
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Important port
Important port


吕贝克汉萨同盟旧城,文化遗产,1987年列入世界遗产名录。 著名的汉萨联盟的首府,建于12世纪,直到16世纪,一直是北欧的商业中心。现在保存着当时的城市布局和15到16世纪的许多建筑,如城墙、城门、碉堡、贵族住宅、记功碑、教堂以及盐库等。 吕贝克旧城位于德国石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州的吕贝克市,是一座典型的中世纪山地城市。自1143年建城以来,一直是欧洲著名的港口及商业城市,它的影响与汉堡、哥本哈根、不来梅等其他汉莎同盟城市相当。回顾历史,早在819年,此地便建有一座城堡,称为"老吕贝克"。11世纪时,吕贝克改名为"留比斯",意为可爱之城。1143年,荷尔斯泰因伯爵阿道夫二世在"可爱之城"的基础上重建吕贝克,形成了如今旧城的雏形。1159年的一场大火之后,吕贝克城重新布局,其鱼骨状的大街和四通八达的小巷成为日后北欧城市布局的模式。1226年,该城成为自由城邦;1358年,吕贝克成为汉萨同盟的总部所在地,确定了它在欧洲的重要地位。16世纪,随着北欧诸国的逐渐强大,吕贝克失去了往日的辉煌。进入二十世纪后,该城早已风光不在,二战后盟军的空袭摧毁了旧城五分之一的建筑,其中包括著名的教堂和市政厅。战后德国政府努力修缮和保护残存的文物古迹,使得吕贝克旧城依旧成为北欧地区的一座保存良好的中世纪古城。 吕贝克旧城分为三部分,第一部分是旧城东部和北部区域,第二部分是旧城的西南区域,第三部分是圣玛丽教堂及市政厅。 旧城区的东部和北部现已被划为保护区,保持着中世纪的完整格局。这一区建筑的最大特点是将10世纪城市特有的宗教性和世俗性和谐地融为一体。城市上空轮廓由7座高耸的教堂塔楼构成,突出体现了该城特有的风格。它同时又是一座活的建筑博物馆:哥特式、巴洛克式、洛克克式、非经典式,从中世纪到现代的各种建筑风格都有。其中哥特式的圣玛丽教堂、罗马式的大教堂等众多教堂尖顶簇拥在旧城区上空,仿佛是一片教堂的森林。1942年,圣玛丽教堂和圣彼得教堂的尖塔曾在空袭中被毁,1956-1962年间重修。不足的是续建的建筑在结构、造型比例和组合形式上与相邻的原有建筑风格相异,未能与旧城传统形式相统一;但由于续建范围小,故未对整个城市景观造成损害。 旧城北区是中世纪城镇特色的典型代表,而这些特色主要通过当地独特的砖造房子和建筑阶梯形的山花显示出来。中世纪由于对空间需求的增长,建筑结构上出现了内院和背街,临街的房子将内院与大街隔离开来,形成了相对封闭的内向性格,同时也造就了旧城的独特风貌。城东区保存一些手工艺人的朴素住宅,这些住宅大都设有内院,有一定的虚实开阖变化。城内的贵族宅邸则更为讲究,它们结构坚固,设施完备,空间富于变化装饰精巧细致,艺术价值很高。其中颇具特色的有:变化丰富的大厅、古色古香的壁炉、彩绘的木制天花板、房间嵌板细工和拉毛粉饰吊顶,还有花园的侧厅。现在这些建筑都加以保护,精心修补。 旧城的西南区是幽静而略显拘谨的城区,也有一些浪漫的田园风格,吕贝克人将这里称为"画家角"。 在旧城中心的制高点,坐落着圣玛丽教堂和市政厅,这二者相毗邻,成为吕贝克最重要的建筑物,并因其艺术的高贵价值而在欧洲享有盛名。这两座建筑当时曾在整个北欧有广泛影响,以致波罗的海沿岸的大量建筑都纷纷模仿。其中圣玛丽教堂被作为哥特式砖构大教堂的典型;而市政厅则被当作该地区市政厅建筑的样板,具有独特的建筑风格,它的一半是哥特式的,而另一半是丽娜莎挪式。在后来的几个世纪,市政厅一直是远近城市争相效仿的典范。 旧城西侧坐落着荷尔斯坦因大门,这个13世纪建成的古城门一直是吕贝克城的象征。它建于1466-1477年,为晚期哥特式风格。登上城门,可以眺望整个吕贝克旧城。城堡现已成为博物馆,陈列着古代的作战地图、兵器和战船模型。二次大战中,吕贝克的许多古建筑遭到战火毁坏,但荷尔斯坦因门侥幸保存下来。 吕贝克旧城的建筑物组合自然,风格统一,有着动人的城市景观效果,表现了吕贝克城市艺术的高度成就。所以联合国教科文组织将这座包括近千座建筑的汉萨同盟古城列入世界遗产名录。
吕贝克(德语:Lübeck),位于德国北部波罗的海沿岸,是石勒苏益格-荷尔施泰因州第二大城市。历史上曾是汉萨同盟城市之一,也是同盟的“首都”。1987年,“汉萨同盟城市吕贝克”经联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产,是欧洲北部第一个入列世界文化遗产的城市。
吕贝克坐落于特拉维河沿岸,是德国在波罗的海最大的港口。旧城部分是被特拉维河和易北河-吕贝克运河围绕起来的一个岛屿。
Die Hansestadt Lübeck[2] ( Anhören?/i) (niederdeutsch: Lübęk, Lübeek; Adjektiv: lübsch, lübisch, spätestens seit dem 19. Jahrhundert auch lübeckisch), lateinisch Lubeca, ist eine kreisfreie Großstadt im Norden Deutschlands und im Südosten Schleswig-Holsteins an der Ostsee (Lübecker Bucht). Mit etwa 220.000 Einwohnern[3] ist Lübeck nach der Landeshauptstadt Kiel die Stadt mit den meisten Einwohnern und eines der vier Oberzentren und eine Regiopole des Landes. Lübeck ist mit rund 214 km² die flächenmäßig größte Stadt Schleswig-Holsteins. Die nächstgelegenen großen Städte sind Hamburg etwa 65 Kilometer südwestlich, Kiel etwa 78 Kilometer nordwestlich und Schwerin etwa 68 Kilometer südöstlich. Lübeck gehört der europäischen Metropolregion Hamburg an.
Anhören?/i) (niederdeutsch: Lübęk, Lübeek; Adjektiv: lübsch, lübisch, spätestens seit dem 19. Jahrhundert auch lübeckisch), lateinisch Lubeca, ist eine kreisfreie Großstadt im Norden Deutschlands und im Südosten Schleswig-Holsteins an der Ostsee (Lübecker Bucht). Mit etwa 220.000 Einwohnern[3] ist Lübeck nach der Landeshauptstadt Kiel die Stadt mit den meisten Einwohnern und eines der vier Oberzentren und eine Regiopole des Landes. Lübeck ist mit rund 214 km² die flächenmäßig größte Stadt Schleswig-Holsteins. Die nächstgelegenen großen Städte sind Hamburg etwa 65 Kilometer südwestlich, Kiel etwa 78 Kilometer nordwestlich und Schwerin etwa 68 Kilometer südöstlich. Lübeck gehört der europäischen Metropolregion Hamburg an.
Die Hansestadt erhielt 1160 das Stadtrecht und wird auch „Stadt der Sieben Türme“ und „Tor zum Norden“ genannt. Sie gilt als „Königin“ und „Mutter der Hanse“, einer Handelsvereinigung, die seit dem 12. Jahrhundert bis in die Neuzeit durch Freihandel und friedliche Zusammenarbeit für großen Wohlstand in Lübeck und anderen Mitgliedsstädten sorgte. St. Marien zu Lübeck gilt als eines der Hauptwerke und als „Mutterkirche“ der Backsteingotik, die vom Wendischen Städtebund aus Verbreitung im nordeuropäischen Raum fand. Die mittelalterliche Lübecker Altstadt mit zahlreichen Kulturdenkmalen ist seit 1987 Teil des UNESCO-Welterbes. Lübeck hatte eine seit 1226 bestehende Tradition als Freie Reichsstadt im Heiligen Römischen Reich und als Freie Stadt bzw. Stadtstaat, diese endete im Jahr 1937 mit dem Gesetz über Groß-Hamburg und andere Gebietsbereinigungen.
リューベック(Lübeck)は、ドイツ連邦共和国の都市。シュレースヴィヒ=ホルシュタイン州に属する。トラヴェ川(英語版、ドイツ語版)沿岸、バルト海に面する北ドイツの代表都市。かつてはハンザ同盟の盟主として繁栄を誇った。正式名称をハンザ都市リューベック(Die Hansestadt Lübeck)という。"Lübeck"の発音は、標準ドイツ語ではドイツ語発音: [ˈlyːbɛk] (![]() 音声ファイル)(リューベックに近い)であるのに対し、地元では[ˈlyːbɛːk](リューベークに近い)となる傾向がある。面積214.14平方キロメートル、人口211,713人(2011年)。
音声ファイル)(リューベックに近い)であるのに対し、地元では[ˈlyːbɛːk](リューベークに近い)となる傾向がある。面積214.14平方キロメートル、人口211,713人(2011年)。
1143年、ホルシュタイン伯アドルフ2世によって建設された。一旦火事で荒廃したものの、ザクセンのハインリヒ獅子公によって再建された。1226年に帝国都市となる。北海・バルト海交易で一時期独占的な地位を築いたハンザ同盟の盟主でもあった。リューベック商人は、ノルウェーのベルゲンに商館を築き、ノルウェーの鱈を南に売却して大きな利益をあげた。また、リューネブルクの岩塩をおさえたことで、塩漬け鰊(ニシン)でも独占的な地位を誇った。近世にはいると、ハンザ同盟の衰退とともに、リューベックも衰退していった。
1806年の神聖ローマ帝国解体により主権国家となるが、ナポレオン戦争に巻き込まれ、1811年から1813年までフランス帝国に併合される。ナポレオンの没落にともない1813年に独立を回復するが、1815年にドイツ連邦に参加する。1867年には北ドイツ連邦に参加し、1871年のドイツ帝国成立に伴い、同国の州となる。ヴァイマル共和国時代も州の地位を保ったが、ナチス政権下の1937年にプロイセン州に併合され、同州の属州であるシュレースヴィヒ=ホルシュタインに編入される。
Lübeck (pronounced [ˈlyːbɛk] ( listen)) is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. On the river Trave, it was the leading city of the Hanseatic League, and because of its extensive Brick Gothic architecture, it is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. In 2015, it had a population of 218,523.
listen)) is a city in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany, and one of the major ports of Germany. On the river Trave, it was the leading city of the Hanseatic League, and because of its extensive Brick Gothic architecture, it is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. In 2015, it had a population of 218,523.
The old part of Lübeck is on an island enclosed by the Trave. The Elbe–Lübeck Canal connects the Trave with the Elbe River. Another important river near the town centre is the Wakenitz. Autobahn 1 connects Lübeck with Hamburg and Denmark. Travemünde is a sea resort and ferry port on the coast of the Baltic Sea. Lübeck Hauptbahnhof links Lübeck to a number of railway lines, notably the line to Hamburg.
Lübeck Écouter est une ville hanséatique d'Allemagne du Nord, dans le Land de Schleswig-Holstein. Avec une population de 212 000 habitants, c'est la deuxième ville du Schleswig-Holstein, après Kiel, la capitale du Land. Son code de plaque d'immatriculation est HL.
Ce port de la mer Baltique est également surnommé « la reine de la Hanse » : c'était en effet la capitale de la Ligue hanséatique.
La ville fait partie de la liste du patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO, notamment pour son architecture de briques rouges.
La Ciudad Hanseática de Lübeck (en alemán: Hansestadt Lübeck  [ˈlyːbɛk] (?·i)), que cuenta con 216 253 habitantes es la segunda ciudad en población del estado federado de Schleswig-Holstein, en el norte de Alemania, después de Kiel. El casco medieval de la ciudad fue nombrado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco en el año 1987, destacando las construcciones de ladrillo en estilo gótico báltico como la Puerta de Holsten.1
[ˈlyːbɛk] (?·i)), que cuenta con 216 253 habitantes es la segunda ciudad en población del estado federado de Schleswig-Holstein, en el norte de Alemania, después de Kiel. El casco medieval de la ciudad fue nombrado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco en el año 1987, destacando las construcciones de ladrillo en estilo gótico báltico como la Puerta de Holsten.1
La ciudad está dividida en diez municipios y 35 distritos. El municipio del Centro (Innenstadt) está localizado en una isla fluvial rodeada por los ríos Trave y Wakenitz. El municipio de Travemünde, a diecisiete kilómetros del centro, está a las orillas del mar Báltico y es un popular balneario y puerto en la desembocadura del río Trave.
Hamburgo se encuentra a unos 58 km al suroeste y Kiel, la capital de Schleswig-Holstein, a 62 km al noroeste. La autopista Autobahn 1 conecta a Lübeck con Hamburgo y Dinamarca.
Lübeck fue varios siglos la "capital" de la liga Hanseática y conocida como la "Reina de la Hansa". Actualmente es también conocida como "La ciudad de las siete torres" (Stadt der Sieben Türme) y como la "Puerta hacia el norte" (Tor zum Norden).
Лю́бек (нем. Lübeck [ˈlyːbɛk]) — город на севере Германии (юго-восток земли Шлезвиг-Гольштейн). Порт на Балтийском море вблизи устья реки Траве. В истории известен как крупнейший центр Ганзейского союза; основные достопримечательности включены в список объектов Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО в Германии. Население — ок. 220 тыс. человек[6] (данные на январь 2017 г.; в 1992 г. было 216 тыс.).



Málaga [ˈmalaɣa] ist die zweitgrößte Stadt in Andalusien und die sechstgrößte Stadt Spaniens. Die Hauptstadt der Provinz Málaga besitzt einen der größten spanischen Flughäfen, einen Handelshafen und eine Universität. Wegen ihres Klimas ist sie eines der wichtigsten Urlaubsziele der Iberischen Halbinsel.
马拉加(西班牙语:Málaga,西班牙语:[ˈmalaɣa])是位于西班牙南部安达卢西亚、地中海太阳海岸的一个城市,也是马拉加省的省会,西班牙的第二大港口。据2019年1月估算,它拥有人口574,626人,是西班牙第六大的城市。而整个马拉加都市圈人口约为1,074,074,是西班牙五大都市圈之一。马拉加被群山和两条注入地中海的河流所环抱,其主要收入来源于农业和旅游观光业。与伊比利亚的其他城市一样,融入了伊斯兰和基督的文化。
画家巴勃罗·毕加索、19世纪政治家安东尼奥·卡诺瓦斯·德尔卡斯蒂略和演员安东尼奥·班德拉斯均出生在马拉加。
 England
England
 England
England
 Manchester
Manchester

 History
History
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 Important port
Important port
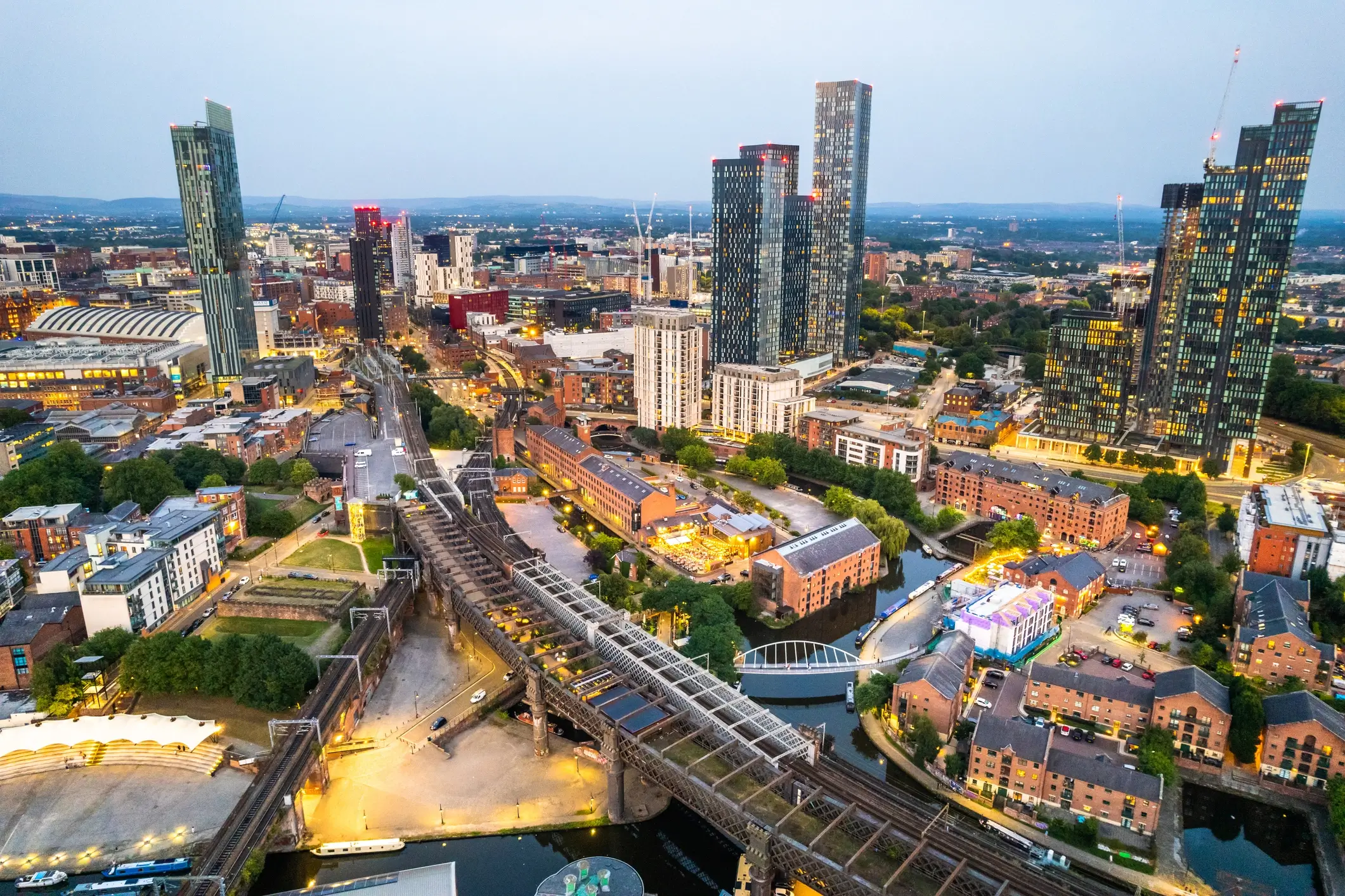

Manchester ([ˈmɛntʃɛstɐ], englisch [ˈmæntʃɪstə])[1] ist eine Stadt im Nordwesten von England im Vereinigten Königreich Großbritannien und Nordirland mit dem Status eines Metropolitan Borough sowie einer City. Sie hat etwa 570.000 Einwohner und liegt im Metropolitan County Greater Manchester, einer der größten Agglomerationen in England mit 2,9 Mio. Einwohnern (2022). Die Einwohner Manchesters werden „Mancunians“ oder verkürzt „Mancs“ genannt.
Die Ursprünge der Stadt Manchester gehen auf ein römisches Kastell am Zusammenfluss der Flüsse Irwell und Medlock zurück. Vor allem im Zeitalter der Industriellen Revolution wurde Manchester zu einem wichtigen Standort der Industrie. Einen besonderen Stellenwert nahm dabei die Textilindustrie ein, deren Anfänge in Manchester auf das Spätmittelalter zurückgehen. Im 20. Jahrhundert erfolgte der stetige Zerfall der Industrie. Heute ist Manchester dennoch eines der wichtigsten Wirtschaftszentren des Vereinigten Königreichs und beherbergt zahlreiche Museen, Hochschulen und Orte der Kunst und Kultur.
曼彻斯特市(英语:City of Manchester),即曼彻斯特(英语:Manchester),是英格兰的城市,都市自治市,位于西北英格兰区域,人口约为55万人,是曼彻斯特都市圈中人口最多的城市,且是英格兰西北第一多,英国第五多的城市。
曼彻斯特在工业革命史中有着重要位置。十八世纪,资本主义在这座城市萌芽,让本是农村地区的曼彻斯特经历急速发展并成为全世界第一座工业化的城市。全世界第一条城际通勤铁路在此诞生。因市内兴盛的纺织业,曼彻斯特在工业革命期间曾因仓库众多而闻名于世,使其获得了“仓库城市”的别称。曼彻斯特在科学技术史上也占有重要位置。成立于2002年的曼彻斯特大学及其前身见证了原子核物理学的诞生,世界上第一台存储程式电脑以及石墨烯的发现。
曼彻斯特被誉为“北方之都”[2][3],是英格兰北部一个极其重要的城市,尤其是在其经济、艺术、文化、交通运输、媒体和体育地位上。步入二十一世纪,曼彻斯特的发展愈发强势,为这座城市带来了与伯明翰竞争英国第二大城市的地位的资本[4]。
1974年,曼彻斯特与周围市镇联合组成大曼彻斯特郡,成为该郡的一个都会区。“曼彻斯特”此名常用来指整个都市区。整个大曼彻斯特的市区总人口在英国排名第二,仅次于伦敦。
マンチェスター (Manchester, IPA: [ˈmænˌtʃɪstə][ヘルプ/ファイル]) は、イングランドの北西部、グレーター・マンチェスターに位置する都市。北部イングランドを代表する都市であり、イギリスで9番目の都市である。1853年に市制(英語版)が布かれ、2011年の時点で、マンチェスター(都市と都市バラ)の人口は49万人である。2011年の近郊を含む都市圏人口は224万人であり、同国第3位である[2]。
[ˈmænˌtʃɪstə][ヘルプ/ファイル]) は、イングランドの北西部、グレーター・マンチェスターに位置する都市。北部イングランドを代表する都市であり、イギリスで9番目の都市である。1853年に市制(英語版)が布かれ、2011年の時点で、マンチェスター(都市と都市バラ)の人口は49万人である。2011年の近郊を含む都市圏人口は224万人であり、同国第3位である[2]。
Manchester (/ˈmæntʃɪstər, -tʃɛs-/)[5][6] is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England, with a population of 545,500 as of 2017.[7] It lies within the United Kingdom's third-most populous metropolitan area, with a population of 3.2 million.[8] Manchester is fringed by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and an arc of towns with which it forms a continuous conurbation. The local authority is Manchester City Council.
The recorded history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort of Mamucium or Mancunium, which was established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. It was historically a part of Lancashire, although areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated in the 20th century.[9] Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchester's unplanned urbanisation was brought on by a boom in textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution,[10] and resulted in it becoming the world's first industrialised city.[11]
Manchester achieved city status in 1853. The Manchester Ship Canal opened in 1894, creating the Port of Manchester and directly linking the city to the Irish Sea, 36 miles (58 km) to the west. Its fortune declined after the Second World War, owing to deindustrialisation, but the IRA bombing in 1996 led to extensive investment and regeneration.[12]
In 2014, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked Manchester as a beta world city, the highest-ranked British city apart from London.[13] Manchester is the third-most visited city in the UK, after London and Edinburgh.[14] It is notable for its architecture, culture, musical exports, media links, scientific and engineering output, social impact, sports clubs and transport connections. Manchester Liverpool Road railway station was the world's first inter-city passenger railway station; scientists first split the atom, developed the stored-program computer and produced graphene in the city. Manchester hosted the 2002 Commonwealth Games.
Manchester Ecoutez (ˈmanˌtʃɪstə) est une ville du Royaume-Uni située dans le comté métropolitain du Grand Manchester. Elle a le statut de cité depuis 1853 et compte 545 500 habitants en 2017. Elle est parfois considérée comme la « deuxième ville d’Angleterre » grâce à son importance économique, culturelle et sportive1, bien que sa superficie et sa population ne lui permettent pas de détrôner Birmingham. Manchester est catégorisée comme une ville « bêta » par Le GaWC (Réseau d’étude sur la mondialisation et les villes mondiales2). Ses habitants s'appellent les Mancunien(ne)s. La ville est au cœur d'une grande agglomération de plus de deux millions et demi d'habitants dont les villes principales sont : Bury, Bolton, Rochdale, Oldham, Ashton-under-Lyne, Stockport, Salford, Altrincham, Wigan. Le nom de « Manchester » est utilisé aussi bien pour désigner l'agglomération que la ville en tant que telle.
Manchester est située à 260 km au nord-ouest de Londres, sur la rive est de la rivière Irwell. La ville est bordée au Sud par la plaine du Cheshire et au Nord et à l'Est par la chaîne montagneuse des Pennines. Historiquement, la majeure partie de la ville faisait partie du Lancashire, mais des zones situées au sud de la rivière Mersey appartenaient au Cheshire. Le vicus créé par les Romains à proximité du fort de Mamucium, construit en 79 sur un monticule rocheux non loin de la confluence entre la Medlock et l'Irwell, est devenu au fil de son histoire une ville majeure du nord de l'Angleterre. Manchester est la première ville au monde à avoir été industrialisée, et elle a joué un rôle important durant la révolution industrielle. Durant le XIXe siècle, la ville acquiert d'ailleurs le surnom de « Cottonopolis » en raison de son importante industrie cotonnière. L'économie de la ville s'est depuis tournée vers le secteur tertiaire, et il s'agit aujourd'hui d'un pôle financier important.
Manchester est une ville importante culturellement, qui héberge de nombreux théâtres, musées et salles de concert. La ville a vu dans les années 1980 l'émergence de divers groupes de rock indépendant autour du club The Haçienda, qui deviendront très célèbres par la suite et que l'on regroupe sous l'appellation « Madchester ». Elle a une économie nocturne bien développée avec de nombreux bars et clubs. La ville est le siège de divers médias, dont de nombreuses stations de radios, des journaux et une importante base de la BBC. L'architecture de la ville est marquée par l'omniprésence des briques rouges. Elle mêle des bâtiments historiques, comme la cathédrale gothique, des édifices de l'époque victorienne et de la période industrielle, avec des bâtiments à l'architecture contemporaine, dont de hauts gratte-ciel. Manchester est la troisième ville la plus visitée par les étrangers au Royaume-Uni.
Manchester est également une importante ville étudiante avec ses deux universités, l'université de Manchester et l'université métropolitaine de Manchester qui, avec entre-autres le Royal Northern College of Music, regroupent plus de 70 000 étudiants.
La ville accueillit en 2002 les jeux du Commonwealth. Elle se démarque également dans le monde sportif par ses deux équipes de Premier League de football, Manchester United et Manchester City.
Manchester (AFI: /ˈmanʧester/[3]; in inglese [ˈmantʃɪstə][4]), in italiano antico Mancunia, è un borgo metropolitano di 503.127 abitanti del Regno Unito, che gode del titolo onorifico di città, ed è capoluogo della contea metropolitana inglese della Greater Manchester. Insediamento celtico poi rinominata dagli antichi romani magna castra, i suoi abitanti vengono chiamati Mancunians (Mancuniani).
Mánchester1 (pronunciado en inglés  /ˈmæntʃɛstə/ (?·i)) es una ciudad y un municipio metropolitano del condado de Gran Mánchester en Inglaterra. Mánchester obtuvo su estatus de ciudad en 1853 y tenía una población estimada de 530.300 habitantes en 2015.2 A su vez, forma parte de la segunda aglomeración urbana del Reino Unido y decimocuarta de la Unión Europea en términos de población.
/ˈmæntʃɛstə/ (?·i)) es una ciudad y un municipio metropolitano del condado de Gran Mánchester en Inglaterra. Mánchester obtuvo su estatus de ciudad en 1853 y tenía una población estimada de 530.300 habitantes en 2015.2 A su vez, forma parte de la segunda aglomeración urbana del Reino Unido y decimocuarta de la Unión Europea en términos de población.
Mánchester es un importante centro artístico, financiero, de medios de comunicación y de educación superior. En una encuesta de líderes empresariales británicos publicada en 2006, Mánchester era considerada como el mejor lugar en el Reino Unido para establecer un negocio. Un informe encargado por la Asociación de Mánchester, publicado en 2007, mostró a Mánchester como la "ciudad con más rápido crecimiento económico". Es la tercera ciudad más visitada en el Reino Unido por turistas extranjeros. Mánchester fue la anfitriona de los Juegos de la Mancomunidad de 2002, y es sede de dos equipos de fútbol de la Premier League, Manchester United y Manchester City.
Históricamente la mayor parte de la ciudad fue parte del condado de Lancashire, con las zonas ubicadas al sur del río Mersey en el condado de Cheshire. Mánchester fue la primera ciudad industrializada del mundo y desempeñó un papel central durante la Revolución industrial. Se convirtió en el principal centro internacional de la fabricación textil y de hilado de algodón. Durante el siglo XIX adquirió el apodo de "Cottonopolis", sugiriendo que era una metrópoli de las fábricas de algodón. El centro de la ciudad se encuentra en una lista provisional del Patrimonio de la Humanidad de la Unesco, debido principalmente a la red de canales y molinos construidos durante los siglos XVIII y XIX.
Манче́стер[2] (англ. Manchester ['mænʧɪstə]) — город и метрополитенский район в Северо-Западной Англии, графство Большой Манчестер. Менее чем полумиллионный город имеет крупнейшую в регионе 2,2-миллионную агломерацию Большой Манчестер. Девятый по величине город Великобритании (и восьмой — Англии).
Наряду с Бирмингемом, Лидсом, Шеффилдом, Ливерпулем и Лондоном Манчестер был одним из центров Промышленной революции. В настоящее время Манчестер — крупный культурный, промышленный, финансовый, коммерческий и транспортный центр страны. Развито машиностроение, текстильная, химическая, лёгкая, бумажная промышленность. Действует морской порт. Манчестерский университет является одним из самых престижных в Великобритании. Имеется городской музей и художественная галерея[3].

马尼拉(他加禄语:Maynila,英语:Manila),又称岷里拉,是菲律宾首都,位于小菲律宾的最大岛—吕宋岛马尼拉湾的东岸;今为菲第二大城,人口有150万;乃全国经济、文化、教育和工业中心。2013年4月,马尼拉都会人口排名全球第6名,达2120万人[1]。
在同属此都会区的众多城市中,仅奎松市人口多于马尼拉市。马尼拉之名在西班牙殖民时,因双方语言不通的误解而命名为:Maynilad,起源于他加禄语:May是这里有的意思,他加禄语:nilad(瓶花木属)是一种生长着白艳花朵、可作为染料的湿地树,许多观赏过的人们都以“那些白色的花开着,便像一双双亮晶晶的眼睛”形容它,两字合起来为他加禄语:Maynilad,本意为他加禄语的这里有白色的花。[2][3]她所属的这个都会区,菲律宾官方称为马尼拉大都会(Metro Manila),一般外国人和非定居者通常简称以马尼拉。全区由17座城市和直辖市所组成。
Manila ([maˈniːla], offiziell englisch City of Manila, Tagalog Lungsod ng Maynila) ist die Hauptstadt der Republik der Philippinen.
Manila liegt auf der Hauptinsel Luzon in der Manilabucht. Sie ist eine von 17 Städten und Gemeinden, die zusammen die 636 Quadratkilometer große Region Metro Manila bilden. Die Stadt Manila zählt rund 1,8 Millionen Menschen, in der Agglomeration Metro Manila wohnen rund 12,9 Millionen Einwohner (1. August 2015).[2] Häufig wird die gesamte Metropolregion als Manila bezeichnet, was jedoch im administrativen Sinne falsch ist.
Die Hauptstadt ist das politische, wirtschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum des Landes sowie Verkehrsknotenpunkt mit Universitäten, Hochschulen, Theater und Museen. Die Schutzpatronin der Stadt ist die La Naval de Manila.
マニラ市(タガログ語: Maynilà [majˈnilaʔ]、英語: Manila [məˈnɪlə])は、フィリピン共和国の首都。メトロ・マニラとも呼ばれるマニラ首都圏に所属する都市。フィリピンのルソン島中西部にあり、マニラ湾東岸に位置している。
『東洋の真珠』などの美称があり、フィリピンがスペイン人によって植民地化された16世紀末よりフィリピンの首府であり、独立後も一貫して首都でありつづけている。市域人口は166万人(2007年)であり、人口1,155万人を抱えるメトロ・マニラの中核都市である。さらに近郊を含む都市圏人口は2016年時点で2,293万人であり、世界有数の大都市圏を形成している[1]。
アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界66位の都市と評価された[2]。東南アジアでは、シンガポール、バンコク、クアラルンプール、ジャカルタに次ぐ5位である。
Manila (/məˈnɪlə/; Tagalog: Maynilà, pronounced [majˈnilaʔ]), officially the City of Manila (Tagalog: Lungsod ng Maynilà [luŋˈsod nɐŋ majˈnilaʔ]), is the capital of the Philippines and a highly urbanized city. It is the most densely populated city proper in the world as of 2019.[11] It was the first chartered city by virtue of the Philippine Commission Act 183 on July 31, 1901 and gained autonomy with the passage of Republic Act No. 409 or the "Revised Charter of the City of Manila" on June 18, 1949.[12] Manila, alongside Mexico City and Madrid are considered the world's original set of Global Cities due to Manila's commercial networks being the first to traverse the Pacific Ocean, thus connecting Asia with the Spanish Americas, marking the first time in world history when an uninterrupted chain of trade routes circled the planet.[13] Manila is also the second most natural disaster-afflicted capital city in the world next to Tokyo,[14] yet it is simultaneously among the most populous and fastest growing cities in Southeast Asia.[15]
The Spanish city of Manila was founded on June 24, 1571, by Spanish conquistador Miguel López de Legazpi. The date is regarded as the city's official founding date; however, a Tagalog fortified polity called Maynilà had already existed on the site, dating back as far as 1258, from which the Spanish and English name of 'Manila' was derived. A Spanish fortified city called Intramuros was built directly on top of the site of old Maynilà, following the defeat of the polity's last indigenous Rajah, Sulayman III, in the Battle of Bangkusay. Manila was the seat of power for most of the country's colonial rulers. It is home to many historic sites, some of which were built during the 16th century. Manila has many of the Philippines' firsts, including the first university (1590),[16] light station (1642), lighthouse tower (1846), water system (1878), hotel (1889), electricity (1895), oceanarium (1913),[17] stock exchange (1927), flyover (1930s), zoo (1959), pedestrian underpass (1960),[18] science high school (1963),[19] city-run university (1965), city-run hospital (1969), and rapid transit system (1984; also considered as the first rapid transit system in Southeast Asia).[20]
The term "Manila" is commonly used to refer to the whole metropolitan area, the greater metropolitan area or the city proper. The officially defined metropolitan area called Metro Manila, the capital region of the Philippines, includes the much larger Quezon City and the Makati Central Business District. It is the most populous region of the country, one of the most populous urban areas in the world,[21] and is one of the wealthiest regions in Southeast Asia.[22] The city proper is home to 1,780,148 people in 2015,[6] and is the historic core of a built-up area that extends well beyond its administrative limits. With 71,263 people per square kilometer, Manila is also the most densely populated city proper in the world.[6][7]
Manille, officiellement la Ville de Manille (en tagalog Lungsod ng Maynila; en filipino Maynila; en anglais City of Manila) est la capitale des Philippines, et l'une des 16 villes de l'aire métropolitaine de Manille, l'une des plus peuplées au monde. Cette dernière, qui se trouve sur la côte ouest de l'île de Luçon, constitue le Grand Manille (NCR ou Metro Manila), et ne fait partie d'aucune province du pays. Elle se trouve sur la rive orientale de la baie de Manille. Les villes voisines sont Navotas et Caloocan au nord, Quezon au nord-est, San Juan et Mandaluyong à l'est, Makati au sud-est et Pasay au sud.
Avec 1 660 714 habitants d'après le recensement de 2007, Manille est la deuxième ville des Philippines, par sa population, après Quezon. Cette population, concentrée sur une superficie d'à peine 38,55 km2, fait de Manille, la ville la plus dense au monde2. La région métropolitaine de Manille est l'aire urbaine la plus peuplée des Philippines et la onzième au monde avec une population estimée à 16 300 000. La mégapole est la douzième plus grande au monde et sa population est estimée à 19 888 419 habitants3.
La ville est divisée en six districts législatifs et seize districts géographiques : Binondo (en), Ermita (en), Intramuros, Malate (en), Paco (en), Pandacan (en), port de Manille, Quiapo (en), Sampaloc (en), San Andres (en), San Miguel (en), San Nicolas (en), Santa Ana (en), Santa Cruz (en), Santa Mesa (en) et Tondo. À l'intérieur de leurs quartiers, on peut trouver des aires de commerces animés et la plupart des points historiques et culturels les plus importants comme le palais de Malacañan résidence officielle du président des Philippines et le siège du Départements exécutifs des Philippines. C'est le siège d'institutions scientifiques et éducatives, mais aussi de nombreux équipements sportifs. Tout cela fait de la ville un centre politique, commercial, culturel, éducatif, religieux et des transports majeur des Philippines.
Manila (AFI: /maˈnila/[2]; in filippino Maynila, nome completo Lungsod ng Maynila) è la capitale delle Filippine. È situata sulla costa est della baia di Manila sulla più grande delle isole delle Filippine, Luzón. Nonostante le sacche di povertà presenti, è una delle città più cosmopolite del mondo e la sua area metropolitana è il centro economico, culturale ed industriale del paese.
È il centro di una prosperosa area metropolitana con oltre 12 milioni di abitanti; l'area di Metro Manila, alla quale la città di Manila appartiene, è un'enorme metropoli costituita da 17 città e municipalità; la città stessa, con il suo milione e mezzo di abitanti, è la seconda città più popolosa delle Filippine. Soltanto Quezon, un'area suburbana nonché precedente capitale del Paese, è più popolosa.
Nacque nel XVI secolo da una colonia musulmana chiamata May Nilad sulle rive del fiume Pasig nella sede del governo coloniale spagnolo che controllò le Filippine per 333 anni. Nel 1898 gli Stati Uniti occuparono e presero il controllo dell'arcipelago fino al 1935 e Manila divenne una delle più note città dell'oriente. Durante la Seconda guerra mondiale, gran parte della città venne distrutta, ma in seguito venne ricostruita. Nel 1975, per gestire meglio quanto avveniva nella regione in rapido sviluppo, la città di Manila e i paesi e città nei dintorni vennero incorporati in un'entità indipendente, Manila Metropolitana. Questo venne stabilito l'8 novembre 1975 mediante il decreto presidenziale numero 824 dal precedente presidente Ferdinand Marcos che creava la "Metropolitan Manila Commission", diventata poi la Metro Manila Development Authority. Oggi la città e l'area metropolitana costituiscono un importante centro economico e culturale, ma esistono grossi problemi legati alla sovrappopolazione, traffico, inquinamento e criminalità.
Manila (en inglés: ![]() [ məˈnɪlə ]; en tagalo: Maynila
[ məˈnɪlə ]; en tagalo: Maynila ![]() [ majˈnilaʔ ]; en pampango: Menila; en zambal: Ibali) es la capital de las Filipinas y la segunda ciudad del país por número de habitantes.
[ majˈnilaʔ ]; en pampango: Menila; en zambal: Ibali) es la capital de las Filipinas y la segunda ciudad del país por número de habitantes.
La ciudad está situada en la costa oriental de la bahía de Manila, en la isla de Luzón, junto a la desembocadura del río Pásig; la ciudad limita al norte con las ciudades de Navotas y Caloocan; al nordeste con Ciudad Quezón; al este con San Juan y Mandaluyong; al sudeste con Makati y al sur con Pasay.
Manila tiene una población total de 1 652 171 de acuerdo con el censo de 2013,1 siendo la segunda ciudad más poblada del país después de la cercana Ciudad Quezón. La población habita un área de apenas 38,55 kilómetros cuadrados (14,88 mi²), lo que hace a Manila una de las ciudades más densamente pobladas del mundo.2 El Gran Manila es el área metropolitana más poblada de toda Filipinas y la décima del mundo, con una población estimada en 20,5 millones.3
La ciudad se divide en seis distritos legislativos y consiste en dieciséis distritos geográficos: Binondo, Ermita, Intramuros, Malate, Paco, Pandacán, Port Area, Quiapo, Sampaloc, San Andrés, San Miguel, San Nicolás, Santa Ana, Santa Cruz, Santa Mesa y Tondo. El comercio más activo y algunos de los lugares más históricos y emblemáticos de gran importancia cultural en el país, como la sede del Ejecutivo filipino y la Suprema Corte de las Filipinas, se encuentran en esta ciudad. Manila es sede de varias instituciones científicas y educativas, numerosas instalaciones deportivas, así como de un amplio elenco de entidades culturales del país y otros lugares cultural e históricamente significativos.
El primer relato escrito acerca de la ciudad es la Inscripción de la Laguna Copperplate, que data del siglo X. La ciudad fue invadida por Bolkiah, sultán de Brunéi, y fue cristianizada ya en el siglo XVI, cuando los conquistadores españoles llegaron por primera vez. Fue incorporada el 24 de junio de 1571 por el conquistador español Miguel López de Legazpi. Manila se convirtió finalmente en el centro de las actividades españolas en el Lejano Oriente y destino de la ruta comercial del Galeón de Acapulco a Manila, el cual conectaba a la América Española con Asia. La ciudad recibió el apodo de la "Perla de Oriente", como resultado de su ubicación central en las vitales rutas del comercio marítimo por el Pacífico. Varias insurrecciones chinas, revueltas locales, una ocupación británica y un motín cipayo se produjeron tiempo después de eso. Manila también vio el surgimiento de la Revolución filipina, que fue seguida por la ocupación estadounidense, contribuyendo a la planificación urbana de la ciudad y al desarrollo sólo para que la mayoría de dichas mejoras se perdiera por la devastación de la Segunda Guerra Mundial. Después de esto, la ciudad ha sido reconstruida.
Мани́ла (тагальск. Maynila, Майнила[1]; англ. и исп. Manila) — столица государства Филиппины, один из 16 городов, формирующих Столичный Регион страны (Метро-Манила). Граничит с городами Навотас и Калоокан (на севере), Кесон-Сити (на северо-востоке), Сан-Хуан и Мандалуйонг (на востоке), Макати (на юго-востоке) и Пасай (на юге). На западе омывается водами Манильского залива. С населением 1 660 714 человек по данным переписи 2007 года, Манила — второй крупнейший город страны после Кесона. Имея площадь всего 38,55 км², Манила считается самым густонаселённым городом мира[источник не указан 990 дней].
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
 France
France
 UEFA European Championship 2016
UEFA European Championship 2016

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture

 2024 Summer Olympics
2024 Summer Olympics

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Silk road
Silk road

 Important port
Important port
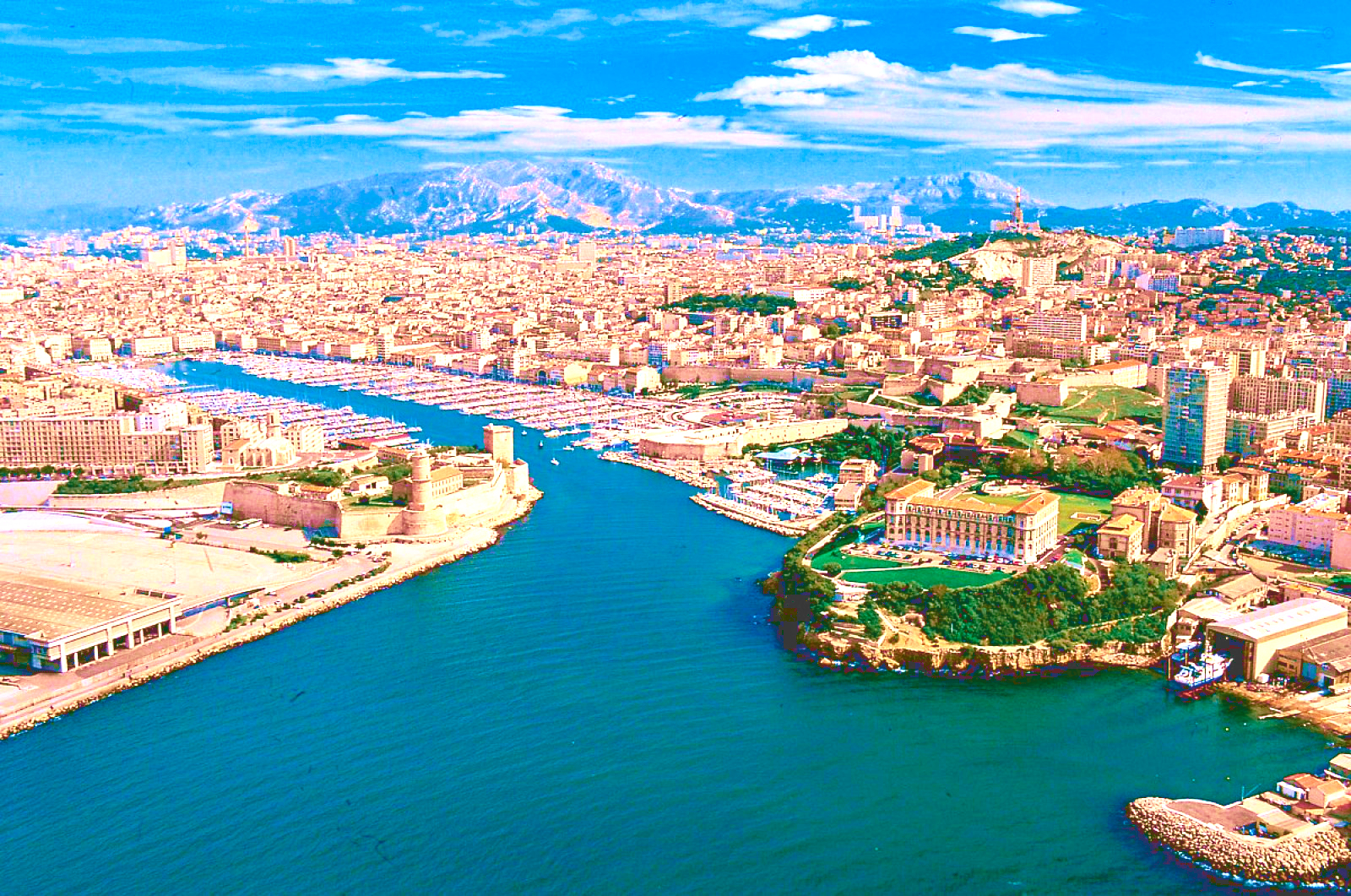


马赛(Marseille)是法国的第二大城市和最大海港,城市人口123万。该市三面被石灰岩山丘所环抱,景色秀丽, 气候宜人。马赛东南濒地中海,水深港阔,无急流险滩,万吨级轮可畅通无阻;西部有罗纳河及平坦河谷与北欧联系,地理位置得天独厚。全港由马赛、拉韦拉、福 斯和罗纳圣路易四大港区组成,年货运量1亿吨,为法国对外贸易最大门户。马赛是法国的一个重要工业中心,这里集中了法国40%的石油加工工业,福斯-塔尔 泊一带有4个大型炼油厂,每年能处理石油4500万吨。马赛的修船工业也相当发达,其修船量占全国此行业的70%。新港区有大小船坞10个,其中第10号 船坞长465米,宽65米,深11~12.5米,能修理世界最大的船只--80万吨级的油轮。
马赛(法语:Marseille,法语发音:[maʁsɛj] (ⓘ);奥克语:Marselha),法国东南部城市,普罗旺斯-阿尔卑斯-蓝色海岸大区罗讷河口省的一个市镇,同时也是所在大区首府及所在省的省会,下辖马赛区[1],2021年1月1日时人口数量为873,076人,在法国城市中排名第二位,仅次于首都巴黎,并与相邻的普罗旺斯地区艾克斯以及周边的数十个市镇共同组成了艾克斯-马赛普罗旺斯都会区[2]。
马赛位于地中海沿岸,市区三面环山、一面靠海,城市自老港向内陆区域延伸,市镇面积达240.6平方公里。马赛是法国艺术与历史之城,公元前六世纪就已有建城记载,被认为是法国最古老的城市之一。马赛在中世纪时为重要的宗教中心,近代因港口而吸引了大批移民,现为法国南部的政治、经济、科教、医疗、文化中心,艾克斯-马赛大学是法国乃至法语区规模最大的高等教育机构。马赛是世界水资源协会的总部所在地,是法国最大的港口城市,在2014年以前,马赛亦是地中海沿岸最大的港口[社 1]。
马赛是法国重要的旅游城市,因当地温暖的气候和充足的日照而闻名,被称为“阳光大道”的法国A7高速公路直通马赛市中心,市区内亦有大量历史建筑。马赛也因同名足球俱乐部而闻名,后者是法国唯一一个获得欧洲冠军联赛总冠军的球队,此外齐内丁·齐达内的标志性的过人动作被称为“马赛回旋”。在艺术方面,法国作家安托南·阿尔托和埃德蒙·罗斯丹出生于马赛,另有大批文学及影视作品取材于此。2013年,马赛获得“欧洲文化之都”的称号。
Marseille (/mɑːrˈseɪ/; French: [maʁsɛj] (![]() listen), locally [mɑχˈsɛjə]; English alternative spelling: Marseilles; Provençal: Marselha [maʀˈsejɔ, -ˈsijɔ]), is the second-largest city of France. The capital of the Bouches-du-Rhône department and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur administrative region, it is on France's south coast and had a population of 852,516 in 2012.[1] It has a metropolitan area of 241 km2 (93 sq mi), the third-largest in France after Paris and Lyon.[3]
listen), locally [mɑχˈsɛjə]; English alternative spelling: Marseilles; Provençal: Marselha [maʀˈsejɔ, -ˈsijɔ]), is the second-largest city of France. The capital of the Bouches-du-Rhône department and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur administrative region, it is on France's south coast and had a population of 852,516 in 2012.[1] It has a metropolitan area of 241 km2 (93 sq mi), the third-largest in France after Paris and Lyon.[3]
Known to the ancient Greeks and Romans as Massalia[4] (Greek: Μασσαλία, Massalía),[5][page needed][6] Marseille was an important trading centre and the main commercial port of the French Republic. Marseille is now France's largest city on the Mediterranean coast and the largest port for commerce, freight and cruise ships. The city was European Capital of Culture in 2013. It hosted matches at the 1998 World Cup and Euro 2016. It is home to Aix-Marseille University.
Marseille [maʁˈsɛj] (deutsch veraltet: Massilien, okzitanisch: Marselha oder Marsiho [maʀˈse.jɔ]) ist die wichtigste französische und eine bedeutende europäische Hafenstadt. Sie liegt am Golfe du Lion, einer Mittelmeerbucht. Die Stadt, deren Einwohner sich Marseillais [maʁ.sɛ.ˈjɛ] nennen, ist Hauptstadt des Départements Bouches-du-Rhône in der Region Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur. Marseille ist mit 861.635 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2015) nach Paris die zweitgrößte Stadt Frankreichs. Die Metropolregion zählt nach Eurostat-Definition rund 3,05 Mio. Einwohner (2015).[1]
Marseille war 2013 gemeinsam mit der slowakischen Stadt Košice Kulturhauptstadt Europas.
Marseille1 (en occitan provençal : Marselha selon la graphie classique, Marsiho selon la graphie mistralienne2) est une commune du Sud-Est de la France, chef-lieu du département des Bouches-du-Rhône et de la région Sud Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur.
En 2015, Marseille est la deuxième commune de France, avec 861 635 habitants3 et la troisième agglomération avec 1 578 584 habitants4. Depuis le 1er janvier 2016, Marseille est le siège de la métropole d'Aix-Marseille-Provence5, la seconde plus peuplée de France avec 1 859 922 habitants6. Son aire urbaine est quant à elle la troisième de France après celles de Paris et Lyon avec 1 752 398 habitants en 20157.
Parmi les plus anciennes villes de France8, fondée sous le nom de Μασσαλία (Massalía) vers 600 av. J.-C. par des marins grecs originaires de Phocée, Marseille est depuis l'Antiquité un important port de commerce et de passage. Elle connait notamment un essor commercial considérable au cours du XIXe siècle devenant une ville industrielle et négociante prospère9.
Héritage de ce passé, le Grand port maritime de Marseille (GPMM) et l'économie maritime sont encore des pôles majeurs de l'activité régionale et nationale10 et Marseille reste le premier port français, le deuxième port méditerranéen11 et le cinquième port européen12.
L'ouverture de Marseille sur la mer Méditerranée en fait depuis ses origines une ville cosmopolite d'échanges culturels et économiques avec l'Europe du Sud, le Proche-Orient, l'Afrique du Nord et l'Asie. Elle est d'ailleurs souvent considérée comme la « Porte de l'Orient »13.
Marsiglia (in francese: Marseille [maʁ.sɛij(ə)], in provenzale: Marselha o Marsiho[Nota 1], in latino: Massilia o Massalia; in greco: Μασσαλία o Μασαλία) è la più grande città della Francia meridionale, capoluogo della regione Provenza-Alpi-Costa Azzurra e del dipartimento delle Bocche del Rodano, oltre che il primo porto della Francia, sesto del Mediterraneo ed a livello europeo[1]. Fondata dai Greci durante l'Antichità, è una delle più antiche città francesi. Considerando il numero di abitanti della sola municipalità risulta essere la seconda città della Francia, dopo Parigi. In realtà Lione, pur avendo meno abitanti di Marsiglia nel territorio comunale, considerando l'area metropolitana supera il milione e mezzo di abitanti, contendendo a Marsiglia il primato di seconda città di Francia.
Marsiglia è stata Capitale europea della cultura nel 2013, assieme a Košice.
Marsella (Marseille en francés ![]() [maʁ.sɛj] (?·i), del griego Μασσαλία, Massalia; en occitano provenzal, Marselha o Marsiho) es una ciudad portuaria del sur de Francia, capital del departamento de Bocas del Ródano y de la región de Provenza-Alpes-Costa Azul.
[maʁ.sɛj] (?·i), del griego Μασσαλία, Massalia; en occitano provenzal, Marselha o Marsiho) es una ciudad portuaria del sur de Francia, capital del departamento de Bocas del Ródano y de la región de Provenza-Alpes-Costa Azul.
Marsella es la segunda ciudad más poblada de Francia después de París con 859 543 habitantes, principal centro económico y mayor metrópoli del Mediodía francés, agrupando cerca de 1 605 000 habitantes en su área urbana, siendo la tercera mayor del país, tras París y Lyon. Es el puerto comercial más importante de Francia y del Mediterráneo, tercero en importancia de Europa tras Róterdam y Amberes, centro de importante actividad industrial especializado en la petroquímica y el refino de petróleo, construcción naval e industrias diversas, es también un nudo de comunicaciones en el que confluyen las rutas entre París, Italia, Suiza y España. Marsella es sede de una Archidiócesis y centro universitario de primer orden fundado en 1409.
Marsella se desarrolló con el nombre de Massalia como colonia comercial fundada por marineros focenses hacia el 600 a. C., conservando los restos más antiguos de la viticultura de Francia introducidos en el siglo IV a. C.. Sede de un vizcondado en el siglo IX dependiente luego del condado de Provenza, fue incorporada a la corona de Francia en 1481 y aprovechó para su crecimiento de la alianza estratégica de ésta con el Imperio otomano durante el Renacimiento y el Antiguo Régimen. Tras la Revolución que bautizó con el nombre de Marsellesa, la marcha militar que más tarde se convirtió en uno de los símbolos nacionales de Francia, la ciudad fue escenario del llamado Terror Blanco y durante el siglo XIX, escenario de un rápido progreso con la expansión colonial francesa hacia Argelia y la apertura del canal de Suez. Fue parcialmente destruida durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial y uno de los objetivos de la Operación Dragoon. Lugar de paso tradicional de los flujos migratorios que fueron incrementando el carácter multicultural de la ciudad, la crisis económica de los años 1970 provocó sin embargo un descenso notable de la población, la pérdida de poder adquisitivo y la acentuación de los conflictos sociales en el último cuarto del siglo XX para ir recuperándose paulatinamente como una de las urbes más importantes de la región Euromediterránea.

Der Chancay Mega-Port ist ein großer Schifffahrtshafen in Chancay, Peru. Er wurde vom chinesischen Unternehmen Cosco Shipping in Zusammenarbeit mit dem peruanischen Unternehmen Volcan gebaut. Der Hafen ist Teil der Belt and Road Initiative und gilt nach peruanischem Recht als privater Hafen für den öffentlichen Gebrauch, der dem Betreiber die Exklusivität zur Erbringung von Hafendienstleistungen gewährt. Der Hafen befindet sich etwa 60 Kilometer nördlich von Lima. Insgesamt werden 3,5 Milliarden US-Dollar (3,3 Milliarden Euro) in den Bau des Hafens und seiner Anlagen investiert. Die Fahrzeit zwischen China und dem Hafen wird auf 10 Tage verkürzt.
 Australia
Australia
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
Women's Soccer World Cup 2023

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race

 Victoria-VIC
Victoria-VIC

 Important port
Important port

墨尔本(英语:Melbourne,缩写作 MEL),简称墨城,是位于澳大利亚东岸维多利亚州南部的一座城市。墨尔本是维多利亚州首府和最大城市,亦是澳大利亚人口排名第二大的城市,也曾是世界最佳宜居城市的榜首[5]。
墨尔本大都会(Greater Melbourne)坐落于菲利普港湾东、北两面的沿岸平原并一直往大分水岭余脉南面的内陆腹地伸延,由31个地方政府区域组成[6],面积达到3858.1平方英里(9992.5平方公里),是全球最广大的都会区之一。雅拉河北岸的墨尔本中央商业区[7]是整个大都会区的中心,位处菲利普港湾北端的雅拉河口湾以东[7],经1993年的行政改制后,现时中央商业区人口约20,000[8],由墨尔本市(City of Melbourne)的地方政府管辖。整个大都会区截止至2016年共有488万人[9][10][11][12][13],市民大多数居住在中央商业区周边30公里范围内,而且居住在城东面的人口远远大于西面。
墨尔本曾经举办过1956年夏季奥运会,是南半球首个举行奥运会的城市;2006年英联邦运动会亦在此举行,被誉为“澳大利亚的文化首都”[14],同时亦是全国的文化、商业、教育、娱乐、餐饮、体育及旅游中心[15]。墨尔本在服饰、艺术、音乐、电视制作、电影及舞蹈等潮流文化领域引领澳大利亚,甚至于全球该领域范围都具备一定的影响力。墨尔本也是澳大利亚多民族文化的中心,拥有着为数众多的移民。
2008年,墨尔本获得英格兰罗浮堡大学的全球化与世界级城市研究小组与网络评为“第一YO级世界都市”[16]。从2002年至今,墨尔本一直占据由《经济学人》选出的世界最佳居住城市的三甲位置[17][18][19][20][21],2011年到2017年连续七年位列第一[22][23]。墨尔本城市的座右铭是“随行聚力”。
Melbourne [ˈmɛɫbən] ist die Hauptstadt des Bundesstaates Victoria in Australien. Sie ist mit 4,3 Millionen Einwohnern nach Sydney die zweitgrößte Stadt des australischen Kontinents (Stand 2018).[1] Die Einwohner von Melbourne werden im Englischen Melburnians genannt.[2] Melbourne wurde 1837 nach dem damaligen britischen Premierminister Lord Melbourne benannt und ist katholischer sowie anglikanischer Erzbischofssitz.
Die aus der Kernstadt Melbourne City mit rund 136.000 Einwohnern (Stand Zensus 2016) und 30 weiteren Gemeinden bestehende Agglomeration ist das wichtigste wirtschaftliche, kulturelle und politische Zentrum Victorias. Die Bevölkerung der Stadt besteht zum größten Teil aus Einwanderern, die u. a. chinesischer, britischer, griechischer, italienischer, irischer, kroatischer oder vietnamesischer Herkunft sind.




 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 United States
United States

 Important port
Important port
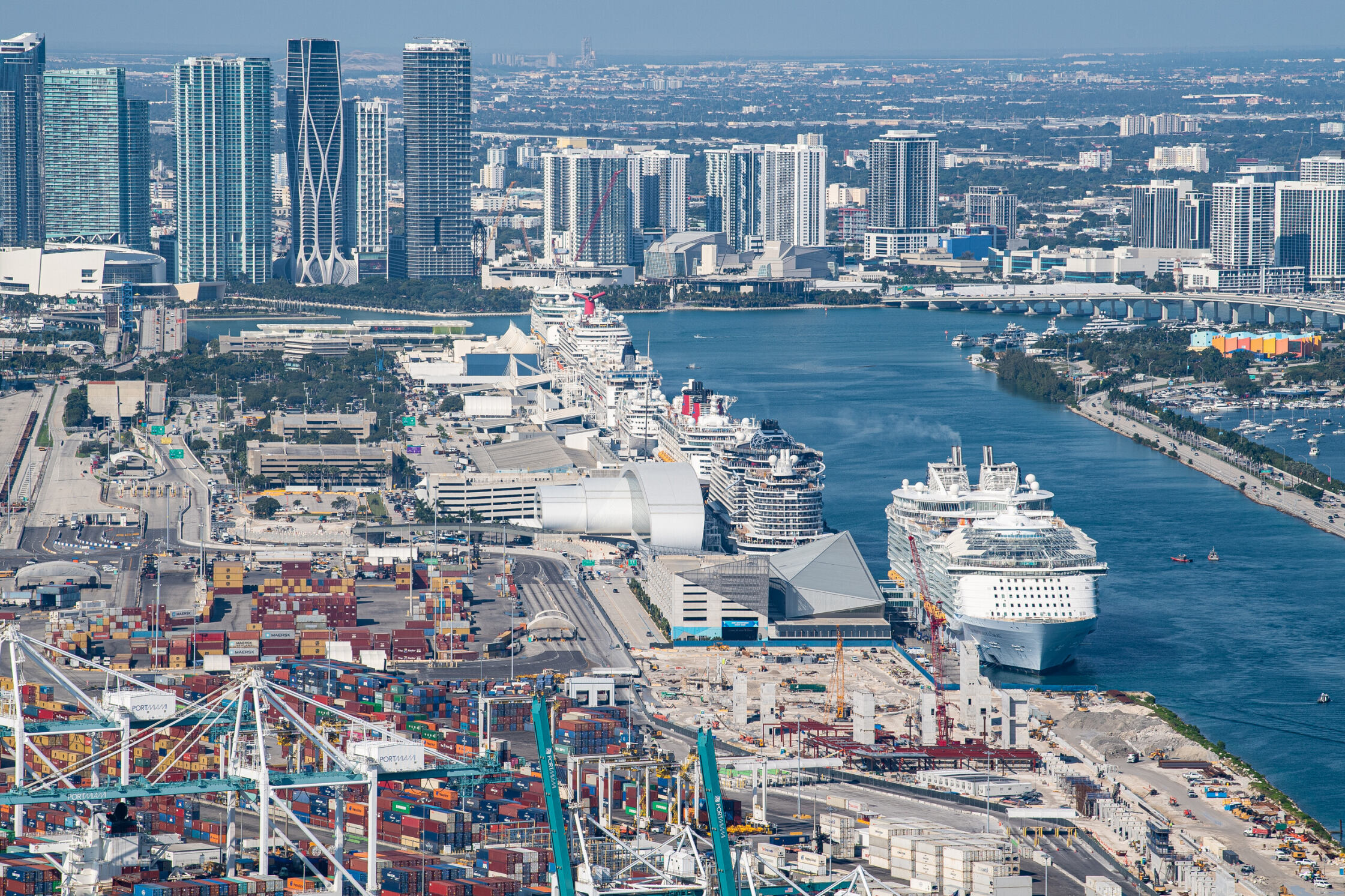




迈阿密(英语:Miami),又译为迈亚美,位于美国佛罗里达州东南角比斯坎湾、佛罗里达大沼泽地和大西洋之间,是该州仅次于杰克逊维尔的第二大城市,也是迈阿密-戴德县最大的城市和县治所在。迈阿密还是迈阿密都会区中最大的城市,这个都市圈由迈阿密-戴德县、布劳沃德县和棕榈滩县组成,人口超过559万人,是美国东南部最大的都市圈,也是全美第四大都市圈[1]。
迈阿密是国际性的大都市,在金融、商业、媒体、娱乐、艺术和国际贸易等方面拥有重要的地位[2],是许多公司、银行和电视台的总部所在。迈阿密还被认为是文化的大熔炉,受庞大的拉丁美洲族群和加勒比海岛国居民的影响很大(当地居民多使用西班牙语和海地克里奥尔语),与北美洲、南美洲、中美洲以及加勒比海地区在文化和语言上关系密切,因此有时还被称为“美洲的首都”。
2008年,迈阿密因其良好的空气质量、大量的植物被覆盖、清洁的饮用水、干净的街道和全市范围的垃圾回收计划而被《福布斯》评为“美国最干净的城市”[3]。2009年,迈阿密还被瑞士联合银行评为美国最富裕城市和全球第五富裕城市[4]。
迈阿密拥有美国第三高的天际线,全市超过300栋摩天大楼。迈阿密市中心是国际银行在美国集中度最高的地方,不少全国性或国际性的公司亦在这里设有办公室[5][6]。迈阿密港在过去20年都被公认为“世界邮轮之都”[7][8]。
Miami [maɪˈæmɪ] (City of Miami) ist eine Stadt und der Verwaltungssitz des Miami-Dade County im US-Bundesstaat Florida mit 442.241 Einwohnern (Stand: 2020).[2] Das Stadtgebiet hat eine Größe von 143,1 km². Die Stadt ist Teil der Metropolregion Miami mit etwa 6,1 Millionen Einwohnern. Der Name „Miami“ kommt von dem indianischen Wort Mayaimi („großes Wasser“), mit dem der Lake Mayaimi (heute Lake Okeechobee) und der dort lebende Indianerstamm Mayaimi bezeichnet wurde. Die Stadt liegt an der Mündung des Miami River in die Biscayne Bay, die ein Teil des Atlantischen Ozeans ist. Nach Jacksonville ist Miami die zweitgrößte Stadt Floridas. Die Mehrheit der Einwohner Miamis spricht Spanisch als Muttersprache.

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Andalusia
Andalusia
