Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
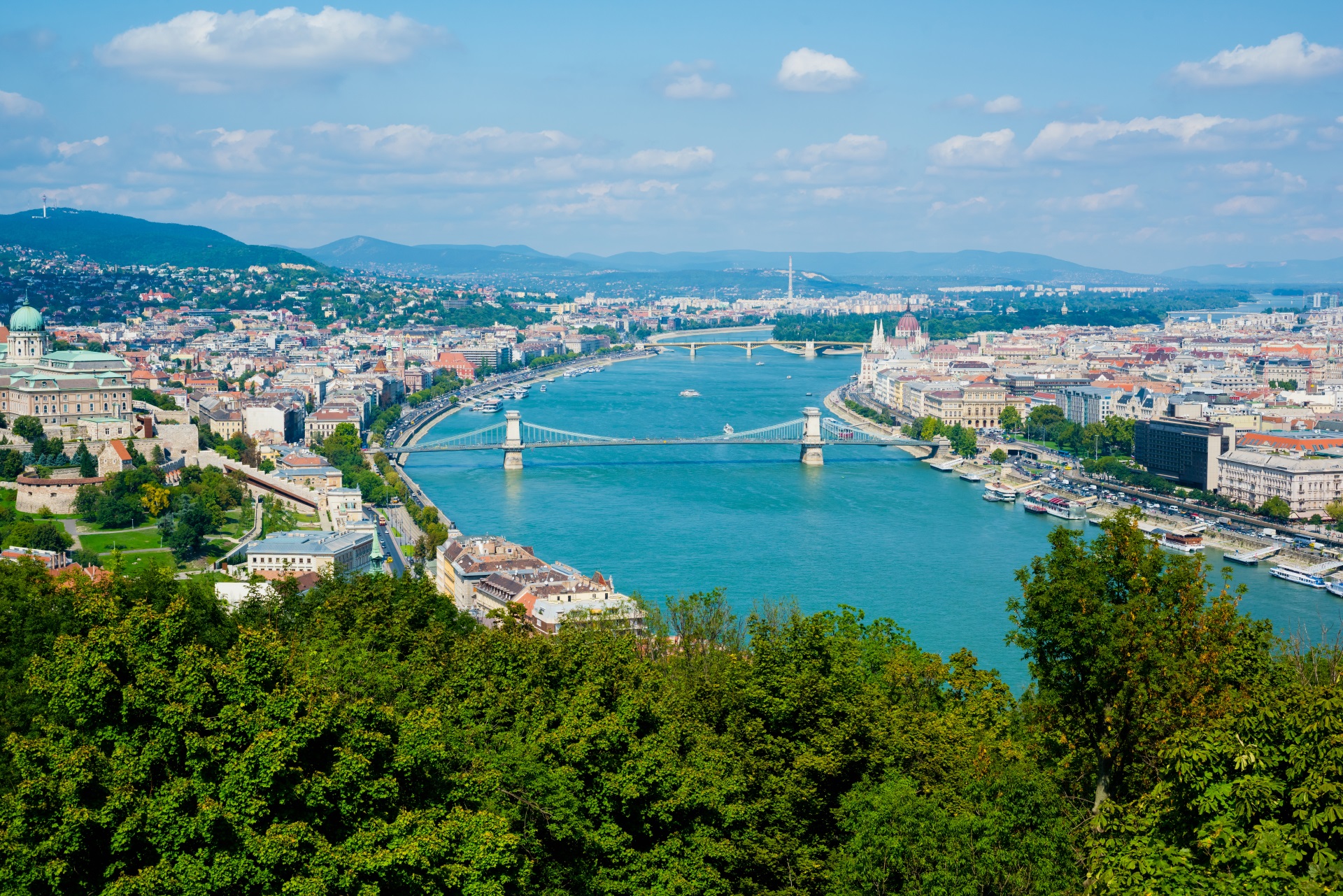
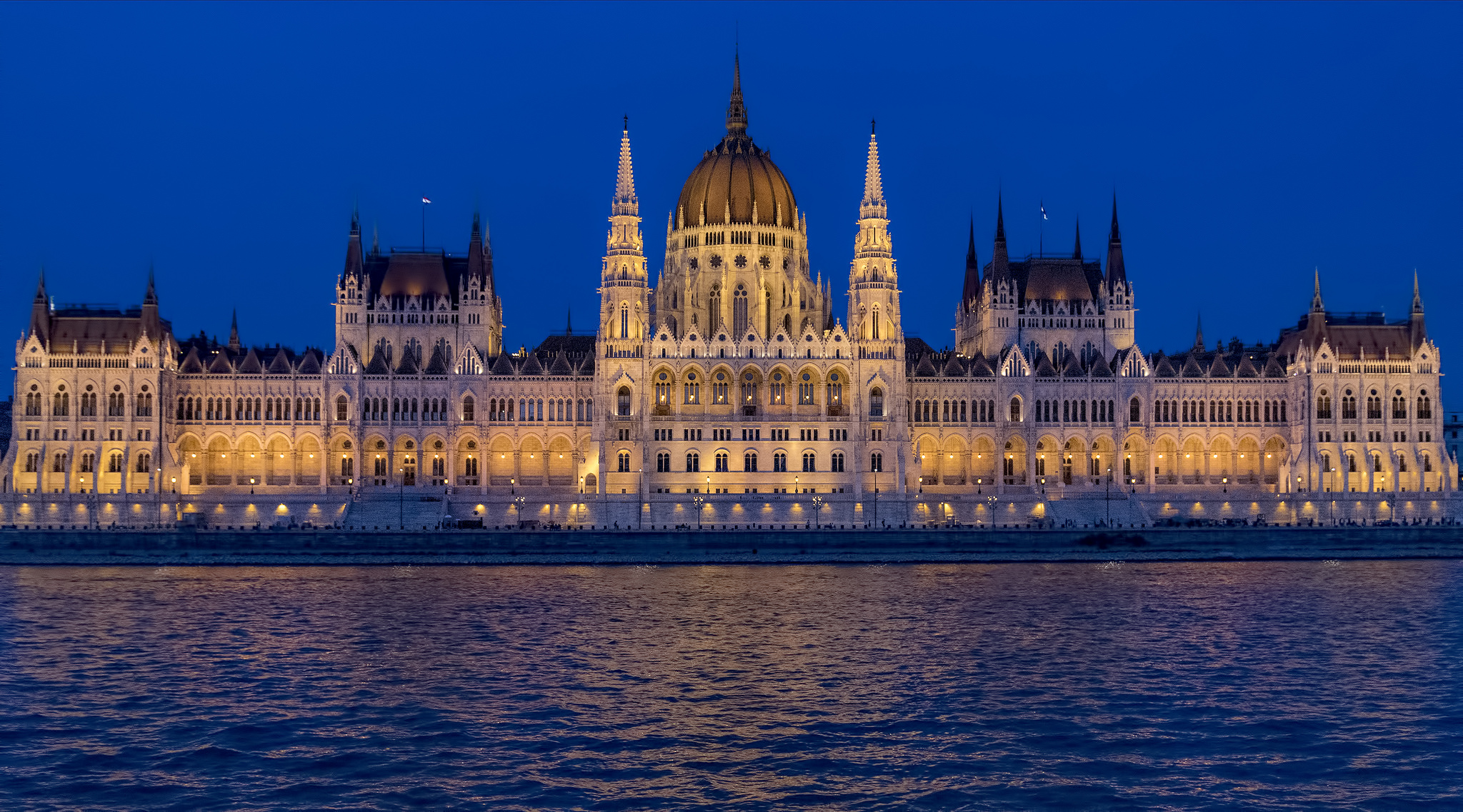
 Hungary
Hungary
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *French political system
*French political system
 Albania
Albania
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Anders Fogh Rasmussen
Anders Fogh Rasmussen
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Dirk Stikker
Dirk Stikker
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 George Robertson
George Robertson
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Javier Solana
Javier Solana
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Joseph Luns
Joseph Luns
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manfred Wörner
Manfred Wörner
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manlio Giovanni Brosio
Manlio Giovanni Brosio
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Paul-Henri Spaak
Paul-Henri Spaak
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Sergio Balanzino
Sergio Balanzino
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Willy Claes
Willy Claes

 History
History
 Greece
Greece
 Iceland
Iceland
 Italy
Italy
 Canada
Canada
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 NATO summit
NATO summit
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen

 Party and government
Party and government
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Sweden
Sweden
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
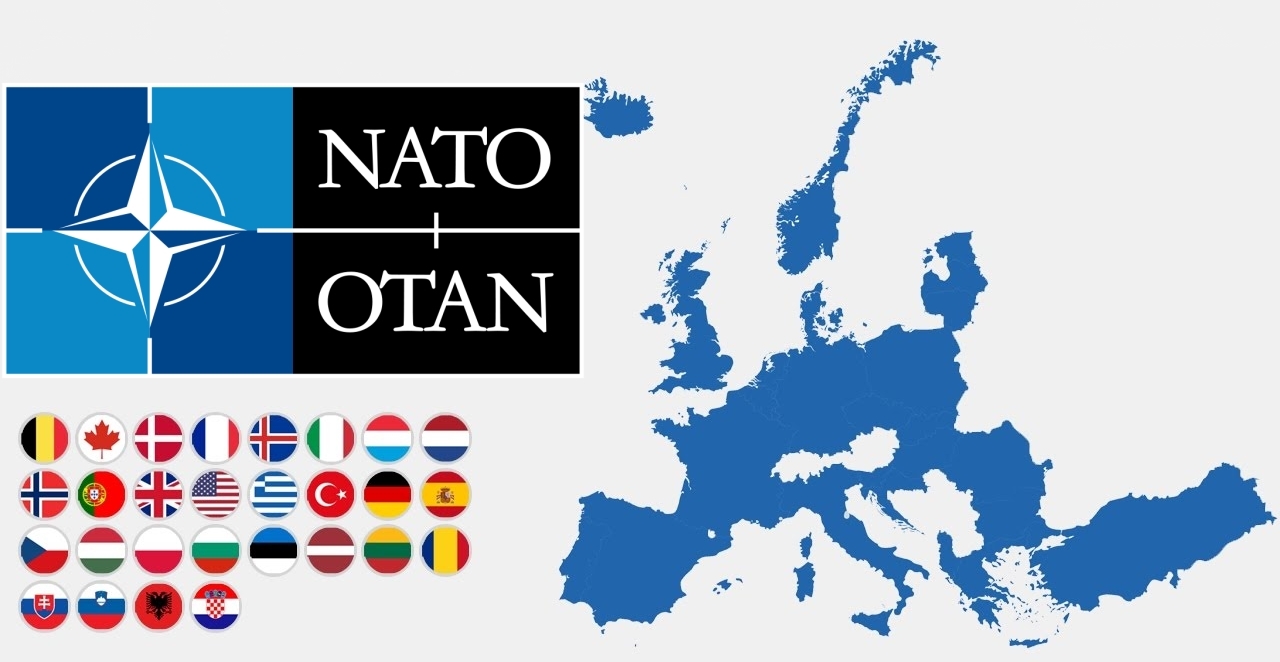
北大西洋公约组织(英语:North Atlantic Treaty Organization,缩写为NATO;法语:Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord,缩写为OTAN),简称北约组织或北约,是欧洲及北美洲国家为实现防卫合作而建立的国际组织。1949年3月18日,美国、英国及法国公开建立北大西洋公约组织,于同年4月4日在美国华盛顿签署《北大西洋公约》后正式成立。为与以前苏联为首的东欧集团国成员相抗衡。及至苏联解体,华沙条约组织宣告解散,北约就成为一个地区性防卫协作组织。北约的最高决策机构是北约理事会。理事会由成员国国家元首及政府高层、外长、国防部长组成。总部设在比利时的布鲁塞尔。最新成员黑山于2017年6月5日加入,至此北约总共有跨域欧洲和北美的29个国家组成。北约军事开支占世界国防开支的70%[4],成员国国防开支占该国GDP的2%左右[5]。
公约第5条规定成员国受到的攻击一旦被确认,其他成员国将作出即时反应。该条款被理解为各国部队将自动参战,并不再次需要各国政府的参战授权。但这一条条款在九一一事件之前,一直都未有动用过[6] 。北约曾协助反海盗行动(counter-piracy operations),在联合国要求下打击亚丁湾、非洲之角和印度洋的海盗[7],并在2011年根据联合国安理会1973号决议将利比亚上空设为禁飞区。
Die NATO (englisch North Atlantic Treaty Organization „Organisation des Nordatlantikvertrags“ bzw. Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation), im Deutschen häufig als Atlantisches Bündnis oder als Nordatlantikpakt bezeichnet (französisch OTAN – Organisation du Traité de l’Atlantique Nord), ist eine Internationale Organisation ohne Hoheitsrechte. Ihre Mitgliedstaaten behalten ihre volle Souveränität und Unabhängigkeit. Basis der NATO ist der Nordatlantikvertrag nach Artikel 51 der UN-Charta. Ihre Organisation versteht sich nicht nur als Verteidigungsbündnis, sondern auch als militärisch-politische Organisation von 29 europäischen und nordamerikanischen Mitgliedstaaten mit dem Ziel eigener Sicherheit und weltweiter Stabilität.
Das NATO-Hauptquartier beherbergt den Nordatlantikrat (das Hauptorgan der NATO) und seine unmittelbar nachgeordneten Einrichtungen, den International Staff (IS) und den International Military Staff (IMS); diese Institution hat seit 1967 ihren Sitz in Brüssel. Nach der Unterzeichnung des Nordatlantikpakts am 4. April 1949 – vorerst auf 20 Jahre – war das Hauptquartier zunächst in London ansässig und anschließend von 16. April 1952 bis 1967 in Paris angesiedelt worden.
Die beiden wichtigsten militärischen Hauptquartiere sind das ACO (aus historischen und juristischen Gründen auch als Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe / SHAPE bezeichnet) im belgischen Casteau bei Mons und das Allied Command Transformation (ACT) in der US-Stadt Norfolk (Virginia).
北大西洋条約機構(きたたいせいようじょうやくきこう)は、北大西洋条約に基づき、アメリカ合衆国を中心とした北アメリカ(=アメリカとカナダ)およびヨーロッパ諸国によって結成された軍事同盟である。29カ国が加盟し、日本など非加盟国とも協力関係にある[1]。前身はブリュッセル条約 (1948年)。ベルギー首都ブリュッセルに本部を置く[2]。
略称は頭字語が用いられ、英語圏では、North Atlantic Treaty Organization を略した NATO(ネイトー)と呼ばれ、日本やドイツ語圏では NATO(ナトー)、フランス語圏・スペイン語圏・ポルトガル語圏等では OTAN(オタン)と呼ばれる。
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO /ˈneɪtoʊ/; French: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord; OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 29 North American and European countries. The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949.[3][4] NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. NATO’s Headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
Since its founding, the admission of new member states has increased the alliance from the original 12 countries to 29. The most recent member state to be added to NATO is Montenegro on 5 June 2017. NATO currently recognizes Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Macedonia and Ukraine as aspiring members.[5] An additional 21 countries participate in NATO's Partnership for Peace program, with 15 other countries involved in institutionalized dialogue programs. The combined military spending of all NATO members constitutes over 70% of the global total.[6] Members have committed to reach or maintain defense spending of at least 2% of GDP by 2024.[7][8]
L’Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique norda (en anglais : North Atlantic Treaty Organization) est l'organisation politico-militaire mise en place par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord afin de pouvoir remplir leurs obligations de sécurité et de défense collectives. Elle est le plus souvent désignée par son acronyme OTAN (en anglais NATO) mais aussi fréquemment nommée l’Alliance atlantique, plus rarement l’Alliance euro-atlantique ou l’Alliance transatlantique5, ou parfois, encore plus brièvement, simplement l’Alliance.
Le texte de ce traité, signé le 4 avril 1949, établit le Conseil de l'Atlantique nord (CAN), et lui donne mission de mettre en place l'organisation nécessaire à son application. Le choc provoqué par le déclenchement de la guerre de Corée conduit le CAN à décider fin 1950 la création d'une organisation militaire intégrée permanente, qui constitue encore actuellement la marque distinctive de l'OTAN et lui assure des capacités militaires qu'aucune autre alliance de défense ne possède. Sous le vocable OTAN, l'usage a prévalu d'englober l'alliance juridiquement conclue par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord, et l'organisation civile et militaire mise en place pour en rendre opérants les objectifs. La France toutefois a fait exception en décidant en 1966, tout en restant membre de l'Alliance atlantique, de quitter l'organisation militaire intégrée, dont elle est redevenue membre à part entière en 2009.
L'Alliance voit le jour dans le contexte général des débuts de la guerre froide et plus spécifiquement pendant le blocus de Berlin exercé par les Soviétiques. Elle a pour vocation initiale d'assurer la sécurité de l'Europe occidentale en instaurant un couplage fort avec les États-Unis, seul moyen aux yeux des Européens après la Seconde Guerre mondiale de se prémunir contre toute tentative expansionniste de l'Union soviétique. Selon le mot de son premier secrétaire général, Lord Ismay, le rôle de l'OTAN consiste à « garder les Russes à l'extérieur, les Américains à l'intérieur et les Allemands sous tutelle »b. L'OTAN constitue le noyau dur du bloc de l'Ouest. Entre 1955 et 1991, l'adversaire désigné de l'OTAN est le pacte de Varsovie formé par les Soviétiques à la suite de l'adhésion de la RFA à l'Alliance atlantique et à son réarmement. L'OTAN s'organise donc pour faire face à cette menace par la définition de concepts stratégiques touchant notamment les questions relatives aux armes nucléaires, par la planification coordonnée entre tous ses membres de leurs moyens militaires, et par des commandements intégrés par zone géographique, dont le SHAPE est de loin le plus important.
Depuis la dissolution de l'URSS et la fin de la guerre froide en 1991, l'Alliance atlantique a perduré malgré la disparition de sa principale raison d'être initiale. Elle a procédé à son élargissement à d'anciens pays du bloc de l'Est et d'anciennes républiques de l'Union soviétique. Elle a pris en compte de nouvelles crises et menaces comme les conflits nationalistes dans l'ex-Yougoslavie, l'essor du terrorisme international ou la prolifération des armes de destruction massive, en conséquence de quoi l'OTAN a revu en profondeur son concept stratégique et son organisation civile et militaire à plusieurs reprises. Elle a développé une politique systématique de partenariats en Europe et dans le monde, au titre de laquelle les pays de l'Alliance ont établi depuis 1994 un partenariat pour la paix (PPP) avec la Russie, les pays de sa zone d'influence et avec les pays neutres d'Europe occidentale. L'OTAN a aussi mis en place en 2002 avec l'UE une relation privilégiée, l'Identité européenne de sécurité et de défense (IESD), qui permet à cette dernière de bénéficier de moyens de l'OTAN pour certaines opérations entrant dans le cadre de sa politique de sécurité et de défense commune.
Le siège de l'OTAN, initialement situé à Londres puis à Paris (dans les locaux désormais occupés par l'université Paris-Dauphine - PSL) se trouve depuis 1966 à Haren (Bruxelles), et son principal commandement militaire, le SHAPE, initialement installé à Rocquencourt (France), se trouve aujourd'hui à Maisières (Mons), également en Belgique.
L'Organizzazione del Trattato dell'Atlantico del Nord (in inglese North Atlantic Treaty Organization, in sigla NATO,[3] in francese: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord, in sigla OTAN) è un'organizzazione internazionale per la collaborazione nel settore della difesa.
Il trattato istitutivo della NATO, il Patto Atlantico, fu firmato a Washington il 4 aprile 1949, ovvero nell'immediato secondo dopoguerra, ed entrò in vigore il 24 agosto dello stesso anno. Attualmente, fanno parte della NATO 29 stati del mondo.
La Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte u OTAN (en inglés: North Atlantic Treaty Organization o NATO; en francés: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord u OTAN), también denominada Alianza del Atlántico, Alianza del Atlántico Norte o Alianza Atlántica, es una alianza militar intergubernamental basada en el Tratado del Atlántico Norte o Tratado de Washington firmado el 4 de abril de 1949. La organización constituye un sistema de defensa colectiva, en la cual los Estados miembros acuerdan defender a cualquiera de sus miembros si son atacados por una potencia externa.3
La sede de la OTAN se encuentra en Bruselas, Bélgica, uno de los veintinueve Estados miembros de la organización que se extiende por Norteamérica y Europa. La última incorporación fue Montenegro, en junio de 2017. Además, veintiún países colaboran con la OTAN dentro del programa Asociación para la Paz, con otros quince involucrados en programas de diálogo y nueve como socios globales. En 2017, el gasto militar combinado de los veintinueve países fue el 52 % del gasto militar mundial.45
En sus primeros años, la OTAN no era mucho más que una asociación política. Sin embargo, la guerra de Corea hizo que se planteara una coalición permanente. Entonces se creó una estructura militar bajo la dirección de los comandantes de Estados Unidos. La Guerra Fría llevó a las naciones rivales a crear el Pacto de Varsovia en 1955.
Siempre se han manifestado dudas sobre la alianza europeo-norteamericana ante una invasión soviética, desacuerdos que se plasmaron con la creación por parte de Francia de la fuerza de choque nuclear y con su retirada de la estructura militar de la alianza entre 1966 y 2009.
Después de la caída del Muro de Berlín en 1989, la organización intervino dentro de la guerra de Yugoslavia, lo que se convirtió en la primera intervención conjunta de la OTAN. En lo político la organización ha mejorado sus relaciones con los antiguos miembros del bloque del Este, dando como resultado la incorporación a la OTAN de varios miembros del Pacto de Varsovia.
La única ocasión en que un país miembro invocó el artículo 5 del tratado reivindicando la ayuda en su defensa, fue Estados Unidos en 2001.6 Desde entonces, los miembros colaboraron con los Estados Unidos en la guerra de Afganistán. El artículo 4 del tratado prevé llamar a consulta a los miembros y ha sido convocado cuatro veces, tres de ellas por Turquía, la primera por la guerra de Irak y las dos restantes por ataques recibidos durante la guerra civil siria,7 la cuarta ha sido invocada por Polonia durante la crisis de Crimea de 2014, debido a la movilización de tropas rusas en la frontera polaca con Kaliningrado y las maniobras rusas en el mar Báltico.
НА́ТО, Организа́ция Североатланти́ческого догово́ра, Североатлантический Альянс (англ. North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO; фр. Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique Nord, OTAN) — военно-политический блок, объединяющий большинство стран Европы, США и Канаду. Основан 4 апреля 1949 года в США, с целью защиты Европы от советского влияния[~ 1][~ 2][~ 3][~ 4][~ 5]. Тогда государствами — членами НАТО стали 12 стран: США, Канада, Исландия, Великобритания, Франция, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Норвегия, Дания, Италия и Португалия. Это «трансатлантический форум» для проведения странами-союзниками консультаций по любым вопросам, затрагивающим жизненно важные интересы его членов, включая события, способные поставить под угрозу их безопасность. Одной из декларированных целей НАТО является обеспечение сдерживания любой формы агрессии в отношении территории любого государства — члена НАТО или защиты от неё.
В настоящее время членами НАТО являются 29 стран. Военные расходы всех членов НАТО в совокупности составляют более 70 процентов от общемирового объёма[1].


 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Chile
Chile
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].
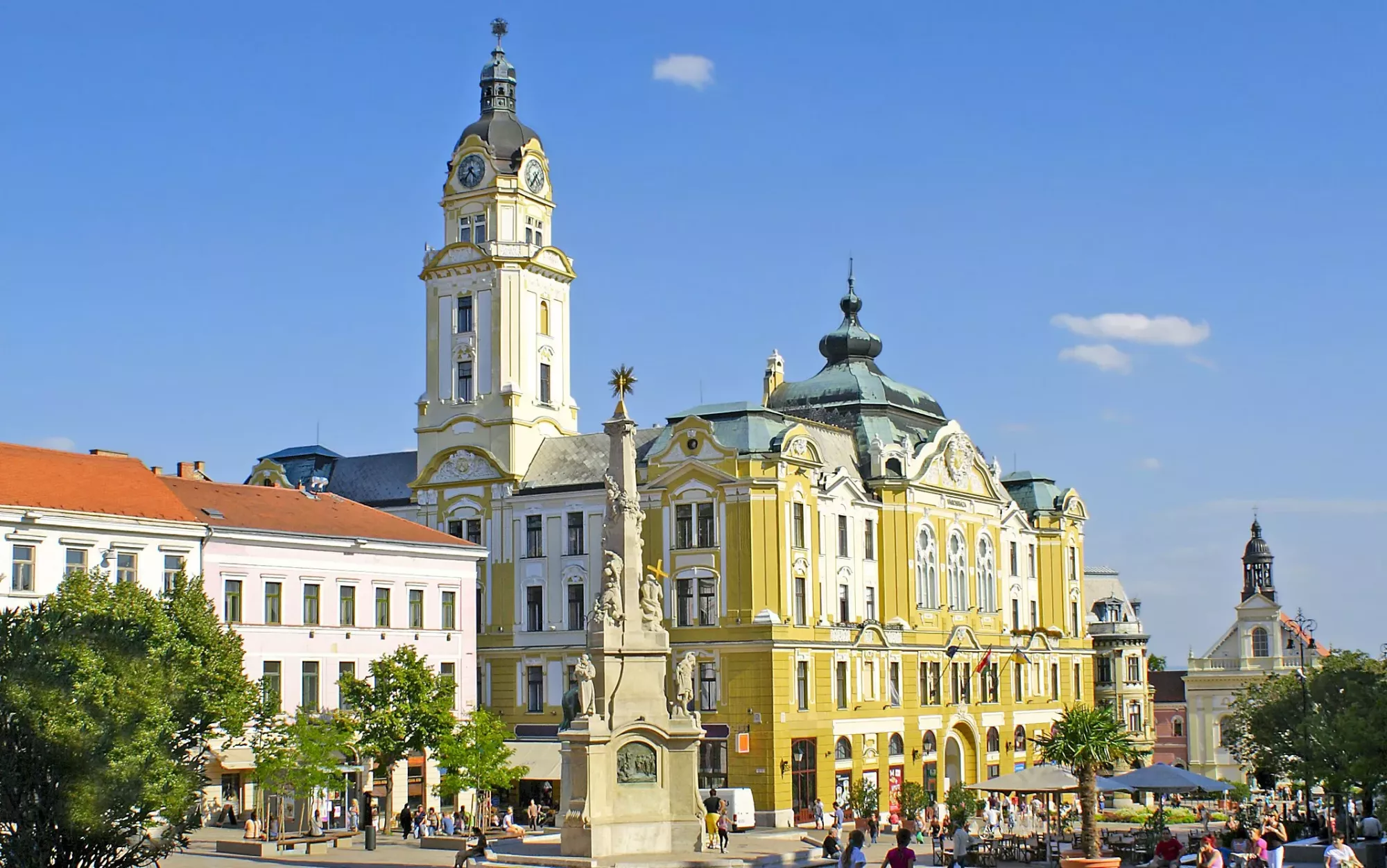






位于多瑙河和德拉瓦河之间的佩奇(Pécs)是匈牙利最具吸引力的城市之一。这里气候宜人,历史悠久,拥有华丽的博物馆和全国最好的土耳其遗迹。佩奇还以音乐、歌剧和芭蕾而闻名。
两千年前,罗马人在潘诺尼亚省兴建了一座重要城市,取名绍比纳,这就是今天的佩奇。1009年,圣伊斯特万国王在这里设立了教会;1367年,安茹王朝的拉约什一世国王在这里创建了匈牙利的第一所大学。除布达外,这里是当年文艺复兴运动的最重要中心。
1543年,土耳其人迅速占领了这座城市和主教城堡。直到1686年撤出前,这里说得上的建筑也就是土耳其人建的两座清真寺和庙宇。
1780年前佩奇一直归主教管辖。在这段和平的几十年间,教会的中心得到恢复,市政得以重建,市中心就是现在的塞切尼广场。广场中央是卡西姆帕夏在 1550年以前建的清真寺,也就是现在教区教堂的核心。它不仅在总体上,而且在许多细节上也都保留了土耳其年代的原貌。 (Quelle:http://eur.bytravel.cn)
佩奇[3](匈牙利语:Pécs,IPA:[peːʧ];德语:Fünfkirchen,音译为芬夫基兴[4],意思是“五座教堂”)是匈牙利第五大城市、巴兰尼亚州首府。面积162.61平方公里,2016年人口为145,347人。
与埃森与伊斯坦布尔并列为2010年欧洲文化之都。其座右铭为“无边界的城市”。佩奇的早期基督教陵墓为世界文化遗产。
佩奇拥有大量的煤炭及铀资源,并为著名的纳伊瓷器瓷器生产中心。教育方面,佩奇大学始建于1367年,为匈牙利第一所大学,由路易一世创立。
1921年8月14日,在此宣布成立巴兰尼亚—巴亚塞尔维亚—匈牙利共和国。
Pécs [ˈpeːʧ], deutsch Fünfkirchen (lateinisch Quinque Ecclesiae, slowakisch Päťkostolie, kroatisch Pečuh, serbisch-kyrillisch Печуј Pečuj), ist mit 138.420 Einwohner (1. Jan. 2022) die fünftgrößte Stadt Ungarns und Sitz des Komitats Baranya und hat selber Komitatsrecht. Sie liegt nahe der kroatischen Grenze.
Die Stadt ist Bischofssitz und Sitz einer Universität sowie Zentrum der Donauschwaben und Heimat von neun ethnischen Minderheiten mit eigenen Selbstverwaltungen.
Pécs liegt am Fuße des Mecsek-Gebirges und die zahlreichen Baudenkmäler verleihen dem Ort eine mediterrane Atmosphäre. Am 19. Oktober 2005 gewann die Stadt die nationale Vorausscheidung für den Titel „Kulturhauptstadt Europas 2010“ und richtete das Jahr unter dem Motto Pécs2010 Kulturhauptstadt Europas aus.
Die Universität Pécs bietet das Studium der Humanmedizin und der Zahnmedizin in deutscher und englischer Sprache[2] sowie ein englischsprachiges Studium der Pharmazie[3]. Ein englischsprachiges Studium kann zusätzlich an der Faculty of musical and visual arts absolviert werden.




 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 States of Europe
States of Europe
 Hungary
Hungary

 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Review
Review
 International cities
International cities
 Music
Music
 European Union
European Union
