漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州


 阿拉巴马州
阿拉巴马州
 阿拉斯加州
阿拉斯加州
 阿利桑那州
阿利桑那州

 阿肯色州
阿肯色州

 教育和研究
教育和研究
 美国的高等院校
美国的高等院校

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州

 科罗拉多州
科罗拉多州

 康涅狄格州
康涅狄格州

 特拉华州
特拉华州

 佛罗里达州
佛罗里达州

 乔治亚州
乔治亚州

 夏威夷州
夏威夷州

 爱达荷州
爱达荷州

 伊利诺斯州
伊利诺斯州

 印第安纳州
印第安纳州

 爱荷华州
爱荷华州

 堪萨斯州
堪萨斯州

 肯塔基州
肯塔基州

 路易斯安那州
路易斯安那州

 缅因州
缅因州

 马里兰州
马里兰州

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 密歇根州
密歇根州

 明尼苏达州
明尼苏达州

 密西西比州
密西西比州

 密苏里州
密苏里州

 蒙大拿州
蒙大拿州

 内布拉斯加州
内布拉斯加州

 内华达州
内华达州

 新罕布什尔州
新罕布什尔州

 新泽西州
新泽西州
 新墨西哥州
新墨西哥州

 纽约州
纽约州

 北卡罗来纳州
北卡罗来纳州

 北达科他州
北达科他州

 俄亥俄州
俄亥俄州

 俄克拉荷马州
俄克拉荷马州

 俄勒冈州
俄勒冈州

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州

 罗得岛州
罗得岛州

 南达科他州
南达科他州

 田纳西州
田纳西州

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州

 美国的大学
美国的大学

 犹他州
犹他州
 美国
美国

 佛蒙特州
佛蒙特州

 弗吉尼亚州
弗吉尼亚州

 华盛顿州
华盛顿州

 华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区

 西弗吉尼亚州
西弗吉尼亚州

 威斯康辛州
威斯康辛州

 怀俄明州
怀俄明州

 阿拉巴马州
阿拉巴马州

 阿拉斯加州
阿拉斯加州

 阿利桑那州
阿利桑那州

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州

 科罗拉多州
科罗拉多州

 康涅狄格州
康涅狄格州

 爱达荷州
爱达荷州

 伊利诺斯州
伊利诺斯州

 印第安纳州
印第安纳州

 爱荷华州
爱荷华州

 缅因州
缅因州

 马里兰州
马里兰州

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 密歇根州
密歇根州

 明尼苏达州
明尼苏达州

 密苏里州
密苏里州

 蒙大拿州
蒙大拿州

 内华达州
内华达州

 新罕布什尔州
新罕布什尔州

 新泽西州
新泽西州

 新墨西哥州
新墨西哥州

 纽约州
纽约州

 北卡罗来纳州
北卡罗来纳州

 北达科他州
北达科他州

 俄亥俄州
俄亥俄州

 俄勒冈州
俄勒冈州

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州

 罗得岛州
罗得岛州

 南达科他州
南达科他州

 体育
体育

 田纳西州
田纳西州

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州

 犹他州
犹他州
 美国
美国

 佛蒙特州
佛蒙特州

 弗吉尼亚州
弗吉尼亚州

 华盛顿州
华盛顿州

 西弗吉尼亚州
西弗吉尼亚州

 威斯康辛州
威斯康辛州

 怀俄明州
怀俄明州
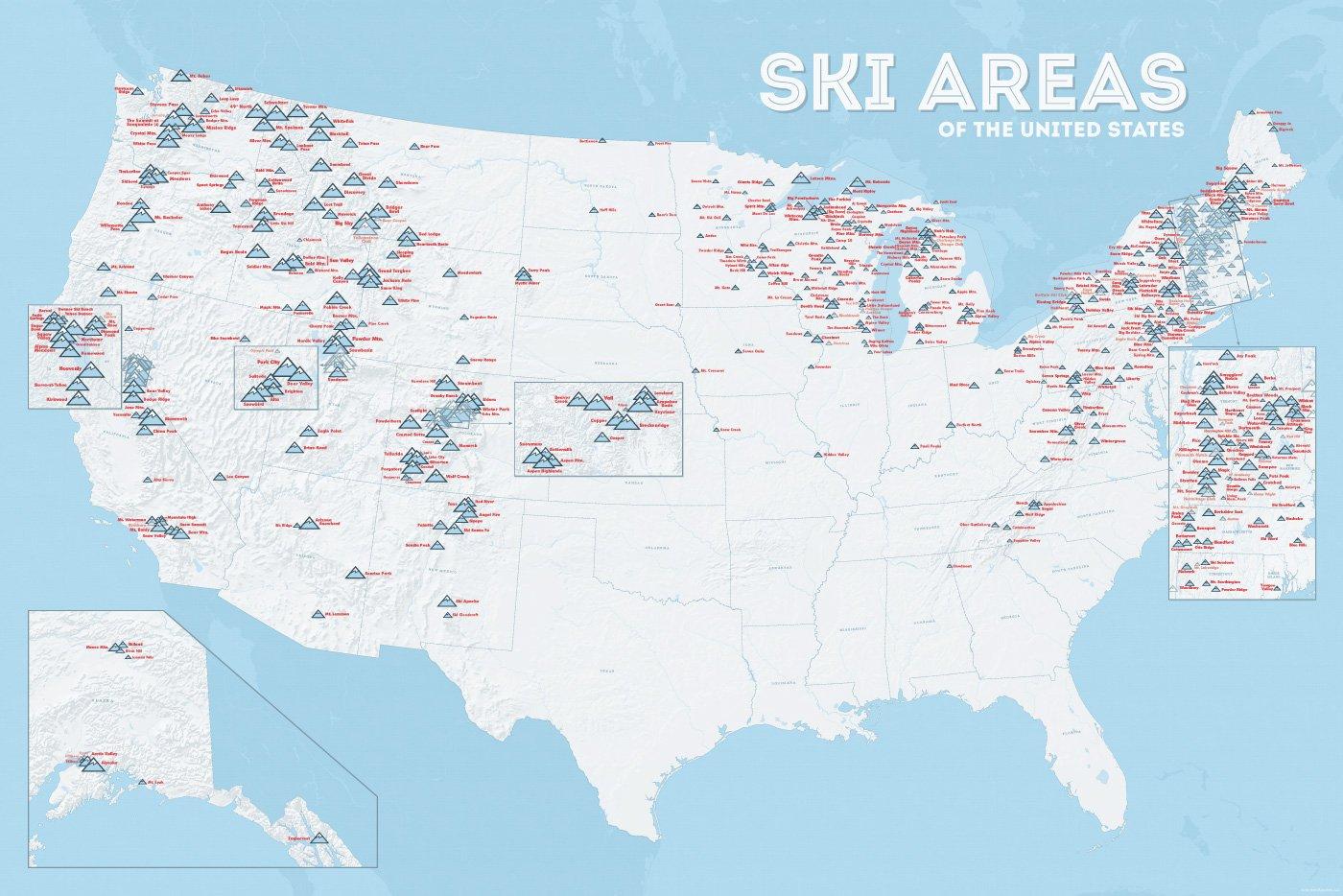
In vielen der 50 Bundesstaaten der USA gibt es Wintersportgebiete, von Maine bis nach Kalifornien. Vor allem drei große Gebirgszüge machen das Skifahren in den Vereinigten Staaten möglich: Zum einen sind dies die Rocky Mountains, die die sogenannten Mountain States durchqueren (Colorado, Nevada, Montana, Wyoming, Idaho und Utah). Die Cascades Range zieht sich von Kanada über Oregon bis hinunter nach Kalifornien. Im Osten der USA befinden sich zudem die Appalachen.
| Name | Orte im Gebiet | Staat | Seehöhe in m |
Liftanlagen1 | Pisten in km |
Weblink | |
| von | bis | ||||||
| Alta Snowbird | Snowbird | Utah | 2365 | 3350 | 1/18/0 | 150 | www.snowbird.com |
| Arapaho Basin | Colorado | 3292 | 3978 | 0/4/0 | 34 | www.arapahoebasin.com | |
| Aspen Highlands | Aspen | Colorado | 2460 | 3536 | 0/5/0 | 58 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Mountain | Aspen | Colorado | 2422 | 3417 | 1/7/0 | 50 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Butermilk | Aspen | Colorado | 2398 | 3013 | 0/5/1 | 34 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Snowmass | Aspen | Colorado | 2473 | 3813 | 2/13/5 | 137 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Beaver Creek Resort | Vail/Beaver Creek | Colorado | 2268 | 3478 | 0/15/8 | 152 | www.beavercreek.com |
| Big Sky Resort | Big Sky Village | Montana | 2072 | 3403 | 2/18/2 | 186 | www.bigskyresort.com |
| Breckenridge | Breckenridge | Colorado | 2926 | 3962 | 1/25/25 | 146 | www.snow.com |
| Deer Valley | Deer Valley | Utah | 2003 | 2918 | 1/20/0 | 105 | www.deervalley.com |
| Grand Targhee | Wyoming | 2438 | 3048 | 0/4/0 | 40 | www.grandtarghee.com | |
| Heavenly | Nevada | 1914 | 3039 | 2/17/6 | 89 | www.heavenly.com | |
| Jackson Hole Mountain | Teton Village | Wyoming | 1924 | 3185 | 3/9/0 | 150 | www.jacksonhole.com |
| Keystone | Keystone | Colorado | 2829 | 3782 | 2/16/16 | 116 | www.snow.com |
| Klamath Falls | Oregon | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | www.oregon.com | |
| Mammoth Mountain | Kalifornien | 2456 | 3362 | 3/23/4 | 112 | www.mammothmountain.com | |
| Park City Mountain | Park City | Utah | 2103 | 3039 | 0/15/0 | 87 | www.parkcitymountain.com |
| Squaw Valley | Squaw Valley | Kalifornien | 1886 | 2664 | 3/26/3 | 88 | www.squaw.com |
| Steamboat | Steamboat Springs | Colorado | 2097 | 3207 | 1/18/0 | 110 | www.steamboat.com |
| Telluride Skiresort | Telluride | Colorado | 2661 | 3735 | 3/11/0 | 98 | www.tellurideskiresort.com |
| The Canyons | Utah | 2061 | 3038 | 2/12/2 | 106 | www.thecanyons.com | |
| Vail | Vail | Colorado | 2450 | 3527 | 1/23/9 | 215 | www.vail.com |
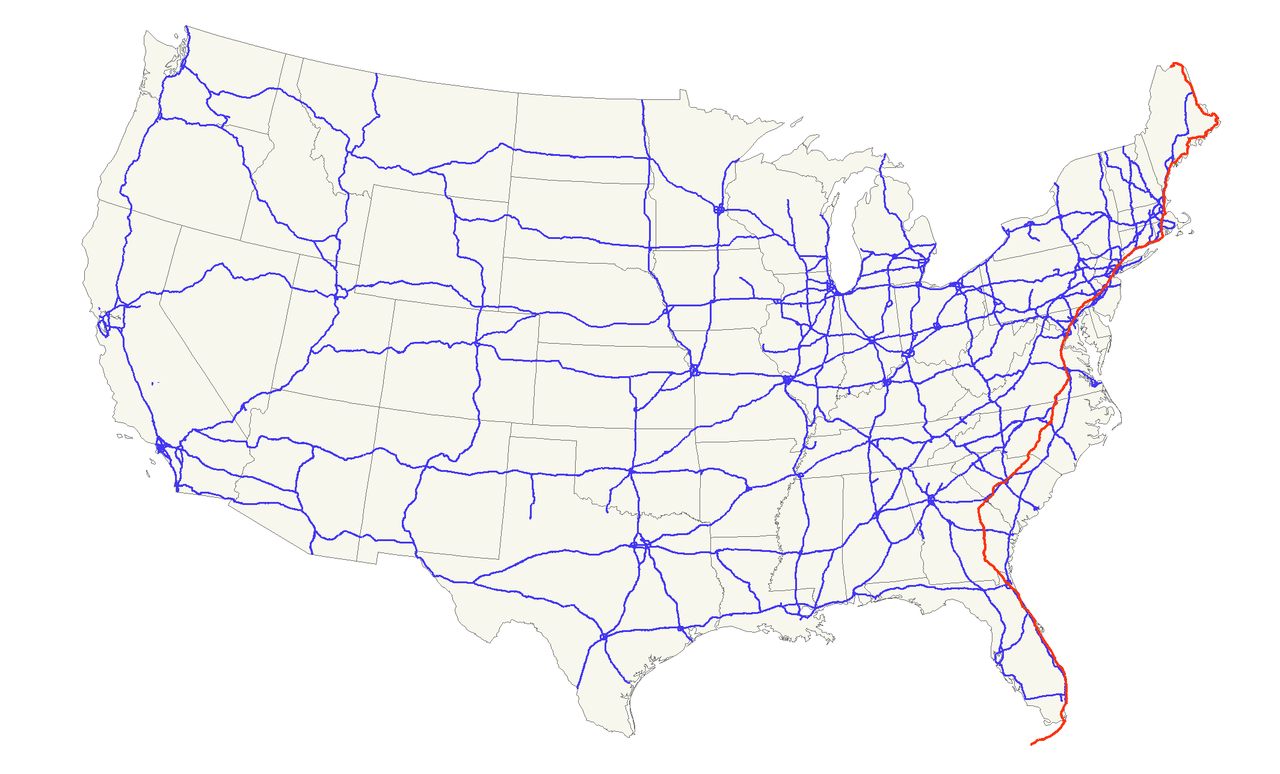
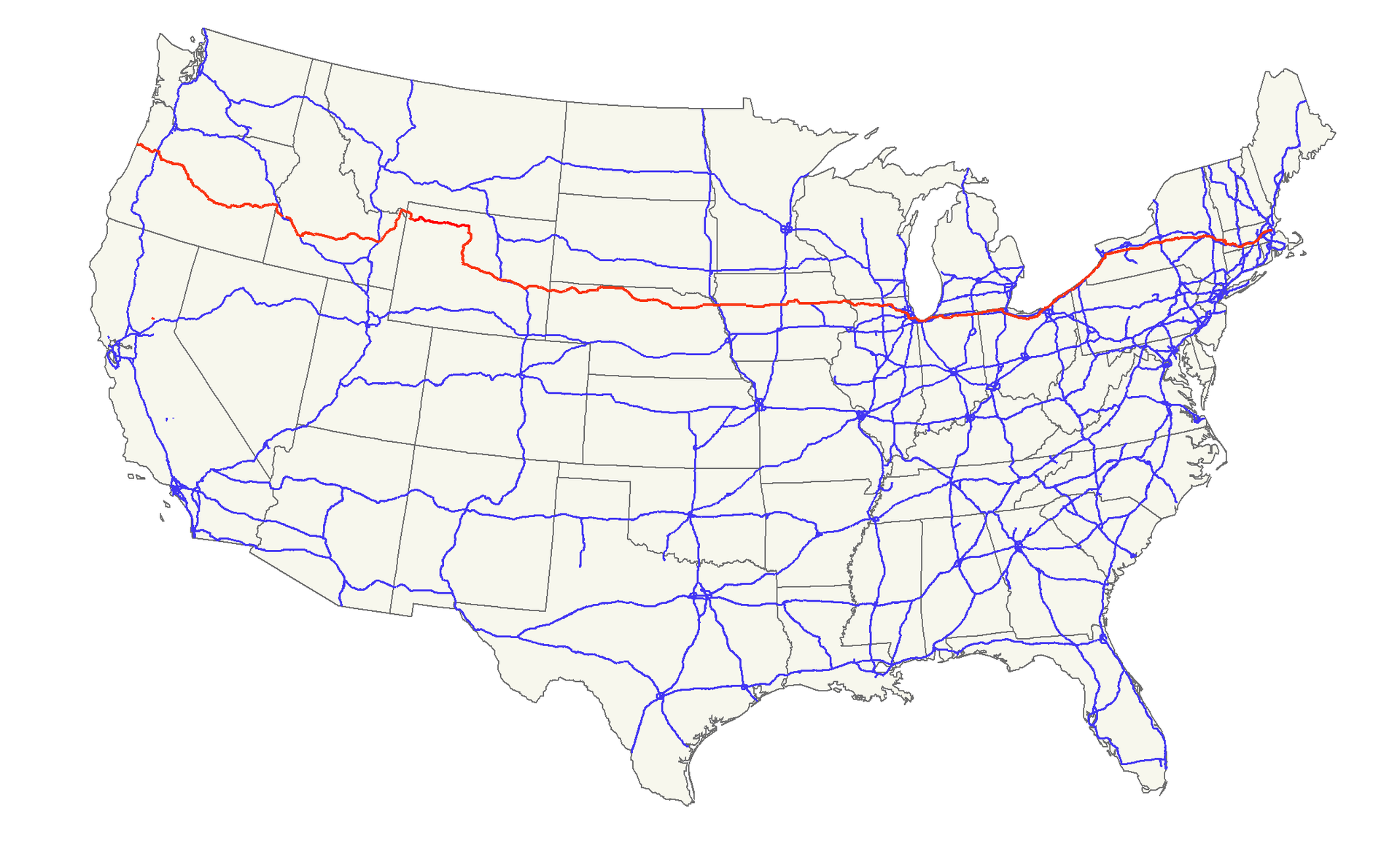
Der U.S. Highway 1 (auch U.S. Route 1 oder US 1) ist ein Highway, der parallel zur US-amerikanischen Ostküste verläuft. Die Gesamtlänge beträgt 3846 Kilometer. Im Norden endet der Highway in Fort Kent in Maine an der kanadischen Grenze. Im Süden ist es Key West an Floridas Küste zum Golf von Mexiko. Die US Route 1 verläuft an vielen Orten parallel zur Interstate 95. Festgelegt wurde sie 1926 zunächst nur zwischen der kanadischen Grenze und dem U.S. Highway 94 in Miami.
Die wichtigsten Städte, die der Highway passiert, sind Miami, Columbia, Richmond, Washington, D.C., Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, Boston und Portland.
Der Highway trägt die Nummer eins, weil er der am östlichsten gelegene ist und Nord-Süd-Highways von Ost nach West nummeriert werden.

 阿拉巴马州
阿拉巴马州

 阿利桑那州
阿利桑那州

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州

 佛罗里达州
佛罗里达州

 乔治亚州
乔治亚州

 路易斯安那州
路易斯安那州

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 密西西比州
密西西比州

 内华达州
内华达州

 新泽西州
新泽西州

 新墨西哥州
新墨西哥州

 纽约州
纽约州

 北卡罗来纳州
北卡罗来纳州

 俄克拉荷马州
俄克拉荷马州

 俄勒冈州
俄勒冈州

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州
 南卡罗来纳州
南卡罗来纳州

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州

 企业
企业

 犹他州
犹他州
 美国
美国

 佛蒙特州
佛蒙特州

 弗吉尼亚州
弗吉尼亚州

 华盛顿州
华盛顿州

 华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区

 西弗吉尼亚州
西弗吉尼亚州

 阿拉巴马州
阿拉巴马州

 阿利桑那州
阿利桑那州

 阿肯色州
阿肯色州

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州

 科罗拉多州
科罗拉多州

 康涅狄格州
康涅狄格州

 能源
能源

 能源
能源
 *电能
*电能

 佛罗里达州
佛罗里达州

 乔治亚州
乔治亚州

 夏威夷州
夏威夷州

 爱达荷州
爱达荷州

 印第安纳州
印第安纳州

 爱荷华州
爱荷华州

 肯塔基州
肯塔基州

 路易斯安那州
路易斯安那州

 缅因州
缅因州

 马里兰州
马里兰州

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 密歇根州
密歇根州

 明尼苏达州
明尼苏达州

 蒙大拿州
蒙大拿州

 新罕布什尔州
新罕布什尔州

 新泽西州
新泽西州

 纽约州
纽约州

 北卡罗来纳州
北卡罗来纳州

 俄克拉荷马州
俄克拉荷马州

 俄勒冈州
俄勒冈州

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州

 南卡罗来纳州
南卡罗来纳州

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州
 美国
美国

 佛蒙特州
佛蒙特州

 弗吉尼亚州
弗吉尼亚州

 华盛顿州
华盛顿州

 威斯康辛州
威斯康辛州

| Last Modified on November 21, 2022 *Capacity noted in (MW) |
| Plant | Location | Feedstock | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agrilectric Power Partners Ltd. | LA | Rice hulls | 12.00 |
| Albany Green Energy | GA | Forest residue, urban wood waste, pecan shells, peanut hulls | 50.00 |
| Allendale Biomass | SC | Mill/forestry residue | 20.00 |
| Altavista Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Arnold O. Chantland Incineration Plant | IA | MSW/Refused-derived fuel (RDF) | 4.00 |
| Barron County Waste-to-Energy & Recycling Facility | WI | MSW | 2.00 |
| Bay Front Power Plant | WI | Wood waste | 56.00 |
| Biomass One | OR | Logging/wood debris | 30.00 |
| Bridgewater Power LP | NH | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Buckeye Florida Biomass | FL | Wood waste, black liquor | 69.40 |
| Burgess BioPower | NH | Wood waste | 75.00 |
| Burney Forest Power | CA | Wood waste | 31.00 |
| Cadillac Renewable Energy | MI | Forest residue | 40.00 |
| City of Spokane Waste to Energy Facility | WA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Collins Pine Co. Power Plant | CA | Forest thinnings/residue | 12.00 |
| Covanta Alexandria | VA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Covanta Babylon | NY | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Bristol | CT | MSW | 16.00 |
| Covanta Camden | NJ | MSW | 21.00 |
| Covanta Dade | FL | MSW, wood waste | 77.00 |
| Covanta Delaware Valley | PA | MSW | 87.00 |
| Covanta Essex | NJ | MSW | 66.00 |
| Covanta Fairfax | VA | MSW | 93.00 |
| Covanta Harrisburg | PA | MSW | 21.00 |
| Covanta Haverhill | MA | MSW | 45.00 |
| Covanta Hempstead | NY | MSW | 72.00 |
| Covanta Hillsborough | FL | MSW | 47.00 |
| Covanta Honolulu | HI | MSW | 90.00 |
| Covanta Huntington | NY | MSW | 24.00 |
| Covanta Indianapolis | IN | MSW | 6.50 |
| Covanta Kent | MI | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Lake | FL | MSW | 15.00 |
| Covanta Lancaster | PA | MSW | 33.00 |
| Covanta Lee | FL | MSW | 57.00 |
| Covanta Long Beach | CA | MSW | 36.00 |
| Covanta MacArthur | NY | MSW | 12.00 |
| Covanta Marion | OR | MSW | 13.00 |
| Covanta Montgomery | MD | MSW | 63.00 |
| Covanta Niagara | NY | MSW | 50.00 |
| Covanta Onondaga | NY | MSW | 39.00 |
| Covanta Palm Beach Renewable Energy #1 | FL | MSW | 62.00 |
| Covanta Palm Beach Renewable Energy #2 | FL | MSW | 95.00 |
| Covanta Pasco | FL | MSW | 30.00 |
| Covanta Pinellas | FL | MSW | 75.00 |
| Covanta Plymouth | PA | MSW | 32.00 |
| Covanta SECONN | CT | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta SEMASS | MA | MSW | 78.00 |
| Covanta Stanislaus | CA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Covanta Tulsa | OK | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Union | NJ | MSW | 42.00 |
| Covanta York | PA | MSW | 42.00 |
| Cox Waste-to-Energy | KY | Wood waste | 5.00 |
| Craven County Wood Energy | NC | Wood chips, forestry residue, mill waste, bark, sawdust, poultry litter | 50.00 |
| Deerhaven Renewable Generating Station | FL | Wood waste | 102.50 |
| Desert View Power | CA | Woody biomass | 45.00 |
| DG Fairhaven Power | CA | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| Dillard Complex Cogeneration Plant | OR | Mill residue | 51.50 |
| Dorchester Biomass | SC | Mill/forestry residue | 20.00 |
| Douglas County Forest Products | OR | Wood residue | 6.00 |
| DTE Stockton Biomass Power | CA | Woody biomass, ag residue | 45.00 |
| Eagle Valley Clean Energy | CO | Forest restoration thinnings/residue | 12.00 |
| Ecomaine Waste-to-Energy Plant | ME | MSW | 14.00 |
| Evergreen Biopower LLC | OR | Mill residue | 10.00 |
| Fernandina Biomass Plant | FL | Mill residuals | 22.50 |
| French Island Generating Station | WI | MSW/RDF, wood waste, railroad ties | 28.00 |
| Genesee Power Station | MI | Landscaping/storm debris, waste wood | 40.00 |
| Grayling Generating Station | MI | Forestry residue, mill waste, bark | 38.00 |
| Green Energy Team LLC | HI | Eucalyptus, albizia | 7.50 |
| GRP-Franklin LLC | GA | C&D waste | 65.00 |
| GRP-Madison LLC | GA | C&D waste | 65.00 |
| Halifax County Biomass Plant | VA | Logging waste, forest slash | 49.90 |
| Hennepin Energy Recovery Center | MN | MSW | 40.00 |
| Hillman Power LLC | MI | Wood waste | 20.00 |
| Honey Lake Power | CA | High-hazard forest material/thinnings | 30.00 |
| Hopewell Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Joseph C McNeil Generating Station | VT | Logging residue, bark, shavings, clean urban wood waste | 50.00 |
| Kapstone Kraft Paper Corp.-Longview | WA | Mill residue, wood waste | 25.00 |
| Kettle Falls Generating Station | WA | Logging/mill residue | 53.00 |
| Koda Energy LLC | MN | Oat/rice hulls, corn, barley and malt screening, urban tree waste | 23.40 |
| L'Anse Warden Electric Company | MI | Wood waste, railroad ties | 20.00 |
| M.L. Hibbard Energy Center | MN | Wood waste | 72.80 |
| Macon Mill | GA | Logging waste | 38.00 |
| McKay Bay Refuse-to-Energy Plant | FL | MSW | 22.00 |
| McKinley Paper Cogeneration Facility | WA | Logging/mill residue | 9.50 |
| Merced Power | CA | Ag waste | 12.50 |
| MMWAC Resource Recovery Facility | ME | MSW | 5.00 |
| Mt. Poso Cogeneration Co. LLC | CA | Wood waste | 44.00 |
| Multitrade Rabun Gap | GA | Woody biomass | 18.00 |
| National Energy-Lincoln | MI | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| National Energy-McBain | MI | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| North Carolina Renewable Power | NC | C&D waste, wood waste, poultry litter | 22.00 |
| North Fork Community Power | CA | High-hazard forest material | 2.00 |
| Novo BioPower LLC | AZ | Wood waste | 27.00 |
| Okeelanta Biomass Cogeneration | FL | Baggasse, natural gas | 74.90 |
| Olmsted Waste-To-Energy Facility | MN | MSW | 9.60 |
| Oswego Energy Recovery Facility | NY | MSW | 4.00 |
| Pacific Ultrapower Chinese Station | CA | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Penobscot Energy Recovery | ME | MSW | 25.00 |
| Piedmont Green Power | GA | Urban wood waste, mill and logging residue | 55.00 |
| Plainfield Renewable Energy | CT | C&D/forestry waste | 37.50 |
| Plummer Cogen | ID | Wood waste | 6.20 |
| Potlatch Land & Lumber Power Plant | AR | Bark, sawdust, shavings | 10.00 |
| Rapids Energy Center | MN | Logging/mill residue | 28.60 |
| Red Wing Generating Station | MN | MSW/RDF | 22.00 |
| ReEnergy Black River | NY | Woody biomass | 60.00 |
| ReEnergy Livermore Falls | ME | Forest residue, C&D waste | 39.00 |
| ReEnergy Stratton | ME | Forest/mill residue | 48.00 |
| Resolute Forest Products Coosa Pines | AL | Wood-processing waste | 30.00 |
| Rio Bravo Fresno | CA | Ag/urban wood waste | 24.30 |
| Rio Bravo Rocklin | CA | High-hazard forest material, ag/urban waste | 24.40 |
| RockTenn-Tacoma Mill | WA | Mill residue | 55.00 |
| Roseburg Forest Products Biomass | CA | Wood waste | 13.00 |
| Rothschild Biomass Cogeneration Plant | WI | Urban wood waste, mill residue | 50.00 |
| Savannah River Site Biomass Cogeneration Facility | SC | Forest residue | 20.00 |
| Scotia Cogen | CA | Wood waste | 28.00 |
| SDS Lumber Gorge Energy Division | WA | Logging/mill residue | 10.00 |
| Shasta-Sustainable Resource Management | CA | Wood waste, forest residue | 56.00 |
| Southampton Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Southern Co. Nacogdoches Generating Facility | TX | Forest/wood processing residue | 115.00 |
| SPI-Aberdeen Biomass Power | WA | Logging/mill residue | 18.00 |
| SPI-Anderson Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 30.00 |
| SPI-Burlington Biomass Power | WA | Logging/mill residue | 28.00 |
| SPI-Burney | CA | Logging/mill residue | 20.00 |
| SPI-Eugene | OR | Mill, forest residue | 19.80 |
| SPI-Lincoln Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 18.00 |
| SPI-Quincy Biomass Power | CA | Mill residue | 35.20 |
| SPI-Sonora Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 10.90 |
| St. Paul Cogeneration LLC | MN | Urban wood residue | 33.00 |
| Stoltze Cogeneration Power Plant | MT | Mill residue | 3.00 |
| Stored Solar Bethlehem | NH | Logging residue, forest thinnings | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar Fitchburg | MA | Woody biomass | 17.00 |
| Stored Solar Jonesboro | ME | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Stored Solar Ryegate | VT | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar Springfield | NH | Woody biomass | 19.00 |
| Stored Solar Tamworth | NH | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar West Enfield | ME | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Stored Solar Whitefield | NH | Woody biomass | 15.00 |
| Telogia Power | FL | Logging/mill residue, hog fuel, peanut hulls | 14.00 |
| U.S. Sugar Corp. Cogeneration Plant | FL | Bagasse | 50.00 |
| Virginia City Hybrid Energy Center | VA | *Woody biomass | 120.00 |
| Wadham Energy LP | CA | Rice hulls | 30.00 |
| Westervelt Renewable Energy Moundville | AL | Wood waste | 13.00 |
| WestRock Covington | VA | Logging, papermaking residue | 75.00 |
| Wheelabrator Baltimore | MD | MSW | 64.50 |
| Wheelabrator Bridgeport | CT | MSW | 67.00 |
| Wheelabrator Concord | NH | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Dutchess County | NY | MSW | 9.00 |
| Wheelabrator Falls | PA | MSW | 53.00 |
| Wheelabrator Gloucester | NJ | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Hudson Falls | NY | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Lisbon | CT | MSW | 15.00 |
| Wheelabrator Millbury | MA | MSW | 48.00 |
| Wheelabrator North Andover | MA | MSW | 40.00 |
| Wheelabrator Portsmouth | VA | MSW | 60.00 |
| Wheelabrator Saugus | MA | MSW | 54.00 |
| Wheelabrator South Broward | FL | MSW | 66.00 |
| Wheelabrator Westchester LP | NY | MSW | 60.00 |
| Wilmarth Generating Station | MN | MSW/RDF, woody biomass | 18.00 |
| Woodland Biomass Power | CA | Wood chips, urban wood waste, ag waste | 25.00 |
| Total Plants: 159 | Total capacity(MW): | 5,583.90 |

Die American Academy of Arts and Sciences (kurz American Academy) ist eine der ältesten und angesehensten Ehrengesellschaften (englisch honor society) der Vereinigten Staaten. Die über fünftausend Mitglieder, die ausschließlich von ihresgleichen in die Akademie gewählt werden können, sind herausragende Persönlichkeiten aus Kunst (engl. art) und Wissenschaft (engl. science). Die Gesellschaft wurde 1780 gegründet, und sie hat ihren Sitz in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
美国人文与科学院(又译为美国艺术与科学院、美国文理科学院,英语:American Academy of Arts and Sciences,简称 American Academy 或 AAAS )是美国历史最悠久的院士机构及地位最为崇高的荣誉团体之一,也是进行独立政策研究的学术中心。自从约翰·亚当斯、约翰·汉考克、詹姆斯·鲍登、罗伯特·崔特·潘恩及其他的建国先贤于独立战争期间创立人文与科学院以来,当选为其院士一直被认为是美国的最高荣誉之一。[1]
人文与科学院负有双重职能:从科学、人文、商业、政治、艺术等领域选举每个世代最优秀的学者及最具影响力的领袖成为其院士,以及针对社会的需要进行政策研究。[2] 目前人文与科学院的主要研究计划聚焦于高等教育与科研、人文与文化研究、科学与技术进展、美国政治、人口与环境、儿童福利等。其主办的季刊《代达罗斯》被广泛的认为是国际最重要的学术刊物之一

Die Region grenzt im Norden an Kanada, im Westen an den Mittleren Westen, im Süden an die Südstaaten und im Osten an den Atlantik.
Der genaue Umfang der Region ist nicht eindeutig definiert. Nach der Definition des United States Census Bureau[1] besteht der Nordosten aus Neuengland (mit den Staaten Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut) und den Mittelatlantikstaaten (New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania). In diesen insgesamt neun Staaten, die unbestritten dem Nordosten zugerechnet werden, lebten im Jahr 2008 etwa 55,9 Millionen Personen.[2]
Andere Behörden ordnen dem Nordosten auch Maryland, Delaware und Washington, D.C.[3] bzw. sogar Virginia und West Virginia[4] zu. Das United States Census Bureau betrachtet die Staaten südlich der Mason-Dixon-Linie sowie Delaware dagegen als der Region South Atlantic und den Südstaaten zugehörig.
美国东北部为美国人口调查局所定义的美国地区。美国东北部北临加拿大,西临中西部,南接美国南部,东向大西洋。此区域乃美国工商业最发达的区域及都市化程度最高的区域,美国第一大都会纽约市即位于该区。
根据人口调查局的定义,美国的东北部包括9个州:康涅狄格州、缅因州、麻塞诸塞州、新泽西州、新罕布什尔州、纽约州、宾夕法尼亚州、罗得岛州、以及佛蒙特州,东北部还可分为新英格兰以及纽约都会区[1]。有些非官方的较广义之分类会因为这些州被包括在波士顿-华盛顿城市带之中,所以有时会将马里兰州、特拉华州、华盛顿特区、弗吉尼亚州、以及西弗吉尼亚州包含在此区域中(所以会因人而异),但是人口调查局官方将这些州定义为南大西洋地区的一部分[1]。而有些较狭义的分类则只将此区域限制于新英格兰、纽约都会区、及费城地区之中。虽然俄亥俄州的绝大部分地区是被分类在中西部之下,但大克里夫兰地区及俄亥俄州东北部在文化上(因为传统以及语言腔调之关系)被认为比该州其他地区较为倾向美国东北部之文化。
美国东北部是全美最富裕的地区。根据2004年的资料,美国人口调查局的报告显示全美10个最富裕的州里有5个就位于东北部。这五个州依据家庭收入排名为:新泽西州(第一)、康涅狄格州(第二)、马里兰州(第三)、麻塞诸塞州(第五)、以及新罕布什尔州(第六)。根据经济分析局2005年的报告指出,全美前五个每人年均收入最高的州依序为:康涅狄格州、马里兰州、麻塞诸塞州、新泽西州和纽约州。在此区域内,纽约市独占美国2005年国内生产总值的8%。此区域内的州都有着富裕的经济收入,不过多数的州的人口以及面积都其他州小,除了纽约州、新泽西州、与宾夕法尼亚州在全美人口数排前10名之列,没有一个州列居于全美面积前10大之列。
 *美国政治
*美国政治

 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州
 联邦储备系统
联邦储备系统

 财政金融
财政金融
 *美国经济情况数据
*美国经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *巴西经济情况数据
*巴西经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *中国经济情况数据
*中国经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *德国经济情况数据
*德国经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *欧盟经济情况数据
*欧盟经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *法国国经济情况数据
*法国国经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *印度经济情况数据
*印度经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *印度尼西亚经济情况数据
*印度尼西亚经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *意大利经济情况数据
*意大利经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *日本经济情况数据
*日本经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *加拿大经济情况数据
*加拿大经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *俄国经济情况数据
*俄国经济情况数据

 财政金融
财政金融
 *英国经济情况数据
*英国经济情况数据

 乔治亚州
乔治亚州

 伊利诺斯州
伊利诺斯州

 马萨诸塞州
马萨诸塞州

 明尼苏达州
明尼苏达州

 密苏里州
密苏里州

 纽约州
纽约州

 俄亥俄州
俄亥俄州

 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州

 企业
企业
 美国
美国

 弗吉尼亚州
弗吉尼亚州

 华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区

 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
 经济与政治研究
经济与政治研究
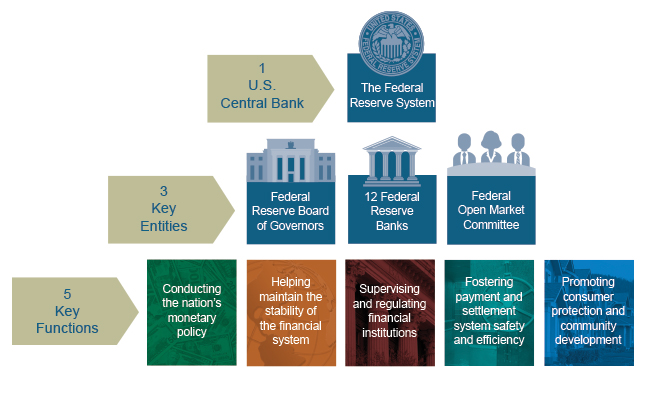


Das Federal Reserve System [ˈfɛdə˞əl rɪˈzɜ˞ːv ˈsɪstəm], oft auch Federal Reserve oder einfach die Fed (als US-Notenbank), ist das Zentralbank-System der Vereinigten Staaten. Es besteht aus dem Board of Governors, zwölf regionalen Federal Reserve Banken, dem Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), einer Vielzahl von Mitgliedsbanken (Mitgliedspflicht ab einer bestimmten Größe) und anderen Institutionen.
Die Fed berichtet regelmäßig an den Kongress der Vereinigten Staaten über ihre Aktivitäten und ihre Pläne zur Geldpolitik. Das Tagesgeschäft und die operativen Entscheidungen der Fed werden von ihr frei und eigenständig entschieden. Der Kongress hat allerdings die Befugnis, die Gesetze betreffend die Geschäftstätigkeit der Fed zu ändern.[1]
联邦储备系统(英语:Federal Reserve System(Fed),简称美联储)是美国的中央银行体系,依据美国国会通过的1913年《联邦储备法案》而创设,以避免再度发生类似1907年的银行危机。整个系统包括联邦储备委员会、联邦公开市场委员会、联邦储备银行、三千家会员银行、及3个咨询委员会(Advisory Councils)。
連邦準備制度(れんぽうじゅんびせいど、英語: Federal Reserve System, FRS)は、アメリカ合衆国の中央銀行制度である。ワシントンD.C.にある連邦準備制度理事会(Federal Reserve Board, FRB)が全国の主要都市に散在する連邦準備銀行(Federal Reserve Bank, FRB)を統括する。連邦準備制度理事会は連邦議会の下にある政府機関であるが、予算の割当や人事の干渉を受けない。各連邦準備銀行は株式を発行する法人(body corporate)である。
The Federal Reserve System (also known as the Federal Reserve or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises.[list 1] Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System.[5][10][11]
The U.S. Congress established three key objectives for monetary policy in the Federal Reserve Act: maximizing employment, stabilizing prices, and moderating long-term interest rates.[12] The first two objectives are sometimes referred to as the Federal Reserve's dual mandate.[13] Its duties have expanded over the years, and currently also include supervising and regulating banks, maintaining the stability of the financial system, and providing financial services to depository institutions, the U.S. government, and foreign official institutions.[14] The Fed also conducts research into the economy and provides numerous publications, such as the Beige Book and the FRED database.
The Federal Reserve System is composed of several layers. It is governed by the presidentially appointed board of governors or Federal Reserve Board (FRB). Twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks, located in cities throughout the nation, regulate and oversee privately owned commercial banks.[15][16][17] Nationally chartered commercial banks are required to hold stock in, and can elect some of the board members of, the Federal Reserve Bank of their region. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) sets monetary policy. It consists of all seven members of the board of governors and the twelve regional Federal Reserve Bank presidents, though only five bank presidents vote at a time (the president of the New York Fed and four others who rotate through one-year voting terms). There are also various advisory councils. Thus, the Federal Reserve System has both public and private components.[list 2] It has a structure unique among central banks, and is also unusual in that the United States Department of the Treasury, an entity outside of the central bank, prints the currency used.[22]
The federal government sets the salaries of the board's seven governors, and it receives all the system's annual profits, after a statutory dividend of 6% on member banks' capital investment is paid, and an account surplus is maintained. In 2015, the Federal Reserve earned a net income of $100.2 billion and transferred $97.7 billion to the U.S. Treasury.[23] Although an instrument of the US Government, the Federal Reserve System considers itself "an independent central bank because its monetary policy decisions do not have to be approved by the President or anyone else in the executive or legislative branches of government, it does not receive funding appropriated by Congress, and the terms of the members of the board of governors span multiple presidential and congressional terms."[24]
La Réserve fédérale (officiellement Federal Reserve System, souvent raccourci en Federal Reserve ou Fed) est la banque centrale des États-Unis. Elle est créée en décembre 1913, durant les fêtes, par le Federal Reserve Act dit aussi Owen-Glass Act, à la suite de plusieurs crises bancaires, dont la panique bancaire américaine de 1907. Son rôle évolue depuis et elle renforce son indépendance lors de l'instabilité monétaire des années 1975 et 1985.
Le Congrès des États-Unis définit trois objectifs de politique monétaire dans le Federal Reserve Act : plein emploi, stabilité des prix, et taux d'intérêt à long terme modérés1. Les deux premiers sont souvent appelés le « double objectif » ou « double mandat » de la Fed2. Outre la politique monétaire, la Fed est maintenant chargée de superviser et réguler le système bancaire, de maintenir la stabilité du système financier, et d'offrir des prestations financières aux organismes de dépôt, au gouvernement fédéral, et aux institutions financières étrangères3. Elle étudie de surcroît l'économie américaine, et publie de nombreux rapports, tels que le livre beige, un résumé des conditions économiques dans chaque région.
La Réserve fédérale se compose d'un conseil des gouverneurs (dont Jerome Powell est le président depuis 2018), du Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), de douze banques régionales (Federal Reserve Banks), des banques membres, et de plusieurs conseils consultatifs4,5. Le FOMC est le comité responsable de la politique monétaire ; il se compose des sept membres du bureau des gouverneurs et des douze présidents des banques régionales (dont cinq seulement ont le droit de vote à un moment donné). La Réserve fédérale comporte ainsi des aspects publics et privés : cette structure est unique au monde pour une banque centrale, et correspond à une volonté de répondre à la fois à l'intérêt public et à ceux, privés, des banques membres. Une autre particularité du système monétaire américain est que ce n'est pas la banque centrale mais le département du Trésor qui crée la monnaie fiduciaire6.
La Fed est une banque centrale indépendante : ses décisions ne sont pas sujettes à l'autorisation du président des États-Unis ou d'une autre partie du gouvernement fédéral, elle ne reçoit pas de budget du Congrès, et les mandats des gouverneurs sont beaucoup plus longs que ceux des élus fédéraux. Le gouvernement peut cependant exercer un contrôle : l'autorité de la Fed est définie par le Congrès et celui-ci peut exercer son droit de surveillance (congressional oversight). Les membres du bureau des gouverneurs, y compris le président et le vice-président, sont nommés par le président des États-Unis et confirmés par le Sénat. Le gouvernement nomme également les hauts fonctionnaires de la banque et fixe leur salaire. Toutes les banques commerciales autorisées à exercer en dehors d'un seul État sont obligatoirement membres de la Réserve fédérale régionale où se trouve leur siège et détiennent des parts dans celle-ci, ce qui autorise ces banques à élire une partie des membres du bureau de chaque Réserve fédérale régionale. Le gouvernement fédéral reçoit tous les profits de la Fed, hormis un dividende de 6 % versé aux banques membres.
Il Federal Reserve System, conosciuto anche come Federal Reserve (it. Riserva federale) ed informalmente come la Fed, è la banca centrale degli Stati Uniti d'America.
El Sistema de la Reserva Federal (en inglés, Federal Reserve System, también conocido como Reserva Federal o informalmente Fed) es el banco central de los Estados Unidos.1 Es un consorcio publico-privado que controla la estructura organizativa en la cual participa una agencia gubernamental, conocida como Junta de Gobernadores, con sede en Washington D. C.2 Así, algunos consideran esto como el aspecto público del sistema, y los 12 Bancos de la Reserva de todo el país el aspecto privado.3 Está encargada de custodiar parte de las reservas de los "bancos miembros" estadounidenses: los federales, y los estatales asociados voluntariamente.4
La Junta de Gobernadores del Sistema de la Reserva Federal es una agencia gubernamental independiente, sin embargo está sujeta a la Ley de Libertad de Información (Freedom of Information Act). Como muchas de las agencias independientes, sus decisiones no tienen que ser aprobadas por el Presidente o por alguna persona del poder ejecutivo o legislativo: son decisiones de carácter unilateral. La Junta de Gobernadores no recibe dinero del Congreso, y su mandato tiene una duración que abarca varias legislaturas. Una vez que el presidente designa a un miembro de la junta, este actúa con "independencia", aunque puede ser destituido por el presidente según lo establecido en la sección 242, Título 12, del Código de Estados Unidos.5
El Sistema de la Reserva Federal fue creado el 23 de diciembre de 1913 por la Ley de la Reserva Federal (Federal Reserve Act). Todos los bancos nacionales tuvieron que unirse al sistema. Los billetes de la Reserva Federal (Federal Reserve Notes) fueron creados para tener una oferta monetaria "flexible".6
Федера́льная резе́рвная систе́ма (Federal Reserve System, ФРС, Федеральный резерв, FED) — специально созданное 23 декабря 1913 года независимое федеральное агентство для выполнения функций центрального банка и осуществления централизованного контроля над коммерческой банковской системой Соединённых Штатов Америки. В ФРС входят 12 федеральных резервных банков, расположенных в крупнейших городах, около трёх тысяч коммерческих так называемых банков-членов, назначаемый президентом Совет управляющих, Федеральный комитет по операциям на открытом рынке и консультационные советы. Основанием для создания является Закон о Федеральном резерве. В управлении ФРС определяющую роль играет государство, хотя форма собственности капитала является частной — акционерная с особым статусом акций.
С точки зрения управления, ФРС является независимым органом в правительстве США. Как национальный центральный банк, ФРС получает полномочия от Конгресса США. Независимость в работе обеспечивается тем, что принимаемые решения о кредитно-денежной политике не должны быть одобрены президентом США или кем-либо иным из исполнительной или законодательной ветвей власти. ФРС не получает финансирование от Конгресса. Срок полномочий членов Совета управляющих Федеральной резервной системы охватывает несколько сроков президентских полномочий и членов Конгресса. В то же время ФРС подконтрольна Конгрессу, который часто анализирует деятельность ФРС и может изменить обязанности ФРС законодательным образом[1].
С 2006 по 2014 год пост председателя совета управляющих ФРС занимал Бен Бернанке. В феврале 2014 года его сменила Джанет Йеллен, которая в течение двух лет работала его заместителем[2]. С 5 февраля 2018 года главой Федеральной резервной системы является Джером Пауэлл.

美国全国经济研究所(英语:National Bureau of Economic Research,缩写:NBER)是美国的一个私营、非营利机构,同时亦是美国最大的经济学研究组织。其宗旨是研究经济的运作,进行实证的经济学研究。三十一个美国诺贝尔经济学奖得奖者中有十六位曾是美国全国经济研究所的研究员。
美国全国经济研究所于1920年创办。不少著名的经济学者如小罗伯特·卢卡斯、罗伯特·巴罗、保罗·克鲁格曼也是其研究员。
Das National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) ist eine US-amerikanische private, überparteiliche Nonprofit-Forschungsorganisation, die sich dem Studium von Theorie und Empirie der Ökonomik widmet, insbesondere der amerikanischen Wirtschaft. Der Sitz ist in Cambridge, Massachusetts (USA). Als Zielsetzung sieht es die unvoreingenommene Forschung vor sowie die Verbreitung von Wissen unter Politikern, Geschäftsleuten und der akademischen Gemeinschaft.
Das NBER wurde 1920 durch Wesley C. Mitchell gegründet und publiziert die NBER Working Papers.
Das NBER ist die größte wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Forschungseinrichtung in den USA.
 滑雪旅游
滑雪旅游
 运输和交通
运输和交通
 地理
地理

 科学技术
科学技术
 乐器
乐器
 生活时尚
生活时尚
 音乐
音乐
