
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Spain
Spain


阿穆德纳圣母主教座堂(西班牙语:Catedral de la Almudena),全名马德里王家阿穆德纳圣母主教座堂(西班牙语:Catedral de Santa María la Real de la Almudena de Madrid),是天主教马德里总教区的主教座堂,位于西班牙首都马德里市中心西侧,北面隔着兵器广场(Plaza de la Armería)与王宫相对。该教堂的主保圣人为阿穆德纳圣母(Virgen de la Almudena),其亦为马德里的主保圣人。
1561年时,西班牙将首都从托莱多迁至马德里,但教会中枢仍然留在托莱多,使得这个新首都一直没有一座主教座堂,虽然西班牙是一个天主教国家。早在16世纪就有修建此教堂的计划,并且已决定将该教堂奉献给阿穆德纳圣母,但迟至1879年才正式开工。在西班牙内战期间,兴建工程曾被迫中断,直到1950年才复工;而该教堂的建筑样式原为哥德复兴式,复工后的建筑外观被改为巴洛克风格,以和白色与灰色建筑立面的王宫相对应。1993年6月15日,该教堂在时任教宗若望·保禄二世的祝圣下正式启用,成为欧洲最新启用的主教座堂。阿穆德纳圣母的原始态像,被供奉于该教堂西侧的小堂内。
Die Almudena-Kathedrale (Santa Iglesia Catedral Metropolitana de Santa María la Real de la Almudena) ist eine römisch-katholische Kathedrale in Madrid (Spanien).
Erste Pläne zur Errichtung einer neuen Kirche, welche man der Hl. Maria von der Almudena (von arab. al-mudayna ‚Zitadelle‘; ein Titel der Gottesmutter Maria als Stadtpatronin von Madrid) widmen wollte, entstanden bereits im 16. Jahrhundert. Doch der Bau der Kathedrale begann nicht vor dem 19. Jahrhundert und wurde erst im Jahr 1993 beendet. In diesem Jahr wurde die Kathedrale von Papst Johannes Paul II. geweiht und zugleich zur Bischofskirche des Erzbistums Madrid erhoben (von der Bistumsgründung 1885 an hatte zunächst die Colegiata de San Isidro als provisorische Kathedrale gedient).
Obwohl die Kirche im neugotischen Stil begonnen wurde, errichtete man die Kathedrale schließlich im Stil des Neoklassizismus, um stilistisch zum angrenzenden Königspalast zu passen. Das Innere der Almudena-Kathedrale ist einzigartig modern, mit einem „Pop-Art“-Dekor, vom Ikonenmaler Kiko Argüello gestaltet.
Am 22. Mai 2004 fand mit der Hochzeit von Kronprinz Felipe von Spanien und Letizia Ortiz Rocasolano die erste königliche Hochzeit in der Kathedrale statt.
Am 7. Februar 2013 konnte ein Sprengstoffanschlag auf die Kathedrale verhindert werden, nachdem ein Geistlicher einen Sprengsatz nahe bei einem Beichtstuhl gefunden hatte. Daraufhin wurde die Kathedrale geräumt und weiträumig abgesperrt, bevor der Sprengsatz entschärft werden konnte.[1]

 Andalusia
Andalusia

 Aragón
Aragón
 Asturias
Asturias

 Cantabria
Cantabria

 Castilla y León
Castilla y León

 Castilla-La Mancha
Castilla-La Mancha
 Cataluña
Cataluña

 Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco
Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco

 Foral Community of Navarra
Foral Community of Navarra

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community

 Extremadura
Extremadura

 Galicia
Galicia

 La Rioja
La Rioja

 Madrid
Madrid

 Murcia
Murcia
 Spain
Spain
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology
 Rad-Schiene-System
Rad-Schiene-System
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology
 Central drive
Central drive

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed traffic
High speed traffic

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology

塞戈维亚位于瓜达拉马山脚下旧卡斯蒂利亚的高原上,坐落在埃里斯马河和克拉莫尔河交汇处一个陡峭的岬角上。
虽然早在史前时期即有人定居在此,但直到公元前146年才有塞戈维亚城的最初记载。历史上该城是工业和政治中心。现为塞戈维亚省的首府。
历史渊源:
在公元前80年被罗马人毁坏而后重建的塞戈维亚城是罗马帝国在西班牙建造的首批城镇之一。经过一段阿拉伯人统治时期后,阿方索六世国王于1088年 重新控制了塞戈维亚,塞戈维亚从此进入了政治和经济繁荣时期。13—15世纪期间,卡斯蒂利亚几代国王都定都塞戈维亚。伊莎贝拉女王于1474年曾在此登 基。公元16世纪,塞戈维亚经历了工业发展的重要时期,并以由摩尔人引进的服装纺织业而闻名于世。
城市布局:
阿方索六世国王于1088年建造的、环绕塞戈维亚整个古城的城防系统被完好保存至今。在中世纪修建的道路网构成了棋盘式的城市布局,它们在阿索格乔 (Azoguejo)广场处交汇。罗马大渡槽位于城市的中心。塞戈维亚城由和谐统一的建筑群组成,这些建筑建于中世纪晚期(11—12世纪)和文艺复兴时 期,这也是塞戈维亚城所经历的两个繁荣时期。著名的具128根立柱的大渡槽、阿方索六世建造的摩尔人国王的宫殿以及16世纪哥特式大教堂是这个城市的重要 建筑。罗马式教堂、穆德哈尔人建筑风格的房屋以及城防建筑也成为具赭石色调的城市风景的一部分。由于拥有许多在漂亮的外观和珍贵的历史价值等方面都十分突 出的建筑群,整个塞戈维亚古城成为了难得的艺术典范。这个城市展现了复杂的历史现实。其邻近城镇的布局、它的街道及其房屋都反映出了不同的文化背景——摩 尔人风格、基督教风格以及犹太教风格——这些文化在中世纪共存于塞戈维亚城,并于16世纪在其工业发展的全盛期达到顶峰。形成于多种风格传统交融的塞戈维 亚是西方城市的杰出典范。(Quelle: www.xiaoyaoyou.info/beta/node/506)


 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Australia
Australia

 California-CA
California-CA
 China
China

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 England
England
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kyūshū
Kyūshū
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 Russia
Russia

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA

美洲杯帆船赛(英语:America's Cup)是赛艇运动中保存的最著名也是最古老的一项体育比赛。
比赛奖杯是银质大口水罐,奖励给来自不同国家的两艘帆船之间举行的九局五胜制比赛的胜者。两艘帆船中,一艘代表卫冕冠军游艇俱乐部,另一艘则代表俱乐部挑战奖杯。
美洲杯帆船赛源于1851年8月22日,一艘由代表纽约游艇俱乐部(New York Yacht Club,NYYC)的财团拥有的30.86米长纵帆船“美洲号”(America),同15艘代表皇家快艇舰队(Royal Yacht Squadron)的帆船在英国南部的怀特岛附近比赛。“美洲号”最终以领先20分钟胜出。拥有“美洲号”的财团后来将奖杯通过馈赠契约捐献给纽约游艇俱乐部。由此,奖杯被托管成为一项鼓励各国之间友谊竞赛的“挑战”奖品。
在当时公认无敌的英国海上霸权遭受如此打击后,一系列英国财团试图赢回奖杯。但纽约游艇俱乐部在超过132年的25次挑战中保持不败,成为体育运动史上最长的连胜纪录。1930年以前,这项赛事一直在纽约港附近举行,余下的NYYC全盛时期内则改在罗德岛的纽波特(Newport,Rhode Island)举行。
Der America’s Cup ist die älteste noch heute ausgetragene Segelregatta. Der Preis ist ein Wanderpokal und hat seinen Ursprung in einer Regatta rund um die britische Insel Isle of Wight im Jahre 1851.[1] Er ist benannt nach seiner erstmaligen Gewinnerin, der Yacht America des New York Yacht Club (NYYC).
Um den America’s Cup treten die Boote zweier Yachtclubs – Verteidiger und Herausforderer – in mehreren Wettfahrten gegeneinander an. Die Yacht, die eine vorher festgelegte Anzahl von Wettfahrten gewinnt, gewinnt den Cup. Laut der Stiftungsurkunde bestimmt der Verteidiger das Segelrevier. Die Stiftungsurkunde sieht vor, dass Verteidiger und Herausforderer innerhalb gewisser Grenzen Vereinbarungen über die Regeln treffen können, z. B. was die Anzahl der Wettfahrten betrifft.[2]
Von der ersten Verteidigung 1870 bis zur 20. Regatta im Jahr 1967 gab es jeweils nur einen Herausforderer. Im Jahr 1970 gab es erstmals mehrere Herausforderer, so dass der veranstaltende New York Yacht Club sich einverstanden erklärte, den offiziellen Herausforderer durch eine Vorausscheidung zu ermitteln. Zwischen 1983 und 2007 bis zum zeitweiligen Rückzug des Sponsors Louis Vuitton und ab 2013 erneut wurde der Herausforderer durch den Louis Vuitton Cup ermittelt. Schon die Teilnahme am Louis Vuitton Cup setzte großes finanzielles Engagement voraus: die Budgets der High-Tech-Yachten betrugen teilweise über 100 Mio. Dollar. Die Yachten mussten im Land des angemeldeten Teams gebaut werden. Wesentliche Neuerungen ergaben sich bei den letzten beiden ACs. 2010 segelten das erste Mal sowohl Verteidiger wie Herausforderer mit Mehrrumpfbooten. 2013 waren Katamarane vereinbart und die teilnehmenden Teams konstruierten „Tragflügelkatamarane“ die über 40 Knoten (75 km/h) schnell segelten. Für 2017 wurden die Boote „AC50F Katamaran“ von ehemals 72 Fuß (fast 22 m) auf 50 ft (gut 15 m) verkürzt, blieben 24 m hoch und wurden im Training erstmals 50 kn (92 km/h) schnell.[3]
アメリカスカップあるいはアメリカズカップ[1](英: America's Cup)は、1851年より現在まで続く国際ヨットレース。また、その優勝杯の名。その成立は近代オリンピックより45年、サッカーのワールドカップより79年、全英オープンよりも9年早く、継続して使用されている世界最古のスポーツトロフィーとして広く一般に認知されている。[2][3]
名称の由来は最初の優勝艇の『アメリカ号』の名を冠した『アメリカ号のカップ』であり、決して『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』という意味ではない。しかし、その後132年に亘ってアメリカ合衆国のヨットクラブがカップを防衛してきたため、事実上『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』と同じ定義で称される。
競技の本質は、カップの寄贈者が記した贈与証書の規定に基づき、アメリカズカップを掛けてマッチレース(1対1)形式で争われるヨットクラブ間の国際親善レースである。しかし、使用されるヨットは出場国で建造しなければならないため、参加各国の造船工学・建築工学・材料工学・流体力学・航空力学・気象学などの最先端技術や軍事からの応用技術が投入される等、参加国の威信を賭けた国別対抗レースとしての一面も持ち合わせている。またこれら最新ヨットにはオリンピックメダリストら多数のトップセーラーが乗り組むことあり、一般にヨットレース全般、或いはインショア(沿海)レースの最高峰として位置づけられており、別名「海のF1」とも称される。
The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
La Coupe de l'America (America's Cup) est une compétition nautique internationale à la voile, voulue par ses initiateurs comme un défi amical et perpétuel entre Yacht Clubs de différentes nations et définie sous cette dénomination en 1857 par les membres du New York Yacht Club (NYYC)2, vainqueurs, six ans plus tôt, en 1851, avec la goélette America, de la régate internationale originelle, organisée autour de l'île de Wight, par le Royal Yacht Squadron (RYS), en marge de l'exposition universelle de Londres.
Le trophée est une aiguière en argent, attribuée au Yacht Club vainqueur du défi jusqu'à sa remise en jeu. Fabriquée en 1848 pour le Royal Yacht Squadron par le bijoutier et orfèvre Robert Garrard de Londres comme trophée de la Coupe de Cent Souverains, elle est ramenée aux États-Unis, en septembre 1851 sous le nom de Coupe de Cent Guinées, pour prendre en juillet 1857 son nom actuel de Coupe de l'America, en hommage à la goélette victorieuse.
C'est une des plus anciennes compétitions sportives encore disputée de nos jours et se révèle être l'un des principaux théâtres de l'évolution de l'architecture navale en matière de voiliers de régates.
À la suite de la régate de 1851 et de la création de la course en 1857, la première édition de la coupe de l'America n'est disputée qu'après la guerre de Sécession, en août 1870. Après ces deux compétitions, lors desquelles un voilier challenger affronte une flotte de voiliers défendeurs, les adversaires se mesurent en duel (match-racing). La deuxième édition de 1871 se déroule en deux duels successifs avec deux défendeurs du NYYC contre l'unique challenger du Royal Thames Yacht Club.
C'est à partir de la troisième édition de 1876 que les régates opposent, le défender, tenant du titre, au challenger qui relève le défi. Ce dernier est désigné par des régates de sélection depuis la 21e édition de 1970, régates qui prennent le nom de Coupe Louis-Vuitton en 1983, lors de la 25e édition.
Chaque édition voit l'établissement d'un règlement particulier, appelé acte de donation, définissant entre autres les conditions de régates et le type de bateau utilisé basé sur une jauge de course, rédigé par le defender et le challenger de référence, c'est-à-dire le premier Yacht Club à défier le tenant du titre.
En 2002, une exposition intitulée L'America's Cup, 150 ans d'histoire racontée par Louis Vuitton est organisée au Musée national de la Marine à Paris.
Le trophée est détenu par Emirates Team New Zealand, représentant le Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron qui s'impose sept à un face au défi Oracle Team USA lors de la 35e édition disputée aux Bermudes. Grant Dalton, patron du défi néo-zélandais, annonce que le nouveau Challenger of Records est Circolo della Vela Sicilia (en) avec Luna Rossa.
L'America's Cup (Coppa America in italiano) è il più famoso trofeo nello sport della vela, nonché il più antico trofeo sportivo del mondo per cui si compete tuttora.
Si tratta di una serie di regate di match race, ovvero tra soli due yacht che gareggiano uno contro l'altro. Le due imbarcazioni appartengono a due Yacht Club differenti, una rappresentante lo yacht club che detiene la coppa e l'altra uno yacht club sfidante.
Nelle edizioni 1995, 2000, 2003 e 2007, la coppa, una brocca d'argento, è stata assegnata al vincitore di un incontro al meglio di nove regate. L'edizione 2010 della competizione è stata vinta dall'imbarcazione statunitense BMW Oracle Racing che ha avuto la meglio sul defender svizzero Alinghi con un risultato di 2-0. Oracle ha mantenuto la Coppa anche durante l'edizione 2013, battendo Emirates Team New Zealand 9-8. Nell'edizione numero 35, svoltasi nel 2017 nelle Isole Bermuda, Emirates Team New Zealand si aggiudica il trofeo sconfiggendo 7-1 il defender Oracle Team USA[1].
La Copa América (America's Cup en inglés y oficialmente) de vela es la competición más importante de ese deporte y algunas fuentes sostienen que es el tercer evento deportivo con mayor impacto económico para el país de acogida después de los Juegos Olímpicos y el Mundial de fútbol.1234
El actual defensor es el Real Escuadrón de Yates de Nueva Zelanda, que venció al Club de Yates Golden Gate en la última edición, celebrada en Hamilton (Bermudas).
El Challenger of Record para la próxima edición es el Círculo de Vela Sicilia.5
Кубок «Америки» (англ. America's Cup) — одна из самых известных и самых престижных регат в мире. Является старейшим в мире международным соревнованием во всех видах спорта, будучи основанным на два десятилетия ранее Кубка Англии по футболу и на 45 лет раньше первых современных Олимпийских игр.
Кубок Америки получил своё название в честь яхты «Америка» , которая выиграла его в престижной английской регате в 1851 году. Трофей остался в Нью-Йоркском яхт-клубе.
Кубок был изготовлен в 1848 году компанией «Гаррард и Ко». Он представляет собой кувшин без дна, на котором выгравированы названия всех яхт — обладателей кубка. По легенде, дно в кубке отсутствует по желанию английской королевы Виктории, не желавшей, чтобы из него пили[1]. Материал кубка — это так называемый британский металл — сплав олова, меди и сурьмы, покрытый серебром. В 1958 и 2003 годах кубок был дополнен основаниями, для размещения названий очередных победителей. В 1997 году вандал, проникший в здание Новозеландского яхт-клуба, изуродовал Кубок кувалдой. Кубок был бесплатно восстановлен английскими мастерами.
Кубок разыгрывается в серии матчевых гонок между представителем страны, победившим в прошлом цикле, и претендентом. Претендентом является победитель предварительных отборочных соревнований. В настоящее время отборочными соревнованиями служит Кубок Луи Виттона. Место поединка выбирает обладатель кубка.

 Cataluña
Cataluña

 Music
Music

 Music charts
Music charts

 Music charts
Music charts
 Listen to the spanish-language hit parade
Listen to the spanish-language hit parade
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 (*)Olympic Anthems
(*)Olympic Anthems




 Andalusia
Andalusia

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
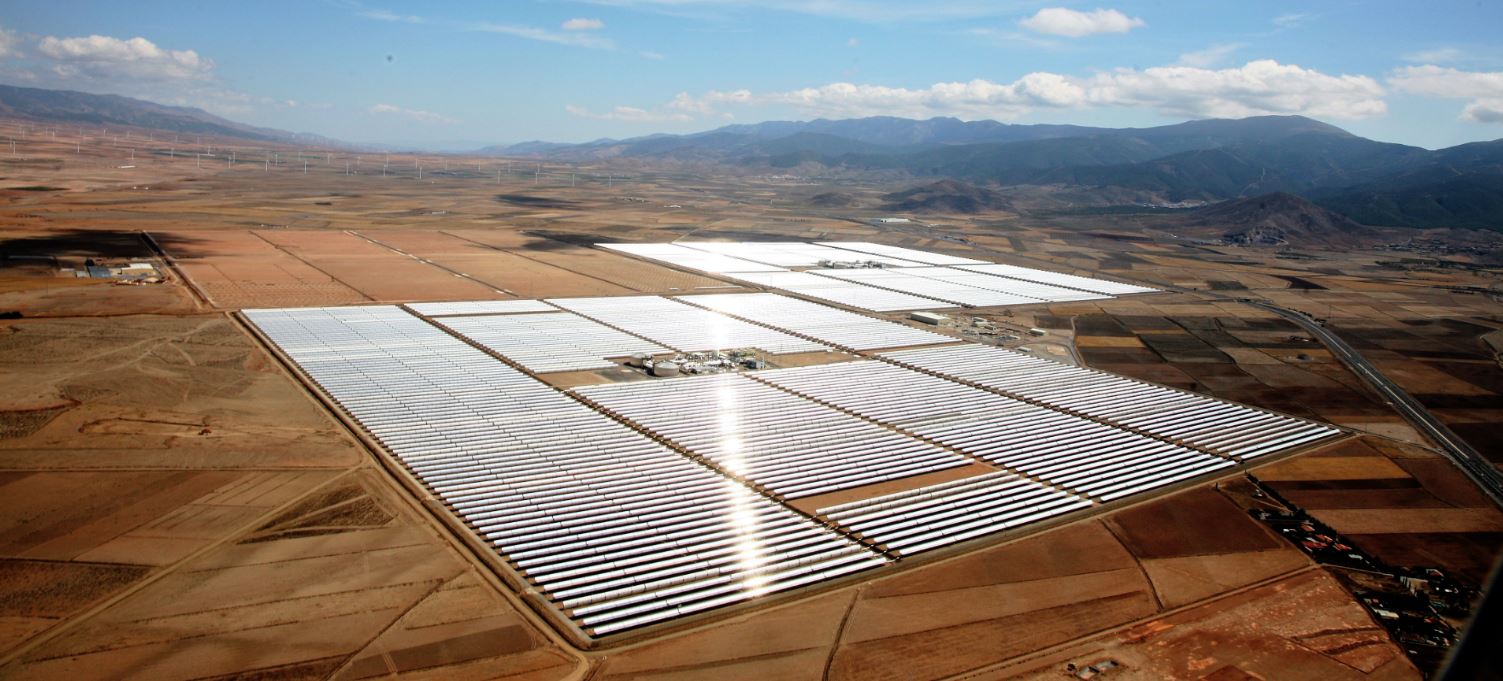
 Solar power plants
Solar power plants
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Solar energy
Solar energy
 Spain
Spain


 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion

 History
History
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Civilization
Civilization

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Companies
Companies
 European Union
European Union