
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Grenada
Grenada
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Caribbean Community and Common Market,CARICOM
Caribbean Community and Common Market,CARICOM
 Andrew Holness
Andrew Holness
 Dominica
Dominica
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Montserrat
Montserrat
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 Suriname
Suriname
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Australia
Australia
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Dominica
Dominica
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 India
India
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nauru
Nauru
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Uganda
Uganda
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 Cyprus
Cyprus

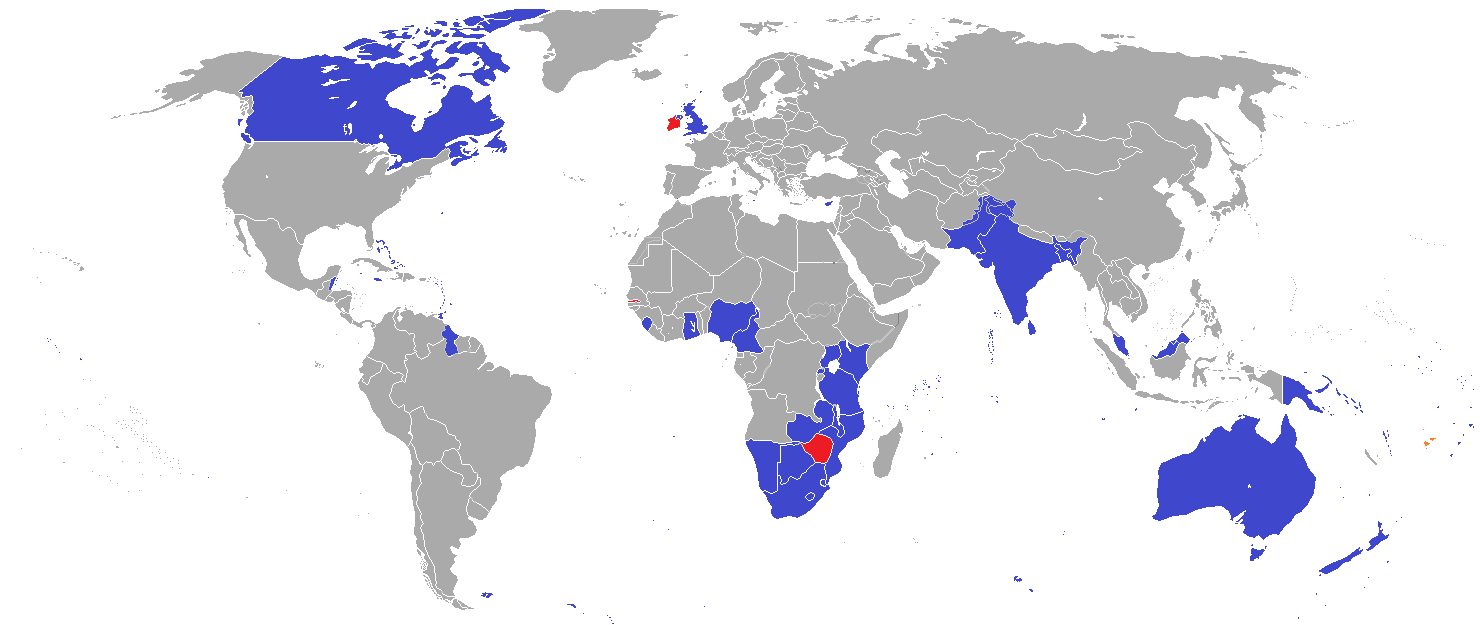
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Barbados
Barbados
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago




 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Mexico
Mexico
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Panama
Panama
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 Suriname
Suriname
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Venezuela
Venezuela




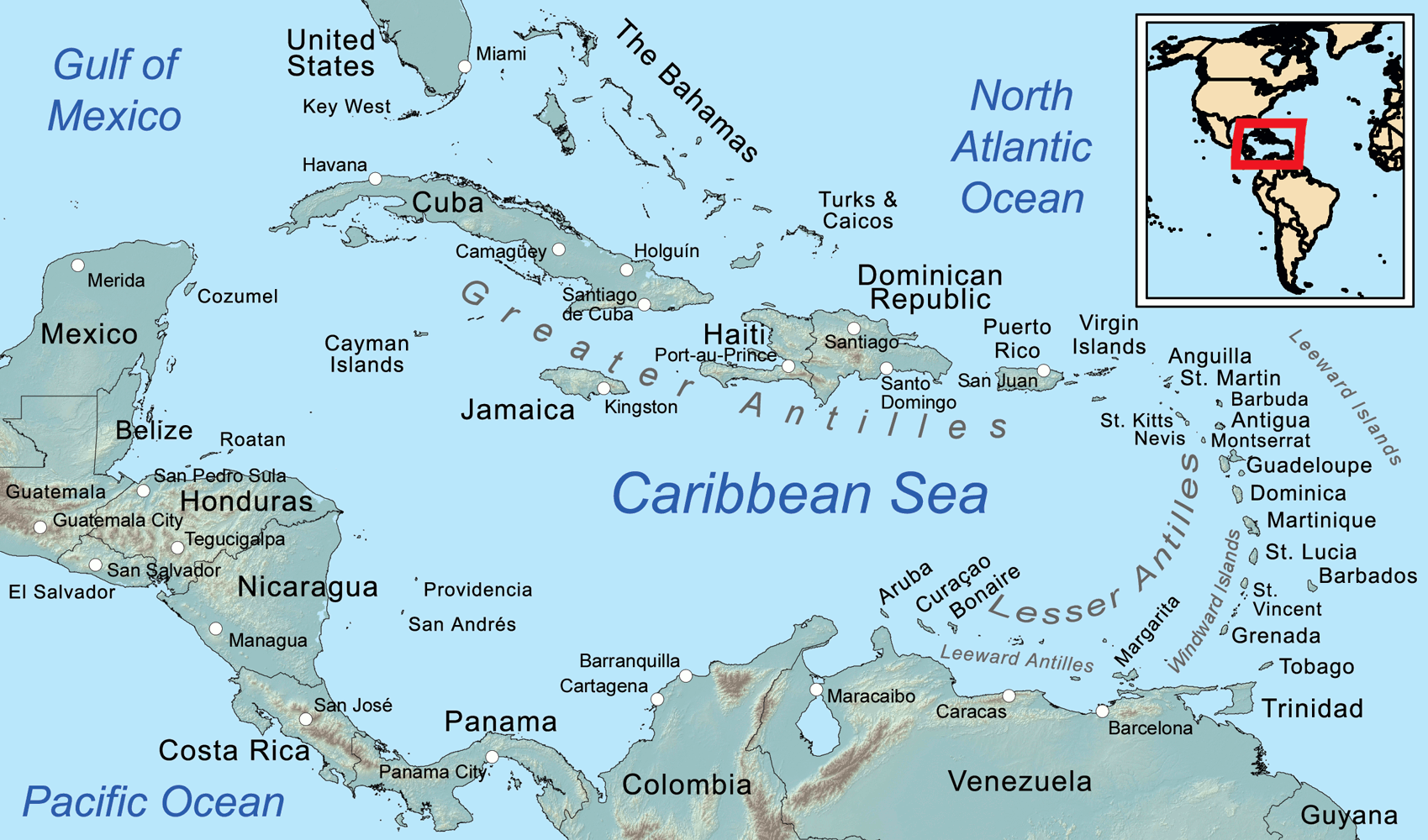
Die Karibik ist eine Region im westlichen, tropischen Teil des Atlantischen Ozeans nördlich des Äquators. Als Teil des mittelamerikanischen Subkontinents besteht sie aus den am und im Karibischen Meer gelegenen Inseln und Inselgruppen und dem Meeresgebiet zwischen ihnen. Am Westende reicht die Karibik in den Golf von Mexiko.
Die Karibik ist nach dem Volk der Kariben benannt, das die spanischen Eroberer auf den Kleinen Antillen (lat. ante ilium, „vorgelagerte Inseln“) vorgefunden haben. Sie wurde bzw. wird auch Westindien genannt, da man sich bei ihrer Entdeckung auf direktem Seeweg nach Indien glaubte.
カリブ海地域(カリブかいちいき、英語: The Caribbean、スペイン語: Caribe、オランダ語: ![]() Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
Caraïben、カリブ・ヒンドゥスターニー語: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); フランス語: Caraïbe ないし Antilles)は、カリブ海と、その海域の島々(カリブ海域内の島々や、カリブ海と北大西洋の境界を成す島々)、周辺海域から構成されている。カリブ海地域はメキシコ湾と北アメリカ大陸の南東、中央アメリカの東、南アメリカ大陸の北に位置している。日本語ではカリブ地域、あるいはこの地域にある国を総称してカリブ諸国とも呼ばれる。
この地方の大部分はカリブプレート上にあり、域内には700以上の島嶼、岩礁、キー(サンゴ礁上の低い島)などがある(カリブ海地域の島の一覧)。島々の多くは島弧を形成して、カリブ海のと東渕と北縁となっている[3]。カリブ海地域の島々は、北側の大アンティル諸島と、南および東側の小アンティル諸島(リーワード・アンティル諸島を含む) から成り、大アンティル諸島やカリブ海より北に位置するバハマ諸島(バハマからタークス・カイコス諸島に至る範囲)をも含んだ、より広い範囲を指す表現としての西インド諸島の一部となっている。広い意味では、大陸の一部であるベリーズ、ベネズエラ、ガイアナ、スリナム、フランス領ギアナもカリブ海地域に含める場合がある。
地政学的には、カリブ海地域の島々は北アメリカの下位区分 (subregion) と見なされることが多く[4][5][6][7][8]、合わせて30の主権国家、海外県、属領から成っている。1954年12月15日から2010年10月10日まで、5つの統治体から成るオランダ領アンティルと称されたオランダ属領があった[9]。また、1958年1月3日から1962年5月31日まで、イギリス属領であった英語圏の領域が構成した、西インド連邦と称された短命な自治国が存在していた。クリケット西インド諸島代表は、その後も、これら諸国の多くを代表して編成され続けている。
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/;[4] Spanish: El Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Haitian Creole: Karayib; Dutch: De Caraïben; Papiamento: Karibe) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea[5] and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean)[6] and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea:[7] the Greater Antilles on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), which are sometimes considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. On the mainland, Belize, Nicaragua, the Caribbean region of Colombia, Cozumel, the Yucatán Peninsula, Margarita Island, and The Guianas (Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Guayana Region in Venezuela, and Amapá in Brazil) are often included due to their political and cultural ties with the region.[8]
A mostly tropical geography, the climates are greatly shaped by sea temperatures and precipitation, with the hurricane season regularly leading to natural disasters. Because of its tropical climate and low-lying island geography, the Caribbean is vulnerable to a number of climate change effects, including increased storm intensity, saltwater intrusion, sea-level rise and coastal erosion, and precipitation variability.[9] These weather changes will greatly change the economies of the islands, and especially the major industries of agricultural and tourism.[9]
The Caribbean was occupied by indigenous people since at least 3600 BC. When European colonization followed the arrival of Columbus, the population was quickly decimated by brutal labor practices, enslavement and disease and on many islands, Europeans supplanted the native populations with enslaved Africans. Following the independence of Haiti from France in the early 19th century and the decline of slavery in the 19th century, island nations in the Caribbean gradually gained independence, with a wave of new states during the 1950s and 60s. Because of the proximity to the United States, there is also a long history of United States intervention in the region.
The islands of the Caribbean (the West Indies) are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or then left as a subregion of their own[10][11] and are organized into 30 territories including sovereign states, overseas departments, and dependencies. From December 15, 1954, to October 10, 2010, there was a country known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five states, all of which were Dutch dependencies.[12] From January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies.
Les Caraïbes, (également nommées la Caraïbe, l'espace caraïbe, ou encore l'espace des Caraïbes) sont une région des Amériques qui comprend la mer des Caraïbes, ses îles (certaines entourées par la mer des Caraïbes et d'autres bordant à la fois la mer des Caraïbes et l'océan Atlantique Nord) et les côtes environnantes. La région est située au sud-est du golfe du Mexique et du continent nord-américain, à l'est de l'Amérique centrale et au nord de l'Amérique du Sud.
Située en grande partie sur la plaque des Caraïbes, la région compte plus de 700 îles, îlots, récifs et cayes. Les arcs insulaires délimitent les bords est et nord de la mer des Caraïbes : les Grandes Antilles au nord et les Petites Antilles au sud et à l'est (qui comprennent les îles sous le vent). Elles forment les Antilles avec l'archipel voisin de Lucayan (les Bahamas et les Îles Turques-et-Caïques), qui sont parfois considérées comme faisant partie des Caraïbes bien qu'elles ne bordent pas la mer des Caraïbes. Sur le continent, le Belize, le Nicaragua, la région caribéenne de Colombie, Cozumel, la péninsule du Yucatán, l'île de Margarita et les Guyanes (Guyane, Suriname, Guyane française, région de Guayana au Venezuela et Amapá au Brésil) sont souvent inclus en raison de leurs liens politiques et culturels avec la région.
La géographie est essentiellement tropicale et le climat est fortement influencé par la température de la mer et les précipitations, la saison des ouragans entraînant régulièrement des catastrophes naturelles. En raison de leur climat tropical et de leur géographie insulaire de basse altitude, les Caraïbes sont vulnérables à un certain nombre d'effets du changement climatique, notamment l'augmentation de l'intensité des tempêtes, l'intrusion d'eau salée, l'élévation du niveau de la mer et l'érosion côtière, ainsi que la variabilité des précipitations.
Les Caraïbes ont été occupées par des peuples indigènes depuis au moins 3600 avant J.-C. Lorsque la colonisation européenne a suivi l'arrivée de Christophe Colomb, la population a été rapidement décimée par des pratiques de travail brutales, l'esclavage et la maladie et sur de nombreuses îles, les Européens ont supplanté les populations indigènes par des Africains réduits en esclavage. Après l'indépendance d'Haïti par rapport à la France au début du XIXe siècle et le déclin de l'esclavage, les nations insulaires ont progressivement acquis leur indépendance, avec une vague de nouveaux États au cours des années 1950 et 1960. En raison de la proximité des États-Unis, il existe également une longue histoire d'intervention américaine dans la région.
Les Antilles sont souvent considérées comme une sous-région de l'Amérique du Nord, bien qu'elles soient parfois incluses dans l'Amérique centrale ou alors laissées comme une sous-région à part entière et sont organisées en 30 territoires comprenant des États souverains, des Département et région d'outre-mer et des dépendances. Du 15 décembre 1954 au 10 octobre 2010, il y avait un pays appelé Antilles néerlandaises composé de cinq États, tous dépendants des Pays-Bas. Du 3 janvier 1958 au 31 mai 1962, il y a également eu une union politique de courte durée, la Fédération des Indes occidentales, composée de dix territoires caribéens anglophones, tous dépendants des Britanniques à l'époque.
I Caraibi sono una vasta regione geografica delle Americhe che comprende tutti i paesi bagnati dal Mare Caraibico, cioè tutte le isole delle Antille e i litorali di alcuni paesi continentali del centro e sud America che si affacciano su di questo mare. L'area caraibica è costituita dalle numerose isole che separano il Golfo del Messico dal mar dei Caraibi e quest'ultimo dall'Oceano Atlantico.
El Caribe es una región conformada por el mar Caribe, sus islas y las costas que rodean a este mar. La región se localiza al sureste de América del Norte, al este de América Central, al oeste de América Insular y al norte de América del Sur.
Анти́льские острова́ (также Карибы или Карибские острова) — острова в Карибском море и Мексиканском заливе, расположенные между Северной Америкой и Южной Америкой. Вместе взятые, образуют площадь в 228 662 км² с населением примерно 42 млн чел. (на начало XXI века).
Впервые название «Антильские» встречается в 1493 году у Петра Мартира д’Ангиера, современника Христофора Колумба, придворного Фердинанда Арагонского и Изабеллы Кастильской. Предположительно, были названы по полумифическому острову или архипелагу Антилия, изображавшемуся на средневековых картах.
Подразделяются на две главные группы: Большие Антильские и Малые Антильские острова:
К первым относятся 4 острова: Куба, Гаити, Ямайка и Пуэрто-Рико; из них первые два и последний (самый малый) образуют почти прямую линию, направленную западным углом Кубы к полуострову Юкатан.[1]
Острова материкового и вулканического происхождения. Большая часть их поверхности гориста; равнинные участки главным образом на Кубе и на Юго-Восточном Гаити, а также на Виргинских и Подветренных островах. Горные сооружения Больших Антильских островов высотой до 3098 м (на острове Гаити) являются продолжением структур Центральной Америки. Климат тропический, пассатный, жаркий, преимущественно летне-влажный. Осадков 1200—2000 мм в год. Характерны сильные ураганы в конце лета. Естественная растительность — саванны, летне-зеленые и листопадно-вечнозелёные тропические леса и кустарники — сохранилась мало. На наветренных склонах гор уцелели вечнозелёные леса.[2]

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Belarus
Belarus
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Fidschi
Fidschi
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Georgia
Georgia
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Guyana
Guyana
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Libanon
Libanon
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Peru
Peru
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Silk road
Silk road
 Serbia
Serbia
 Serbia
Serbia
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Syria
Syria
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
 Cyprus
Cyprus

丝绸之路(德语:Seidenstraße;英语:Silk Road),常简称为丝路,此词最早来自于德意志帝国地理学家费迪南·冯·李希霍芬男爵于1877年出版的一套五卷本的地图集。[1]
丝绸之路通常是指欧亚北部的商路,与南方的茶马古道形成对比,西汉时张骞以长安为起点,经关中平原、河西走廊、塔里木盆地,到锡尔河与乌浒河之间的中亚河中地区、大伊朗,并联结地中海各国的陆上通道。这条道路也被称为“陆路丝绸之路”,以区别日后另外两条冠以“丝绸之路”名称的交通路线。因为由这条路西运的货物中以丝绸制品的影响最大,故得此名。其基本走向定于两汉时期,包括南道、中道、北道三条路线。但实际上,丝绸之路并非是一条 “路”,而是一个穿越山川沙漠且没有标识的道路网络,并且丝绸也只是货物中的一种。[1]:5
广义的丝绸之路指从上古开始陆续形成的,遍及欧亚大陆甚至包括北非和东非在内的长途商业贸易和文化交流线路的总称。除了上述的路线之外,还包括约于前5世纪形成的草原丝绸之路、中古初年形成,在宋代发挥巨大作用的海上丝绸之路和与西北丝绸之路同时出现,在宋初取代西北丝绸之路成为路上交流通道的南方丝绸之路。
虽然丝绸之路是沿线各君主制国家共同促进经贸发展的产物,但很多人认为,西汉的张骞在前138—前126年和前119年曾两次出使西域,开辟了中外交流的新纪元,并成功将东西方之间最后的珠帘掀开。司马迁在史记中说:“于是西北国始通于汉矣。然张骞凿空,其后使往者皆称博望侯,以为质与国外,外国由此信之”,称赞其开通西域的作用。从此,这条路线被作为“国道”踩了出来,各国使者、商人、传教士等沿着张骞开通的道路,来往络绎不绝。上至王公贵族,下至乞丐狱犯,都在这条路上留下了自己的足迹。这条东西通路,将中原、西域与大伊朗、累范特、阿拉伯紧密联系在一起。经过几个世纪的不断努力,丝绸之路向西伸展到了地中海。广义上丝路的东段已经到达了朝鲜、日本,西段至法国、荷兰。通过海路还可达意大利、埃及,成为亚洲和欧洲、非洲各国经济文化交流的友谊之路。
丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路(英语:The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road[1]),简称一带一路(英语:The Belt and Road Initiative,缩写B&R)[1],是中华人民共和国政府于2013年倡议[2]并主导的跨国经济带[3]。
一带一路范围涵盖历史上丝绸之路和海上丝绸之路行经的中国、中亚、北亚和西亚、印度洋沿岸、地中海沿岸的国家和地区。中国政府指出,“一带一路”倡议坚持共商、共建、共享的原则,努力实现沿线区域基础设施更加完善,更加安全高效,以形成更高水平的陆海空交流网络。同时使投资贸易的便利化水平更有效的提升,建立高品质、高标准的自由贸易区域网。以使沿线各国经济联系更加紧密,政治互信更加的深入,人文交流更加的广泛[4]。
Als Seidenstraße (chinesisch 絲綢之路 / 丝绸之路, Pinyin Sīchóu zhī Lù ‚die Route / Straße der Seide‘; mongolisch ᠲᠣᠷᠭᠠᠨ ᠵᠠᠮ Tôrgan Jam; kurz: 絲路 / 丝路, Sīlù) bezeichnet man ein altes Netz von Karawanenstraßen, dessen Hauptroute den Mittelmeerraum auf dem Landweg über Zentralasien mit Ostasien verband. Die Bezeichnung geht auf den im 19. Jahrhundert lebenden deutschen Geografen Ferdinand von Richthofen zurück, der den Begriff 1877 erstmals verwendet hat.
Auf der antiken Seidenstraße wurde in westliche Richtung hauptsächlich Seide, gen Osten vor allem Wolle, Gold und Silber gehandelt.[1] Nicht nur Kaufleute, Gelehrte und Armeen nutzten ihr Netz, sondern auch Ideen, Religionen und ganze Kulturkreise diffundierten und migrierten auf den Routen von Ost nach West und umgekehrt: hierüber kamen z. B. der Nestorianismus (aus dem spätantiken Römischen Reich) und der Buddhismus (von Indien) nach China.[1]
Die 6.400 Kilometer[1] lange Route begann in Xi’an und folgte dem Verlauf der Chinesischen Mauer in Richtung Nordwesten, passierte die Taklamakan-Wüste, überwand das Pamirgebirge und führte über Afghanistan in die Levante; von hier wurden die Handelsgüter dann über das Mittelmeer verschifft. Nur wenige Kaufleute reisten auf der gesamten Route, die Waren wurden eher gestaffelt über Zwischenhändler transportiert.
Ihre größte Bedeutung erreichte das Handels- und Wegenetz zwischen 115 v. Chr. und dem 13. Jahrhundert n. Chr. Mit dem allmählichen Verlust römischen Territoriums in Asien und dem Aufstieg Arabiens in der Levante wurde die Seidenstraße zunehmend unsicher und kaum noch bereist. Im 13. und 14. Jahrhundert wurde die Strecke unter den Mongolen wiederbelebt, u. a. benutzte sie zu der Zeit der Venezianer Marco Polo um nach Cathay (China) zu reisen. Nach weit verbreiteter Ansicht war die Route einer der Hauptwege, über die Mitte des 14. Jahrhunderts Pestbakterien von Asien nach Europa gelangten und dort den Schwarzen Tod verursachten.[1]
Teile der Seidenstraße sind zwischen Pakistan und dem autonomen Gebiet Xinjiang in China heute noch als asphaltierte Fernstraße vorhanden (-> Karakorum Highway). Die alte Straße inspirierte die Vereinten Nationen zu einem Plan für eine transasiatische Fernstraße. Von der UN-Wirtschafts- und Sozialkommission für Asien und den Pazifik (UNESCAP) wird die Einrichtung einer durchgehenden Eisenbahnverbindung entlang der Route vorangetrieben, der Trans-Asian Railway.[1]
Die "Neue Seidenstraße", das "One Belt, One Road"-Projekt der Volksrepublik China unter ihrem Staatspräsident Xi Jinping umfasst landgestützte (Silk Road Economic Belt) und maritime (Maritime Silk Road) Infrastruktur- und Handelsrouten, Wirtschaftskorridore und Transportlinien von China über Zentralasien und Russland bzw. über Afrika nach Europa, dazu werden verschiedenste Einrichtungen (z. B. Tiefsee- oder Containerterminals) und Verbindungen (wie Bahnlinien oder Gaspipelines) entwickelt bzw. ausgebaut. Bestehende Korridore sind einerseits Landverbindungen über die Türkei oder Russland und andererseits Anknüpfungen zum Hafen von Shanghai, über Hongkong und Singapur nach Indien und Ostafrika, Dubai, den Suez-Kanal, den griechischen Hafen Piräus nach Venedig.[2]
Das Projekt One Belt, One Road (OBOR, chinesisch 一帶一路 / 一带一路, Pinyin Yídài Yílù ‚Ein Band, Eine Straße‘, neuerdings Belt and Road, da „One“ zu negativ besetzt war) bündelt seit 2013 die Interessen und Ziele der Volksrepublik China unter Staatspräsident Xi Jinping zum Auf- und Ausbau interkontinentaler Handels- und Infrastruktur-Netze zwischen der Volksrepublik und zusammen 64 weiteren Ländern Afrikas, Asiens und Europas. Die Initiative bzw. das Gesamtprojekt betrifft u. A. rund 62 % der Weltbevölkerung und ca. 35 % der Weltwirtschaft.[1][2]
Umgangssprachlich wird das Vorhaben auch „Belt and Road Initiative“ (B&R, BRI) bzw. ebenso wie das Projekt Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA) auch „Neue Seidenstraße“ (新絲綢之路 / 新丝绸之路, Xīn Sīchóuzhīlù) genannt. Es bezieht sich auf den geografischen Raum des historischen, bereits in der Antike genutzten internationalen Handelskorridors „Seidenstraße“; zusammengefasst handelt es sich um zwei Bereiche, einen nördlich gelegenen zu Land mit sechs Bereichen unter dem Titel Silk Road Economic Belt und einen südlich gelegenen Seeweg namens Maritime Silk Road.
シルクロード(絹の道、英語: Silk Road, ドイツ語: Seidenstraße, 繁体字:絲綢之路, 簡体字:丝绸之路)は、中国と地中海世界の間の歴史的な交易路を指す呼称である。絹が中国側の最も重要な交易品であったことから名付けられた。その一部は2014年に初めて「シルクロード:長安-天山回廊の交易路網」としてユネスコの世界遺産に登録された。
「シルクロード」という名称は、19世紀にドイツの地理学者リヒトホーフェンが、その著書『China(支那)』(1巻、1877年)においてザイデンシュトラーセン(ドイツ語:Seidenstraßen;「絹の道」の複数形)として使用したのが最初であるが、リヒトホーフェンは古来中国で「西域」と呼ばれていた東トルキスタン(現在の中国新疆ウイグル自治区)を東西に横断する交易路、いわゆる「オアシスの道(オアシスロード)」を経由するルートを指してシルクロードと呼んだのである。リヒトホーフェンの弟子で、1900年に楼蘭の遺跡を発見したスウェーデンの地理学者ヘディンが、自らの中央アジア旅行記の書名の一つとして用い、これが1938年に『The Silk Road』の題名で英訳されて広く知られるようになった。
シルクロードの中国側起点は長安(陝西省西安市)、欧州側起点はシリアのアンティオキアとする説があるが、中国側は洛陽、欧州側はローマと見る説などもある。日本がシルクロードの東端だったとするような考え方もあり、特定の国家や組織が経営していたわけではないのであるから、そもそもどこが起点などと明確に定められる性質のものではない。
現在の日本でこの言葉が使われるときは、特にローマ帝国と秦・漢帝国、あるいは大唐帝国の時代の東西交易が念頭に置かれることが多いが、広くは近代(大航海時代)以前のユーラシア世界の全域にわたって行われた国際交易を指し、南北の交易路や海上の交易路をも含める。つまり、北方の「草原の道(ステップロード)」から南方の「海の道(シーロード)」までを含めて「シルクロード」と呼ばれるようになっているわけである。
シルクロード経済ベルトと21世紀海洋シルクロード(シルクロードけいざいベルトと21せいきかいようシルクロード、拼音: Sīchóu zhī lù jīngjìdài hé èrshíyī shìjì hǎishàng sīchóu zhī lù、英語: The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road)とは、2014年11月10日に中華人民共和国北京市で開催されたアジア太平洋経済協力首脳会議で、習近平総書記が提唱した経済圏構想である。
略称は一帯一路(いったいいちろ、拼音: Yídài yílù、英語: The Belt and Road Initiative, BRI; One Belt, One Road Initiative, OBOR)。
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West. It was central to cultural interaction between the regions for many centuries.[1][2][3] The Silk Road refers to both the terrestrial and the maritime routes connecting East Asia and Southeast Asia with East Africa, West Asia and Southern Europe.
The Silk Road derives its name from the lucrative trade in silk carried out along its length, beginning in the Han dynasty (207 BCE–220 CE). The Han dynasty expanded the Central Asian section of the trade routes around 114 BCE through the missions and explorations of the Chinese imperial envoy Zhang Qian.[4] The Chinese took great interest in the safety of their trade products and extended the Great Wall of China to ensure the protection of the trade route.[5]
Trade on the Road played a significant role in the development of the civilizations of China, Korea,[6] Japan,[2] India, Iran, Afghanistan, Europe, the Horn of Africa and Arabia, opening long-distance political and economic relations between the civilizations.[7] Though silk was the major trade item exported from China, many other goods were traded, as well as religions, syncretic philosophies, sciences, and technologies. Diseases, most notably plague, also spread along the Silk Road.[8] In addition to economic trade, the Silk Road was a route for cultural trade among the civilizations along its network.[9]
Traders in ancient history included the Bactrians, Sogdians, Syrians, Jews, Arabs, Iranians, Turkmens, Chinese, Malays, Indians, Somalis, Greeks, Romans, Georgians, Armenians, and Azerbaijanis.[10]
In June 2014, UNESCO designated the Chang'an-Tianshan corridor of the Silk Road as a World Heritage Site. The Indian portion is on the tentative site list.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) or the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road is a development strategy adopted by the Chinese government. The 'belt' refers to the overland interconnecting infrastructure corridors; the Silk Road Economic Belt (SREB) component. The 'road' refers to the sea route corridors; the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (MSR) component.[2] The initiative focuses on connectivity and cooperation between Eurasian countries, primarily the People's Republic of China (PRC).
Until 2016 the initiative was known in English as the One Belt and One Road Initiative (OBOR) but the Chinese came to consider the emphasis on the word "one" as misleading.[3]
The Chinese government calls the initiative "a bid to enhance regional connectivity and embrace a brighter future".[4] Independent observers, however, see it as a push for Chinese dominance in global affairs with a China-centered trading network.[5][6]
La route de la soie est un réseau ancien de routes commerciales entre l'Asie et l'Europe, reliant la ville de Chang'an (actuelle Xi'an) en Chine à la ville d'Antioche, en Syrie médiévale (aujourd'hui en Turquie). Elle tire son nom de la plus précieuse marchandise qui y transitait : la soie.
La route de la soie était un faisceau de pistes par lesquelles transitaient de nombreuses marchandises, et qui monopolisa les échanges Est-Ouest pendant des siècles. Les plus anciennes traces connues de la route de la soie, comme voie de communication avec les populations de l'Ouest, remontent à « 2000 avant notre ère au moins ». Les Chinois en fixent l'ouverture au voyage de Zhang Qian en 138-1261. Mais la route de la soie s'est développée surtout sous la dynastie Han (221 av. J.-C. - 220 ap. J.-C.), en particulier Han Wudi.
Puis sous la dynastie Tang (618-907). À partir du XVe siècle, la route de la soie est progressivement abandonnée, l'instabilité des guerres turco-byzantines, puis la chute de Constantinople poussent en effet les Occidentaux à chercher une nouvelle route maritime vers les Indes. L'abandon de la route de la soie correspond ainsi au début de la période des « Grandes découvertes » durant laquelle les techniques de transport maritime deviennent de plus en plus performantes. Du côté chinois, les empereurs Ming Yongle, puis Ming Xuanzong chargent, à la même époque, l'amiral Zheng He d'expéditions maritimes similaires.
La nouvelle route de la soie ou la Ceinture et la Route2 (stratégie aussi appelée OBOR en anglais pour One Belt, One Road3) est à la fois un ensemble de liaisons maritimes et de voies ferroviaires entre la Chine et l'Europe passant par le Kazakhstan, la Russie, la Biélorussie, la Pologne, l'Allemagne, la France et le Royaume-Uni.
Le nouveau nom est Initiative route et ceinture (Belt and Road Initiative, B&R selon l’acronyme anglais) afin de marquer le fait que ce projet ne se limite pas à une seule route4.
Outre l'amélioration de la connectivité ferroviaire, il s'agit aussi d'une stratégie de développement pour promouvoir la coopération entre les pays sur une vaste bande s'étendant à travers l'Eurasie et pour renforcer la position de la Chine sur le plan mondial, par exemple en préservant la connexion de la Chine avec le reste du monde en cas de tensions militaires sur ses zones côtières5.
La Nouvelle route de la soie a été dévoilée à l'automne 2013 par le gouvernement chinois en tant que pendant terrestre du collier de perles6 ; elle est l'une des priorités de la diplomatie chinoise, sous la présidence de Xi Jinping7.
Selon CNN, ce projet englobera 68 pays représentant 4,4 milliards d’habitants et 62 % du PIB mondial8.
Per via della seta (in cinese: 絲綢之路T, 丝绸之路S, sī chóu zhī lùP; persiano: راه ابریشم, Râh-e Abrisham) s'intende il reticolo, che si sviluppava per circa 8.000 km, costituito da itinerari terrestri, marittimi e fluviali lungo i quali nell'antichità si erano snodati i commerci tra l'impero cinese e quello romano.
Le vie carovaniere attraversavano l'Asia centrale e il Medio Oriente, collegando Chang'an (oggi Xi'an), in Cina, all'Asia Minore e al Mediterraneo attraverso il Medio Oriente e il Vicino Oriente. Le diramazioni si estendevano poi a est alla Corea e al Giappone e, a Sud, all'India. Il nome apparve per la prima volta nel 1877, quando il geografo tedesco Ferdinand von Richthofen (1833-1905) pubblicò l'opera Tagebucher aus China. Nell'Introduzione von Richthofen nomina la Seidenstraße, la «via della seta».
La destinazione finale della seta che su di essa viaggiava (non certo da sola ma insieme a tante altre merci preziose) era Roma, dove per altro non si sapeva con precisione quale ne fosse l'origine (se animale o vegetale) e da dove provenisse. Altre merci altrettanto preziose viaggiavano in senso inverso, e insieme alle merci viaggiavano grandi idee e religioni (concetti fondamentali di matematica, geometria, astronomia) in entrambi i sensi, manicheismo, e nestorianesimo verso oriente. Sulla via della seta compì un complesso giro quasi in tondo anche il buddhismo, dall'India all'Asia Centrale alla Cina e infine al Tibet (il tutto per trovare itinerari che permettessero di evitare le quasi invalicabili montagne dell'Himalaya).
Questi scambi commerciali e culturali furono determinanti per lo sviluppo e il fiorire delle antiche civiltà dell'Egitto, della Cina, dell'India e di Roma, ma furono di grande importanza anche nel gettare le basi del mondo medievale e moderno.
La Nuova via della seta è un'iniziativa strategica della Cina per il miglioramento dei collegamenti e della cooperazione tra paesi nell'Eurasia. Comprende le direttrici terrestri della "zona economica della via della seta" e la "via della seta marittima del XXI secolo" (in cinese: 丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路S, Sīchóu zhī lù jīngjìdài hé èrshíyī shìjì hǎishàng sīchóu zhī lùP), ed è conosciuta anche come "iniziativa della zona e della via" (一带一路S, tradotta comunemente in inglese con Belt and Road Initiative, BRI) o "una cintura, una via" e col corrispondente iniziale acronimo inglese OBOR (One belt, one road), poi modificato in BRI per sottolineare l'estensione del progetto non esclusivo solo della Cina[1], nonostante la prospettiva sinocentrica, com'è stato illustrato in un recente studio italiano[2].
Partendo dallo sviluppo delle infrastrutture di trasporto e logistica, la strategia mira a promuovere il ruolo della Cina nelle relazioni globali, favorendo i flussi di investimenti internazionali e gli sbocchi commerciali per le produzioni cinesi. L'iniziativa di un piano organico per i collegamenti terrestri (la cintura) è stata annunciata pubblicamente dal presidente cinese Xi Jinping a settembre del 2013, e la via marittima ad ottobre dello stesso anno, contestualmente alla proposta di costituire la Banca asiatica d'investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), dotata di un capitale di 100 miliardi di dollari USA, di cui la Cina stessa sarebbe il principale socio, con un impegno pari a 29,8 miliardi e gli altri paesi asiatici (tra cui l'India e la Russia) e dell'Oceania avrebbero altri 45 miliardi (l'Italia si è impegnata a sottoscrivere una quota di 2,5 miliardi).
La Ruta de la Seda fue una red de rutas comerciales organizadas a partir del negocio de la seda china desde el siglo I a. C., que se extendía por todo el continente asiático, conectando a China con Mongolia, el subcontinente indio, Persia, Arabia, Siria, Turquía, Europa y África. Sus diversas rutas comenzaban en la ciudad de Chang'an (actualmente Xi'an) en China, pasando entre otras por Karakórum (Mongolia), el Paso de Khunjerab (China/Pakistán), Susa (Persia), el Valle de Fergana (Tayikistán), Samarcanda (Uzbekistán), Taxila (Pakistán), Antioquía en Siria, Alejandría (Egipto), Kazán (Rusia) y Constantinopla (actualmente Estambul, Turquía) a las puertas de Europa, llegando hasta los reinos hispánicos en el siglo XV, en los confines de Europa y a Somalia y Etiopía en el África oriental.
El término "Ruta de la Seda" fue creado por el geógrafo alemán Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen, quien lo introdujo en su obra Viejas y nuevas aproximaciones a la Ruta de la Seda, en 1877. Debe su nombre a la mercancía más prestigiosa que circulaba por ella, la seda, cuya elaboración era un secreto que solo los chinos conocían. Los romanos (especialmente las mujeres de la aristocracia) se convirtieron en grandes aficionados de este tejido, tras conocerlo antes del comienzo de nuestra era a través de los partos, quienes se dedicaban a su comercio. Muchos productos transitaban estas rutas: piedras y metales preciosos (diamantes de Golconda, rubíes de Birmania, jade de China, perlas del golfo Pérsico), telas de lana o de lino, ámbar, marfil, laca, especias, porcelana, vidrio, materiales manufacturados, coral, etc.
En junio de 2014, la Unesco eligió un tramo de la Ruta de la Seda como Patrimonio de la Humanidad con la denominación Rutas de la Seda: red viaria de la ruta del corredor Chang’an-Tian-shan. Se trata de un tramo de 5000 kilómetros de la gran red viaria de las Rutas de la Seda que va desde la zona central de China hasta la región de Zhetysu, situada en el Asia Central, incluyendo 33 nuevos sitios en China, Kazajistán y Kirguistán.1
La Iniciativa del Cinturón y Ruta de la Seda o Belt and Road Initiative, abreviada BRIZNA (también One Belt, One Road, abreviado OBOR y también la Nueva Ruta de la Seda) y NRS (Nueva Ruta de la Seda) por las siglas en español, es el nombre con que se conoce el proyecto político-económico del Secretario General del Partido Comunista de China, Xi Jinping, que propuso en septiembre de 2013 en sus respectivos viajes a Rusia, Kazajistán y Bielorrusia. Bajo el pretexto de que "hace más de dos milenios, las personas diligentes y valientes de Eurasia exploraron y abrieron nuevas vías de intercambio comercial y cultural que unían las principales civilizaciones de Asia, Europa y África, colectivamente llamadas ruta de la seda por generaciones posteriores", el proyecto quiere conectar Europa, Asia del Sur-Oriental, Asia Central y el Oriente Medio, mediante el modelo económico, e implícitamente político, chino.12
El proyecto parte de la reconstrucción de la antigua ruta de la seda y la creación de una ruta marítima paralela, de aquí el nombre de "Cinturón y Ruta". El proyecto afecta a 60 países, el 75% de las reservas energéticas conocidas al mundo, el 70% de la población mundial y generaría el 55% del PIB mundial. El gobierno comunista chino tiene previsto invertir unos 1,4 billones de dólares. Se trataría de un cinturón económico, pero, que algunos comentaristas occidentales ya denominamos "Plan Marshall del siglo XXI al estilo chino". Esta afirmación se sostiene por el hecho que el propio Secretario General Xi Jinping asegura que el proyecto tiene cinco pilares: comunicación política, circulación monetaria, entente entre pueblos, conectividad vital y fluidez. Todo ello se ha visto reflejado de acá el inicio de su puesta en marcha a través de las inversiones importantes con planes de ayuda para empresas chinas interesadas en el mercado exterior. China por el contrario se defiende y argumenta que no se trata de ningún plan Marshall visto que las condiciones políticas impuestas entonces con el Plan Marshall no existen en este proyecto. Pero, artículos de prensa van más allá de las simples afirmaciones de Plan Marshall a la china y hablan directamente de "nuevo orden mundial chino", atrás quedaría la orden mundial norteamericano.3
Nicola Casarini, director de Investigación para Asia del Instituto Affari Internacionali de Roma, sostiene que se trata de una iniciativa ambiciosa que pretende dar cabida en exceso de capacidad interna y a la voluntad de reestructuración de diferentes sectores estratégicos del país, como la industria pesando. La ruta, sin embargo, ha reactivado, a pesar de pretender ser un medio de pacificación de Oriente Medio, las antiguas tensiones del siglo XIX. A la India y Japón, se añade ahora Rusia y los EE.UU. El presidente proyecta la Belt and Road Initiative por unos treinta años. Así el proyecto tendría que estar terminado para el 2049, año donde el país rememoraría los 100 años de fundación de la República Popular.
Вели́кий шёлковый путь — караванная дорога, связывавшая Восточную Азию со Средиземноморьем в древности и в Средние века. В первую очередь использовался для вывоза шёлка из Китая, с чем и связано его название. Путь был проложен во II веке до н. э., вёл из Сианя через Ланьчжоу в Дуньхуан, где раздваивался: северная дорога проходила через Турфан, далее пересекала Памир и шла в Фергану и казахские степи, южная — мимо озера Лоб-Нор по южной окраине пустыни Такла-Макан через Яркенд и Памир (в южной части) вела в Бактрию, а оттуда — в Парфию, Индию и на Ближний Восток вплоть до Средиземного моря. Термин введён немецким географом Фердинандом фон Рихтгофеном в 1877 году.
«Оди́н по́яс и один путь» (кит. 一带一路) — выдвинутое в 2010-х годах Китайской Народной Республикой (КНР) предложение объединённых проектов «Экономического пояса Шёлкового пути» и «Морского Шёлкового пути XXI века».
Предложение было впервые выдвинуто председателем КНР Си Цзиньпином во время визитов в Казахстан и в Индонезию осенью 2013 года[1]. В таких политических документах, как «План социально-экономического развития на 2015 год» и «Доклад о работе правительства», строительство «Одного пояса и одного пути» было включено в список важных задач, поставленных перед новым правительством Китая. Министр иностранных дел Китая Ван И подчеркнул, что осуществление этой инициативы станет «фокусом» внешнеполитической деятельности КНР в 2015 году. Подтверждено, что этот огромный проект будет включён и в план «13-й пятилетки», который будет принят в 2016 году[2]. Суть данной китайской инициативы заключается в поиске, формировании и продвижении новой модели международного сотрудничества и развития с помощью укрепления действующих региональных двусторонних и многосторонних механизмов и структур взаимодействий с участием Китая. На основе продолжения и развития духа древнего Шёлкового пути «Один пояс и один путь» призывает к выработке новых механизмов регионального экономического партнерства, стимулированию экономического процветания вовлечённых стран, укреплению культурных обменов и связей во всех областях между разными цивилизациями, а также содействию мира и устойчивого развития[3]. По официальным данным Китая, «Один пояс и один путь» охватывает большую часть Евразии, соединяя развивающиеся страны, в том числе «новые экономики», и развитые страны. На территории мегапроекта сосредоточены богатые запасы ресурсов, проживает 63 % населения планеты, а предположительный экономический масштаб — 21 трлн долларов США[4].

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Angola
Angola
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Australia
Australia
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belize
Belize
 Benin
Benin
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brazil
Brazil
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Cuba
Cuba
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Germany
Germany
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia
 Georgia
Georgia
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Japan
Japan
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liberia
Liberia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mexico
Mexico
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Panama
Panama
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Genf
Genf
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Togo
Togo
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tschad
Tschad
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uganda
Uganda
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Roberto Azevêdo
Roberto Azevêdo
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Mike Moore
Mike Moore
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Pascal Lamy
Pascal Lamy
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Peter Sutherland
Peter Sutherland
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Renato Ruggiero
Renato Ruggiero
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Supachai Panitchpakdi
Supachai Panitchpakdi
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic
 Cyprus
Cyprus


世界贸易组织(简称世贸组织或世贸;英语:World Trade Organization,缩写为 WTO;法语:Organisation Mondiale du Commerce,缩写为 OMC;西班牙语:Organización Mundial del Comercio,缩写为 OMC)是负责监督成员经济体之间各种贸易协议得到执行的一个国际组织,前身是1948年起实施的关税及贸易总协定的秘书处。
世贸总部位于瑞士日内瓦,现任总干事是罗伯托·阿泽维多。截至2016年7月29日,世界贸易组织共有164个成员。[5]世界贸易组织的职能是调解纷争,加入WTO不算签订一种多边贸易协议,但其设置的入会门槛可以做为愿意降低关税、法政上配合、参与国际贸易的门票,它是贸易体制的组织基础和法律基础,是众多贸易协定的管理者,是各成员贸易立法的监督者,是就贸易提供解决争端和进行谈判的场所。该机构是当代最重要的国际经济组织之一,其成员间的贸易额占世界贸易额的绝大多数,被称为“经济联合国”。
Die Welthandelsorganisation (englisch World Trade Organization, WTO; französisch Organisation mondiale du commerce, OMC; spanisch Organización Mundial de Comercio, OMC) ist eine internationale Organisation mit Sitz in Genf, die sich mit der Regelung von Handels- und Wirtschaftsbeziehungen beschäftigt. Sie wurde am 15. April 1994 aus dem General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in der Uruguay-Runde nach siebenjähriger Verhandlungszeit gegründet. Am 1. Januar 1995 nahm sie ihre Arbeit in Genf auf. Die WTO ist neben dem IWF und der Weltbank eine der zentralen internationalen Organisationen, die Handels- und Wirtschaftspolitik mit globaler Reichweite verhandelt.
世界貿易機関(せかいぼうえききかん、英: World Trade Organization、略称:WTO)は、自由貿易促進を主たる目的として創設された国際機関である。常設事務局がスイスのジュネーブに置かれている。
GATT(ガット)ウルグアイ・ラウンドにおける合意によって、世界貿易機関を設立するマラケシュ協定(WTO設立協定)に基づいて1995年1月1日にGATTを発展解消させて成立した。
本来GATTは、第二次世界大戦後の安定を見据え、国際通貨基金および国際復興開発銀行とともに設立が予定されていた国際貿易機関(ITO)の設立準備の際に、暫定協定として結ばれたものであった。国際貿易機関の設立が廃案となり、GATTがその代替として発展強化されていくうちに、再びこの分野の常設機関が求められ、WTOが設立されることとなった。発展解消であるため、GATTの事務局及び事務局長もWTOへと引き継がれることとなった[4]。
WTOはGATTを継承したものであるが、GATTが協定(Agreement)に留まったのに対し、WTOは機関(Organization)であるのが根本的な違いである。
を基本原則としている。また、物品貿易だけでなく金融、情報通信、知的財産権やサービス貿易も含めた包括的な国際通商ルールを協議する場である。
対抗処置の発動では、紛争処理機関(パネル)の提訴に対し全加盟国による反対がなければ採択されるというネガティブ・コンセンサス方式(逆コンセンサス方式)を採用した強力な紛争処理能力を持つ。これは国際組織としては稀な例であり、コンセンサス方式を採っていたGATTとの大きな違いで、WTOの特徴の一つといえる。
新多角的貿易交渉(新ラウンド)は、2001年11月にカタールのドーハで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議で開始を決定し、ドーハ・ラウンドと呼ばれていた。2002年2月1日の貿易交渉委員会で新ラウンドがスタートした。しかし9年に及ぶ交渉は先進国と、急速に台頭してきたBRICsなど新興国との対立によって中断と再開を繰り返した末、ジュネーブで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議(2011年12月17日)で「交渉を継続していくことを確認するものの、近い将来の妥結を断念する」(議長総括)となり事実上停止状態になった。
その後、2013年のバリ島における閣僚会議で、貿易円滑化協定を含む合意が成立し、2014年7月まで貿易円滑化協定をWTO協定に加える(附属書1Aに追加)するための文書を一般理事会で採択すべきとされた[5]。しかしインドが合意を蒸し返す状態で反対したため期限までに採択できなかった[6]。その後食糧備蓄への補助金の問題で先進国側が譲歩することでようやくインドが合意し、2014年11月27日の一般理事会で貿易円滑化協定が採択された[6]。WTO加盟国の3分の2が改正を受諾した日に発効することになっており、2017年2月22日にこの要件を満たし、協定が発効した。
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 124 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. It is the largest international economic organization in the world.[5][6]
The WTO deals with regulation of trade in goods, services and intellectual property between participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a dispute resolution process aimed at enforcing participants' adherence to WTO agreements, which are signed by representatives of member governments[7]:fol.9–10 and ratified by their parliaments.[8] The WTO prohibits discrimination between trading partners, but provides exceptions for environmental protection, national security, and other important goals.[9] Trade-related disputes are resolved by independent judges at the WTO through a dispute resolution process.[9]
The WTO's current Director-General is Roberto Azevêdo,[10][11] who leads a staff of over 600 people in Geneva, Switzerland.[12] A trade facilitation agreement, part of the Bali Package of decisions, was agreed by all members on 7 December 2013, the first comprehensive agreement in the organization's history.[13][14] On 23 January 2017, the amendment to the WTO Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement marks the first time since the organization opened in 1995 that WTO accords have been amended, and this change should secure for developing countries a legal pathway to access affordable remedies under WTO rules.[15]
Studies show that the WTO boosted trade,[16][17][9] and that barriers to trade would be higher in the absence of the WTO.[18] The WTO has highly influenced the text of trade agreements, as "nearly all recent [preferential trade agreements (PTAs)] reference the WTO explicitly, often dozens of times across multiple chapters... in many of these same PTAs we find that substantial portions of treaty language—sometime the majority of a chapter—is copied verbatim from a WTO agreement."[19]
L'Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC ; en anglais : World Trade Organization, WTO, en espagnol : Organización Mundial del Comercio, OMC) est une organisation internationale qui s'occupe des règles régissant le commerce international entre les pays. Au cœur de l'organisation se trouvent les accords de l'OMC, négociés et signés en avril 1994 à Marrakech1 par la majeure partie des puissances commerciales du monde2 et ratifiés par leurs assemblées parlementaires. L'OMC a pour but principal de favoriser l'ouverture commerciale. Pour cela, elle tâche de réduire les obstacles au libre-échange, d'aider les gouvernements à régler leurs différends commerciaux et d'assister les exportateurs, les importateurs et les producteurs de marchandises et de services dans leurs activités.
