
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS

 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS

 History
History
 L 1000 - 1500 AD
L 1000 - 1500 AD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
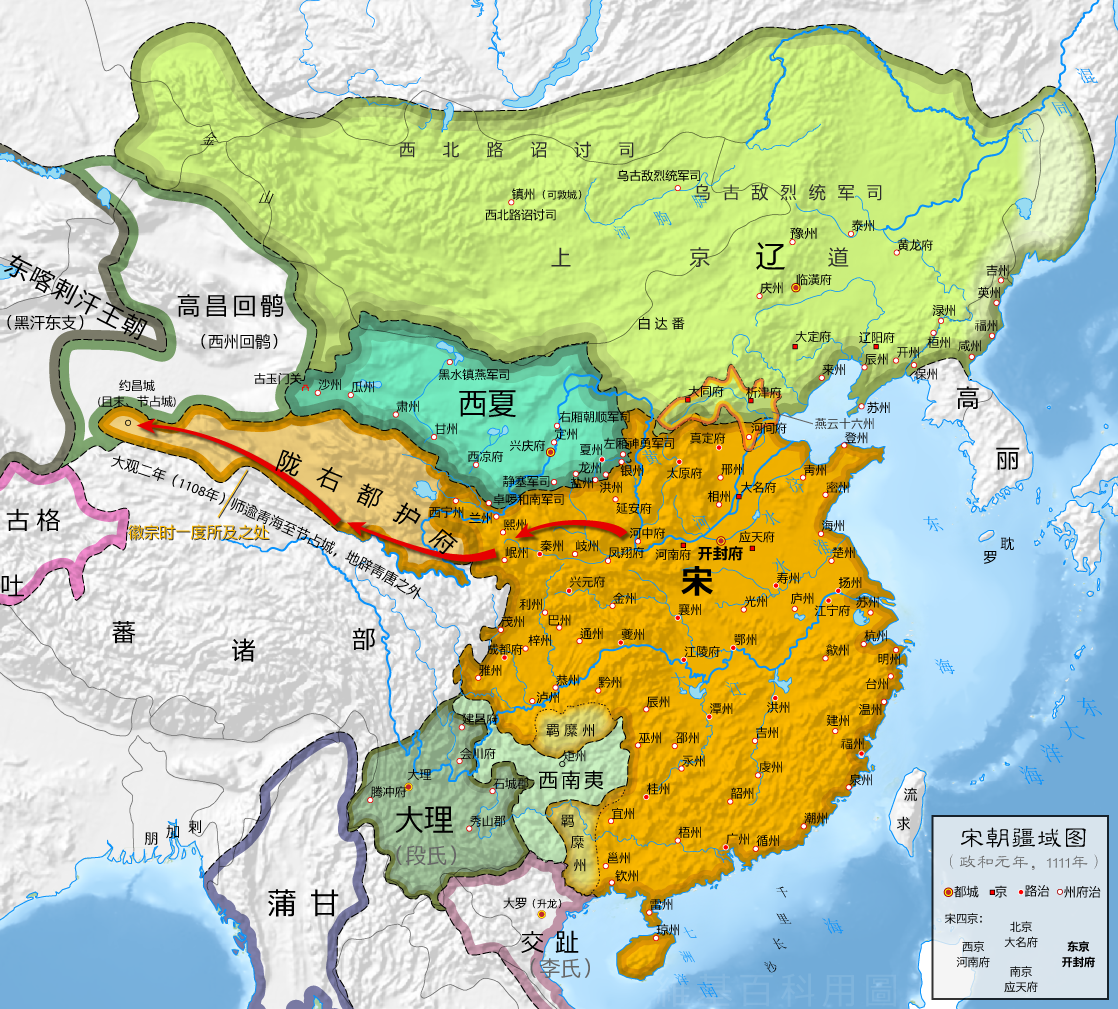
辽朝(907年-1125年),国号大辽,又称大契丹国(契丹国,契丹大字:![]() )[注 1],是中国历史上由契丹人建立的一个朝代,国祚210年[2]。
)[注 1],是中国历史上由契丹人建立的一个朝代,国祚210年[2]。
契丹族首领耶律阿保机吞并了契丹各个部落后,于916年称帝建国“契丹”。918年定都临潢府(今内蒙古巴林左旗南)。契丹屡次南下中原,946年阿保机之子耶律德光攻灭后晋后确定国号为“大辽”[注 2],983年改为“契丹”,1066年改为“大辽”[3],直到1125年3月26日为金朝所灭为止。除了辽朝之外,契丹族尚建立相关国家。1122年,天祚帝北逃夹山,耶律淳于辽南京被立为帝,史称北辽[3]。辽朝灭亡后,耶律大石西迁到中亚楚河流域,1132年建立西辽。1211年西辽被屈出律篡位,1218年被蒙古帝国所灭。
史学界对“契丹”含义最广为接受的说法是镔铁或刀剑之意。后来改国名为“辽”也是“铁”的意思,同时“辽”也是契丹人发祥地辽水的名字,以示不忘本之意。又因与南方的中原政权长期对峙,而称“北朝”,而称中原王朝为“南朝”[4]。辽朝926年灭渤海国,938年据燕云十六州,后灭后晋,自居为继承后晋的中原正统,即使之后退回北方。依据五行德运说的五行相生规律,后晋的“木”德之后为“水”德,因此辽朝以水为德运,并相应以黑色为正色。[5]
辽朝全盛时期疆域东到日本海,西至阿尔泰山,北到额尔古纳河、大兴安岭一带,南到河北省南部的白沟河。契丹族本是游牧民族,辽朝皇帝使农牧业共同发展繁荣,各得其所,建立独特的、比较完整的管理体制。辽朝将重心放在民族发祥地,为了保持民族性将游牧民族(契丹人)与农业民族(汉人)分开统治,主张因俗而治,开创出两院制的政治体制。并且创造契丹文字,保存自己的文化。此外,吸收渤海国、五代、北宋、西夏及西域各国的文化,成效地促进辽朝政治、经济和文化各个方面发展。辽朝的军事力量与影响力涵盖西域地区,因此在唐朝灭亡后中亚、西亚与东欧等地区常将辽朝(契丹,英语作Cathay)当做中国,[6]。
Die Liao-Dynastie (chinesisch 遼朝 / 辽朝, Pinyin Liáocháo) war eine Dynastie im Norden Chinas von 916 bis 1125. Das Herrscherhaus und ein Teil der Untertanen waren Angehörige des (proto-)mongolischen Volks der Kitan. Der Dynastie-Gründer war Abaoji († 926).
遼(りょう、簡体字:辽、拼音:Liáo)は、遼朝(りょうちょう)ともいい、内モンゴルを中心に中国の北辺を支配した契丹人(キタイ人)耶律氏(ヤリュート氏)の征服王朝。916年から1125年まで続いた。中原に迫る大規模な版図(現在の北京を含む)を持ち、かつ長期間続いた最初の異民族王朝であり、いわゆる征服王朝(金、元、清が続く)の最初とされる。ただし、後の3つの王朝と異なって中原を支配下にはおいていない。
The Liao dynasty (/ljaʊ/;[5] Khitan: Mos Jælud; traditional Chinese: 遼朝; simplified Chinese: 辽朝; pinyin: Liáo cháo),[6] also known as the Liao Empire, officially the Great Liao (大遼; 大辽; Dà Liáo), or the Khitan (Qidan) State (Khitan: Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur),[7] was an empire in East Asia that ruled from 907 to 1125 over present-day Northern and Northeast China, Mongolia and portions of the Russian Far East and North Korea.[8] The empire was founded by Yelü Abaoji, Khagan of the Khitans around the time of the collapse of Tang China and was the first state to control all of Manchuria.[9]
Almost immediately after its founding, the Khitan Empire began a process of territorial expansion, with Abaoji leading a successful conquest of Balhae. Later emperors would gain the Sixteen Prefectures by fueling a proxy war that led to the collapse of the Later Tang (923–936) and would establish tributary relationships with Goryeo after losing in Goryeo–Khitan Wars (1018) against Goryeo.[10] In 1004, Liao Dynasty launched an imperial expedition against the Northern Song. After heavy fighting and large casualties between two countries, the two sides worked out the Chanyuan Treaty. Through the treaty Liao forced the Northern Song to recognize them as peers.
Tension between traditional Khitan social and political practices and Chinese influence and customs was a defining feature of the dynasty. This tension led to a series of succession crises; Liao emperors favored the Chinese concept of primogeniture, while much of the rest of the Khitan elite supported the traditional method of succession by the strongest candidate. So different were Khitan and Chinese practices that Abaoji set up two parallel governments. The Northern Administration governed Khitan areas following traditional Khitan practices, while the Southern Administration governed areas with large non-Khitan populations, adopting traditional Chinese governmental practices.
Differences between Chinese and Khitan society included gender roles and marital practices: the Khitans took a more egalitarian view towards gender, in sharp contrast to Chinese cultural practices that segregated men's and women's roles. Khitan women were taught to hunt, managed family property, and held military posts. Many marriages were not arranged, women were not required to be virgins at their first marriage, and women had the right to divorce and remarry.
The Liao dynasty was destroyed by the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in 1125 with the capture of Emperor Tianzuo of Liao. However, the remnant Khitan, led by Yelü Dashi, established the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty), which ruled over parts of Central Asia for almost a century before being conquered by the Mongols. Although cultural achievements associated with the Liao dynasty are considerable, and a number of various statuary and other artifacts exist in museums and other collections, major questions remain over the exact nature and extent of the influence of the Liao Khitan culture upon subsequent developments, such as the musical and theatrical arts.
La dynastie Liao (chinois simplifié : 辽朝 ; chinois traditionnel : 遼朝 ; pinyin : ; Khitan : Mos Jælud)1, également connue sous le nom d'Empire Khitan (chinois simplifié : 契丹国 ; chinois traditionnel : 契丹國 ; pinyin : ; Khitan : Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur)2, est un empire d'Asie orientale qui a régné sur la Mongolie, une partie de la Russie orientale et du nord de la Chine continentale entre 907 et 1125. Elle a été fondée par le Khagan Khitan Yelü Abaoji à la suite de la chute de la dynastie chinoise Tang.
Bien que couvrant essentiellement les steppes mongoles et quelques provinces du Nord de la Chine actuelle, la majorité de la population sous le contrôle de la dynastie était d'origine Chinoise Han. Le gouvernement Khitan a donc instauré un système administratif inédit visant à prendre en compte les spécificités de chaque partie du territoire, afin de mieux contrôler les populations locales. Cette période fut également une étape importante pour les Khitans, qui formalisent leur langue écrite à cette époque et commencent à intégrer de plus en plus les coutumes traditionnelles des Chinois Han.
L'empire a été détruit par les Jürchens de la dynastie Jin en 1125. Toutefois, certains survivants du peuple Khitan, menés par Yelü Dashi, ont établi la dynastie des Liao occidentaux. Connue également sous le nom de Khanate Kara-Khitans, cette dynastie a régné sur des parties de l'Asie centrale pendant près d'un siècle, avant d'être conquise à son tour par l'armée mongole de Genghis Khan.
La dinastia Liao (cinese tradizionale: 遼朝; cinese semplificato: 辽朝; pinyin: Liáo Cháo), 907-1125, conosciuta anche come impero Kitai (契丹國 / 契丹国 / Qìdān Guó), fu una dinastia che regnò sulle regioni della Manciuria, della Mongolia e su parte della Cina settentrionale. Fu fondata dalla tribù Yelü (耶律 Yēlǜ) del popolo Kitai nell'ultimo periodo della dinastia Tang, anche se il primo sovrano, Ābǎojī (阿保機 / 阿保机), proclamò il primo periodo di regno solo nel 916.
Nel 947 (o secondo altre fonti nel 938) l'imperatore Yelü Ruǎn adottò ufficialmente il nome "Liáo" (formalmente "Grande Liáo"). Abbandonato nel 983, il nome fu poi ripreso nel 1066.
Il regno dei Liao fu distrutto dagli Jurchi della dinastia Jīn nel 1125. I superstiti, guidati da Yelü Dashi, fondarono la dinastia Liao occidentale 1125-1220 o Kara Khitay, che sopravvisse fino all'arrivo dell'esercito mongolo di Gengis Khan.
La dinastía Liao (chino tradicional: 遼朝, chino simplificado: 辽朝, pinyin: Liáo Cháo, Wade-Giles: Liao2-Ch'ao2, kitán: Mos Jælut),12 907-1125, también conocida como Imperio kitán (契丹國 pinyin: Qìdān Guó, kitán: Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur)3 fue una dinastía china, de origen extranjero, que gobernó gran parte del nordeste del territorio chino actual.
Los kitán, uno de los grupos étnicos tunguses, de origen altaico, que habitaban hace siglos en la actual Manchuria, fundaron en el año 907 un estado que recibió inicialmente el nombre de Estado Kitán. Más adelante, tras conquistar el norte de China, el estado asumió formas de gobierno de estilo chino tomando el nombre dinástico de Liao, por el río del mismo nombre (en la actual provincia china de Liaoning) de su tierra ancestral. El imperio de los Liao convivió con la dinastía Song, al sur, y con el Imperio Tangut (o Xia Occidental), que gobernaba parte del noroeste chino.
El imperio de los kitán cayó definitivamente en el año 1125, derrotado por otro pueblo altaico, los yurchen, que conquistaron el territorio de los Liao, y fundaron su propia dinastía, la Jin.
Del nombre "kitán" deriva el nombre "Catay" con el que se conoció a China en Europa durante la Edad Media. El nombre actual de China en ruso (Kitái), mongol (Qitad) y uigur (Hitay) tiene también este mismo origen.
Ляо (монг. Кидан улс, кит. трад. 遼朝, упр. 辽朝, пиньинь: Liao chao, палл.: Ляо Чао) — государство кидань-монголов, которое занимало просторы Северо-Восточного Китая с момента основания киданьской государственности племенным вождём Абаоцзи (Амбагай) в 907 году до мятежа чжурчжэней в 1125 году. Столицы — Шанцзин (верховная, ныне Хуэйнинфу), Ляоян (восточная), Датун (западная), Наньцзин (южная, в районе современного Пекина).
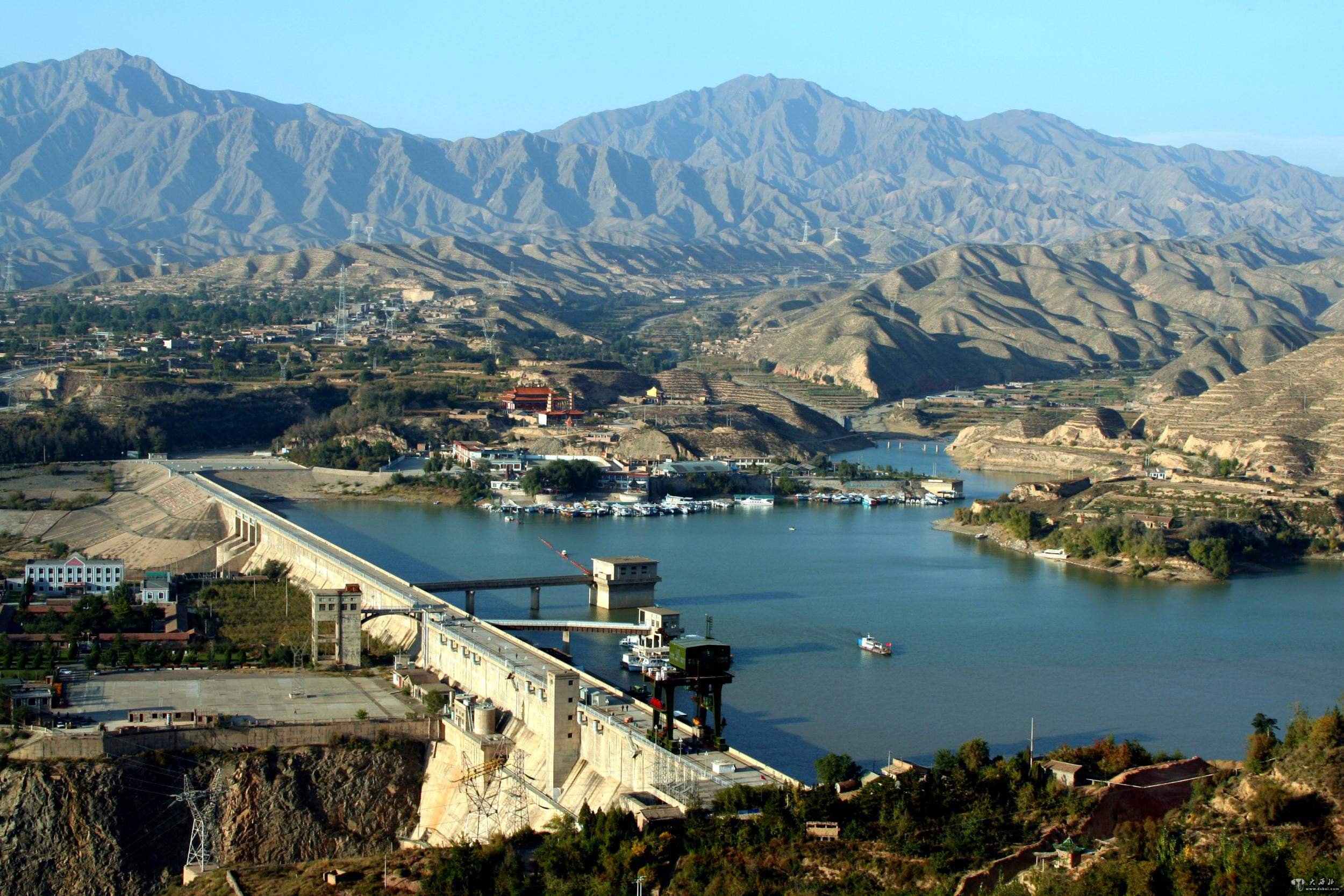
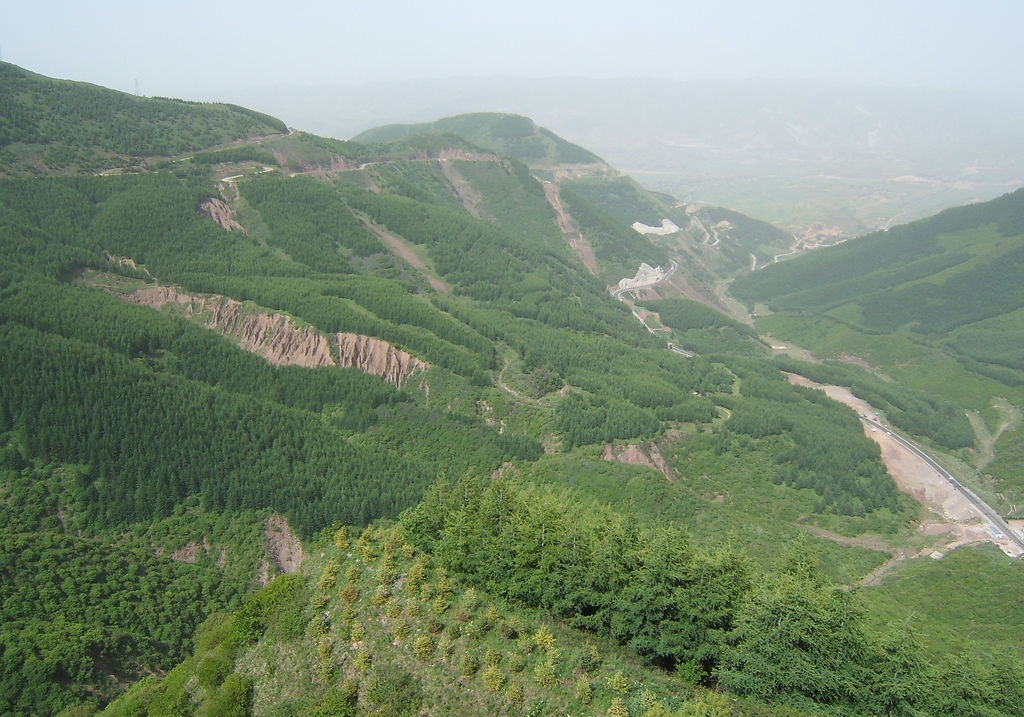



Das Liupan-Gebirge (Liupan Shan 六盘山, auch Liupan Shanmai 六盘山脉 oder (für den südlichen Teil) Long Shan 陇山) in Süd-Ningxia und Ost-Gansu ist einer der wenigen von Norden nach Süden verlaufenden Gebirgszüge Chinas im Grenzgebiet der chinesischen Provinzen Ningxia, Gansu und Shaanxi. Es ist ca. 240 km lang und bildet die Wasserscheide zwischen den Flüssen Wei He 渭河 und Jing He 泾河. Sein Hauptgipfel ist der Migang Shan 米缸山 an der Grenze von Jingyuan 泾源 und Longde 隆德 mit 2.942 Metern.

 *Yellow river
*Yellow river
 China
China
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
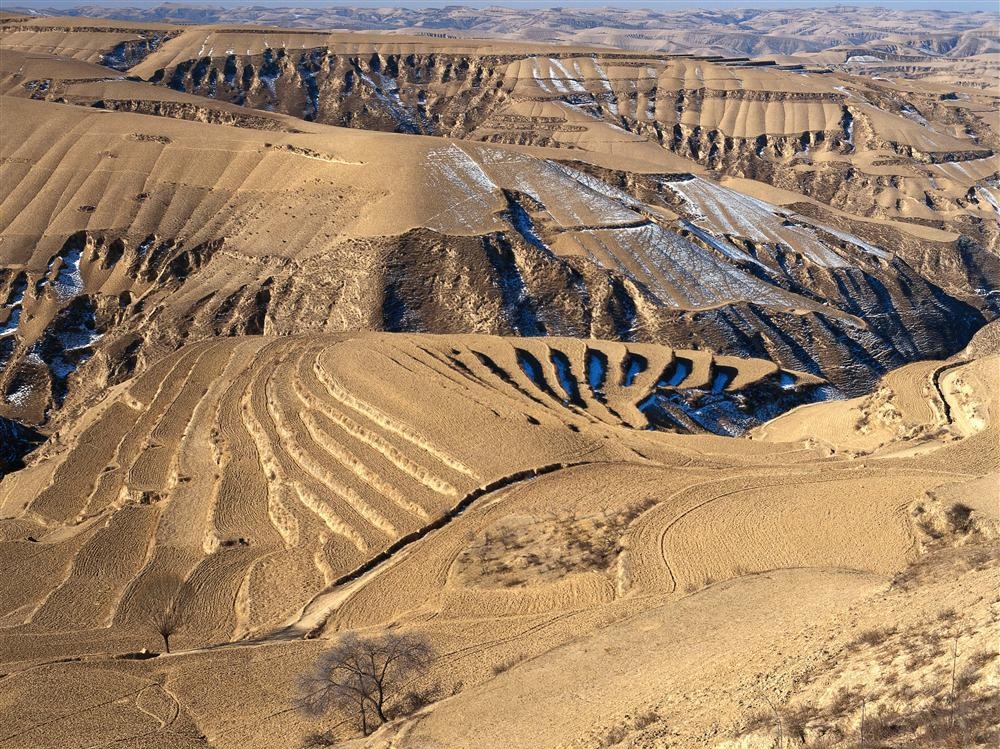

Das Lössplateau, Löss-Hochland (Huangtu gaoyuan 黃土高原) oder Löss-Bergland in Huabei (Nordchina) ist eine Hochlandstufe, die den Übergang vom Nordchinesischen Tiefland zum Hochland der (Inneren) Mongolei im Norden sowie dem Hochland von Tibet im Westen darstellt. Der Südrand wird durch die ebenfalls von Löss geprägten Gebiete im Flusstal des Gelben Flusses sowie dessen wichtigstem Nebenfluss, den Wei He, gebildet, die im Süden von den felsigen Gebirgsketten des Qin Ling überragt werden. Das Lössplateau dehnt sich ungefähr 1000 km ost-westlich und 700 km nord-südlich aus und umfasst weitgehend die Provinzen Shanxi und Shaanxi sowie Teilregionen der Provinzen Hebei, Henan, Gansu, Qinghai und der Inneren Mongolei. Die Lössschichten im Bergland der Provinzen Henan, Shaanxi, Shanxi und Gansu sind bis zu 300 m mächtig.
Traditionell haben die Bewohner dieser Gebiete ihre Behausungen häufig in den Löss hinein gearbeitet. Die Lösswohnungen zeichnen sich durch ein ausgesprochen angenehmes, ausgeglichenes Raumklima aus, das die Temperaturextreme der kalten Winter und heißen Sommer besser abzumildern vermag als moderne Neubauten.
Der Löss ist als äolisches Sediment, das vor allem aus Schluff besteht, ein aus den innerasiatischen Wüsten und Steppen ausgeblasenes Feinmaterial. Der verfestigte Flugstaub ist gelbbraun und äußerst nährstoffreich. Im ostasiatischen Lössbergland finden sich die weltweit mächtigsten Lössablagerungsschichten.
Entlang des Gelben Flusses, der seinen Namen von den mitgeführten Sedimenten hat, steht er in Ablagerungsschichten von bis zu 400 m an. Weltweit verfügt kein Fluss über eine stärkere Sedimentfracht, fast 40 Kilogramm pro Kubikmeter Wasser. Auf Grund der Sedimentation erhöht der Gelbe Fluss sein Bett im Tiefland und muss durch immer höhere Deiche eingedämmt werden. Bei Kaifeng und Zhengzhou liegt der Wasserspiegel bereits zehn Meter über dem Umland.


马家窑文化(公元前3300年 - 前2100年),为约间存在于甘肃西部、青海东部的彩陶新石器时代文化,與仰韶文化有許多共同特徵,与西北的齐家文化一样出土过早期的青铜器物。马家窑文化到底属不属于青铜文化仍有争议,甘肃省东乡林家遗址中曾出土过“青铜刀”,年代约在公元前2900年到公元前2740年,[1]为中国最早的青铜物品,同时该遗址还出土过铜渣,被認為可能已經有冶煉青铜器的能力。[2]
马家窑文化的製陶技術十分興盛,尤其是彩陶發現的數量驚人,而且十分精美。
马家窑文化主要分布在甘肃中南部地区,以陇西黄土高原为中心,东起渭河上游,西至河西走廊和青海省东北部,北达宁夏南部,南抵四川省北部。
Die Majiayao-Kultur (chinesisch 馬家窰文化 / 马家窑文化, Pinyin Mǎjiāyáo wénhuà, englisch Majiayao Culture) ist eine spätneolithische Kultur in der Region des oberen Gelben Flusses in Gansu und Qinghai, China. Sie wird nach der Radiokohlenstoffmethode auf die Zeit von 3000 bis 2000 v. Chr. datiert.
 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

| 分片名称 | 主要分布地区 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 郑开片 | 中原北侧:河南郑州、开封、鹤壁、濮阳,冀南大名县、魏县东。 | 属于淮北河南话,毗邻晋语邯新片区及冀鲁官话区。平翘音为郑开型。 |
| 洛嵩片 | 中原西北豫西洛阳市,此片都分布在河南境内。 | 属于淮北河南话,东有郑开片,西有关中片,南有南鲁片,北为晋语邯新片区。以洛阳话为代表。平翘音为洛阳型。 |
| 南鲁片 | 中原西南:豫西南南阳、豫中许昌、平顶山,以及陕东南商南县。 | 属于淮北河南话,东有漯项片,西过渡至西南官话川黔片汉中话,南有信蚌片及西南官话湖广片,北接郑开、洛嵩二片。平翘音为蔡鲁型。 |
| 漯项片 | 中原中央偏西:豫东南漯河、周口、驻马店,此片都分布在河南境内。 | 属于淮北河南话,东有商阜片,西有南鲁片,南有信蚌片,北有郑开片,四面都被中原官话包围。平翘音为蔡鲁型。 |
| 商阜片 | 中原中央偏东:豫东商丘,皖北阜阳、亳州、宿州。 | 属于淮北河南话,东有徐淮片,西有漯项片,南有信蚌片,北有兖菏片及郑开片,四面都被中原官话包围。 |
| 信蚌片 | 中原东南边缘:豫南信阳,皖东北蚌埠。 | 属于淮南河南话,毗邻江淮官话黄孝片及洪巢片宁庐方言区。 |
| 兖菏片 | 中原东北:鲁西南兖州、菏泽、枣庄、郯城、临沂等市,豫东北的范县、台前县,几乎在山东境内。 | 毗邻山东的冀鲁官话区,是山东话的一种,平翘音兼具三种类型。 |
| 徐淮片 | 中原东侧:苏北徐州、宿迁,皖北淮北、宿州,豫东永城市、夏邑县,鲁西南枣庄。 | 位于黄淮平原边界,毗邻江淮官话洪巢片扬淮方言区,平翘音有洛阳型及蔡鲁型。以徐州话为代表。 |
| 汾河片 | 晋南汾河下游的临汾、运城,陕东韩城。 | 与晋语吕梁片有关联,是晋语演化成中原官话的过渡区。是否归属于晋语,目前存在争议。 |
| 关中片 | 陕西西安、铜川、咸阳、渭南、商洛,宁夏泾源县,甘肃宁县,豫西三门峡湖滨区。 | 即关中东府话,以西安话为代表。 |
| 秦陇片 | 陕西宝鸡,宁夏固原,甘肃东南平凉、庆阳、陇南,在青海西宁有方言飞地。 | 即关中西府话。毗邻兰银官话区。 |
| 陇中片 | 甘肃东南天水、定西,宁夏西吉县、隆德县。 | |
| 河州片 | 甘肃临夏回族自治州,青海民和回族土族自治县、循化撒拉族自治县、乐都、同仁。 | 毗邻兰银官话区,词汇多为汉语词,但语法为突厥语架构。 |
| 南疆片 | 甘肃敦煌,新疆塔里木盆地吐鲁番、库尔勒、喀什、和田、阿克苏、阿图什等。 | 包含新疆生产建设兵团河南移民的“团场话”。 |




Maulid an-Nabī (arabisch مولد النبي ‚Geburtstag des Propheten‘) ist ein islamisches Fest zu Ehren des Propheten Mohammed. Es wird am 12. Tag des Monats Rabīʿ al-auwal des Islamischen Kalenders gefeiert. In mehreren islamischen Ländern, darunter Indonesien und Malaysia, ist der Tag Staatsfeiertag.[1] In Indonesien wird dieser Festtag auch maulud oder mulud (von arab. maulūd) genannt.
 Music
Music
 Architecture
Architecture
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Geography
Geography
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic