Staaten der Blockfreien-Bewegung vertreten 55 Prozent der Weltbevölkerung und halten nahezu zwei Drittel der Sitze in der UN-Generalversammlung.
Das Ziel der Organisation ist die Gleichberechtigung zwischen den Staaten und eine positive wirtschaftliche Entwicklung der Mitgliedstaaten.
不结盟运动(英语:Non-Aligned Movement, NAM)是一个拥有120个成员国和17个观察员国的松散国际组织[3]。它成立于冷战时期,其成员国奉行独立自主的外交政策,不与美苏两个超级大国中的任何一个结盟。联合国中有三分之二的会员是该组织的成员国,全球约55%的人口也生活在不结盟运动国家。不结盟运动定期举行首脑会议,到目前为止已经在前南斯拉夫、埃及、赞比亚、阿尔及利亚、斯里兰卡、古巴、印度、津巴布韦、印尼、哥伦比亚、南非、马来西亚、塞尔维亚、委内瑞拉、阿塞拜疆和乌干达[4]举行会议。
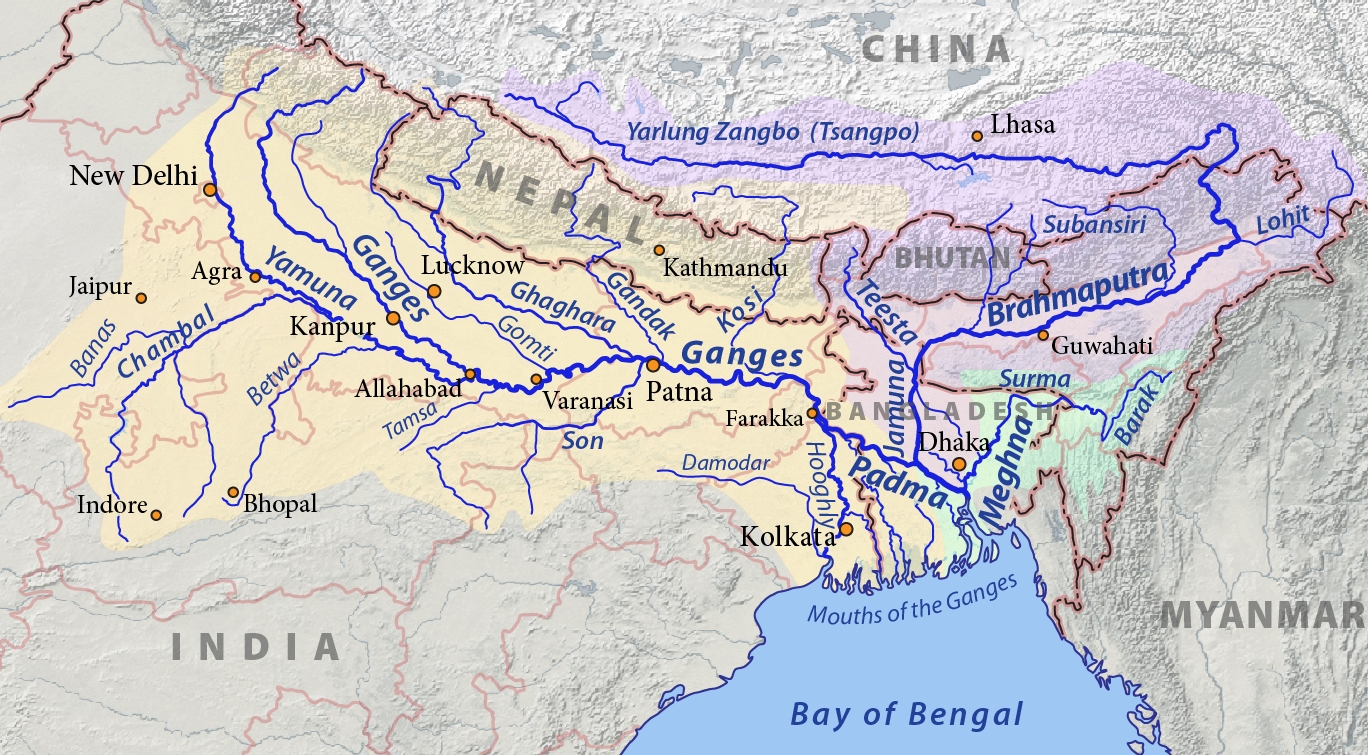
Der Brahmaputra ist der Hauptstrang des als Meghna in den Indischen Ozean mündenden wasserreichsten Stromes in Asien. Er fließt mit einer Länge von rund 3100 Kilometern bis zum Zusammenfluss mit dem Ganges durch das Gebiet der Staaten China, Indien und Bangladesch. Sein Lauf ist teils veränderlich, teils schwer zugänglich und quert mehrere Kulturräume, was zu vielen unterschiedlichen Namen für Teilabschnitte geführt hat.
Der nach Osten gerichtete Oberlauf des Brahmaputra in Tibet heißt auf Tibetisch Matsang bzw. Tachog Tsangpo (in Wylie-Transliteration: rta mchog gtsang po), auf Chinesisch Mǎquán Hé 馬泉河 / 马泉河; danach heißt er auf Tibetisch Yarlung Tsangpo ཡར་ཀླུང་གཙང་པོ (yar klung gtsang po), der Reinigende, nach anderer Quelle „vom höchsten Gipfel herabkommendes Wasser“, und auf Chinesisch Yǎlǔ Zàngbù Jiāng 雅魯藏布江 / 雅鲁藏布江.
Im indischen Bundesstaat Arunachal Pradesh hat der scharf nach Süden abgeknickte Fluss den Namen Dihang oder Siang. Nach einem Richtungswechsel nach Westen an der Einmündung des größten Nebenflusses, des Lohit, heißt er, nun den Bundesstaat Assam durchfließend, Brahmaputra (ब्रह्मपुत्र), was im Sanskrit „Sohn des Brahma“ bedeutet. Ein älterer Name dieses Flussabschnittes war (in Sanskrit-Schriften und in Teilen Assams) Luit oder Lohitya, da früher statt des größeren Dihang der Lohit als der Oberlauf galt. Heute wird der Name auf Hindi ब्रह्मपुत्र, Brahmaputra gesprochen, auf Assamesisch ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ und auf Bengalisch ব্রহ্মপুত্র Brohmoputro.
Bei einer Wendung nach Süden tritt der Fluss in das Staatsgebiet von Bangladesch ein und führt teils ab dort, teils ab der Abzweigung des Alten Brahmaputra (früher der Hauptstrom) den Namen Jamuna. Ab dem Zusammentreffen mit dem deutlich weniger voluminösen Ganges schwenkt der Strom in dessen südöstliche Richtung ein und heißt nun Padma, bis er ab der Mündung des letzten großen Nebenflusses bis zur Mündung in den Golf von Bengalen dessen Namen Meghna annimmt.
布拉马普特拉河,亚洲主要大河之一,被藏族视为“摇篮”和“母亲河”。以长度来说为中国第5大河(仅次于长江、黄河、黑龙江和珠江)、西藏地区第一大河,以水量来说是印度和孟加拉国的第二大河(仅次于恒河)。上游是世界海拔最高的大河,也是中国坡降最陡的大河。藏语中雅鲁藏布江意为“高山流下的雪水”,梵语中布拉马普特拉河意为“梵天之子”。它发源于西藏喜马拉雅山脉北麓的杰马央宗冰川,从藏南(印度称阿鲁纳恰尔邦)进入印度,在藏南(阿鲁纳恰尔邦)境内称底杭河(Dihang river)或香江(Siang river)。在藏南巴昔卡附近的印度阿萨姆邦境内与其他两河合流后始称布拉马普特拉河。流经孟加拉国后称为贾木纳河,于瓜伦多卡德与恒河汇合,形成巨大的恒河三角洲,最后注入孟加拉湾。全长为2900公里。
布拉马普特拉河(梵語:ब्रह्मपुत्र,印地語:ब्रम्हपुत्र)字面意思是“(印度教三主神之一的)梵天之子”,南亚的一条重要国际河流。
布拉马普特拉河的上游在中国境内,称为雅鲁藏布江,长2057km;流入印度后称为布拉马普特拉河,长644km;流入孟加拉国后称贾木纳河,长240km;在阿里恰与恒河汇流后称帕德玛河,长100km;在琴德普尔与梅格纳河汇合后仍称梅格纳河长241km;最后注入孟加拉湾。以水量、长度来说,此河是南亚第一大河。包括上游雅鲁藏布江在内的全长为2900公里。总流域面积6.22×105km2,流域国有中国、印度、不丹、孟加拉国,四国分别占该河流域面积的51.1%、34%、6.7%、8.2%。
ブラマプトラ川(ブラマプトラがわ、英:Brahmaputra River, ヒンディー語:ब्रह्मपुत्र Bramhaputra, ベンガル語:ব্রহ্মপুত্র Brohmoputro)は、チベットに発しバングラデシュでガンジス川と合流し、ベンガル湾へ注ぐ河川である。チベットではヤルンツァンポ川(表記によってはヤル・ツアンポー川とも。チベット語:ཡར་ལུང་གཙང་པོ་ Yar-lung gTsang-po, 中国語:雅鲁藏布江)、バングラデシュではジョムナ川(英:Jamuna River, ベンガル語:যমুনা Jomuna)と呼ばれている。 全長2,900km。源流はヒマラヤ山脈の北側で、マーナサローワル湖から流れでてチベット高原南部を東進した後ヒマラヤ山脈東端をかすめ南下、インドのアッサム州を西へ向け横断、ガンジスに合流する。その合流点では世界最大の広大な三角洲を形成している。中流から下流域にかけて堆積平野が広がり、主に農業が営まれる。雨季にはしばしば氾濫し、氾濫のためにできた沼沢地や池が残る。
The Brahmaputra (/ˌbrɑːməˈpuːtrə/) is one of the major rivers of Asia, a trans-boundary river which flows through China, India and Bangladesh. As such, it is known by various names in the region: Assamese: লুইত luit [luɪt], ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ নৈ Brohmoputro noi, ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ নদ (the tatsama 'নদ' nod, masculine form of the tatsama 'নদী' nodi "river") Brohmoputro [bɹɔɦmɔputɹɔ]; Sanskrit: ब्रह्मपुत्र, IAST: Brahmaputra; Tibetan: ཡར་ཀླུངས་གཙང་པོ་, Wylie: yar klung gtsang po Yarlung Tsangpo; simplified Chinese: 布拉马普特拉河; traditional Chinese: 布拉馬普特拉河; pinyin: Bùlāmǎpǔtèlā Hé. It is also called Tsangpo-Brahmaputra (when referring to the whole river including the stretch within Tibet).[2] The Manas River, which runs through Bhutan, joins it at Jogighopa, in India. It is the ninth largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest.
With its origin in the Manasarovar Lake region, located on the northern side of the Himalayas in Burang County of Tibet as the Yarlung Tsangpo River,[1] it flows across southern Tibet to break through the Himalayas in great gorges (including the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon) and into Arunachal Pradesh (India).[3] It flows southwest through the Assam Valley as Brahmaputra and south through Bangladesh as the Jamuna (not to be mistaken with Yamuna of India). In the vast Ganges Delta, it merges with the Padma, the popular name of the river Ganges in Bangladesh, and finally the Meghna and from here it is known as Meghna before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.[4]
About 3,848 km (2,391 mi)[1] long, the Brahmaputra is an important river for irrigation and transportation. The average depth of the river is 38 m (124 ft) and maximum depth is 120 m (380 ft). The river is prone to catastrophic flooding in the spring when Himalayas snow melts. The average discharge of the river is about 19,800 m3/s (700,000 cu ft/s),[3] and floods can reach over 100,000 m3/s (3,500,000 cu ft/s).[5] It is a classic example of a braided river and is highly susceptible to channel migration and avulsion.[6] It is also one of the few rivers in the world that exhibit a tidal bore. It is navigable for most of its length.
The river drains the Himalaya east of the Indo-Nepal border, south-central portion of the Tibetan plateau above the Ganga basin, south-eastern portion of Tibet, the Patkai-Bum hills, the northern slopes of the Meghalaya hills, the Assam plains, and the northern portion of Bangladesh. The basin, especially south of Tibet, is characterized by high levels of rainfall. Kangchenjunga (8,586 m) is the only peak above 8,000 m, hence is the highest point within the Brahmaputra basin.
The Brahmaputra's upper course was long unknown, and its identity with the Yarlung Tsangpo was only established by exploration in 1884–86. This river is often called Tsangpo-Brahmaputra river.
The lower reaches are sacred to Hindus. While most rivers on the Indian subcontinent have female names, this river has a rare male name, as it means "son of Brahma" in Sanskrit (putra means "son").[7]
Le Brahmapoutre - du sanskrit ब्रह्मपुत्र (Brahmaputra) signifiant « fils de Brahmâ »3 - est un fleuve de l'Asie du Sud, long de 2 900 kilomètres, ayant sa source principale dans l'Himalaya tibétain, à 5 542 m d'altitude, au glacier Gyima Yangzoin, dans le xian de Zhongba 29° 17′ 41″ N, 83° 46′ 23″ E 4. D'autres sources sont situées au pied des glaciers des monts Kubi-gangri et Ganglung-gangri. C'est le Dyardanes ou l’Œdanes des Grecs anciens. Son parcours tropical fait de la vallée de ce fleuve un des plus riches sites mondiaux au regard de la biodiversité. Ses crues importantes permettent une fertilisation du sol mais sont dévastatrices. Dans son cours inférieur, qui est sacré pour les hindous, le fleuve est utilisé pour le transport de produits agricoles.
Il Brahmaputra (ཡར་ཀླུང་གཙང་པོ་ in tibetano, 布拉马普特拉河 in cinese) è un fiume che nasce nel Tibet sud-occidentale, dove prende il nome Yarlung Tsangpo, e scorre verso est, lungo il versante settentrionale dell'Himalaya, in territorio cinese. Dopo avere aggirato la catena himalayana, piega bruscamente a sud, e col nome di Brahmaputra attraversa gli stati indiani dell'Arunachal Pradesh e dell'Assam, entrando poi nel Bangladesh, dove confluisce nel Gange in corrispondenza del delta di questo per sfociare nel golfo del Bengala.
È lungo 2.900 km, ha una profondità media di 38 metri e massima di 120, si dirama spesso in un intreccio di bracci soggetti a fenomeni di avulsione ed è uno dei pochi fiumi al mondo in cui si verifica la cosiddetta marea fluviale. Il suo bacino idrografico copre una superficie di 670.000 km².[1]
Ha un regime idrico caratterizzato da portata sempre elevatissime: le minime non scendono mai sotto i 5.000 m³/s, ma le massime possono raggiungere anche i 168.500 m³/s, si tratta di portate massime che trovano paragone solo nel Rio delle Amazzoni ed in pochissimi altri fiumi del pianeta. Durante l'estate, quando lo scioglimento dei ghiacciai coincide con l'arrivo del monsone, il fiume è soggetto a catastrofiche esondazioni, che insieme a quelle del Gange allagano intere regioni e sommergono buona parte del Bangladesh, causando ingenti perdite di vite umane e gravissimi danni alle abitazioni e all'agricoltura.[2]
È navigabile per buona parte del suo corso, ma nell'ultima parte del tratto tibetano è caratterizzato da un corso assai impetuoso, con rapide e cascate (una, alta circa 35 metri, è stata scoperta dopo il 2000 nel corso di un'esplorazione britannica). A causa delle gole inaccessibili che attraversa in questa zona disabitata, per lungo tempo non si seppe che il Brahmaputra e lo Yarlung fossero lo stesso fiume, la continuità tra i due corsi è stata scoperta da un'esplorazione compiuta tra il 1884 ed il 1886.
El río Brahmaputra (en idioma sánscrito, ब्रह्मपुत्र, que significa «el hijo de Brahmā») es uno de los ríos más largos de Asia.
Nace en el glaciar Kubigangri, cerca del monte Kailāsh, en el Himalaya, y discurre en dirección este por territorio chino, por la parte oeste del Tíbet, pasando cerca de Lhasa. Después de un recorrido de 2896 km desagua en el golfo de Bengala, en Bangladés, formando parte del delta del Ganges, el mayor delta del mundo. El río es conocido como Tsangpo en el Tíbet y en la zona central de Bangladés se divide en dos ramales, siendo el principal el río Jamuna, nombre con el que es conocido en esa región, y el otro, de menor caudal, el río Shitalakshya.
Es el Dyardanes o "Œdanes" de los antiguos griegos. Su recorrido por la zona tropical hace de su valle uno de los más ricos en diversidad biológica del mundo. Sus principales inundaciones permiten la fertilización del suelo, aunque son devastadoras. En su parte más baja, el río se considera sagrado para los hindúes, y se utiliza para el transporte de productos agrícolas.
Брахмапу́тра[2] (кит. 雅鲁藏布江, тиб. ཡར་ཀླུང་གཙང་པོ།, хинди ब्रह्मपुत्र, ассам. ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰ, англ. Brahmaputra, бенг. ব্রহ্মপুত্র) — река в Китае, Индии и Бангладеш, левый приток Ганга; одна из крупнейших водных артерий в Южной Азии.







 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute

 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 History
History
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Civilization
Civilization
 Film & TV Produktion
Film & TV Produktion
 Companies
Companies
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink