
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Chile
Chile

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Canada
Canada



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 National Optical Astronomy Observatory
National Optical Astronomy Observatory
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom


 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA






Hawaii ([haˈva͜ii], englisch [həˈwɑːiː], hawaiisch Hawaiʻi bzw. Mokupuni o Hawaiʻi) ist eine Inselkette im Pazifischen Ozean und seit 1959 der 50. Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten. Sie ist benannt nach der größten Insel des Archipels, die inoffiziell auch Big Island heißt. Die Inselgruppe gehört zum polynesischen Kulturraum, bildet die nördliche Spitze des sogenannten polynesischen Dreiecks und wird zu den Südseeinseln gezählt.[1] Sie wurden früher auch Sandwich-Inseln genannt. Der Beiname des US-Bundesstaates Hawaii ist Aloha State („Aloha-Staat“).
Hawaiis vielfältige Landschaften, ein ganzjährig warmes Klima und viele öffentliche Strände machen es zu einem beliebten Zielpunkt von Touristen, Surfern, Biologen und Geologen. Durch seine Lage mitten im Pazifik wirken auf Hawaii mit seiner eigenen polynesischen Kultur sowohl ostasiatische als auch nordamerikanische Einflüsse.
夏威夷州(夏威夷语:Mokuʻāina o Hawaiʻi,英语:State of Hawaii),是美国的州份之一,由夏威夷群岛组成,距离美国本土3,700公里,属于太平洋沿岸地区;所属的大洲则是大洋洲。在1778至1898年间,夏威夷也被称为“三明治群岛”(Sandwich Islands)。首府及最大都市为火奴鲁鲁。夏威夷州成立于1959年8月21日,是距今最近加入美国的州,与美国其他各州有着明显的区别:它除了是美国最南方的州外,也是美国唯一一个全部位于热带的州;它与阿拉斯加州是美国各州中,仅有的两个不与其他各州相连的州份,也是美国唯一一个没有任何土地位于美洲大陆的州。论美国所有领土而言,夏威夷州是除了美国海外属地和群岛以外,最南端的一州,但非最南端的领土(美国最南端的领土在美属萨摩亚群岛)。在族群分布上,它是两个非白种人居多数州份的其中之一,比起其他各州,夏威夷州拥有最大的亚裔人口比例。生态及农业方面,它是全世界拥有最多濒危物种的地方,也是美国唯一生产咖啡具有工业规模的州份。
ハワイ州(英: State of Hawaii [həˈwaɪ.i] (![]() 音声ファイル) 、ハワイ語: Hawaiʻi[1])は、太平洋に位置するハワイ諸島にあるアメリカ合衆国の州。州都はオアフ島のホノルル市である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で最後に加盟した州である。漢字では「布哇」と書く。海域として定められたミクロネシアの北端でもある。
音声ファイル) 、ハワイ語: Hawaiʻi[1])は、太平洋に位置するハワイ諸島にあるアメリカ合衆国の州。州都はオアフ島のホノルル市である。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で最後に加盟した州である。漢字では「布哇」と書く。海域として定められたミクロネシアの北端でもある。
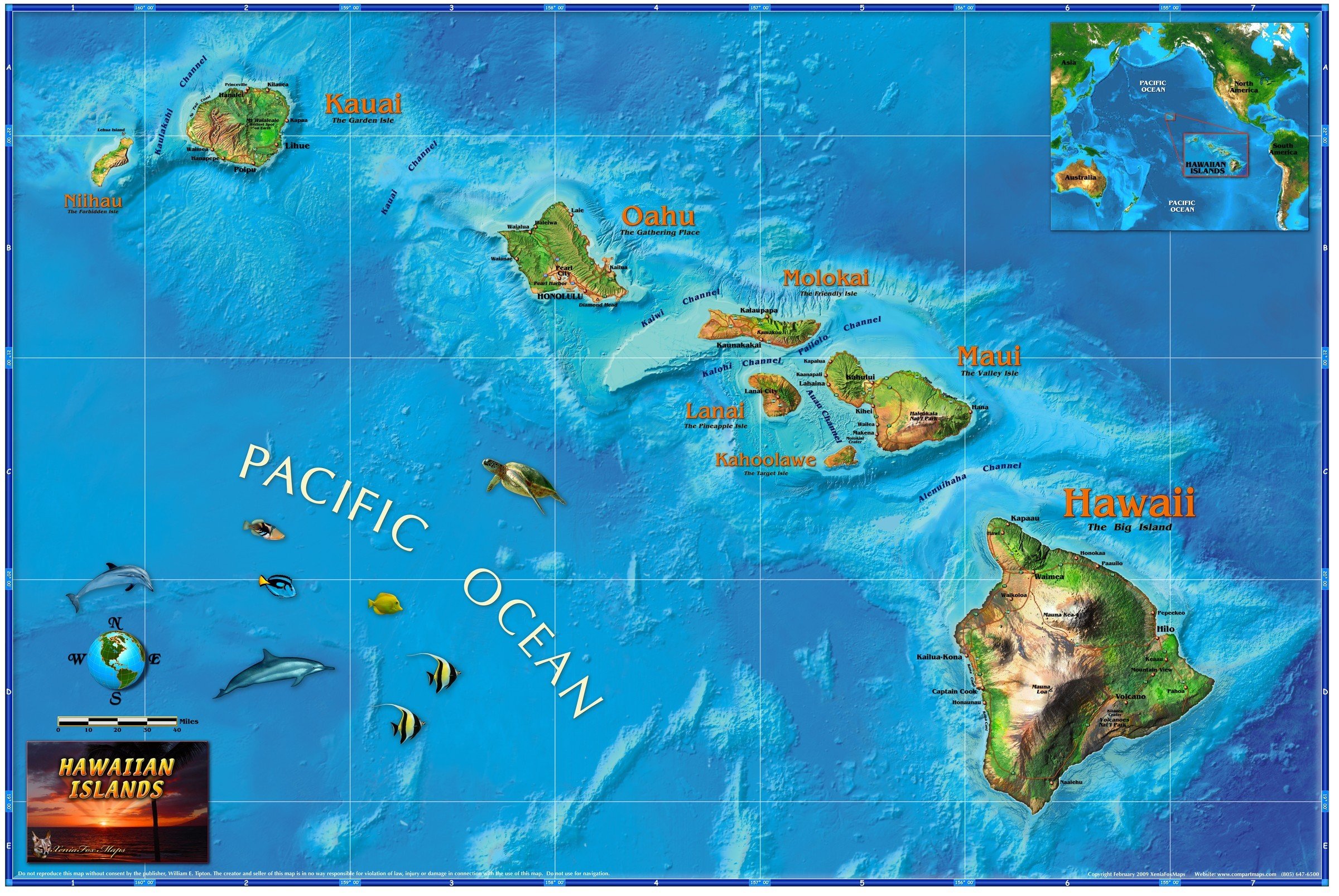
ハワイ島、マウイ島、オアフ島、カウアイ島、モロカイ島、ラナイ島、ニイハウ島、カホオラウェ島の8つの島と100以上の小島からなるハワイ諸島のうち、ミッドウェー環礁を除いたすべての島が、ハワイ州に属している。北西ハワイ諸島の北西端からハワイ諸島の南東端のハワイ島まで、全長1,500マイル(2,400キロ)にわたっている。州全体が島だけで構成されるアメリカ合衆国で唯一の州である。
アメリカ合衆国本土の南西、日本の南東、オーストラリアの北東と、太平洋の中央に位置し、地理的にも民族的にも近いポリネシアでは最も北にある列島で構成されている。その自然の多様な景観、暖かい熱帯性気候、豊富な公共の海浜と大洋に取り囲まれていること、および活火山の活動があることで、観光客、サーファー、生物学者、火山学者などに人気のある目的地になっている。日本で最も人気な海外リゾート地のひとつ。独特の文化がある他に太平洋の中心にあることで、北アメリカやアジアの影響も多く受けている。130万人を超える人口のほか、常に観光客やアメリカ軍軍事関係者が滞在している。
Hawaii (/həˈwaɪi/ (![]() listen) hə-WY-ee; Hawaiian: Hawaiʻi [həˈvɐjʔi]) is a state of the United States of America located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the only U.S. state located outside North America, the only island state, and the only state in the tropics.
listen) hə-WY-ee; Hawaiian: Hawaiʻi [həˈvɐjʔi]) is a state of the United States of America located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the only U.S. state located outside North America, the only island state, and the only state in the tropics.
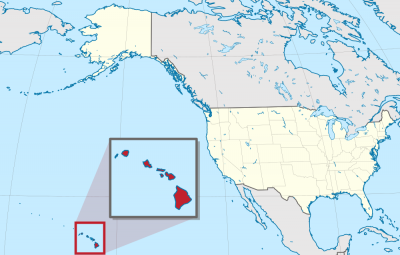
The state encompasses nearly the entire Hawaiian archipelago, which consists of 137 volcanic islands spanning 1,500 miles (2,400 km), which are physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania.[11] The state's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth longest in the U.S, at about 750 miles (1,210 km).[b] The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui, and Hawaiʻi, after which the state is named; it is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago.
Of the 50 U.S. states, Hawaii is the eighth-smallest geographically and the 11th-least populous, but the 13th-most densely populated. It has more than 1.4 million residents, and is among the most diverse states in the country, with the nation's only Asian American demographic majority. The state capital and largest city is Honolulu on the island of Oʻahu. Settled by Polynesians some time between 124 and 1120 AD, Hawaii was an independent nation until 1898, when it was annexed by the United States. It became the most recent state to join the union, on August 21, 1959.[12]
Hawaii's diverse natural scenery, warm tropical climate, abundance of public beaches, oceanic surroundings, active volcanoes, and clear skies on the Big Island make it a popular destination for tourists, surfers, biologists, volcanologists, and astronomers. Due to its central location in the Pacific and successive waves of labor migration, Hawaii is a unique melting pot of Southeast Asian, East Asian and North American cultures, in addition to its indigenous Hawaiian culture.
Hawaï (/a.waj/2 ; en hawaïen : Hawai‘i, prononcé /ha.ˈvaj.ʔi/3 ; en anglais : Hawaii, prononcé /hə.ˈwaɪ.(j)i/4) est un État des États-Unis. Constitué d'un archipel de 137 îles5, il s'agit du seul État américain situé en dehors du continent nord-américain, puisqu'il est situé en Océanie, et de l'un des deux États américains non contigus, avec l'Alaska. Les huit principales îles sont Niihau, Kauai, Molokai, Lanai, Kahoolawe, Maui, l'île d'Hawaï et Oahu, où se trouve la capitale Honolulu. L'archipel fait partie de la Polynésie et se situe dans le centre de l'océan Pacifique nord, à 3 718 kilomètres au sud de la péninsule d'Alaska, à 3 792 kilomètres à l'ouest-sud-ouest de Punta Gorda, sur la côte californienne, et à 5 713 kilomètres à l'est de l'île de Hokkaidō au Japon. En outre, il est le 50e et dernier État à avoir été admis dans l'Union, le 21 août 1959. La variété de ses paysages, marqués notamment par un volcanisme très actif (Hualālai, Kīlauea, Mauna Kea, Mauna Loa), un climat tropical humide et un patrimoine naturel endémique, en font une destination prisée aussi bien des touristes que des scientifiques6.
L'archipel était habité par des peuples polynésiens depuis plusieurs siècles à l'arrivée de l'explorateur britannique James Cook en 1778, qui le baptise Îles Sandwich. Les îles sont unifiées en un royaume vers 1810 par Kamehameha Ier, qui fonde une dynastie qui perdure jusqu'en 1893. Lui succèdent une éphémère République d'Hawaï (1894-1898) et le territoire d'Hawaï, créé lors de l'annexion de l'archipel par les États-Unis. En décembre 1941, l'île d'Oahu est le théâtre de l'attaque de Pearl Harbor. Le territoire est dissous en 1959 lorsque Hawaï devient le 50e État américain. Il compte environ 1 360 000 habitants en 2010, principalement dans l'aire urbaine de Honolulu. La population est composée de nombreux groupes ethniques, principalement d'origine asiatique (Philippins, Japonais). Les autochtones hawaïens comptent aujourd'hui pour 22 % de la population7.
Situé au cœur de l'océan Pacifique, Hawaï mêle de nombreuses influences culturelles, entre les apports nord-américains et asiatiques, et sa propre culture ancestrale. Proche des cultures polynésiennes et maories, elle demeure très active, notamment autour de traditions musicales. La musique hawaïenne, essentiellement jouée à la guitare hawaïenne et au ukulélé, fut popularisée dans le monde par Sol Hoopii et, plus tard, par le chanteur Iz. Le mode de vie hawaïen se diffuse également avec la pratique du surf et de la spiritualité locale, le Hoʻoponopono. Ses deux grands parcs nationaux (Parc national des volcans d'Hawaï, Parc national de Haleakalā) et ses nombreuses plages en font une destination touristique majeure. De tradition démocrate, Hawaii est le lieu de naissance du 44e président des États-Unis, Barack Obama.
Le isole Hawaii (/aˈvai/ o /aˈwai/[3]; hawaiano Hawaiʻi, [həˈvɐjʔi], inglese , /həˈwaɪ.iː/ ) sono uno Stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America (il 50º ed ultimo Stato, in ordine cronologico d'istituzione), è un arcipelago vulcanico situato nell'oceano Pacifico formato da otto isole principali e molte isole minori, scogli e secche. Le isole maggiori sono, da nord-ovest a sud-est, Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lanai, Kahoolawe, Maui e l'isola di Hawaii. Quest'ultima è la più estesa ed è spesso chiamata "La Grande Isola" per evitare confusione con lo Stato omonimo.
Politicamente quindi l'arcipelago è compreso nello Stato di Hawaii, facente parte dal 21 agosto 1959 degli Stati Uniti d'America, e ha come capitale Honolulu, situata sull'isola di Oahu. La linea costiera dello stato, lunga approssimativamente 1 210 km (750 miglia), è la quarta più lunga degli USA dopo quelle di Alaska, Florida e California.[4] Lo stato Hawaii è il 50º Stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America e ha giurisdizione su tutte le isole dell'arcipelago con l'eccezione dell'Atollo di Midway, il quale è sotto diretto controllo federale. Le Hawaii sono il 43º stato per superficie, il 40º per popolazione, ma il 13º più densamente popolato dei 50 stati degli Stati Uniti d'America. Come l'Alaska, non fa parte dei cosiddetti Stati Uniti contigui (distano quasi 4 000 km dalla costa americana: il punto più vicino è la California)
Il soprannome dello stato è Aloha State (che riprende il tipico saluto hawaiano "aloha"), mentre l'animale scelto come simbolo è la foca monaca delle Hawaii. Nonostante non siano simboli veri e propri, sono direttamente collegati alle Hawaii anche lo strumento musicale dell'ukulele e lo sport del surf.
Le Hawaii sono uno dei due stati della nazione che non adottano l'ora legale; l'altro è l'Arizona.
Il caldo clima tropicale, l'abbondanza di spiagge pubbliche e di ambienti oceanici e di vulcani attivi rendono l'arcipelago una destinazione apprezzata da turisti, surfisti, biologi e vulcanologi.
Grazie alla loro posizione al centro dell'Oceano Pacifico, le Hawaii hanno ricevuto molte influenze, mescolatesi poi con la cultura già presente in loco, sia dall'America sia dall'Asia, tanto che le Hawaii sono l'unico Stato con una collettività di asioamericani.
Hawái1 (en inglés, Hawaii; en hawaiano, Hawai‘i) es uno de los cincuenta estados que conforman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Honolulu, en la isla de Oʻahu. Es el único estado insular y extracontinental del país, y el último en ser admitido como tal; el 21 de agosto de 1959. Su población alcanza casi el millón y medio de habitantes.
Está ubicado en el océano Pacífico central, al suroeste de los Estados Unidos continentales, y comprende casi todo el archipiélago de Hawái (excepto las islas Midway que son un territorio incorporado) el grupo de islas más septentrional de la Polinesia (Oceanía). En el extremo sureste se hallan las ocho islas principales, de noroeste a sureste: Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui y Hawáiʻi. Esta última es la más grande, por lo que se la llama The Big Island, «Isla Grande».
Hawái posee 28 311 km² de superficie, por lo cual es el octavo menos extenso de la Unión, por delante de Massachusetts, Vermont, Nuevo Hampshire, Nueva Jersey, Connecticut, Delaware y Rhode Island.
Debido a su ubicación en Oceanía y su carácter de escala en la ruta entre América y Asia, Hawái presenta, además de su rica cultura nativa de raíz polinesia, influencias americanas (en especial del oeste estadounidense, pero también mexicanas) y asiáticas (japonesas, filipinas y chinas).
Гава́йи[2][3][4] (англ. Hawaii, американское произношение: [həˈwaɪi] (![]() слушать)) — штат США. Расположен на Гавайских островах в центральной части Тихого океана в Северном полушарии на расстоянии 3700 км от континентальной части США. В состав федерации на правах штата Гавайи вошли 21 августа 1959 года, став 50-м по счёту штатом.
слушать)) — штат США. Расположен на Гавайских островах в центральной части Тихого океана в Северном полушарии на расстоянии 3700 км от континентальной части США. В состав федерации на правах штата Гавайи вошли 21 августа 1959 года, став 50-м по счёту штатом.
Население — 1 419 561 человек (по данным на 2014 год). Городского населения около 70 %. Официальный язык — английский. В туристических районах наряду с английским используется японский, многие надписи на английском продублированы иероглифами (каной)[5]. В быту, среди различных этнических групп, сохраняются и другие языки, в том числе гавайский.
Столица и крупнейший город штата — Гонолулу. Другие крупные города — Хило, Каилуа-Кона, Канеохе. Экономически наиболее развит остров Оаху.

 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC

 Australian Capital Territory-ACT
Australian Capital Territory-ACT
 Australia
Australia
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kantō
Kantō
 Kinki
Kinki
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Die Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (für englisch Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, kurz APEC, auch übersetzt als Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftskooperation oder Asien-Pazifik-Forum) ist eine internationale Organisation, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, im pazifischen Raum eine Freihandelszone einzurichten.
In den 21 APEC-Staaten lebt knapp die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung. Der Wirtschaftsraum erbringt mehr als die Hälfte der Weltwirtschaftsleistung und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Wirtschaftsregionen der Welt.
亚太经济合作组织(简称亚太经合组织;英语:Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,缩写:APEC),是亚太区内各地区之间促进经济成长、合作、贸易、投资的论坛。此组织的创办在历史上取代了该区域的冷战结构,但由于日本在该区域会因过去历史记忆引发负面评价,所以由澳大利亚主导创始事项[1]。
始设于1989年,现有21个经济体成员。亚太经合组织是经济合作的论坛平台,其运作是通过非约束性的承诺与成员的自愿,强调开放对话及平等尊重各成员意见,不同于其他经由条约确立的政府间组织。“APEC”与“Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation”均是亚太经济合作组织的注册商标。[2]
アジア太平洋経済協力会議(アジアたいへいようけいざいきょうりょくかいぎ、英: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)は、環太平洋地域における多国間経済協力を進めるための非公式なフォーラム[2]である。略称、APEC(エイペック[3][4])。
「アジア太平洋」という概念が最初に打ち出されたのは、永野重雄が1967年に発足させた太平洋経済委員会(PBEC)という経済団体の設立時であるとされるが[5][6][7]、具体的にこうした地域概念が政府レベルの協力枠組みに発展する萌芽は、1978年、日本の大平正芳首相が就任演説で「環太平洋連帯構想」を呼びかけたことにある。これを具体化した大平政権の政策研究会「環太平洋連帯研究グループ」(議長:大来佐武郎、幹事佐藤誠三郎)の報告を受け、大平がオーストラリアのマルコム・フレイザー首相に提案して強い賛同を得たことが、1980年9月の太平洋経済協力会議(PECC)の設立につながった。PECCは地域における様々な課題を議論し研究するセミナーといった趣のものであったが、これを土台にして、各国政府が正式に参加する会合として設立されたのが、APECである[8][9]。
APECは、1989年にオーストラリアのホーク首相の提唱で、日本・アメリカ合衆国・カナダ・韓国・オーストラリア・ニュージーランド及び当時の東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟6か国の計12か国で発足し、同国のキャンベラで閣僚会議(Ministerial Meeting)を開催した。また、1993年には米国のシアトルで初の首脳会議(Economic Leaders' Meeting)がもたれた。現在は、首脳会議、及び、外相、経済担当相による閣僚会議をそれぞれ年1回開いている。シンガポールに常設事務局を置き、開催国から任期1年で事務局長が選任されている[10]。 参加しているメンバーは、21カ国・地域で、2012年現在、人口では世界の41.4%、GDP(国内総生産)では57.8%、貿易額では47%を占めている。
APECは、開かれた地域協力によって経済のブロック化を抑え、域内の貿易・投資の自由化を通じて、世界貿易機関(WTO)のもとでの多角的自由貿易体制を維持・発展することを目的としてきたが、近年のWTOの新ラウンドの停滞や自由貿易協定締結の動きの活発化などによって、その存在意義が問われている。
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies[2] that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Inspired from the success of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)’s series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, the APEC was established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; and to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[3][4][5] Headquartered in Singapore, the APEC is recognised as one of the oldest forums and highest-level multilateral blocs in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting is attended by the heads of government of all APEC members except Republic of China (Taiwan) (which is represented by a ministerial-level official under the name Republic of China as economic leader).[12] The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15][16][17]
La Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (en anglais : Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) est un forum économique intergouvernemental visant à faciliter la croissance économique, la coopération, les échanges et l'investissement de la région Asie Pacifique. Elle se réunit chaque année1.
L'Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), ossia Cooperazione Economica Asiatico-Pacifica, è un organismo nato nel 1989 allo scopo di favorire la cooperazione (o, più in generale, la crescita) economica, il libero scambio e gli investimenti nell'area asiatico-pacifica. Tale area (come suggerisce il logo stesso dell'APEC) coincide non solo con l'Asia Pacifica, ma potenzialmente con l'intero Pacific Rim.
L'APEC ha sede a Singapore, Paese considerato una delle tigri dell'Asia.
Dal punto di vista del diritto internazionale l'APEC si definisce organismo e non organizzazione internazionale perché, essendo composto da economie e non da Stati, è privo di una piena personalità giuridica. Ciò spiega, fra l'altro, come mai possano farne parte contemporaneamente la Cina continentale, Hong Kong e Taiwan, ossia tre realtà che, territorialmente (secondo Pechino e secondo tutti i governi che intrattengono relazioni diplomatiche con Pechino), appartengono a un unico Stato: la Repubblica Popolare di Cina.
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, en español Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico) es un foro multilateral creado en 1989, con el fin de consolidar el crecimiento y la prosperidad de los países del Pacífico, que trata temas relacionados con el intercambio comercial, coordinación económica y cooperación entre sus integrantes.1
Como mecanismo de cooperación y concertación económica, está orientado a la promoción y facilitación del comercio, las inversiones, la cooperación económica y técnica y al desarrollo económico regional de los países y territorios de la cuenca del océano Pacífico. Fomentando un crecimiento económico inclusivo, equitativo, sustentable e innovador.2
La suma del Producto Nacional Bruto de las veintiuna economías que conforman el APEC equivale al 56 % de la producción mundial, en tanto que en su conjunto representan el 46 % del comercio global.
La APEC no tiene un tratado formal. Sus decisiones se toman por consenso y funciona con base en declaraciones no vinculantes. Tiene una Secretaría General, con sede en Singapur, que es la encargada de coordinar el apoyo técnico y de consultoría. Cada año uno de los países miembros es huésped de la reunión anual de la APEC. La vigésimo novena cumbre se realizó en noviembre de 2017 en Da Nang, Vietnam; y la próxima será en Santiago, Chile.
Азиатско-Тихоокеанское экономическое сотрудничество (АТЭС) (англ. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) — форум 21 экономики Азиатско-Тихоокеанского региона для сотрудничества в области региональной торговли и облегчения и либерализации капиталовложений.
Целью АТЭС является повышение экономического роста, процветания в регионе и укрепление азиатско-тихоокеанского сообщества. В экономиках-участницах проживает около 40 % мирового населения, на них приходится приблизительно 54 % ВВП и 44 % мировой торговли[1].
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 International cities
International cities
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Companies
Companies
 Animal world
Animal world
 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 Architecture
Architecture
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade