
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
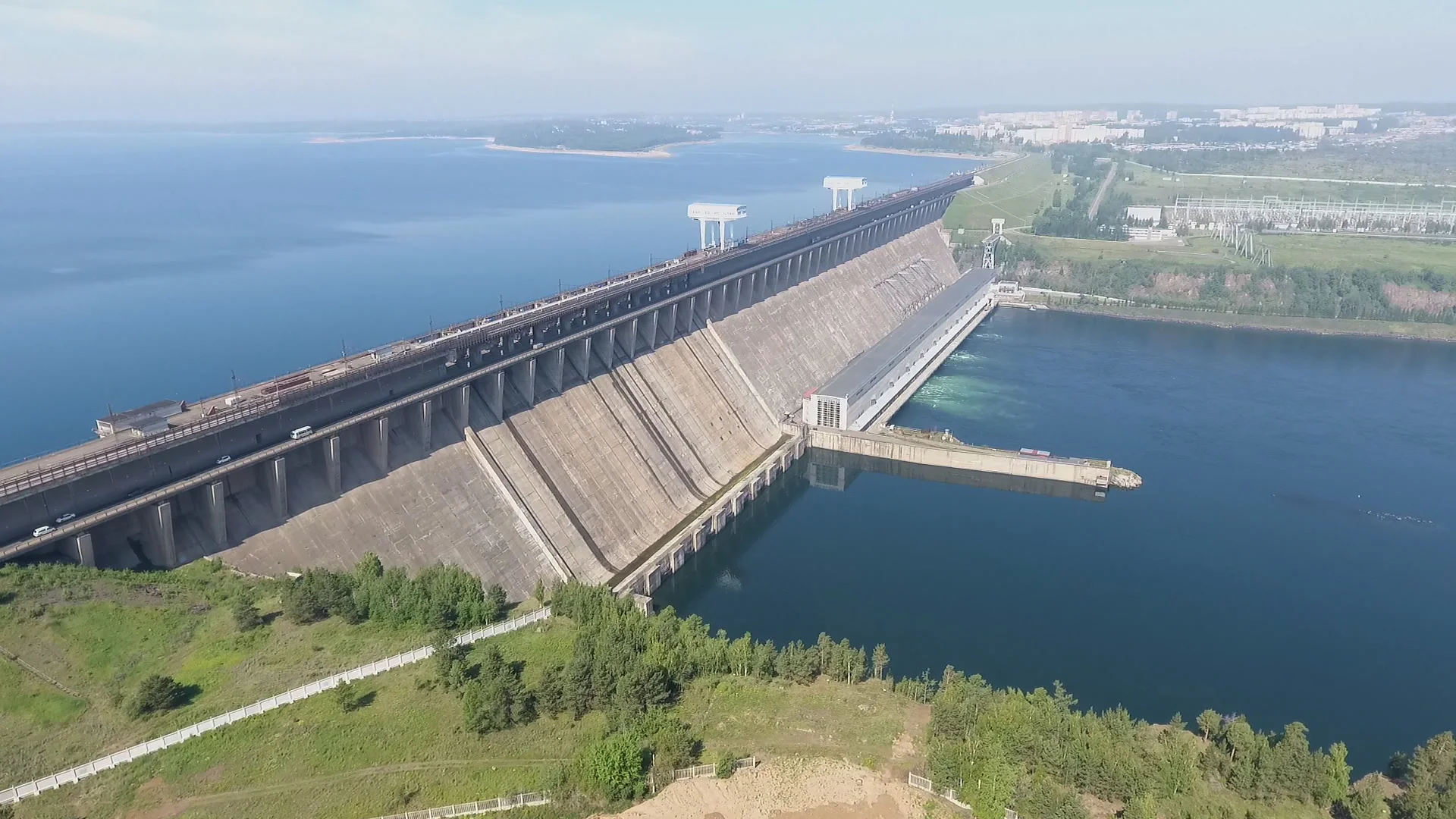
 Hydroelectric power plants
Hydroelectric power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Hydropower
Hydropower
 Russia
Russia




 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
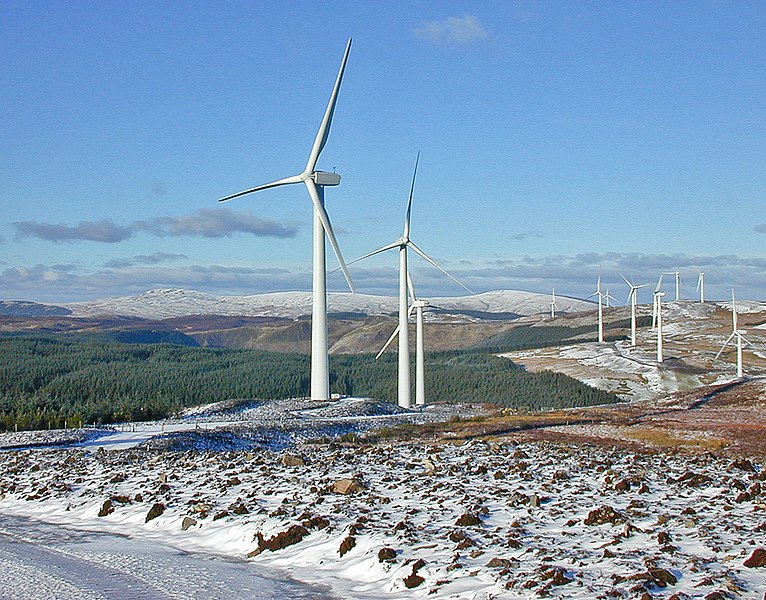
 Onshore and offshore wind farms
Onshore and offshore wind farms

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Windenergie
Windenergie
 Wales
Wales


 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Solar power plants
Solar power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Solar energy
Solar energy

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV


 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Solar power plants
Solar power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Solar energy
Solar energy

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV



 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Solar power plants
Solar power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
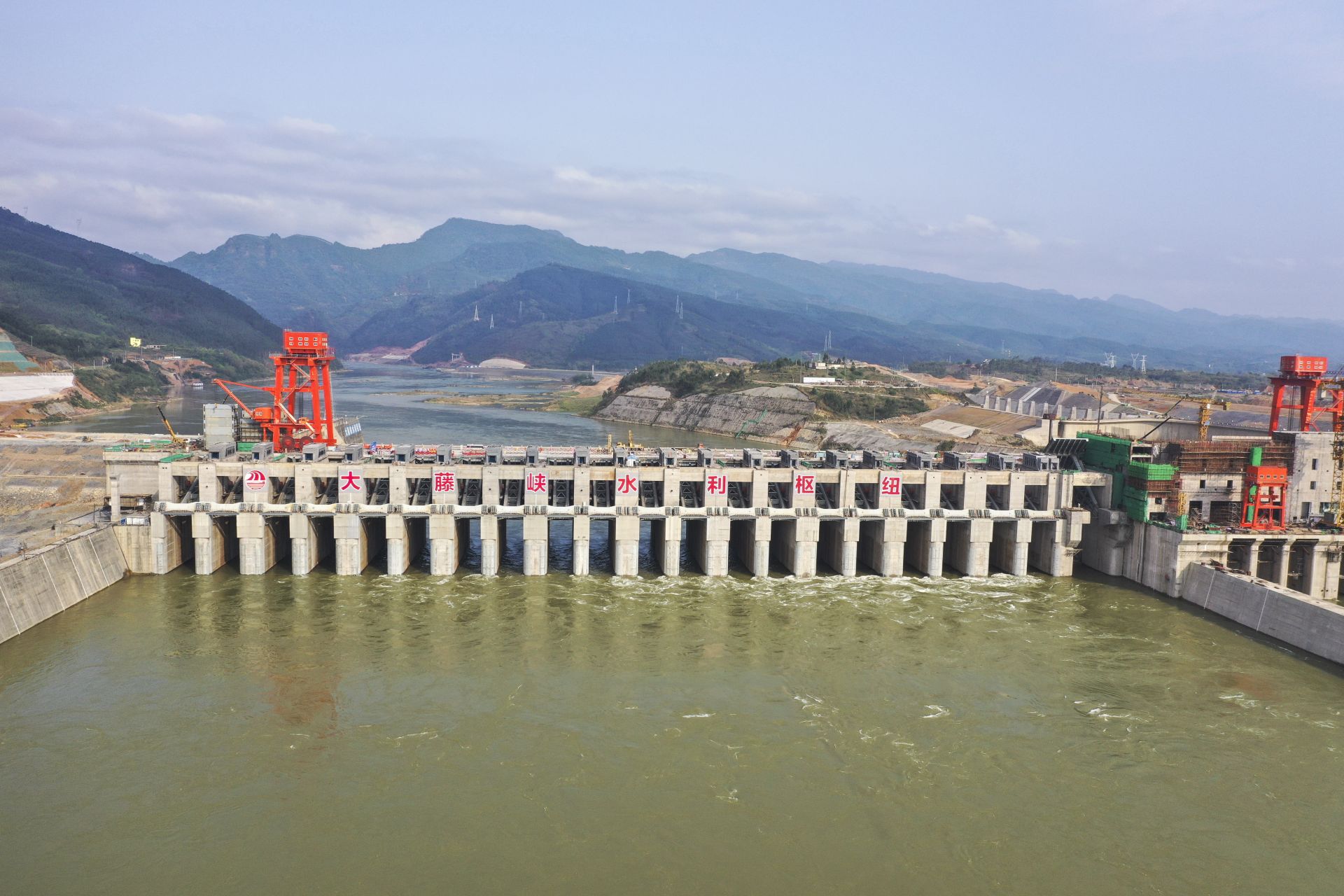
 Solar energy
Solar energy
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX

 *Changjiang|Yangtze River
*Changjiang|Yangtze River

 Architecture
Architecture
 China
China

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Hydroelectric power plants
Hydroelectric power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Hydropower
Hydropower
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
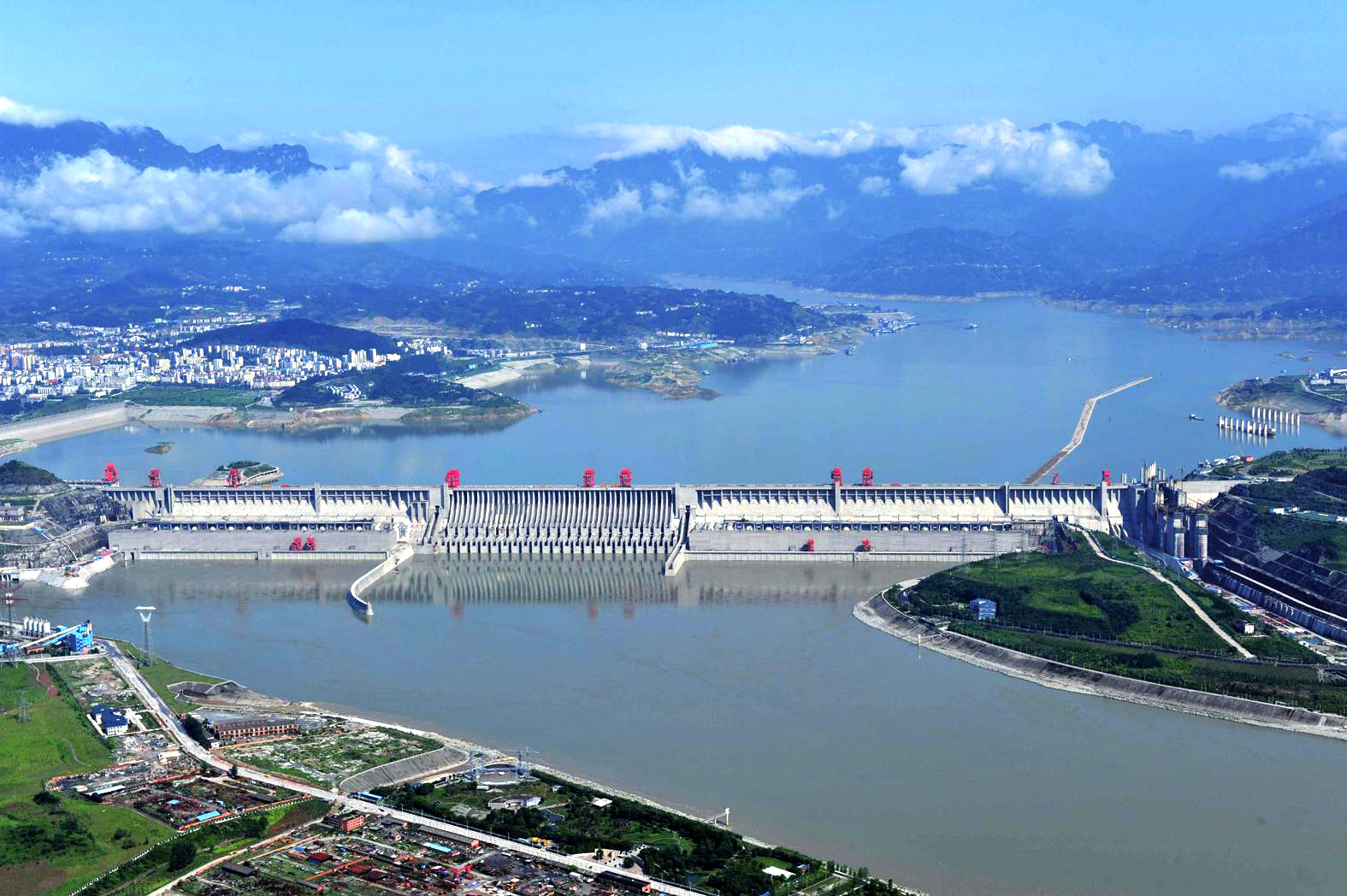

