
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Kuwait
Kuwait


 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Iraq
Iraq
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Katar
Katar
 Comoros
Comoros
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Oman
Oman
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Somalia
Somalia
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
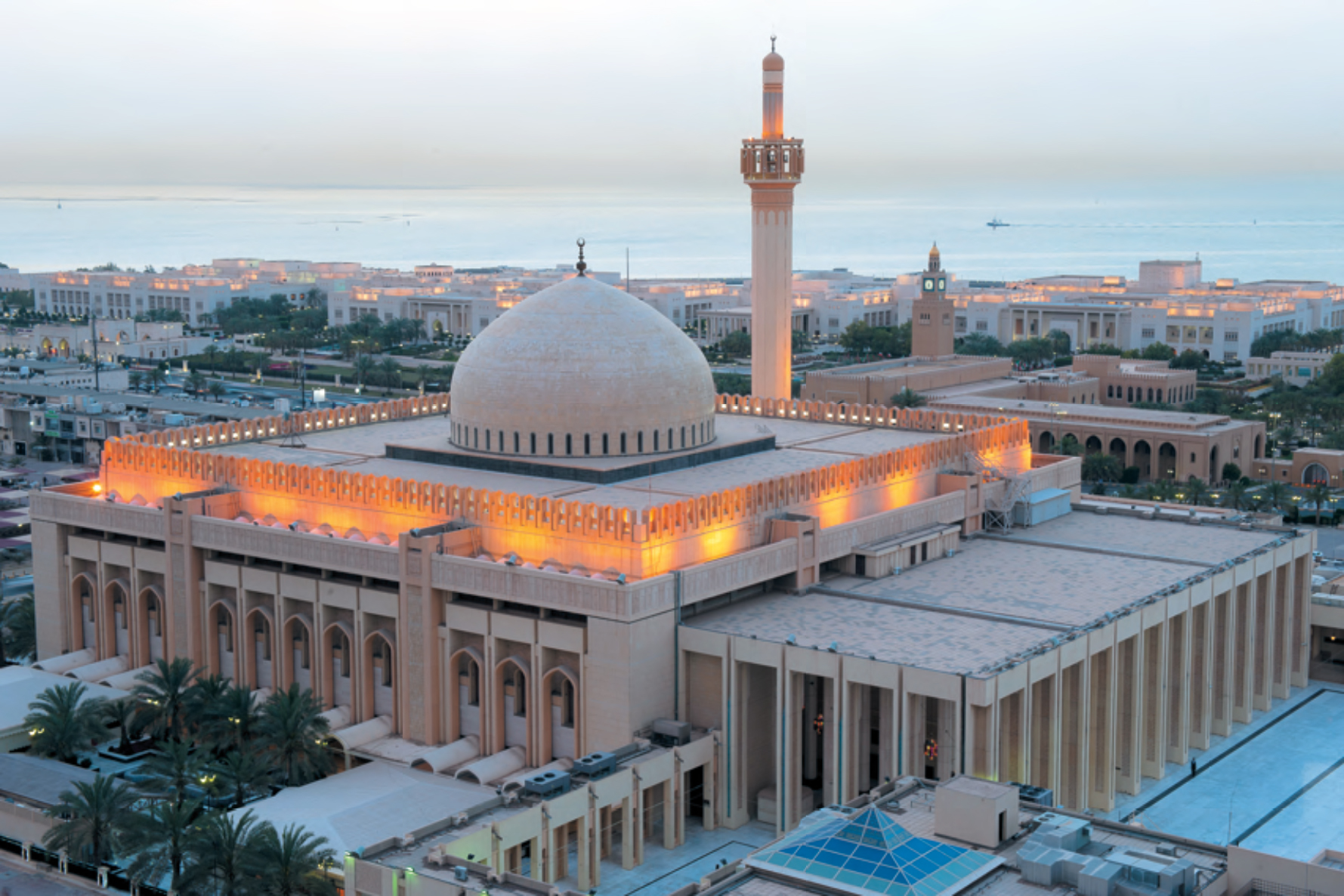


Die Große Moschee Kuwait (arabisch المسجد الكبير, DMG al-masǧid al-kabīr) ist die größte Moschee Kuwaits.
Das in der Stadt Kuwait gelegene Gesamtareal umfasst 45.000 m2, von denen 20.000 m2 überbaut sind. Die Moschee bietet im 5.000 m2 großen Männergebetssaal 7.000 und im separaten Frauengebetssaal noch einmal 950 Gläubigen Platz. Der Bau verfügt über eine mächtige Kuppel (Durchmesser 26 m; Höhe 47 m), ein 70 m hohes Minarett und eine monumentale Portikus (Höhe: 15 m). Auf dem Gelände befinden sich weiterhin eine Bibliothek und eine unterirdische 5-stöckige Tiefgarage mit 550 Stellplätzen.
Entworfen wurde die Moschee 1976 vom irakischen Architekten Mohammed Saleh Makiya. Der Bau dauerte von 1979 bis 1986. Ein bekannter Imam der Moschee ist Mischari Raschid al-Afasi.
科威特大清真寺(阿拉伯语:المسجد الكبير,DMG al-masǧid al-kabīr)是科威特最大的清真寺。
清真寺位于科威特城内,总占地面积为 45 000 平方米,其中 20 000 平方米为地上建筑。清真寺 5000 平方米的男礼拜堂可容纳 7000 人,单独的女礼拜堂可容纳 950 人。该建筑有一个巨大的圆顶(直径 26 米,高 47 米)、一个 70 米高的尖塔和一个不朽的门廊(高 15 米)。清真寺内还有一个图书馆和一个 5 层高的地下停车场,共有 550 个停车位。
清真寺于 1976 年由伊拉克建筑师穆罕默德-萨利赫-马基雅设计。清真寺著名的伊玛目之一是米沙里-拉希德-阿法西(Mishari Rashid al-Afasi)。
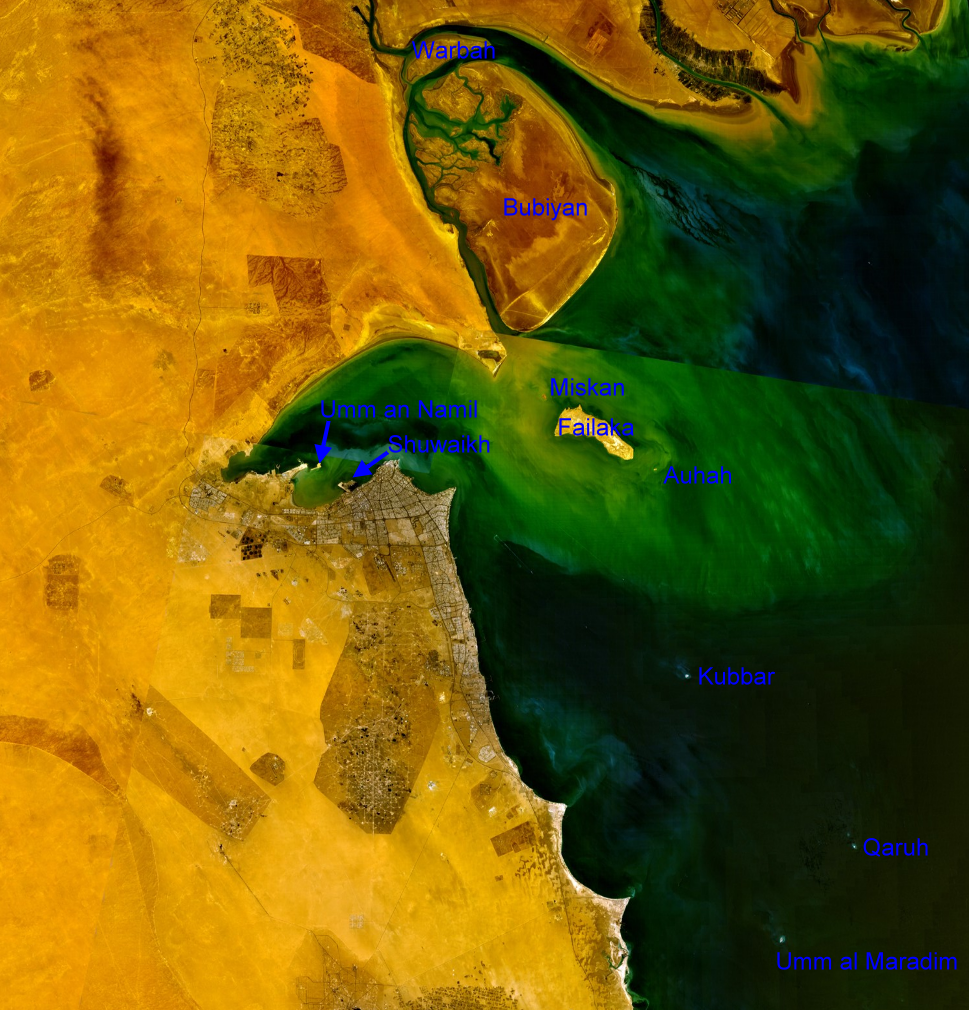
| NASA Visible Color Satellite Image with islands of Kuwait | ||||||||
| Island | Arabic | Area km² | Coordinates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| northern mudflat islands (Al Jahra Governorate) | ||||||||
| Warbah Island | جَزِيرَة وَرْبَة | 37 |  29°59′38″N 48°04′00″E 29°59′38″N 48°04′00″E | |||||
| Bubiyan Island | جَزِيرَة بُوبِيَان | 863 |  29°44′41″N 48°21′03″E 29°44′41″N 48°21′03″E | |||||
| Failaka with satellite islands (Al Asimah Governorate) | ||||||||
| Miskan Island | جَزِيرَة مِسْكَان | 0.75 |  29°29′05″N 48°15′05″E 29°29′05″N 48°15′05″E | |||||
| Failaka Island | جَزِيرَة فَيْلَكَا | 20 |  29°26′26″N 48°20′05″E 29°26′26″N 48°20′05″E | |||||
| Auhah Island | جَزِيرَة عَوْهَة | 0.35 |  29°22′40″N 48°26′21″E 29°22′40″N 48°26′21″E | |||||
| islands of Kuwait Bay (Al Asimah Governorate) | ||||||||
| Umm an Namil Island | جَزِيرَة أُمّ اَلنَّمْل | 0.569 |  29°22′54″N 47°52′01″E 29°22′54″N 47°52′01″E | |||||
| Shuwaikh Island1) | جَزِيرَة قُرَيْن | 0.012 |  29°21′16″N 47°54′35″E 29°21′16″N 47°54′35″E | |||||
| southern islands (Al Ahmadi Governorate) | ||||||||
| Kubbar Island | جَزِيرَة كُبَّر | 0.11 |  29°04′20″N 48°29′36″E 29°04′20″N 48°29′36″E | |||||
| Qaruh Island | جَزِيرَة قَارُوه | 0.035 |  28°49′03″N 48°46′35″E 28°49′03″N 48°46′35″E | |||||
| Umm al Maradim Island | جَزِيرَة أُمّ اَلْمَرَادِم | 0.165 |  28°40′42″N 48°39′10″E 28°40′42″N 48°39′10″E | |||||
| Islands of Kuwait | 922 | |||||||
| 1) former island | ||||||||
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libya
Libya
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdul Rahman bin Hamad Al Attiyah
Abdul Rahman bin Hamad Al Attiyah
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdullah Yaccoub Bishara
Abdullah Yaccoub Bishara
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani
Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Fahim bin Sultan Al Qasimi
Fahim bin Sultan Al Qasimi
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf,CCASG
 Jamil Ibrahim Al-Hejailan
Jamil Ibrahim Al-Hejailan
 Katar
Katar
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Oman
Oman
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade

海湾阿拉伯国家合作委员会(阿拉伯语:مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسي),原名海湾合作委员会(阿拉伯语:مجلس التعاون الخليج الفارسي),中文简称海合会,是一个包括阿拉伯波斯湾地区的6个国家(即波斯湾六国)在内的政府国际组织和贸易集团,其目标主要针对经济和社会方面。
Der Kooperationsrat der Arabischen Staaten des Golfes (englisch Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, CCASG) (arabisch مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية, DMG Maǧlis at-taʿāwun li-duwal al-ḫalīǧ al-ʿarabiyya), auch als Golf-Kooperationsrat (englisch Gulf Cooperation Council, GCC) bekannt, ist ein Staatenbund, der sechs Staaten der Arabischen Halbinsel umfasst. Er wurde am 25. Mai 1981 in Abu Dhabi durch Kuwait, Bahrain, Saudi-Arabien, Katar, Vereinigte Arabische Emirate und Oman gegründet, um diese Staaten von den Auswirkungen der Islamischen Revolution im Iran im Jahr 1979 und des Ausbruch des Ersten Golfkriegs 1980 abzuschirmen.[1]
Die Organisation strebt die Zusammenarbeit ihrer Mitglieder in der Außen- und Sicherheitspolitik sowie die Förderung der wirtschaftlichen und gesellschaftlichen Beziehungen zwischen ihnen an, wozu 1982 im Rahmen des Unified Economic Agreement der Warenverkehr liberalisiert wurde. Für 2005 wurde eine Zollunion beschlossen, die schließlich auf das Jahr 2003 vorgezogen wurde. Bis 2010 war die Einführung einer gemeinsamen Währung vorgesehen. Unterschiedliche politische Ziele und eine Reihe trennender Fragen behindern jedoch die Integrationsbemühungen.
Die Mitglieder sind zu gegenseitigem Beistand im Verteidigungsfall verpflichtet. Der GCC unterhält eine gemeinsame Verteidigungstruppe, die 5.000 Mann umfasst. Der GCC kooperierte eng mit den Vereinigten Staaten, um gegen den Iran geschützt zu sein.
Für die Europäische Union ist die GCC-Region von strategischer Bedeutung. Der GCC ist der wichtigste Handelspartner der Union in der arabischen Welt. Auf ihn entfallen etwa die Hälfte des gesamten Handels mit den arabischen Staaten und etwa 4 Prozent der Gesamtausfuhr der Europäischen Union in Drittländer.
Waffenexporte Deutschlands in Länder des GCC hatten 2012 einen Wert von 1,42 Milliarden Euro (2011: 570 Millionen Euro). [2]
湾岸協力会議(わんがんきょうりょくかいぎ、英語:Gulf Cooperation Council、英略称:GCC、アラビア語:مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية)は、中東・アラビア湾岸地域における地域協力機構である。正式名称は「Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf(湾岸アラブ諸国協力会議、CCASG)」。日本政府での呼称は湾岸協力理事会(GCC)[1]。
1981年5月25日にアブダビで設立[2][3]。本部はリヤド。現在の事務局長はバーレーンのアブドゥッラティーフ・ビン・ラーシド・ザイヤーニー。
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (Arabic: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية), originally (and still colloquially) known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC, مجلس التعاون الخليجي), is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union consisting of all Arab states of the Persian Gulf except Iraq. Its member states are Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.[2][3] The Charter of the Gulf Cooperation Council was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.[4]
All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain),[5][6] two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen.[7][8]
A 2011 proposal to transform the GCC into a "Gulf Union" with tighter economic, political and military coordination has been advanced by Saudi Arabia, a move meant to counterbalance the Iranian influence in the region.[9][10] Objections have been raised against the proposal by other countries.[11][12] In 2014, Bahrain prime minister Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa said that current events in the region highlighted the importance of the proposal.[13]
In order to reduce their dependence on oil in the future, the GCC states are pursuing unprecedented economic structural reform initiatives.[14]
Le Conseil de coopération des États arabes du Golfe (arabe : مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية) ou Conseil de coopération du Golfe (CCG) (arabe :مجلس التعاون الخليج العربي) est une organisation régionale regroupant six monarchies arabes et musulmanes du golfe Persique : l'Arabie saoudite, Oman, le Koweït, Bahreïn, les Émirats arabes unis et le Qatar.
Il Consiglio di cooperazione del Golfo (in inglese Gulf Cooperation Council, GCC; in arabo: مجلس التعاون الخليج الفارسی, Majlis al-Taʿāwun al-Khalījī), il cui nome completo è Consiglio di cooperazione degli Stati del golfo Persico (in inglese Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, CCASG; in arabo: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسی, Majlis al-Taʿāwun li-duwal al-Khalīj al-Fārisī, è un'Organizzazione internazionale regionale che riunisce sei stati del golfo Persico.
El Consejo de Cooperación para los Estados Árabes del Golfo (en árabe: مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج الفارسی – también conocida por sus siglas; CCEAG) es una organización regional formada por seis naciones del Próximo Oriente, antiguamente denominada como; Consejo de Cooperación del Golfo (مجلس التعاون الخليجي). Creada el 25 de mayo de 1981,12 el Consejo lo forman Baréin, Kuwait, Omán, Catar, Arabia Saudita y los Emiratos Árabes Unidos.34
La principal fuente de riqueza de los miembros del consejo es el petróleo. No obstante, se trata de una región vulnerable política y económicamente, fundamentalmente por su dependencia de una única fuente de riqueza, su escasa población, su gran superficie y su escasa capacidad militar.
Existe una unión aduanera entre todos los miembros del Consejo, los cuales pertenecen también a la Organización Mundial del Comercio. El Consejo se encuentra en la actualidad (2005) negociando un acuerdo de libre comercio con la Unión Europea.
Совет сотрудничества арабских государств Персидского залива (ССАГПЗ) (англ. Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf; араб. مجلس التعاون لدول الخليج العربية) — региональная закрытая международная организация. В официальном названии организации слово Персидский отсутствует, поскольку арабские государства предпочитают называть этот залив Арабским.
Организация создана 25 мая 1981[1][2], её политика определена в Хартии, ратифицированной в 1982 году. Основная цель организации — координация, сотрудничество и интеграция во всех экономических, социальных и культурных делах. Относительное регулирование было осуществлено в экономических и финансовых вопросах; коммерции, таможне и коммуникациях; образовании и культуре; социальных проблемах и проблемах здравоохранения; СМИ и туризме; в законодательных и административных вопросах. Соглашение также должно стимулировать научный и технологический прогресс в промышленности, сельском хозяйстве и сохранении водных ресурсов. По условиям Объединённого экономического соглашения, тарифные барьеры между шестью государствами были упразднены, и народы Залива свободны в открытии производства и осуществлении контрактов в любом государстве на равных правах. Кроме того, в планах имеется создание объединённых сил обороны для быстрого развертывания. Органы Совета сотрудничества государств Персидского залива включают в себя Верховный совет глав государств, которые встречаются ежегодно, Совет министров, который заседает раз в три месяца. Генеральный секретариат находится в Эр-Рияде, Саудовская Аравия.
6 марта 2012 года шесть членов ССАГПЗ заявили, что Совет сотрудничества стран Залива будет развиваться от регионального блока в конфедерацию.
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 A320neo
A320neo
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 A320-100 / -200
A320-100 / -200
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 777-300ER
777-300ER
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 ACJ319
ACJ319
 Airbus A320
Airbus A320
 ACJ320
ACJ320
 Airbus A330
Airbus A330
 A330-200
A330-200
 Airbus A330
Airbus A330
 A330-800neo
A330-800neo
 Airbus A340
Airbus A340
 A340-500
A340-500
 Airbus A350
Airbus A350
 A350-900
A350-900
 Boeing 737
Boeing 737
 737-900ER
737-900ER
 Boeing 747
Boeing 747
 747-8I
747-8I
 Boeing 777
Boeing 777
 777-300ER
777-300ER
 Boeing Business Jets
Boeing Business Jets
 BBJ 3
BBJ 3
 Gulfstream
Gulfstream
 Gulfstream V
Gulfstream V
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Kuwait Airways
Kuwait Airways



 Aerospace
Aerospace

 Companies
Companies



 Sport
Sport
 Architecture
Architecture
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Religion
Religion
 Geography
Geography
 Financial
Financial
 States of Asia
States of Asia


 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Exhibition
Exhibition