
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

唐朝(618年-907年),中国历史上的朝代,国祚共历289年,21位皇帝。由唐高祖李渊所建立。唐室出身自关陇世族,先祖李虎在南北朝的西魏是八柱国之一,封为唐国公[1]:254。其后代李渊为隋朝晋阳(在今山西太原西南)留守,在隋末民变时出兵入关中以争夺天下,于618年受隋恭帝杨侑禅位,在唐朝统一战争中统一天下。唐朝定都长安(今陕西省西安市),690年到705年为武周,定都神都洛阳[2]。
唐朝历史可以概略分成数个时期,大致上以安史之乱为界。初唐时国力强盛,李渊建立唐朝,是为唐高祖,其子秦王李世民以玄武门之变,杀害兄李建成、弟李元吉,逼迫高祖内禅帝位,即为唐太宗,是唐朝多次首都兵变的开端。太宗一手将唐朝带向盛世,击败强敌东突厥,受尊为“天可汗”,成就贞观之治。唐高宗时期击败西突厥、高句丽等强敌,建立永徽之治,把唐朝版图扩到最大。高宗去世后,其皇后武后先后拥立儿子中宗和睿宗当傀儡,最后于690年废睿宗自立为皇帝,改国号曰“周”,即武周,人称“武则天”,而此时女主政治也达到高峰。直到705年中宗因神龙革命而复辟,唐朝国号得以恢复。但接着还有韦后专权,之后宗室李隆基与其姑姑太平公主共同发起唐隆之变,才扫荡韦氏势力,结束自从中宗复辟后朝政紊乱的情况。李隆基也实际掌权,成为日后的唐玄宗。玄宗即位后便发动先天之变,赐死太平公主,结束数十年来的女主政治与百年来的政变时代,进入盛唐时期,是唐朝的第二高峰与转折,开元时期唐玄宗革除前朝弊端,政治开明,威服四周国家,史称开元盛世[3]:36。到天宝时期,政治逐渐混乱,于755年爆发安史之乱,唐朝盛极而衰。中唐时,唐朝受到河朔三镇、吐蕃的侵扰、宦官专权与牛李党争等内忧外患的影响而衰退。其间虽然有唐宪宗的元和中兴、唐武宗的会昌中兴与唐宣宗的大中之治,但是都未能根治唐朝的内忧外患。在晚唐时因为政治腐败,爆发唐末民变,其中黄巢之乱破坏江南经济,使唐朝经济完全瓦解,导致全国性的藩镇割据。唐室最后被藩镇朱全忠控制,他迫使唐昭宗迁都洛阳,并于907年逼唐哀帝禅位,唐灭亡,共289年。朱全忠建国梁,史称后梁,进入五代十国时期[4]:424。
唐朝的疆域广大,但时常变动,630年就超过隋朝极盛时的版图。唐朝也是自秦汉以来,第一个不使用前朝所筑长城及不筑长城的统一王朝[5][6][7]。其鼎盛时期为7世纪,当时中亚的绿洲地带受唐朝支配。其最大范围南至罗伏州(今越南河静)、北括玄阙州(今俄罗斯安加拉河流域)、西及安息州(今乌兹别克斯坦布哈拉)、东临哥勿州(今吉林通化)的辽阔疆域[8],国土面积达1076万平方千米[9]。中唐后漠北、西域的领地相继失去,到晚唐时衰退到等同中国本部的大小,但仍然保有河套地区及河西走廊[3]:36。天宝十三年(754年)户口统计为五千二百八十八万四百八十八人[10],不过许多学者考虑到当时统计不严,存在大量没有计入统计的瞒报户口[11],此外还有隐户、佃农、奴婢、士兵、僧道等人群不纳入户口统计,故大多数学者认为唐朝人口峰值在八千万左右[12][13][14]。此时,京兆府辖区人口估算在200万人左右,而市区则是100万人[15][16][17][18][19]。
唐朝在文化、科技、政治、经济、外交等方面都达到很高的成就。在中国历史上有大量的科技发明,四大发明中的火药即诞生于唐朝、雕版印刷开始广泛应用。其政治为三省六部制,前期中央权力在皇帝与宰相,中后期宦官影响力大增。同隋朝推行科举制度,使得晋朝南朝的世族制度不再兴起,中国历史上第一个状元、三元及第,都诞生于唐朝,即622年状元孙伏伽(一说651年的颜康成)[20]。军事制度前期采用府兵制,军力强盛,多次击败外族。后期则出现节度使(藩镇)的军政制度,割据一方,到唐朝后期还出现四十八个藩镇。唐朝是当时世界的强国,与突厥、高句丽、吐蕃、大食争夺四方霸权。借由羁縻制度控制回纥、契丹等北方各族,还调度漠北地区的突厥诸部军队攻打西突厥、高句丽[21],并且让南诏、高昌、龟兹、粟特、吐蕃、新罗、渤海国和日本等国家吸收唐朝的文化与政治体制[3]:38。唐朝的经济富盛,结合华北、关中与江南的经济,到后期更加依重江南赋税。土地、盐铁与赋税制度随着社会改变而改革,由均田制与租庸调制转向两税制,并且增加许多杂税。其中两税制影响中国后半期的赋税制度[4]:424。唐朝文化兼容并蓄,接纳各个民族与宗教,进行交流融合,成为开放的国际文化[22]:126。其文学发展达到高峰,以诗最为兴盛。当时有李白、杜甫等诗人,以及推行古文运动的韩愈,其史书与传奇(小说的前身)也十分发达。由于吸收西域特征与宗教色彩,唐朝艺术与前后朝代都迥然不同,其壁画、雕刻、书法与音乐都很发达[23]:758。唐朝声誉远及海外,其历史地位深重,到明清时期海外多称中国人为“唐人”[24]。
Die Tang-Dynastie (618-907) hatte 20 Kaiser und eine Kaiserin aus 14 Generationen und war mit einer Dauer von 289 Jahren die längste Dynastie in der chinesischen Geschichte. Davon fiel fast die Hälfte der Dauer mit fast 130 Jahren auf das sogenannte Goldene Zeitalter.
Aufstieg und Entwicklung zum Goldenen Zeitalter
唐(とう、拼音: 、618年 - 907年)は、中国の王朝である。李淵が隋を滅ぼして建国した。7世紀の最盛期には、中央アジアの砂漠地帯も支配する大帝国で、中央アジアや、東南アジア、北東アジア諸国、例えば朝鮮半島や渤海、日本などに、政制・文化などの面で多大な影響を与えた世界帝国である。日本の場合は遣唐使などを送り、894年(寛平6年)に菅原道真の意見でその回の遣唐使を中止し、結果としてそれ以降遣唐使は送られず、それまでは積極的な交流をしていた。首都は長安に置かれた。
690年に唐王朝は廃されて武周王朝が建てられたが、705年に武則天が失脚して唐が復活したことにより、この時代も唐の歴史に含めて叙述することが通例である。
日本では唐の滅亡後も唐、唐土の語はそれ以降の王朝、さらには外国全般を漠然と指す語として用いられた。しかし、天竺同様昔の呼称のため、正確に対応するわけではない。詳しくは中国を参照のこと。
The Tang dynasty (/tɑːŋ/;[4] Chinese: 唐朝[a]) or the Tang Empire was an imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture.[6] Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Tang capital at Chang'an (present-day Xi'an) was the most populous city in the world in its day.
The Lǐ family (李) founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire. The dynasty was briefly interrupted when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Second Zhou dynasty (690–705) and becoming the only Chinese empress regnant. In two censuses of the 7th and 8th centuries, the Tang records estimated the population by number of registered households at about 50 million people.[7][8] Yet, even when the central government was breaking down and unable to compile an accurate census of the population in the 9th century, it is estimated that the population had grown by then to about 80 million people.[9][10][b] With its large population base, the dynasty was able to raise professional and conscripted armies of hundreds of thousands of troops to contend with nomadic powers in dominating Inner Asia and the lucrative trade-routes along the Silk Road. Various kingdoms and states paid tribute to the Tang court, while the Tang also conquered or subdued several regions which it indirectly controlled through a protectorate system. Besides political hegemony, the Tang also exerted a powerful cultural influence over neighboring East Asian states such as those in Japan and Korea.
The Tang dynasty was largely a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule, until the An Lushan Rebellion and the decline of central authority in the later half of the dynasty. Like the previous Sui dynasty, the Tang dynasty maintained a civil-service system by recruiting scholar-officials through standardized examinations and recommendations to office. The rise of regional military governors known as jiedushi during the 9th century undermined this civil order. Chinese culture flourished and further matured during the Tang era; it is traditionally considered the greatest age for Chinese poetry.[11] Two of China's most famous poets, Li Bai and Du Fu, belonged to this age, as did many famous painters such as Han Gan, Zhang Xuan, and Zhou Fang. Scholars of this period compiled a rich variety of historical literature, as well as encyclopedias and geographical works. The adoption of the title Tängri Qaghan by the Tang Emperor Taizong in addition to his title as emperor was eastern Asia's first "simultaneous kingship".[12]
Many notable innovations occurred under the Tang, including the development of woodblock printing. Buddhism became a major influence in Chinese culture, with native Chinese sects gaining prominence. However, in the 840s the Emperor Wuzong of Tang enacted policies to persecute Buddhism, which subsequently declined in influence. Although the dynasty and central government had gone into decline by the 9th century, art and culture continued to flourish. The weakened central government largely withdrew from managing the economy, but the country's mercantile affairs stayed intact and commercial trade continued to thrive regardless. However, agrarian rebellions in the latter half of the 9th century resulted in damaging atrocities such as the Guangzhou massacre of 878–879.
La dynastie Tang (chinois : 唐朝 ; Wade : T'ang ; EFEO : T'ang, Ten quelquefois) (18 juin 618 - 1er juin 907) est une dynastie chinoise précédée par la dynastie Sui (581-618) et suivie par la période des Cinq Dynasties et des Dix Royaumes. Elle a été fondée par la famille Li, qui prit le pouvoir durant le déclin et la chute de l'empire Sui.
Venant après une longue période de division de la Chine qui dura de 220 à 581, à laquelle l'éphémère dynastie Sui avait mis fin, les premiers empereurs de cette dynastie eurent d'abord pour tâche de stabiliser l'empire récemment réunifié, et de lui redonner la puissance qu'avait eue la Chine à l'époque des Han. Ils firent rapidement mieux que ces derniers dans le domaine des conquêtes extérieures. Sous les premiers empereurs Tang (en particulier Taizong, l'impératrice Wu Zetian et Xuanzong), l'empire chinois connut une période de prospérité et un rayonnement culturel considérable. Sa capitale Chang'an, la plus grande ville du monde, reflétait toute la puissance et le cosmopolitisme, qui reposait notamment sur le dynamisme des échanges à longue distance le long de la route de la soie et des voies maritimes méridionales. Cette période a été vue par les générations suivantes comme un véritable âge d'or de la civilisation chinoise, symbolisé notamment par les brillants poètes Li Bai et Du Fu, et plus largement l'émergence d'un groupe de nombreux lettrés passés par les examens impériaux qui furent mis en place par les premiers empereurs Tang.
L'histoire de la dynastie bascula en 755 avec la révolte d'An Lushan, conséquence dramatique des évolutions politiques et militaires de l'empire à la période de son apogée. Après la difficile répression de ce soulèvement, l'organisation de l'empire se présenta sous un jour nouveau : la vieille aristocratie qui l'appuyait déclina irrémédiablement, supplantée par des hommes nouveaux disposant des charges militaires provinciales les plus importantes ou des grandes commissions fiscales et financières. Les empereurs ne parvinrent pas à contenir les forces centrifuges qui leur firent perdre l'autorité sur leurs provinces, même si cela n'entrava pas la prospérité de leur empire, portée par l'expansion démographique et économique des régions du Sud. Après une série de révoltes dans les dernières décennies du IXe siècle, la dynastie Tang s'éteint en 907, alors que son empire avait été dépecé. Les évolutions politiques, sociales, économiques et intellectuelles de cette période avaient déjà fait pénétrer la Chine dans une période que les historiens considèrent couramment comme « moderne », annonciatrice de la période de la dynastie Song (960-1272) qui réunifia la Chine quelques décennies après la fin des Tang.
Plusieurs innovations importantes sont apparues durant la dynastie Tang, dont le développement des caractères d'imprimerie en bois. Dans le domaine religieux, le bouddhisme eut une influence majeure dans la culture chinoise, avec l'affirmation de sectes bouddhistes aux racines spécifiquement chinoises et le développement d'un art remarquable. Toutefois, cette religion fut par la suite persécutée et son influence déclina, tandis que le taoïsme conservait une grande importance et que s'amorçait le retour du confucianisme, porté par les écrits de Han Yu.
La dinastia Tang (唐朝T, TángcháoP, 618-907) seguì la dinastia Sui, che aveva riportato l'unità politica in Cina, e fu seguita da un'epoca di disunione nota come il periodo delle Cinque dinastie e dieci regni.
Gli effetti del suddetto consolidamento iniziano a notarsi sotto l'imperatore Tai Zong (627 – 649), che ristabilisce il protettorato cinese sulla regione del bacino del Tarim (Asia centrale). Egli unisce la casa imperiale del Tibet alla Cina tramite matrimonio, intraprende la conquista della Corea e mantiene relazioni con il Giappone e i reami del Funan e del Champa. Con l'imperatore Xuan Zong (713 – 756) la Cina conosce un periodo di pace e prosperità, che favorisce il fiorire di produzioni artistiche.
La dinastía Tang (chino simplificado y tradicional: 唐朝, pinyin: Táng Cháo, Wade-Giles: T'ang2 Ch'ao2; ![]() tʰɑ̌ŋ tʂʰɑ̌ʊ̯ (?·i)) (618-907) fue la sucesora de la dinastía Sui y predecesora del período de las Cinco Dinastías y los Diez Reinos en China. La dinastía fue interrumpida por la segunda dinastía Zhou (690-705), cuando la emperatriz Wu Zetian usurpó el trono y fundó su propia dinastía. La dinastía Tang, con su capital en Chang'an (actual Xi'an), la ciudad más poblada del mundo en ese entonces, está considerada por los historiadores como un momento de esplendor de la civilización china, igual —o incluso superior— al del período Han.
tʰɑ̌ŋ tʂʰɑ̌ʊ̯ (?·i)) (618-907) fue la sucesora de la dinastía Sui y predecesora del período de las Cinco Dinastías y los Diez Reinos en China. La dinastía fue interrumpida por la segunda dinastía Zhou (690-705), cuando la emperatriz Wu Zetian usurpó el trono y fundó su propia dinastía. La dinastía Tang, con su capital en Chang'an (actual Xi'an), la ciudad más poblada del mundo en ese entonces, está considerada por los historiadores como un momento de esplendor de la civilización china, igual —o incluso superior— al del período Han.
Эпоха Тан (Династия Ли 李) (18 июня 618 — 4 июня 907, кит. 唐朝, Танчао) — китайская императорская династия, основанная Ли Юанем. Его сын, император Ли Шиминь, после окончательного подавления крестьянских восстаний и сепаратистских феодальных сил начал проводить прогрессивную политику. Именно эпоха Тан традиционно считается в Китае периодом наивысшего могущества страны, когда она опережала остальные современные ей страны мира в своём развитии.







 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ

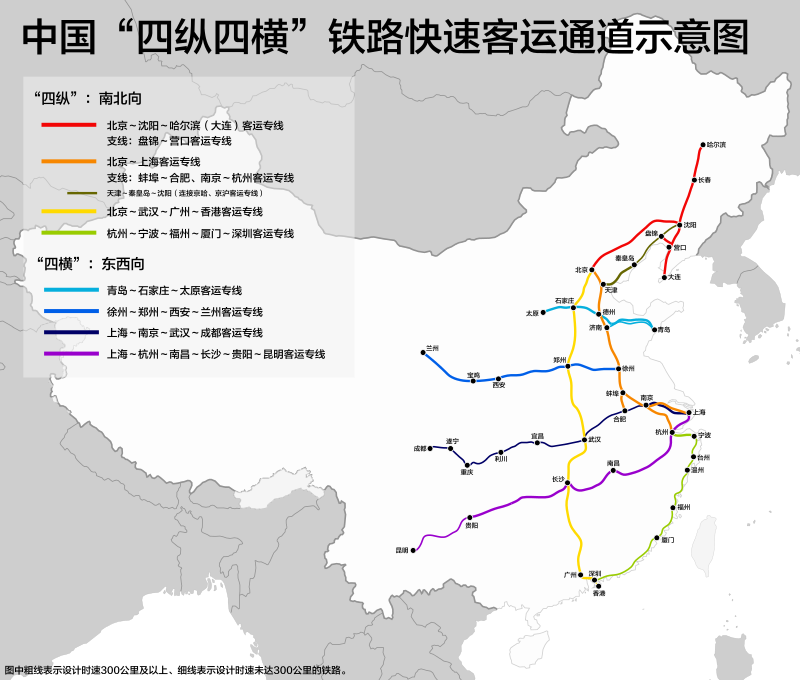
 Transport und Verkehr
Transport und Verkehr
 Hochgeschwindigkeitsverkehr
Hochgeschwindigkeitsverkehr
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
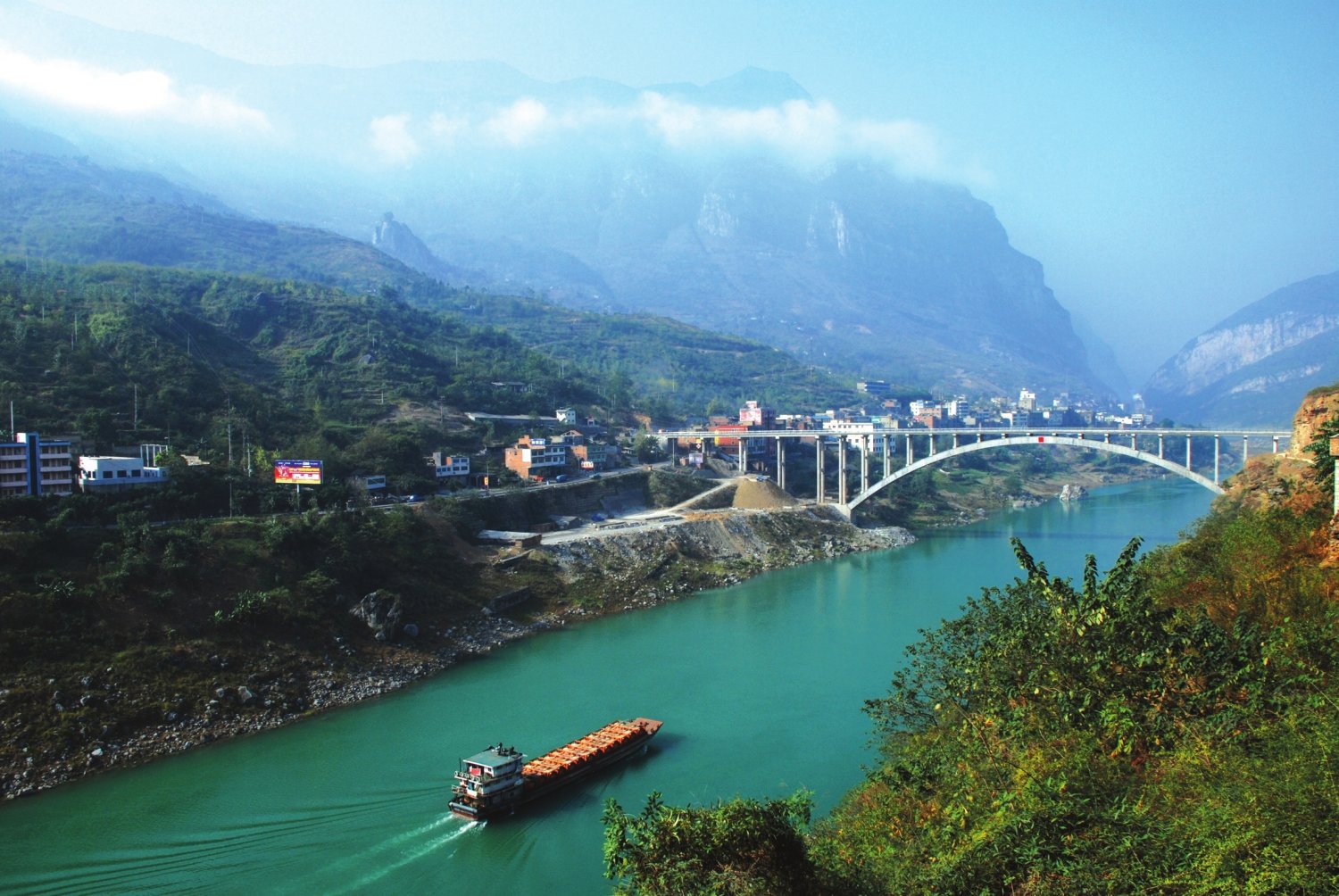


Der Wu Jiang (chinesisch 乌江) ist ein rechter Nebenfluss des Jangtsekiang. Er hat eine südliche und nördliche Quelle, die südliche ist der Sancha He (三岔河), die nördliche der Liuchong He (六冲河).
Nach dem Zusammenfluss heißt der Fluss zunächst Yachi, erst ab Wujiangdu (乌江渡) im Kreis Zunyi trägt er den Namen Wu Jiang. Die Quelle des Sancha He liegt im Westteil der Provinz Guizhou im Kreis Weining (威宁县) am östlichen Fuß des Gebirges Wumeng Shan (乌蒙山). Er fließt durch den Norden Guizhous und den Süden von Chongqing, im Gebiet von Fuling (涪陵区) mündet er in den Jangtsekiang. Der Wu Jiang ist über 1000 km lang. Mittel- und Unterlauf sind schiffbar.
Zu seinen Nebenflüssen zählen Liuchong He (六冲河), Maotiao He (猫跳河), Qingshui Jiang (清水江), Xiang Jiang (湘江), Zhuo He (濯河), Hongdu He (洪渡河), Yu Jiang (郁江) und Furong Jiang (芙蓉江).

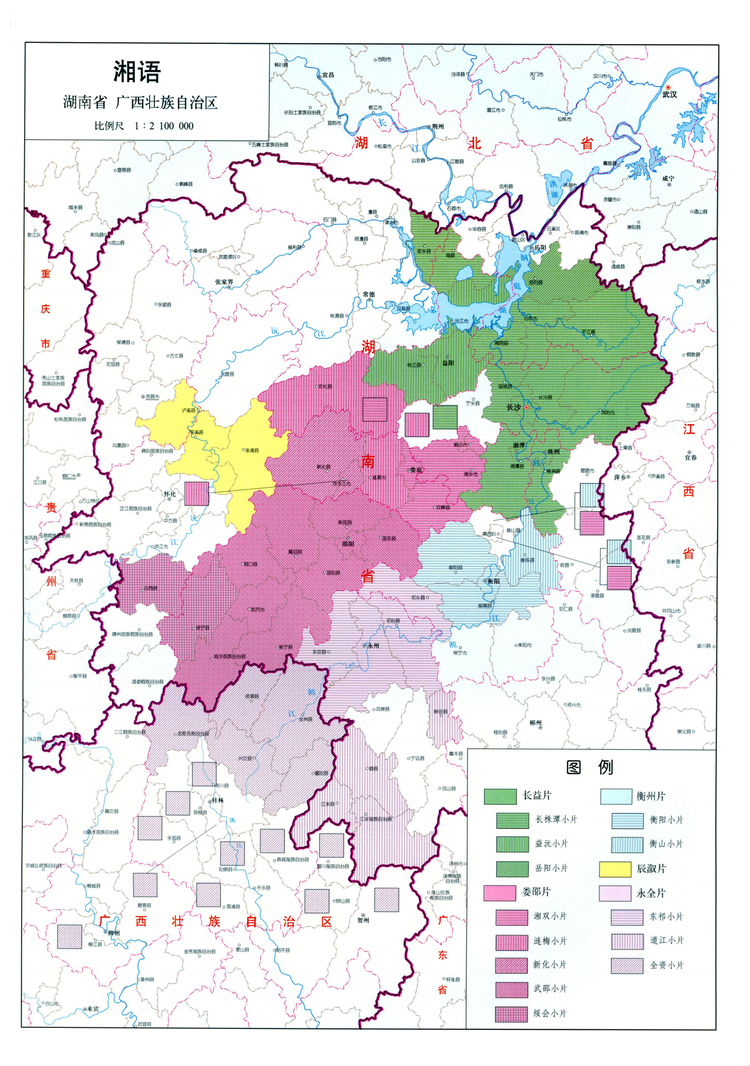
湘语(新湘语长沙话:/ɕiæ̃334 y42/;老湘语娄底话:/siɔŋ44 ny42/),又称作湘方言,有时也被泛称为湖南话,是汉藏语系汉语族的一门语言[3],是生活在中国洞庭湖、湘江、资江流域一带的湖湘民系使用的母语。现在,湘语使用者主要分布在湖南的大部分地区,包括长沙、湘潭、株洲、益阳、岳阳、娄底、衡阳、邵阳、怀化、永州等,以及广西壮族自治区的东北角一带。[3]
湘语是汉语的一支。若视汉语为“汉语族”的话,则湘语为一种单独的语言,而湘语内部可以划分出数支不同的湘语方言。无论如何划分,湘语的地位都跟官话、吴语、粤语、闽语、晋语、客语、赣语等相同,要么同为汉语之下的一级方言,要么同为汉语族里一种单独的语言。
Xiang, veraltet Hsiang, (chinesisch 湘語 / 湘语, Pinyin Xiāngyǔ, auch 湘方言, Xiāngfāngyán – „Xiang-Regionalsprache, Xiang-Mundart“) ist eine der chinesischen Sprachen. Sie ist nach dem Xiang-Fluss benannt und wird von über 30 Millionen Menschen vor allem in der Provinz Hunan gesprochen. Daher wird die Regiolekt auch als Hunan-Dialekt (湖南语, Húnányǔ, auch 湖南话, Húnánhuà) bezeichnet. Xiang war auch die Muttersprache Mao Zedongs.
 Geographie
Geographie
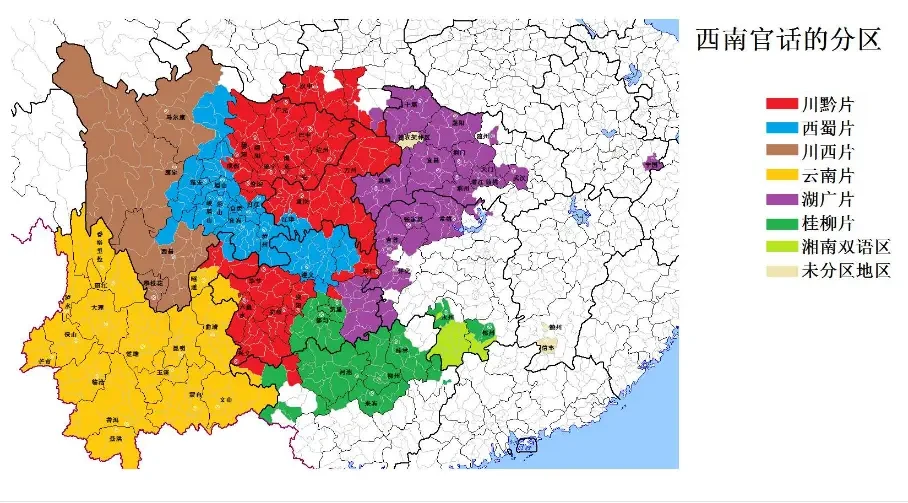
 Geschichte
Geschichte

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Sport
Sport
 Urlaub und Reisen
Urlaub und Reisen



 Essen und Trinken
Essen und Trinken