长江三峡水利枢纽工程,常简称三峡工程或三峡大坝,是中华人民共和国长江上游段建设的大型水利工程项目。分布在重庆市到湖北省宜昌市的长江干流上,大坝位于三峡西陵峡内的宜昌市夷陵区三斗坪,并和其下游不远的葛洲坝水电站形成梯级调度电站。它是世界上规模最大的水电站,是中国有史以来建设的最大的水坝[2]。
三峡水电站的机组布置在大坝的后侧,共安装32台70万千瓦(700MW)水轮发电机组,其中左岸14台、右岸12台、右岸地下6台,另外还有2台5万千瓦的电源机组,总装机容量2,250万千瓦,年发电量约1,000亿千瓦·时,相当于计热电发电效率后燃烧标煤0.319亿吨的发电量,年直接减排二氧化碳0.858亿吨。而它在发电、防洪及航运方面带来巨大利益的同时,附带引起的移民、环境等问题,使它从开始筹建的那一刻起便始终与繁杂的各种争议相伴[3][4]。
三峡ダム(さんきょうダム)は、中国・長江中流域の湖北省宜昌市三斗坪にある大型重力式コンクリートダムである。
1993年に着工、2009年に完成した。洪水抑制・電力供給・水運改善を主目的としている。三峡ダム水力発電所は、2,250万kWの発電が可能な世界最大の水力発電ダムである[2][3]。 ダムは長江三峡のうち最も下流にある西陵峡の半ば(湖北省宜昌市夷陵区三斗坪鎮)に建設された。貯水池は宜昌市街の上流の三斗坪鎮に始まり、重慶市街の下流にいたる約660 kmに渡り、下流域の洪水を抑制するとともに、長江の水運に大きな利便性をもたらす。このダムの建設によって、それまで重慶市中心部には排水量3,000 t級の船しか遡上できなかったのが、10,000 t級の大型船舶まで航行できるようになった[4]。加えて、水力発電所は中国の年間消費エネルギーの1割弱の発電能力を有し、電力不足の中国において重要な電力供給源となる。また、火力発電と比べ発電時のCO2発生も抑制することができる。しかし、その一方で建設過程における住民110万人の強制移住、三峡各地に残る名所旧跡の水没、更には水質汚染や生態系への悪影響等、ダム建設に伴う問題も指摘されている。
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downstream of the Three Gorges. The Three Gorges Dam has been the world's largest power station in terms of installed capacity (22,500 MW) since 2012.[5][6] In 2018, the dam generated 101.6 terawatt-hours (TWh), breaking its previous record,[7] but was still slightly lower than the Itaipú Dam, which had set the world record in 2016 after producing 103.1 TWh.[8]
The dam body was completed in 2006. The power plant of the dam project was completed and fully functional as of July 4, 2012,[9][10] when the last of the main water turbines in the underground plant began production. Each main water turbine has a capacity of 700 MW.[11][12] Coupling the dam's 32 main turbines with two smaller generators (50 MW each) to power the plant itself, the total electric generating capacity of the dam is 22,500 MW.[11][13][14] The last major component of the project, the ship lift, was completed in December 2015.[15]
As well as producing electricity, the dam is intended to increase the Yangtze River's shipping capacity. By providing flood storage space, the dam reduces the potential for floods downstream which could possibly affect millions. China regards the project as a monumental social and economical success,[16] with the design of state-of-the-art large turbines,[17] and a move toward limiting greenhouse gas emissions.[18] However, the dam flooded archaeological and cultural sites, displaced some 1.3 million people, and had caused significant ecological changes including an increased risk of landslides.[19][20] Because of that the dam has been controversial both domestically and abroad.[21][22][23][24]
Le barrage des Trois-Gorges (chinois simplifié : 三峡大坝 ; chinois traditionnel : 三峽大壩 ; pinyin : ) est un barrage sur le Yangzi Jiang, situé dans la province du Hubei, au centre de la Chine. Il a été mis en service par étapes de 2003 à 2012 et a créé une retenue de 600 kilomètres de longueur.
Il s'agit de la plus grande centrale hydroélectrique au monde1.
La diga delle Tre Gole, denominata anche progetto Tre Gole, è una diga per la produzione di energia elettrica costruita sul Fiume Azzurro, nella provincia di Hubei in Cina, nonché la seconda diga più grande al mondo dopo la Diga di Itaipú. È una centrale idroelettrica a bacino di accumulo e per far arrivare l'acqua alle turbine sfrutta la pressione dell'acqua dell'intero bacino: con 2309 metri di larghezza, detiene i record mondiali per la diga più grande e per la centrale idroelettrica più potente, capace di soddisfare il 3% dell'enorme fabbisogno energetico del paese.
Completata il 20 maggio 2006, la diga fa parte di un più vasto complesso ad essa annesso, che è stato interamente ultimato nel giugno del 2009. Il progetto è stato fin dal principio contestato dalle associazioni ambientaliste per l'elevato impatto ambientale e per l'elevato numero di persone sfollate. La realizzazione dell'opera sarebbe stata necessaria per il contenimento del rischio di inondazioni nella parte meridionale del paese, per rendere navigabile l'alto corso del fiume Yangtze e per produrre energia elettrica. Con la sua potenza di 22,5 gigawatt (GW) e 98,8 terawatt (TWh) generati ogni anno, è l'impianto energetico più potente al mondo.[2]
La presa de las Tres Gargantas (Chino: 长江三峡水利枢纽工程) es una planta hidroeléctrica situada en el curso del río Yangtsé en China. Es la planta hidroeléctrica más grande del mundo en extensión y en capacidad instalada. El proyecto en su conjunto, que incluye la presa propiamente dicha, las centrales eléctricas, el transporte, los desvíos y la construcción de otros edificios relacionados, totaliza 27,47 millones de m³, según las cifras oficiales de 2012. La obra ha costado más que cualquier otro proyecto de construcción en la historia, con estimaciones no oficiales de hasta US$75 mil millones.1
A su máxima capacidad, la presa retiene el agua a 91 metros sobre el nivel del río. Ello equivale a un peso aproximado de 42 millardos de toneladas concentradas en una extensión lo suficientemente reducida como para alterar el curso terrestre como si de un terremoto se tratara. Como resultado, según expertos de la NASA, la Tierra ha alterado su rumbo 2 centímetros desde su eje.2
La presa, ya sugerida por el máximo dirigente del Partido Comunista de China Mao Zedong en los años 1950, comenzó a construirse en 1993 para responder a la creciente demanda energética del delta del Yangtsé, y también para intentar reducir las inundaciones y crecidas del río. En 2016, China dio por finalizadas las obras de la presa con la puesta en marcha del último detalle de la obra, un ascensor para que los barcos puedan superar el dique.3
Los opositores del proyecto han criticado el desplazamiento de cerca de 1,28 millones de personas para su construcción, además del negativo impacto ambiental y la pérdida del patrimonio cultural que ha quedado sumergido bajo las aguas.4
Три ущелья (кит. трад. 三峽, упр. 三峡, пиньинь Sānxiá, палл. Санься) — гравитационная плотинная гидроэлектростанция, расположенная на реке Янцзы в провинции Хубэй, Китай. Является крупнейшей в мире электростанцией по установленной мощности в 22,5 ГВт[прим. 1]. За 2014 год ГЭС «Три ущелья» произвела рекордные для мира 98,8 млрд кВт⋅ч[прим. 2][4].
По состоянию на 2018 год, «Три ущелья» является крупнейшим по массе сооружением мира. Его бетонная плотина, в отличие от «Итайпу», является сплошной и весит более 65,5 млн т[прим. 3][5]. По совокупной стоимости работ «Три ущелья» оценивается в 203 млрд ¥, или около 30,5 млрд $, и в рамках проекта поворота китайских рек является пятым по стоимости инвестиционным проектом в мире[6]. Образованное плотиной водохранилище содержит 39,3 км³ воды и является 27-м по объему в мире. Для его заполнения с прибрежных районов было переселено 1,3 млн человек, что стало самым масштабным переселением в истории для возведения искусственных сооружений. Затраты на переселение людей составили около трети всего бюджета на строительство[1].
Помимо выработки экологичной электроэнергии (и, как следствие, снижения выброса парниковых газов от ТЭС), плотина защищает нижележащие по течению города от губительных паводков Янцзы. Увеличение глубины реки вверх по течению улучшило также условия судоходства; оборудованный пятью шлюзами гидроузел увеличил местный грузооборот в десять раз. У проекта такого масштаба имеются и негативные последствия: затопление плодородных земель в областях выше по течению, удержание наносного ила плотиной (и снижение естественной удобряемости земель в нижних районах при прежних ежегодных разливах Янцзы), затопление археологических объектов, повышение риска оползней, снижение биологического разнообразия. При прорыве плотины в зоне затопления находится более 360 млн человек, поэтому сам объект и окрестные воды патрулируются армией КНР с использованием вертолетов, дирижаблей, бронемашин и роботов для разминирования бомб[7].
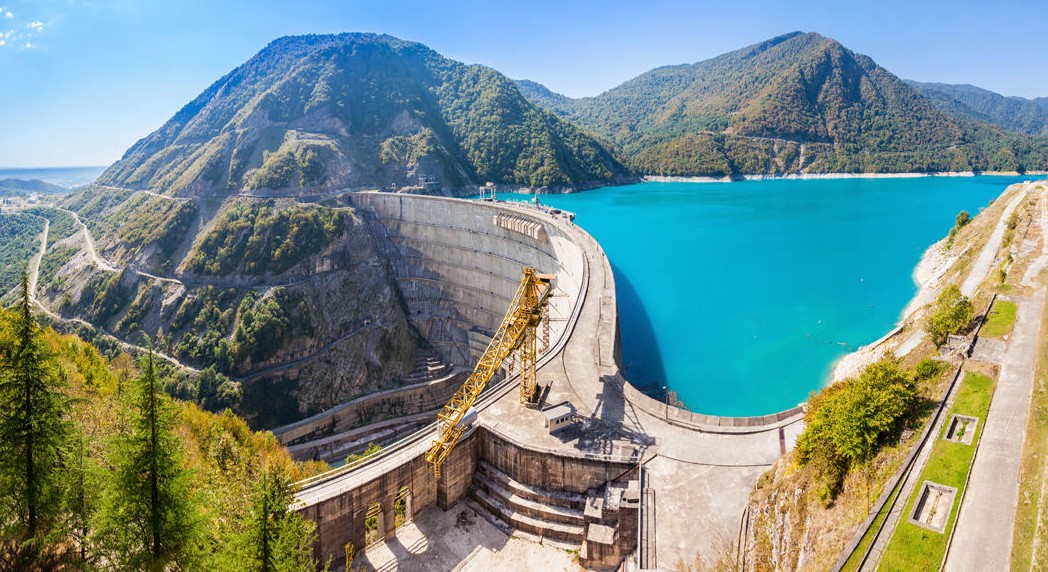


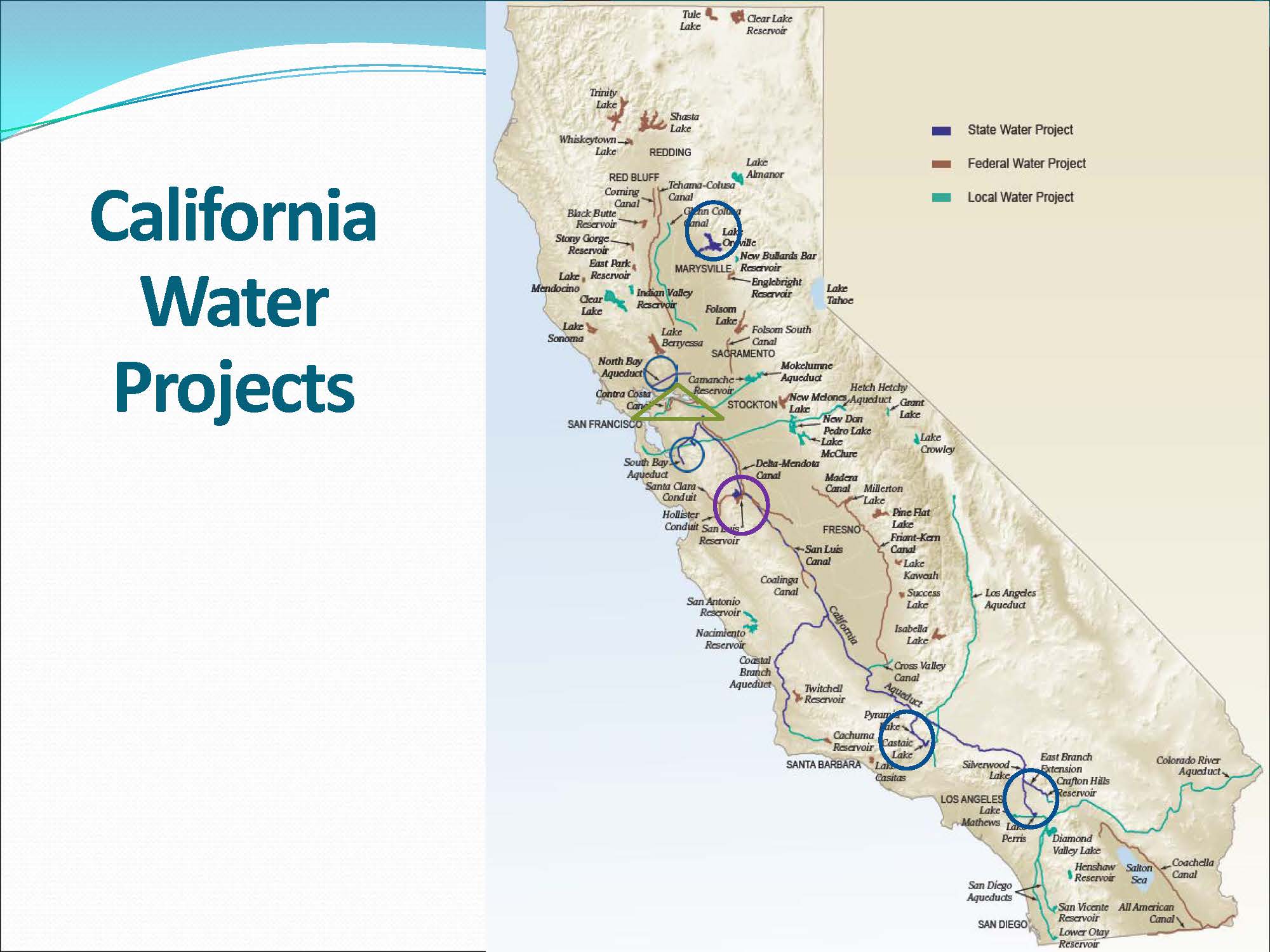
 California-CA
California-CA