
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Canada
Canada

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA
 Canada
Canada

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
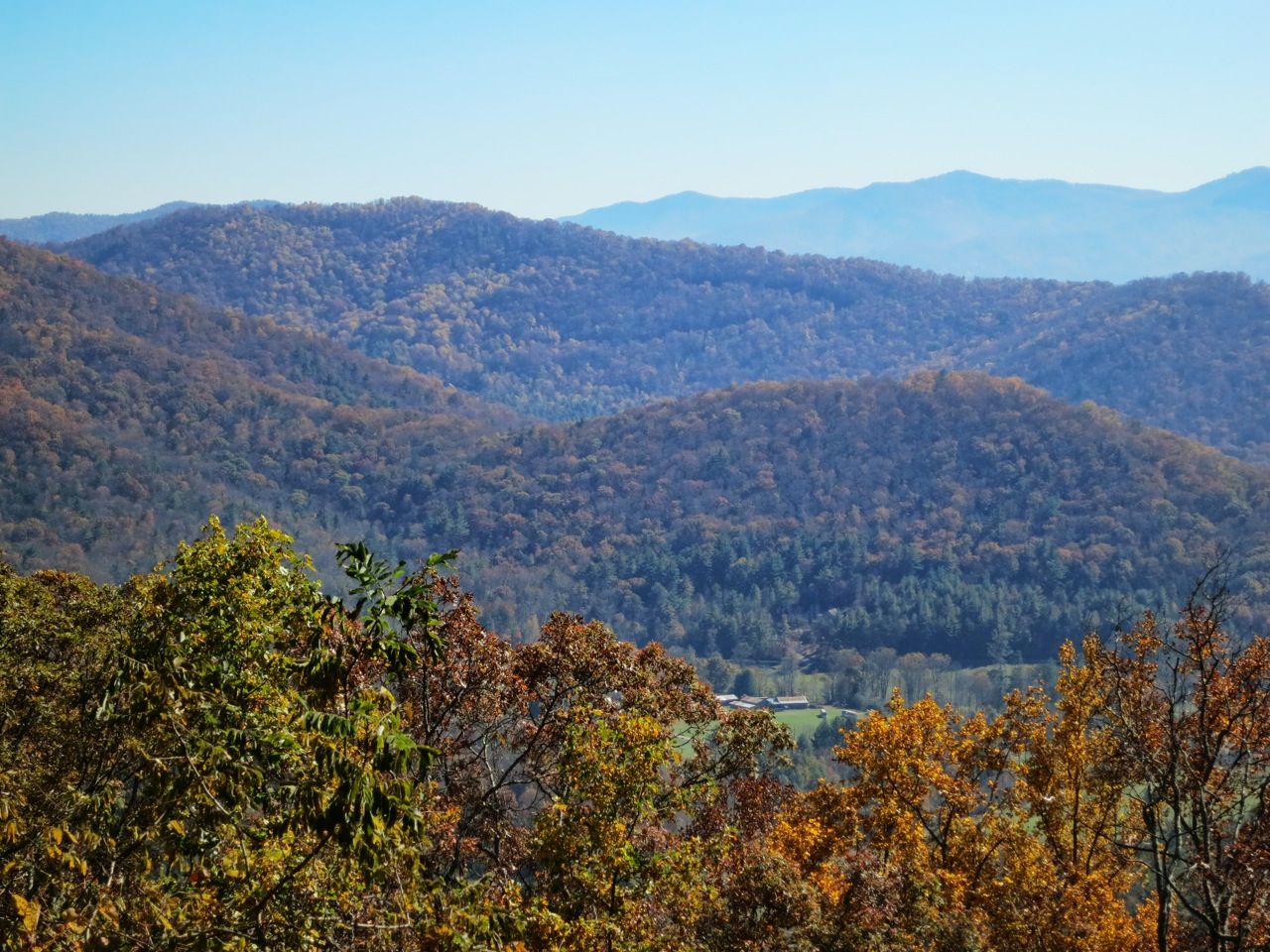

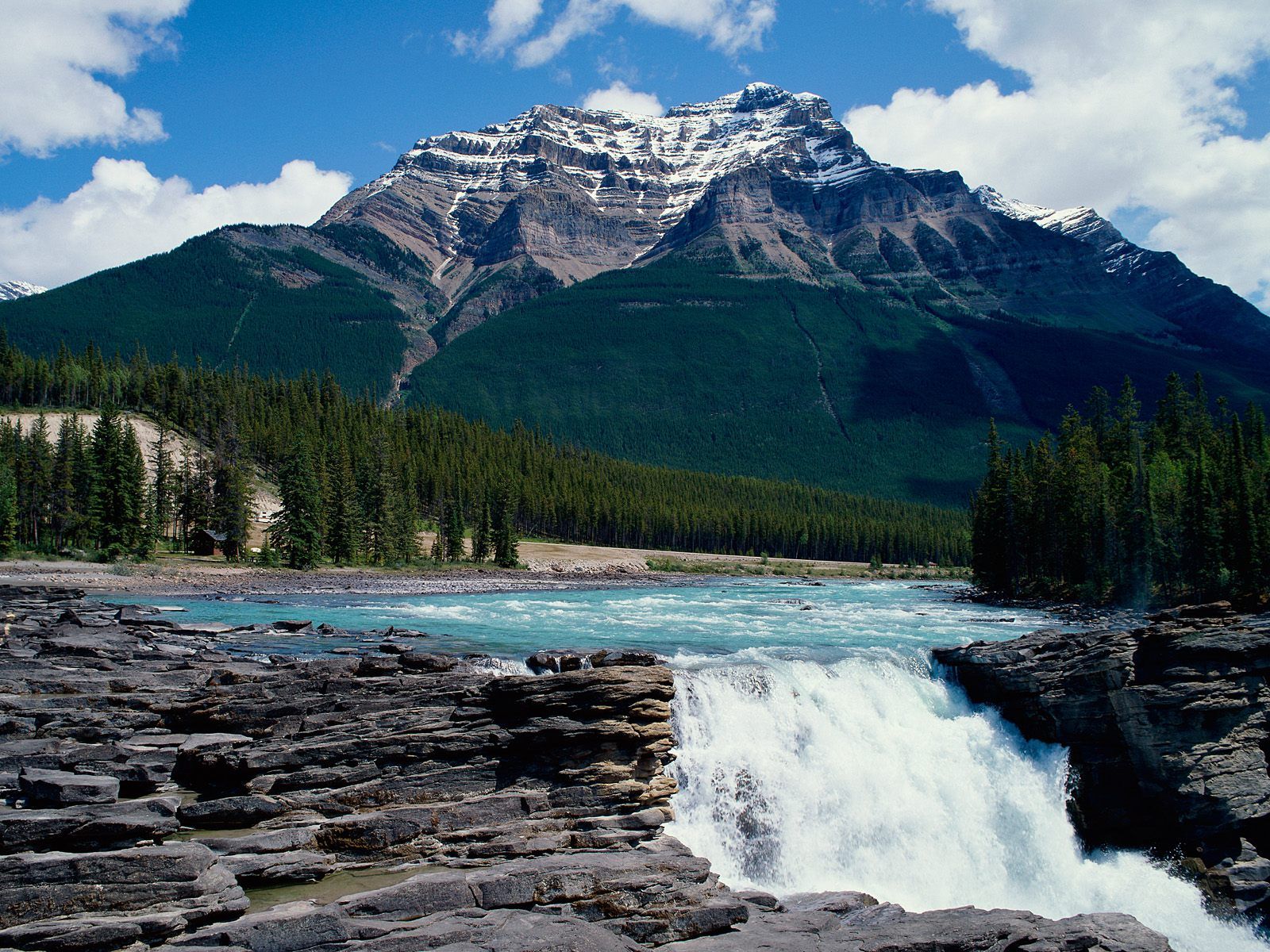
阿巴拉契亚山脉(Appalachian Mountains),又譯阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
阿巴拉契亚山脉(英语:Appalachian Mountains),又译阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
构成阿巴拉契亚山脉的有纽芬兰省的长岭山、魁北克的圣母山、缅因州的朗费罗山、新罕布夏州的怀特山、佛蒙特州的格林山脉、塔库尼克山;马萨诸塞州的勃克夏山;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州和西佛吉尼亚州三州的阿勒格尼山脉;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州、西佛吉尼亚州以及佛吉尼亚州四州的阿巴拉契亚岭谷。还有从宾夕法尼亚州南部到佐治亚州北部的蓝岭山脉。
实际上阿巴拉契高地 严格的边界范围存有争议,阿第伦达克山脉一般被认为是属于加拿大地盾,而非阿巴拉契亚高地。
Die Appalachen (englisch Appalachian Mountains) sind ein bewaldetes Gebirgssystem im Osten Nordamerikas, das sich über eine Länge von 2400 Kilometer von den Long Range Mountains an der Westküste der kanadischen Insel Neufundland bis in den Norden des US-Bundesstaates Alabama erstreckt. Obwohl ihr höchster Gipfel mehr als 2000 Meter hoch ist, haben die Appalachen sowohl hinsichtlich ihrer Höhe als auch ihrer Morphologie einen Mittelgebirgscharakter. Nur wenige Berge erheben sich über mehr als 1200 m Höhe, und viele Bergkuppen bleiben deutlich unter 800 m.
Benannt sind die Appalachen nach dem indigenen Stamm der Apalachee. Für die Appalachenregion als Kultur- und Wirtschaftsraum wird auch die Bezeichnung Appalachia verwendet.[1]
アパラチア山脈(Appalachian Mountains)は、カナダ及びアメリカ合衆国東北部に位置し、北東から南西方向に全長約2,600kmにわたって延びる丘陵・山脈。狭義では、そのうちのウエストバージニア州、バージニア州、ケンタッキー州、テネシー州、ノースカロライナ州等の南側の部分のみを指すこともある。
複雑に褶曲した山脈で、侵食が進んだ丘陵性の古い山脈である。北端はカナダニューファンドランド島で、そこから北アメリカ大陸東部を南西方向に縦断し、南端はアラバマ州の中央に至る。また、その裾野はミシシッピ州北西部にまで及んでいる。個々の山の標高は平均して1,000m前後で、最高峰はノースカロライナ州にあるミッチェル山(標高2,037m)。
山脈の西部では石油・石炭が盛んに採掘されているなど地下資源が豊富。山脈の東側には都市が発達している。国立公園が多く、グレート・スモーキー山脈国立公園やシェナンドー国立公園が有名である。
The Appalachian Mountains,[a] often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion.[4][5] The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.
Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the Appalachian Highlands physiographic division as consisting of thirteen provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, Saint Lawrence Valley, Appalachian Plateaus, New England province, and the Adirondack areas.[6][7] A common variant definition does not include the Adirondack Mountains, which geologically belong to the Grenville Orogeny and have a different geological history from the rest of the Appalachians.[8][9][10]
Les Appalaches sont une chaîne de montagnes située dans l'Est de l'Amérique du Nord et s'étendant de Terre-Neuve (Canada), au nord, jusqu'au centre de l'État de l'Alabama, au sud (États-Unis). Elle culmine au mont Mitchell (2 037 mètres) en Caroline du Nord.
Les Appalaches séparent la plaine côtière atlantique (à l'est) du bassin du fleuve Mississippi et des Grands Lacs (à l'ouest). Elles s'étirent sur près de 2 000 km de longueur.
L'exploitation du charbon, qui fournit la moitié de l'électricité américaine, y a fortement périclité, et l'industrie métallurgique est en grande difficulté.
Les Appalaches ont donné leur nom à un type de relief, le relief appalachien, qui désigne les vestiges d'une ancienne montagne fortement arasée. De longs couloirs s'étendent parallèlement à des échines rectilignes. Les cluses appalachiennes forment des passages étroits à travers les chaînons de la montagne.
Le Sentier des Appalaches (AT) parcourt les sommets de la chaîne depuis le Maine jusqu'à la Géorgie et le Sentier international des Appalaches (SIA - IAT) passe par les sommets du nord du Maine jusqu'au cap Gaspé, en Gaspésie. Leur point d'intersection est le sommet du mont Katahdin.
Gli Appalachi (AFI: /appaˈlaki/) o Appalaci (/appaˈlaʧi/[1]; in inglese Appalachian Mountains, in francese Appalaches) sono una catena montuosa situata nella parte orientale dell'America del Nord.
Si sviluppa, quasi parallelamente alla costa orientale atlantica, dal golfo del fiume San Lorenzo fino all'Alabama, per almeno 2500 km con picchi non molto elevati (i più alti sono con 2037 m il monte Mitchell e con 1917 m il monte Washington). Gli Appalachi riguardano anche l'isola di Terranova (Canada) e l'isola francese di Miquelon parte della collettività territoriale di Saint-Pierre e Miquelon[2][3]. La porzione sud degli Appalachi viene chiamata monti Unakas.
Per via dell'età geologica, gli Appalachi sono la catena montuosa più vecchia delle Americhe. Gli Appalachi statunitensi sono una delle zone economicamente più depresse degli Stati Uniti.
Apalaches o montes Apalaches (en inglés: Appalachian Mountains o Appalachians; en francés: Appalaches1) es una importante cordillera ubicada en el este de Norteamérica. Se extiende desde la Isla de Terranova en Canadá, pasado por la colectividad de ultramar francés de San Pedro y Miquelón, hasta Alabama en los Estados Unidos, aunque su parte más septentrional termina en la península de Gaspé, en Quebec. Constituye el elemento morfológico más sobresaliente de la parte oriental de América del Norte.
Se originó en antiguas montañas formadas en el periodo Paleozoico con relieves suavizados por la prolongada acción de los agentes exógenos. El sistema está dividido en una serie de cordilleras, en las que la medida de altura de los picos es de unos 1000 m s. n. m. (metros sobre el nivel del mar). La cima más elevada es el monte Mitchell, en Carolina del Norte, mide 2037 m s. n. m. y es el punto más alto de los Estados Unidos al este del río Misisipi y de todo el este de Norteamérica.
Аппала́чи[2] (англ. Appalachian Mountains) — горная система на востоке Северной Америки, в США и Канаде. Длина — 2600 км.
Северные Аппалачи (к северу от рек Мохок и Гудзон) — холмистое плоскогорье с отдельными массивами высотой до 1916 м (гора Вашингтон), имеют следы древнего оледенения. Южные Аппалачи в осевой зоне состоят из параллельных хребтов и массивов, разделённых широкими долинами; к осевой зоне прилегают с востока плато Пидмонт, с запада — Аппалачское плато. Высота — до 2037 м (гора Митчелл). В горах имеются месторождения каменного угля, нефти и газа, железных руд, титана; широколиственные, хвойные и смешанные леса.
Горы образовались в пермский период в результате столкновения двух материков (возникновение Пангеи).


安大略美术馆(英語:Art Gallery of Ontario)是加拿大安大略省多伦多的一个博物馆,收藏欧洲、美国、加拿大等地的艺术品,藏品超过四万件,为北美洲第八大艺术博物馆,收藏品的时间跨度从公元100年至今。
Die Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO abgekürzt) im kanadischen Toronto gehört zu den bedeutendsten und mit rund 45.000 Quadratmetern Ausstellungsfläche auch zu den größten Kunstmuseen Nordamerikas.
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC

 Australian Capital Territory-ACT
Australian Capital Territory-ACT
 Australia
Australia
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kantō
Kantō
 Kinki
Kinki
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

亚太经济合作组织(简称亚太经合组织;英语:Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,缩写:APEC),是亚太区内各地区之间促进经济成长、合作、贸易、投资的论坛。此组织的创办在历史上取代了该区域的冷战结构,但由于日本在该区域会因过去历史记忆引发负面评价,所以由澳大利亚主导创始事项[1]。
始设于1989年,现有21个经济体成员。亚太经合组织是经济合作的论坛平台,其运作是通过非约束性的承诺与成员的自愿,强调开放对话及平等尊重各成员意见,不同于其他经由条约确立的政府间组织。“APEC”与“Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation”均是亚太经济合作组织的注册商标。[2]
Die Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (für englisch Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, kurz APEC, auch übersetzt als Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftskooperation oder Asien-Pazifik-Forum) ist eine internationale Organisation, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, im pazifischen Raum eine Freihandelszone einzurichten.
In den 21 APEC-Staaten lebt knapp die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung. Der Wirtschaftsraum erbringt mehr als die Hälfte der Weltwirtschaftsleistung und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Wirtschaftsregionen der Welt.
アジア太平洋経済協力会議(アジアたいへいようけいざいきょうりょくかいぎ、英: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)は、環太平洋地域における多国間経済協力を進めるための非公式なフォーラム[2]である。略称、APEC(エイペック[3][4])。
「アジア太平洋」という概念が最初に打ち出されたのは、永野重雄が1967年に発足させた太平洋経済委員会(PBEC)という経済団体の設立時であるとされるが[5][6][7]、具体的にこうした地域概念が政府レベルの協力枠組みに発展する萌芽は、1978年、日本の大平正芳首相が就任演説で「環太平洋連帯構想」を呼びかけたことにある。これを具体化した大平政権の政策研究会「環太平洋連帯研究グループ」(議長:大来佐武郎、幹事佐藤誠三郎)の報告を受け、大平がオーストラリアのマルコム・フレイザー首相に提案して強い賛同を得たことが、1980年9月の太平洋経済協力会議(PECC)の設立につながった。PECCは地域における様々な課題を議論し研究するセミナーといった趣のものであったが、これを土台にして、各国政府が正式に参加する会合として設立されたのが、APECである[8][9]。
APECは、1989年にオーストラリアのホーク首相の提唱で、日本・アメリカ合衆国・カナダ・韓国・オーストラリア・ニュージーランド及び当時の東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟6か国の計12か国で発足し、同国のキャンベラで閣僚会議(Ministerial Meeting)を開催した。また、1993年には米国のシアトルで初の首脳会議(Economic Leaders' Meeting)がもたれた。現在は、首脳会議、及び、外相、経済担当相による閣僚会議をそれぞれ年1回開いている。シンガポールに常設事務局を置き、開催国から任期1年で事務局長が選任されている[10]。 参加しているメンバーは、21カ国・地域で、2012年現在、人口では世界の41.4%、GDP(国内総生産)では57.8%、貿易額では47%を占めている。
APECは、開かれた地域協力によって経済のブロック化を抑え、域内の貿易・投資の自由化を通じて、世界貿易機関(WTO)のもとでの多角的自由貿易体制を維持・発展することを目的としてきたが、近年のWTOの新ラウンドの停滞や自由貿易協定締結の動きの活発化などによって、その存在意義が問われている。
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies[2] that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Inspired from the success of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)’s series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, the APEC was established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; and to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[3][4][5] Headquartered in Singapore, the APEC is recognised as one of the oldest forums and highest-level multilateral blocs in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting is attended by the heads of government of all APEC members except Republic of China (Taiwan) (which is represented by a ministerial-level official under the name Republic of China as economic leader).[12] The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15][16][17]
La Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (en anglais : Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) est un forum économique intergouvernemental visant à faciliter la croissance économique, la coopération, les échanges et l'investissement de la région Asie Pacifique. Elle se réunit chaque année1.
L'Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), ossia Cooperazione Economica Asiatico-Pacifica, è un organismo nato nel 1989 allo scopo di favorire la cooperazione (o, più in generale, la crescita) economica, il libero scambio e gli investimenti nell'area asiatico-pacifica. Tale area (come suggerisce il logo stesso dell'APEC) coincide non solo con l'Asia Pacifica, ma potenzialmente con l'intero Pacific Rim.
L'APEC ha sede a Singapore, Paese considerato una delle tigri dell'Asia.
Dal punto di vista del diritto internazionale l'APEC si definisce organismo e non organizzazione internazionale perché, essendo composto da economie e non da Stati, è privo di una piena personalità giuridica. Ciò spiega, fra l'altro, come mai possano farne parte contemporaneamente la Cina continentale, Hong Kong e Taiwan, ossia tre realtà che, territorialmente (secondo Pechino e secondo tutti i governi che intrattengono relazioni diplomatiche con Pechino), appartengono a un unico Stato: la Repubblica Popolare di Cina.
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, en español Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico) es un foro multilateral creado en 1989, con el fin de consolidar el crecimiento y la prosperidad de los países del Pacífico, que trata temas relacionados con el intercambio comercial, coordinación económica y cooperación entre sus integrantes.1
Como mecanismo de cooperación y concertación económica, está orientado a la promoción y facilitación del comercio, las inversiones, la cooperación económica y técnica y al desarrollo económico regional de los países y territorios de la cuenca del océano Pacífico. Fomentando un crecimiento económico inclusivo, equitativo, sustentable e innovador.2
La suma del Producto Nacional Bruto de las veintiuna economías que conforman el APEC equivale al 56 % de la producción mundial, en tanto que en su conjunto representan el 46 % del comercio global.
La APEC no tiene un tratado formal. Sus decisiones se toman por consenso y funciona con base en declaraciones no vinculantes. Tiene una Secretaría General, con sede en Singapur, que es la encargada de coordinar el apoyo técnico y de consultoría. Cada año uno de los países miembros es huésped de la reunión anual de la APEC. La vigésimo novena cumbre se realizó en noviembre de 2017 en Da Nang, Vietnam; y la próxima será en Santiago, Chile.
Азиатско-Тихоокеанское экономическое сотрудничество (АТЭС) (англ. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) — форум 21 экономики Азиатско-Тихоокеанского региона для сотрудничества в области региональной торговли и облегчения и либерализации капиталовложений.
Целью АТЭС является повышение экономического роста, процветания в регионе и укрепление азиатско-тихоокеанского сообщества. В экономиках-участницах проживает около 40 % мирового населения, на них приходится приблизительно 54 % ВВП и 44 % мировой торговли[1].

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Kimimasa Tarumizu
Kimimasa Tarumizu
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Haruhiko Kuroda
Haruhiko Kuroda
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masao Fujioka
Masao Fujioka
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masatsugu Asakawa
Masatsugu Asakawa
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Mitsuo Sato
Mitsuo Sato
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Shiro Inoue
Shiro Inoue
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Tadao Chino
Tadao Chino
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takeshi Watanabe
Takeshi Watanabe
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Taroichi Yoshida
Taroichi Yoshida
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sweden
Sweden
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tonga
Tonga
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


亚洲开发银行(英语:Asian Development Bank,缩写:ADB,简称亚银、亚行、亚开行),香港旧译亚洲发展银行,属于亚太地区的政府之间金融机构,其目的是为了促进亚洲经济与社会的发展。1966年12月19日成立,有31个创始会员国,目前有68个成员体,其中亚太有49个。总部设置于菲律宾马尼拉并在世界各地拥有31个办事处。亚洲开发银行仿照世界银行的股权制度,依照成员体的资本比例,得到相应比例的投票权。2014年以来,亚洲开发银行发布亚太创意生产指数年度报告。[3][4]亚洲开发银行为联合国观察员。
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966,[4] which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world[5] to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries.[6] From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public.[7] The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. Upon completion of their study programs, scholars are expected to contribute to the economic and social development of their home countries.[8] ADB is an official United Nations Observer.[9]
El Banco Asiático de Desarrollo (BAsD) es una organización financiera para el desarrollo económico de Asia y el Pacífico. Su objetivo principal es la erradicación de la pobreza y facilitar ayudas para mejorar el nivel de vida de la población de la región a través de préstamos y colaboración técnica.
Creado en 1966 por 31 países. Hoy cuenta con 67 miembros (48 regionales y 19 no regionales). Estados Unidos y Japón son sus principales accionistas, con el 15,6% del capital cada uno.
El Banco tiene como su principal objetivo la lucha contra la pobreza. Para ello busca promover el crecimiento económico y la cooperación en la región de Asia-Pacífico, y acelerar el proceso de desarrollo económico de sus países miembros. Las dos terceras partes de personas pobres del mundo (aquellos que viven con menos de dos dólares diarios por persona), cerca de 1.800 millones de pobres, viven en esta región. El BAsD aprobó una nueva Estrategia a Largo Plazo (2008-2020) centrada en un crecimiento económico, medioambientalmente sostenible e integración regional.
Азиа́тский банк разви́тия (англ. Asian Development Bank) — банк, основанный в 1966 году, его главной задачей является стимулировать рост экономики в Азии и на Дальнем Востоке, направляя в эти регионы прямые займы и оказывая техническое содействие.
Штаб-квартира в Маниле (Филиппины). Президентом АБР с 28 апреля 2013 года является японец Такэхико Накао. 17 января 2020 года президентом станет Масацугу Асакава, избранный 2 декабря 2019 года[1].


 Badminton World Federation
Badminton World Federation
 BWF World Championships
BWF World Championships
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 England
England
 France
France
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Schottland
Schottland
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 United States
United States

国际羽联世界锦标赛,通常称世界羽毛球锦标赛,是一项由国际羽毛球联合会组织的羽毛球单项锦标赛事,以之为世界顶尖的羽毛球选手加冕。
该赛由1977年开始举办,1983年以前每三年举办一次。然而,在头两届比赛时国际羽联遇到过麻烦:世界羽毛球联合会(后来与国际羽毛球联合会合并)在国际羽联世界锦标赛后一年以相同的目的举办相同性质的比赛。1981年两组织合并后,该问题也随之解决。
从1985年起,该项赛事改为两年举办一次,直到2005年止。2006年起,锦标赛成为了国际羽联日程表上一年一次的赛事,目的在于给与运动员们更多机会去赢得官方的“世界冠军”称号。但每到奥运会举办的年份,锦标赛不举办,以便为奧運會羽毛球比賽让路。(Quelle:Wikipedia)


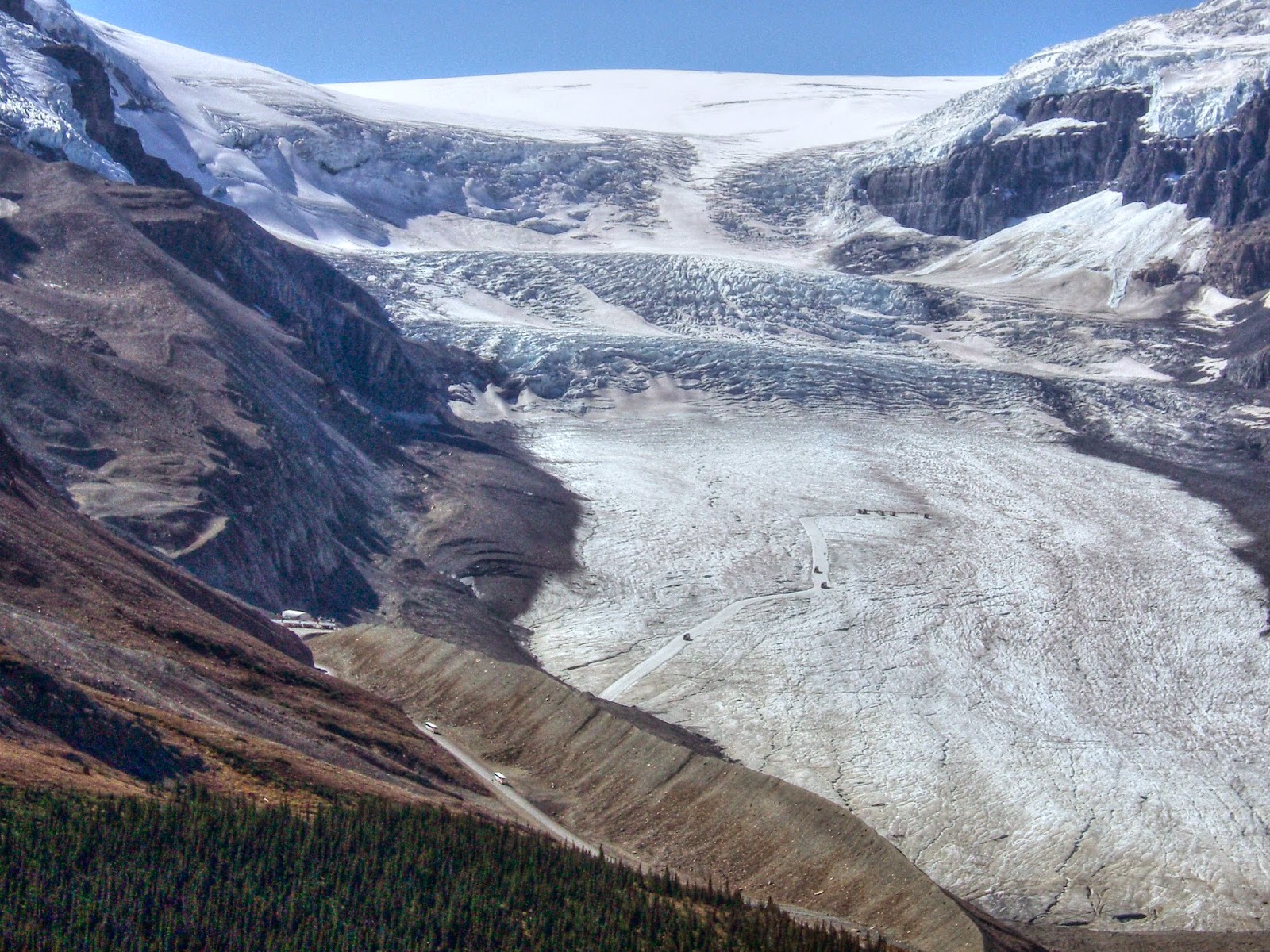
班芙国家公园(英语:Banff National Park,法语:Le Parc national Banff)建于1885年,是加拿大历史最悠久的国家公园。它坐落于落基山脉北段,距加拿大艾伯塔省卡尔加里以西约110-180千米处。公园共占地6641平方千米,[2]遍布冰川、冰原、松林和高山。冰原公路从路易斯湖开始,一直连接到北部的贾斯珀国家公园。西面是省级森林和幽鹤国家公园,南面与库特尼国家公园毗邻,卡纳纳斯基斯镇位于其东南方。公园内主要的商业区为弓河山谷的班夫镇。它作为“加拿大落基山脉公园群”的一部分,与其它加拿大落基山脉的国家和省立公园一起被列入世界遗产名录中。
加拿大太平洋铁路是早期通往班夫的方式,太平洋铁路集团在公园内建造了班夫温泉酒店和路易斯湖城堡酒店,吸引了大量游客前往。20世纪初期,在一战和大萧条期间,通往班夫的公路建成。1960年开始公园全年对外开放,1990年游客数量达到了500万人次。[3] 上百万的游客通过加拿大横贯公路前往。[4]由于班夫国家公园是全球最受欢迎的公园之一,[5]生态系统开始受到影响和破坏。1990年代中期,加拿大公园管理局启动了一个为期两年的研究项目,颁布了一系列的措施,试图控制游客数量,保护生态环境。
Der in der kanadischen Provinz Alberta gelegene Banff-Nationalpark (englisch Banff National Park of Canada, französisch Parc national du Canada Banff) wurde 1885 gegründet und war der erste Nationalpark Kanadas, der zweite in Nordamerika und weltweit der dritte ausgewiesene Park. Mit seinen 6641 km² Fläche gehört er zu den größeren Nationalparks in den kanadischen Rocky Mountains. Seinen Namen trägt der Park nach dem schottischen Banffshire, der Heimatregion zweier Geldgeber der Canadian Pacific Railway.
Der Nationalpark wurde 1984 von der UNESCO, zusammen mit dem Jasper-, dem Kootenay und dem Yoho-Nationalpark als Teil der Canadian Rocky Mountain Parks, zum Welterbe erklärt.[2][3] Bei dem Park handelt es sich um ein Schutzgebiet der IUCN-Kategorie II[4] (Nationalpark), welcher von Parks Canada, einer Crown Agency (Bundesbehörde), verwaltet wird. Drei Skigebiete, unter anderem das von Lake Louise, liegen dennoch innerhalb der Grenzen des Banff-Nationalparks.


 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 Art
Art
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB
 Sport
Sport
 Music
Music
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts
 Animal world
Animal world
 Companies
Companies