Depuis 2001, le cycle de négociation mené par l'OMC est le Cycle de Doha3. Bien que l'OMC ne soit pas une agence spécialisée de l'ONU, elle entretient des liens avec cette dernière4. Le siège de l'OMC est au Centre William-Rappard, à Genève. Depuis le 1er septembre 2013, l'organisation est présidée par le Brésilien Roberto Azevêdo qui a été élu directeur général.
L'Organizzazione mondiale del commercio, abbreviato in OMC (in inglese: World Trade Organization, WTO), è un'organizzazione internazionale creata allo scopo di supervisionare numerosi accordi commerciali tra gli stati membri. Vi aderiscono[3] 164 Paesi, a cui se ne aggiungono altri 22 con ruolo di osservatori,[4] comprendendo così oltre il 95% del commercio mondiale di beni e servizi.[5]
La sede dell'OMC si trova, dal 1995, presso il Centro William Rappard a Ginevra, Svizzera.[6]
La Organización Mundial del Comercio (OMC) fue establecida en 1995. Tiene su sede en Ginebra, Suiza, y sus idiomas oficiales son el inglés, el francés y el español. La OMC no forma parte del sistema de las Naciones Unidas, y tampoco de los organismos de Bretton Woods como el Banco Mundial o el FMI.Nota 1
Всеми́рная торго́вая организа́ция (ВТО; англ. World Trade Organization (WTO), фр. Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), исп. Organización Mundial del Comercio) — международная организация, созданная 1 января 1995 года с целью либерализации международной торговли и регулирования торгово-политических отношений государств-членов. ВТО образована на основе Генерального соглашения по тарифам и торговле (ГАТТ), заключенного в 1947 году и на протяжении почти 50 лет фактически выполнявшего функции международной организации, но не являвшегося тем не менее международной организацией в юридическом смысле.
ВТО отвечает за разработку и внедрение новых торговых соглашений, а также следит за соблюдением членами организации всех соглашений, подписанных большинством стран мира и ратифицированных их парламентами. ВТО строит свою деятельность, исходя из решений, принятых в 1986—1994 годах в рамках Уругвайского раунда и более ранних договоренностей ГАТТ. Обсуждения проблем и принятие решений по глобальным проблемам либерализации и перспективам дальнейшего развития мировой торговли проходят в рамках многосторонних торговых переговоров (раунды). К настоящему времени проведено 8 раундов таких переговоров, включая Уругвайский, а в 2001 году стартовал девятый в Дохе, Катар. Организация пытается завершить переговоры по Дохийскому раунду переговоров, который был начат с явным акцентом на удовлетворение потребностей развивающихся стран. По состоянию на декабрь 2012 года будущее раунда переговоров в Дохе остаётся неопределённым: программа работы состоит из 21 части, а первоначально установленный окончательный срок 1 января 2005 года был давно пропущен[3]. В ходе переговоров возник конфликт между стремлением к свободной торговле и стремлением множества стран к протекционизму, особенно в плане сельскохозяйственных субсидий. До сих пор эти препятствия остаются главными и мешают любому прогрессу для запуска новых переговоров в рамках Дохийского раунда. По состоянию на июль 2012 года, существуют различные группы переговоров в системе ВТО для решения текущих вопросов в плане сельского хозяйства, что приводит к застою в самих переговорах[4].
Штаб-квартира ВТО расположена в Женеве, Швейцария. Глава ВТО (генеральный директор) — Роберту Карвалью ди Азеведу, в штате самой организации около 600 человек[5].
На 26 апреля 2015 года в ВТО состояли 162 страны[6].
Правила ВТО предусматривают ряд льгот для развивающихся стран. В настоящее время развивающиеся страны — члены ВТО имеют (в среднем) более высокий относительный уровень таможенно-тарифной защиты своих рынков по сравнению с развитыми. Тем не менее, в абсолютном выражении общий размер таможенно-тарифных санкций в развитых странах гораздо выше, вследствие чего доступ на рынки высокопередельной продукции из развивающихся стран серьёзно ограничен[7].
Правила ВТО регулируют только торгово-экономические вопросы. Попытки США и ряда европейских стран начать дискуссию об условиях труда (что позволило бы считать недостаточную законодательную защиту работников конкурентным преимуществом) были отвергнуты из-за протестов развивающихся стран, которые утверждали, что такие меры только ухудшат благосостояние работников в связи с сокращением числа рабочих мест, снижением доходов и уровня конкурентоспособности[7].
Mitglieder der WTO
| Staat | Beitrittsdatum |
|---|---|
| 30. Juni 1995 | |
| 29. Juli 2016 | |
| 8. September 2000 | |
| 23. November 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 5. Februar 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 12. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Dezember 1996 | |
| 3. Juni 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 21. Januar 1996 | |
| 7. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. November 1999 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 14. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Oktober 1996 | |
| 14. Juni 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Juli 1995 | |
| 25. Oktober 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 26. Juni 2014 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. April 2000 | |
| 13. Oktober 2004 | |
| 13. Dezember 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 2008 | |
| 30. November 2015 | |
| 13. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 20. Dezember 1998 | |
| 30. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1997 | |
| 27. März 1997 | |
| 30. November 2000 | |
| 20. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. Februar 2013 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 10. Februar 1999 | |
| 14. Juli 2016 | |
| 1. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 17. November 1995 | |
| 29. April 2012 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 4. April 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. Juli 2001 | |
| 29. Januar 1997 | |
| 26. August 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. April 2004 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 3. September 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. Dezember 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. November 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 6. September 1997 | |
| 9. Juni 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Mai 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. August 2012 | |
| 26. Juli 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2005 | |
| 10. Mai 2012 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. April 2015 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 5. März 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. März 2013 | |
| 1. Januar 2002 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 27. Juli 2007 | |
| 1. März 1995 | |
| 19. Oktober 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 29. März 1995 | |
| 26. März 1995[2] | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 16. Mai 2008 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 10. April 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 24. August 2012 | |
| 11. Januar 2007 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 |
 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 History
History