
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Conservative Party
Conservative Party
 Liz Truss
Liz Truss
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Conservative Party
Conservative Party
 Europäische Konservative und Reformer,EKR
Europäische Konservative und Reformer,EKR

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
*Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

Die Conservative and Unionist Party (deutsch Konservative und Unionistische Partei), kurz Conservative Party oder umgangssprachlich Tories genannt, ist eine politische Partei im Vereinigten Königreich im rechten beziehungsweise mittig-rechten Spektrum und besteht seit dem 19. Jahrhundert. Ausrichtung Konservatismus Neoliberalismus[1] Wirtschaftsliberalismus EU-Skepsis Britischer Unionismus Farbe(n) blau Jugendorganisation Young Conservatives
保守党(英语:Conservative Party),正式名称是保守与统一党(Conservative and Unionist Party),俗称托利党(Tory Party),是英国中间偏右政党,也是英国历史最悠久的政党,与工党并列为英国两大主要政党。意识形态: 保守主义 一国保守主义, 英国保守主义, 新自由主义, 经济自由主义, 英国联合主义, 欧洲怀疑主义 政治立场 中间偏右至右翼 派系: 欧洲组织 欧洲保守派和改革主义者党 国际组织 国际民主联盟 官方色彩 蓝色


 *UK political system
*UK political system

 European Union
European Union
 Supreme Court of the Member States of the EU
Supreme Court of the Member States of the EU

 Party and government
Party and government
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Labour Party
Labour Party

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
*Political parties with more than a hundred years of history
 Social Democratic Party of Europe
Social Democratic Party of Europe
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

工党(英语:Labour Party)是英国中间偏左政党,与保守党并列为英国两大主要政党。目前为英国下议院最大党,亦是英国的执政党。意识形态 社会民主主义 民主社会主义 社会自由主义 进步主义 政治立场 中间偏左 国内组织 劳工与合作党 欧洲组织 欧洲社会党
Die Labour Party [ˈleɪbə ˈpɑːti][3] (englisch für „Arbeitspartei“ oder „Partei der Arbeit“; auch nur Labour genannt) ist eine sozialdemokratische Partei im Vereinigten Königreich. Bald nach ihrer Gründung 1900 wurde sie neben der Conservative Party und den Liberal Democrats zu einer der drei großen politischen Parteien des Vereinigten Königreichs mit Ausnahme Nordirlands, wo die Partei nicht aktiv ist. Dort kooperiert die Labour Party stattdessen mit der Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP). Die genossenschaftliche Co-operative Party agiert als Schwesterpartei von Labour und tritt bei Wahlen unter der Bezeichnung „Labour and Co-operative Party“ an.

Das Parlament des Vereinigten Königreichs (englisch Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland; kurz UK Parliament) ist ein Verfassungsorgan der britischen Monarchie. Es besteht aus zwei Kammern, dem House of Commons (Unterhaus) und dem House of Lords (Oberhaus). Beide tagen im Palace of Westminster in London.
大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国议会(英语:The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland),中文简称为英国议会或联合王国议会,是英国和英国海外领地(独自享有议会主权)的最高立法机关。英国议会的首领为英国君主;它还包括上议院和下议院。上议院议员分为两种:上议院灵职议员(Lords Spiritual,即英国国教中的高级神职人员)和上议院俗职议员(Lords Temporal,即贵族成员)。上议院议员大部分是以指派方式产生。下议院则恰恰相反,是由选举产生。上议院和下议院位于大伦敦威斯敏斯特市威斯敏斯特宫(即议会大厦)的上议院厅和下议院厅。
议会是由早期为君主提出治国建议的政务会发展而来。理论上议会的权力并不归属于议会,而属于“君临议会”(Crown-in-Parliament)。尽管有争议,议会中的君王仍常被认为是完整的君主主权。现代的议会权力属于通过民主选举而产生的下议院;君主仅作为象征意义的领袖,而由非选举产生的上议院,其权力也十分有限。




 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Australia
Australia
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Dominica
Dominica
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 India
India
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nauru
Nauru
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Uganda
Uganda
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 Cyprus
Cyprus

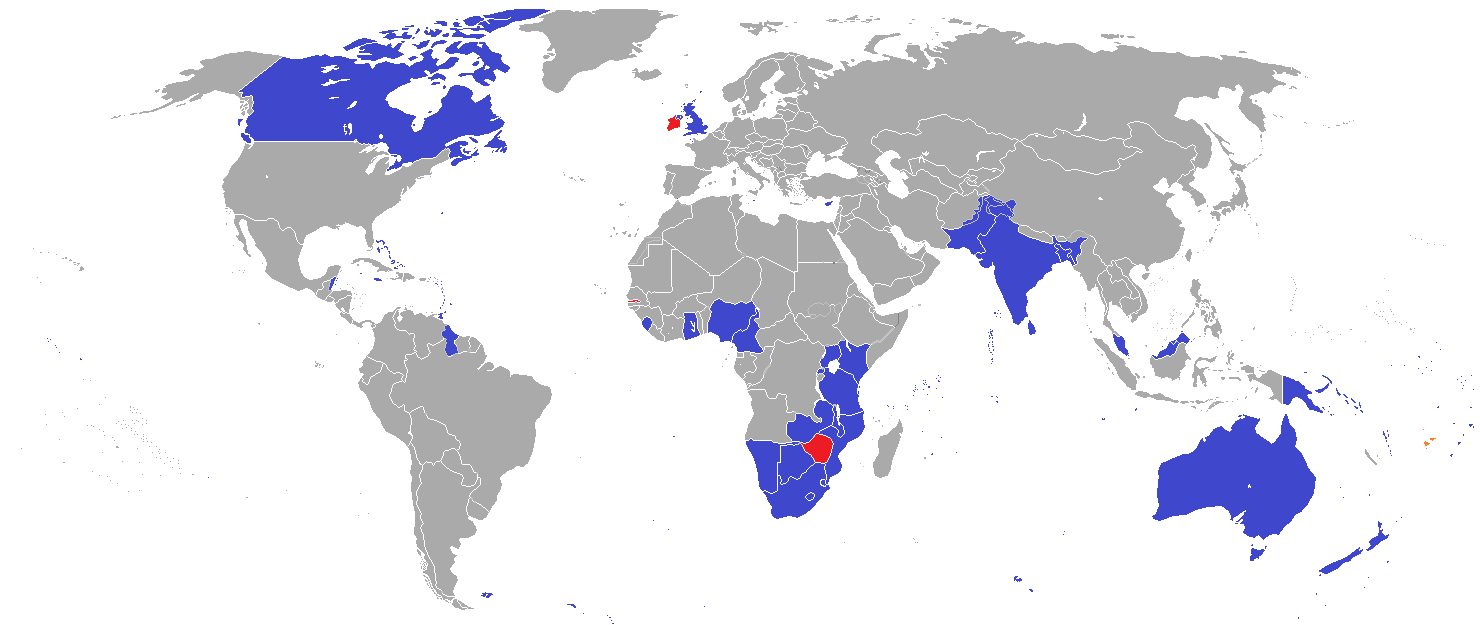
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].




 Law
Law
 Geography
Geography