
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg

 Andorra
Andorra
 Belgien
Belgien
 Frankreich
Frankreich

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institut für Kultur und Sprache
Institut für Kultur und Sprache
 Kanada
Kanada
 Literatur
Literatur
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Monaco
Monaco
 Schweiz
Schweiz

 Vereinte Nationen
Vereinte Nationen
 Amtssprachen
Amtssprachen
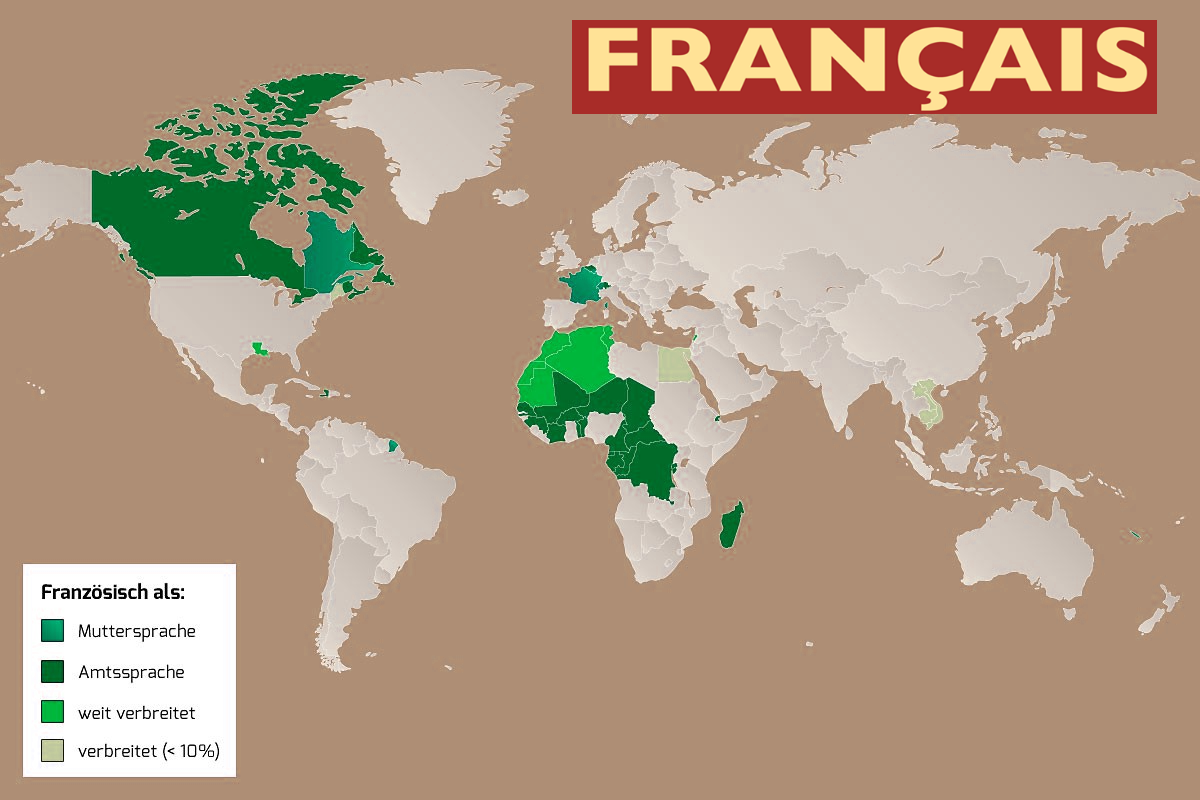
Französisch (Eigenbezeichnung: (le) français [(lə) fʁɑ̃ˈsɛ], (la) langue française [(la) lɑ̃ɡ fʁɑ̃ˈsεz]) gehört zu der romanischen Gruppe des italischen Zweigs der indogermanischen Sprachen. Damit ist diese Sprache unter anderem mit dem Italienischen, Spanischen, Okzitanischen, Katalanischen, Portugiesischen und Rumänischen näher verwandt.
Französisch wird von etwa 235 Millionen Menschen täglich verwendet[3] und gilt als Weltsprache, da es von rund 321 Millionen[4] Sprechern auf allen Kontinenten in über 50 Ländern gesprochen wird.[5]
Französisch ist unter anderem Amtssprache in Frankreich und seinen Überseegebieten, in Kanada, Belgien, der Schweiz, in Luxemburg, im Aostatal, in Monaco, zahlreichen Ländern West- und Zentralafrikas sowie in Haiti, während es im arabischsprachigen Nordafrika und in Südostasien als Nebensprache weit verbreitet ist. Zudem ist es Amtssprache der Afrikanischen Union und der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten, eine der Amtssprachen der Europäischen Union[6] und eine der sechs Amtssprachen sowie neben Englisch Arbeitssprache der Vereinten Nationen,[7] weiterhin Amtssprache des Weltpostvereins.
Französisch ist die fünftmeistgesprochene Sprache der Welt, im Internet wird sie am vierthäufigsten verwendet,[8] außerdem wird sie weltweit am zweithäufigsten als Fremdsprache erlernt.[9] Im Jahr 2050 werden nach Angaben der OIF weltweit rund 700 Millionen Gesamtsprecher leben.[9]
Auf die französische Sprache wirken normierend ein die Académie française, die sogenannte Loi Toubon (ein Gesetz zum Schutz der französischen Sprache in Frankreich), das Office québécois de la langue française (eine Behörde in Québec), der Service de la langue française (eine belgische Institution zur Pflege der französischen Sprache) sowie die Délégation générale à la langue française et aux langues de France.
法语(法语:français,发音:[fʁɑ̃sɛ] (ⓘ)),属于印欧语系罗曼语族的高卢-罗曼语支。法语和所有罗曼语族语言一样,都是从罗马帝国的拉丁语衍生的,法语从高卢地区(特别是北高卢)的拉丁语口语所演进而来。法语是除英语之外最多国家使用的官方语言、联合国工作语言之一,也是联合国、欧盟、北约、奥运会、世贸和国际红十字会等众多国际组织的官方语言及正式行政语言,其影响力仅次于英语。由于法国和比利时建立的殖民帝国将法语引入美洲、非洲及亚洲等地区,非洲法语成为大部分国家的第二语言,特别是加蓬、阿尔及利亚、摩洛哥、突尼斯、毛里求斯、塞内加尔及科特迪瓦等国[2]。
现时全世界有1亿人将法语作为母语,另有2.8亿人使用法语(包括把它作为第二语言的人),这些数字目前仍在增长中,尤其是在非洲大陆。现今法国法语(français métropolitain)和魁北克法语(québécois)是世界上最主要的两大法语分支,两者在发音与口语词汇上有所区别,但书面形式则一致。

 Astronomie
Astronomie



 Automobil
Automobil
 *Selbstfahrendes Kraftfahrzeug
*Selbstfahrendes Kraftfahrzeug
 Belgien
Belgien
 Dänemark
Dänemark
 Deutschland
Deutschland

 Europäische Union
Europäische Union
 Finnland
Finnland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Griechenland
Griechenland
 Irland
Irland


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Italien
Italien

 Landwirtschaft, Forstwirtschaft, Viehzucht, Fischerei
Landwirtschaft, Forstwirtschaft, Viehzucht, Fischerei



 Luft- und Raumfahrt
Luft- und Raumfahrt
 *DLR
*DLR



 Luft- und Raumfahrt
Luft- und Raumfahrt
 *ESA
*ESA



 Luft- und Raumfahrt
Luft- und Raumfahrt
 *CNES
*CNES



 Luft- und Raumfahrt
Luft- und Raumfahrt
 *ASI
*ASI
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg




 Militär,Verteidigung und Ausrüstung
Militär,Verteidigung und Ausrüstung
 Navigation Satellite System
Navigation Satellite System
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Österreich
Österreich
 Portugal
Portugal
 Rumänien
Rumänien

 Schiffe und Nautik
Schiffe und Nautik
 Schweden
Schweden
 Spanien
Spanien

 Transport und Verkehr
Transport und Verkehr
 Tschechien
Tschechien
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich

 Wissenschaft und Technik
Wissenschaft und Technik
伽利略定位系统(意大利语:Galileo),是一个正在建造中的卫星定位系统,该系统由欧盟通过欧洲空间局和欧洲导航卫星系统管理局建造[3],总部设在捷克共和国的布拉格。该系统有两个地面操控站,分别位于德国慕尼黑附近的奥伯法芬霍芬和意大利的富齐诺。这个造价五十亿欧元[4]的项目是以意大利天文学家伽利略的名字命名的。伽利略系统的目的之一是为欧盟国家提供一个自主的高精度定位系统,该系统独立于俄罗斯的格洛纳斯系统和美国的全球定位系统(GPS),在这些系统被关闭时,欧盟就可以使用伽利略系统。该系统的基本服务(低精度)是提供给所有用户免费使用的,高精度定位服务仅提供给付费用户使用。伽利略系统的目标是在水平和垂直方向提供精度1米以内的定位服务,并且在高纬度地区提供比其他系统更好的定位服务。[5]
伽利略系统是中地球轨道搜救卫星系统的一部分,可提供一种新的全球搜救方式。伽利略系统的卫星安装有转发器,可以把求救信号从事故地点发送到救援协调中心,救援协调中心就会开始组织救援。同时,该系统还会发射一个返回信号到事故地点处,通知求救人员他们的信号已被收到,相应的救援也正在展开。现有的全球卫星搜救系统是不具备反馈信号功能的,所以伽利略系统这个发消息功能被认为是对全球卫星搜救系统的一个重要升级。[6]2014年,研究人员对伽利略系统的搜救功能进行了测试,该系统是作为当时的全球卫星搜救系统的一部分工作的,测试结果显示,该系统对77%的模拟求救位置定位精度在2千米以内,95%的求救位置定位精度在5千米以内。[7]
伽利略系统的第一颗试验卫星GIOVE-A于2005年12月28日发射,第一颗正式卫星于2011年8月21日发射。该系统计划发射30颗卫星,截止2016年5月,已有14颗卫星发射入轨。伽利略系统于2016年12月15日在布鲁塞尔举行激活仪式,提供早期服务。于2017年到2018年提供初步工作服务,最终于2019年具备完全工作能力。[8] 该系统的30颗卫星预计将于2020年前发射完成,其中包含24颗工作卫星和6颗备用卫星。[9]
Galileo ist ein im Aufbau befindliches, teilweise bereits operationelles, europäisches globales Satellitennavigations- und Zeitgebungssystem unter ziviler Kontrolle (europäisches GNSS).[1]
Es liefert weltweit Daten zur genauen Positionsbestimmung und ähnelt dem US-amerikanischen NAVSTAR-GPS, dem russischen GLONASS-System und dem chinesischen Beidou-System. Die Systeme unterscheiden sich hauptsächlich durch die Frequenznutzungs-/Modulationskonzepte, die Art und Anzahl der angebotenen Dienste und die Art der Kontrolle (GLONASS, Beidou und GPS sind militärisch kontrolliert).
Auftraggeber von Galileo ist die Europäische Union. Der Sitz der Agentur für das Europäische GNSS (Galileo-Agentur, GSA) befindet sich seit 2014 in der tschechischen Hauptstadt Prag.[2]
Mit Stand Ende 2017 sind 22 der vorgesehenen 30 Satelliten in ihrem Orbit.[3] Bis Ende 2019 sollen alle Satelliten in ihre Umlaufbahn gebracht werden. Das Satellitennavigationssystem ist für die Allgemeinheit seit dem 15. Dezember 2016 zugänglich.[4][5]
ガリレオ(Galileo)は、EUが構築した全地球航法衛星システム。
ガリレオはEUによる全地球航法衛星システムである。高度約24000kmの上空に30機の航法衛星を運用することを予定している。民間主体としては初の衛星航法システムであり、EUはアメリカ国防総省が運営するGPSのように、軍事上の理由によるサービスの劣化及び中断を避けられる利点があるとコメントしている。さらに、測位にかかる時間が短縮され、GPSの数メートルに比べて1メートルまで精度を向上できる。
試験衛星は2005年12月28日に1機目のGIOVE-A衛星が打ち上げられ、2006年1月12日から試験電波が発射されており、2007年5月2日に英Surrey Satellite Technologyによって作成された航法メッセージがギルドフォード地球局からGIOVE-A衛星にアップロードされ放送された。2006年中に打ち上げ予定だった2機目の試験衛星GOOV-Bは、打上げが2008年4月まで遅れた。本格利用開始は2010年頃とされていたが、2013年へと先送りされ、2010年末段階計画では2014年末に18機による初期運用とし2016年末に規定の機数による本格運用に入る計画で進められている。年間の運用コストはEGNOSと合わせて8億ユーロになると見積もられている。
無料で利用できるGPSに対して、莫大な費用を投資し有料での活用を予定しているガリレオの採算性を疑問視する意見も多い。当初の事業費は36億ユーロないし38億ユーロと見込まれており、うち民間企業が24億ユーロを負担する予定だったが、2007年に共同事業体が解散し計画の中止が検討された。2007年5月にEUは公的資金で全額を肩代わりすることを決定し、11月に承認された。2010年には、Wikileaksによって漏出したアメリカ外交当局の資料に、ガリレオに用いる14機の衛星製造を請け負っているドイツの契約企業の担当役員が、ガリレオ計画を「フランスの国益に基づく馬鹿げたアイデア」だとコメントしたことが明らかとなり、問題の役員が解任される騒ぎがあった[1]。
Galileo is the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016,[4] created by the European Union (EU) through the European GNSS Agency (GSA),[5] headquartered in Prague in the Czech Republic,[6] with two ground operations centres, Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich in Germany and Fucino in Italy. The €10 billion project[3][7] is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European nations do not have to rely on the U.S. GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time.[8] The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services will be free and open to everyone. The higher-precision capabilities will be available for paying commercial users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1-metre precision, and better positioning services at higher latitudes than other positioning systems. Galileo is also to provide a new global search and rescue (SAR) function as part of the MEOSAR system.
The first Galileo test satellite, the GIOVE-A, was launched 28 December 2005, while the first satellite to be part of the operational system was launched on 21 October 2011. As of July 2018, 26 of the planned 30 active satellites are in orbit.[9][10] Galileo started offering Early Operational Capability (EOC) on 15 December 2016,[1] providing initial services with a weak signal, and is expected to reach Full Operational Capability (FOC) in 2019.[11] The complete 30-satellite Galileo system (24 operational and 6 active spares) is expected by 2020.[12]
Le programme Galileo est un système de positionnement par satellites (radionavigation) développé par l'Union européenne et incluant un segment spatial dont le déploiement doit s'achever vers 2020. Comme les systèmes américain GPS, russe GLONASS et chinois Beidou, il permet à un utilisateur muni d'un terminal de réception d'obtenir sa position. La précision attendue pour le service de base, gratuit, est de 4 mètres horizontalement et de 8 mètres en altitude[réf. nécessaire]. Un niveau de qualité supérieur sera fourni dans le cadre de services payants proposés aux professionnels.
Le segment spatial de Galileo sera constitué à terme de 30 satellites dont 6 de rechange. Chaque satellite, d'une masse d'environ 700 kg, circule sur une orbite moyenne (23 222 kilomètres) dans trois plans orbitaux distincts ayant une inclinaison de 56°. Ces satellites émettent un signal qui leur est propre et retransmettent un signal de navigation fourni par le segment de contrôle de Galileo. Ce dernier est constitué par deux stations chargées également de surveiller l'orbite et l'état des satellites.
Le projet Galileo, après une phase de définition technique qui débute en 1999, est lancé le 26 mai 2003 avec la signature d'un accord entre l'Union européenne et l'Agence spatiale européenne chargée du segment spatial. Une des motivations principales du projet est de mettre fin à la dépendance de l'Europe vis-à-vis du système américain, le GPS. Contrairement à ce dernier, Galileo est uniquement civil. Le projet parvient à surmonter l'opposition de certains membres de l'UE et d'une partie des décideurs américains ainsi que les difficultés de financement (le coût final est évalué à 5 milliards d'euros). Les tests de Galileo débutent fin 2005 grâce aux lancements des satellites précurseurs Giove-A et Giove-B en décembre 2005 et avril 2008. Les premiers satellites en configuration opérationnelle (FOC) sont lancés en août 2014. Au 15 août 2018, vingt-six satellites ont été lancés, dont 18 sont opérationnels et 4 en cours de mise en service1. Les premiers services de Galileo sont opérationnels depuis le 15 décembre 20162,3. La précision maximale ne sera pas atteinte avant 2020, lorsque 24 des 30 satellites seront opérationnels3,4. En janvier 2018, Galileo compte déjà près de 100 millions d'utilisateurs5, et 200 millions en septembre6.
Il sistema di posizionamento Galileo è un sistema di posizionamento e navigazione satellitare civile (in inglese GNSS - Global Navigation Satellite System), sviluppato in Europa come alternativa al Global Positioning System (NAVSTAR GPS), controllato invece dal Dipartimento della Difesa degli Stati Uniti d'America.
La sua entrata in servizio prevista per la fine del 2019[1] è stata anticipata al 15 dicembre 2016[2]. Il sistema una volta completato potrà contare su 26 satelliti artificiali orbitanti (24 operativi più 2 di scorta)[3] su 3 piani inclinati rispetto al piano equatoriale terrestre di circa 56° e ad una quota di circa 23.925 km[3]. Le orbite che saranno seguite dai satelliti sono quelle MEO (Medium earth orbit). A luglio 2018 si trovano in orbita 26 satelliti ma non tutti sono completamente operativi.
Galileo es el programa europeo de radionavegación y posicionamiento por satélite desarrollado por la Unión Europea (UE) conjuntamente con la Agencia Espacial Europea. Este programa dota a la Unión Europea de una tecnología independiente del GPS estadounidense y el GLONASS ruso.1 Al contrario de estos dos, será de uso civil.2 El sistema se pudo poner en marcha el 15 de diciembre del 20163 con alrededor de media constelación y será completado para 2020.4
«Галиле́о» (Galileo) — совместный проект спутниковой системы навигации Европейского союза и Европейского космического агентства, является частью транспортного проекта Трансевропейские сети (англ. Trans-European Networks). Система предназначена для решения геодезических и навигационных задач. В последнее время всё больше производителей ГССН-оборудования интегрируют в свои спутниковые приёмники и антенны возможность принимать и обрабатывать сигналы со спутников «Галилео», этому способствует достигнутая договорённость о совместимости и взаимодополнении с системой NAVSTAR GPS третьего поколения. Финансирование проекта будет осуществляться в том числе за счёт продажи лицензий производителям приёмников.
Помимо стран Европейского Союза, в проекте участвуют: Китай, Израиль, Южная Корея, Украина. Кроме того, ведутся переговоры с представителями Аргентины, Австралии, Бразилии, Чили, Индии, Малайзии. Ожидалось, что «Галилео» войдёт в строй в 2014—2016 годах, когда на орбиту будут выведены все 30 запланированных спутников (24 операционных и 6 резервных[1]). Но на 2018 год спутниковая группировка «Галилео» так и не достигла необходимого количества аппаратов. Компания Arianespace заключила договор на 10 ракет-носителей «Союз» для запуска спутников, начиная с 2010 года[2]. Космический сегмент будет обслуживаться наземной инфраструктурой, включающей в себя три центра управления и глобальную сеть передающих и принимающих станций.
В отличие от американской GPS и российской ГЛОНАСС, система «Галилео» не контролируется национальными военными ведомствами, однако в 2008 году парламент ЕС принял резолюцию «Значение космоса для безопасности Европы», согласно которой допускается использование спутниковых сигналов для военных операций, проводимых в рамках европейской политики безопасности. Разработку системы осуществляет Европейское космическое агентство. Общие затраты оцениваются в 4,9 млрд евро.
Спутники «Галилео» выводятся на круговые геоцентрические орбиты высотой 23 222 км (или 29 600 км от центра Земли), проходят один виток за 14 ч 4 мин 42 с и обращаются в трёх плоскостях, наклонённых под углом 56° к экватору. Долгота восходящего узла каждой из трёх орбит отстоит на 120° от двух других. На каждой из орбит при полном развёртывании системы будет находиться 8 действующих и 2 резервных спутника. Эта конфигурация спутниковой группировки обеспечит одновременную видимость из любой точки земного шара по крайней мере четырёх аппаратов. Временна́я погрешность атомных часов, установленных на спутниках, составляет одну миллиардную долю секунды, что обеспечит точность определения места приёмника около 30 см на низких широтах. За счёт более высокой, чем у спутников GPS, орбиты, на широте Полярного круга будет обеспечена точность до одного метра.
Каждый аппарат «Галилео» весит около 675 кг, его габариты со сложенными солнечными батареями составляют 3,02×1,58×1,59 м, а с развёрнутыми — 2,74×14,5×1,59 м, энергообеспечение равно 1420 Вт на солнце и 1355 Вт в тени. Расчётный срок эксплуатации спутника превышает 12 лет.





 Albanien
Albanien
 Aleksandar Vučić
Aleksandar Vučić
 Alexander De Croo
Alexander De Croo
 Alexander Stubb
Alexander Stubb
 Andorra
Andorra
 Andrej Plenković
Andrej Plenković
 Armenien
Armenien
 Aserbaidschan
Aserbaidschan
 Belgien
Belgien
 Bjarni Benediktsson
Bjarni Benediktsson
 Bosnien-Herzegowina
Bosnien-Herzegowina
 Bulgarien
Bulgarien
 Charles Michel
Charles Michel
 Dänemark
Dänemark
 Denis Bećirović
Denis Bećirović
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Dick Schoof
Dick Schoof
 Donald Tusk
Donald Tusk
 Edi Rama
Edi Rama
 Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron
 England
England
 Estland
Estland

 Europäische Union
Europäische Union
 Evika Siliņa
Evika Siliņa
 Finnland
Finnland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Georgien
Georgien
 Giorgia Meloni
Giorgia Meloni
 Gitanas Nausėda
Gitanas Nausėda
 Griechenland
Griechenland
 Hristijan Mickoski
Hristijan Mickoski
 Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Aliyev
 Irland
Irland
 Island
Island
 Italien
Italien
 Jakov Milatović
Jakov Milatović
 Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg
 Jonas Gahr Støre
Jonas Gahr Støre
 Kaja Kallas
Kaja Kallas
 Keir Starmer
Keir Starmer
 Klaus Johannis
Klaus Johannis
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Kroatien
Kroatien
 Kyriakos Mitsotakis
Kyriakos Mitsotakis
 Lettland
Lettland
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Litauen
Litauen
 Luc Frieden
Luc Frieden
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Maia Sandu
Maia Sandu
 Malta
Malta
 Mette Frederiksen
Mette Frederiksen
 Moldawien
Moldawien
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Nikol Paschinjan
Nikol Paschinjan
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Olaf Scholz
Olaf Scholz
 Österreich
Österreich

 Parteien und Regierung
Parteien und Regierung

 Parteien und Regierung
Parteien und Regierung
 Gipfel der Europäischen Politischen Gemeinschaft
Gipfel der Europäischen Politischen Gemeinschaft
 Pedro Sánchez
Pedro Sánchez
 Petr Fiala
Petr Fiala
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal
 Robert Abela
Robert Abela
 Robert Golob
Robert Golob
 Rumänien
Rumänien
 Rumen Radew
Rumen Radew
 San Marino
San Marino
 Schweden
Schweden
 Schweiz
Schweiz
 Serbien
Serbien
 Simon Harris
Simon Harris
 Slowakei
Slowakei
 Slowenien
Slowenien
 Spanien
Spanien
 Tschechien
Tschechien
 Türkei
Türkei
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Ungarn
Ungarn
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich
 Viktor Orbán
Viktor Orbán
 Viola Amherd
Viola Amherd
 Wolodymyr Selenskyj
Wolodymyr Selenskyj
 Zypern
Zypern




 Europäische Union
Europäische Union
 Geschichte der Europäischen Union
Geschichte der Europäischen Union

 Europäische Union
Europäische Union
 *Gründerstaaten
*Gründerstaaten
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC

 Finanz
Finanz
 ***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center
***Globales Finanzzentrum/Global Financial Center

 Geographie
Geographie

 Geographie
Geographie
 ***IWF Entwickelte Länder
***IWF Entwickelte Länder

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus
M 1500 - 2000 nach Christus

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus
N 2000 - 2100 nach Christus

 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 *Kulturhauptstadt Europas
*Kulturhauptstadt Europas

 Internationale Städte
Internationale Städte
 Europäische Stadt
Europäische Stadt
 IWF entwickelte Länder
IWF entwickelte Länder
 IWF entwickelte Länder
IWF entwickelte Länder
 TOP6
TOP6
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 Staaten Europas
Staaten Europas
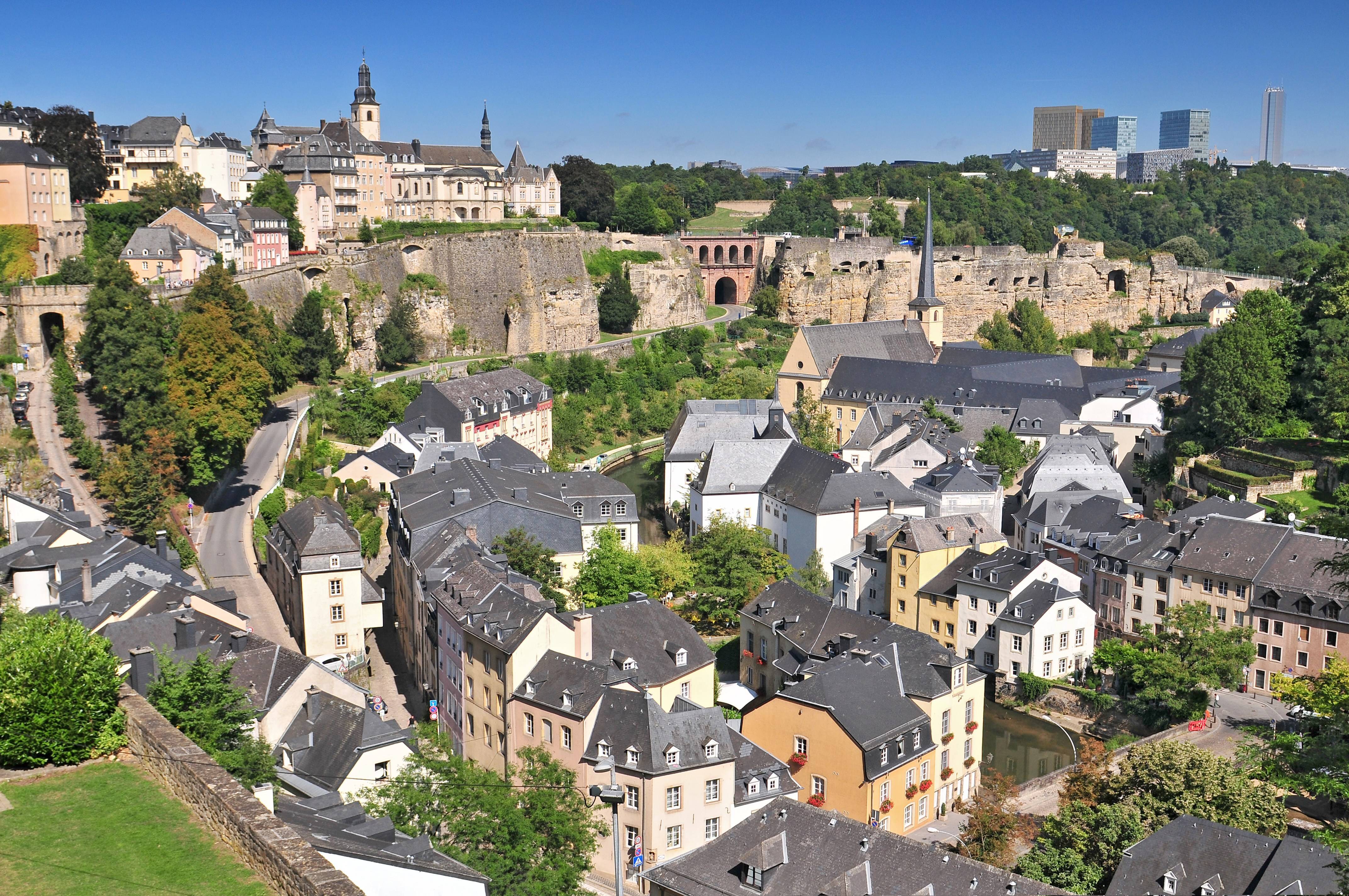
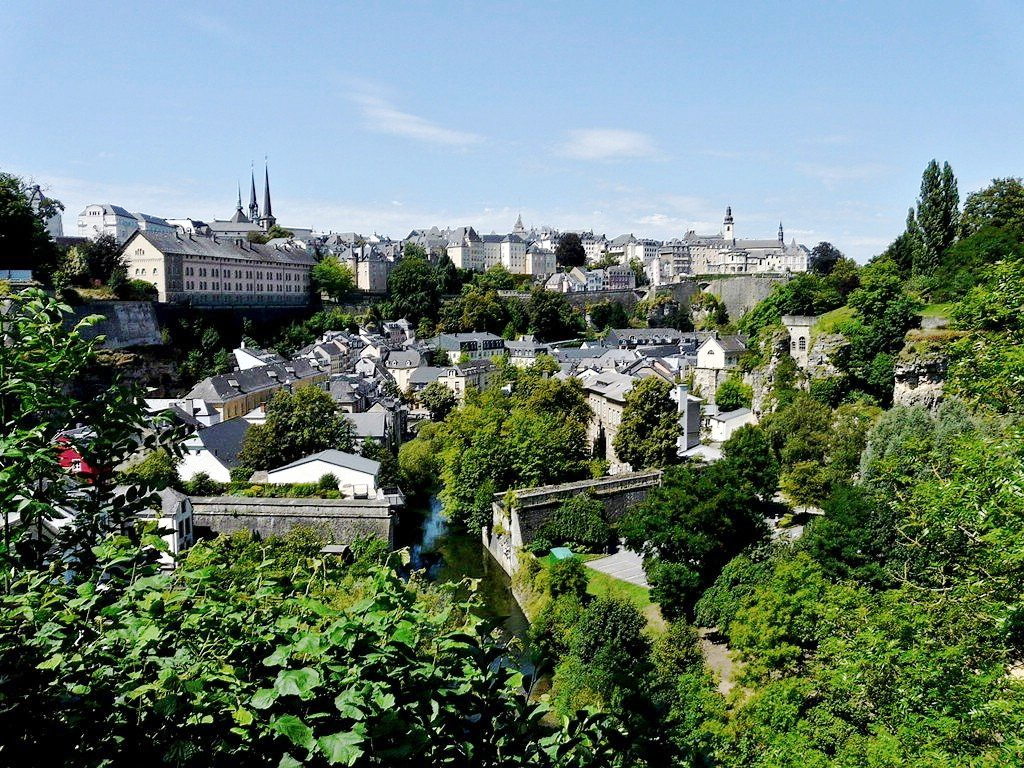


卢森堡是一个高度发达的资本主义国家,也是欧盟和北约创始成员国之一,拥有欧盟多个下设机构,如欧洲法院、欧洲审计院以及欧洲投资银行,被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。同时是高度发达的工业国家,还是欧元区内最重要的私人银行中心,及全球第二大仅次于美国的投资信托中心。金融、广播电视、钢铁是其三大经济支柱产业,该国失业率极低,人均寿命80岁。
卢森堡大公国(卢森堡语:Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg[注 1];法语:Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; 德语:Großherzogtum Luxemburg[注 2]),通称卢森堡(卢森堡语:Lëtzebuerg;法语:Luxembourg;德语:Luxemburg),被邻国法国、德国和比利时包围,是一个位于欧洲的内陆国家,也是现今欧洲大陆仅存的大公国,首都卢森堡市。卢森堡是欧盟成员国,因境内有欧洲法院、欧洲审计院、欧洲投资银行等多个欧盟机构被称为继布鲁塞尔和斯特拉斯堡之后的欧盟“第三首都”。
Das Großherzogtum Luxemburg (luxemburgisch Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg [ˈgʀəʊsˌhɛχtsoːktuːm ˈlətsəbuəɕ], französisch Grand-Duché de Luxembourg [ɡʁɑ̃ dyʃe də lyksɑ̃buʁ]) ist ein demokratischer Staat in Form einer parlamentarischen Monarchie[1] im Westen Mitteleuropas. Es ist das letzte Großherzog- bzw. Großfürstentum (von einst zwölf) in Europa. Das Land gehört zum mitteldeutschen Sprachraum. Landessprache ist Luxemburgisch, Verwaltungs- und Amtssprachen sind Französisch, Deutsch und Luxemburgisch. Gemeinsam mit seinem Nachbarn Belgien und mit den Niederlanden bildet Luxemburg die Beneluxstaaten.
ルクセンブルク大公国(ルクセンブルクたいこうこく)、通称ルクセンブルクは、西ヨーロッパに位置する立憲君主制国家。首都は国名と同名のルクセンブルク市。隣接国は、南のフランス、西と北のベルギー、東のドイツである。ベルギー、オランダと併せてベネルクスと呼ばれる。
Luxembourg (/ˈlʌksəmbɜːrɡ/ (![]() listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] (
listen)) (Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg [ˈlətsəbuə̯ɕ] (![]() listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
listen); French: Luxembourg ; German: Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg,[note 2] is a small landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, together with Brussels and Strasbourg, is one of the three official capitals of the European Union[6] and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language, Luxembourgish (sometimes considered a dialect of German). The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.[7]
With an area of 2,586 square kilometres (998 sq mi), it is one of the smallest sovereign states in Europe.[8] In 2016, Luxembourg had a population of 576,249, which makes it one of the least-populous countries in Europe,[9] but by far the one with the highest population growth rate.[10] Foreigners account for nearly half of Luxembourg's population.[11] As a representative democracy with a constitutional monarch, it is headed by Grand Duke Henri and is the world's only remaining grand duchy. Luxembourg is a developed country, with an advanced economy and one of the world's highest GDP (PPP) per capita. The City of Luxembourg with its old quarters and fortifications was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 due to the exceptional preservation of the vast fortifications and the old city.[12]
The history of Luxembourg is considered to begin in 963, when count Siegfried I acquired a rocky promontory and its Roman-era fortifications known as Lucilinburhuc, ′little castle′, and the surrounding area from the Imperial Abbey of St. Maximin in nearby Trier.[13][14] Siegfried's descendants increased their territory through marriage, war and vassal relations. At the end of the 13th century, the Counts of Luxembourg reigned over a considerable territory. [15] In 1308, Henry VII, Count of Luxembourg became King of the Germans and Holy Roman Emperor. The House of Luxembourg produced four Holy Roman Emperors at the high time of the Middle Ages. In 1354, Charles IV elevated the County to the Duchy of Luxembourg. Since Sigismund had no male heir, the Duchy became part of the Burgundian Circle and then one of the Seventeen Provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands.[16] Over the centuries, the City and Fortress of Luxembourg, of great strategic importance situated between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg territories, was gradually built up to be one of the most reputed fortifications in Europe. After belonging to both the France of Louis XIV and the Austria of Maria Theresia, Luxembourg became part of the First French Republic and Empire under Napoleon.[17]
The present-day state of Luxembourg first emerged at the Congress of Vienna in 1815. The Grand-Duchy, with its powerful fortress, became an independent state under the personal possession of William I of the Netherlands with a Prussian garrison to guard the city against another invasion from France. [18] In 1839, following the turmoil of the Belgian Revolution, the purely Oil-speaking part of Luxembourg was ceded to Belgium and the Luxembourgish-speaking part (except the Arelerland, the area around Arlon) became what is the present state of Luxembourg. [19]
The steel industry exploiting the Red Lands' rich iron-ore grounds in the beginning of the 20th century drove the country's industrialisation. ArcelorMittal, the world's largest steel producer with headquarters in Luxembourg City, is still a reminder of these times. After the decline of the steel industry in the 1970s, the country focused on establishing itself as a global financial centre and developed into the banking hub it is reputed for. Since the beginning of the 21st century, its governments have focused on developing the country into a knowledge economy, with the founding of the University of Luxembourg and a national space programme, projecting the first involvement in a robotic lunar expedition by 2020.[20]
Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union, OECD, United Nations, NATO, and Benelux. The city of Luxembourg, which is the country's capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the EU. Luxembourg served on the United Nations Security Council for the years 2013 and 2014, which was a first in the country's history.[21] In 2016 Luxembourgish citizens had visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 172 countries and territories, ranking the Luxembourgish passport 15th in the world, tied with countries such as Canada and Switzerland.[22]
Le Luxembourg, en forme longue le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg2,b,c ou le grand-duché de Luxembourgd, en luxembourgeois Lëtzebuerg et Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, en allemand Luxemburg et Großherzogtum Luxemburg, est un pays d'Europe de l'Ouest sans accès à la mere Il est bordé par la Belgique à l'ouest et au nord, l'Allemagne à l'est, et la France au sud. Il comprend deux régions principales : l'Oesling au nord, qui est une partie du massif des Ardennes, et le Gutland au sud, prolongement de la Lorraine au sens géologique du terme. Le Luxembourg compte 602 005 habitants au 1er janvier 20181, et s'étend sur une superficie de 2 586 km2, faisant de lui l'une des plus petites nations souveraines d'Europe.
Le Luxembourg est une démocratie représentative et une monarchie constitutionnelle avec un grand-duc pour chef d'État, faisant du pays le seul grand-duché encore existant. Son économie dynamique en fait un des pays les plus riches et des plus prospères du monde, avec le PIB par habitant le plus élevé du monde selon le FMI en 2014. L'économie est principalement centrée sur les activités financières (environ la moitié du produit intérieur brut), favorisée par une fiscalité attractive voire dérisoire dans certains domaines (quasi-exonération d'impôts pour les bénéfices issus de l'exploitation de brevets ou de logiciels). La localisation centrale du territoire luxembourgeois en Europe a historiquement fait de lui un lieu d'une grande importance stratégique pour de nombreuses puissances, depuis sa fondation en tant que fortin romain7, son accueil d'un château franc durant le Haut Moyen Âge, et son rôle de bastion pour le chemin des Espagnols entre les XVIe et XVIIe siècles.
Le Luxembourg est le plus petit membre fondateur de l'Union européenne, de la zone euro, de l'OTAN, de l'OCDE, de l'ONU, de l'OSCE, du Conseil de l'Europe8,9,10,11 et du Benelux, reflétant son consensus politique en faveur de l'intégration économique, politique et militaire. La ville de Luxembourg, sa capitale et sa plus grande ville, est le siège de plusieurs établissements et institutions de l'UE. En 2012, le Luxembourg a été élu pour la première fois de son histoire à un siège temporaire au Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies. En raison de sa position géographique, la culture luxembourgeoise est une fusion de l'Europe germanique et romane, intégrant chacune des deux. De ce fait, le Luxembourg est un pays trilingue : le luxembourgeois, le français et l'allemand sont les trois langues officielles et, depuis 1984, le luxembourgeois a légalement le statut de « langue nationale »12.
Il Granducato di Lussemburgo (in francese: le Grand-Duché de Luxembourg; in lussemburghese: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg; in tedesco: Großherzogtum Luxemburg) è un paese membro dell'Unione europea situato tra Germania, Francia e Belgio. È uno stato senza sbocco sul mare.
Membro fondatore dell'Unione europea, della NATO, del Benelux e delle Nazioni Unite, la sua capitale, l'omonima città di Lussemburgo, è sede di numerose istituzioni e agenzie europee oltre ad essere uno snodo finanziario di primaria importanza.
È l'unico granducato rimasto al mondo.
Luxemburgo, oficialmente denominado Gran Ducado de Luxemburgo (luxemburgués: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, francés: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, alemán: Großherzogtum Luxemburg), es un pequeño país de Europa Central que forma parte de la Unión Europea. Se trata de un Estado sin litoral, rodeado por Francia, Alemania y Bélgica. Luxemburgo cuenta con una población de medio millón de habitantes sobre un área de 2586 kilómetros cuadrados.1
El gobierno de Luxemburgo es una monarquía constitucional y parlamentaria, siendo el único gran ducado soberano en la actualidad. El Estado tiene una economía altamente desarrollada, con el mayor producto interior bruto por cápita del mundo de acuerdo al Banco Mundial, y el segundo de acuerdo al Fondo Monetario Internacional.
Luxemburgo es miembro de la Unión Europea, la Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte, la Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico, las Naciones Unidas y el Benelux, reflejando la orientación política a favor de la integración económica, política y militar. Su capital, Luxemburgo, es sede de numerosas instituciones y agencias de la Unión Europea.
Luxemburgo posee culturas y tradiciones diversas por encontrarse entre la Europa romana y la Europa germánica. El país tiene tres lenguas oficiales: alemán, francés y luxemburgués. La localidad Schengen, que dio su nombre al espacio de Schengen, está ubicada en Luxemburgo.
Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Lëtzebuerg), официально Вели́кое Ге́рцогство Люксембу́рг (люксемб. Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, фр. Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, нем. Großherzogtum Luxemburg) — государство (великое герцогство) в Западной Европе. Граничит с Бельгией на севере, на западе и на юге с Францией, на востоке с Германией, не имеет выхода к морю. Название происходит от древневерхненемецкого «lucilinburch» — «малый город». Общая площадь Люксембурга составляет 2586,4 км², что делает его одним из самых маленьких суверенных государств в Европе[5]. Население на 1 января 2018 года составляет 602 005 человек[2].
Член Европейского союза с 1957 года, также является членом НАТО, ОЭСР и ООН. Вместе с Бельгией и Нидерландами входит в состав Бенилюкса.

 Belgien
Belgien
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 Frankreich
Frankreich
 Italien
Italien
 Luxemburg
Luxemburg
 Niederlande
Niederlande
 Österreich
Österreich
 Polen
Polen
 Portugal
Portugal

 Religion
Religion
 Schweiz
Schweiz
 Spanien
Spanien
 Tschechien
Tschechien

 Urlaub und Reisen
Urlaub und Reisen
 Vereinigtes Königreich
Vereinigtes Königreich

圣雅各之路或圣地牙哥朝圣之路(西班牙语:El Camino de Santiago)是前往基督教的圣地之一西班牙加利西亚圣地牙哥康波斯特拉的朝圣之路。主要指从法国各地经由比利牛斯山通往西班牙北部之道路,是联合国教科文组织所登录的世界遗产。
Als Jakobsweg (spanisch Camino de Santiago, galicisch: Camiño de Santiago) wird eine Anzahl von Pilgerwegen durch ganz Europa bezeichnet, die alle das angebliche Grab des Apostels Jakobus in Santiago de Compostela in Galicien (Spanien) zum Ziel haben. In erster Linie wird darunter der Camino Francés verstanden, jene hochmittelalterliche Hauptverkehrsachse Nordspaniens, die von den Pyrenäen zum Jakobsgrab führt und die Königsstädte Jaca, Pamplona, Estella, Burgos und León miteinander verbindet. Diese Route, so wie sie heute noch begangen wird, entstand in der ersten Hälfte des 11. Jahrhunderts.
Ein Pilgerführer des 12. Jahrhunderts, der im Jakobsbuch (lateinisch Liber Sancti Jacobi), der Hauptquelle zur Jakobusverehrung im Hochmittelalter, enthalten ist, nannte für den französischen Raum vier weitere Wege, die sich im Umfeld der Pyrenäen zu einem Strang vereinigen. Nach der Wiederbelebung der Pilgerfahrt nach Santiago de Compostela in den 1970er und 1980er Jahren wurde der spanische Hauptweg 1993 in das UNESCO-Welterbe aufgenommen. 1998 erhielten auch die vier im Liber Sancti Jacobi beschriebenen französischen Wege diesen Titel. Zuvor schon hatte der Europarat im Jahre 1987 die Wege der Jakobspilger in ganz Europa zur europäischen Kulturroute erhoben und ihre Identifizierung empfohlen.
サンティアゴ・デ・コンポステーラの巡礼路(サンティアゴ・デ・コンポステーラのじゅんれいろ)は、キリスト教の聖地であるスペイン、ガリシア州のサンティアゴ・デ・コンポステーラへの巡礼路。おもにフランス各地からピレネー山脈を経由しスペイン北部を通る道を指す。
The Camino de Santiago (Latin: Peregrinatio Compostellana, "Pilgrimage of Compostela"; Galician: O Camiño de Santiago),[1] known in English as the Way of Saint James among other names,[2][3][4] is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle Saint James the Great in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tradition has it that the remains of the saint are buried. Many follow its routes as a form of spiritual path or retreat for their spiritual growth. It is also popular with hiking and cycling enthusiasts and organized tour groups.
The French Way (Camino Francés) and the Routes of Northern Spain are the courses which are listed in the World Heritage List by UNESCO.
Le pèlerinage de Saint-Jacques-de-Compostelle ou pèlerinage de Compostelle est un pèlerinage catholique dont le but est d'atteindre le tombeau attribué à l'apôtre saint Jacques le Majeur, situé dans la crypte de la cathédrale de Saint-Jacques-de-Compostelle en Galice (Espagne). C'est un « Chemin semé de nombreuses démonstrations de ferveur, de pénitence, d'hospitalité, d'art et de culture, qui nous parle de manière éloquente des racines spirituelles du Vieux Continent »1.
Créé et instauré après l'invention des reliques de Jacques de Zébédée au début du IXe siècle, le pèlerinage de Compostelle devient à partir du XIe siècle un grand pèlerinage de la Chrétienté médiévale. Mais c'est seulement après la prise de Grenade en 1492, sous le règne de Ferdinand d'Aragon et d'Isabelle la Catholique, que le pape Alexandre VI déclare officiellement Saint-Jacques-de-Compostelle lieu d'un des « trois grands pèlerinages de la Chrétienté », avec ceux de Jérusalem et de Rome.
Récemment, l'interprétation du sanctuaire catholique subit une évolution doctrinale : le mot « tombeau » a disparu des discours des derniers papes depuis Jean-Paul II. Jean-Paul II parlant du « mémorial de saint Jacques », sans utiliser le mot « reliques » et Benoît XVI disant simplement que la cathédrale Saint-Jacques-de-Compostelle « est liée à la mémoire de saint Jacques ».
Les chemins de Compostelle, qui correspondent à plusieurs itinéraires en Espagne et en France, ont été déclarés en 1987 « Premier itinéraire culturel » par le Conseil de l'Europe. Depuis 2013, les chemins de Compostelle attirent plus de 200 000 pèlerins chaque année, avec un taux de croissance de plus de 10 % par an. Les pèlerins viennent essentiellement à pied, et souvent de villes proches (demandant peu de jours de marche pour atteindre Santiago). Le Camino francés rassemble les 2/3 des marcheurs, mais les autres chemins « mineurs » connaissent une croissance de leur fréquentation supérieure au chemin traditionnel. Les mois d'été sont les plus fréquentés par les pèlerins, et les pèlerins espagnols y sont majoritaires (les pèlerins d'origine étrangère dominent le reste de l'année).
Il Cammino di Santiago di Compostela è il lungo percorso che i pellegrini fin dal Medioevo intraprendono, attraverso la Francia e la Spagna, per giungere al santuario di Santiago di Compostela, presso cui ci sarebbe la tomba dell'Apostolo Giacomo il Maggiore.
Le strade francesi e spagnole che compongono l'itinerario sono state dichiarate Patrimonio dell'umanità dall'UNESCO. Si tratta grossomodo (a seconda del sentiero e dell'allenamento) di un percorso di 800 km per la durata di 1 mese.
El Camino de Santiago o peregrinación de Santiago de Compostela es una peregrinación católica de origen medieval cuyo propósito es llegar a la tumba atribuida al apóstol Santiago el Mayor, situada en la cripta de la catedral de Santiago de Compostela en Galicia (España). Ha sido, y sigue siendo, la ruta más antigua, más concurrida y más celebrada del viejo continente. Se trata de un «camino sembrado de numerosas manifestaciones de fervor, de arrepentimiento, de hospitalidad, de arte y de cultura, que nos habla de manera elocuente de las raíces espirituales del Viejo Continente».1
Creado e instaurado después del descubrimiento de las reliquias de Santiago el Zebedeo a principios del siglo IX, la peregrinación a Compostela se convirtió desde el siglo XI en una de las grandes peregrinación de la cristiandad medieval. Aunque hasta después de la caída de Granada en 1492, durante el reinado de Fernando de Aragón e Isabel la Católica, Santiago de Compostela no será declarada oficialmente por el papa Alejandro VI como lugar de una de las «tres grandes peregrinaciones en la cristiandad», con Jerusalén y Roma con sus vías romeas. Después el Camino fue un tanto olvidado y en la actualidad ha vuelto a tomar un gran auge, siendo recorrido por caminantes y andadores de todo el mundo que a pie, corriendo, en bicicleta o a caballo, emprenden una experiencia que entremezcla la antigua devoción religiosa con la aventura, el encuentro y el conocimiento personal, el deporte y disfrute de la naturaleza y la cultura. Es parte del sendero de larga distancia GR-65.
Recientemente, la interpretación del santuario católico ha sufrido una evolución doctrinal: la palabra tumba ha desaparecido del discurso de los últimos papas desde Juan Pablo II, que habló del «memorial del santo Santiago», sin usar la palabra «reliquias», y de Benedicto XVI que dijo simplemente que la catedral de Santiago de Compostela «está vinculada a la memoria de Santiago».
Los Caminos de Santiago, que corresponden a varios itinerarios en España y en Francia, fueron declarados en 1987 el primer «Itinerario Cultural Europeo» por el Consejo de Europa.
El Camino de Santiago Francés y las rutas francesas del Camino fueron declarados por la Unesco Patrimonio de la Humanidad en 1993 y 1998 respectivamente.23 La declaración española fue ampliada en 2015 incluyendo el Camino Primitivo, el Camino Costero, el Camino vasco-riojano y el Camino de Liébana.4
En 2004 la Fundación Príncipe de Asturias le concedió el Premio Príncipe de Asturias de la Concordia «como lugar de peregrinación y de encuentro entre personas y pueblos que, a través de los siglos, se ha convertido en símbolo de fraternidad y vertebrador de una conciencia europea».5 Además, ha recibido el título honorífico de «Calle mayor de Europa».6
Desde 2013, atrae a más de 200 000 peregrinos cada año, con una tasa de crecimiento de más del 10 % anual. Los peregrinos llegan principalmente a pie, y a menudo de las ciudades cercanas (necesitando unos pocos días para llegar a Santiago). El Camino francés recoge 2/3 de los caminantes, pero otros caminos menores están experimentando un crecimiento incluso mayor que el camino tradicional. Los meses de verano son los más frecuentados por los peregrinos, especialmente por los peregrinos españoles, siendo en su mayoría peregrinos procedentes del extranjero los que dominan el resto del año.
Путь Свято́го Иа́кова, Эль Ками́но де Сантья́го (исп. El Camino de Santiago) — паломническая дорога к предполагаемой могиле апостола Иакова в испанском городе Сантьяго-де-Компостела, главная часть которой пролегает в Северной Испании. Благодаря своей популярности и разветвлённости этот маршрут оказал большое влияние на распространение культурных достижений в эпоху Средневековья. C 1993 года входит в число памятников всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
Во второй половине XX века значительный вклад в дело восстановления паломнического маршрута внёс Элиас Валинья Сампедро, благодаря стараниям которого, начиная с 1980-х годов, популярность маршрута вновь начала возрастать: так, если в 1978 году по нему прошли всего 13 человек[1], то в 2009 — более 145 тысяч[2]. Определённую роль в популяризации Пути Святого Иакова сыграл роман Пауло Коэльо «Дневник мага», изданный в 1987 году[3].

 Architektur
Architektur
 Gesetz
Gesetz
 Royalty
Royalty
 Unternehmen
Unternehmen
 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe