
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Canada
Canada
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation

 Financial
Financial
 ***Key regulatory authorities
***Key regulatory authorities
 France
France
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Camille Gutt
Camille Gutt
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Christine Lagarde
Christine Lagarde
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Strauss-Kahn
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Horst Köhler
Horst Köhler
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Ivar Rooth
Ivar Rooth
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Jacques de Larosière
Jacques de Larosière
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Johan Witteveen
Johan Witteveen
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Michel Camdessus
Michel Camdessus
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Per Jacobsson
Per Jacobsson
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Rodrigo Rato
Rodrigo Rato
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Kristalina Georgiewa
Kristalina Georgiewa
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

Der Internationale Währungsfonds (IWF; englisch International Monetary Fund, IMF; auch bekannt als Weltwährungsfonds) ist eine rechtlich, organisatorisch und finanziell selbständige Sonderorganisation der Vereinten Nationen mit Sitz in Washington, D.C., USA.
Hauptaufgabe des IWF ist die Vergabe von Krediten an Länder ohne ausreichende Währungsreserven, die in Zahlungsbilanzschwierigkeiten geraten sind. Weitere Tätigkeitsfelder sind die Förderung der internationalen Zusammenarbeit in der Währungspolitik, Ausweitung des Welthandels, Stabilisierung von Wechselkursen, Überwachung der Geldpolitik und technische Hilfe.
Der IWF und seine Schwesterorganisation Weltbank haben ihren Ursprung im 1944 geschaffenen Bretton-Woods-System fester Wechselkurse, das auf der damals mit Gold gedeckten Leitwährung US-Dollar beruhte. Sie waren als internationale Steuerungsinstrumente geplant, mit denen eine Wiederholung der Währungsturbulenzen der Zwischenkriegszeit und der Fehler des Goldstandards aus den 1920er Jahren verhindert werden sollte. Beide Organisationen werden daher als Bretton-Woods-Institution bezeichnet. Die Kreditvergabe des IWF ist an wirtschaftspolitische Auflagen geknüpft, die die Rückzahlung der Kredite sichern sollen. Anders als der IWF vergibt die Weltbank auch Kredite für spezielle Projekte.
Der IWF hat zurzeit (Stand April 2020) 189 Mitgliedstaaten, deren Stimmrecht sich an ihrem Kapitalanteil orientiert. Die Mitgliedstaaten mit den größten Stimmanteilen sind: USA 16,51 %, Japan 6,15 %, China 6,08 %, Deutschland 5,32 %, Frankreich 4,03 %, Vereinigtes Königreich 4,03 % und Italien 3,02 %. Von den deutschsprachigen Ländern haben außerdem Luxemburg 0,29 %, Österreich 0,81 % und die Schweiz 1,18 % Stimmenanteile.[4]
Beschlüsse müssen im IWF mit einer Mehrheit von 85 % getroffen werden. Dadurch verfügen jeweils die USA allein und die EU-Staaten gemeinsam de facto über eine Sperrminorität.[5]
国际货币基金组织(法语:Fonds Monétaire International,缩写:FMI;英语:International Monetary Fund,缩写:IMF)于1945年12月27日成立,与世界银行同为世界两大金融机构,由189个国家组成,致力于促进全球货币合作,确保金融稳定,促进国际贸易。职责是监察货币汇率和各国贸易情况、提供技术和资金协助[3][4][5],确保全球金融制度运作正常;其总部设置于美国华盛顿特区。
国際通貨基金(こくさいつうかききん、英語: International Monetary Fund, IMF)は、国際金融、並びに、為替相場の安定化を目的として設立された国際連合(国連)の専門機関である。本部は、アメリカ合衆国の首都ワシントンD.C.にある。2018年現在、加盟国は189か国である[2]。
加盟国の経常収支が著しく悪化した場合などに融資などを実施することで、国際貿易の促進、加盟国の高水準の雇用と国民所得の増大、為替の安定、などに寄与する事を目的としている。 また、為替相場の安定のために、経常収支が悪化した国への融資や、為替相場と各国の為替政策の監視などを行っている。各国の中央銀行の取りまとめ役のような役割を負う。世界銀行と共に、国際金融秩序の根幹を成す。
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world while periodically depending on the World Bank for its resources.[1] Formed in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes,[6] it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international payment system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises.[7] Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had XDR 477 billion (about US$ 667 billion).[8]
Through the fund and other activities such as the gathering of statistics and analysis, surveillance of its members' economies, and the demand for particular policies,[9] the IMF works to improve the economies of its member countries.[10] The organization's objectives stated in the Articles of Agreement are:[11] to promote international monetary co-operation, international trade, high employment, exchange-rate stability, sustainable economic growth, and making resources available to member countries in financial difficulty.[12] IMF funds come from two major sources: quotas and loans. Quotas, which are pooled funds of member nations, generate most IMF funds. The size of a member's quota depends on its economic and financial importance in the world. Nations with larger economic importance have larger quotas. The quotas are increased periodically as a means of boosting the IMF's resources in the form of special drawing rights.[13]
The current Managing Director (MD) and Chairwoman of the IMF is Bulgarian Economist Kristalina Georgieva, who has held the post since October 1, 2019.[14]
Gita Gopinath was appointed as Chief Economist of IMF from 1 October 2018. She received her PhD in economics from Princeton University. Prior to her IMF appointment she was economic adviser to the Chief Minister of Kerala, India.[15]
Le Fonds monétaire international (FMI) est une institution internationale regroupant 189 pays, dont le but est de promouvoir la coopération monétaire internationale, garantir la stabilité financière, faciliter les échanges internationaux, contribuer à un niveau élevé d’emploi, à la stabilité économique et faire reculer la pauvreté2.
Le FMI a ainsi pour fonction d'assurer la stabilité du système monétaire international (SMI) et la gestion des crises monétaires et financières. Pour cela, il fournit des crédits aux pays qui connaissent des difficultés financières mettant en péril l'organisation gouvernementale du pays, la stabilité de son système financier (banques, marchés financiers) ou les flux d'échanges de commerce international avec les autres pays.
Lors d'une crise financière, pour éviter qu’un pays ne fasse « défaut » (c’est-à-dire que ce pays ne puisse plus rembourser ses créanciers, voire ne plus payer ses dépenses courantes), le FMI lui prête de l’argent le temps que la confiance des agents économiques revienne. Le FMI conditionne l’obtention de prêts à la mise en place de certaines réformes économiques visant en principe à réguler la gestion des finances publiques (ingérence financière) et à établir une croissance économique équilibrée à long terme.
L'institution a été créée le 27 décembre 1945 et devait à l'origine garantir la stabilité du système monétaire international, dont l'écroulement après le krach de 1929 avait eu des effets catastrophiques sur l'économie mondiale. Après 1976 et la disparition d’un système de change fixe, le FMI perd l'essentiel de sa raison d'être et hérite d'un nouveau rôle face aux problèmes d'endettement des pays en développement et à certaines crises financières.
Il Fondo Monetario Internazionale (in sigla FMI; in inglese International Monetary Fund, IMF) è un'organizzazione internazionale pubblica[1] a carattere universale composta dai governi nazionali di 189 Paesi e insieme al gruppo della Banca Mondiale fa parte delle organizzazioni internazionali dette di Bretton Woods, dal nome della località in cui si tenne la famosa conferenza che ne sancì la creazione. L'FMI è stato formalmente istituito il 27 dicembre 1945, quando i primi 44 stati firmarono l'accordo istitutivo e l'organizzazione nacque nel maggio del 1946. Attualmente gli Stati membri sono 189.
El Fondo Monetario Internacional o FMI (en inglés: International Monetary Fund, IMF) es una organización financiera internacional con sede en Washington D. C., Estados Unidos. Nace como idea el 22 de julio de 1944 en los acuerdos de Bretton Woods, una reunión de 730 delegados de 44 países aliados de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, entrando en vigor oficialmente el 27 de diciembre de 1945. Después de 1976 y de la desaparición del sistema de cambio fijo, el FMI toma un papel preponderante ante países en desarrollo y crisis financieras internacionales. En 2010, durante la 14ª revisión general de cuotas los fondos financieros disponibles del FMI se situaban en 755 700 millones de U.S.dólares.1
A través del fondo y otras actividades como la recolección de estadísticas y datos, monitoreo de las actividades económicas de los países miembros, y la demanda de políticas concretas,2 el FMI trabaja para mejorar la economía de sus países miembros.3 Los objetivos proclamados por la organización son:4 promover la cooperación monetaria internacional, comercio internacional, reducir la desocupación, conseguir tasas de cambio sustentables, lograr crecimiento económico, y otorgar razonablemente recursos a países miembros en dificultades económicas.5 El FMI se financia con dos grandes herramientas: cuotas y préstamo. Las cuotas son aportes realizados por los países miembros al fondo común de la organización. Las mayores economías hacen aportes proporcionales mayores que las economías más pequeñas. Además, las obligaciones de cuotas aumentan periódicamente como forma de aumentar los recursos de los que puede disponer el FMI en forma de derechos especiales de giro.6
Esta organización ha sido fuertemente criticada en las últimas décadas. Las principales críticas se centran en el papel dominante que tienen los países desarrollados dentro del organismo, lo que causa que el FMI oriente sus políticas globales al fomento de un capitalismo que suele denominarse neoliberal,7 a causa de haber impuesto a los países en vías de desarrollo —y más recientemente a algunos países europeos— sus programas económicos basados en el Consenso de Washington que consisten en la reducción del déficit y del gasto público y consecuentemente de servicios y prestaciones sociales, con fundamento en las políticas y teorías monetaristas y en el principio de libre mercado,8 que deben llevarse a cabo como condiciones de los préstamos realizados y que según sus críticos ha provocado un aumento de la brecha entre ricos y pobres y un empeoramiento de los servicios públicos, como la sanidad.9 También está acusada por haber apoyado y financiado a las dictaduras militares en Latinoamérica y Africa,10 y se le han criticado puntualmente sus políticas sobre medio ambiente11 y alimentación.12
Международный валютный фонд, (МВФ) (англ. International Monetary Fund, IMF) — специализированное учреждение (валютный фонд) Организации объединённых наций (ООН) с главным офисом в городе Вашингтон, США.
189 стран являются членами МВФ, в его структурах работают 2500 человек из 133 государств мира. МВФ предоставляет кратко- и среднесрочные кредиты при дефиците платёжного баланса государства. Предоставление кредитов обычно сопровождается набором определённых условий и рекомендаций. Политика и рекомендации МВФ в отношении развивающихся стран неоднократно подвергались критике, суть которой состоит в том, что выполнение рекомендаций и условий, в итоге, направлено не на повышение самостоятельности, стабильности и развитие национальной экономики государства, а лишь на привязывание её к международным финансовым потокам.
В отличие от Всемирного банка, деятельность МВФ сосредоточена на относительно кратковременных макроэкономических кризисах. Всемирный банк предоставляет кредиты только бедным странам, МВФ может давать кредиты любой из своих стран-членов, которая испытывает нехватку иностранной валюты для покрытия краткосрочных финансовых обязательств.
 Eastern Conference NHL
Eastern Conference NHL
 Atlantic-Division
Atlantic-Division
 Eastern Conference NHL
Eastern Conference NHL
 Metropolitan-Division
Metropolitan-Division
 Canada
Canada
 National Hockey League NHL 2016/17
National Hockey League NHL 2016/17
 Eastern Conference NHL
Eastern Conference NHL
 National Hockey League NHL 2016/17
National Hockey League NHL 2016/17
 Western Conference NHL
Western Conference NHL

 Sport
Sport
 (W)National Hockey League NHL
(W)National Hockey League NHL
 United States
United States
 Western Conference NHL
Western Conference NHL
 Central-Division
Central-Division
 Western Conference NHL
Western Conference NHL
 Pacific-Division
Pacific-Division

Die National Hockey League (NHL, im französischsprachigen Teil Kanadas «Ligue nationale de hockey», LNH) ist eine seit 1917 bestehende Eishockey-Profiliga in Nordamerika. In den USA gehört die NHL neben der Football-Liga NFL, der Baseball-Liga MLB und der Basketball-Liga NBA zu den vier beliebtesten Ligen, den sogenannten Big 4. In Kanada ist sie die populärste Liga.
Von den insgesamt 32 Teams sind 7 in Kanada und 25 in den USA beheimatet. Die Siegertrophäe für den Saisongewinner, der nach der regulären Saison in den Play-offs nach dem Modus Best-of-Seven ermittelt wird, ist der Stanley Cup. Titelträger der Saison 2023/24 ist das Team der Florida Panthers. Gestiftet wurde der Stanley Cup 1892 vom damaligen Generalgouverneur von Kanada, Lord Stanley. Die Namen aller teilnehmenden Spieler, Trainer und Manager der Siegermannschaft der Finalspiele werden auf den Pokal graviert. Außerdem darf jeder Spieler des Siegerteams den Pokal für einen Tag behalten. Ursprünglich war der Stanley Cup ein Wanderpokal, der zwischen den Siegern mehrerer Ligen ausgespielt wurde. Seit 1927 wird er ausschließlich dem Sieger der NHL verliehen.
Die NHL ist eng mit der American Hockey League und der ECHL verzahnt, so sind die Teams der NHL mit Mannschaften dieser Ligen verbunden, als sogenannte Farmteams. Viele Spieler, die im NHL Entry Draft von den NHL-Franchises ausgewählt werden, spielen zuerst oft in der AHL, um so Spielpraxis und Erfahrung zu sammeln. Der Entry Draft ist die in der NHL übliche Veranstaltung, bei der sich die Clubs die Rechte an Nachwuchsspielern sichern können. Dieser Mechanismus soll dazu dienen, junge Talente möglichst gleichmäßig auf die Teams zu verteilen.
国家冰球联盟(英语:National Hockey League,简称NHL;法语:Ligue nationale de hockey,简称LNH;又被译作北美冰球职业联赛、北美冰联)是一个由北美冰球队伍所组成的职业运动联盟,也是一个非注册非营利性的联盟。NHL与欧亚大陆的大陆冰球联赛(KHL)同为全世界最高层级的职业冰球比赛,为北美四大职业运动之一。队伍共分成东、西两个大区,每个大区各分为三个分区,每年东西两区的冠军会在联盟总决赛中争夺斯坦利杯。联盟于1917年在魁北克省蒙特利尔成立,成立之初有五支队伍,在一系列的扩展之后,现在共有32支球队,25支位于美国,7支位于加拿大。传统上,因为联盟的加拿大血统,大多数的球员都为加拿大籍。在NHL积极向美国扩展以及它相较于其他联盟的高标准和东欧铁幕垮台后的现成高水准球员的输出,欧洲球员和美国球员人数有着明显增加的趋势。即便如此,2005-2006赛季球员名单中有一半的球员仍是在加拿大出生的。

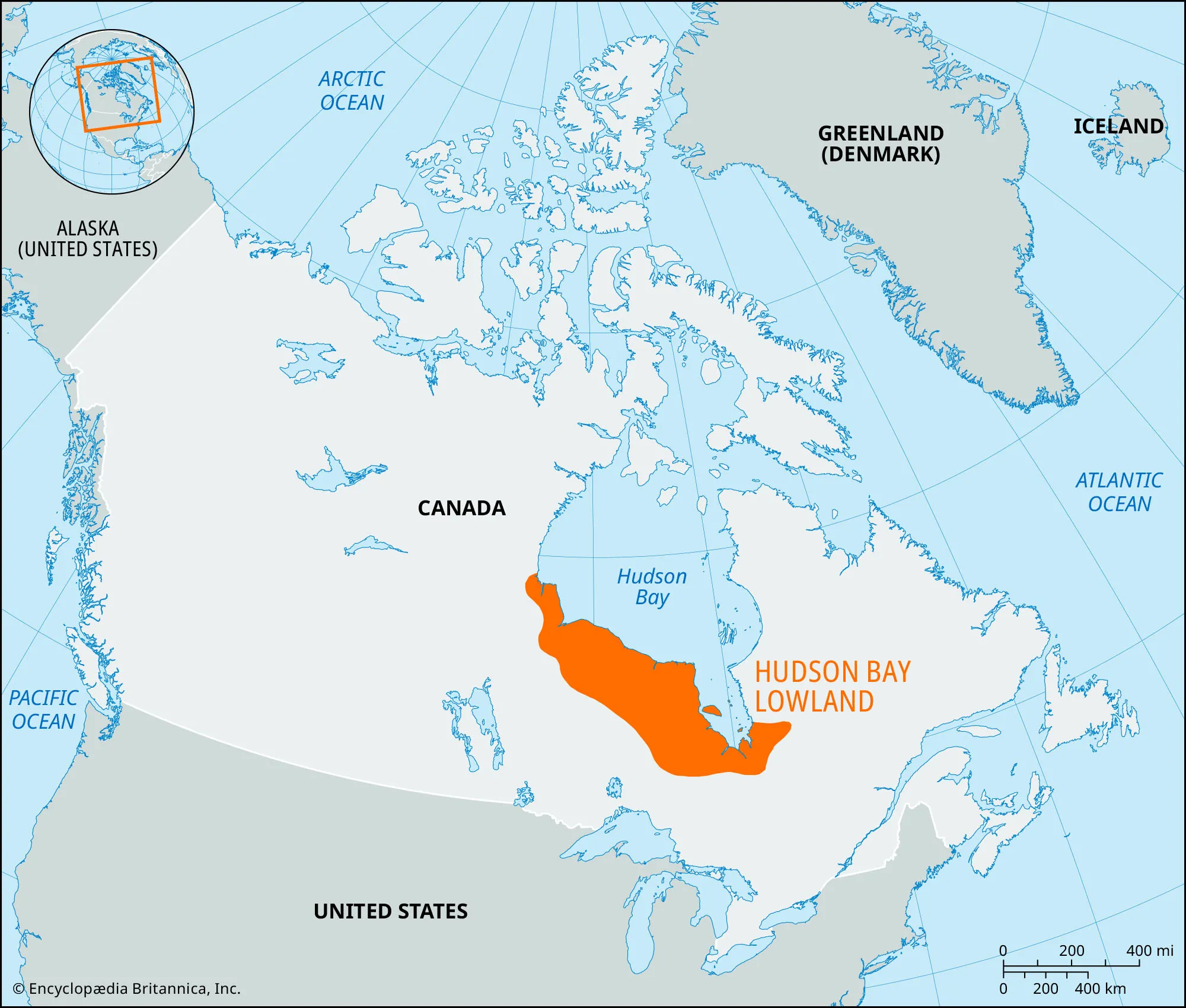
Die Hudson Bay (französisch Baie d'Hudson, Inuktitut Kangiqsualuk Ilua, deutsch auch Hudsonbai oder Hudson-Bucht) ist ein über 1,23 Millionen km² großes Randmeer im nordöstlichen Teil Kanadas. An der über die Hudson-Straße mit dem Atlantik verbundenen Meeresbucht haben die kanadischen Provinzen Manitoba, Ontario, Québec sowie das Territorium Nunavut Anteil. Die Hudson Bay ist nach Henry Hudson benannt, der die Bucht 1610 für die Virginia Company und die British East India Company entdeckte.
哈德森湾(英语:Hudson Bay,或称哈德森湾)位于加拿大东北部巴芬岛与拉布拉多半岛西侧的大型海湾。海湾处于努纳武特地区[2],水体面积123万平方千米。平均水深100米。哈德森湾是世界上面积最大的内海。而气象层面上,哈德森湾可被视为北冰洋的边缘海。北部时常会有北极熊出现。主要港口有丘吉尔港。
哈德森湾流域覆盖面积非常广大[3],约386万平方公里,覆盖努纳武特东南部,艾伯塔省,萨斯喀彻温省,安大略省,魁北克省,曼尼托巴省的全部地区,以及通过美国各州的水路间接覆盖明尼苏达州,北达科他州,南达科他州和蒙大拿州。
哈德森湾的南部分支称为詹姆斯湾。
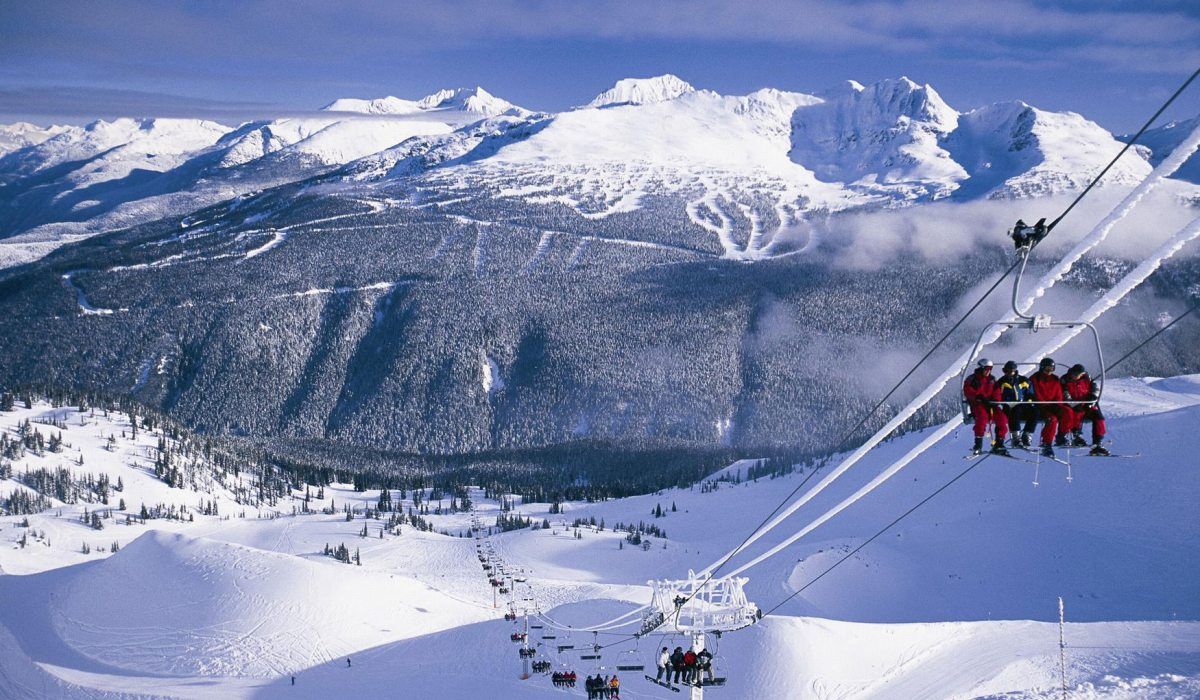







惠 斯勒山滑雪场于1966年启用,占地3,657英亩,标高1,530公尺,共有超过100个滑雪道,是加拿大滑雪道最多的滑雪场。其中有25%的专业滑雪 道、55%为中级滑雪者设计的滑雪道,20%适合初学者所用的滑雪道,3种可供选择,变化很多,惠斯勒的滑雪期亦很长,每年十一月开始至翌年五月终结,有 时会延至八月还可以作夏季滑雪。1988年,惠斯勒山启用了10人高速缆车,运载逐年增加的滑雪人潮;1996年惠斯勒山另设了一条能供6人乘坐的高速缆 车载运上山路线。
惠斯勒除了是被选为全球最佳的“滑雪乐园”,也是世界闻名的理想渡假胜地,其受欢迎的程度完全没有受季节限制,春季滑雪一般开放到五月底左右,由于黑梳山山顶终年积雪,想要享受滑雪乐趣,不见得一定要等到冬季,夏季也到黑梳山顶享受在冰河上滑行的乐趣。
 United Nations
United Nations
 Companies
Companies
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON
 Geography
Geography
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Nunavut-NU
Nunavut-NU
 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 Architecture
Architecture
 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB
 Music
Music



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation