
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 英国
英国
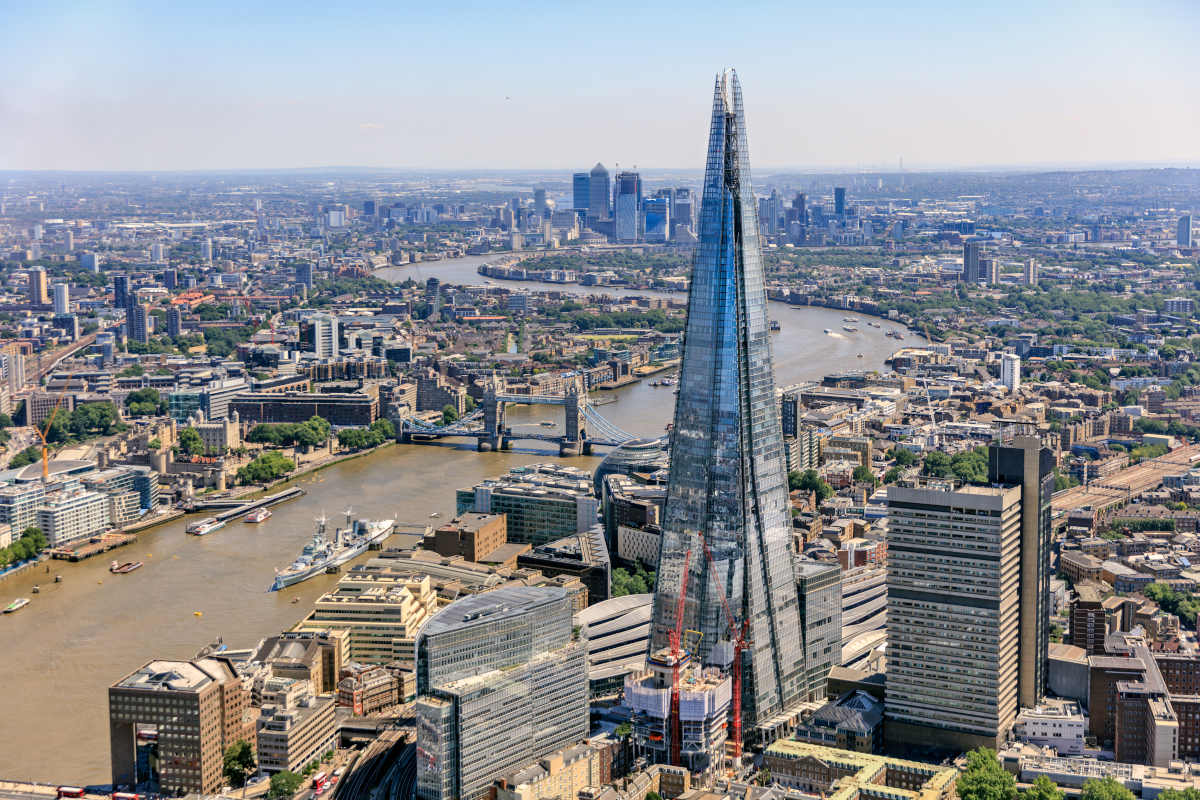

泰晤士河(英语:River Thames,![]() i/tɛmz/,TEMZ)是位于南英格兰的一条河流,全长约346公里,流经英格兰的三个郡,为英格兰最长之河流、英国第二长河,次于354公里的塞文河,也是全世界水面交通最繁忙的都市河流和伦敦地标之一。在泰晤士流域形成了许多英格兰城市,除去伦敦之外,还有牛津、雷丁和温莎等。
i/tɛmz/,TEMZ)是位于南英格兰的一条河流,全长约346公里,流经英格兰的三个郡,为英格兰最长之河流、英国第二长河,次于354公里的塞文河,也是全世界水面交通最繁忙的都市河流和伦敦地标之一。在泰晤士流域形成了许多英格兰城市,除去伦敦之外,还有牛津、雷丁和温莎等。
泰晤士河在英国有非常重要的经济地位,在工业革命之后因为大规模的河上运输导致河流污染,因而引发了包括瘟疫、大恶臭等一系列的问题,随着重工业的减少其情况已经改善了许多。
而其于英国文化意义也不可忽视。泰晤士河是许多英国水上运动,如牛津剑桥赛艇对抗赛、1908年夏季奥运会划艇赛、1948年夏季奥运会划艇赛的举办地。《柳林风声》等文学作品也是以泰晤士河流域的风物为背景写成的。
Die Themse (englisch River Thames [tɛmz]; in der Antike lateinisch Tamesis, bei Tacitus auch lateinisch Tamesa oder altgriechisch Τάμεσα Támesa bei den griechischen Geographen) ist ein durch Südengland fließender Fluss, der London mit der Nordsee (Mündung) verbindet. Nach dem Severn ist die Themse mit 346 km der zweitlängste Fluss in Großbritannien.
Trotz ihrer Bekanntheit und ihrer Flusslänge wird die Themse meist nicht zu den großen europäischen Flüssen gezählt. Der mittlere Abfluss in Kingston upon Thames beträgt 66 m³/s, dies ist weniger als zum Beispiel die Wasserführung der Ruhr oder der Ems. Weil sie – auch im Stadtgebiet Londons – durchaus breit ist, fließt sie sehr langsam.
テムズ川(River Thames ![]() [temz])は、南イングランドを流れる川であり、ロンドンを海とつないでいる。代表的なエスチュアリーの入り江をつくる河川である。テームズ川とも表記される。
[temz])は、南イングランドを流れる川であり、ロンドンを海とつないでいる。代表的なエスチュアリーの入り江をつくる河川である。テームズ川とも表記される。
ルネサンス期にギリシア語が語源であるという誤った認識が広まり、読み方を変えずにTemeseからThamesに綴りが変更されている。
The River Thames, (/tɛmz/ (![]() listen) TEMZ) known alternatively in parts as the Isis is a river that flows through southern England including London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.
listen) TEMZ) known alternatively in parts as the Isis is a river that flows through southern England including London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.
It flows through Oxford (where it is called the Isis), Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. It rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire, and flows into the North Sea via the Thames Estuary. The Thames drains the whole of Greater London.[1]
Its tidal section, reaching up to Teddington Lock, includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of 7 metres (23 ft). Running through some of the driest parts of mainland Britain and heavily abstracted for drinking water, the Thames' discharge is low considering its length and breadth: the Severn has a discharge almost twice as large on average despite having a smaller drainage basin. In Scotland, the Tay achieves more than double the Thames' average discharge from a drainage basin that is 60% smaller.
Along its course are 45 navigation locks with accompanying weirs. Its catchment area covers a large part of south-eastern and a small part of western England; the river is fed by 38 named tributaries.[citation needed] The river contains over 80 islands. With its waters varying from freshwater to almost seawater, the Thames supports a variety of wildlife and has a number of adjoining Sites of Special Scientific Interest, with the largest being in the remaining parts of the North Kent Marshes and covering 5,449 hectares (13,460 acres).[2]
La Tamise (en anglais : Thames [ˈtemz]) est un fleuve du sud de l'Angleterre, qui se jette dans la mer du Nord.
D'une longueur totale de 346 km, c’est le plus long fleuve dont le cours se trouve entièrement en Angleterre (qui à la fois commence et finit en Angleterre) et le second plus long pour le Royaume-Uni (après la Severn). La Tamise prend sa source à Thames Head, dans le Gloucestershire, puis coule en direction de l'est, vers Oxford et Reading, puis traverse Londres, dont elle tire sa renommée et aboutit enfin dans la mer du Nord, grâce à son estuaire.
La marée remonte jusqu'à Teddington Lock (en). Le bassin versant recouvre une grande partie du sud-est et de l'ouest de l’Angleterre. La Tamise est alimentée par de nombreux affluents et est parsemée de plus de 80 îles. La faune et la flore y sont très variées, grâce à de grandes étendues d’eau douce et d’eau de mer à la fois.
L'activité humaine a profité de la Tamise pendant des milliers d’années pour en tirer son eau, sa nourriture, et son énergie. Le fleuve est une voie commerciale majeure pour le commerce international grâce au port de Londres, et le système britannique des canaux (en) permet d’en faire profiter le reste de son cours. La position stratégique de la rivière en a fait un lieu central de l’histoire de l'Angleterre et du Royaume-Uni1.
Plus récemment, la rivière est devenue une aire majeure de loisirs grâce au tourisme et aux sports, tels l'aviron, la voile, le kayak, le skiff et la péniche. La rivière a un attrait particulier auprès des écrivains, des peintres, des musiciens et des réalisateurs de cinéma. Elle est encore l’objet de nombreux débats, à propos de son tracé, de sa nomenclature et de son histoire.
Il Tamigi (AFI: /taˈmiʤi/[1]; in inglese Thames, pron. /tɛmz/, dal latino Tamĕsis) è un fiume dell'Inghilterra meridionale che attraversa Londra e sfocia ad est nel Mare del Nord: ancorché non sia il maggiore per lunghezza e portata, è da considerare di gran lunga il primo fiume del Regno Unito per importanza storica ed economica. Il suo bacino idrografico è abitato da circa 15 milioni di persone.
El río Támesis (del latín Taměsis; en inglés, River Thames, pronunciado /tɛmz/) es un río del sur de Inglaterra. Nace en el condado de Gloucestershire, pasa por Oxford, Eton y Londres y desemboca en el mar del Norte. Su longitud es de 346 km. Hoy en día es el río más importante de Inglaterra y la principal fuente de abastecimiento de agua en Londres.
Те́мза (англ. Thames [ˈtɛmz], лат. Tamesis, в пределах Оксфорда также А́йзис, англ. Isis) — река на юге Великобритании.
Длина — 334 км, площадь бассейна — 15 300 км². Средний расход воды — 65,8 м³/с.[источник не указан 545 дней]
Берёт начало на возвышенности Котсуолд-Хилс (высота истока — 110 м над уровнем моря[источник не указан 545 дней]), протекает в черте Лондона, впадает в Северное море, образуя эстуарий. Ширина реки в черте Лондона 200—250 м, ширина эстуария от 650 м (близ восточной окраины Лондона) до 16 км (близ устья). Питание дождевое. Средний расход воды в низовьях 260 м³/с, максимальный — зимой.
Ледостав наблюдается лишь в очень холодные зимы. Нижнее течение Темзы подвержено влиянию приливов (их высота в Лондоне до 6—6,5 м), которые достигают Теддингтона (где русло Темзы перегорожено плотиной). Для защиты прилегающих к Темзе территорий от наводнений берега нижнего течения реки и эстуария укреплены защитными дамбами, а в городах — набережными.
Судоходна почти на всём протяжении; небольшие баржи доходят до города Лечлейд (311 км от устья). До Лондона поднимаются суда водоизмещением до 800 т, а океанские суда доходят до города Тилбери. На Темзе — столица Великобритании город Лондон, города Оксфорд, Рединг.
Темза соединена старыми каналами (Оксфордский канал и др.) с Бристольским заливом, Ирландским морем и промышленными районами центральной части страны. На Темзе регулярно проводится Королевская регата Хенли.
 阿尔萨斯
阿尔萨斯
 安道尔
安道尔

 奥弗涅-罗纳-阿尔卑斯
奥弗涅-罗纳-阿尔卑斯
 比利时
比利时
 勃艮第-弗朗什-孔泰
勃艮第-弗朗什-孔泰
 香槟-阿登
香槟-阿登
 丹麦
丹麦
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 英格兰
英格兰
 弗朗茨-孔代
弗朗茨-孔代
 法国
法国

 大东部大区
大东部大区

 上法兰西大区
上法兰西大区

 法兰西岛
法兰西岛
 意大利
意大利
 洛林
洛林
 北部-加来海峡
北部-加来海峡

 北莱茵-威斯特法伦州
北莱茵-威斯特法伦州

 新阿基坦大区
新阿基坦大区

 奥克西塔尼大区
奥克西塔尼大区
 瑞士
瑞士
 西班牙
西班牙
 托斯卡纳大区
托斯卡纳大区
 环法自行车赛 2015
环法自行车赛 2015
 环法自行车赛 2016
环法自行车赛 2016
 环法自行车赛 2017
环法自行车赛 2017
 环法自行车赛 2018
环法自行车赛 2018
 UCI世界巡回赛
UCI世界巡回赛
 英国
英国
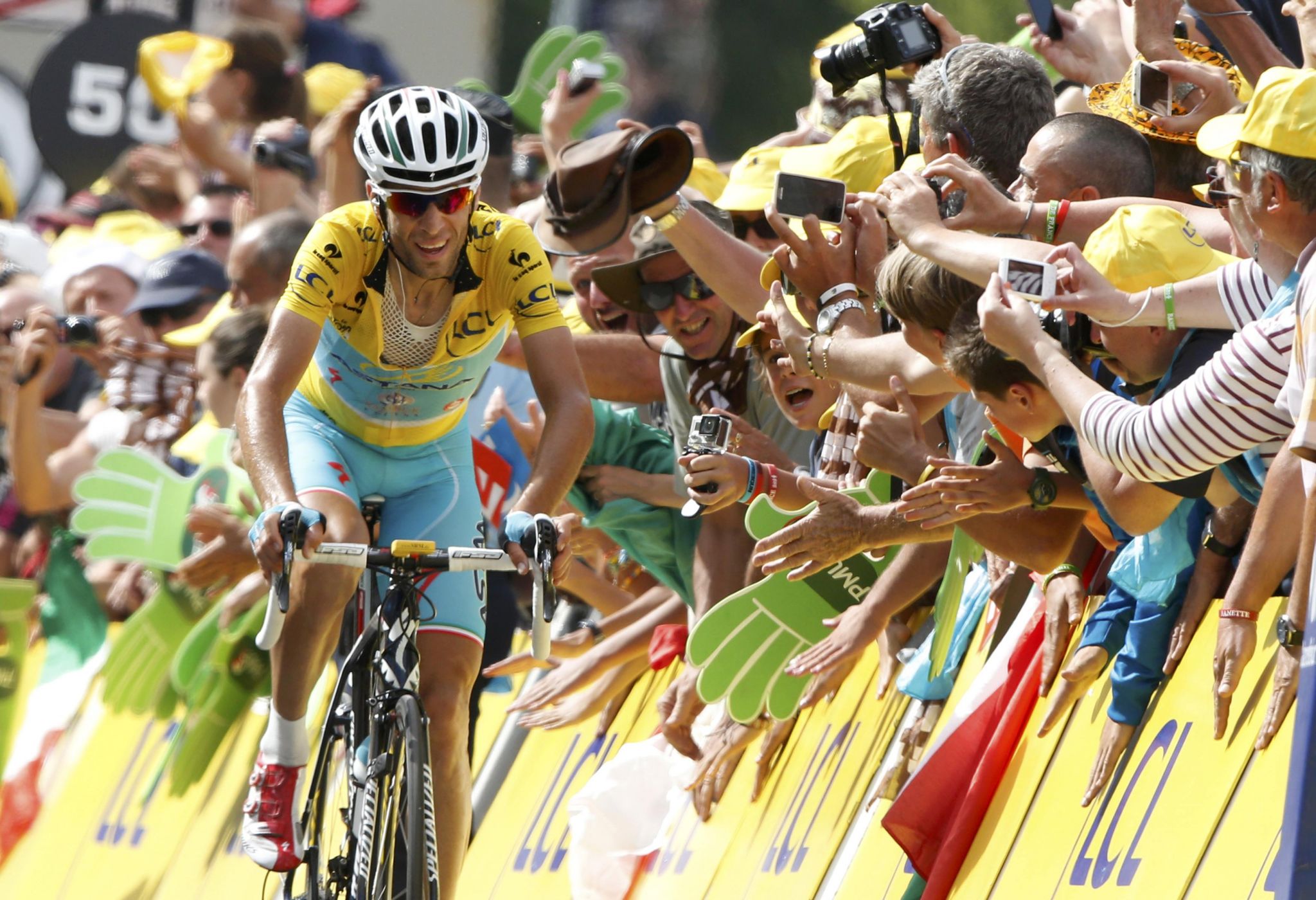





环法自行车赛(Tour de France)是一项分赛程的长距离自行车骑行比赛,它由法国人亨利・戴斯格朗日(Henri Desgrange)于1903年创立。每年夏天的七月份,来自世界各国的骑行高手们就会云集法国,在这里翻山越岭穿村过市,在举世闻名的自行车赛界的最高竞技中一决高下。
环法自行车赛的产生及历史
亨利・戴斯格朗日曾是一位自行车运动员,后来做了记者,但他从未放弃对骑行的热爱。他于1903年创立了环法自行车赛最初的规则。其中有一些规则给参赛选手专心进行体育竞技带来了很大的不便。比如说参赛者不可以使用助手,也就是说如果参赛者的自行车出现了机械故障,要由他自己停下来把车修好才可以再上路。
其实环法自行车赛不仅限于法国境内,它还经过比利时、西班牙等一些法国的邻国。比赛属于分段计时赛,冠军为各段赛程所用时间累计最少者。
(Quelle:http://www.faguo-lvyou.cn)
环法自行车赛(法语:Le Tour de France)是一个每年举办的多赛段公路自行车赛,主要在法国进行,但有时也出入周边国家(如英国、比利时、德国、西班牙)。自从1903年开始以来,每年于夏季举行,每次赛期23天,平均赛程超过3500公里(约2200英里)。完整赛程每年不一,但大都大体上环绕法国一周。近年来,比赛结束前总是会穿越巴黎市中心的香榭丽舍大道,并且经过埃菲尔铁塔。比赛全程分成许多段,从一个城镇到下一个,每一段分别计时排名。所有段成绩累计起来决定每一位赛手的总成绩,总冠军为各段时间累计最少者。在每日赛事结束时,领先者将可穿上黄色领骑衫,最佳冲刺者将被赠与一件绿色车衣,山间赛事中之最佳骑手将会得到一件波尔卡点运动衣,其有时被称作登山王。
像其他公路大赛一样,选手们组织队伍参赛。每一队由9名选手组成,共有20至22个小队。传统上,只有一流的专业赛车队才能收到参赛邀请。近年来,大赛组织者采用国际自行车联盟的计分系统来决定参赛队伍,另留下2-4个名额给予知名车队或落选的法国车队。每个车队由其最大赞助商命名,穿着其队服。比赛时,各车队采取战术,队友之间互相帮助,通常车队后面还有一部支援车带着配件等备急紧跟着他们[1][2]。
Am 8. Dez. 1867 fand das erste Radrennen der Welt in Paris statt. Anfangs noch auf dem Vélocipèd, ohne Bereifung, wurden selten Geschwindigkeiten von 10 km/h erreicht. Etwa 100 Teilnehmer starteten auf den Champs-Elysées und fuhren etwa 23 km bis zum Schloß von Versaille. Das zweite Rennen fand am 24. Mai 1868 am Pré Catalan im Bois du Boulongne statt.
Das erste "Langstreckenrennen" der Welt, Paris-Rouen über 122 km wurde am 7. Nov. 1869 gefahren.
Bis kurz vor 1890 wurden verschiedene Rennen mit dem Hochrad ausgetragen, was sehr gefährlich war. Mit der Erfindung der Luftbereifung 1888 endete die ära der Hochräder abrupt.
Diese "Sicherheits-Niederräder" entsprechen grob dem Aussehen heutiger Fahrräder und wurden erstmalig in Großserie produziert.
Bereits 1891 wurden 2 berühmte Radrennen ins Leben gerufen, die noch heute gefahren werden: Paris-Brest-Paris über ca. 1.200 km und Bordeaux-Paris, welches halb so lang ist.(Quelle:http://www.fahrradmonteur.de/tour-de-france.php)
Die Tour de France [ˌtuʀdəˈfʀɑ̃ːs], auch Grande Boucle [gʀɑ̃dˈbukl] (französisch für Große Schleife) oder einfach Le Tour [ləˈtuːʀ] genannt, ist das berühmteste und für die Fahrer bedeutendste Radrennen der Welt.
Seit 1903 wird es alljährlich im Juli ausgetragen und führt dabei in wechselnder Streckenführung quer durch Frankreich und das nahe Ausland. Während des Ersten Weltkriegs fiel die Tour zwischen 1915 und 1918 aus, der Zweite Weltkrieg bedingte eine Unterbrechung von 1940 bis 1946. Das Etappenrennen wird von der Amaury Sport Organisation (ASO) veranstaltet. Die Tour wird oft als das nach den Olympischen Spielen und der Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft drittgrößte Sportereignis der Welt[1][2] oder als das größte jährlich stattfindende Sportereignis[3] bezeichnet und gilt als das härteste Radrennen der Welt.[4]
Eine Tour de France der Frauen, La Grande Boucle Féminine Internationale, wurde mit Unterbrechungen von 1984 bis 2009 ausgetragen. Länge und Bedeutung waren im Vergleich zur Tour der Männer gering. Als Nachfolgeveranstaltung wird seit 2014 La Course by Le Tour de France, zu Beginn als Rundstreckenrennen vor der Schlussetappe der Tour de France 2014, ausgetragen.
ツール・ド・フランスまたは(ル・)トゥール・ド・フランス(仏: Le Tour de France、以下「ツール」)とは毎年7月にフランスおよび周辺国を舞台にして行われる自転車プロロードレースである。1903年から開催されている。主催は傘下にスポーツ新聞レキップや一般紙ル・パリジャンなどを抱えるフランスの大企業・アモリ・スポル・オルガニザシオン (ASO, Amaury Sport Organisation)。
名称はフランス語で「フランス一周」を意味する[1]。フランス語による同様の名称のレースには、スイスで行われるツール・ド・スイスなどがある。単にル・ツール(Le Tour:ル・トゥール)と称されることもある。
The Tour de France (French pronunciation: [tuʁ də fʁɑ̃s]) is an annual men's multiple stage bicycle race primarily held in France,[1] while also occasionally passing through nearby countries. Like the other Grand Tours (the Giro d'Italia and the Vuelta a España), it consists of 21 day-long stages over the course of 23 days.
The race was first organized in 1903 to increase sales for the newspaper L'Auto[2] and is currently run by the Amaury Sport Organisation.[3] The race has been held annually since its first edition in 1903 except when it was stopped for the two World Wars.[4] As the Tour gained prominence and popularity, the race was lengthened and its reach began to extend around the globe. Participation expanded from a primarily French field, as riders from all over the world began to participate in the race each year. The Tour is a UCI World Tour event, which means that the teams that compete in the race are mostly UCI WorldTeams, with the exception of the teams that the organizers invite.[5][6]
Traditionally, the race is held primarily in the month of July. While the route changes each year, the format of the race stays the same with the appearance of time trials,[1] the passage through the mountain chains of the Pyrenees and the Alps, and the finish on the Champs-Élysées in Paris.[7][8] The modern editions of the Tour de France consist of 21 day-long segments (stages) over a 23-day period and cover around 3,500 kilometres (2,200 mi).[9] The race alternates between clockwise and counterclockwise circuits of France.[10]
There are usually between 20 and 22 teams, with eight riders in each. All of the stages are timed to the finish; the riders' times are compounded with their previous stage times.[1] The rider with the lowest cumulative finishing times is the leader of the race and wears the yellow jersey.[1][11] While the general classification garners the most attention, there are other contests held within the Tour: the points classification for the sprinters, the mountains classification for the climbers, young rider classification for riders under the age of 26, and the team classification for the fastest teams.[1] Achieving a stage win also provides prestige, often accomplished by a team's cycling sprinter specialist.
Le Tour de France, souvent appelé « Le Tour » ou « la Grande Boucle », est une compétition cycliste par étapes masculine qui a lieu principalement en France chaque année, tout en traversant occasionnellement les pays voisins. La course est organisée pour la première fois en 1903 par Henri Desgrange et Géo Lefèvre, pour augmenter les ventes du journal L'Auto. Le Tour est actuellement organisé par ASO (Groupe Amaury). La course a lieu chaque année depuis sa première édition en 1903, excepté lors des deux guerres mondiales. Le Tour gagne en importance et en popularité au fil des éditions, sa durée est allongée et sa portée s'étend dans le monde entier. La participation s'élargit, on passe d'un peloton principalement français lors des premières éditions, à des éditions comptant jusqu'à 40 nationalités.
Le Tour de France, le Tour d'Italie et le Tour d'Espagne constituent les trois grands tours, les épreuves les plus prestigieuses du cyclisme sur route. Le Tour de France est le plus ancien et est généralement considéré comme le plus prestigieux des trois. Traditionnellement, la course se déroule principalement au mois de juillet. Bien que le parcours change chaque année, le format de la course reste le même avec au moins deux contre-la-montre1, le passage à travers les chaînes de montagnes des Pyrénées et des Alpes et l'arrivée sur les Champs-Élysées à Paris. Les éditions modernes du Tour de France se composent de 21 étapes réparties sur une période de 23 jours et couvrent près de 3 500 kilomètres. Le tracé du parcours alterne entre le sens horaire et antihoraire de la France.
Le Tour est une des épreuves de l'UCI World Tour, ce qui signifie que les équipes sont en majorités composées d'UCI WorldTeams, à l'exception des équipes que les organisateurs invitent. Le nombre d'équipes varie habituellement entre 20 et 22, avec chacune huit coureurs. Après chaque étape, les temps des coureurs sont ajoutés avec leurs temps précédents. Le coureur avec le temps total le plus faible est classé premier du classement général et porte le très convoité maillot jaune le distinguant des autres coureurs. Le classement général est le plus réputé des classements car il détermine le vainqueur du Tour, mais d'autres classements secondaires sont organisés lors du Tour : le classement par points pour les sprinteurs, le classement de la montagne pour les grimpeurs, le classement des jeunes pour les coureurs de 25 ans et moins, et le classement par équipes pour les équipes les plus rapides.
Quatre coureurs ont remporté cinq fois le Tour de France : Jacques Anquetil, Eddy Merckx, Bernard Hinault et Miguel Indurain. Lance Armstrong, vainqueur de sept Tours entre 1999 et 2005, fut le recordman jusqu'en 2012 lorsque ses sept victoires furent effacées pour cause de dopage. Christopher Froome est toujours en activité, avec quatre succès à son actif.
Le Tour de France (it. Il Giro di Francia) è uno dei tre grandi giri maschili di ciclismo su strada e uno tra i più importanti avvenimenti sportivi del mondo. È parte del calendario professionistico UCI World Tour.
Detto anche Tour o Grande Boucle, a partire dal 1903 la corsa si è svolta ogni anno (risultando il più antico grande Giro), ad eccezione dei periodi della prima e della seconda guerra mondiale, durante il mese di luglio, nell'arco di circa tre settimane e su un percorso ogni volta diverso attraverso la Francia e i paesi confinanti. Attualmente l'organizzazione della gara è affidata alla Société du Tour de France, una sussidiaria dell'Amaury Sport Organisation, che fa parte del gruppo mediatico de L'Équipe.
A partire dal 1984 e fino al 1993 venne organizzato parallelamente anche un Tour de France femminile, con un percorso e tappe più brevi.
El Tour de Francia (oficialmente Le Tour de France), también conocido simplemente como el Tour, es una vuelta por etapas profesional de ciclismo en ruta disputada a lo largo de la geografía francesa. Se celebra en julio y pertenece al calendario UCI WorldTour, máxima categoría de las carreras profesionales
Considerada la carrera más importante del mundo,1 el Tour se disputó por primera vez en 1903. Desde su creación, la carrera se ha visto interrumpida en dos ocasiones debido a las dos guerras mundiales: desde 1915 hasta 1918 y desde 1940 hasta 1946.2
Es la más antigua de las conocidas tres "Grandes Vueltas" del ciclismo, junto al Giro de Italia y la Vuelta a España.
El ganador del Tour de Francia obtiene 1800 puntos para el Salón de la Fama del Ciclismo (Cycling Hall of Fame), siendo la prueba ciclista que más puntos otorga al ganador.
Con cinco triunfos, son cuatro los ciclistas que poseen el récord de victorias en La Grande Boucle: Jacques Anquetil (1957, 1961, 1962, 1963 y 1964), Eddy Merckx (1969, 1970, 1971, 1972 y 1974), Bernard Hinault (1978, 1979, 1981, 1982 y 1985) y Miguel Indurain (1991, 1992, 1993, 1994 y 1995).
El Tour de Francia fue galardonado con el Premio Príncipe de Asturias de los Deportes en el año 2003.3
Existió un Tour de Francia femenino que comenzó en 1955 (desde 1984 disputándose con regularidad) hasta 2009, siendo de las pocas carreras femeninas con una duración superior a una semana junto al Giro de Italia Femenino y el Tour de l'Aude Femenino (este también ya desaparecido), aunque durante sus últimos 15 años sin relación con la de hombres.
Тур де Франс[1] (нескл.; фр. Le Tour de France) — шоссейная многодневная велогонка, один из трёх гранд-туров. Самая известная и престижная велосипедная гонка мира, проводимая уже более ста лет во Франции[2]. Неофициальное название — «Большая петля».
Велогонка «Тур де Франс» изначально была учреждена как рекламный проект газеты L’Auto (предок нынешнего L'Équipe), его редактором и соучредителем, Анри Дегранжем (Henri Desgrange) и был призван конкурировать с велогонкой Париж — Брест — Париж (спонсируемой газетой Le Petit Journal) и велогонкой Бордо-Париж.
Идея создания французской петли принадлежит журналисту L’Auto Жео Лефевру (Géo Lefèvre), с которым Анри Дегранж обедал в парижском кафе Café de Madrid 20 ноября 1902 года (точная дата). Успех гонки Le Tour de France стал большим успехом и для газеты L’Auto, число подписчиков которой выросло в 1903 году с 25 тысяч (до Тура) до 65 тысяч после Тура; в 1908 году число подписчиков газеты перевалило за 250 тысяч, а во время «Тур де Франс» 1923 года продавалось 500 тысяч экземпляров газеты в день. Рекордный тираж газеты был достигнут в течение «Тур де Франс» 1933 года — 854 тысячи экземпляров в день. Сегодня Тур организовывает «Общество Тур-де-Франс» — филиал Amaury Sport Organisation (ASO), который является частью медиа-холдинга, в который входит газета L'Équipe.
Тур, который проводится во Франции и в близлежащем зарубежье, проходит ежегодно в течение трёх недель в июле. Только во время первой (1915—1918) и Второй мировой войны (1940—1946) тур был отменён. Велогонку проводит фирма Amaury Sport Organisation (ASO), которая также проводит Ралли Дакар.

Die Turks- und Caicosinseln, manchmal auch nur Turks & Caicos genannt, sind ein Britisches Überseegebiet auf den Westindischen Inseln. Es besteht aus zwei Inselgruppen, den Turks- und den Caicos-Inseln.
特克斯和凯科斯群岛(英语:Turks and Caicos Islands,/ˈtɜːks/和/ˈkeɪkəs/ / /ˈkeɪkoʊs/ / /ˈkeɪkɒs/)),中文简称特凯,位于中美洲巴哈马群岛东南的英国海外领土,属西印度群岛内卢卡亚群岛的一部分。由特克斯群岛[6]和凯科斯群岛30多个岛屿组成,其中8个岛屿常年有人定居,面积430平方千米,欧洲联盟资料为417平方千米(161平方英里)[12]。
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术

 媒体和新闻
媒体和新闻
 企业
企业

 地理
地理
 体育
体育

 音乐
音乐
 欧洲的高等院校
欧洲的高等院校

 历史
历史




 汽车
汽车



 美食家
美食家
