
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Thailand
Thailand

普吉府(泰语:จังหวัดภูเก็ต,皇家转写:Changwat Phuket,泰语发音:[t͡ɕāŋ.wàt pʰūː.kèt]),华人旧称通扣、通扣坡,马来人称之为武吉(马来语:Bukit),是泰国77个一级行政区之一,府治为与行政区同名的普吉市。该行政区全境以普吉岛再加上32个离岛为范围。普吉岛是泰国境内最大的岛屿,位于泰国南部安达曼海海域上,也是唯一一个拥有自己独立一级行政区划的岛屿。普吉是世界知名的热带观光胜地,其丰富的天然资源也替泰国带来不小的财富。
Phuket (thailändisch ภูเก็ตⓘ/? [pʰūː.kèt]) ist eine Provinz (Changwat) von Thailand. Sie besteht aus der gleichnamigen Insel und einer Reihe kleinerer Nebeninseln in der Andamanensee vor der Küste Südthailands. Phuket ist auch der Name der Provinzhauptstadt.





 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam
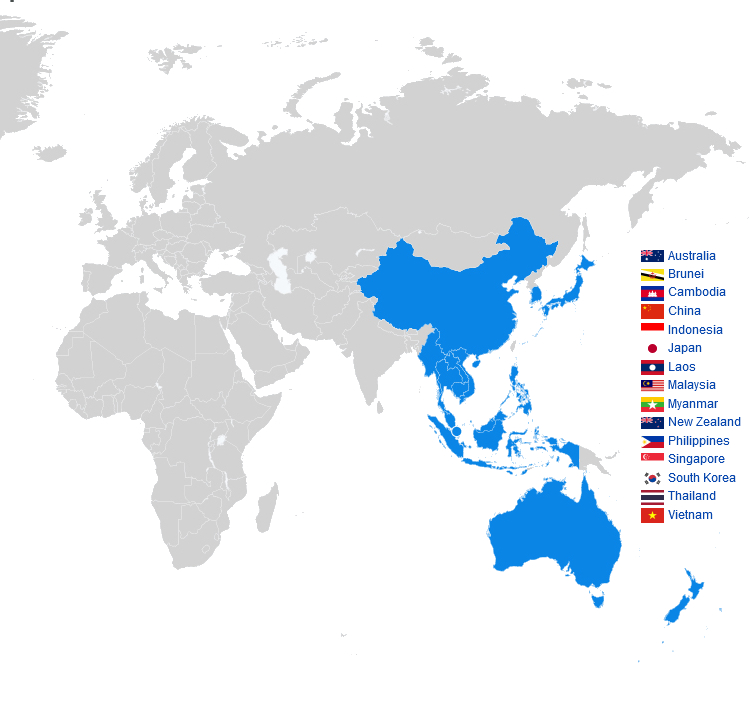
Die Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (kurz RCEP, deutsch Regionale, umfassende Wirtschaftspartnerschaft) ist ein seit 2020 bestehendes Freihandelsabkommen zwischen den zehn ASEAN-Mitgliedsstaaten und fünf weiteren Staaten in der Region Asien-Pazifik. Es ist die größte Freihandelszone der Welt.[1]
Das Projekt zur Gründung der RCEP entstand 2012, als die ASEAN-Staaten Verhandlungen mit der Volksrepublik China, Japan und Südkorea (ASEAN+3) sowie mit Indien, Australien und Neuseeland (ASEAN+6) aufgenommen hatten. Ursprünglich war die Einführung der Freihandelszone für 2017 geplant gewesen. Aufgrund von Bedenken verließ Indien 2019 die Verhandlungen. Am 15. November 2020, zum Abschluss des 37. ASEAN-Gipfeltreffens in der vietnamesischen Hauptstadt Hanoi, fand schließlich die Vertragsunterzeichnung statt.[2][3]
東アジア地域包括的経済連携(ひがしアジアちいきほうかつてきけいざいれんけい、英語: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership; RCEP、アールセップ、域内包括的経済連携)とは、ASEAN加盟10カ国(ブルネイ、カンボジア、インドネシア、ラオス、マレーシア、ミャンマー、フィリピン、シンガポール、タイ、ベトナム)と、そのFTAパートナー5カ国(オーストラリア、中国、日本、ニュージーランド、韓国)の間で提案されている、アジア太平洋地域の自由貿易協定であり、世界の人口の3割、世界のGDPの3割を占める15カ国が交渉に参加している。交渉国15カ国は世界の人口の30%、GDPの30%弱を占めている[1]。
FTAパートナーであるインドは、交渉が開始された2011年からRCEP交渉に参加していたが、主に中国からの製造品やオーストラリアやニュージーランドからの農産物・乳製品のダンピング懸念を理由に、交渉の最終時点の2019年11月に交渉から離脱した[2]。2020年11月15日に第4回RCEP首脳会議の席上で協定は署名された[3]。
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP; /ˈɑːrsɛp/ AR-sep) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history.[1] It was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam, and will take effect within two years, after it has been ratified by the member countries.[2][3][4]
The trade pact, which includes a mix of high-income,[note 1] middle-income,[note 2] and low-income countries,[note 3] was conceived at the 2011 ASEAN Summit in Bali, Indonesia, while its negotiations were formally launched during the 2012 ASEAN Summit in Cambodia.[5][6][7] It was expected to eliminate about 90% of the tariffs on imports between its signatories within 20 years of coming into force, and establish common rules for e-commerce, trade, and intellectual property.[8]
The RCEP is the first free trade agreement between China, Japan, and South Korea, three of the four largest economies in Asia.[8] At the time it was signed, analysts predicted that it would help stimulate the economy amid the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as "pull the economic centre of gravity back towards Asia," and amplify the decline of the United States in economic and political affairs.[6][9][10]
Le partenariat régional économique global1, ou en anglais : Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), est un projet d'accord de libre-échange entre quinze pays autour de l'océan Pacifique. C'est l'accord commercial le plus important du monde2.
Il inclut les dix pays membres de l'ASEAN, à savoir : la Birmanie, Brunei, le Cambodge, l'Indonésie, le Laos, la Malaisie, les Philippines, Singapour, la Thaïlande et le Vietnam ; ainsi que cinq autres pays qui possèdent déjà un accord de libre-échange bilatéral avec l'ASEAN, à savoir : l'Australie, la Chine, le Japon, la Corée du Sud et la Nouvelle-Zélande.
Il Partenariato Economico Globale Regionale (in lingua inglese Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) è un accordo di libero scambio nella regione dell'Asia Pacifica tra i dieci stati dell'ASEAN (cioè Brunei, Cambogia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Filippine, Singapore, Thailandia e Vietnam) e cinque dei loro partner di libero scambio: Australia, Cina, Giappone, Nuova Zelanda e Corea del Sud. I 15 paesi membri rappresentano circa il 30% della popolazione mondiale e del PIL, rendendolo il più grande blocco commerciale.[1] È stato firmato al vertice dell'ASEAN virtuale ospitato in Vietnam il 15 novembre 2020,[2][3] e dovrebbe entrare in vigore entro due anni, dopo che sarà stato ratificato dai paesi membri.[4]
Il patto commerciale, che comprende un mix di alto reddito, reddito medio, e paesi a basso reddito, è stato concepito al vertice dell'ASEAN del 2011 a Bali,[5] mentre i negoziati sono stati avviati ufficialmente nel corso del vertice dell'ASEAN del 2012 in Cambogia.[6]
L'RCEP è il primo accordo di libero scambio tra Cina, Giappone e Corea del Sud (tre delle quattro maggiori economie asiatiche) ed è il primo accordo multilaterale di libero scambio a includere la Cina.[7] Al momento della firma, gli analisti prevedevano che avrebbe aiutato a stimolare l'economia durante la pandemia di COVID-19, e "avrebbe attirato il centro di gravità economico verso l'Asia".
La Asociación Económica Integral Regional (abreviado RCEP por sus siglas en inglés) es un acuerdo de libre comercio (TLC) entre los diez estados miembros de la Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN) (Brunéi, Camboya, Indonesia, Laos, Malasia, Myanmar, Filipinas, Singapur, Tailandia , Vietnam) y cinco estados de Asia-Pacífico con los que la ASEAN tiene acuerdos de libre comercio existentes (Australia, China, Japón, Corea del Sur y Nueva Zelanda). El tratado fue firmado en la Cumbre de la ASEAN del 15 de noviembre de 202012 y se espera que entre en vigor en un plazo inferior a dos años, después de que sea ratificado por todos los estados miembros.
Incluye estados con PIBs muy diversos,3 conformando entre los 15 países en torno al 30% de la población mundial y el 30% del Producto Mundial Bruto.
Las negociaciones se iniciaron formalmente en noviembre de 2012 en la Cumbre de la ASEAN en Camboya.4 El RCEP se considera una alternativa al Acuerdo de Asociación Transpacífico (TPP, por sus siglas en inglés), un acuerdo comercial propuesto que incluye varias naciones de Asia y América, pero excluye a China y la India.5 Tras la salida de Estados Unidos durante la presidencia de Donald Trump del TPP se retomaron con más fuerza las negociaciones en el RCEP y se firmó el acuerdo en noviembre de 2020 por las naciones de la ASEAN, incluida China.6 El pacto entrará en vigor cuando los países que lo han firmado procedan a tramitar su ratificación a nivel nacional.7
El tratado RCEP es el primer tratado de libre comercio entre China, Japón y Corea del sur (tres de las cuatro grandes economías asiáticas), y es el primer tratado multilateral que incluye a China.8 En el momento de la firma, los analistas predijeron que ayudaría en la recuperación de la economía tras la pandemia de COVID-19, así como a empujar el centro de gravedad de la economía mundial hacia Asia.9
Всесторо́ннее региона́льное экономи́ческое партне́рство, сокращенно ВРЭП (англ. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) — это соглашение о «зоне свободной торговли плюс» («ЗСТ +»), охватывающее 10 государств-членов Ассоциации государств Юго-Восточной Азии (АСЕАН) (Бруней, Вьетнам, Индонезия, Камбоджа, Лаос, Малайзия, Мьянма, Сингапур, Таиланд, Филиппины) и 6 государств, с которыми у АСЕАН уже подписаны соглашения о свободной торговле (Австралия, Индия, КНР, Новая Зеландия, Республика Корея и Япония). ВРЭП охватывает 4 развитые и 12 развивающихся государств. Начало переговоров было положено 20 ноября 2012 г. на саммите АСЕАН в Камбодже[1].
Соглашение о создании ВРЭП было подписано в Ханое 15 ноября 2020 года. Его вступление в силу создаст крупнейшую в мире зону свободной торговли с примерно 2,2 млрд потребителями и объемом ВВП в $28 трлн, что составляет более 32% от общего мирового объема ВВП.[2].


怒江(藏文:རྒྱལ་མོ་རྔུལ་ཆུ་,威利:rgyal mo rngul chu),是萨尔温江上游中国境内河段的名称,发源于西藏自治区那曲市安多县境内唐古拉山南麓的将美尔岗尕楼冰川,流经西藏自治区、云南省,流入缅甸后改称萨尔温江。干流长度2,013公里,流域面积12.48万平方公里。[1][2]。
怒江上游因江水深黑,中国最早的地理著作《禹贡》把它称为黑水河;藏语名为那曲(藏文:ནག་ཆུ་,威利:nag chu),义同。怒江在当地的怒族中被称为阿怒日美,“阿怒”是怒族人的自称,“日美”在汉语中译为江,“阿怒日美”就是怒族人居住区域的江,故名怒江。流入缅甸后改称萨尔温江(缅甸语:သံလွင်မြစ်,[θàɴlwɪ̀ɴ mjɪʔ])。 怒江上游为那曲,发源于西藏自治区那曲市安多县境内唐古拉山南麓的将美尔岗尕楼冰川,源流区河段名为将美尔曲[2]。它先向南转西再转西南流,汇集左侧支流后改称朵尔丁曲。它向南以“S”形流,汇集右侧支流仲朵曲后改称朵果尔曲[3]。该曲流至帮美附近纳左侧支流后,改称桑曲,随后河道转向西南流,穿越青藏铁路后注入错那湖[4]。干流由错那湖南端流出后,始称那曲[5]。
Der Saluen (chinesisch 怒江, Pinyin Nù Jiāng) entspringt im Hochland von Tibet (Volksrepublik China) als Nag-Tschu. Dort liegt seine Quelle in 5450 m ü. NN Höhe in einem (variablen) Gletschertor zwischen dem nördlichen (5881 m ü. NN) und dem südlichen Chrebet-Peak (5722 m ü. NN) im östlichen Tanggula Shan (34 km südöstlich des nördlichen Tanggula-Passes, 5231 m ü. NN). Der Gletscher schmilzt stark zurück. Der Nag-Tschu verläuft in südöstlicher Richtung durch die chinesische Provinz Yunnan. In Myanmar (ehemals Birma) durchschneidet er das Shan-Hochland dort, wo er die Grenze von China und Myanmar bildet. In dieser Gegend fließen nur wenig weiter östlich der Mekong und der Jangtsekiang in ebenfalls tief eingeschnittenen Tälern. In seinem Unterlauf bildet er auf einer kurzen Strecke die Grenze zwischen Myanmar und Thailand und mündet schließlich beim Hafen von Mawlamyine an der Küste von Myanmar in das Andamanische Meer, ein Teil des Indischen Ozeans.
Der Saluen ist aufgrund seiner zahlreichen Stromschnellen nur auf etwa 120 km oberhalb der Mündung schiffbar, flussaufwärts verkehren jedoch kleinere Motorboote und Frachtkähne. Der Fluss ist bis ins Jahr 2005 noch relativ naturbelassen.
Der Saluen ist durch die menschlichen Entwaldungen erheblichen Gefahren für Hangrutschungen (Muren) ausgesetzt. Hierdurch hat sich die Sedimentfracht deutlich erhöht.
サルウィン川(ビルマ語: သံလွင်မြစ်; sam lwang mrac; モン語:သာန်လာန်; san lon; チベット語: རྒྱལ་མོ་རྔུལ་ཆུ།; ワイリー方式:rgyal mo rngul chu; 蔵文拼音:Gyalmo Ngulchu; 中国語: 怒江[1])はチベットを源流とし、中国雲南省を流れ、ミャンマー(ビルマ)北東部のシャン台地にあるカヤー州・カレン州を南下してマルタバン湾(アンダマン海)に注ぐ川。一部ミャンマーとタイの国境を成す。長さは2,815kmにおよぶ。
急流が多く、しばしばこの流域は “中国のグランドキャニオン”、“アジアの大地溝帯” などとよばれ、河口から119kmの地点までしか船が入れない。そのため経済的には流域の殆どの地域で役に立っておらず、ミャンマーの一部地域で木材の搬出に利用されている程度である。
その一方、流域には7,000種を超える植物と、80種の希少種および絶滅危惧種の動物と魚が暮らす。ユネスコはこの流域を「世界で最も多様性に富む温帯生態系かもしれない」とし、2003年、上流域を世界遺産に登録した。(→三江併流)ヌー族(怒族)は中華人民共和国が公的に認知している56の少数民族の一つで、この民族名はこの川の中国名 怒江から名づけられた。
The Salween or, officially, Thanlwin[2] River (Phlone ကၟံင့်ယှောတ်ခၠေါဟ်; Burmese: သံလွင်မြစ်; MLCTS: sam lwang mrac; IPA: [θàɴlwɪ̀ɴ mjɪʔ]; Thai: แม่น้ำสาละวิน Mae Nam Salawin; IPA: [mɛ̂ː náːm sǎːləwin]),[a] known in China as the Nu River (Chinese: 怒江; pinyin: Nù Jiāng[b]), is a river about 2,815 kilometres (1,749 mi) long that flows from the Tibetan Plateau into the Andaman Sea in Southeast Asia.
It drains a narrow and mountainous watershed of 324,000 square kilometres (125,000 sq mi) that extends into the countries of China, Burma and Thailand. Steep canyon walls line the swift, powerful and undammed Salween, one of the longest free-flowing rivers in the world.[4][5] Its extensive drainage basin supports a biodiversity comparable with the Mekong and is home to about 7 million people. In 2003, key parts of the mid-region watershed of the river were included within the Three Parallel Rivers of Yunnan Protected Areas, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[6]
The people who live on the Salween are relatively isolated from the rest of the world. The river is only navigable up to 90 kilometres (56 mi) from the mouth, and only in the rainy season.
The Burma Road was constructed between 1937 and 1938 during the Second Sino-Japanese War and crossed the river at the Huitong bridge. The Huitong bridge was blown by the retreating Chinese army and the river became the frontline from 1942 to 1944. The Salween Campaign of World War II, was launched in order to liberate occupied China and open the Burma Road again and connect it to the Ledo Road.
Logging began on the mountains surrounding the Salween in the late 20th century, and has damaged the river's ecology. In recent years, there have been a number of proposals to dam the Salween River, both upstream in China and downstream in Myanmar, which have prompted social and environmental concerns as well as widespread opposition.[4][7] Construction of at least one upstream dam on a tributary of the Salween is currently underway in China's Yunnan province, with many more expected to follow.
La Salouen (tibétain : རྒྱ་མོ་དངུལ་ཆུ་, Wylie : rGya mo dNGul chu ; chinois : 怒江 ; pinyin : , Birman : Thanlwin Myit, Thaï : สาละวิน (Saalawin), en français fleuve nu ou fleuve en colère) est un fleuve de Chine et de Birmanie, dont le bassin s'étend également sur la Thaïlandenotes 1, le deuxième par sa longueur en Asie du Sud-Est après le Mékong, mais devant l'Irrawaddy. Son bassin, étroit et peu peuplé, est surtout caractérisé par une très riche biodiversité aujourd'hui menacée par les projets de construction de nombreux barrages hydroélectriques perturbant l'écosystème.
Il Saluen (in inglese: Salween; in tibetano: རྒྱལ་མོ་རྔུལཆུ།, Wylie: rGyl mo rNGul chu o Gyalmo Ngulchu; in cinese: 怒江S, NùjiāngP, in birmano: သံလွင်မြစ်, birmano traslitterato: Thanlwin; in shan: ၼမ်ႉၶူင်း, shan traslitterato: Nam Kong; in thai: สาละวิน, RTGS: Salawin; in mon: သာန်လာန်, mon traslitterato: San Lon) è un fiume asiatico che nasce nel Tibet centro orientale e sfocia nel golfo di Martaban, che fa parte del mare delle Andamane, nella Birmania meridionale. Con i suoi 2.815 km di lunghezza,[1] poco meno del Danubio, è il fiume più lungo dell'Indocina dopo il Mekong.
El río Salween (también transliterado Saluén o Salawi) (en chino, Nù Jiāng) es un largo río que discurre por el Sureste Asiático.
Nace en el este del Tíbet, fluyendo generalmente hacia el sur durante casi 2400 km a través de la provincia de Yunnan, China, y al este de Birmania, desembocando en el golfo de Martaban del mar de Andamán en Mawlamyaing.
En su curso inferior delimita la frontera entre Birmania y Tailandia por cerca de 130 km. Es el segundo río más largo de Birmania, después del río Irawadi. Solamente es navegable en embarcaciones pequeñas en ciertos tramos, ya que hay zonas de peligrosos rápidos que impiden su uso como vía navegable.
China planea construir en los próximos años una gran cantidad de represas en la región, sin coordinación ni acuerdo previo alguno con las otras dos naciones que se encuentran río abajo. Está considerado como el segundo río más contaminado del mundo, detrás del río Citarum.
Салуи́н[1] (бирм. သံလွင်မြစ် — Танлуин[2], на тер. Китая — Наг-Чу[3] (тиб. ནག་ཆུ) и Нуцзя́н[4] (кит. 怒江)) — река в Китае, Мьянме и Таиланде. Длина 2400 км (по другой оценке — около 3200 км), площадь бассейна 325 тыс. км².[источник не указан 759 дней] Также носит названия Нам-Конг[5], Кагчу[6], Акчу[7].
Салуин берёт начало в Тибетском автономном районе Китая, на высоте около 4547 м, из озера Цлацо[7]. Течёт на юго-восток, затем через провинцию Юньнань — почти строго на юг, сохраняя это направление практически до самого устья. В нижнем течении русло реки проходит вдоль восточных границ Мьянмы, на отрезке длиной порядка 100 км Салуин образует границу между Мьянмой и Таиландом. Река впадает в залив Моутама Андаманского моря (часть Индийского океана).
 Geography
Geography
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Companies
Companies

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
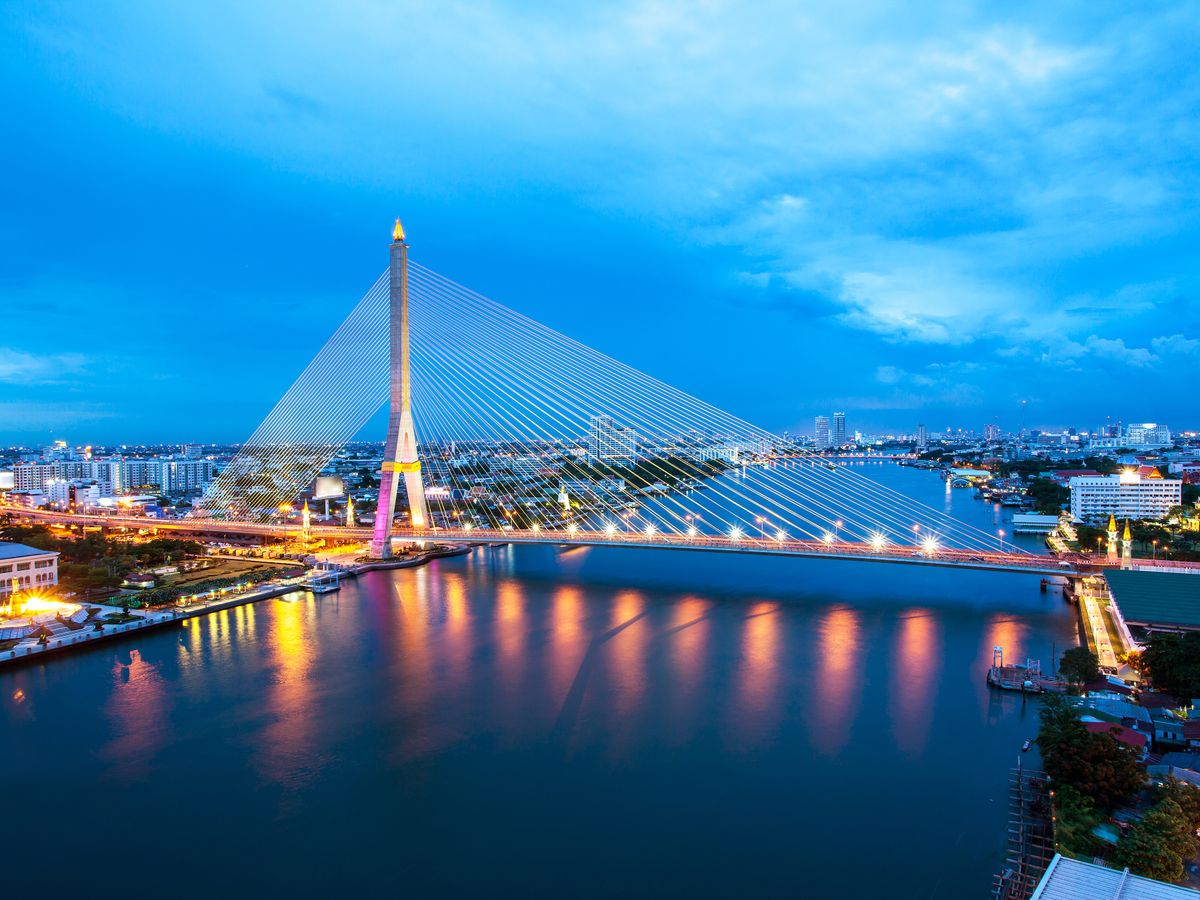
 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 History
History
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Animal world
Animal world