
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Vietnam
Vietnam

ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム(博鰲アジアフォーラム、Boao Forum for Asia、略称BFA、中国語:博鳌亚洲论坛、ピンイン:Bóáo Yàzhōu Lùntán)は、中華人民共和国に本拠を置く国際非営利組織。
スイスのダボスで開催されている世界の政治家・財界人・知識人が集まる国際会議(ダボス会議)を主催する世界経済フォーラムにならい、そのアジア版を目指して、中国政府の全面的支援を受けて構想された。2001年2月27日の設立にはアジアの25カ国とオーストラリアの計26カ国が参加している。
ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム主催の最初の国際会議は2002年4月12日・4月13日に開催され、日本からは小泉純一郎内閣総理大臣が出席して演説を行った[1]。国際会議の会場は、2001年の発足会議以来、中国・海南省の海浜リゾート地・ボアオ(博鰲、海南島東海岸の瓊海市)に固定されている。会議は毎年行われ、各国首脳や大企業経営者、学者、NGO代表など政府・民間のハイレベルの人材が集い、アジアや世界の経済動向、金融政策、経済統合、経済投資、国際協力、社会問題、環境問題などに関する討議が行われる。また多くの経済人や政治家、社会運動家らが直接話し合い、国家間協力や企業提携などのトップ会談が持たれる。 過去の議題には中国の世界貿易機関(WTO)への加入問題、90年代後半のアジア金融危機問題などが取り上げられ、2004年には中国の地政学的な「和平崛起」(平和的台頭)戦略の可否が議題となった。
The Boao Forum for Asia (BFA; Chinese: 博鳌亚洲论坛; pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán) is a non-profit organisation that hosts high-level forums for leaders from government, business and academia in Asia and other continents to share their vision on the most pressing issues in this dynamic region and the world at large. BFA is modelled on the World Economic Forum held annually in Davos, Switzerland. Its fixed address is in Bo'ao, Hainan province, China, although the Secretariat is based in Beijing. The forum, sometimes known as the “Asian Davos”, takes its name from the town of Boao, located in China’s southern Hainan province, which has been the permanent venue for its annual conference since 2002.[1]
The Forum is committed to promoting regional economic integration and bringing Asian countries even closer to their development goals. Initiated in 1998 by Fidel V. Ramos, former President of the Philippines, Bob Hawke, former Prime Minister of Australia, and Morihiro Hosokawa, former Prime Minister of Japan, the Boao Forum for Asia was formally inaugurated in February 2001. The founding of the BFA was driven by the People's Republic of China and founded by 26 Asian and Australasian states on 27 February 2001. The organisation held its first meeting from 12–13 April 2002.
Discussions at the BFA focus on economics, integration, cooperation, society and the environment. In the past the forum also addressed China's entry into the World Trade Organization, as well as Southeast Asia's economic crisis during the 1990s. The geopolitical strategy 'China's peaceful rise' was a topic of discussion for the forum in 2004. In addition to its annual meeting, the BFA also sponsors other forums and meetings related to Asian issues.
El Foro de Boao para Asia (en chino: 博鳌亚洲论坛, pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán), conocida también por sus siglas en inglés BFA, es una organización no lucrativa que organiza foros de alto nivel para líderes del gobierno, los negocios y la academia en Asia y otros continentes para compartir su visión sobre los asuntos más apremiantes en esta región y en el mundo entero. El Foro Boao es el modelo del Foro Económico Mundial que se celebra anualmente en Davos, Suiza. Tiene su sede en Bo'ao, Hainan, China, aunque la Secretaría se encuentra en Pekín.
El Foro tiene como objetivos promover la integración económica regional y acercar a los países asiáticos hacia sus metas de desarrollo.1 Fue creado en 1998 por Fidel V. Ramos, expresidente de Filipinas, Bob Hawke, ex primer ministro de Autralia y Morihiro Hosokawa, ex primer ministro de Japón.2 El Foro de Boao para Asia fue formalmente inaugurado en febrero de 2001. La creación del foro fue liderado por la República Popular de China y fundada por 26 países de Asia y Australasia el 27 de febrero de 2001. La organización tuvo su primera reunión el 12 y 13 de abril de 2002.
Las discusiones del Foro Boao se centran en economía, cooperación, sociedad y medio ambiente. En e pasado el foro también abordaba el ingreso de China en la Organización Mundial del Comercio, así como la crisis financiera asiática de los años noventa. Además de su reunión anual, el foro también patrocina otros foros y reuniones relacionados con temas asiáticos.
Боаоский Азиатский Форум, БАФ (кит: 博鳌亚洲论坛; пиньинь: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán, англ: Boao Forum for Asia, аббр: BFA), также известен как «Восточный Давос» — неправительственная и некоммерческая международная организация, имеющая своей целью поддержку и развитие экономического обмена, взаимодействия и сотрудничества как в Азии, так и за её пределами путём проведения ежегодных встреч высокого уровня с участием представителей правительственных, деловых, промышленных и научных кругов и обсуждения актуальных экономических, социальных, экологических и др. проблем.
Учреждён в 2001 году. Ежегодные конференции в Боао проводятся с 2002 года.
Главный офис организации находится в г. Боао, пров. Хайнань, КНР.
В 2018 году Боаоский азиатский форум /БАФ/ пройдет 8-11 апреля. Главными темами мероприятия станут реформы, открытость, инновации и "Пояс и путь"[1].
韩国东南端的港市,位于首尔南东部450km处,东经129度,北纬35度。东南滨朝鲜海峡(韩国称:大韩海峡,Korea Strait ),与日本对马岛相望;西临洛东江。西北山地耸峙,南有群岛屏障,为著名深水良港,半岛南部门户。总面积是758,21平方公里,人口400万,人口居住面积是386万多平(2000年为 准),划分为1个郡和15个区,是韩国第二大城市。釜山西部是落东江下流,南部是大韩海峡。所以有很多海水浴场、温泉等,年中有非常多的游客到此来休假。 可以称得上第二个首都的釜山在1万5千年前旧石器时代开始就开始有人居住,是历史悠久的城市。这里不但有梵鱼寺、忠烈祠等重要的文化财产,还有金井山城等 风景优美的景点。又是韩国的第一港口城市,是海外贸易活跃的地方。市政府所在地是中区中央洞7街20番地。原为渔村。1441年开港,1876年辟为贸易 港。二十世纪初,京釜、京义线通车后发展迅速。1929年定为庆尚南道首府。岭南工业地带核心,以纺织、食品、化学、造船、电子、建材工业为主。近郊多果 园、菜园和养猪、养鸡场。附近盛产稻。暖流通过沿岸,远洋渔业基地,西港为著名渔港。海陆空交通枢纽。南部最大贸易港,输出以水产品、纺织品、铁、石墨、 机械制品为主。有东莱城迹、温泉、海云台等旅游地。
釜山的历史 看到现在为止出土的先史时代的遗迹和遗物,可以得知釜山是从新石器时代以后才开始真正有人开 始居住。釜山是1876年由日本建立成为开港场,之后一直在经济发展上起着飞跃的作用,逐渐发展成为城市。1905年开通了连接首尔和釜山的庆釜线之后, 开始进入很多码头和港口的港湾设施。1925年庆南道厅迁移到釜山,釜山就逐渐发展为城市,1950年韩国战争时这里还被认定为临时的首都。1963年被 指定为直辖市,1960~70年代对国家经济发展起了先导的作用,1995年根据城市的扩张被予名为‘釜山广域市’。釜山(Busan)于2002年成功 举办了第14届亚运会。
(Quelle:http://goabroad.sohu.com/20090420/n263510611.shtml)
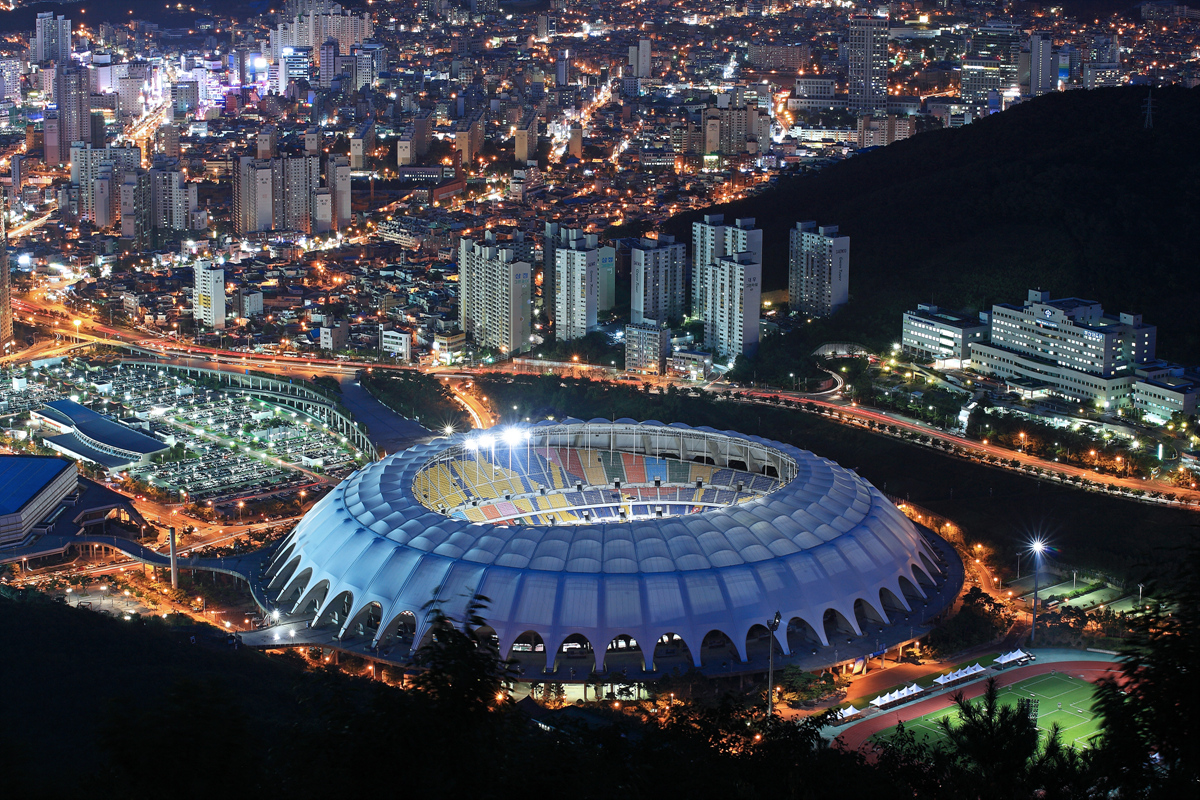
釜山广域市(朝鲜语:부산광역시/釜山廣域市 Busan gwangyeoksi */?),简称釜山,是韩国继首尔之后的第二大城市。2010年,釜山市人口360万,[2]釜山都市圈(包括周边的金海市和梁山市)的人口有400多万。[3] 釜山是韩国最大港口城市也是世界第5大港。[4] 釜山位于韩国东南端,洛东江与水营河之间的峡谷是釜山最密集的地区。行政上,釜山是个广域市,包括15个主要行政区和一个郡。
釜山是个国际会议中心,是2002年亚运会和2005年APEC的承办城市,也是2002年世界杯足球赛的一个分会场[5] 位于釜山的新世界Centum City是世界上最大的百货商店,并已被记录为吉尼斯世界纪录。
Busan (kor. 부산, Hanja 釜山, frühere Schreibweisen: Pusan; Fusan[2][3]) ist nach der Hauptstadt Seoul die zweitgrößte Stadt Südkoreas und liegt am südöstlichen Ende der Koreanischen Halbinsel an der Küste des Japanischen Meeres.Busan gehört zur Provinz Gyeongsangnam-do, ist aber seit dem Jahr 1963 politisch eine unabhängige Einheit.
Der Name Busan bedeutet etwa „Kesselberg“ und spielt auf die Geländegestalt an, die eine amphitheater-artige, von einer Bergkette umgebene Ebene an der Küste ist. Die Stadt liegt an der Mündung des Nakdonggang und hat in der über die politischen Grenzen hinausgehenden Agglomeration 4.562.012 Einwohner (2005). Die vielen Buchten machen Busan zu einem guten Naturhafen. Während die Ostküste wenig Inseln oder Buchten zu bieten hat, findet man diese umso mehr, folgt man dem großzügigen Bogen der Küste nach Südwesten zur Südküste. In der Stadt gibt es mehrere Hügel und Berge zwischen 100 und 400 Metern Höhe, den Gudeoksan, den Baegyangsan, den Sanghaksan, den Hwangnyeeongsan, den Gaejwasan und Jangsan, die meist zu Parks oder Naherholungswäldern ausgebaut sind. Der Hafen wird durch die direkt vor der Küste liegende Insel Yeongdo unterteilt und geschützt.
Der bis zu 700 Meter hohe Höhenzug Geumjeongsan nördlich Busans ist ein beliebtes Ausflugsziel und Erholungsgebiet für die Einwohner der Stadt. Busan zieht auch nationale Touristen an, speziell mit dem Strand von Haeundae.
釜山広域市(プサンこういきし、韓国語: 부산광역시、英語:Busan)は、大韓民国南東部に位置する広域市。韓国第2の都市である。対馬海峡に面し、古くから日本と朝鮮半島とを結ぶ交通の要衝として栄えてきた港湾都市である。首都ソウルに次ぐ韓国第二の都市として、政治・経済・文化の面で重要な役割を担ってきた。
朝鮮半島南東端に位置し、韓国の主要都市中で最も日本の近くに位置する。対馬海峡西水道(朝鮮海峡)を挟んで対馬を望む事ができ(海雲台区の冬柏などから肉眼で見える日が年間約60日あり)、下関市・福岡市までは200kmほどの距離である。このため、日本との関係も密接であり、とくに下関市・福岡市などの北部九州や山口県との関係が深い。
現在は広域市に位置づけられ、道には属さないが、1962年までは慶尚南道に属していた。道から独立後も1983年6月まで慶尚南道庁の所在地であった。朝鮮の地方区分でいう慶尚道地方(嶺南地方)の中心都市である。
Busan (Korean pronunciation: [pu.sɐn]), formerly known as Pusan and now officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second most-populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.5 million inhabitants.[5] It is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern Korea, with its port—Korea's busiest and the 9th-busiest in the world[a]—only about 120 miles (190 km) from the Japanese islands of Kyushu and Honshu. The surrounding "Southeast Economic Zone" (including Ulsan and South Gyeongsang) is now South Korea's largest industrial area.
Busan is divided into 15 major administrative districts and a single county, together housing a population of approximately 3.6 million. The full metropolitan area, including the adjacent cities of Gimhae and Yangsan, has a population of approximately 4.6 million. The most densely built-up areas of the city are situated in a number of narrow valleys between the Nakdong and the Suyeong Rivers, with mountains separating most of the districts. The Nakdong is Korea's longest river and Busan's Haeundae Beach is also the country's largest.
Busan is a center for international conventions, hosting APEC in 2005. It is also a center for sports tournaments in Korea, having hosted the 2002 Asian Games and FIFA World Cup. It is home to the world's largest department store, the Shinsegae Centum City.[7] Busan was added to the UNESCO Creative Cities Network as a "City of Film" in December 2014.[8]
Pusan (부산광역시, hanja : 釜山廣域市, romanisation révisée : Busan gwangyeoksi ; littéralement : Ville métropolitaine de Busan (Busan (釜山) signifiant montagne-chaudron)1, orthographiée officiellement sous Busan est une ville portuaire très importante de Corée du Sud, qui compte plus de 3 700 000 habitants. Historiquement connue sous le nom de « Pusan », cette métropole est désormais officiellement appelée Busan (Busan Metropolitan City). C'est la deuxième ville la plus peuplée de Corée du Sud après Séoul. C'est le centre économique, culturel et éducatif du sud-est de la Corée, avec son port le plus achalandé et le 9e le plus achalandé au monde, à environ 190 km des îles japonaises de Kyushu et de Honshu. La « Zone économique du Sud-est » (incluant Ulsan et le Gyeongsang du Sud) est maintenant la plus grande zone industrielle de la Corée du Sud.
Pusan est divisée en 15 districts administratifs majeurs et un seul comté. La zone métropolitaine complète, y compris les villes adjacentes de Gimhae et Yangsan, a une population d'environ 4,6 millions d'habitants. Les zones les plus densément construites de la ville sont situées dans un certain nombre de vallées étroites entre les fleuves Nakdong et Suyeong, avec des montagnes séparant la plupart des districts. Le Nakdong est le plus long fleuve de Corée et la plage Haeundae de Pusan est également la plus grande du pays.
Pusan est un centre de conventions internationales ; elle a accueilli en 2005 la Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (APEC). C'est aussi un centre de tournois sportifs en Corée, ayant accueilli les Jeux Asiatiques et la Coupe du Monde de la FIFA en 2002. Pusan abrite par ailleurs le plus grand magasin du monde, la Shinsegae Centum City.
Pusan[1][2][3][4][5] (부산 광역시?, 釜山廣域市?, Busan gwang-yeoksiLR), conosciuta anche come Busan[6][7], è la città portuale più grande della Corea del Sud. Con la sua popolazione di 3.650.000 abitanti[8], Pusan è la seconda città più popolata della Corea del Sud, dopo la capitale Seul. Dal punto di vista amministrativo è una città metropolitana autoamministrata con rango di provincia.
Busan (hangul: 부산, RR: Busan, MR: Pusan)?, pronunciado: [pu.san], oficialmente Ciudad Metropolitana de Busan (hangul: 부산광역시, RR: Busan-gwangyeoksi, MR: Pusan-gwangyŏkshi)? y anteriormente conocida como Pusan, es una de las seis ciudades metropolitanas que, junto a las nueve provincias, la ciudad especial y la ciudad autónoma especial, forman Corea del Sur.
Está ubicada en el extremo sureste del país, limitando al norte con Gyeongsang del Sur, al noreste con Ulsan y al sur con el mar del Japón. Es la segunda ciudad más grande de Corea del Sur por detrás de Seúl, con una población de aproximadamente 3,6 millones de habitantes.
Presenta una amplia extensión, con distritos separados por las montañas que la rodean al norte y oeste y por la cuenca del río Nakdong, el más largo del sur. Durante el siglo XX ha vivido una completa transformación, primero con la llegada de refugiados de la guerra de Corea y después con el desarrollo económico del país, en el que Busan se convirtió en centro de referencia. Dispone del puerto más importante de Corea del Sur y el quinto mayor del mundo por tonelaje de carga.1 Además es la sede de la Bolsa de Corea del Sur y en 2005 organizó la cumbre del Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico.2
Busan fue subsede de los Juegos Olímpicos de Seúl 1988 para las pruebas marítimas, sede de la Copa Mundial de Fútbol de 2002 y organizadora de los XIV Juegos Asiáticos de 2002, lo que la convierte en una de las localidades más relevantes en el ámbito deportivo nacional. En el plano cultural, celebra desde 1996 el Festival Internacional de Cine de Busan.
En 1963 se separó de la región de Gyeongsang del Sur y desde 1995 es una de las ciudades metropolitanas del país.3
Пуса́н (кор. 부산?, 釜山?) — город в Республике Корея. Является городом-метрополией (до 1995 — городом прямого подчинения).
Второй по величине город страны, после Сеула. Крупнейший порт страны, известный как «Морская столица Республики Корея». Официальное название города — Город-метрополия Пусан (кор. 부산광역시?, 釜山廣域市? Пусан-кванъёкси). Пусан расположен на юго-восточной оконечности Корейского полуострова на берегу Корейского пролива. Наиболее густо застроенные районы расположены в нескольких узких долинах между реками Нактонган и Суёнган, горы служат естественными границами некоторых городских районов.
В 2002 году в Пусане проводились Азиатские игры и чемпионат мира по футболу FIFA World Cup, а в 2005 году город стал столицей форума АТЭС. 14 ноября 2005 года Пусан вместе с Ульсаном был объявлен претендентом на проведение Олимпийских Игр 2028 года.
Пусан — один из современнейших городов Азии. Город известен своими многочисленными небоскрёбами и другими архитектурными достопримечательностями. Здесь находится самый большой универмаг в мире — «Синсеге Сентум Сити» В городе также возводятся другие мегасооружения — небоскрёб «Сентум Лидерс Марк» и самый высокий офис в стране «Пусанский международный финансовый центр».








 Australia
Australia
 Badminton World Federation
Badminton World Federation
 Badminton World Federation
Badminton World Federation
 BWF Super Series
BWF Super Series
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 All England Open Badminton Championships
All England Open Badminton Championships
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Australian Open
Australian Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 China Open
China Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Denmark Open
Denmark Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Hong Kong Open
Hong Kong Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 India Open
India Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Indonesia Open
Indonesia Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Japan Open
Japan Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Korea Open
Korea Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Malaysia Open
Malaysia Open
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Open de France
Open de France
 BWF World Superseries
BWF World Superseries
 Singapore Open
Singapore Open
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 England
England
 France
France
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore



昌德宫(韩语:창덕궁)位于韩国首尔市钟路区,由朝鲜王朝(1392年–1897年)一众国王所建,是“朝鲜五大宫殿”之一。1997年被联合国教科文组织登入为世界文化遗产。[1] 位处景福宫东面,作为其之外的离宫建筑。导致昌德宫与昌庆宫—得到“东阙”的称号 (동궐)。昌德宫是最受许多朝鲜王子欢迎的宫殿,并保留了许多未被纳入到景福宫建筑的朝鲜三国时代时期的元素。事实是,昌德宫的建筑物是与周遭的自然地形混合而不是强行混合。
Der Changdeokgung (Palast der glänzenden Tugend) ist einer von fünf noch erhaltenen Königspalästen aus der Joseon-Dynastie in Südkoreas Hauptstadt Seoul.
Der Changdeokgung wurde zwischen 1405 und 1412 als zweiter Palast neben dem Gyeongbokgung (Palast des glänzenden Glücks), der eigentlichen Hauptresidenz der Joseon-Dynastie, von dem König "Taejong" errichtet. Da er östlich des Gyeongbokgung liegt, wurde der Changdeokgung auch Dongwol (Ostpalast) genannt. Bis er 1592 in der Hideyoshi-Invasion von kriegerischen Japanern in Brand gesetzt und 19 Jahre später vom 15. König Kwan Naegum erstmals wieder errichtet wurde. Nach der Wiedererrichtung diente er im Jahre 1872 als königliche Residenz und Sitz der Regierung. Ab 1907 lebte im Changdeokgung Koreas letzter König, König Sunjong. Auch nach seinem Rücktritt 1910 und seinem Tod 1926 lebten hier die letzten Mitglieder der königlichen Familie bis 1989. Bis zur Amtszeit des vorletzten Königs sollten 13 Herrscher im Palast wohnhaft gewesen sein.
Zwischen 1910 und 1945, als Korea eine Provinz Japans war, galt die Japanische Sprache als Nationalsprache. Die Hanja bzw. Kanji des Palastnamens (jap. 昌徳宮) wurden daher japanisch ausgesprochen, und er hieß in dieser Zeit Shōtokyū.
昌徳宮 (しょうとくきゅう、朝鮮語読み チャンドックン)は韓国ソウル特別市に所在する李氏朝鮮の宮殿。
正宮である景福宮に対する離宮[1]として創建された。現在の韓国国内の宮殿の内、最も創建時の面影を残している宮殿であり、日本の梨本宮家から嫁ぎ、大韓帝国最後の皇太子李垠の妃となった李方子(まさこ)もこの宮殿で暮らした。
正門にあたる敦化門は大韓民国最古の門といわれる。また、敦化門をくぐった先にある錦川橋は大韓民国最古の橋とされる。儀式の執り行われた正殿の仁政殿、国王が執務をしていた宣政殿、王と王妃の寝殿だった大造殿など13棟の木造建築が現存している。宮殿の北に広がる李朝時代の王朝庭園である後苑は秘苑とも呼ばれ、園内には多くのあずまやや人工池などがあり、韓国造園技術の極致といわれる。現在のものは1623年に再建された景観である。
Changdeokgung (Hangul, 창덕궁, 昌德宮; literally, "Prospering Virtue Palace"), also known as Changdeokgung Palace or Changdeok Palace, is set within a large park in Jongno-gu, Seoul, South Korea. It is one of the "Five Grand Palaces" built by the kings of the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1897).[1] As it is located east of Gyeongbok Palace, Changdeokgung—along with Changgyeonggung—is also referred to as the "East Palace" (동궐, 東闕, Donggwol).
Changdeokgung was the most favored palace of many Joseon princes and retained many elements dating from the Three Kingdoms of Korea period that were not incorporated in the more contemporary Gyeongbokgung. One such element is the fact that the buildings of Changdeokgung blend with the natural topography of the site instead of imposing themselves upon it. It, like the other Five Grand Palaces in Seoul, was heavily damaged during the Japanese occupation of Korea (1910–1945). Currently, only about 30% of the pre-Japanese structures of the East Palace Complex (Changdeokgung together with Changgyeonggung) survive.[2]
Changdeokgung ou Palais de la Prospérité (en hangeul 창덕궁) est un palais situé à Séoul en Corée du Sud. C'est l'un des cinq grands palais construits par les rois de la dynastie Joseon. Se trouvant à l'est du Palais de Gyeongbokgung, Changdeokgung est souvent appelé Palais de l'Est.
Changdeokgung était le palais favori de nombreux rois de la dynastie Joseon. Il présente de nombreuses caractéristiques[Quoi ?] spécifiques du Trois Royaumes de Corée, qui n'apparaissent plus dans l'architecture plus formaliste du Gyeongbokgung. Par exemple, les bâtiments de Changdeokung se confondent avec la topographie du site au lieu de s'imposer sur la nature.
Changdeokgung (in coreano: 창덕궁 in hangŭl, 昌德宮 in hanja, letteralmente il palazzo della prospera virtù) è un palazzo che si trova all'interno di un parco di Seul, in Corea del Sud. Si tratta di uno dei Cinque grandi palazzi costruiti dai sovrani della Dinastia Chosun; a causa della sua posizione a est del palazzo Gyeongbokgung spesso è chiamato semplicemente palazzo orientale.
Changdeokgung era il palazzo favorito di molti sovrani coreani del Medioevo e mantiene molti dei caratteri tipici dello stile coreano del periodo dei tre regni, come per esempio il fatto che si armonizza nell'ambiente circostante invece di imporvisi.
Changdeokgung (hangul: 창덕궁, hanja: 昌德宮, romanización revisada: Changdeokgung, McCune-Reischauer: Ch'angdŏkkung)? es un conjunto de palacios dentro de un gran parque en Seúl, Corea del Sur. Es uno de los grandes palacios construidos por la Dinastía Chosŏn y, por causa de su localización al este del Palacio de Gyeongbok es muchas veces llamado Palacio del Este.
Ch'angdokkgung era el palacio preferido de muchos reyes de la dinastía de Chosŏn y tiene muchos elementos coreanos datados del período de los Tres Reinos de Corea que no fueron incorparados en el más formal Gyeongbokgung.
Чхандоккун (кор. 창덕궁?, 昌德宮? Дворец Чхандок или Дворец Процветающей Добродетели) — дворцовый комплекс внутри большого парка в Сеуле, Южная Корея. Является одним из «Пяти Больших Дворцов», построенных ванами династии Чосон.
Сооружение дворца началось в 1405 году и было закончено в 1412 году после постройки главных ворот Тонхвамун. Ван Седжо расширил территорию комплекса на 500 тыс. квадратных метров. Дворец был полностью разрушен во время японских нашествий 1592-1598 гг. и восстановлен в 1609 году ваном Сонджо и ваном Кванхэгуном. В следующий раз дворец сгорел в 1623 году после одного из восстаний против Кванхэгуна. Чхандоккун был местом жительства королевского двора и правительства страны до 1872 года, пока не был восстановлен дворец Кёнбоккун. Последний монарх Кореи — император Сунджон жил там до своей смерти в 1926 году.




 Architecture
Architecture
 International cities
International cities
 Important port
Important port

 Sport
Sport
 Party and government
Party and government
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 History
History
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Film & TV Produktion
Film & TV Produktion
 Companies
Companies
 Life and Style
Life and Style