
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Geography
Geography


 Argentina
Argentina

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
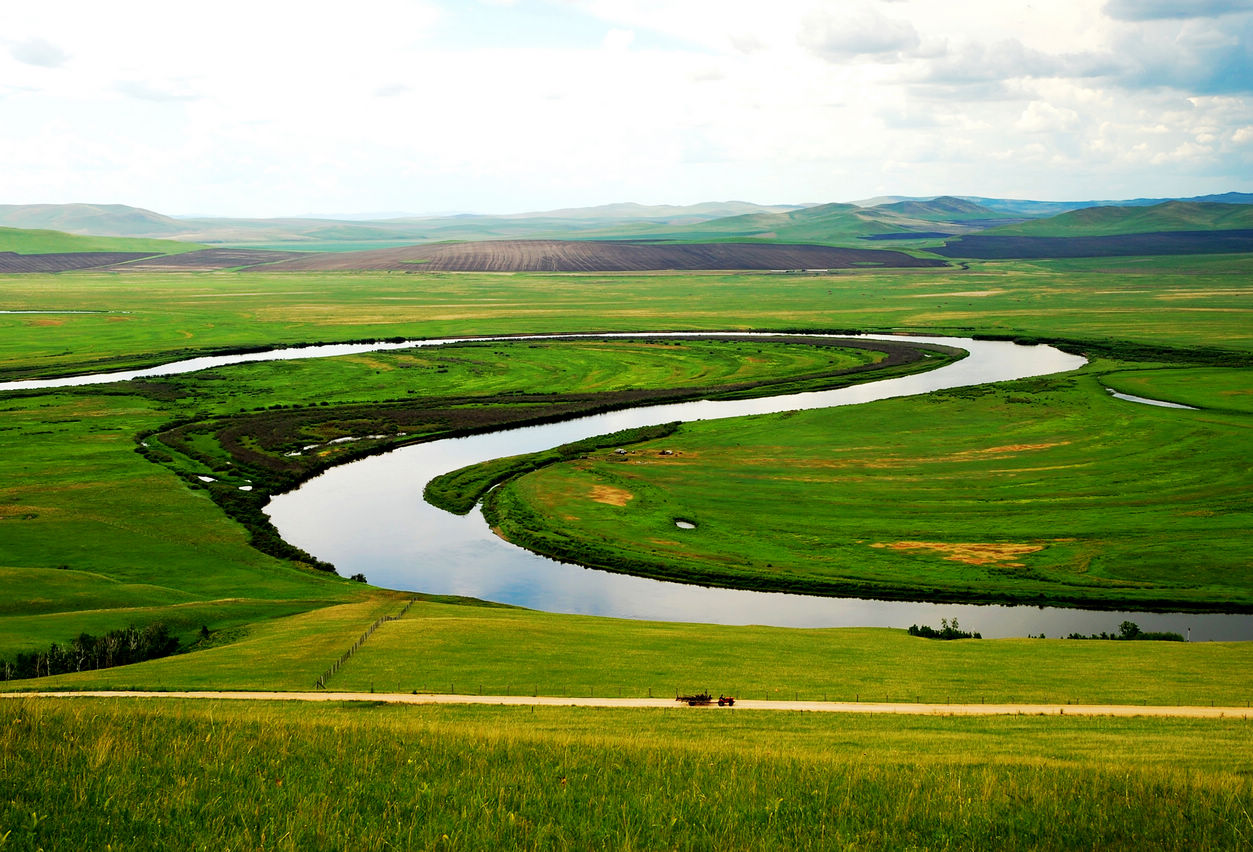



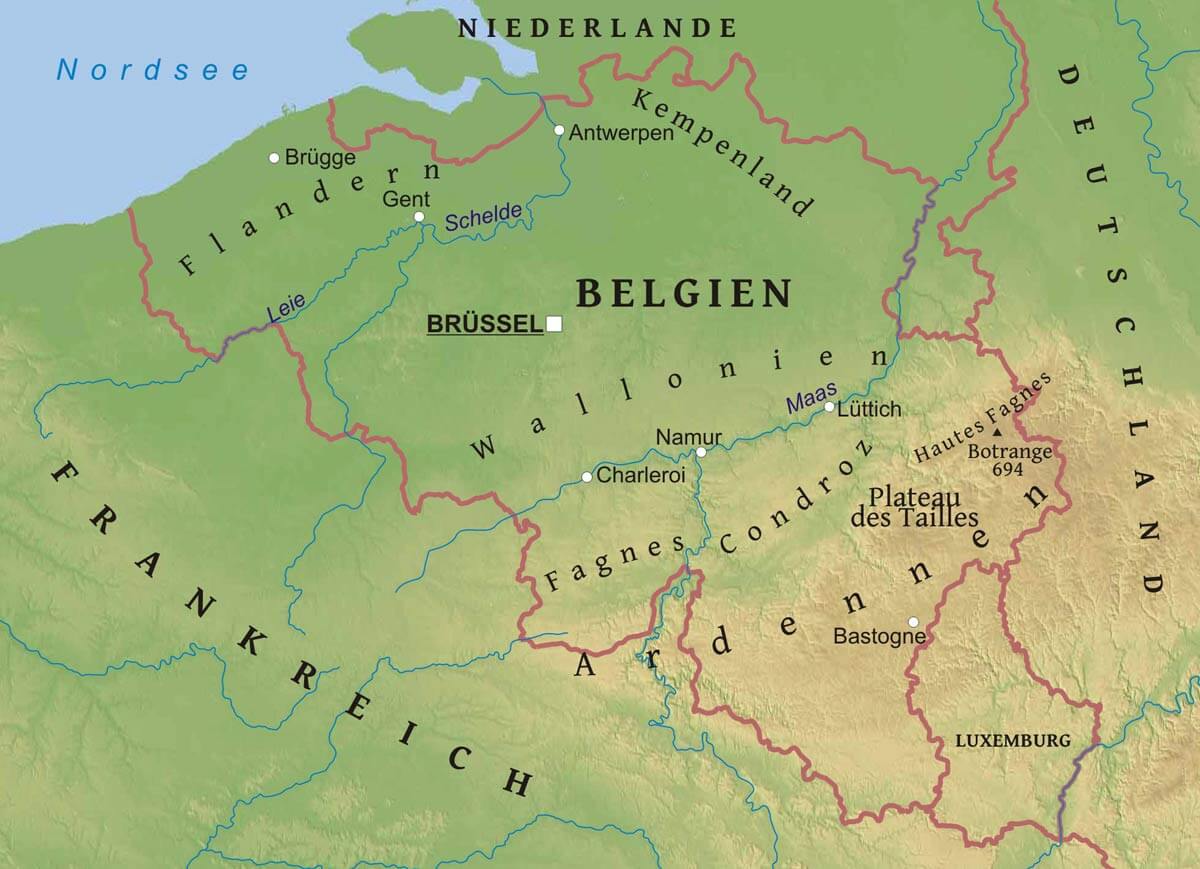
Der Argun bzw. Ergun (burjatisch für „breiter Fluss“; russisch Аргунь/Argun; chinesisch 額爾古納河 / 额尔古纳河, Pinyin E'erguna He) ist der etwa 1620 km lange rechte, d. h. südliche Quellfluss des Amur (Heilong Jiang) in Nordost-China (Asien).
额尔古纳河[a](蒙古语:ᠡᠷᠬᠥᠨᠠ
ᠭᠣᠣᠯ,西里尔字母:Эргүнэ гол;布里亚特语:Үргэнэ гол,罗马化:Ürgene gol),清代也作额尔古讷河(满语:ᡝᡵᡤᡠᠨᡝ
ᠪᡳᡵᠠ,穆麟德转写:ergune bira),俄罗斯称阿尔贡河(俄语:река́ Аргу́нь,罗马化:reká Argúnʹ),是位于中国内蒙古自治区呼伦贝尔盟和俄罗斯联邦外贝加尔边疆区之间的一条河流,自南偏西流向北偏东,蜿蜒在呼伦贝尔草原上。额尔古纳河和俄罗斯境内的石勒喀河交汇后形成黑龙江。
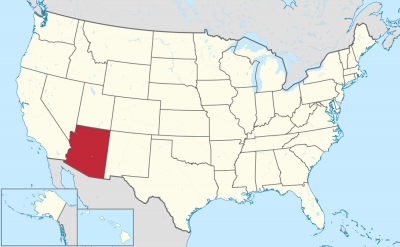


亚利桑那州(英语:Arizona,![]() i/ɛərᵻˈzoʊnə, ærᵻ-/)是美国一个位于西南部的州份,同时也是西部和山区州份之一。此州是美国第6大及人口第14大的州份。首府和最大城市是菲尼克斯。亚利桑那州也是四角落州之一,与新墨西哥州、犹他州、内华达州、加利福尼亚州与墨西哥接壤,以及其中一点与科罗拉多州西南角接触。亚利桑那州与墨西哥的边界长389英里(626千米),位于墨西哥索诺拉州和下加利福尼亚州边界北面。
i/ɛərᵻˈzoʊnə, ærᵻ-/)是美国一个位于西南部的州份,同时也是西部和山区州份之一。此州是美国第6大及人口第14大的州份。首府和最大城市是菲尼克斯。亚利桑那州也是四角落州之一,与新墨西哥州、犹他州、内华达州、加利福尼亚州与墨西哥接壤,以及其中一点与科罗拉多州西南角接触。亚利桑那州与墨西哥的边界长389英里(626千米),位于墨西哥索诺拉州和下加利福尼亚州边界北面。
亚利桑那州是第48个,也是美国本土最后加入的州份,1912年2月14日加入。历史上曾为新西班牙的上加利福尼亚省领土一部分,自1821年起成为独立的墨西哥一部分。1848年美墨战争落败后,墨西哥将此领土大部分割让予美国。此州最南的部分在1853年盖兹登购地购入。
亚利桑那州南部以其沙漠炎热的夏天和温暖的冬天闻名。亚利桑那州北部有松树林、花旗松及云杉树;科罗拉多高原;部分山脉(例如圣弗兰西斯科山脉);以及大而深的峡谷,有更多温和的夏季气温,冬天也有相当的降雪。该地区的弗拉格斯塔夫、阿尔派恩及图森还有滑雪场。除了大峡谷国家公园,还有若干国家森林、国家公园及国家纪念碑。
全州大约四分之一[7]是印第安保留地,作为27个联邦承认的美国原住民的驻在地,包括美国最大的保留地纳瓦霍族保留地,超过300,000人居住。虽然联邦法律在1924年赋予美国原住民投票权,亚利桑那州排除了保留地居民的投票权,直至1948年其州最高法院判处美国原住民原告胜诉[8][9]。
Arizona (amerik. Aussprache [æɹɪˈzoʊ̯nə]) ist ein Bundesstaat, der im Südwesten der Vereinigten Staaten liegt; die Abkürzung ist AZ. Arizona trägt den Beinamen Grand Canyon State. Seine Hauptstadt ist Phoenix.
Der Namensursprung ist unklar. Seit Anfang des 20. Jahrhunderts vertraten Historiker überwiegend die These, der Name stamme von der Bezeichnung alĭ ṣonak („kleine Quelle“) der O’odham-Sprache. Er bezeichnete ursprünglich ausschließlich eine Gegend um Planchas de Plata in der Nähe von Nogales (Sonora) in der heutigen Grenzregion zwischen Mexiko und den USA. Die Tohono O’Odham bezeichnen die Region noch heute mit diesem Namen, der ausgesprochen wie Arissona klingt.
Seit 1979 findet auch die These Unterstützung von Historikern, dass baskische Einwanderer die Benennung aritz ona (gute Eiche) aus ihrer Sprache vergeben hätten.[2]
Eine weitverbreitete volksetymologische Herleitung vom spanischen Wort für Aride Zone ist nicht haltbar, da aus der Bezeichnung zona árida der Name Zonarida folgen müsste.[3]
アリゾナ州(英: State of Arizona [ɛərᵻˈzoʊnə, ærᵻ-] (![]() 音声ファイル)、ナバホ語: hoozdo hahoodzo [xòːztò xɑ̀xòːtsò])は、アメリカ合衆国の南西部にある州である。地域区分としてはロッキー山脈西部およびアメリカ合衆国西部にも含められる。世界遺産のグランド・キャニオンを擁することで知られる。元来銅と綿花の生産がさかんで、1980年代に南部サンベルトの一角として発展したが、1990年代に入るまで、ハイテク産業の発展に追いつけなかった。今日ではハイテク産業の一大拠点となっており、カリフォルニア州からの企業流入が著しい。
音声ファイル)、ナバホ語: hoozdo hahoodzo [xòːztò xɑ̀xòːtsò])は、アメリカ合衆国の南西部にある州である。地域区分としてはロッキー山脈西部およびアメリカ合衆国西部にも含められる。世界遺産のグランド・キャニオンを擁することで知られる。元来銅と綿花の生産がさかんで、1980年代に南部サンベルトの一角として発展したが、1990年代に入るまで、ハイテク産業の発展に追いつけなかった。今日ではハイテク産業の一大拠点となっており、カリフォルニア州からの企業流入が著しい。
州都および最大都市はフェニックス市である。第2の都市はツーソンであり、その後に続くのはフェニックス都市圏に入っている8都市、すなわちメサ、グレンデール、チャンドラー、スコッツデール、ギルバート、テンピ、ピオリア、サプライズ、さらにユマ郡のユマである。
アメリカ合衆国の州になったのは1912年2月14日で、48番目の州であり、合衆国本土では最後の州だった。非常に暑い夏と温暖な冬の砂漠気候が特徴であるが、北部の松林や山岳部では低地の砂漠よりもかなり涼しい気候になる。
アリゾナ州はいわゆるフォー・コーナーズと呼ばれる4州の1つである。ニューメキシコ州、ユタ州、ネバダ州およびカリフォルニア州と境を接しており、コロラド州とは州北東部のフォーコーナーズの1点で接している。メキシコのソノラ州とバハ・カリフォルニア州とも国境で接しており、その総延長は389マイル (626 km) になる。人口規模はアメリカ合衆国の内陸州としては最大である。州内にはグランド・キャニオン国立公園がある他、多くの国立の森、公園、保護地域がある。領域の4分の1以上は連邦信託地となっており[1]、ナバホ族、ホピ族、トホノ・オーダム族とアパッチ族、さらにはヤヴァパイ族、クチャン族、フアラパイ族、ユマン部族といった、様々な先住民族が暮らす土地になっている。
Arizona (/ˌærɪˈzoʊnə/ (![]() listen); Navajo: Hoozdo Hahoodzo Navajo pronunciation: [xòːztò xɑ̀xòːtsò]; O'odham: Alĭ ṣonak Uto-Aztecan pronunciation: [ˡaɺi ˡʂonak]) is a state in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the Western and the Mountain states. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and New Mexico; its other neighboring states are Nevada and California to the west and the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California to the south and southwest.
listen); Navajo: Hoozdo Hahoodzo Navajo pronunciation: [xòːztò xɑ̀xòːtsò]; O'odham: Alĭ ṣonak Uto-Aztecan pronunciation: [ˡaɺi ˡʂonak]) is a state in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the Western and the Mountain states. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and New Mexico; its other neighboring states are Nevada and California to the west and the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California to the south and southwest.
Arizona is the 48th state and last of the contiguous states to be admitted to the Union, achieving statehood on February 14, 1912. Historically part of the territory of Alta California in New Spain, it became part of independent Mexico in 1821. After being defeated in the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded much of this territory to the United States in 1848. The southernmost portion of the state was acquired in 1853 through the Gadsden Purchase.
Southern Arizona is known for its desert climate, with very hot summers and mild winters. Northern Arizona features forests of pine, Douglas fir, and spruce trees; the Colorado Plateau; mountain ranges (such as the San Francisco Mountains); as well as large, deep canyons, with much more moderate summer temperatures and significant winter snowfalls. There are ski resorts in the areas of Flagstaff, Alpine, and Tucson. In addition to the internationally known Grand Canyon National Park, which is one of the world's seven natural wonders, there are several national forests, national parks, and national monuments.
About one-quarter of the state[7] is made up of Indian reservations that serve as the home of 27 federally recognized Native American tribes, including the Navajo Nation, the largest in the state and the United States, with more than 300,000 citizens. Although federal law gave all Native Americans the right to vote in 1924, Arizona excluded those living on reservations in the state from voting until the state Supreme Court ruled in favor of Native American plaintiffs in Trujillo v. Garley (1948).[8][9]
L'Arizona (/a.ʁi.zo.na/ ; en anglais : /ˌæɹɪˈzoʊnə/2 Écouter) est un État de l'Ouest des États-Unis. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Phoenix. Avec une superficie de 295 254 km2, il est le sixième État américain le plus vaste, et le seizième plus peuplé avec 6 392 017 habitants en 2010. Bordé par la Californie, le Nevada, l'Utah, le Nouveau-Mexique et les États mexicains de la Basse-Californie et du Sonora au sud, l'Arizona est l'un des quatre États des Four Corners. Il fait en outre partie de la Sun Belt (« ceinture du soleil ») qui connaît une forte croissance démographique en raison de l'héliotropisme. Situé au sud des Montagnes Rocheuses, l'Arizona est un des États des montagnes. Traversé par le fleuve Colorado, l'État comprend de spectaculaires formations géologiques, telles que le Grand Canyon, le Meteor Crater et Monument Valley.
Le territoire est sous souveraineté espagnole à partir du XVIe siècle, en tant que région de la Nouvelle-Espagne. Le Mexique en prend possession en 1821 lors de son indépendance : il devient une partie de la Haute-Californie. En 1848, à l'issue de la guerre américano-mexicaine, les États-Unis annexent l'Arizona, puis agrandissent son territoire en 1853 lors de l'achat Gadsden. Il adhère tardivement à l'Union, le 14 février 1912, et en devient le 48e État. Il est divisé en quinze comtés, et près du quart de son territoire est constitué par vingt-et-une réserves indiennes. Les Navajos et d'autres peuples Apaches y sont majoritaires.
L'État a connu une croissance démographique importante et soutenue au cours du XXe siècle : il ne comptait que 750 000 habitants en 1950 et a vu sa population multipliée par sept en soixante ans. La ville de Tucson, située à une centaine de kilomètres de la frontière mexicaine, a ainsi accueilli d'importants flux migratoires. En 2010, l'État de l'Arizona avait la quatrième plus forte proportion d'Hispaniques après le Nouveau-Mexique (46,30 %), le Texas (37,62 %) et la Californie (37,62 %) ainsi que le troisième plus grand nombre d'Amérindiens.
Une grande partie de l'État est constituée de paysages désertiques, dans lesquels furent tournés de nombreux westerns. L'Arizona est un État très touristique, comprenant trois parcs nationaux (le Grand Canyon, Saguaro et Petrified Forest) et plusieurs monuments nationaux américains (Sunset Crater Volcano, Rainbow Bridge, Montezuma Castle).
L'État est en outre un bastion du Parti républicain. La ville de Phoenix accueille également l'une des équipes de la NBA, les Suns de Phoenix. Par ailleurs, la peine de mort y est en vigueur.
L'Arizona (/ariʣˈʣɔna/, in inglese , [ærɪˈzoʊnə]) è uno Stato federato del sud-ovest degli Stati Uniti d'America (il 48° a essere ammesso nell'Unione) che fa parte della Regione delle Montagne Rocciose. È anche parte degli Stati Uniti d'America sud-occidentali. Confina a ovest con la California e il Nevada, a nord con lo Utah e, in un solo punto, con il Colorado, a est con il Nuovo Messico e a sud con il Messico. Il confine dell'Arizona con il Messico è di 389 miglia (626 km) di lunghezza, sul confine settentrionale degli stati messicani di Sonora e Baja California. È il sesto più grande e il 16° più popoloso dei cinquanta stati. La sua capitale e città più grande è Phoenix. Altre città importanti sono Tucson, Flagstaff, Yuma e Mesa.
Lo Stato dell'Arizona è stato il 48º e ultimo degli stati contigui a essere ammesso all'Unione, ottenendo statualità il 14 febbraio 1912 (dopo l'Arizona sono entrati a fare parte degli USA solo Alaska e Hawaii i cui territori però non sono direttamente collegati al resto degli Stati Uniti). In precedenza faceva parte del territorio dell'Alta California in Nuova Spagna, prima di diventare indipendente dal Messico e in seguito ceduto agli Stati Uniti d'America dopo la guerra messicano-statunitense. La porzione meridionale dello Stato è stata acquisita nel 1853 attraverso l'Acquisto Gadsden.
Il soprannome dell'Arizona è Grand Canyon State (usato anche nelle targhe automobilistiche, in onore del Grand Canyon), ma sono abbastanza diffusi anche Baby State (in quanto è il più giovane stato degli USA continentali) e Sweetheart State (in relazione alla sua entrata negli USA il giorno di San Valentino)[4].
L'animale scelto come simbolo dell'Arizona è il gatto dalla coda anellata (chiamato anche bassarisco del Nordamerica), un mammifero simile al procione.
L'Arizona è noto per il clima desertico della sua metà meridionale, con estati molto calde e inverni abbastanza miti. Oltre al Grand Canyon National Park, ci sono diversi foreste, parchi e monumenti nazionali. Circa un quarto dello Stato è costituito da riserve indiane che costituiscono il territorio di residenza di un certo numero di tribù di nativi americani. Tra i suoi luoghi più famosi vi sono il Grand Canyon, la Monument Valley, il Meteor Crater, l'Horseshoe Bend e il Deserto di Sonora.
Arizona es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C. forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Phoenix. Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas. Limita al norte con Utah, al noreste con Colorado, al este con Nuevo México, al sur con Sonora (México), y al oeste con el río Colorado que lo separa de California y Nevada. Con 295 000 km² es el sexto estado más extenso, por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California, Montana y Nuevo México. Fue el tercero más tardío en ser admitido en la Unión, el 14 de febrero de 1912, como el estado número 48, por delante de Alaska y Hawái, el más tardío.
Se encuentra asentado en Aridoamérica y sobre la Sierra Madre Occidental, y por su territorio discurre el río Colorado que forma el famoso Gran Cañón del Colorado, al norte del estado. También son famosos su paisaje desértico y sus cactus.
Gran parte de Arizona tiene un clima árido o semiárido. Estas regiones reciben menos de 40 centímetros de lluvia al año, siendo muy calurosas en verano y suaves en invierno. No obstante, las regiones montañosas de mayor altitud poseen un clima más húmedo y frío. La mayoría del estado está escasamente habitado: la mayor parte de la población de Arizona se concentra en dos centros urbanos: Phoenix, la ciudad con mayor crecimiento de Estados Unidos, la mayor ciudad y capital del estado, y Tucson.
El apodo de Arizona es «el estado del Gran Cañón», pues el norte del estado alberga una de las atracciones turísticas naturales más conocidas de Estados Unidos y del mundo, el Gran Cañón. Otro apodo de Arizona es «el estado del Cobre», que se debe a que posee grandes yacimientos de cobre, e incluso ya fue el mayor productor nacional de este mineral. Hasta nuestros días, la minería del cobre es una importante fuente de ingresos de Arizona.4
Miles de años antes de la llegada de los primeros europeos, pueblos indígenas vivían en la región donde actualmente se localiza Arizona. Hoy aún existe una población importante: se estima que unos 280 000 indígenas viven en Arizona,5 repartidos por las numerosas reservas indias del estado.
En un principio, Arizona fue colonizada por España, pasando a control mexicano en 1821, cuando México se independizó de España. En 1848, con el fin de la intervención estadounidense en México, la mayor parte de Arizona (al norte del río Gila) pasó a manos estadounidenses. El presidente Santa Anna de México vendió lo que se convertiría en la parte sur del Estado en la Venta de La Mesilla en 1853. El 14 de febrero de 1912, Arizona se convirtió en el último territorio estadounidense dentro de los 48 estados contiguos (es decir, sin contar a Alaska y Hawái, los cuales no limitan con ningún otro estado) en adquirir el estatuto de estado.6
En la actualidad Arizona se encuentra en el centro de la polémica desde que en mayo de 2010 aprobó la Arizona SB1070,5, la más amplia y estricta ley contra la inmigración ilegal de las últimas décadas. Esta ley ha recibido la atención nacional e internacional y ha provocado una controversia considerable. Importantes representantes del propio Gobierno de los Estados Unidos de América la han calificado como "una violación de los derechos civiles", "un tipo de apartheid" y han afirmado que "su aplicación puede forzar a la diferenciación basada en razones étnicas".7
Аризо́на[2][3] (англ. Arizona, МФА: [ɛrɪˈzoʊnə]; [ærɪˈzoʊnə] ![]() слушать) — 48-й штат[4], вошедший в состав США. Расположен на юго-западе страны. Наряду с Ютой, Колорадо и Нью-Мексико входит в число «штатов четырёх углов». Столица и крупнейший город штата — Финикс (Phoenix). По оценкам на июль 2014 года, население штата составляло 6 731 484[1] человека — по этому показателю Аризона занимает 15-е место в США. Для климата Аризоны характерны мягкие зимы и высокая температура в летнее время года.
слушать) — 48-й штат[4], вошедший в состав США. Расположен на юго-западе страны. Наряду с Ютой, Колорадо и Нью-Мексико входит в число «штатов четырёх углов». Столица и крупнейший город штата — Финикс (Phoenix). По оценкам на июль 2014 года, население штата составляло 6 731 484[1] человека — по этому показателю Аризона занимает 15-е место в США. Для климата Аризоны характерны мягкие зимы и высокая температура в летнее время года.
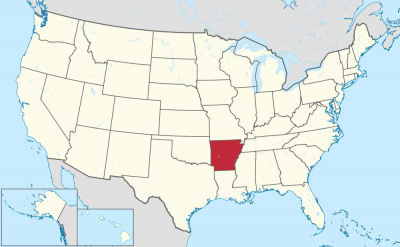


阿肯色州(英语:State of Arkansas /ˈɑːrkənsɔː/),是美国南部的一个州份,位处密西西比河中下游,北接密苏里州,西界俄克拉荷马州,南邻路易斯安那州,西南与得克萨斯州接壤,东隔密西西比河与田纳西州和密西西比州相望。其面积137,539平方公里,在五十个州内列第29位。2017年人口超过3百万,人口排名33。其首府是小石城。
アーカンソー州(英: State of Arkansas [ˈɑrkənsɔː] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国南部[1]の州である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第29位、人口では第32位である。州の北はミズーリ州に接し、東はテネシー州とミシシッピ州に、西はオクラホマ州とテキサス州に、南はルイジアナ州に接している。略称Ark.,AR。州都かつ人口最大の都市は、州中央部に位置するリトルロック市である。前身のアーカンソー準州から1836年6月15日に合衆国25番目の州に昇格した[2]。
地形的にはアメリカ内陸高原を構成するオザーク高原やワシタ山地(Ouachita Mountains)のある山岳地から、東部のミシシッピ川やアーカンソー・デルタのある低地まで多様である。
Arkansas (/ˈɑːrkənsɔː/)[c] is a state in the south central region of the United States, home to more than three million people as of 2018.[7][8] Its name is from the Osage language, of Siouan derivation; it denoted their related kin, the Quapaw people.[9] The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and the Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta.
Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 33rd most populous of the 50 United States. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, located in the central portion of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, such as the Fayetteville–Springdale–Rogers Metropolitan Area and Fort Smith metropolitan area, is a population, education, and economic center. The largest city in the state's eastern part is Jonesboro. The largest city in the state's southeastern part is Pine Bluff.
The Territory of Arkansas was admitted to the Union as the 25th state on June 15, 1836.[10] Much of the Delta had been developed for cotton plantations, and the state landowners there largely depended on enslaved African Americans as workers. In 1861, Arkansas seceded from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America during the Civil War.
On returning to the Union in 1868, the state continued to suffer due to its reliance on the large-scale plantation economy. Cotton continued as the leading commodity crop, although the cotton market declined. Because farmers and businessmen did not diversify and there was little industrial investment, the state fell behind in terms of its economy and opportunities for residents.
White rural interests dominated the state's politics by disenfranchisement of African Americans and by refusal to reapportion the legislature. It was not until after the civil rights movement and federal intervention that more African Americans were able to vote. The Supreme Court overturned rural domination in the South and other states that had refused to reapportion their state legislatures, or retained rules based on geographic districts. In the landmark ruling of one man, one vote, it ruled that states had to organize both houses of their legislatures by districts that held approximately equal populations, and that these had to be redefined as necessary after each decade's census.
Following World War II, Arkansas began to diversify its economy. In the 21st century, its economy is based on service industries, aircraft, poultry, steel, and tourism; along with important commodity crops of cotton, soybeans and rice.
The culture of Arkansas is observable in museums, theaters, novels, television shows, restaurants, and athletic venues across the state. Notable people from the state include politician and educational advocate William Fulbright; former president Bill Clinton, who also served as the 40th and 42nd governor of Arkansas; general Wesley Clark, former NATO Supreme Allied Commander; Walmart founder and magnate Sam Walton;[11] singer-songwriters Johnny Cash, Charlie Rich, Jimmy Driftwood, and Glen Campbell; actor-filmmaker Billy Bob Thornton; poet C. D. Wright; and physicist William L. McMillan, who was a pioneer in superconductor research.
L'Arkansas (prononcé : /aʁ.kɑ̃(n).sa(s)/3), les Arkansas (/aʁ.kɑ̃.sa/3), ou simplement les Arcs (/ɑɹk/4), (prononcé en anglais : /ˈɑɹkənsɔ/5), est un État du Sud des États-Unis. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Little Rock, située au centre du territoire. Avec une population de 2 915 918 habitants en 2010, estimée à 3 017 804 habitants en 2019, sur une superficie de 137 732 km2, l'État est le 32e plus peuplé et le 29e plus vaste du pays. L'Arkansas est entouré par six États : l'Oklahoma à l'ouest, le Missouri au nord, le Tennessee et le Mississippi à l'est, le Texas au sud-ouest et la Louisiane au sud. Il est divisé en 75 comtés. Surnommé The Natural State (« l'État naturel »), il présente des paysages variés : des chaînes montagneuses telles que les Monts Ozarks ou les Montagnes Ouachita ; au sud, des forêts denses nommées Timberlands de l'Arkansas (en) ; à l'est, les plaines du Mississippi et du delta de l'Arkansas (en).
Le nom de l'État provient du nom de la langue Sioux et désigne les Indiens Quapaw. Il forme un territoire dès 1819 et est admis dans l'Union le 15 juin 1836, dont il devient le 25e État. Esclavagiste, il repose sur l'économie de plantation (coton, riz) et se joint aux États confédérés durant la Guerre de Sécession (1861-1865). Après avoir réintégré l'Union, l'Arkansas connaît une crise due à l'effondrement des structures économiques et sociales antérieures. Les intérêts des Blancs ruraux dominent la vie politique locale jusqu'au Mouvement des droits civiques, au milieu du XXe siècle. L'État demeure ségrégationniste jusqu'à la fin des années 1960. Il est aujourd'hui un territoire populaire, conservateur, dont l'ancrage républicain se confirme depuis les années 2000. Néanmoins, l'État demeure de tradition démocrate au niveau local et beaucoup d'électeurs se considèrent toujours Dixiecrats. La tradition conservatrice de cet État s'illustre par l'application de la peine de mort par injection létale et l'interdiction du mariage homosexuel à la suite d'un référendum.
L'Arkansas demeure un État à dominante agricole. En plus des plantations traditionnelles, il produit du soja, et tend à se spécialiser dans l'arboriculture et l'élevage de poulets. Les ressources en hydrocarbures ont également permis une industrialisation durant l'après-guerre, avec la création de papeteries, de scieries, d'usines métallurgiques (aluminium) et textiles. Durant les dernières décennies, l'Arkansas voit son économie se diversifier dans les services, accueillant des sièges sociaux de grandes entreprises (Walmart, Tyson Foods), ainsi que des aciéries et des constructeurs aéronautiques. En outre, des personnalités comme le sénateur J. William Fulbright, le chanteur de country Johnny Cash ou l'ancien président Bill Clinton en sont originaires.
L'Arkansas (pronuncia italianizzata, AFI: /arˈkansas/[2]; in inglese , /ˈɑrkənsɔː/) è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, la cui capitale è Little Rock. Confina a nord con il Missouri, a est con il Tennessee e il Mississippi, a sud con la Louisiana e il Texas, e ad ovest con l'Oklahoma.
Il nome dello Stato deriva dalla parola Akansa (termine utilizzato dai nativi Algonchini per indicare i nativi Quapaw), modificata nella pronuncia attuale dai francesi del XVII secolo.[3]
Arkansas es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Little Rock.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Centro Suroeste. Limita al norte con Misuri al este con el río Mississippi que lo separa de Tennessee y Mississippi, al sur con Louisiana, al suroeste con Texas y al oeste con Oklahoma. Fue admitido en la Unión el 15 de junio de 1836, como el estado número 25.
Aparte de la frontera este que forma el río Misisipi, por su territorio discurre en dirección este el río Arkansas. El nombre del estado deriva de la palabra kansas (el término con que los indios algonquinos designaban a los indios quapaw), tal como la pronunciaban los franceses en el siglo XVII.3 La geografía diversa del estado parte de las regiones montañosas del Ozark y las montañas de Ouachita, que componen las tierras altas del interior de los EE. UU., a la tierra densamente boscosa en el sur conocida como el Arkansas Timberlands, hasta las tierras bajas del este a lo largo del río Misssissippi y el delta de Arkansas. Conocido como «el estado natural», las diversas regiones de Arkansas ofrecen a los residentes y turistas una variedad de oportunidades de recreación al aire libre.
Арканза́с[1][2] (также Арка́нзас[3]; англ. Arkansas, [ˈɑːrkənsɔː] ![]() слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
слушать[4]) — штат[5] на юге США, относится к группе штатов Юго-Западного Центра. Население 2 937 979 человек (32-е место среди штатов США; данные 2011 г.). Столица и крупнейший город — Литл-Рок[6].
Официальное прозвище — «Естественный штат» (англ. Natural State).
Слово «арканзас» является алгонкинским экзонимом сиуского племени куапо.



英吉利海峡,又名拉芒什海峡(英语:English Channel;法语:la Manche;布列塔尼语:Mor Breizh;威尔士语:Môr Udd、康瓦尔语:Mor Bretannek),是分隔英国与欧洲大陆的法国、并连接大西洋与北海的海峡。海峡长560公里(350英里),宽240公里(150英里),最狭窄处又称多佛尔海峡,仅宽34公里(21英里)。英国的多佛尔与法国的加莱在此处隔海相望。
Der Ärmelkanal (englisch English Channel, wörtlich ‚Englischer Kanal‘; französisch La Manche, wörtlich‚ Der Ärmel‘) ist ein Meeresarm des Atlantiks und verbindet diesen über die Straße von Dover mit der Nordsee.
Der Ärmelkanal liegt zwischen Großbritannien im Norden und Frankreich im Süden. Nach der Definition der International Hydrographic Organization wird die Ostgrenze zur Nordsee durch eine Linie gebildet, die etwa zehn Kilometer östlich der Line Dover-Calais zwei historische Landmarken[1] verbindet. Die Westgrenze wird durch die Linie von Land’s End zum Leuchtturm der Île Vierge gebildet.
Im Kanal liegen die britischen Kanalinseln und die Isle of Wight, die von einem Seitenarm, dem Solent, umschlossen wird. Der größte Fluss, der in den Kanal mündet, ist die Seine. Bekannte Städte am Kanal sind Southampton und Plymouth (beide Großbritannien) und Le Havre (Frankreich).
Der Ärmelkanal ist maximal 248 km breit. Die schmalste Stelle ist die Straße von Dover (frz. Pas de Calais) im Osten – die Strecke von Dover nach Cap Gris-Nez misst nur 34 km. Der Kanal hat in der Nähe des offenen Atlantiks eine durchschnittliche Tiefe von 120 m; an der östlichen Einmündung in die Nordsee sind es seichtere 45 m.

Das Armenische Hochland (armenisch Հայկական լեռնաշխարհ oder Բարձր Հայք / Bardsr Hajk[1]), im Deutschen auch Armenisches Gebirge[2] oder Ararathochland genannt, bildet den zentralen Teil des nordanatolisch-nordiranischen Kettengebirges und umfasst im breiten Sinne auch den Kleinkaukasus.[3]
Je nach Definition ist das Armenische Hochland 300.000 bis 400.000 Quadratkilometer groß[4] und umfasst Gebiete der Türkei (vor allem die ehemaligen armenischen Provinzen des Osmanischen Reiches), des Iran, Georgiens, Aserbaidschans und fast vollständig die heutige Republik Armenien.
Viele Gebirge im Armenischen Hochland stellen eine Aneinanderreihung von Vulkanen dar. Zu diesen zählen das Dschawacheti-Gebirge, das Arsiani-Gebirge (Yalnızçam Dağları), das Geghamgebirge und der Haykakan Par (Ağri Dağları).[3] Die höchste Erhebung ist der 5137 m hohe Ararat, ein erloschener Vulkan. Große Seen sind der Vansee (Salzsee) und der Sewansee (Süßwassersee).
亚美尼亚高原(Armenian Highlands,亚美尼亚语:Հայկական լեռնաշխարհ,罗马化:Haykakan leṙnašxarh,英文名称另有Armenian Upland, Armenian plateau,或是Armenian tableland,[1])是组成西亚北部的三个高原中,位居中央,高度最高的一座。[1]亚美尼亚高原从西方,顺着时钟方向,受安纳托利亚高原、高加索、库拉-阿拉斯低地、伊朗高原、美索不达米亚所包围。亚美尼亚高原受到亚拉拉特平原(其中有亚拉拉特山)所分隔,而分成东西两个区域。所谓西亚美尼亚就是今日所称的东部安那托利亚地区,而所谓的东亚美尼亚即为今日的小高加索山脉,也称Caucasus Minor,或是古代所称的Anti-Caucasus,[2][3]即“在高加索对面”的意思。
 Grand Est
Grand Est
 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ
 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR
 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS
 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment