
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY





 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Canada
Canada
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
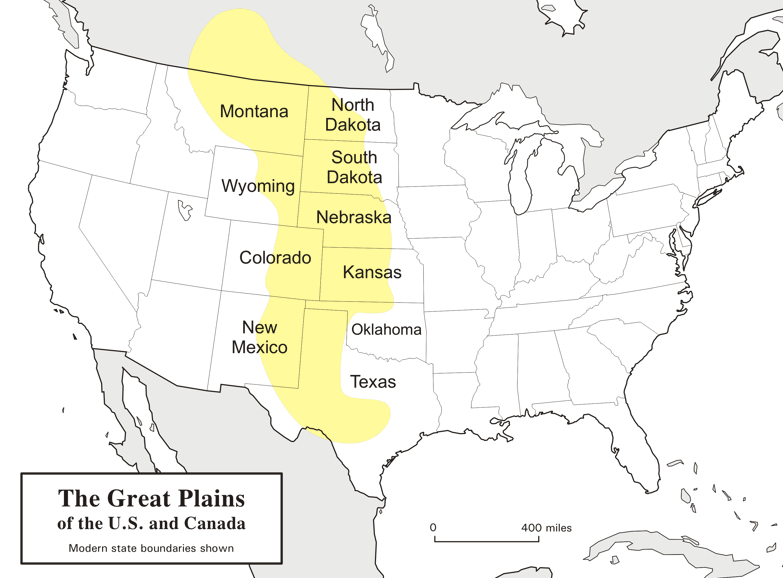
Die Great Plains (deutsch „Große Ebenen“) sind ein trockenes Gebiet östlich der Rocky Mountains in Nordamerika. Naturräumlich sind sie die klassischen Kurzgras-Prärien des amerikanischen Westens, heute werden sie intensiv landwirtschaftlich genutzt. Sie reichen von den kanadischen Prärieprovinzen (Alberta, Saskatchewan und Manitoba) bis nach Texas; manchmal wird auch ein kleiner Teil Mexikos dazu gezählt.
Die Great Plains umfassen (je nach Grenzziehung) eine Fläche von knapp 2 Millionen Quadratkilometern und erstrecken sich insgesamt etwa auf einer maximalen Breite von über 750 km und einer Länge von fast 3000 km. Während sie an den Rocky Mountains noch über 1800 m hoch sind, fallen sie nach Osten auf ca. 500 m ab. Damit sind sie insgesamt als Hochebene zu betrachten, die sich als „Piedmont-Plateau“, zum Teil in Schichtstufen ansteigend, vor dem Gebirge ausbreitet.
Man kann die Great Plains in zwei klimatische Regionen unterteilen, da man westlich des 100. Längengrades einen spärlichen Niederschlagsdurchschnitt vorfindet (weniger als 500 mm pro Jahr), wohingegen die östliche Region ein vergleichsweise humides Klima hat. Entsprechend dominiert im Westen die Viehwirtschaft und im Osten der Getreideanbau.
大平原(英语:Great Plains),多称北美大平原、北美大草原,是北美洲中部一块广袤的平原地区,大致位于密西西比河以西、洛基山脉以东、格兰德河以北。自然植被以草为主。
大平原东西长800千米,南北长3,200千米。另根据内布拉斯加-林肯大学大平原研究中心的定义,其总面积约130万平方千米。大平原主要包括了美国的科罗拉多州、堪萨斯州、蒙大拿州、内布拉斯加州、新墨西哥州 、北达科他州、俄克拉荷马州、南达科他州、得克萨斯州和怀俄明州,以及加拿大的草原三省(艾伯塔省、曼尼托巴省和萨斯喀彻温省)还有墨西哥的一小部分。

大棱镜温泉(The Grand Prismatic Spring),又称大虹彩温泉,位于美国黄石国家公园经纬坐标44.524569, -110.837975处,直径约100米,是美国最大,世界第三大的温泉。它宽约75至91米,49米深,水温高达85℃,每分钟约会涌出2000升泉水。最早于1839年为探险家所发现。
大棱镜温泉也是黄石公园里最有名的间歇泉之一。大棱镜温泉的美在于湖面的颜色随季节而改变,春季,湖面从绿色变为灿烂的橙红色,这是由于富含矿物质 的水体中生活着的藻类和含色素的细菌等微生物,它们体内的叶绿素和类胡萝蔔素的比例会随季节变换而改变,于是水体也就呈现出不同的色彩。在夏季,叶绿素含 量相对较低,显现橙色、红色,或黄色。但到了冬季,由于缺乏光照,这些微生物就会产生更多的叶绿素来抑制类胡萝蔔素的颜色,于是就看到水体呈现深绿色。


 *Capitols in the United States
*Capitols in the United States
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System

 Architecture
Architecture
 Neo-Renaissance architecture
Neo-Renaissance architecture
 United States
United States

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY




Wyoming (engl. Aussprache [wai̯ˈoʊ̯mɪŋ]) ist mit 579.315 Einwohnern[1][2] (2017) der bevölkerungsärmste Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika und, nach Alaska, der Bundesstaat mit der zweitgeringsten Bevölkerungsdichte.[3][4] Er liegt im Westen der Vereinigten Staaten und steigt von den Great Plains Ost-Wyomings zu den Rocky Mountains hin an.
Der Name stammt aus der Sprache der Algonkin-Indianer und bedeutet „Große Ebenen“. Er wurde der poetischen Erzählung Gertrude of Wyoming entnommen, die Thomas Campbell 1809 geschrieben hatte.
Der größte Ort ist die Hauptstadt Cheyenne. Der Spitzname ist Equality State nach dem Motto des Staates: „Equal Rights“ (deutsch: gleiche Rechte).
Mit seinen 253.336 km² ist Wyoming flächenmäßig der zehntgrößte Bundesstaat der USA. Nach Colorado ist er mit 2044 m auch der durchschnittlich am zweithöchsten gelegene Staat des Landes. Er befindet sich im westlichen Zentrum des US-Staatsgebiets und zählt somit durch seine Lage (wie auch seine Kultur) zum legendären sogenannten (Wilden) Westen (daher auch der Kosename Cowboy State).
Wyoming erstreckt sich auf einer Breite von 450 km zwischen etwa 41° N und 45° N und einer Länge von 550 bis 580 km zwischen etwa 104° W und 111° W und gehört gemeinsam mit seinen südlichen und westlichen Nachbarstaaten Colorado und Utah zu den Bundesstaaten, deren Grenzen fast ausschließlich nach geographischen Längen- und Breitengraden definiert wurden. Die Grenzziehung entspricht (auf einem entsprechenden Kartennetzentwurf, etwa der Mercator-Projektion) mit geringfügigen Abweichungen einem Rechteck.
Im Prinzip ist das Gebiet von Wyoming ein weites, gebrochenes Plateau, aus dem verschiedene Bergkämme der Rocky Mountains aufragen. Aus einer Querschnittsperspektive gesehen, befindet sich dieses Plateau in einer Schräglage, die von einem höher gelegenen Westen in einen tieferen Osten übergeht. Diese Neigung beschreibt auch den Übergang von den weiten östlichen Ebenen der Prärien über zentrale Beckenlandschaften zum westlich gelegenen Felsengebirge. Wyoming ist ein Staat, der die großen Kulturlandschaften der Great Plains und der Rocky Mountains verbindet – eine Position, die er nur mit drei der 50 weiteren Bundesstaaten teilt: Montana im Norden sowie Colorado und New Mexico im Süden.
Eine weitere geographische Bedeutsamkeit ist Wyomings Lage an der Great Continental Divide, der großen kontinentalen Wasserscheide des nordamerikanischen Kontinents, die die Bundesstaatsfläche in nordwestlich-südöstlicher Richtung durchzieht. Sie verläuft entlang der Absaroka Range und Wind River Ranges und setzt sich im Great Divide Basin, und später der Park Range (großteils in Colorado), fort. Alle Flüsse, die östlich dieser Linie entspringen, entwässern Richtung Osten und münden irgendwann alle in den Missouri River, der in den Mississippi River und schließlich in den Atlantischen Ozean (Golf von Mexiko) fließt. Jene Flüsse, die westlich der Wasserscheide ihren Lauf beginnen, enden im Pazifik (entweder im offenen Ozean, wenn sie dem Columbia River westwärts folgen, oder im Golf von Kalifornien, wenn sie nach Süden in den Green River und später den Colorado River entwässern).
Wyoming kann in drei große geographische Räume gegliedert werden, die alle grob ein Drittel des Staatsgebiets umfassen: die Great Plains, die Intermountain Basins (Gebirgsbecken) und die Rocky Mountains.
ワイオミング州(英: State of Wyoming [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
州都はシャイアン市。陸地面積は全米50州の中で第10位だが、人口は563,626人(2010年国勢調査)[1]と全米50州の中で最も少なく[2]、州都シャイアンからわずか160km南にあるコロラド州の州都デンバーを含む、全米の31都市よりも少ない。人口密度は2人/km2で、全米50州の中では、アラスカ州に次いで2番目に低い。ワイオミングとはアルゴンキン語族インディアンの言葉で「大平原」を意味し、州の東側3分の1はハイプレーンズと呼ばれ、広大なグレートプレーンズの西部にあたる標高の高い平原地帯が広がっている。西側3分の2はロッキー山脈東部の山岳地帯と丘陵の牧草地帯である。州の愛称は「平等の州 (Equality State)」、「カウボーイ州 (Cowboy State)」である。
Wyoming (/waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
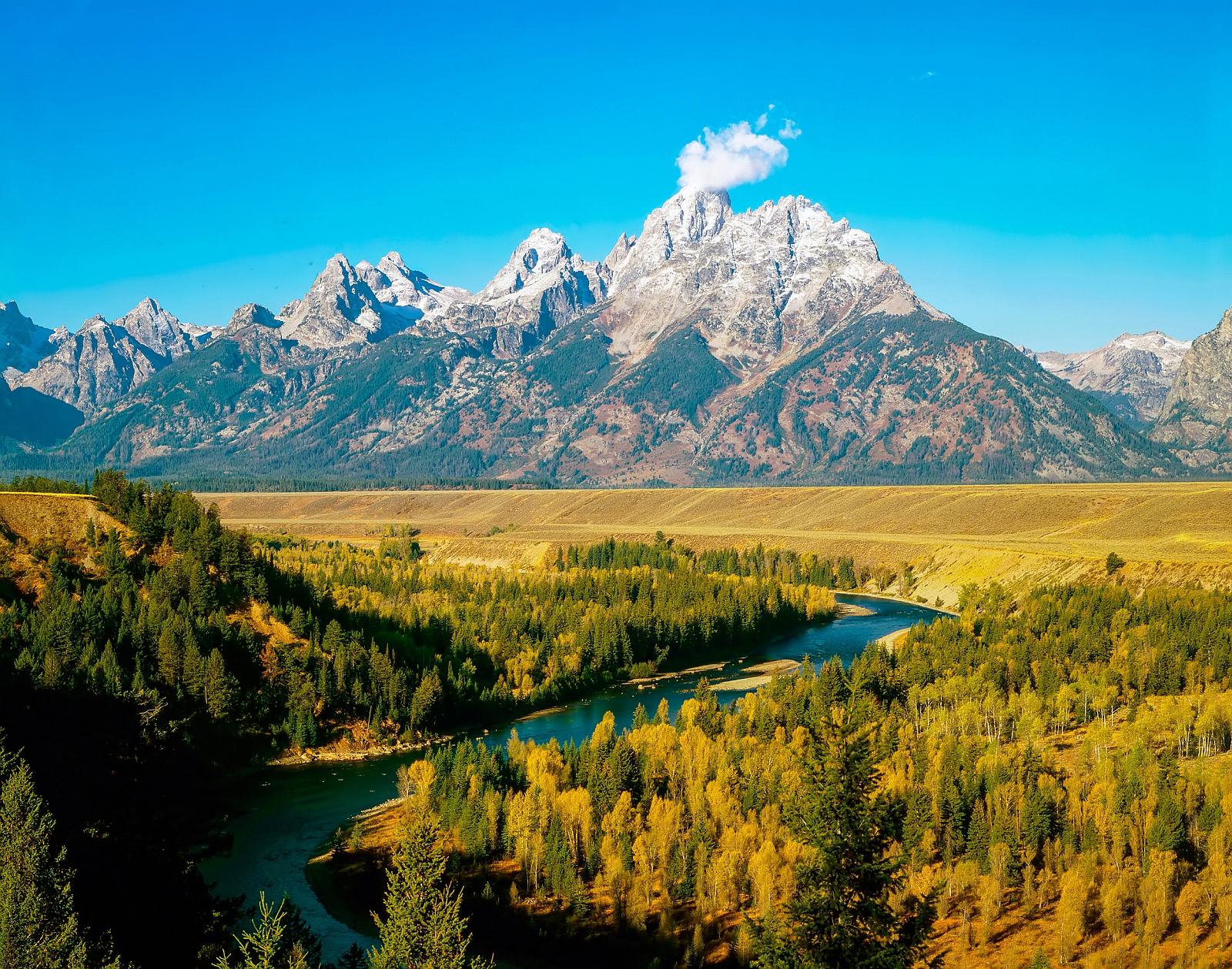
Wyoming's western half is mostly covered by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie called the High Plains. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the U.S. government, leading Wyoming to rank sixth by area and fifth by proportion of a state's land owned by the federal government.[8] Federal lands include two national parks—Grand Teton and Yellowstone—two national recreation areas, two national monuments, several national forests, historic sites, fish hatcheries, and wildlife refuges.
Original inhabitants of the region include the Arapaho, Crow, Lakota, and Shoshone. Southwest Wyoming was claimed by the Spanish Empire and then as Mexican territory until it was ceded to the U.S. in 1848 at the end of the Mexican–American War. The region acquired the name "Wyoming" when a bill was introduced to Congress in 1865 to provide a temporary government for the territory of Wyoming. The name had been used earlier for the Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania, and is derived from the Munsee word xwé:wamənk, meaning "at the big river flat".[9][10]
The main drivers of Wyoming's economy are tourism and extraction of minerals such as coal, oil, natural gas, and trona. Agricultural commodities include livestock, hay, sugar beets, grain (wheat and barley), and wool. The climate is semi-arid and continental, drier and windier than the rest of the country with greater temperature extremes. Wyoming has been a politically conservative state since the 1950s, with the Republican nominee carrying the state in every presidential election since 1968.[11] Donald Trump won it by 46 points in 2016, which was the best performance in the 21st century in the state and Trump's best performance in any state.
Le Wyoming /wi.o.miŋ/ (prononciation en anglais : /waɪ.ˈoʊ.mɪŋ/) est un État de l'Ouest des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest par l'Idaho, au nord par le Montana, à l'est par le Nebraska et le Dakota du Sud et au sud par le Colorado et l'Utah. Le tiers de l’État est situé dans les Grandes Plaines, mais le Wyoming est montagneux sur tout le reste de son territoire. C'est aussi l'État le moins peuplé des États-Unis avec ses 563 626 habitants. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Cheyenne.
Il Wyoming è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, quello con minore popolazione. Confina a nord con il Montana, a est con il Dakota del Sud e il Nebraska, a sud con il Colorado e a ovest con lo Utah e l'Idaho. La capitale dello Stato è Cheyenne. Il nome Wyoming deriva dalla parola in lingua munsee xwé:wamənk che significa presso il grande fiume calmo usata in origine per denominare la Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania.
Wyoming (pronunciación en inglés: /waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
Con 586 107 habitantes en 2015 es el estado menos poblado, con 253 336 km², el décimo más extenso —por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, Nuevo México, Arizona, Nevada, Colorado y Oregón— y con 2,2 hab/km², el segundo menos densamente poblado, por detrás de Alaska. Fue admitido en la Unión el 10 de julio de 1890, como el estado número 44.2 Con una tasa de 449 empleados cada 10 000 habs., es el estado con mayor proporción de empleo público no federal del país.3
Dos tercios del territorio oeste están cubiertos, mayormente, por las sierras y montañas de las Montañas Rocosas, mientras que el resto este del estado son praderas de grandes alturas sobre el nivel del mar conocidas como High Plains. Casi la mitad de la tierra de Wyoming es propiedad del gobierno estadounidense, haciendo de Wyoming el sexto estado con mayor número de acres en manos del gobierno federal. Estas tierras federales incluyen dos parques nacionales —Grand Teton y Yellowstone— dos áreas recreativas nacionales, dos monumentos nacionales, así como varios bosques nacionales, sitios históricos, zonas de pescas y áreas protegidas para la vida silvestre.
Las naciones indias Crow, Arapajó, Lakota y Shoshón son algunos de los pobladores originales de la región. La región suroeste del estado fue incluida en el Imperio Español y, consecuentemente, en territorio mexicano, hasta que fue cedido a los Estados Unidos en 1848 como resultado de la intervención estadounidense en México. La región adquirió el nombre de Wyoming cuando un proyecto de ley fue introducido al Congreso en 1865 para proveer "un gobierno temporal al territorio de Wyoming". El territorio fue nombrado por el Valle de Wyoming en Pensilvania, siendo el nombre derivado de la palabra xwé:wamənk, en idioma munsee, que significa "en el gran río plano".45
La industria de extracción de minerales—especialmente carbón, petróleo, gas natural y trona—junto con el turismo son los principales motores de la economía de Wyoming. La agricultura ha sido históricamente un importante componente de la economía del estado. El clima es generalmente semiárido y continental, siendo más seco y con más vientos que el resto de los Estados Unidos, con temperaturas extremas comunes.
Exceptuando las elecciones de 1964, Wyoming ha sido un estado políticamente conservador desde la década de 1950, con el Partido Republicano ganando todas las elecciones presidenciales en el estado desde entonces.
Вайо́минг[1][2] (англ. Wyoming, американское произношение: [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.
слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.

黄石国家公园(简称黄石公园,英语:Yellowstone National Park)是美国第一个国家公园。主要位于怀俄明州,部分位于蒙大拿州和爱达荷州,于1872年3月1日美国总统尤利西斯·辛普森·格兰特签署国会通过的法案后建立[4][5],是世界上第一个国家公园[6]。黄石公园以其丰富的野生动物种类和地热资源闻名,老忠实间歇泉更是其中最富盛名的景点之一[7]。公园中有着多种类型的生态系统,其中以亚高山带森林为主。
美洲原住民已经在黄石公园地区生活了至少1万1千年[8],19世纪早期的刘易斯与克拉克远征也绕过了这一区域。对该地区的有组织的勘探活动直到1860年代末才开始出现,此前只有一些选择在野外捕猎和居住的山地人在19世纪早期到中叶曾偶尔进入。美国陆军在公园刚刚建立后就受委托对其进行监管。1917年后,公园的管理工作移交给了之前一年刚刚成立的美国国家公园管理局。园中有数以百计因其建筑学和历史学意义而保护起来的建筑物,研究人员已经发现了超过1000个考古遗迹。
黄石国家公园占地面积约为8983平方千米[1],其中包括湖泊、峡谷、河流和山脉[7]。公园内最大的湖泊是位于黄石火山中心的黄石湖,是整个北美地区最大的高海拔湖泊之一。黄石火山是北美最大且仍处于活跃状态的超级火山,在过去两百万年中它曾数次以巨大的力量爆发[9]。喷出的熔岩和火山灰也覆盖了公园内的绝大部分地区。得益于其持续的活跃状态,世界上的地热资源有半数位于黄石公园地区[10]。黄石公园也是大黄石生态系统的核心所在,这是北温带地区现存最大且仍然近乎完好的自然生态系统[11]。
公园内有记录的哺乳动物、 鸟类、鱼类和爬行动物有数百种之多,其中包括多种濒危或受威胁物种[7],广袤的森林和草原中同样存有多种独特的植物。黄石公园是美国本土最大和最著名的巨型动物居住地。公园中有灰熊、狼、美洲野牛和加拿大马鹿的栖息地。黄石公园野牛群是美国最古老也最大的野牛群。公园内每年都会发生山火,其中最大的一次是1988年黄石公园大火,公园内近三分之一的面积被烧毁。黄石公园也是休闲娱乐的好去处,园内可进行远足、露营、划船、钓鱼、度假和观光等活动。沿着园内铺设的道路可以就近接触到主要的地热区域以及一些湖泊和瀑布。冬天,游客们则往往会在导游指引下乘坐雪上摩托车等冰上交通工具来造访公园。
イエローストーン国立公園(イエローストーンこくりつこうえん、Yellowstone National Park)はアイダホ州、モンタナ州、及びワイオミング州に位置するアメリカ合衆国の国立公園である。1872年に世界初の国立公園に指定されており [1]、ワイオミング州北西部を中心として3,470平方マイル(8,980㎢)にわたる。この国立公園には様々な間欠泉や温泉、地熱による観光スポットが散在していることで有名であるが、グリズリーやオオカミ、アメリカバイソン(バッファロー)やワピチ(エルク)の群れが生息していることでも知られる。ここは地上に残された数少ない手付かずの巨大温帯生態系の一つであるイエローストーン圏生態系 (Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem) の中心になっている。アメリカで最も人気のある国立公園で、2015年には410万人の観光客が訪れた。
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho. It was established by the U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872.[5][6] Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world.[7] The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular features.[8] It has many types of ecosystems, but the subalpine forest is the most abundant. It is part of the South Central Rockies forests ecoregion.
Native Americans have lived in the Yellowstone region for at least 11,000 years.[9] Aside from visits by mountain men during the early-to-mid-19th century, organized exploration did not begin until the late 1860s. Management and control of the park originally fell under the jurisdiction of the Secretary of the Interior, the first being Columbus Delano. However, the U.S. Army was subsequently commissioned to oversee management of Yellowstone for a 30-year period between 1886 and 1916.[10] In 1917, administration of the park was transferred to the National Park Service, which had been created the previous year. Hundreds of structures have been built and are protected for their architectural and historical significance, and researchers have examined more than a thousand archaeological sites.
Yellowstone National Park spans an area of 3,468.4 square miles (8,983 km2),[2] comprising lakes, canyons, rivers and mountain ranges.[8] Yellowstone Lake is one of the largest high-elevation lakes in North America and is centered over the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest supervolcano on the continent. The caldera is considered an active volcano. It has erupted with tremendous force several times in the last two million years.[11] Half of the world's geysers[12][13] and hydrothermal features[14] are in Yellowstone, fueled by this ongoing volcanism. Lava flows and rocks from volcanic eruptions cover most of the land area of Yellowstone. The park is the centerpiece of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, the largest remaining nearly-intact ecosystem in the Earth's northern temperate zone.[15] In 1978, Yellowstone was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Hundreds of species of mammals, birds, fish, and reptiles have been documented, including several that are either endangered or threatened.[8] The vast forests and grasslands also include unique species of plants. Yellowstone Park is the largest and most famous megafauna location in the contiguous United States. Grizzly bears, wolves, and free-ranging herds of bison and elk live in this park. The Yellowstone Park bison herd is the oldest and largest public bison herd in the United States. Forest fires occur in the park each year; in the large forest fires of 1988, nearly one third of the park was burnt. Yellowstone has numerous recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, boating, fishing and sightseeing. Paved roads provide close access to the major geothermal areas as well as some of the lakes and waterfalls. During the winter, visitors often access the park by way of guided tours that use either snow coaches or snowmobiles.
Le parc national de Yellowstone (en anglais : Yellowstone National Park) est un parc national des États-Unis, ainsi qu'un site du patrimoine mondial protégé par l'UNESCO, couvrant trois États au nord-ouest du Wyoming, au sud-est de l'Idaho (en bordure de la forêt nationale de Caribou-Targhee) et au sud-ouest du Montana (adjacent à la forêt nationale de Gallatin). Créé le 1er mars 1872 par le président Ulysses S. Grant, Yellowstone est le plus ancien parc national du monde2. Il s'étend sur 8 983 km2 (898 300 hectares), soit une superficie plus importante que celle de la Corse.
Il constitue le deuxième plus grand parc naturel des États-Unis hormis ceux localisés en Alaska. La caldeira de Yellowstone est célèbre pour ses phénomènes géothermiques ; il contient deux tiers des geysers de la planète et de nombreuses sources chaudes3. L'une des figures emblématiques du parc est le geyser « Old Faithful ». Le parc abrite aussi de nombreux grands mammifères comme des ours noirs, des grizzlys, des coyotes, des loups, des orignaux, des cerfs ou encore des troupeaux sauvages de bisons et de wapitis. Il constitue le cœur d'un vaste habitat naturel préservé, l'un des derniers écosystèmes relativement intacts des zones tempérées. Parmi les différents écosystèmes du parc, la forêt subalpine domine. Il est inscrit sur la liste des réserves de biosphère de l'UNESCO en 19764 et au Patrimoine mondial depuis 19785. Il reçoit chaque année la visite d'environ trois millions de personnes6, ce qui en fait l'un des parcs nationaux américains les plus fréquentés.
Il Parco nazionale di Yellowstone (Yellowstone National Park) si trova negli Stati Uniti d'America e più precisamente nell'estremo settore nord-occidentale dello Stato del Wyoming e sconfina, per un piccolo tratto, negli Stati del Montana (a Nord) e dell'Idaho (a Ovest)[1], occupando un'ampia zona delle Montagne Rocciose[2].
Il nome Yellowstone (pietra gialla) deriva dai fenomeni vulcanici attivi e la pietra gialla probabilmente deriva dallo zolfo presente in zona.
È il nucleo centrale del Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, uno dei più grandi ecosistemi intatti della zona temperata rimasto sulla Terra, oltre ad essere il più antico Parco nazionale del mondo (fondato nel 1872 durante la presidenza di Ulysses S. Grant) e la più grande area protetta statunitense e, dal 1978, dichiarato Patrimonio dell'umanità dall'Unesco.
Nel 2015, il Parco è stato visitato da più di 4.000.000 di persone[3].
El parque nacional de Yellowstone (en inglés: Yellowstone National Park) fue creado por el Congreso de los Estados Unidos y convertido en ley por el entonces presidente Ulysses S. Grant el 1 de marzo de 1872,23 es un parque nacional ubicado en los Estados Unidos, principalmente en el estado de Wyoming, aunque se extiende por Montana e Idaho. Yellowstone, el primer parque nacional de los Estados Unidos, también se considera ampliamente el parque nacional más antiguo del mundo.4 Se encuentra encima de la caldera del mayor volcán de América, muy vivo pero sin erupción desde hace 640 000 años. Consecuencia son sus numerosos fenómenos geotérmicos, especialmente el géiser Old Faithful, una de sus atracciones más populares.5 Es famoso también por su diversidad en fauna, beneficiada por la prohibición de caza durante los últimos 150 años. A pesar de que posee múltiples ecosistemas, domina el bosque subalpino.
Los nativos americanos vivieron en la región de Yellowstone al menos durante 11 000 años.6 La expedición de Lewis y Clark, a principios del siglo XIX, circunvaló la región. Aparte de las visitas de los mountain men a mediados del siglo XIX, las exploraciones organizadas no comenzaron hasta la década de 1860. La armada de los Estados Unidos fue comisionada para supervisar el parque desde su establecimiento. En 1917, la administración del parque se transfirió al Servicio de Parques Nacionales, creado el año anterior. Desde entonces, se han construido y protegido cientos de estructuras, tanto por su importancia arquitectónica como histórica. Los investigadores estiman que hay más de 1000 sitios arqueológicos.
El parque nacional de Yellowstone se extiende en un área de 8983 km².7 Comprende lagos, cañones, ríos y cadenas montañosas.5 El lago Yellowstone es el lago de montaña más grande de América del Norte y su mitad meridional se encuentra la Caldera Yellowstone, el supervolcán más grande del continente, considerado un volcán activo. Se tienen datos de que al menos en los últimos millones de años ha entrado en erupción con una fuerza tremenda en varias ocasiones.8 Al menos la mitad de las atracciones geotermales del mundo se localizan en Yellowstone, provocadas por su fuerte y consistente actividad volcánica.9 Los flujos de lava y rocas emanados por las erupciones volcánicas cubren la mayor parte del área de Yellowstone. El parque es el centro del Gran Ecosistema de Yellowstone, el más grande ecosistema restante y casi intacto en la zona norte de la Tierra.10
Se han documentado cientos de especies de mamíferos, aves, peces y reptiles, incluyendo muchos en peligro o amenaza de extinción.5 Los vastos bosques y pastizales también incluyen especies únicas de plantas. El parque Yellowstone es el lugar más extenso con la megafauna más famosa en los Estados Unidos continentales. Osos grizzly, lobos, manadas de bisontes y alces pastan libremente y viven en el parque. El rebaño de bisontes del Yellowstone Park es el rebaño de bisontes más grande y antiguo abierto al público en los Estados Unidos.
A pesar de medidas de protección, los incendios forestales ocurren en el parque casi todos los años, tal y como el incendio de Yellowstone de 1988, donde casi un tercio del parque se quemó. Yellowstone tiene numerosas actividades recreacionales, que incluyen alpinismo, acampadas, paseos en bote, pesca y avistamientos de su fauna. Los caminos pavimentados proveen acceso cercano a las áreas de mayor actividad geotérmica, así como a algunos de los lagos y cataratas. Durante el invierno, a menudo los visitantes acceden al parque con paseos guiados en los que se usan vehículos para la nieve o motonieve.
Йе́ллоустонский национа́льный парк[3][4][5][6], Йе́ллоустон (англ. Yellowstone National Park) — международный биосферный заповедник, объект Всемирного Наследия ЮНЕСКО, первый в мире национальный парк (основан 1 марта 1872 года). Находится в США, на территории штатов Вайоминг, Монтана и Айдахо. Парк знаменит многочисленными гейзерами и другими геотермическими объектами, богатой живой природой, живописными ландшафтами. Площадь парка — 898,3 тыс. га.
Согласно археологическим данным люди начали жить на территории, занимаемой парком, 11 000 лет назад. Современные исследователи впервые появились в регионе в 1805 году (участники экспедиции Льюиса и Кларка), но до 1860-х годов здесь не проводилось никакой хозяйственной или научной деятельности. В первые годы после возникновения парка он находился под управлением армии США, а в 1917 году управление было передано созданной за два года до этого Службе национальных парков.
На огромной территории парка находятся озёра, реки, каньоны и пещеры. Озеро Йеллоустон, одно из самых больших высокогорных озёр в Северной Америке, расположено в центре Йеллоустоунской кальдеры, самого большого супервулкана на континенте. Кальдера считается дремлющим супервулканом; он извергался с огромной силой несколько раз за последние два миллиона лет. Большая часть территории парка покрыта застывшей лавой; в парке находится одно из пяти существующих в мире гейзерных полей.
В парке растёт около двух тысяч видов растений, встречаются несколько сотен видов млекопитающих, птиц, пресмыкающихся и рыб, в том числе находящихся под угрозой уничтожения. Большая часть территории покрыта лесом, меньшая — степью. Каждый год случаются лесные пожары; около трети всех лесов выгорело в результате катастрофических пожаров 1988 года. В парке проложено несколько сот километров асфальтовых дорог, по которым осуществляется доступ посетителей. Имеются многочисленные возможности для активного отдыха.

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA
 Canada
Canada

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD
 United States
United States

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY


Die Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) ist eine Eisenbahngesellschaft mit einem fast 22.300 Kilometer langen normalspurigen Schienennetz in Kanada und den USA. Sie ist, neben der Canadian National Railway, eine der zwei kanadischen Class 1-Eisenbahngesellschaften. Sitz des an der Toronto Stock Exchange im S&P/TSX 60 gelisteten Unternehmens ist Calgary. Die Hauptstrecke der Gesellschaft, die zwischen 1881 und 1885 erbaute transkontinentale Verbindung, verläuft zwischen Montréal im Osten am Nordatlantik und Vancouver im Westen am Pazifik.
Mit dem Bau der Strecke wurde ein Versprechen an die Provinz British Columbia erfüllt, die 1871 der Kanadischen Konföderation beigetreten war und eine Verkehrsverbindung in den Osten des Landes gefordert hatte. Die Strecke trug wesentlich zur Besiedlung der kanadischen Prärieprovinzen Alberta, Manitoba und Saskatchewan bei. Heute betreibt die Canadian Pacific Railway ausschließlich Güterverkehr, nachdem der Personenverkehr 1978 an VIA Rail übertragen wurde.
Die Canadian Pacific Railway war von 1971 bis 2001 ein Teil der Canadian Pacific Limited, des weltweit größten Transport- und Rohstoffkonzerns (Schifffahrt, Luftfahrt, Eisenbahn, Lkw-Transporte, Telekommunikation, Minen, Erdöl, Erdgas). Im Zeitraum von 1968 bis 1996 wurden die Dienstleistungen der Eisenbahn unter der Bezeichnung CP Rail vermarktet. 1996 erfolgte eine Reorganisation des Gesamtkonzerns. Dabei wurden fünf separate Tochtergesellschaften gebildet, darunter die Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, die das Eisenbahngeschäft übernahm. Mit Wirkung vom 1. Oktober 2001 wurden die einzelnen Tochtergesellschaften rechtlich und wirtschaftlich eigenständige Unternehmen, während sich der Konzern auflöste.
In den USA betreibt die Canadian Pacific Railway die beiden Tochterunternehmen Soo Line Railroad und Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H).
加拿大太平洋铁路(清末民初音译坎拿大诗丕亚铁路,英语:Canadian Pacific Railway)是加拿大的一级铁路之一,由加拿大太平洋铁路公司(Canadian Pacific Railway Limited)营运。其网络横跨西部温哥华至东部蒙特利尔,并设有跨境路线,通往美国的明尼阿波利斯、芝加哥、纽约市等大型城市。公司总部设于艾伯塔省卡尔加里。
该铁路系统的前身是加拿大东部至不列颠哥伦比亚省之间的铁路线,于1881年至1885年间兴建,用以连接渥太华谷及乔治亚湾两地的既有铁路,实现了不列颠哥伦比亚于1871年加入加拿大邦联的回报承诺。这条铁路也是加拿大首条越洲铁路,现时主要行驶货运列车,在之前曾有一段长时间作为全加拿大唯一的长途客运运输工具,也为加拿大西部地区发展带来贡献。

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Saskatchewan-SK
Saskatchewan-SK

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

Der Louisiana Purchase (Louisiana-Kauf; im Französischen vente de la Louisiane, d. h. Verkauf von Louisiana) war der Kauf von 2.144.476 km² Land, das die USA 1803 von Frankreich erwarben. Der Kaufpreis betrug damals 15 Millionen US-Dollar oder 80 Millionen französische Francs (7 US-Dollar pro km²). Gemessen an der Kaufkraft entspricht das einem heutigen Wert von circa 251 Millionen US-Dollar oder knapp 117 Dollar pro km² (Stand 2018).[1]
Verkauft wurde das Gebiet der ehemaligen Kolonie Louisiana, das westlich des Mississippi River lag. Dieses Gebiet ist viel größer als der heutige Staat Louisiana: Es umfasst außer Teilen des heutigen Louisiana auch die heutigen Staaten Arkansas, Missouri, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas und Nebraska sowie Teile von Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, außerdem noch Randgebiete der kanadischen Provinzen Manitoba, Saskatchewan und Alberta.
Der Louisiana Purchase war das größte Grundstücksgeschäft der Geschichte. Das gekaufte Land verdoppelte damals das Territorium der Vereinigten Staaten und macht fast ein Viertel des heutigen Staatsgebiets aus.
路易斯安那购地(英语:Louisiana Purchase;法语:Vente de la Louisiane)是美国于1803年以每英亩三美分向法国购买超过529,911,680英亩(2,144,476平方公里)土地的交易案,该交易的总价为1500万美元或相当于8000万法郎;若计算通货膨胀等因素,此数额在今日相当于3亿100万美元。如以国内生产总值相对比例计算,此数额在2004年相当于4,178亿美元。而土地上所有后续条约和财务结算的总成本,估计约为26亿美元。[1]。
法属路易斯安那的版图远超今日美国的路易斯安那州。从南至北,该属地范围包括了现今美国路易斯安那州密西西比河两岸(包括新奥尔良市)、阿肯色州、奥克拉荷马州、德克萨斯州北部边界地带、新墨西哥州东北角、密苏里州、堪萨斯州、科罗拉多州洛基山脉以东、爱荷华州、内布拉斯加州、怀俄明州大部(落基山脉以东)、明尼苏达州密西西比河以西、南达科他州、北达科他州大部、蒙大拿州大部(除西端),以及现今加拿大马尼托巴、萨斯喀彻温、艾伯塔各省之密苏里河流域地区(也即南部边境地带)。购地所涉土地面积是今日美国国土的22.3%,与当时美国原有国土面积大致相当,因此使得当时美国的国土翻倍。
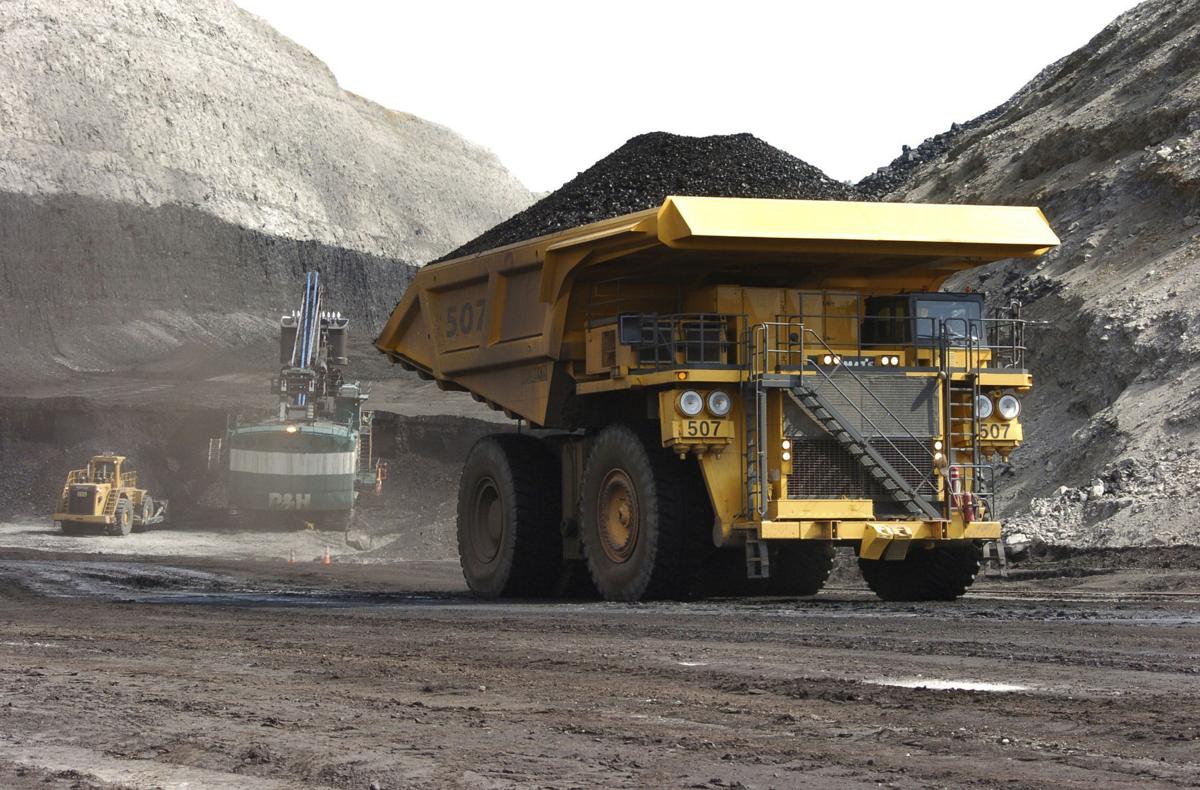
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Geography
Geography
 Animal world
Animal world
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 History
History