
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Argentina
Argentina
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Brazil
Brazil

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Ecuador
Ecuador

 Geography
Geography
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Honduras
Honduras
 Canada
Canada
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR
 Panama
Panama
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Paraná
Paraná
 Peru
Peru
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
 Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul
 Santa Catarina
Santa Catarina
 São Paulo
São Paulo
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United States
United States

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Yukon-YT
Yukon-YT
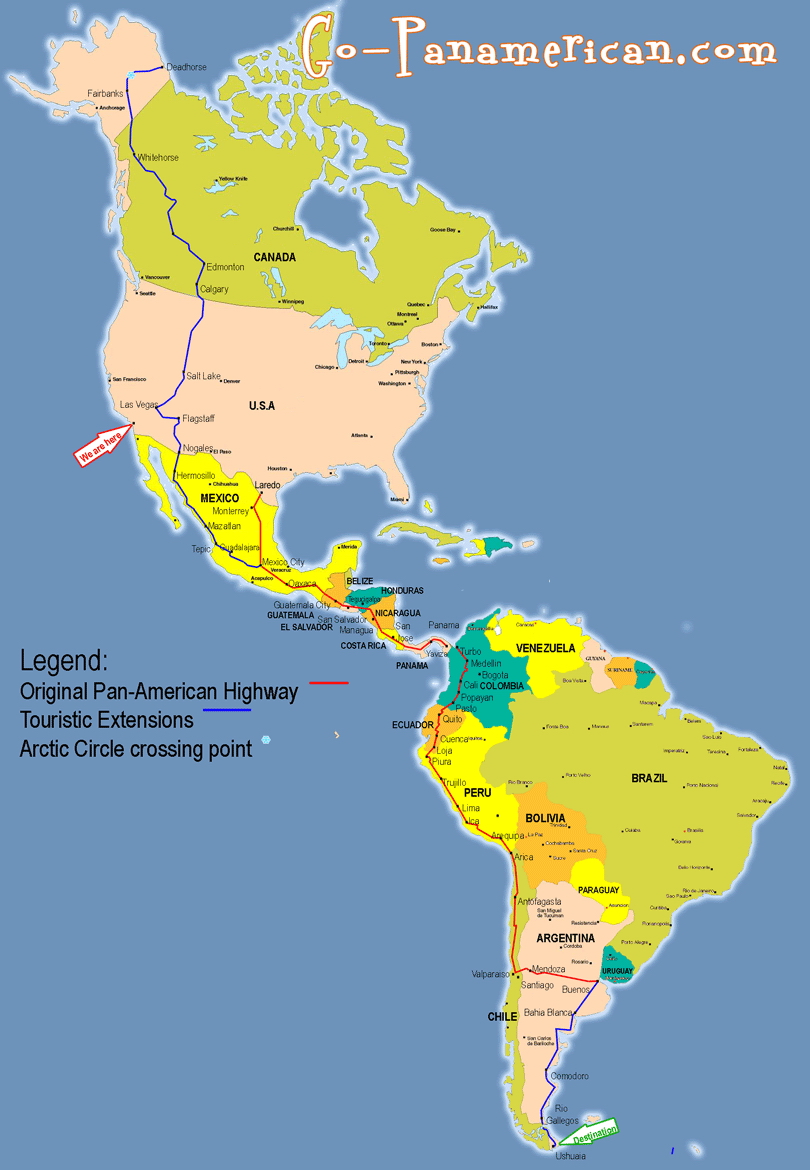
泛美公路(英語:Pan-American Highway,西班牙語:Carretera Panamericana,葡萄牙語:Rodovia Pan-americana,法語:Route panaméricaine)是贯穿整个美洲大陆的公路系统。北起阿拉斯加,南至火地岛,全长约48,000公里,主干线自美国阿拉斯加的费尔班克斯至智利的蒙特港,将近26,000公里。除了巴拿马到哥伦比亚(达连隘口)之间至今仍未修建公路以外,美洲大陆各国都通过这个公路网连接起来[1]。
Die Panamericana (englisch Pan-American Highway, spanisch Carretera Panamericana und Ruta Panamericana) ist ein System von Schnellstraßen, das – mit wenigen Lücken – Alaska mit Feuerland verbindet, sich also über die gesamte Nord-Süd-Ausdehnung des amerikanischen Doppel-Kontinents erstreckt. Das Netzwerk umfasst etwa 48.000 km Schnellstraße und ist in seiner längsten Nord-Süd-Verbindung etwa 25.750 km lang. Auf der Fünften Internationalen Konferenz der Amerikanischen Staaten im Jahre 1923 entstand die Idee einer einzigen kontinentübergreifenden Schnellstraße. Die Konvention über die Carretera Panamericana wurde schließlich am 23. Dezember 1936 auf der Interamerikanischen Konferenz zur Festigung des Friedens in Buenos Aires unterzeichnet.
Die projektierte Fertigstellung des Teilstücks hat viele Gegner, die verschiedene Gründe vorbringen: So würden der tropische Regenwald und die Lebensweisen der dortigen indigenen Völker bedroht; der Drogenhandel aus Kolumbien nach Nordamerika und die Verbreitung der Maul- und Klauenseuche in Südamerika würden gefördert.
Die Panamericana passiert viele Klimazonen, sowohl dichten Dschungel als auch Pässe des Hochgebirges. Außerdem durchquert sie 14 bis 19 verschiedene Staaten und ist deshalb weit entfernt von einer einheitlichen Beschilderung und auch Nutzbarkeit. So kann man Teile der Straße nur in der Trockenzeit befahren, in anderen ist die Benutzung das ganze Jahr über gefährlich. Die Jahresdurchschnittstemperatur reicht vom Gefrierpunkt bis zu über 25 °C.


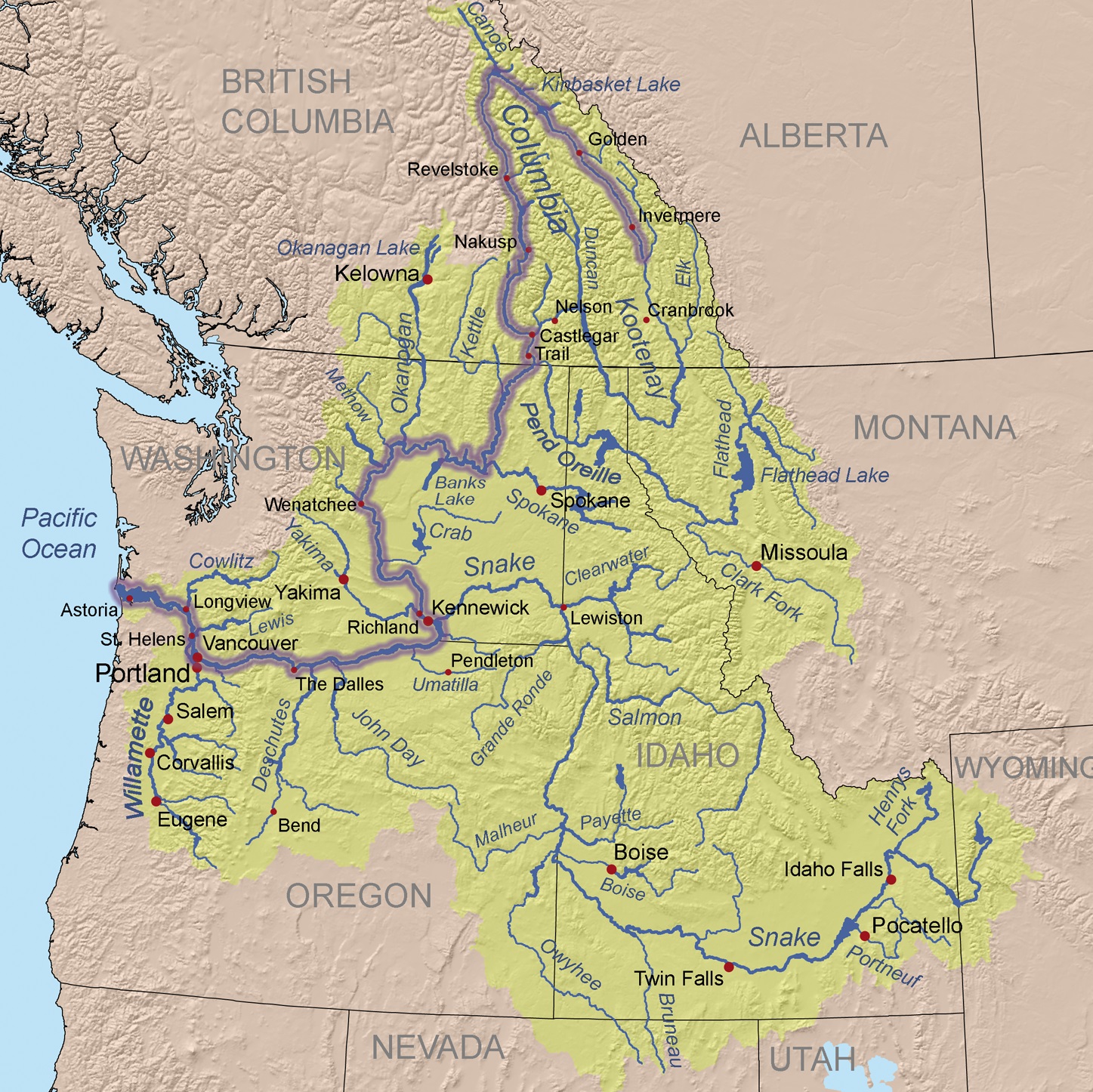
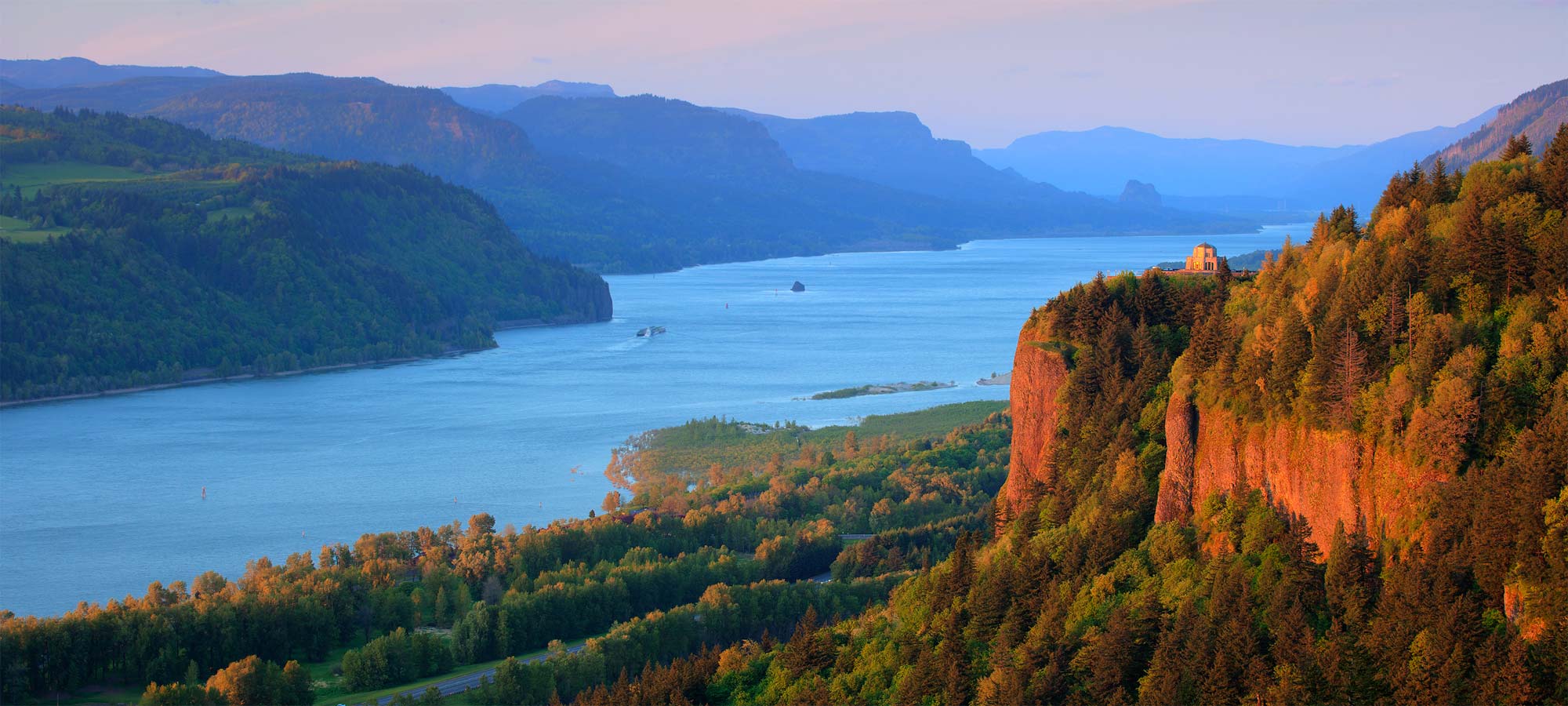
Der Columbia River ist ein 1953 Kilometer langer Fluss im westlichen Nordamerika. Er ist der wasserreichste aller nordamerikanischen Flüsse, die in den Pazifischen Ozean münden.
Mit seinem linken Nebenfluss, dem Snake River, zusammen hat er eine Länge von 2240 km. Sein Einzugsgebiet umfasst 668.217 km², wovon etwa 15 % innerhalb Kanadas[1] liegen.
Der Fluss ist nach dem Schiff Columbia Rediviva des US-amerikanischen Kapitäns Robert Gray benannt, der am 11. Mai 1792 als erster Weißer den Columbia River hinauffuhr. Gray reiste in den pazifischen Nordwesten, um mit Fellen zu handeln.[2]
Die Lewis-und-Clark-Expedition erreichte 1805 vom Osten auf dem Landweg die Mündung des Flusses. Der Columbia River wurde 1814 erstmals vollständig von David Thompson kartografiert.
Von den 1820er Jahren bis in die 1840er Jahre folgte der York Factory Express, eine Handelsroute der Hudson’s Bay Company zwischen der York Factory an der Hudson Bay und dem Fort Vancouver, abschnittsweise dem Flusslauf.
哥伦比亚河(英语:Columbia River),位于北美太平洋西北地区,全长2,044公里,流域面积415,211平方公里,平均流量每秒7,500立方米。哥伦比亚河起源于洛矶山脉在加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚内的部分,向西北方向蜿蜒,然后向南流入美国境内的华盛顿州,然后沿着华盛顿州和俄勒冈州的边界向西流动,最后注入太平洋。整段河流流经的美国州级行政单位和加拿大的省级行政单位共7个。哥伦比亚河是北美洲太平洋西北地区最大的河流。1792年罗伯特·格雷船长率领哥伦比亚号发现了这条河,并将此河用自己的帆船名来命名。
コロンビア川(コロンビアがわ、Columbia River)は、カナダのブリティッシュコロンビア州およびアメリカ合衆国太平洋岸北西部を流れる川である。
ブリティッシュコロンビア州のカナディアンロッキーに源を発する。そこからアメリカ、ワシントン州を流れ、ポートランドにて支流のウィラメット川を合わせ、オレゴン州のアストリアにて太平洋に注ぐ。最後の480kmはワシントン州とオレゴン州の境界となっている。
コロンビア川には、ボンネビル・ダム、グランドクーリーダムなどの水力発電用のダムがある。
マンハッタン計画以来半世紀間操業したハンフォード・サイトのプルトニウム生産炉による放射能汚染が深刻な問題となっている。
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: Wimahl or Wimal; Sahaptin: Nch’i-Wàna or Nchi wana; Sinixt dialect swah'netk'qhu) is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America.[10] The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the US state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is 1,243 miles (2,000 km) long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific.
The Columbia and its tributaries have been central to the region's culture and economy for thousands of years. They have been used for transportation since ancient times, linking the region's many cultural groups. The river system hosts many species of anadromous fish, which migrate between freshwater habitats and the saline waters of the Pacific Ocean. These fish—especially the salmon species—provided the core subsistence for native peoples.
The first documented European discovery of the Columbia River was that of Bruno de Heceta, who in 1775 sighted the river's mouth. In the late 18th century, a private American ship became the first non-indigenous vessel to enter the river; it was followed by a British explorer, who navigated past the Oregon Coast Range into the Willamette Valley. In the following decades, fur trading companies used the Columbia as a key transportation route. Overland explorers entered the Willamette Valley through the scenic but treacherous Columbia River Gorge, and pioneers began to settle the valley in increasing numbers. Steamships along the river linked communities and facilitated trade; the arrival of railroads in the late 19th century, many running along the river, supplemented these links.
Since the late 19th century, public and private sectors have heavily developed the river. To aid ship and barge navigation, locks have been built along the lower Columbia and its tributaries, and dredging has opened, maintained, and enlarged shipping channels. Since the early 20th century, dams have been built across the river for power generation, navigation, irrigation, and flood control. The 14 hydroelectric dams on the Columbia's main stem and many more on its tributaries produce more than 44 percent of total US hydroelectric generation. Production of nuclear power has taken place at two sites along the river. Plutonium for nuclear weapons was produced for decades at the Hanford Site, which is now the most contaminated nuclear site in the US. These developments have greatly altered river environments in the watershed, mainly through industrial pollution and barriers to fish migration.
Le Columbia (se prononce /kə.lʌm.bi.ə/ ou « co-lemb-bia » et se nomme Columbia River /kə.lʌm.bi.ə ˈɹɪvəɹ/ en anglais) est un fleuveNote 1 circulant du Canada aux États-Unis avant de se jeter dans l'océan Pacifique.
C'est le plus grand cours d'eau de la région Nord-Ouest Pacifique de l'Amérique du Nord, que ce soit par sa longueur totale, la taille du bassin versant ou son débit à l'embouchure. Il prend sa source dans les montagnes Rocheuses en Colombie-Britannique, au Canada, puis coule dans les États américains de Washington et de l'Oregon avant de se jeter dans l'océan Pacifique à la hauteur de la ville d'Astoria. Le fleuve mesure environ 2 000 kilomètres et son principal affluent est la Snake. Son bassin versant est d'environ 670 000 kilomètres carrés, soit un peu plus que la taille de la France, et s'étend sur sept États américains et une province canadienne.
Le Columbia est le quatrième fleuve des États-Unis par son volume et est celui des fleuves d'Amérique du Nord qui se jettent dans l'océan Pacifique qui a le plus grand débit. Son débit abondant et son dénivelé relativement important lui donnent un énorme potentiel pour la production d'énergie hydroélectrique. Les quatorze barrages hydroélectriques sur le cours principal du Columbia produisent à eux seuls plus d'énergie hydroélectrique que ceux de tout autre fleuve nord-américain.
