
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Kenya
Kenya
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Angola
Angola
 Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Ghana
Ghana
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Kenya
Kenya
 Libya
Libya



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Mali
Mali
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia



 African Union
African Union
 Alpha Condé
Alpha Condé
 African Union
African Union
 Bingu wa Mutharika
Bingu wa Mutharika
 African Union
African Union
 Denis Sassou Nguesso
Denis Sassou Nguesso
 African Union
African Union
 Hailemariam Desalegn
Hailemariam Desalegn
 African Union
African Union
 Idriss Déby
Idriss Déby
 African Union
African Union
 Jakaya Kikwete
Jakaya Kikwete
 African Union
African Union
 Joaquim Chissano
Joaquim Chissano
 African Union
African Union
 John Agyekum Kufuor
John Agyekum Kufuor
 African Union
African Union
 Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz
Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz
 African Union
African Union
 Muammar al-Gaddafi
Muammar al-Gaddafi
 African Union
African Union
 Olusegun Obasanjo
Olusegun Obasanjo
 African Union
African Union
 Robert Mugabe
Robert Mugabe
 African Union
African Union
 Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo
Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo
 African Union
African Union
 Thabo Mbeki
Thabo Mbeki
 African Union
African Union
 Thomas Boni Yayi
Thomas Boni Yayi
 African Union
African Union
 Paul Kagame
Paul Kagame
 African Union
African Union
 Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
 African Union
African Union
 Moussa Faki
Moussa Faki
 African Union
African Union
 Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma
Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma
 African Union
African Union
 Jean Ping
Jean Ping
 African Union
African Union
 Alpha Oumar Konaré
Alpha Oumar Konaré
 African Union
African Union
 Amara Essy
Amara Essy
 African Union
African Union
 Mohamed Ould Ghazouani
Mohamed Ould Ghazouani
 African Union
African Union
 Azali Assoumani
Azali Assoumani
 African Union
African Union
 Félix Tshisekedi
Félix Tshisekedi
 African Union
African Union
 Macky Sall
Macky Sall
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Angola
Angola
 Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Benin
Benin
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Demokratische Arabische Republik Sahara
Demokratische Arabische Republik Sahara
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia

 Geography
Geography
 Ghana
Ghana
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kenya
Kenya
 Comoros
Comoros
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Liberia
Liberia
 Libya
Libya
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Mali
Mali
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Republik Südsudan
Republik Südsudan
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Sambia
Sambia
 Sao Tome und Principe
Sao Tome und Principe
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Togo
Togo
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Uganda
Uganda

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic


非洲联盟(法语:Union Africaine; 英语:African Union),简称非盟(UA或AU),是一个包涵了55个非洲国家的联盟,是属于集政治、经济和军事于一体的全非洲性政治实体。非洲联盟于未来有计划统一使用货币、联合防御力量、以及成立跨国家的机关,这包括一个管理非洲联盟的内阁政府。此联盟的主要目的是帮助发展及稳固非洲的民主、人权、以及能永续发展的经济,除此之外亦希望减少非洲内部的武装战乱及创造一个有效的共同市场,最终目标是建立“非洲合众国”。
前身是1963年在埃塞俄比亚首都亚的斯亚贝巴成立的“非洲统一组织”。2002年7月在南非改组。[6]2017年在第28届非盟首脑会议上,摩洛哥获得了54个成员国中的42国同意,时隔33年重新成为该组织成员国,至此非洲联盟已涵盖所有非洲主权国家。[7]
Die Afrikanische Union (arabisch الاتحاد الأفريقي, DMG al-Ittiḥād al-Ifrīqī, englisch African Union, französisch Union africaine, portugiesisch União Africana)[2] ist eine Internationale Organisation, die 2002 die Nachfolge der Organisation für Afrikanische Einheit (OAU) angetreten hat und sich für Kooperation auf allen Gebieten einsetzen soll. Sie ist ein Zusammenschluss von anfangs 53 afrikanischen Staaten (Westsahara ist Mitglied der Afrikanischen Union, sein völkerrechtlicher Status allerdings umstritten).
Der Hauptsitz der Organisation befindet sich im äthiopischen Addis Abeba, das Panafrikanische Parlament im südafrikanischen Midrand. Mitgliedstaaten der AU sind alle international allgemein anerkannten afrikanischen Staaten, einschließlich Westsaharas. Geplant ist in der AU unter anderem ein Afrikanischer Gerichtshof. Marokko wurde am 30. Januar 2017 nach 33 Jahren Abwesenheit wieder in die Afrikanische Staatengemeinschaft aufgenommen.[3]
アフリカ連合(アフリカれんごう)は、アフリカの国家統合体。アフリカ統一機構 (OAU) が、2002年に発展改組して発足した[3]。エチオピアのアディスアベバに本部を置いている。
1963年に創設されたアフリカ統一機構は、モロッコを除くアフリカ大陸の53か国(当時)全てが加入する世界最大の地域統合であったが、「統一機構」という名とは裏腹に各国間の内政不干渉を原則としており、各国で頻発する内戦やクーデターといった危機に対して有効な手段をとることができておらず、機能不全に陥っていた[4]。また、各国間の経済統合なども遅々として進んでいなかった。こうした状況に一石を投じたのが、1991年に締結されたアブジャ条約である。この条約では、アフリカ各国は2028年までに大陸統一通貨「アフロ」を導入し、アフリカ経済共同体(AEC)を創設することが謳われた。これによりアフリカ大陸が経済統合の方向に向かう中、より一層のアフリカ大陸の統合を進めるために新しい機構の創設が求められるようになった。
こうしたなか、アフリカ統一機構により強い権限を持たせ、政治・経済的統合を進めて最終的に欧州連合的な形態にアフリカ大陸を持っていくことを目的として、旧統一機構をアフリカ連合へと改組することを提案したのが、リビアの元首だったムアンマル・アル=カッザーフィーであった。カッザーフィーは1997年以降急速にアラブからアフリカへと外交重心を転換させていたが、1999年9月のスルトにおけるOAU首脳会談においてAUへの移行がリビアによって正式提案された[5]。この提案は各国に受け入れられ、アフリカ統一機構からアフリカ連合への移行のため、2000年7月のロメOAU首脳会議でアフリカ連合制定法(アフリカ連合を創設するための条約)が採択され、各国の批准を待って、2001年に発効した[6]。2002年7月のダーバン首脳会議を経て、アフリカ連合は正式に発足した。
アフリカ連合は、アフリカの一層高度な政治的経済的統合の実現及び紛争の予防解決への取組強化のため発足した地域統合体である。アフリカ諸国と諸国民間の一層の統一性及び連帯性の強化、アフリカの政治的経済的社会的統合の加速化、アフリカの平和と域内紛争や独裁政治の根絶、安全保障及び安定の促進、民主主義原則と国民参加統治の促進、持続可能な開発の促進、教育及び科学等での協力、グローバリゼーション時代におけるアフリカ諸国の国際的な地位向上、等を目指している。また、欧州連合(EU)をモデルとした地域統合を目標に掲げており、将来的には統一した国家へ発展させ、アフリカ合衆国を創ることも視野に入れている。
2001年にはアフリカ開発のための新パートナーシップ(NEPAD)を採択し、アフリカ大陸の開発のための指針を表明した。また、これに基づいて、各国が加盟国のガバナンスなどの状況を審査するアフリカン・ピア・レビュー・メカニズム(アフリカにおける相互審査システム、APRM)が創設され、2005年にはガーナの、2006年にはルワンダの報告書が作成された[7]。
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa, with exception of various territories of European possessions located in Africa. The bloc was founded on 26 May 2001 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and launched on 9 July 2002 in South Africa.[6] The intention of the AU is to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments. The most important decisions of the AU are made by the Assembly of the African Union, a semi-annual meeting of the heads of state and government of its member states. The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa.
In result of its geographical location, the African Union has an area of around 29 million km2 (11 million sq mi) and includes popular world landmarks, including the Sahara and the Nile.[7] They have adopted a gold, green and red based emblem and flag to represent the continental union, where they held a competition for citizens to design a flag in which they chose a submission to replace the old flag. Their main celebration occurs on Africa Day on 25 May. The primary languages spoken include Arabic, English, French and Portuguese and the languages of Africa. Within the African Union, there are official bodies such as the Peace and Security Council and the Pan-African Parliament.
L'Union africaine (UA) est une organisation d'États africains créée en 2002, à Durban en Afrique du Sud, en application de la déclaration de Syrte du 9 septembre 1999. Elle a remplacé l'Organisation de l'unité africaine2 (OUA). La mise en place de ses institutions (Commission, Parlement panafricain et Conseil de paix et de sécurité) a eu lieu en juillet 2003 au sommet de Maputo au Mozambique.
Son premier président a été le Sud-Africain Thabo Mbeki, précédemment président de l'OUA.
Ses buts sont d'œuvrer à la promotion de la démocratie, des droits de l'Homme et du développement à travers l'Afrique, surtout par l'augmentation des investissements extérieurs par l'intermédiaire du programme du Nouveau partenariat pour le développement de l'Afrique (NEPAD). Ce programme considère que la paix et la démocratie sont des préalables indispensables au développement durable.
L'Unione africana (UA) è un'organizzazione internazionale comprendente tutti gli Stati africani, con sede ad Addis Abeba, in Etiopia. Les objectifs de l'UA comportent la création d'une banque centrale de développement.
Si tratta di un'organizzazione internazionale molto giovane, nata ufficialmente con il primo vertice dei capi di Stato e di governo del 9 luglio 2002 a Durban, in Sudafrica, durante il quale ne assunse la presidenza Thabo Mbeki, presidente sudafricano. Nel corso del vertice, al quale presenziava tra gli altri il segretario generale delle Nazioni Unite Kofi Annan, furono sottoscritti i primi atti riguardanti gli organi dell'Unione, ovvero il protocollo relativo allo stabilimento del Consiglio di pace e sicurezza e lo statuto della commissione, e furono stabilite regole e procedure per l'Assemblea, il consiglio esecutivo e il comitato dei rappresentanti permanenti.
Le fasi del processo di sviluppo precedenti al vertice di Durban avvennero all'interno dell'Organizzazione dell'unità africana. Nella sessione straordinaria del 1999 a Sirte, in Libia, (luogo di nascita del Leader libico Mu'ammar Gheddafi promotore dell'organizzazione, anche con cospicui capitali) l'Organizzazione decise la nascita della nuova Unione.
Il Sahara Occidentale è ammesso come Repubblica democratica araba Sahrawi, pur non essendo a tutti gli effetti indipendente trattandosi di un territorio conteso con il Marocco.
Nel 2000 fu adottato l'atto costitutivo, che entrò in vigore il 26 maggio 2001, un mese esatto dopo la sottoscrizione della Nigeria, il trentaseiesimo Stato ad averlo ratificato. Come previsto dall'atto per un anno vi fu coesistenza tra le due organizzazioni.
Il 15 agosto 2002 le è stato riconosciuto lo status di osservatore dell'Assemblea generale delle Nazioni Unite.
La Unión Africana (por su acrónimo UA, o AU en inglés u otras de sus lenguas oficiales) es una unión política formada por 55 Estados africanos. La UA se creó el 26 de mayo de 2001 en Adís Abeba y comenzó a funcionar el 9 de julio de 2002 en Durban (Sudáfrica),2 reemplazando a la Organización para la Unidad Africana (OUA). Las decisiones más importantes de la UA son tomadas por la Asamblea de la Unión Africana, una reunión semestral de jefes de Estado y de gobierno de sus Estados miembros. El secretariado de la UA, la Comisión de la Unión Africana, tiene su sede en Adís Abeba, capital de Etiopía.
Африка́нский сою́з (сокращённо АС, АфроСоюз) — международная межправительственная организация, объединяющая 55 государств Африки, правопреемник Организации африканского единства (ОАЕ). Основана 9 июля 2002 года[4]. Важнейшие решения в рамках организации принимаются на Ассамблее Африканского союза — собрании глав государств и правительств государств — членов организации, которое проводится раз в полгода. Секретариат Африканского союза и Комиссия Африканского союза расположены в Аддис-Абебе, столице Эфиопии. В феврале 2009 года было принято решение о преобразовании Комиссии Африканского союза в Полномочный орган Африканского союза (англ. African Union Authority)[5].

 Amapá
Amapá
 Amazonas
Amazonas
 Brazil
Brazil
 Columbia
Columbia
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Gabun
Gabun
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Kenya
Kenya
 Pará
Pará
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Roraima
Roraima
 Sao Tome und Principe
Sao Tome und Principe
 Somalia
Somalia
 Uganda
Uganda

赤道通常指地球表面的点随地球自转产生的轨迹中周长最长的圆周线,长约40,000公里。如果把地球看做一个绝对的球体的话,赤道距离南北两极相等。它把地球分为南北两半球,其以北是北半球,以南是南半球,是划分纬度的基线,赤道的纬度为0°。赤道的78.7%被海洋覆盖,余下的21.3%为陆地。
赤道的纬度被定义为0°,与两条极圈及两条回归线——北回归线和南回归线组成地球表面五条重要的纬线,而赤道又是其中唯一一个大圆。地球赤道在天球上的投影则是天球赤道。
在太阳的季节性视运动中,每年经过赤道两次,分别在春分、秋分。此时太阳光在赤道处与地球表面垂直,即直射赤道。
由于太阳几乎全年都垂直地升落,赤道上看到的日出和日落是地球表面最快的。赤道上的昼长(日出到日落)也几乎全年保持不变[1];由于大气折射[2],以及日出日落是太阳的边缘而非中心触及地平线的缘故,每天的白昼都比夜晚长约14分钟。
Der Äquator eines Planeten oder sonstigen rotationsellipsoiden Himmelskörpers ist der auf seiner Oberfläche angenommene Großkreis, auf dessen Ebene (der Äquatorebene) die Rotationsachse senkrecht steht.[1] Die Erdoberfläche wird vom Äquator in eine Nord- und eine Südhälfte unterteilt, woher der lat. Name „Gleichmacher“ (veraltet „Gleicher“) stammt. Er ist Bezugskreis für die parallelen Kleinkreise, die zur Bemaßung der Erde in Nord-Süd-Richtung mit Hilfe von Breitenkreisen verwendet werden. Er selbst hat die geographische Breite 0°.
Der Schnitt der Äquatorebene der Erde mit der um die Erde gedachten Himmelskugel ist der Himmelsäquator.
In der Geometrie wird der Begriff Äquator allgemein auf die Kugel in Verbindung mit einer durch ihren Mittelpunkt festgelegten Achse angewendet.
Der 5199 Meter hohe Batian ist nach dem Kibo der zweithöchste Berg Afrikas und der höchste im Hochgebirge des Mount-Kenya-Massivs. Er liegt etwa 140 Kilometer nordöstlich der kenianischen Hauptstadt Nairobi im Zentrum des Landes. Seine Dominanz beträgt 324 Kilometer, die Schartenhöhe 3825 Meter.[1]
Die Erstbesteigung des Batian gelang am 13. September 1899 dem Briten Halford Mackinder gemeinsam mit César Ollier und Joseph Brocherel.[2]
Wie bei fast allen der sogenannten Seven Second Summits ist auch hier die Besteigung erheblich anspruchsvoller als auf den höchsten Berg des Kontinents. Der Batian ist zwar fast 700 Meter niedriger als der Kibo und erfordert dadurch weniger Akklimatisierung an die Höhenluft. Allerdings führen auf den Kibo einfache Trekkingpfade, während die schroffe Felsspitze des Batian Kletterkenntnisse verlangt; die einfachste Route wird mit 5.6 bis 5.8 auf der Sierra-Skala bewertet, was V− bis VI− auf der UIAA-Skala entspricht.
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Belarus
Belarus
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Cuba
Cuba
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine

 Party and government
Party and government
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam


Afghanistan Ägypten Algerien Angola Antigua und Barbuda Äquatorialguinea Äthiopien Aserbaidschan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesch Barbados Belarus Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivien Botswana Brunei Burkina Faso Burundi Chile Demokratische Republik Kongo Dominica Dominikanische Republik Dschibuti Ecuador Elfenbeinküste Eritrea Eswatini Fidschi Gabun Gambia Ghana Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Indien Indonesien Irak Iran Jamaika Jemen Jordanien Kambodscha Kamerun Kap Verde Katar Kenia Kolumbien Komoren Kuba Kuwait Laos Lesotho Libanon Liberia Libyen Madagaskar Malawi Malaysia Malediven Mali Marokko Mauretanien Mauritius Mongolei Mosambik Myanmar Namibia Nepal Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Nordkorea Oman Osttimor Pakistan Palästina Panama Papua-Neuguinea Peru Philippinen Republik Kongo Ruanda Saint Lucia Sambia São Tomé und Príncipe Saudi-Arabien Senegal Seychellen Sierra Leone Simbabwe Singapur Somalia Sri Lanka St. Kitts und Nevis St. Vincent und die Grenadinen Südafrika Sudan Suriname Syrien Tansania Thailand Togo Trinidad und Tobago Tschad Tunesien Turkmenistan Uganda Usbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vereinigte Arabische Emirate Vietnam Zentralafrikanische Republik
Die Bewegung der Blockfreien Staaten (kurz Bewegung der Blockfreien oder Blockfreien-Bewegung, englisch Non-Aligned Movement) ist eine Internationale Organisation von Staaten, deren erklärtes Ziel es war, sich im Ost-West-Konflikt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg neutral zu verhalten und keinem der beiden Militärblöcke anzugehören. Die Gründung der Organisation ging auf eine Initiative des jugoslawischen Präsidenten Josip Broz Tito, des ägyptischen Staatschefs Nasser, des indischen Premiers Nehru sowie des indonesischen Präsidenten Sukarno zurück. Die Organisation konstituierte sich 1961 auf ihrer ersten Sitzung in Belgrad.[1] Ihr traten viele ehemalige afrikanische und asiatische Kolonien bei, die sich soeben erst als Staaten konstituiert hatten oder noch um ihre Unabhängigkeit rangen.[2]
Die Organisation verurteilte die Blockbildung in der Zeit des Ost-West-Konfliktes wegen der Gefahr eines Dritten Weltkrieges und setzte sich für die friedliche Koexistenz und Abrüstung ein. Die steigende Zahl der Mitglieder machte es der Organisation jedoch zunehmend schwer, sich auf eine gemeinsame Politik zu einigen. Mit der Auflösung des Warschauer Paktes Anfang der 1990er Jahre verlor sie an Bedeutung. Die heterogene Zusammensetzung der Bewegung machte es schwer, gemeinsame Ziele zu definieren und zu verfolgen.[3] Die Staaten der Blockfreien-Bewegung vertreten 55 Prozent der Weltbevölkerung und halten nahezu zwei Drittel der Sitze in der UN-Generalversammlung.
Das Ziel der Organisation ist die Gleichberechtigung zwischen den Staaten und eine positive wirtschaftliche Entwicklung der Mitgliedstaaten.
不结盟运动(英语:Non-Aligned Movement, NAM)是一个拥有120个成员国和17个观察员国的松散国际组织[3]。它成立于冷战时期,其成员国奉行独立自主的外交政策,不与美苏两个超级大国中的任何一个结盟。联合国中有三分之二的会员是该组织的成员国,全球约55%的人口也生活在不结盟运动国家。不结盟运动定期举行首脑会议,到目前为止已经在前南斯拉夫、埃及、赞比亚、阿尔及利亚、斯里兰卡、古巴、印度、津巴布韦、印尼、哥伦比亚、南非、马来西亚、塞尔维亚、委内瑞拉、阿塞拜疆和乌干达[4]举行会议。
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Australia
Australia
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Dominica
Dominica
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 India
India
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nauru
Nauru
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Uganda
Uganda
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 Cyprus
Cyprus

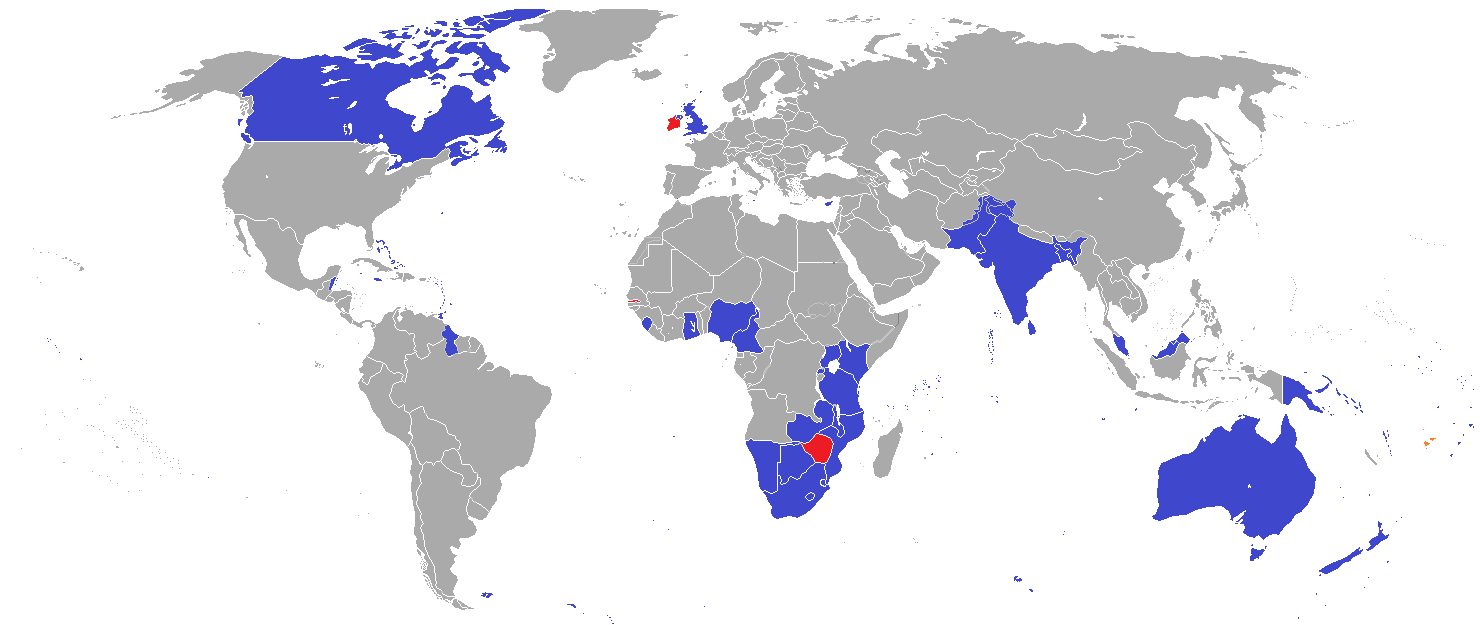
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].


东非大裂谷(Great Rift Valley),位于非洲东部,是一个在3500万年前由非洲板块的地壳运动所形成的地理奇观,纵贯东非的大裂谷是世界上最大的断裂带,属于生长边界。其所形成的生态、地理和人类文化都相当独特,目前观光的主要景点则由肯尼亚进入。东非大裂谷的整个形状可画成不规则三角形,最深达2000米,宽30公里至100公里,全长6000公里(3700英里),是世界最长的不连续谷,由探险家约翰·华特·古格里所命名。东非大裂谷的详细地理位置以三角形的三个点来描述的话,南点在莫桑比克入海口,西北点则远到苏丹尼罗河,北点则可进入死海。中间有相当多个湖泊、火山群。
Der Große Afrikanische Grabenbruch (englisch Great Rift Valley oder East African Rift System (EARS)) ist ein Grabenbruch, der sich von Ostafrika nach Südwestasien erstreckt.
Der Grabenbruch besteht aus einer Abfolge von divergenten Plattengrenzen. Das Rote Meer ist durch die Abspaltung der Arabischen Platte von der Afrikanischen Platte während der letzten 35 Millionen Jahre entstanden. Es wird angenommen, dass sich von der Afrikaplatte entlang des Grabenbruches eine neu entstehende Platte abtrennt, für die die Bezeichnung Somaliaplatte verwendet wird.
Erforscht und in seiner geologischen Bedeutung erkannt wurde der Grabenbruch zuerst durch den Schotten John Walter Gregory, nach dem er auch manchmal Gregory-Rift genannt wird.
Aufgrund der aktiven Tektonik ist der Grabenbruch eine Region mit vielen Erdbeben.

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Financial
Financial
 Climate
Climate
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 United Nations
United Nations