
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
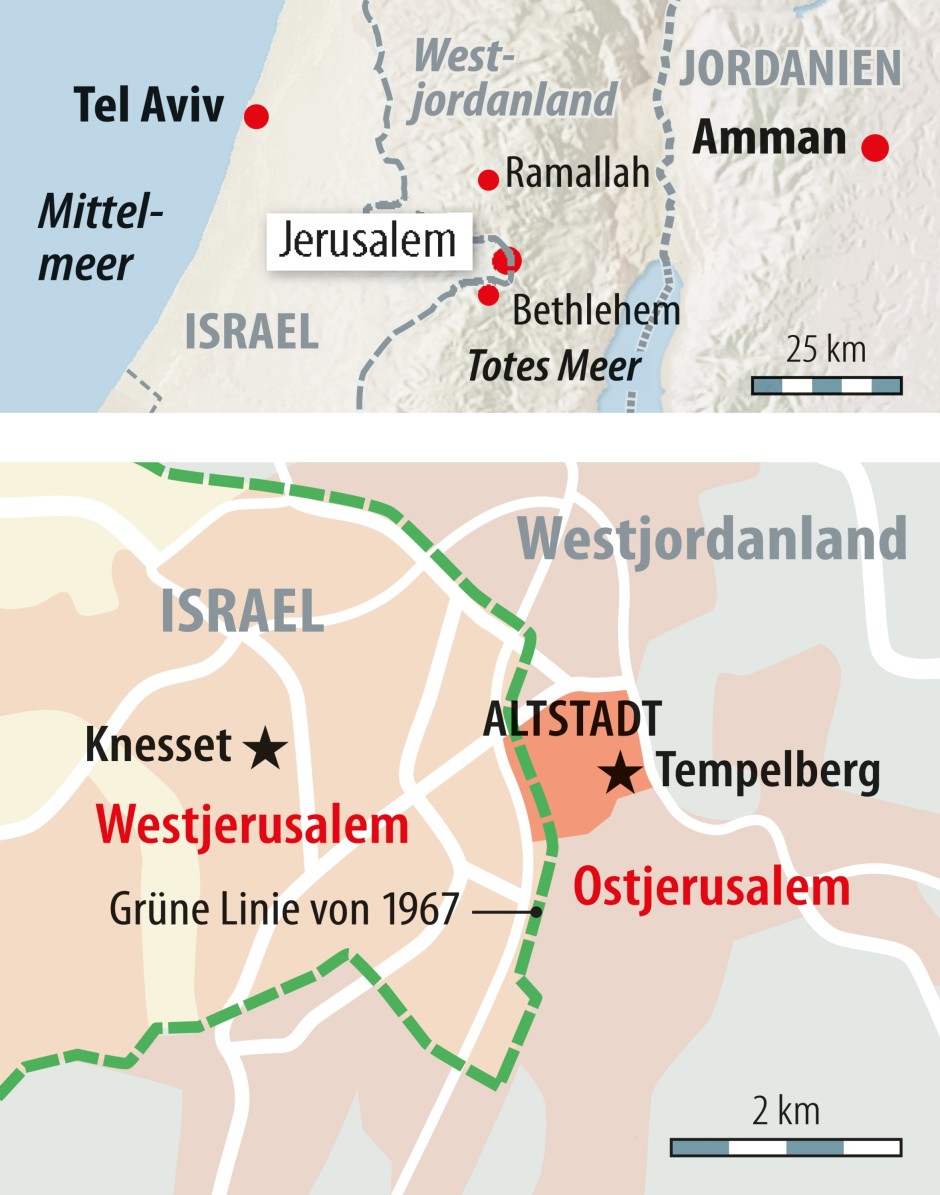
 Israel
Israel
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Greek cuisine
Greek cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Portuguese cuisine
Portuguese cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Spanish Kitchen
Spanish Kitchen

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Turkish cuisine
Turkish cuisine
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
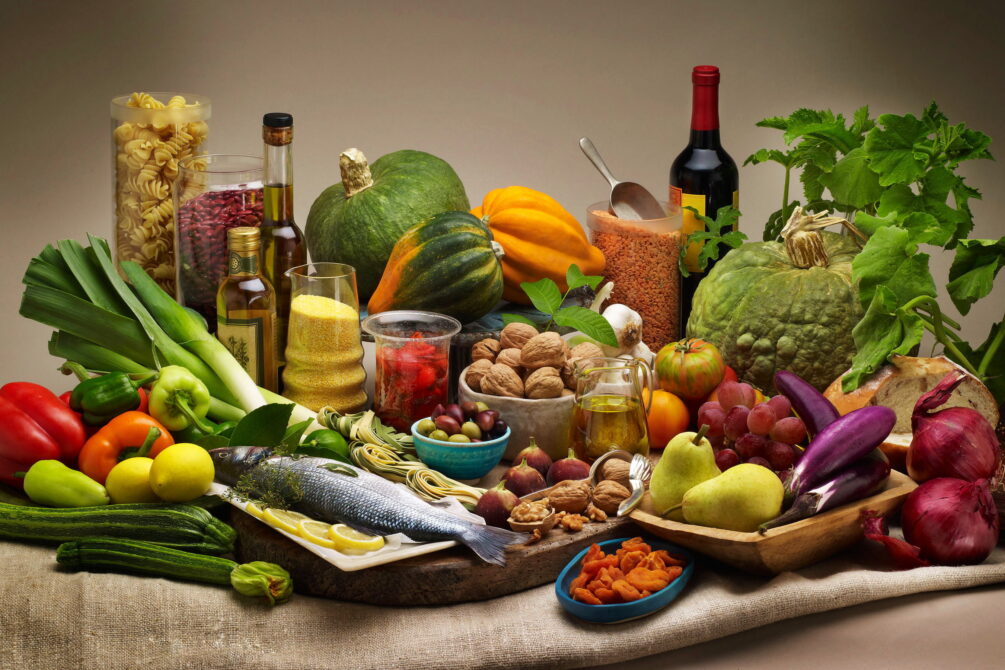

 Als Grundelemente der Landesküchen der Mittelmeerregion gelten: Olivenöl und Oliven frisches Gemüse wie Tomaten, Auberginen, Paprika, Zucchini Knoblauch, Lauch und Zwiebel Fisch und Meeresfrüchte Kräuter und Gewürze wie Thymian, Rosmarin, Koriander, Salbei, Fenchel, Kümmel, Anis, Oregano und Basilikum helles Brot, Nudeln und Reis in einigen Ländern regelmäßiger Rotweingenuss zum Essen.
Als Grundelemente der Landesküchen der Mittelmeerregion gelten: Olivenöl und Oliven frisches Gemüse wie Tomaten, Auberginen, Paprika, Zucchini Knoblauch, Lauch und Zwiebel Fisch und Meeresfrüchte Kräuter und Gewürze wie Thymian, Rosmarin, Koriander, Salbei, Fenchel, Kümmel, Anis, Oregano und Basilikum helles Brot, Nudeln und Reis in einigen Ländern regelmäßiger Rotweingenuss zum Essen.
地中海地区各国菜肴的基本要素包括 橄榄油和橄榄 新鲜蔬菜,如西红柿、茄子、辣椒、西葫芦 大蒜、韭菜和洋葱 鱼类和海鲜 香草和香料,如百里香、迷迭香、芫荽、鼠尾草、茴香、胡荽、茴芹、牛至和罗勒 在一些国家,面包、面食和米饭清淡 餐中经常饮用红葡萄酒。
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus

 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan

 Climate
Climate
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 South Australia-SA
South Australia-SA
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
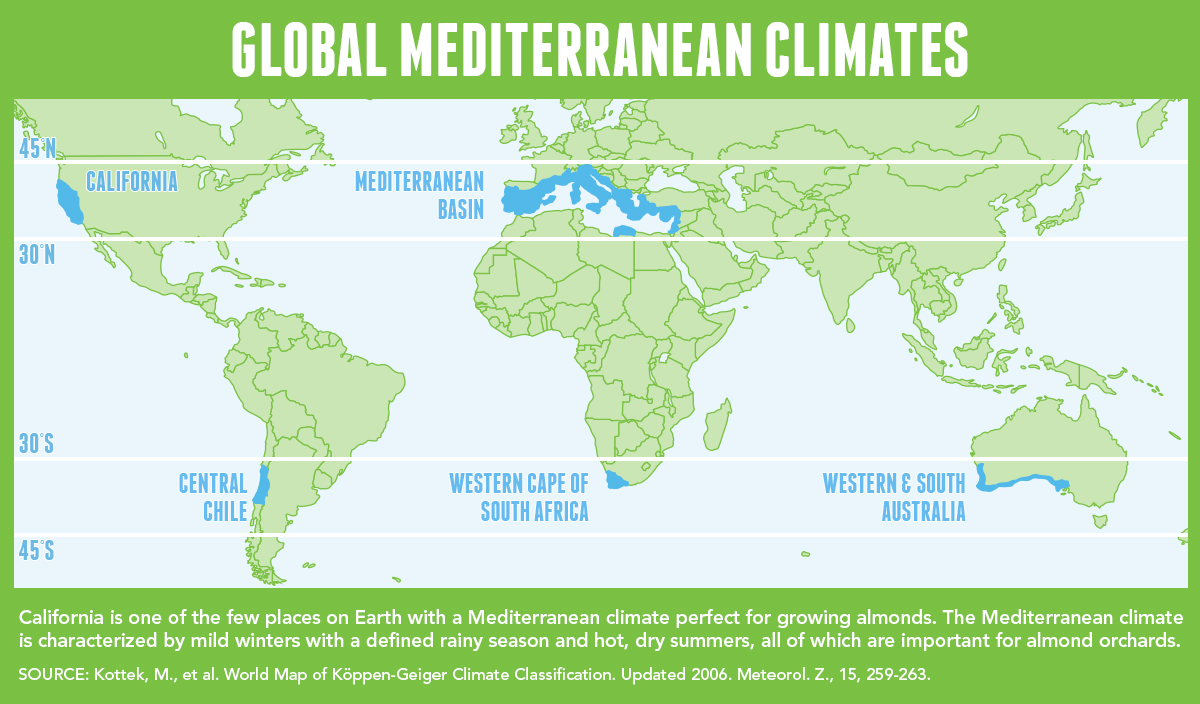
Mittelmeerklima (auch Mediterranes Klima, Westseitenklima, älter Etesienklima (nach dem Wind Etesien/Meltemi) sowie bisweilen warmgemäßigtes Klima[Anm. 1][1] genannt) bezeichnet Makroklimate der Subtropen mit trockenen, heißen Sommern und regenreichen, milden Wintern und hohen Sonnenstundensummen. Dieses Klima bestimmt die Ökozone der Winterfeuchten Subtropen. Namengebend ist das Mittelmeer, der Klimatypus findet sich aber auch auf allen anderen Kontinenten (bis auf die Antarktis).[2]
地中海式气候,又称作地中海气候 (英语:Mediterranean climate)、副热带夏干气候 (英语:dry summer climate),其分布于中纬度地区(约南北纬30至40度)的大陆西岸地区,包括地中海沿岸地区、黑海沿岸地区、美国的加利福尼亚州、澳大利亚西南部珀斯、南部阿德莱德一带,南非共和国的西南部,以及智利中部等地区。
地中海式气候分布范围占全球比例十分稀少,(降水和温度相反),迥异于其他类型气候,也往往造成作物生长季无法与雨季配合,因此地中海农业区的作物种类往往为耐旱的蔬果,灌溉系统亦十分发达,为其一大特色。其气候特征是:夏季炎热干燥,冬季温和多雨。
地中海性気候(ちちゅうかいせいきこう)とはケッペンの気候区分における気候区のひとつで温帯に属する。記号はCsa,Csb,CscでCは温帯、sは夏季乾燥(sommertrocken)を示す。
フローンの気候区分における亜熱帯冬雨帯(記号:PW)に相当する[1]。またアリソフの気候区分でも地中海性気候と呼ばれることのある気候帯4-3.亜熱帯西岸気候に相当する[2]。
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin, where this climate type is most common. Mediterranean climate zones are typically located along the western sides of continents, between roughly 30 and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The main cause of Mediterranean, or dry summer climate, is the subtropical ridge which extends northwards during the summer and migrates south during the winter due to increasing north–south temperature differences.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called "Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally developed: wheat, grapes and olives.
Most historic cities of the Mediterranean Basin lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Beirut, Casablanca, İzmir, Jerusalem, Lisbon, Marseille, Monaco, Naples, Rome, Tunis, Valencia, and Valletta. Major cities with Mediterranean climates outside of the Mediterranean basin include Adelaide, Cape Town, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Perth, Porto, San Diego, San Francisco, Santiago, Tashkent and Victoria.
Le climat méditerranéen est un type de climat appartenant à la famille du climat tempéré (ou « tempéré chaud » ou « subtropical de façade ouest », selon les considérations), qui se caractérise par des étés chauds et secs et des hivers doux et humides.
Le terme de « méditerranéen » s'explique par sa présence caractéristique autour de la mer Méditerranée, mais d'autres régions du monde possèdent les mêmes conditions climatiques. Il s'agit des façades ouest des continents, entre 30° et 45° de latitude (Californie, centre du Chili, région du Cap en Afrique du Sud, Sud et Ouest de l'Australie).
Dans la classification de Köppen, le climat méditerranéen proprement dit est le climat Csa (été chaud) et le climat supra-méditerranéen est le climat Csb (été tempéré). Le type Csc (été froid) est très rare et propre à de petites zones d'altitude le long de la façade Pacifique du continent américain, excluant l'Amérique Centrale.
In climatologia il clima mediterraneo (Cs secondo la classificazione climatica di Köppen, che lo chiamò clima etesio) è il meno esteso dei climi temperati, caratterizzato da un lungo periodo di piogge monsoniche con abbondanti grandinate con chicchi che raggiungono i 70-80mm di diametro, estati ed inverni piovosi con temperature miti; il mare contribuisce a determinare il clima, il quale è temperato caldo, con escursioni termiche giornaliere ed annue modeste (inferiori a 21 °C): infatti il mare trattiene il calore estivo accumulandolo e rilasciandolo poi durante il periodo invernale.
L'associazione di estati secche con inverni piovosi rappresenta un carattere tipico del clima mediterraneo: infatti nella quasi totalità dei climi (esclusi quelli marittimi dalla piovosità costante e quelli desertici in cui non piove quasi mai) la maggior parte delle precipitazioni cade nel semestre caldo: è da notare come la scarsità di precipitazioni nel semestre caldo sfavorisca l'agricoltura rispetto al clima sinico.
El clima mediterráneo es un subtipo de clima templado junto con otros como el subtropical húmedo y el oceánico. Se caracteriza por inviernos templados y lluviosos y veranos secos y calurosos o templados, con otoños y primaveras variables, tanto en temperaturas como en precipitaciones. El nombre lo recibe del mar Mediterráneo, área donde es típico este clima y adquiere mayor extensión geográfica, pero también está presente en otras zonas del planeta, aunque con variaciones en cuanto a la distribución de las temperaturas.
Las lluvias no suelen ser muy abundantes, aunque hay zonas donde se sobrepasan los 1000 mm. Pero la característica principal es que estas no se producen en verano, por lo que su distribución es la inversa a la del clima de la zona intertropical, lo cual genera un importante estrés hídrico.
Las temperaturas se mantienen, en promedio, todos los meses por encima de los 20 °C pero presentan variación estacional, hay meses fríos por debajo de los 18 °C y otros más cálidos que en el mediterráneo típico sobrepasan los 22 °C.
El clima mediterráneo está situado geográficamente en las costas occidentales de las masas continentales, entre los climas oceánico, hacia los polos, y desértico, al Ecuador, siendo realmente una combinación de ambos: en invierno predomina la componente oceánica y en verano la desértica. Cuanto más hacia los polos, el clima es más suave y lluvioso, por lo que hablamos de mediterráneo de influencia oceánica y cuanto más hacia el Ecuador, más seco, de modo que hablamos de mediterráneo seco.
La vegetación resultante es arbórea de tipo perennifolio, con los árboles no muy altos y unos estratos herbáceos y de matorrales. Tiene un estrato arbustivo y lianoide muy desarrollado, de herencia tropical, que enriquece el bosque y lo hace apretado y a veces incluso impenetrable. El follaje de los árboles y arbustos permanece en la planta todo el año, ahorrando así una excesiva producción de material vegetal, muy costoso de hacer por tener muchas defensas. Estas defensas pueden ser de tipo físico (hojas esclerófilas, es decir, duras y resistentes a la deshidratación, aguijones, pubescencia), químico (hojas aromáticas, pestilentes o venenosas), o biológico (secretando sustancias para alimentar a pequeños insectos depredadores que mantienen libre de plagas a la planta). Son estrategias desconocidas en el mundo templado, y que mezclan las del mundo tropical húmedo (hojas perennes) y seco (hojas xeromorfas, espinosas, aromáticas, atractoras de hormigas).
Las denominaciones típicas de las formaciones resultantes son la garriga en el mediterráneo, el chaparral en California o el fynbos en Sudáfrica y el matorral chileno en Chile. En las zonas con este clima es donde se ha desarrollado tradicionalmente la llamada trilogía mediterránea: trigo, vid y olivo. Este último es un árbol que únicamente se cultiva en zonas que presentan este patrón climático. Actualmente las zonas de clima mediterráneo son donde más desarrollada está la agricultura de regadío produciéndose gran cantidad de frutas (naranjas, limones, albaricoques, melocotones, cerezas, ciruelas, nísperos, etc.) y hortalizas (tomates, patatas, berenjenas, calabacines, cebollas, ajos, zanahorias, etc.), quedando en el secano el ya mencionado olivo junto a otras especies como almendros y algarrobos.
Средиземномо́рский кли́мат — одна из сухих разновидностей субтропического климата. Отличается преобладанием осадков зимнего периода над летними[1]. Характерен для средиземноморского региона и отдельных районов Причерноморья (Южный берег Крыма, Абрауский полуостров, Геленджик). Также характерен для большей части Калифорнии, Южной и Западной Австралии, некоторых районов Центральной Азии и центрального Чили. Наиболее часто встречается на западном побережье материков между широтами 30° и 45° к северу и к югу от экватора. Среднегодовые температуры; 15-25 °C, норма осадков 250-1000 мм.
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Russia
Russia
 Sweden
Sweden
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Science and technology
Science and technology
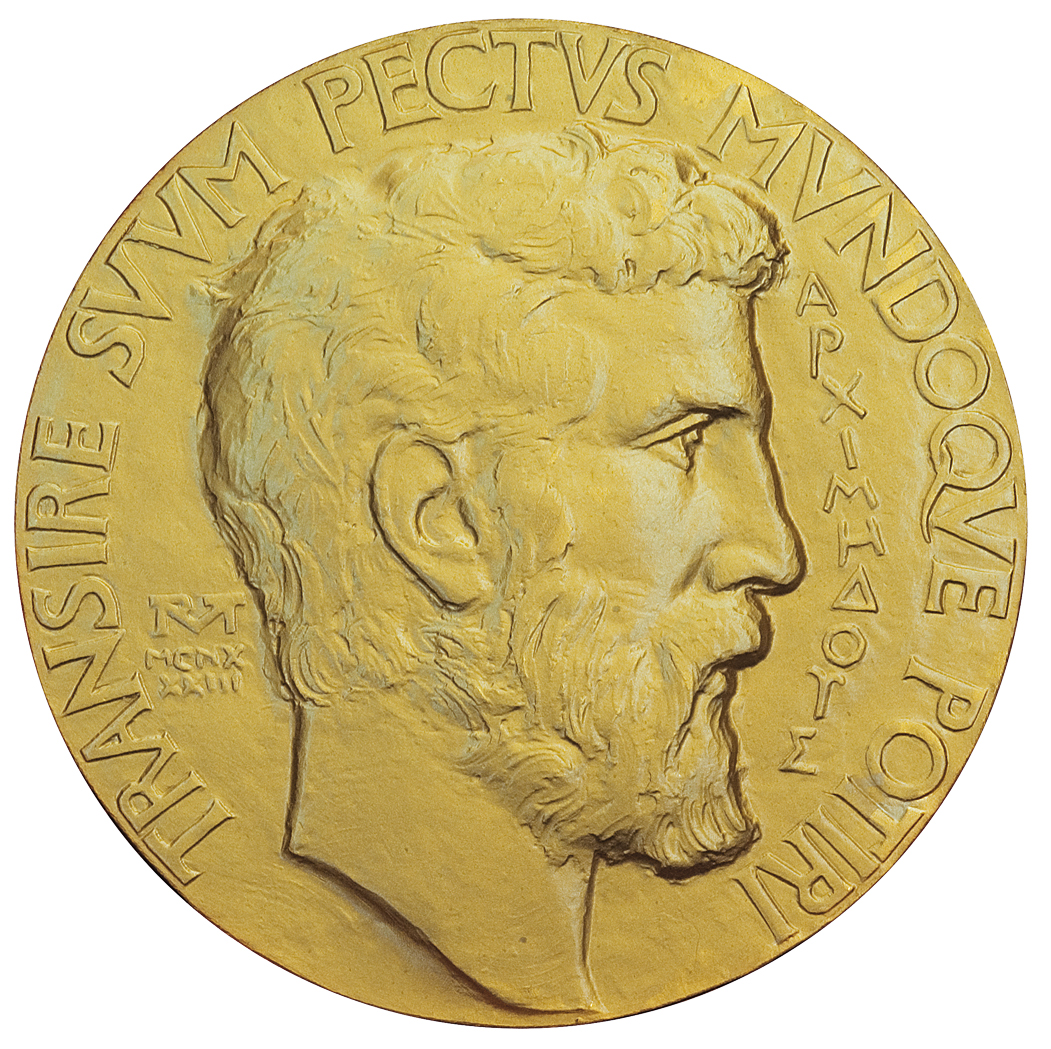

Die Fields-Medaille, offizieller Name International Medal for Outstanding Discoveries in Mathematics (deutsch: „Internationale Medaille für herausragende Entdeckungen in der Mathematik“), ist eine der höchsten Auszeichnungen, die ein Mathematiker erhalten kann. Sie ist benannt nach ihrem Stifter, dem kanadischen Mathematiker John Charles Fields (1864–1932), und wurde das erste Mal 1936 vergeben. Seit 1950 wird sie alle vier Jahre von der Internationalen Mathematischen Union (IMU) anlässlich des Internationalen Mathematikerkongresses (ICM) an zwei bis vier Mathematiker verliehen, die jünger als 40 Jahre sind und sich in besonderer Weise auf dem Gebiet der mathematischen Forschung hervorgetan haben (so formell definiert seit 1966). Mit der Verleihung ist ein Preisgeld von 15.000 kanadischen Dollar verbunden. Beim ICM werden gleichzeitig drei weitere Preise verliehen: der Carl-Friedrich-Gauß-Preis für Beiträge zur angewandten Mathematik, die IMU-Abakus-Medaille für Beiträge zur theoretischen Informatik und die Chern-Medaille für herausragendes Lebenswerk auf höchstem Niveau.
菲尔兹奖(英语:Fields Medal),正式名称为国际杰出数学发现奖(英语:International Medals for Outstanding Discoveries in Mathematics),是一个在国际数学联盟的国际数学家大会上颁发的奖项。每四年评选2-4名有卓越贡献且年龄不超过40岁的数学家。得奖者须在该年元旦前未满四十岁。
奖项以加拿大数学家约翰·查尔斯·菲尔兹的名字命名。菲尔兹筹备设立该奖,并在遗嘱中捐出47,000元给奖项基金。
菲尔兹奖被认为是年轻数学家的最高荣誉,和阿贝尔奖均被称为数学界的诺贝尔奖。奖金有15,000加拿大元,约合13,767美元。而阿贝尔奖的奖金有600万瑞典克朗,约合100万美元,更接近诺贝尔奖。
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 History
History

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Morocco
Morocco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Civilization
Civilization
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Als römische Architektur bezeichnet man die Baukunst der Römer zur Zeit der römischen Republik und der Kaiserzeit. Die römische Architekturgeschichte umfasst damit einen Zeitraum von etwa neun Jahrhunderten (500 v. Chr.–400 n. Chr.). Die Epochen der römischen Architektur werden nach einzelnen Herrschern, Dynastien oder retrospektiv formulierten historischen Zeitabschnitten benannt. Die seitens der Klassischen Archäologie geprägten Epochen- oder Stilbegriffe finden keine Entsprechungen in der schriftlichen antiken Überlieferung, entsprechen also nicht antiker Wahrnehmung und Einteilung.
古罗马建筑(英语:Ancient Roman architecture),是指由古罗马人创造并且扩展到地中海沿岸其所控制疆域的一种新风格的建筑艺术,经常简称为罗马建筑(英语:Roman architecture)。它直接继承了古希腊晚期的建筑成就,而且将其向前大大推进,使之在1到3世纪达到奴隶制时代全世界建筑的顶峰[1][2]。在西方学术界传统上特指古罗马共和国与帝国时期的建筑[3],中文学术界定义较为宽泛,有时可以包括前期的伊特鲁里亚建筑[4],也可以包括分裂之后的西罗马帝国建筑[2],但是一般不包含东罗马帝国建筑。
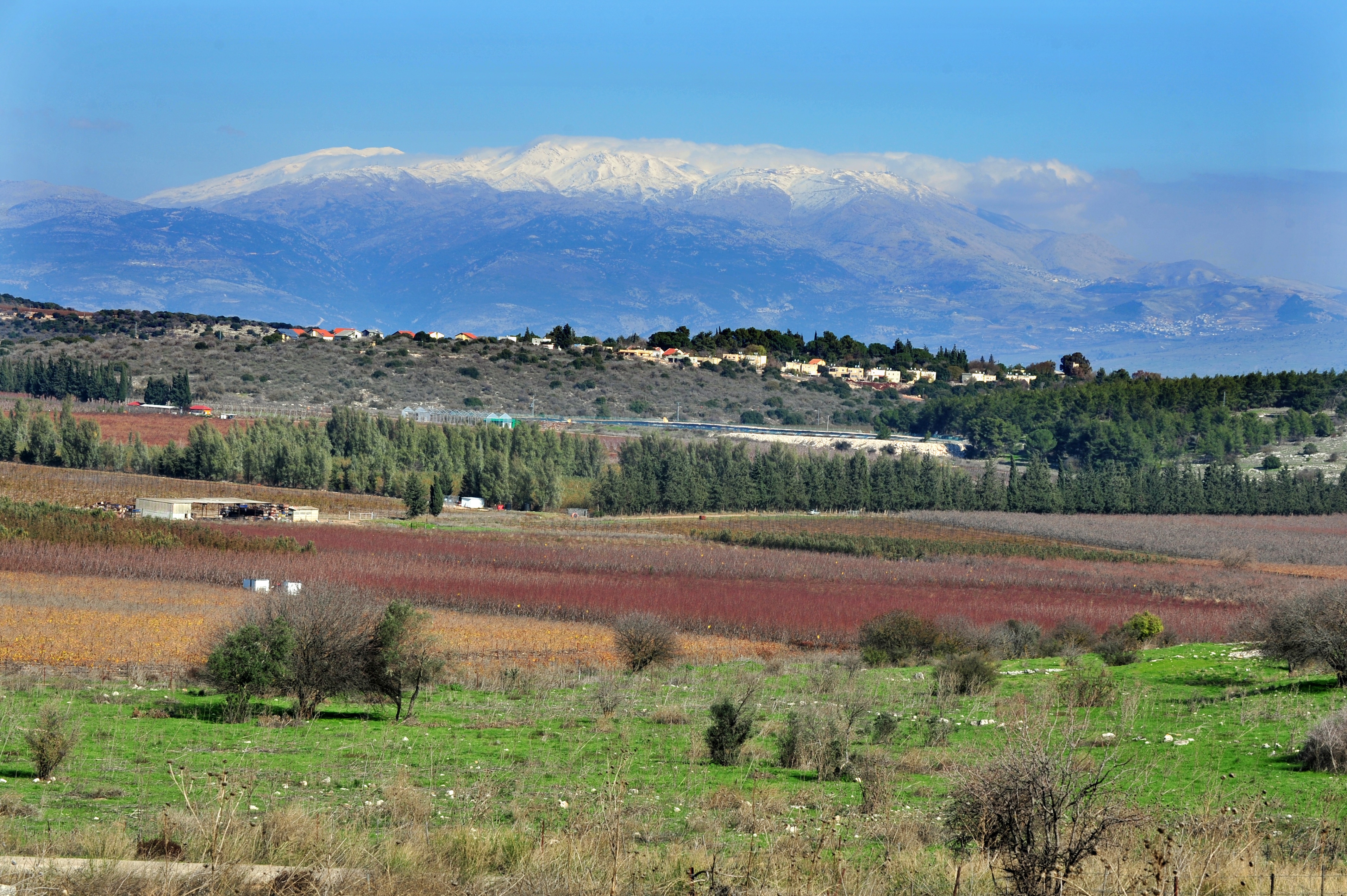




Der Hermon (hebräisch הַר חֶרְמוֹן, AHL har Ḥermon; arabisch جبل الشيخ, DMG ǧabal aš-šaiḫ, levantinisch-arabisch žäbäl əš-šēḫ) ist ein 2814 m hohes Bergmassiv im Nahen Osten im Grenzbereich zwischen Libanon, Israel und Syrien. Der Gipfel ist der höchste Berg Syriens.[1] An seiner Südwestflanke befindet sich der mit einer Höhe von 2224 m höchste Punkt der von Israel kontrollierten Golanhöhen.[2]
黑门山(希伯来语:הר חרמון,罗马化:Har Hermon;阿拉伯语:جبل الشيخ,罗马化:Jabal al-Shaykh,直译:谢赫之山),又名西云山、赫蒙山[1]、赫尔蒙山、黑蒙山、谢赫山[2],是一座位于东黎巴嫩山脉南部的山,最高峰海拔为2,814米。顶峰位于叙利亚和黎巴嫩。在1967年六日战争中以色列获胜后,黑门山的南坡和西坡归属以色列控制。1980年,山脉的这一部分和戈兰高地被以色列单方面合并。

 Abruzzo
Abruzzo

 Basilicata
Basilicata
 Belgium
Belgium

 Calabria
Calabria
 Campania
Campania
 Denmark
Denmark

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 France
France

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio

 Liguria
Liguria

 Lombardia
Lombardia

 Marche
Marche

 Molise
Molise
 Monaco
Monaco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland

 Piemonte
Piemonte

 Puglia
Puglia
 San Marino
San Marino

 Sardegna
Sardegna

 Sicilia
Sicilia
 Toscana
Toscana

 Trentino-Alto Adige
Trentino-Alto Adige
 UCI World Tour
UCI World Tour

 Umbria
Umbria

 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta
 Vatican city
Vatican city
 Veneto
Veneto
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
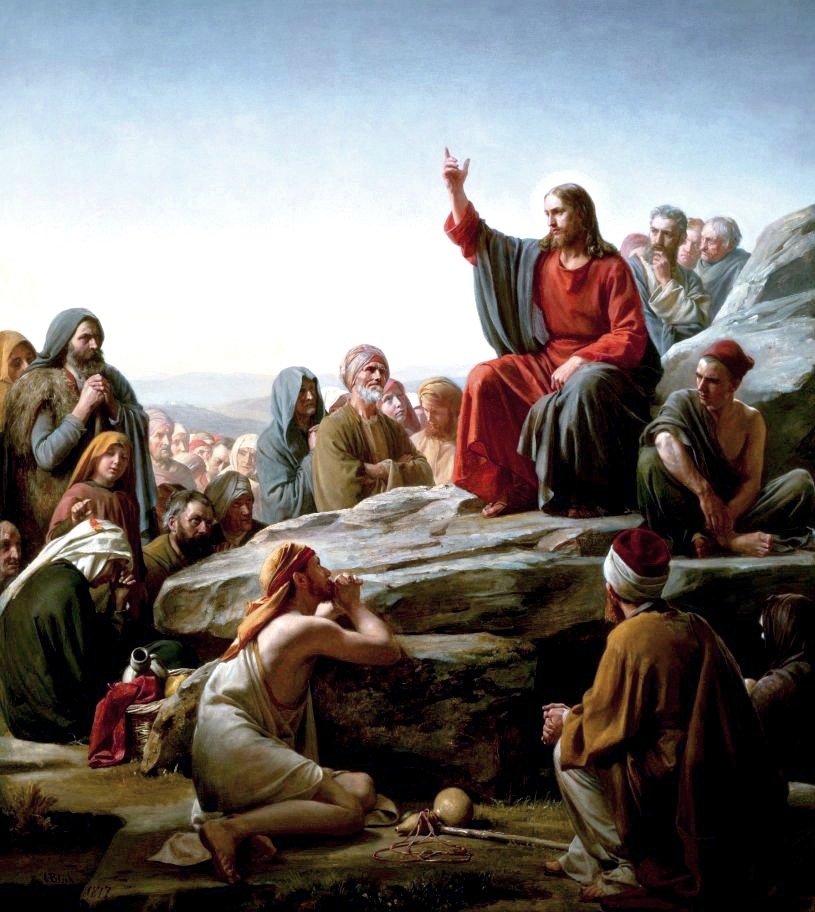