Le Columbia et ses affluents ont été au centre de la culture et de l'économie de la région depuis des milliers d'années. Ils ont été utilisés pour le transport et comme axe de communication, reliant les nombreux groupes de populations de la région. Le système fluvial accueille de nombreuses espèces de poissons anadromes qui migrent entre les habitats d'eau douce et de mer de l'océan Pacifique. Ces poissons, surtout les espèces de saumons, fournirent une nourriture de base pour les peuples autochtones et, dans les siècles passés, les commerçants de tout l'Ouest de l'Amérique du Nord sont venus commercer ces poissons.
À la fin du XVIIIe siècle, le Columbia Rediviva, un navire américain, devint le premier à entrer dans l'embouchure du fleuve depuis l'océan Pacifique, et son commandant Robert Gray nomma sa découverte du nom de son bateau. Il fut suivi par l'explorateur britannique William Robert Broughton qui explora la chaîne côtière de l'Oregon dans la vallée de la Willamette. Dans les décennies suivantes, les compagnies commerciales de traite des fourrures utilisèrent le Columbia comme une voie de transport clé. Les explorateurs à terre venus de l'est entrèrent dans la vallée de la Willamette par la gorge du Columbia et les pionniers commencèrent à s'installer dans la vallée de la Willamette en nombre croissant depuis les deux voies d'accès découvertes. Les bateaux à vapeur naviguant le long du fleuve facilitèrent le commerce et les communications et l'arrivée du chemin de fer à la fin du XIXe siècle, avec des lignes suivant le lit du fleuve, permit de compléter ces liens.
Depuis la fin du XIXe siècle, les installations diverses, privées et publiques, se sont fortement développées sur le fleuve. Pour faciliter la navigation des navires et des barges, des écluses ont été construites le long du bas Columbia et de ses affluents, et le dragage a ouvert et maintenu des chenaux de navigation praticables. Dès le début du XXe siècle, des barrages furent construits sur le fleuve pour la production d'électricité, la navigation, l'irrigation agricole et le contrôle des inondations. Au début des années 2010, du côté américain, un lac de barrage est présent presque tous les milles sur le fleuve. La production d'énergie nucléaire a lieu sur deux sites le long du fleuve et du plutonium pour des armes nucléaires a été produit pendant des décennies sur le site du laboratoire national de Hanford, qui est maintenant le site nucléaire le plus contaminé aux États-Unis. Toutes ces évolutions eurent un impact énorme sur les écosystèmes locaux, et peut-être plus particulièrement par la pollution industrielle et les obstacles à la migration des poissons.
Il Columbia è il fiume più grande sfociante nel Pacifico nord-occidentale, in Nord America.
Il fiume nasce dalle Montagne Rocciose della Columbia Britannica, in Canada. Scorre con andamento nord-ovest e poi verso sud, entrando negli Stati Uniti d'America, nello stato di Washington; successivamente inizia a scorrere verso ovest per fungere da confine tra Washington e l'Oregon, prima di sfociare nell'Oceano Pacifico. La lunghezza del fiume è di 2.000 km, e il suo più grande affluente lo Snake. Il suo bacino idrografico ha quasi le dimensioni della Francia.
Il Columbia è il quarto fiume più grande degli Stati Uniti, ed il fiume con più portata tra quelli sfocianti nel Pacifico nord-occidentale. L'enorme portata e la relativa velocità delle sue acque conferiscono al Columbia un enorme potenziale per la generazione di energia idroelettrica. Le 14 dighe poste sul fiume, e quelle poste lungo il corso degli affluenti, producono più energia di qualsiasi altro fiume nordamericano.
Il fiume e i suoi affluenti sono stati per migliaia di anni molto importanti per la cultura e l'economia delle regioni che attraversano. Essi sono stati utilizzati per il trasporto fin dall'antichità, collegando un sistema di culture molto diverse tra loro. Le fasce fluviali del Columbia e dei suoi affluenti ospitano molte specie di pesci anadromi, che migrano dalle acque dolci a quelle salate dell'Oceano Pacifico. Questi pesci, soprattutto il salmone, sono stati fondamentali per la sopravvivenza dei nativi e per i commercianti provenienti da tutto il Nord America.
El río Columbia (también conocido como Wimahl o Gran Río por los nativos de los pueblos chinook que viven en su curso bajo) es un río del suroeste de Canadá y noroeste de Estados Unidos que fluye en dirección norte-sur-oeste por la provincia de Columbia Británica, en Canadá, y los estados de Washington y Oregón en Estados Unidos, desembocando en el océano Pacífico. Con 2044 km es el sexto río más largo de América del Norte, por detrás del Misuri, Misisipi, Bravo, Arkansas y Colorado.
Toma el nombre del Columbia Rediviva, el primer barco occidental conocido que haya remontado el río. Nace en la provincia canadiense de la Columbia Británica y tras cruzar el estado de Washington (EE. UU.) y luego delimitar gran parte de la separación administrativa entre los estados de Washington y Oregón, desemboca en el Pacífico. Su cuenca hidrográfica, que drena gran parte de la Columbia Británica, Idaho, Oregón, Washington y pequeñas regiones de Montana, Wyoming, Utah y Nevada, comprende 668 000 km².
En términos de caudal (7500 m³/s en su desembocadura), el Columbia es el río de Norteamérica más caudaloso de la vertiente del Pacífico y el cuarto más caudaloso de los Estados Unidos. La fuerte corriente del río y el elevado salto o descenso de altura en una relativamente corta longitud, le proporciona un tremendo potencial de producción de electricidad que ya ha sido explotado, siendo el río que más energía hidroeléctrica produce de Norteamérica, con catorce presas a lo largo de su curso —tres en Canadá y once en Estados Unidos— y otras muchas en varios de sus afluentes.
Su desembocadura fue descubierta y cartografiada en 1775 por el buque español Santiago al mando del comandante Bruno de Heceta. En 1792 fue explorado por el comerciante y aventurero estadounidense Robert Gray. Entre 1807 y 1811, la peletera Compañía del Noroeste explotó todo su curso. Desde la década de 1810 el río sirvió como vía de comunicación en la región noroccidental del subcontinente.1
Después del establecimiento de numerosos asentamientos estadounidenses y europeos en sus orillas, el río Columbia ha prestado muchos servicios para el desarrollo de los propósitos humanos, incluyendo trabajos de draga para permitir la navegación de mayores barcos por sus aguas, la construcción de presas para la generación de electricidad, agua para el riego de cultivos y control de crecidas e inundaciones, e incluso para refrigerar instalaciones de energía nuclear. Todos esos proyectos han entrado en conflicto con la conservación del medioambiente y el movimiento de especies píscicolas y animales, produciendo una contaminación indeseada en sus aguas.
Колумбия (англ. Columbia River) — река на северо-западе Северной Америки[1]. Пересекает канадскую провинцию Британская Колумбия, а также американские штаты Вашингтон и Орегон. Длина — 2000[2] км.
Полноводная Колумбия имеет ледниковое питание и горный скоротечный характер течения. Большой объём воды и значительный перепад высот на относительно короткой дистанции создаёт благоприятные условия для производства гидроэлектроэнергии. Колумбия является рекой с самым большим производством электроэнергии в Северной Америке. На реке построено 14 гидроэлектростанций как в США, так и в Канаде.
Первыми из европейцев по реке спустились участники экспедиции Льюиса и Кларка 1805—1807 годов. В 1806—1811 годах бассейн реки обследовал и нанёс на карту торговец пушниной и картограф Дэвид Томпсон. Он же стал первым, кто прошёл реку от истоков до устья.









Washington (engl. Aussprache [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən]) ist ein Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Er liegt im Nordwesten der USA an der Küste des Pazifischen Ozeans, nördlich von Oregon, westlich von Idaho und südlich von British Columbia in Kanada.
Gemessen an seiner Fläche steht Washington unter den US-Bundesstaaten mit 184.665 Quadratkilometern an 18. Stelle, gemessen an seiner Bevölkerung von 6.724.540 Einwohnern an 13. Stelle (Stand 2010). Der Großteil der Bevölkerung konzentriert sich rund um den Puget Sound, eine etwa 150 km lange, inselreiche und weitverzweigte Bucht im Westen des Staates, an der auch die Hauptstadt Olympia sowie die mit Abstand größte Stadt Seattle liegen.
Der Staat wurde nach dem ersten US-Präsidenten, George Washington, benannt und als 42. Staat im Jahr 1889 in die Vereinigten Staaten aufgenommen. Aufgrund der Vielzahl von Nadelbäumen trägt der Staat den Spitznamen Evergreen State (deutsch Immergrüner Staat).
Um den Bundesstaat von der ebenfalls nach George Washington benannten, an der Ostküste befindlichen Hauptstadt der USA, Washington, D.C., abzugrenzen, wird für den Staat oft die Bezeichnung Washington State verwendet.
ワシントン州(英: State of Washington, 英語発音: [ˈwɑʃɪ̞ŋʔn̩])は、アメリカ合衆国西海岸最北部の州。州都はオリンピアであるが、規模・経済の面での中心都市はシアトルである。北はカナダのブリティッシュコロンビア州、南はオレゴン州、東はアイダホ州と接している。1846年にオレゴン境界紛争を解決するためのオレゴン条約が結ばれた結果、イギリスから割譲されたワシントン準州の西側が現在のワシントン州になった。1889年にアメリカ合衆国42番目の州として認められた。
カリフォルニア州、オレゴン州と共にリベラルな気風で、保守的な中西部に対して「レッドウッド・カーテンの向こう側」と称される。
近年ではマイクロソフトの本拠地であり、スターバックスの発祥の地などとして知られる。州の中心都市シアトルがMLBシアトル・マリナーズの本拠地である。
2010年国勢調査によると、州の人口は6,724,540人となっている。そのおよそ60%はセイリッシュ海のピュージェット湾に沿った交通、事業、産業の中心であるシアトル都市圏に集中している。ピュージェット湾は太平洋からの入江であり、氷河が侵食した多くの島、深いフィヨルドおよび湾がある。州の西部は深い温帯雨林があり、西部、中部、北東部および最南東部には山脈がある。東部の亜乾燥盆地は徹底した農業が行われている。アメリカ合衆国の西海岸や西部ではカリフォルニア州に次いで2番目に人口の多い州である。
州の名はアメリカ建国の父で初代アメリカ合衆国大統領ジョージ・ワシントンに由来しており、大統領の名前が付けられたことでは合衆国の中で唯一の州である。首都ワシントンD.C.と区別するためにワシントン州と呼ばれるが、州民、近在の州およびカナダのブリティッシュコロンビア州南部の住人は単に「ワシントン」と呼び、首都の方は「ワシントンD.C.」あるいは単純に「D.C.」のみで呼んでいる。元々ワシントン州のある地域はコロンビア川にちなんで「コロンビア」と呼ばれており、ワシントンD.C.がコロンビア特別区と呼ばれることから、混乱を避けるためにワシントン州とされた。
Washington (/ˈwɒʃɪŋtən/ (![]() listen)), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Named for George Washington, the first U.S. president, the state was made out of the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, in accordance with the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state, which is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north, was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C.
listen)), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Named for George Washington, the first U.S. president, the state was made out of the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, in accordance with the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state, which is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north, was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C.
Washington is the 18th largest state, with an area of 71,362 square miles (184,827 km2), and the 13th most populous state, with more than 7.6 million people. Approximately 60 percent of Washington's residents live in the Seattle metropolitan area, the center of transportation, business, and industry along Puget Sound, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean consisting of numerous islands, deep fjords, and bays carved out by glaciers. The remainder of the state consists of deep temperate rainforests in the west; mountain ranges in the west, central, northeast, and far southeast; and a semi-arid basin region in the east, central, and south, given over to intensive agriculture. Washington is the second most populous state on the West Coast and in the Western United States, after California. Mount Rainier, an active stratovolcano, is the state's highest elevation, at almost 14,411 feet (4,392 meters), and is the most topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous U.S.
Washington is a leading lumber producer; its rugged surface is rich in stands of Douglas fir, hemlock, ponderosa pine, white pine, spruce, larch, and cedar. Washington is the nation's largest producer of apples, hops, pears, red raspberries, spearmint oil, and sweet cherries, and ranks high in the production of apricots, asparagus, dry edible peas, grapes, lentils, peppermint oil, and potatoes. Livestock and livestock products make important contributions to total farm revenue, and the commercial fishing of salmon, halibut, and bottomfish makes a significant contribution to the state's economy. Washington ranks second only to California in wine production.
Manufacturing industries in Washington include aircraft and missiles, shipbuilding, and other transportation equipment, food processing, metals and metal products, chemicals, and machinery. Washington has more than a thousand dams, including the Grand Coulee Dam, built for a variety of purposes including irrigation, power, flood control, and water storage.
Washington is one of the wealthiest and most socially liberal states in the country.[4] The state consistently ranks among the best for life expectancy and low unemployment.[5] Along with Colorado, Washington was one of the first to legalize medicinal and recreational cannabis, was among the first thirty-six states to legalize same-sex marriage, doing so in 2012, and was one of only four U.S. states to have been providing legal abortions on request before the 1973 Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade loosened abortion laws nationwide. Similarly, Washington voters approved a 2008 referendum on legalization of physician-assisted suicide, and is currently one of only five states, along with Oregon, California, Colorado and Vermont, as well as the District of Columbia to have legalized the practice. The state is also one of eight in the country to have criminalized the sale, possession and transfer of bump stocks, with California, Florida, New Jersey, New York, Vermont, Maryland, and Massachusetts also having banned these devices.
Washington (/ˈwɑʃ.ɪŋ.tən/3 Écouter) est un État des États-Unis situé à l'extrême nord-ouest du Mainland, soit les États-Unis contigus, (l'Alaska étant l'État à l'extrême nord-ouest de tous les États-Unis).
Il est bordé au nord par la province canadienne de la Colombie-Britannique, à l'est par l'Idaho, au sud par l'Oregon et à l'ouest par l'océan Pacifique.
Il ne faut pas confondre l'État de Washington et la capitale des États-Unis, Washington (district de Columbia), située à l'est du pays, qui tiennent tous les deux leurs noms du président américain George Washington.
Washington è uno stato federato del nord-ovest degli Stati Uniti d'America, posto sulla costa del Pacifico ad est, a nord dell'Oregon, a ovest dell'Idaho e a sud della provincia canadese della Columbia Britannica. Prende il nome da George Washington, primo presidente degli Stati Uniti, e deriva dalla parte occidentale del Territorio di Washington che era stato ceduto dalla Gran Bretagna nel 1846 con il Trattato dell'Oregon, annesso poi all'Unione come 42º stato nel 1889. La città più grande è Seattle, situata a ovest, seguita da Spokane, situata ad est, mentre la capitale è Olympia. È il 18° più esteso e il 13° più popoloso dei 50 Stati membri: dopo la California è il secondo Stato più popoloso sulla West Coast e negli Stati Uniti nord-occidentali, con circa il 60% dei residenti dello Stato che vive nella zona metropolitana di Seattle, il centro dei trasporti, del commercio e dell'industria lungo lo stretto di Puget (Puget Sound), un'insenatura del Pacifico costituita da numerose isole, profondi fiordi e valli scavate da ghiacciai. Il resto dello Stato è costituito da foreste pluviali temperate ad ovest, catene montuose nella parte occidentale, centrale, nordorientale e sudorientale, e una regione semi-arida a est, al centro e al sud, dedita all'agricoltura intensiva.
È uno dei principali produttori di legname essendo la sua superficie frastagliata ricca di foreste di abete di Douglas, cicuta, ponderosa e pino bianco, abete rosso, larice e cedro; è inoltre il più grande produttore di mele, luppoli, pere, lamponi rossi, olio di menta e ciliegie, e si colloca ai primi posti anche nella produzione di albicocche, asparagi, piselli, uva, lenticchie e patate; inoltre, animali e prodotti derivati danno un contributo importante al fatturato totale delle aziende agricole e la pesca commerciale del salmone, dell'halibut, e dei pesci dei fondali dà un contributo significativo all'economia dello Stato.
Anche se il suo nome inequivocabile è "The State of Washington", il nome dello Stato è spesso invertito e definito come "Washington State"' per evitare di confonderlo con Washington DC, il territorio della capitale degli Stati Uniti d'America che è invece situato nella parte opposta del paese (East Coast).
Washington, también llamado estado de Washington para diferenciarlo de Washington D. C., es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Olympia y su ciudad más poblada, Seattle. Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Pacífico, limitando al norte con Canadá, al este con Idaho, al sur con Oregón y al oeste con el océano Pacífico. Fue admitido en la Unión el 11 de noviembre de 1889, como el estado número 42.
Fue nombrado en homenaje al líder de las fuerzas estadounidenses de la Guerra de la Independencia de EE. UU. de 1776 y primer presidente de Estados Unidos, George Washington. Los nombres de muchas ciudades y condados de Estados Unidos rinden homenaje a diversos presidentes estadounidenses, pero el estado de Washington es el único estado en ser nombrado en homenaje a un presidente estadounidense. Para diferenciarla de la capital de Estados Unidos, Washington D. C., en Estados Unidos, se suele llamar "estado de Washington" al estado y "D. C." (abreviatura de "Distrito de Columbia", District of Columbia en inglés), "ciudad federal" o "ciudad de Washington" o a la capital nacional.
Washington cuenta con enormes bosques de coníferas, que le han valido el apodo de Evergreen State (estado siempre verde, o estado de la hoja perenne). Estos bosques hacen de Washington un líder de la industria maderera estadounidense. Se encuentra cortado por varios ríos y salpicado por varios lagos, lo que crea un terreno propicio para la instalación de presas. Aquí se localiza la mayor del país, la presa Grand Coulee, en el río Columbia. Su economía, sin embargo, se centra principalmente en el turismo y en la industria aeroespacial. El segundo mayor fabricante de aviones del mundo, Boeing, tiene su sede en este estado, así como varias de sus fábricas.
Los primeros europeos en explorar esta región fueron los castellanos, y posteriormente, los británicos fundaron los primeros asentamientos. La región formaba parte originalmente de una mayor llamada Oregon Country, un territorio disputado entre los estadounidenses y los británicos entre las décadas de 1810 y 1840. En 1846, el Tratado de Oregón establece que todas las tierras al sur del paralelo 49 del Oregon Country pasarían al control de Estados Unidos (a excepción de la isla de Vancouver). Hasta 1859, Washington formó parte del territorio de Oregón, creado a partir de la parte estadounidense del Oregon Country. En 1859, se crea el territorio de Washington, que fue nombrado en homenaje a George Washington.
Вашингто́н[1][2] (англ. Washington, американское произношение: [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən] (![]() слушать)) — штат[3] на северо-западе США, 42-й штат в составе страны. Столица — город Олимпия, крупнейший город — Сиэтл. Население — 7 546 410 человек (2019 г.).
слушать)) — штат[3] на северо-западе США, 42-й штат в составе страны. Столица — город Олимпия, крупнейший город — Сиэтл. Население — 7 546 410 человек (2019 г.).
Во избежание путаницы со столицей США, название последней обычно сопровождают словосочетанием «округ Колумбия» (в англоязычном варианте — «Washington, D.C.»). Официальное прозвище — «Вечнозелёный штат».

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Companies
Companies
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Architecture
Architecture
 Life and Style
Life and Style