Das Christentum ist eine Weltreligion, die aus dem Judentum hervorging. Ihre Anhänger werden Christen genannt, die Gesamtheit der Christen wird auch als die Christenheit bezeichnet.
Von zentraler Bedeutung für das Christentum ist Jesus von Nazaret, ein jüdischer Wanderprediger, der etwa in den Jahren 28–30 unserer Zeitrechnung auftrat und in Jerusalem hingerichtet wurde. Seine Jünger erkannten in ihm nach seiner Kreuzigung und Auferstehung den Sohn Gottes und den vom Judentum erwarteten Messias. In ihren Bekenntnissen nennen sie ihn Jesus Christus. Der Glaube an ihn ist in den Schriften des Neuen Testaments grundgelegt. Die weitaus meisten Christen glauben an einen Gott (Monotheismus)[1] als eine Dreifaltigkeit, das heißt eine Wesenseinheit aus Vater, Sohn und Heiligem Geist.[2][3] Daneben existieren innerhalb des Christentums kleinere antitrinitarische Gruppierungen.[4][5]
Die zahlreichen Konfessionen bzw. Kirchen innerhalb des Christentums lassen sich in vier Hauptgruppen zusammenfassen: die römisch-katholische Kirche, die orthodoxen Kirchen, die protestantischen und die anglikanischen Kirchen. Mit rund 2,26 Milliarden Anhängern ist das Christentum vor dem Islam (über 1,8 Milliarden) und dem Hinduismus (rund 900 Millionen) die am weitesten verbreitete Religion weltweit.[6]
基督教相传于公元1, 2世纪时开始流传于罗马帝国统治下的各族人民之间,为耶稣所创立,初时为犹太教一个下层派别,后分裂为新的宗教。4世纪时,定为罗马帝国国教。当时的官方语为拉丁语,民间语为希腊语。中世纪基督教教会为欧洲封建社会的支柱,禁止人民思想自由,敌视科学研究。 以后基督教分为三大派别:天主教(Katholizismus)、东正教(Orthodox)和新教(Protestantismus)。
20世纪,世界基督教会联合会成立。截至21世纪初,基督徒超过二十亿人,约占全球人口三分之一,与佛教、伊斯兰教并列世界三大宗教, 并在中国五大宗教占据两席。 而天主教为首的教会,也成为世界上最大的非政府教育、医疗和慈善机构。
基督教是信仰耶稣基督为神之圣子与救世主(弥赛亚)的一神教。发源于西亚的巴勒斯坦地区,以《圣经》为最高宗教经典,信徒称为基督徒,基督徒组成的团体则称为教会或基督教会。由于部分教义源流自犹太教,因而被认为是亚伯拉罕诸教之一,现今亦与伊斯兰教、佛教共同视为世界三大宗教。其分为天主教、东正教、新教等三大宗派,但因历史发展的缘故,汉语所称的“基督教”常专指新教,基督教整体则又另以“基督宗教”、“基督信仰”或“广义基督教”称之。
基督教的共同信仰认为三位一体的独一神(汉语亦译为上帝或天主)创造了世界,并按照神自己的形像造人,由人来管理世界[1],后来人犯罪堕落,带来了死亡;圣父派遣其子耶稣道成肉身,在其在世33年的最后,为世人的罪被钉死在十字架上,在三天后从死里复活而后升天,赐下圣灵与信徒同在;他的死付上了罪的赎价,使一切信他的人得到拯救,并在神内有永生。
按照基督教在4世纪的历史纪载,第一个教会在耶稣升天与圣灵降临(约公元30至33年)后由耶稣的使徒建立,之后耶稣的使徒及信徒们不断向外宣教,并快速在当时管辖巴勒斯坦的罗马帝国境内及周边地区传播;虽曾长期遭罗马帝国政府迫害,但约于公元325年由君士坦丁大帝宣布合法化,狄奥多西大帝时更定为罗马帝国的国教,至此成为西方世界的主要宗教。之后因罗马帝国分裂后西方世界东西部的差异化发展,导致11世纪发生东西教会大分裂,形成以罗马教宗为首的公教会(天主教)、以及君士坦丁堡普世牧首为首的正教会(东正教)。16世纪时,西欧又爆发了反对教宗权威的宗教改革运动,马丁·路德(路德派)、约翰·喀尔文(喀尔文派)、乌里希·慈运理等神学家与英国国王亨利八世(安立甘派)先后脱离天主教而自立教会,日后出现了许多教义相近的教会,这些教会即为后世所统称的新教。
基督教虽起源于中东,但在7世纪创立的伊斯兰教兴起后,今日在当地的信徒人口反而居于少数。由于基督教重视传教事业(又称为“大使命”),加上西方国家自地理大发现以来对世界经济及文化发展上强势的影响力,使得基督教的传布范围遍及整个世界,基督教文化更成为世界许多文明的重要骨干。粗估统计全球超过三分之一的人口信仰基督教,至今信徒人口逾24亿,是当今世界信仰人口最多的宗教,三大宗派中又以天主教的信徒占约半数最多;基督徒最多的国家则是美国及巴西,大约占人口的75%[2][3]。
キリスト教(キリストきょう、基督教、ギリシア語: Χριστιανισμός、ラテン語: Religio Christiana、英語: Christianity)は、ナザレのイエスをキリスト(救い主)として信じる宗教[1][2]。イエス・キリストが、神の国の福音を説き、罪ある人間を救済するために自ら十字架にかけられ、復活したものと信じる[2]。その多く(カトリック教会[3]・聖公会[4]・プロテスタント[5][6][7][8]・正教会[9]・東方諸教会[10]など)は「父なる神」[注 1]と「その子キリスト」[注 2]と「聖霊」を唯一の神(三位一体・至聖三者)として信仰する。
世界における信者数は22億人を超えており、すべての宗教の中で最も多い[11]。
Christianity[note 1][2] is a Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as described in the New Testament. Its adherents, known as Christians, believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of God and savior of all people, whose coming as the Messiah was prophesied in the Old Testament.[3] Most Christians get baptized, celebrate the Lord's Supper, pray the Lord's Prayer and other prayers, have clergy, and attend group worship services.
Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their successors, the Apostolic Fathers, spread the religion across large parts of the Middle East, Europe, Ethiopia, Transcaucasia, and some other parts of Asia, despite initial persecution. The Roman emperor Constantine the Great converted to Christianity and decriminalized it in the Edict of Milan (313). He convened the First Council of Nicaea (325), where Early Christianity was consolidated into what would become the state religion of the Roman Empire (380).[4][5][6] The council formulated the Nicene Creed (325), and the Church Fathers supervised the compilation of the Christian Bible (5th century).[7] The period of the first seven ecumenical councils is sometimes referred to as the Great Church, the united full communion of the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Church, and Oriental Orthodoxy before their schisms. Oriental Orthodoxy split after the Council of Chalcedon (451) over differences in Christology. The Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church separated in the East–West Schism (1054), especially over the authority of the Pope. Similarly, in 1521 Protestants were excommunicated from the Roman Catholic Church in the Protestant Reformation over Papal primacy, the nature of salvation and other ecclesiological and theological disputes.[8]
Christianity and Christian ethics have played a prominent role in the development of Western civilization,[9][10][11][12][13] particularly around Europe during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Following the Age of Discovery (15th–17th century), Christianity was spread into the Americas, Oceania, sub-Saharan Africa and the rest of the world via missionary work and colonization.[14][15][16]
It is the world's most populous religious group,[17][18] with over 2.4 billion followers,[19][20][21] or 33% of the global population, comprising a majority of the population in about two-thirds of the countries in the world.[21] Today, the four largest branches of Christianity are the Catholic Church (1.3 billion), Protestantism (920 million), the Eastern Orthodox Church (260 million)[22] and Oriental Orthodoxy (86 million).
Le christianisme est une religion abrahamique, originaire du Proche-Orient, fondée sur l'enseignement, la personne et la vie de Jésus de Nazareth, tels qu'interprétés à partir du Nouveau Testament. Il s'agit d'une religion du salut considérant Jésus-Christ comme le Messie annoncé par les prophètes de l'Ancien Testament. La foi en la résurrection de Jésus est au cœur du christianisme car elle signifie le début d'un espoir d'éternité libéré du mal.
Les premières communautés chrétiennes naissent au Ier siècle en Judée et dans les grandes villes de la diaspora juive telles que Rome, Éphèse, Antioche et Alexandrie. Le christianisme se développe à partir du IIe siècle dans l'Empire romain, dont il devient la religion officielle à la fin du IVe siècle, mais aussi en Perse, en Inde et en Éthiopie. Au Moyen Âge, le christianisme devient majoritaire en Europe, tandis qu'il s'amenuise face à l'islam au Proche-Orient. Il est devenu la religion la plus importante de la planète en raison de son expansion en Amérique à partir du XVIe siècle et en Afrique depuis le XXe siècle. Il est actuellement présent dans tous les pays. En 2015, le nombre total de chrétiens dans le monde est évalué à 2,4 milliards, ce qui en fait la religion comptant le plus de fidèles, devant l'islam et l'hindouisme.
Les Églises chrétiennes sont regroupées en différentes branches, dont les principales sont le catholicisme, le christianisme orthodoxe et le protestantisme représentant respectivement 51 %, 11 % et 38 % du total des chrétiens en 2017.
Il cristianesimo è una religione a carattere universalistico, originatasi dal giudaismo nel I secolo, fondata sulla venuta e predicazione, contenuta nei Vangeli, di Gesù di Nazareth, inteso come figlio del Dio d'Israele e quindi Dio egli stesso, incarnato, morto e risorto per la salvezza dell'umanità, ovvero il Messia promesso, il Cristo.[1][2]
Insieme a ebraismo e islam, il cristianesimo è classificato da alcuni come "religione abramitica"[3][4], è una monolatria. Il Cristianesimo è la religione più diffusa, con una stima di circa 2,1 miliardi di fedeli nel mondo al 2000[5].
Il cristianesimo emerge dal giudaismo nel I secolo; alle origini si presenta con il duplice aspetto di giudeo-cristianesimo (i cui membri ritenevano che solo i circoncisi potevano essere salvati) ed etno-cristianesimo (o cristianesimo dei Gentili, che comunque devono osservare la legge di Mosè), come si desume dai racconti degli Atti di Luca e da alcune lettere di Paolo (come la Lettera ai Galati, le lettere ai Corinzi), mostrando tuttavia che le due anime convivono senza alcuna scissione, e di avere raggiunta una formula di concordia con il primo concilio di Gerusalemme (Atti 15).
I cristiani assunsero dal giudaismo le sue Sacre scritture, definite poi Antico Testamento, nella versione tradotta in greco ellenistico (anche a causa della prevalente origine greco-romana della maggioranza dei primi adepti), dottrine fondamentali come il monoteismo, la fede in un messia o cristo, alcune forme del culto (incluso il sacerdozio), concetti di luoghi e tempi sacri, l'idea che il culto debba essere modellato secondo il modello celeste, l'uso dei Salmi nelle preghiere comuni.
Il cristianesimo inteso come religione distinta da quella ebraica iniziò a delinearsi dopo il cosiddetto "Sinodo di Jamnia" in cui venne presa posizione decisa circa l'estraneità della "Via"[6] dall'ebraismo ortodosso, a partire dalla seconda metà del II secolo.
Successivamente la Chiesa post-apostolica lentamente si organizzò attorno alla cosiddetta pentarchia dei cinque patriarcati di Roma, Costantinopoli, Alessandria, Antiochia e Gerusalemme.
Inizialmente si ebbe una secolare contesa critica tra varie correnti per la formazione della prima Cristianità, correnti che si rifacevano a diverse raccolte di testi ritenuti sacri. Tale contesa terminò nel IV secolo con la conversione dell'Imperatore Costantino I (battezzato in punto di morte da un vescovo ariano[7]) il quale fece indire il Concilio di Nicea per far emergere una sola corrente ed eliminare le altre. Contestualmente la Cristianità divenne una religione approvata ufficialmente e i vescovi Cristiani, vittime in precedenza del potere militare, ne passarono al comando[8].
Nel 380 Teodosio con l'Editto di Tessalonica la rese l'unica religione ufficiale dell'impero romano ricorrendo anche a mezzi cruenti per reprimere le resistenze dei pagani.[9]
Nel 1054 contese teologiche circa i dogmi trinitari, il celibato ecclesiastico ed altre questioni minori culminarono nel Grande Scisma tra Chiesa cattolica e Chiesa ortodossa.
Circa cinque secoli dopo lo scandalo delle indulgenze spinse Lutero a causare un altro scisma e quindi a fondare il Protestantesimo.
Nell'Europa dell'est l'instaurazione di regimi marxisti, per definizione materialisti, ha avuto come conseguenza un processo di scristianizzazione pianificata di stato che è avvenuto iniziando dalla Russia (ex Unione Sovietica) e poi, nel dopoguerra, nei paesi governati da regimi comunisti satelliti dell'URSS. In seguito alla caduta dei regimi, dopo il 1989, è stata ristabilita, in buona parte dei casi, la libertà di culto.
El cristianismo (del latín christianismus, y este del griego χριστιανισμός)1 es una religión abrahámica monoteísta basada en la vida, enseñanzas y milagros de Jesús de Nazaret, tal y como se presentan en el Nuevo Testamento, que es la segunda parte de la Biblia, el libro sagrado de los cristianos. Con 2400 millones de seguidores,234 una de cada tres personas en el mundo es cristiana, por lo que es la religión más extensa del mundo.56 Los cristianos creen que Jesús es el hijo de Dios, así como el Mesías (o Cristo) profetizado en el Antiguo Testamento, que sufrió, fue crucificado, descendió al infierno y resucitó de entre los muertos para dar vida eterna a quienes crean y confíen en él para la redención de sus pecados. Las cuatro ramas más importantes del cristianismo son el catolicismo (1300 millones de adherentes), el protestantismo (920 millones), la Iglesia ortodoxa (270 millones) y las Iglesias ortodoxas orientales (86 millones). El movimiento que busca restaurar la unidad de la Iglesia cristiana recibe el nombre de ecumenismo.
El cristianismo surgió del judaísmo789 a mediados del siglo I d. C.1011 en la provincia romana de Judea. Los primeros líderes de las comunidades cristianas fueron los apóstoles y sus sucesores los padres apostólicos. Este cristianismo primitivo se extendió, pese a ser una religión minoritaria y perseguida, por Judea, Siria, Europa, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, Transcaucasia, Egipto y Etiopía. El cristianismo fue legalizado en el Imperio romano mediante el Edicto de Milán, en el año 313. El emperador Constantino se convirtió al cristianismo y convocó el Concilio de Nicea (325), en el que se formuló el credo niceno. El cristianismo se convirtió en la religión oficial del Imperio romano en el año 380, bajo el emperador Teodosio I el Grande.121314 Durante estos primeros siglos, los Padres de la Iglesia gradualmente consolidaron las doctrinas del cristianismo y supervisaron el desarrollo del canon del Nuevo Testamento.15
La Iglesia de los primeros siete concilios ecuménicos se conoce frecuentemente como la «Gran Iglesia», porque la Iglesia católica, la Iglesia ortodoxa y las Iglesias ortodoxas orientales estaban en plena comunión.16 Las Iglesias orientales se separaron tras el Concilio de Calcedonia (451) por diferencias cristológicas. La Iglesia ortodoxa se separó de la Iglesia católica en 1054 por diferencias acerca de la autoridad del papa. El protestantismo, aunque es en realidad un conjunto de denominaciones, aparece por primera vez durante la Reforma protestante del siglo XVI, y criticaban lo que percibían como importantes desviaciones teológicas y eclesiológicas por parte de la Iglesia católica.17 El descubrimiento de América en
 Architecture
Architecture
 Geography
Geography
 Party and government
Party and government
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Music
Music
 International cities
International cities
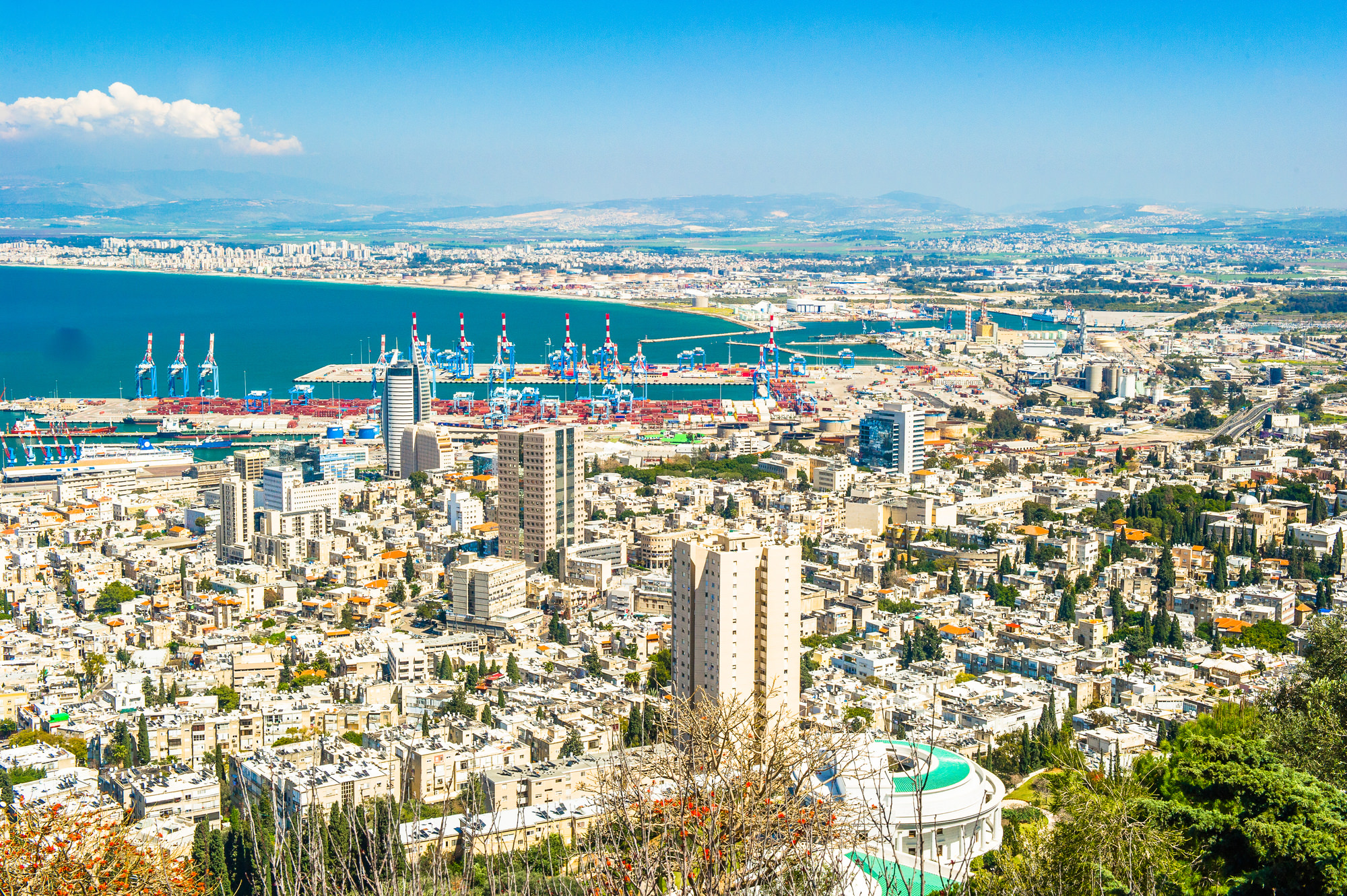
 Important port
Important port
 Sport
Sport
 Religion
Religion
 Art
Art
 Literature
Literature
 World Heritage
World Heritage