
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 AFC Champions League 2015
AFC Champions League 2015
 AFC Champions League 2016
AFC Champions League 2016
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2018
AFC Champions League 2018
 AFC Champions League 2019
AFC Champions League 2019
 AFC Champions League 2020
AFC Champions League 2020
 AFC Champions League 2021
AFC Champions League 2021
 AFC Champions League 2022
AFC Champions League 2022
 AFC Champions League 2023
AFC Champions League 2023
 AFC Champions League 2024
AFC Champions League 2024
 AFC Champions League 2025
AFC Champions League 2025
 Australia
Australia
 China
China
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Katar
Katar
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Thailand
Thailand
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates



 Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
Abd al-Fattah as-Sisi
 Abdullah II.
Abdullah II.
 Aleksandar Vučić
Aleksandar Vučić
 Aljaksandr Lukaschenka
Aljaksandr Lukaschenka
 António Costa
António Costa
 António Guterres
António Guterres
 Charles III.
Charles III.
 Charles Michel
Charles Michel
 Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron
 Fumio Kishida
Fumio Kishida
 Giorgia Meloni
Giorgia Meloni

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah
 Henri, Großherzog von Luxemburg
Henri, Großherzog von Luxemburg
 Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Aliyev
 Joko Widodo
Joko Widodo
 Kaja Kallas
Kaja Kallas
 Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
 Mark Rutte
Mark Rutte
 Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan
 Narendra Modi
Narendra Modi
 Pedro Sánchez
Pedro Sánchez
 Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan
 Rishi Sunak
Rishi Sunak
 Ukhnaagiin Khürelsükh
Ukhnaagiin Khürelsükh
 Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula von der Leyen
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates


 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 §Shipping company
§Shipping company

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Container Ship
Container Ship
 United Arab Shipping Company,UASC
United Arab Shipping Company,UASC
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Bahrain
Bahrain

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institute of Culture and Language
Institute of Culture and Language
 India
India
 Katar
Katar
 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Oman
Oman
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

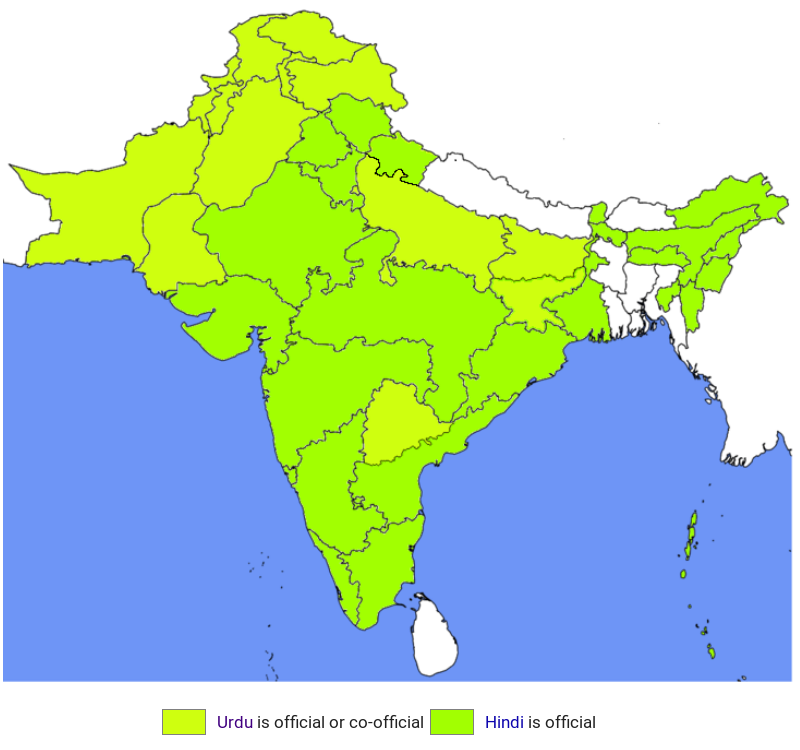
Urdu (anhörenⓘ/?) (persisch: اردو DMG urdū; kurz für زبان اردو معلہ DMG zabān-i urdū-yi muʿalla, deutsch ‚Sprache des königlichen Lagers‘)[1] ist eine indoarische Sprache und gehört zum indoiranischen Zweig der indogermanischen Sprachfamilie. Die Bezeichnung „Urdu“ tauchte erstmals im Jahr 1780 in den Gedichten von Ghulam Hamdani Mushafi auf. Ältere und heute weniger gebräuchliche indigene Namen waren لشکری Laschkarī, abgekürzt von لشکری زبان laschkarī zubān, deutsch ‚Armeesprache‘, کھڑی بولی kharī bolī, deutsch ‚stehende / etablierte Sprache‘ oder einfach ہندوی Hindavī, deutsch ‚indisch‘.
乌尔都语(乌尔都语:اُردُو)是属于印欧语系印度-伊朗语族的印度-雅利安语支。从使用人数来看,乌尔都语大约排名世界第20名,是巴基斯坦的国语,也是印度的24种规定语言之一。如果从宏观角度来看,乌尔都语可看成是印度斯坦语的一部分,所有印度斯坦语言构成世界上第四大的语言。在1200年到1800年,南亚在德里苏丹国和莫卧儿帝国的统治下,乌尔都语受到波斯语、突厥语、库尔德语和阿拉伯语的影响。




Die Vereinigten Arabischen Emirate (arabisch الإمارات العربية المتحدة, DMG al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida; amtlich: arabisch دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة, DMG Dawlat al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida ‚Staat der Vereinigten Arabischen Emirate‘), kurz VAE, sind eine Föderation von sieben Emiraten im Osten der Arabischen Halbinsel in Südwestasien. An der Küste des Persischen Golfs gelegen und mit Zugang zum Golf von Oman, grenzt das Land an Saudi-Arabien und Oman. Es besteht aus den Emiraten Abu Dhabi, Adschman, Dubai, Fudschaira, Ra’s al-Chaima, Schardscha und Umm al-Qaiwain.
Die Hauptstadt der VAE ist Abu Dhabi, als eine der fünf großen Städte des Landes neben Dubai, Schardscha, Adschman und Al-Ain ist es auch ein wichtiges Wirtschafts- und Kulturzentrum.[5]
Vor der Unabhängigkeit 1971 waren die VAE wegen der Protektoratsverträge, die die einheimischen Herrscher im 19. Jahrhundert mit dem Vereinigten Königreich abgeschlossen hatten, als „Vertragsküste“ oder „Vertragsstaaten“ bekannt. Das politische System gründet auf der Verfassung von 1971. Der Islam ist die offizielle Religion und Arabisch die offizielle Sprache. Das siebte Emirat Ra’s al-Chaima kam 1972 dazu.
Die VAE besitzen die siebtgrößten Ölvorkommen der Welt, sind die am weitesten entwickelten Volkswirtschaften des Nahen Ostens[6] und eines der reichsten Länder der Welt mit einem Pro-Kopf-Bruttoinlandsprodukt von $ 67.871 (Kaufkraftbereinigt).[7] Das Land steht beim Index der menschlichen Entwicklung auf dem 35. Platz (Stand 2019).[8][9] Der Internationale Währungsfonds klassifiziert die VAE als “high income developing economy”.
Das Land ist Gründungsmitglied des Golf-Kooperationsrates sowie Mitgliedsstaat der Arabischen Liga, der Vereinten Nationen, der Organisation für Islamische Zusammenarbeit, der OPEC und der Welthandelsorganisation.
アラブ首長国連邦(アラブしゅちょうこくれんぽう、アラビア語: الإمارات العربية المتحدة、英: United Arab Emirates,UAE)は、西アジア・中東に位置し、7つの首長国からなる連邦制国家。首都はアブダビ市。
アラビア半島のペルシア湾(アラビア語圏ではアラビア湾と呼ぶ)に面した地域にある。東部ではオマーンと、南部および西部ではサウジアラビアと隣接する。カタールとは国境を接していないが、カタールとの間のサウジアラビアの一部地域の領有権をめぐる論争がある。
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; Arabic: الإمارات العربية المتحدة al-ʾImārāt al-ʿArabīyyah al-Muttaḥidah), sometimes simply called the Emirates (Arabic: الإمارات al-ʾImārāt), is a country in Western Asia at the northeast end of the Arabian Peninsula on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman to the east and Saudi Arabia to the south and west, as well as sharing maritime borders with Qatar to the west and Iran to the north. The sovereign constitutional monarchy is a federation of seven emirates consisting of Abu Dhabi (which serves as the capital), Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah and Umm Al Quwain. Their boundaries are complex, with numerous enclaves within the various emirates.[9] Each emirate is governed by a ruler; together, they jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the rulers serves as the President of the United Arab Emirates.[10] In 2013, the UAE's population was 9.2 million, of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million are expatriates.[11][12][13]
Human occupation of the present UAE has been traced back to the emergence of anatomically modern humans from Africa some 125,000 BCE through finds at the Faya-1 site in Mleiha, Sharjah. Burial sites dating back to the Neolithic Age and the Bronze Age include the oldest known such inland site at Jebel Buhais. Known as Magan to the Sumerians, the area was home to a prosperous Bronze Age trading culture during the Umm Al Nar period, which traded between the Indus Valley, Bahrain and Mesopotamia as well as Iran, Bactria and the Levant. The ensuing Wadi Suq period and three Iron Ages saw the emergence of nomadism as well as the development of water management and irrigation systems supporting human settlement in both the coast and interior. The Islamic age of the UAE dates back to the expulsion of the Sasanians and the subsequent Battle of Dibba. The UAE's long history of trade led to the emergence of Julfar, in the present-day emirate of Ras Al Khaimah, as a major regional trading and maritime hub in the area. The maritime dominance of the Persian Gulf by Emirati traders led to conflicts with European powers, including the Portuguese Empire and the British Empire.
Following decades of maritime conflict, the coastal emirates became known as the Trucial States with the signing of the General Maritime Treaty with the British in 1820 (ratified in 1853 and again in 1892), which established the Trucial States as a British Protectorate. This arrangement ended with independence and the establishment of the United Arab Emirates on 2 December 1971, immediately following the British withdrawal from its treaty obligations. Six emirates joined the UAE in 1971, the seventh, Ras Al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972.[14]
Islam is the official religion and Arabic is the official language of the UAE. The UAE's oil reserves are the sixth-largest in the world while its natural gas reserves are the world's seventh-largest.[15][16] Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure.[17] The UAE's economy is the most diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, while its most populous city of Dubai is an important global city and international aviation and maritime trade hub.[18][19] Consequently, the country is much less reliant on oil and gas than in previous years and is economically focusing on tourism and business. The UAE government does not levy income tax although there is a system of corporate tax in place and Value Added Tax at 5% was established in 2018.[20]
The UAE's rising international profile has led to it being recognised as a regional and a middle power.[21][22] It is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, OPEC, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
Les Émirats arabes unis Écouter (abrégés en EAU ou Émirats ; en arabe : الإمارات العربية المتحدة (al-imārāt al-ʿarabiyyat al-muttaḥida) دولة الإمارات العربيّة المتّحدة (dawlat al-imārāt al-ʿarabiyyat al-muttaḥida)) sont un État fédéral, créé en 1971, situé au Moyen-Orient entre le golfe Persique et le golfe d'Oman. Il est composé de sept émirats : Abou Dabi, Ajman, Charjah, Dubaï, Fujaïrah, Ras el Khaïmah et Oumm al Qaïwaïn4. Sa capitale fédérale est la ville d'Abou Dabi.
Les Émirats arabes unis comptent parmi les plus importants producteurs et exportateurs de pétrole.
En 2018, il comptent 9 701 315 habitants. L'ONU estime que 90 % de la population est constituée d'immigrants2.
Les principales réserves gazières et pétrolières sont dans l'émirat d'Abou Dabi, déjà membre de l'Organisation des pays exportateurs de pétrole avant la création de la fédération. Les sept Émirats ne sont pas égaux entre eux en ce qui concerne les ressources pétrolières.
L'émirat de Dubaï s'est tourné depuis quelques années vers de nouvelles ressources telles que les ports francs, les nouvelles technologies mais surtout le tourisme de luxe. La ville de Dubaï est d'ailleurs devenue la capitale économique de la fédération.
Gli Emirati Arabi Uniti (in arabo: دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة, Dawlat al-Imārāt al-ʿArabiyya al-Muttaḥida, «Stato degli Emirati Arabi Uniti») sono uno Stato nel sud-est della Penisola araba, nell'Asia sud-occidentale. Esso è composto da sette emirati: Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujaira, Ras al-Khaima, Sharja e Umm al-Qaywayn. Prima del 1971, erano noti come gli Stati della tregua (Trucial States), con riferimento a una tregua imposta nel XIX secolo dai britannici ad alcuni sceicchi arabi che non contrastavano, e anzi foraggiavano, attività piratesche miranti a colpire il naviglio transitante nel tratto di mare di loro competenza. La nazione confina con l'Oman a sud-est, con l'Arabia Saudita a sud-Ovest ed è bagnata dal Golfo Persico a nord.
Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos (en árabe, دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدة Dawlat Al-Imārāt al-‘Arabīya al-Muttaḥida) —o simplemente conocido como EAU— es un país soberano constituido en monarquía federal5 de Oriente Medio, situado en la península de Arabia. Está compuesto por siete emiratos:6 Abu Dabi, Ajmán, Dubái, Fuyaira, Ras al-Jaima, Sarja y Umm al-Qaywayn. Limita con Omán al sureste, con el golfo Pérsico al norte y con Arabia Saudita al oeste y sur.
El petróleo es la principal fuente de ingresos y el componente esencial de su PIB.7 Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos son la 30ª economía por volumen de PIB y en cuanto al índice de desarrollo humano elaborado por Naciones Unidas fueron situados en el puesto n.º 42 de entre de 188 países en 2016.8
Los primeros asentamientos importantes en la región datan de la Edad del Bronce.9 En el siglo VII d.C. se vio la llegada del Islam y durante el siglo XVI, el territorio cayó bajo la influencia de las potencias coloniales europeas, asentándose finalmente el dominio británico. Tras el fin del protectorado del Reino Unido en diciembre de 1971, seis jeques formaron la unión suscribiendo la Constitución de 1971, a la cual se unió Ras al-Jaima unos meses después.10 Cada emirato conserva una considerable autonomía política, judicial y económica.11
Объединённые Ара́бские Эмира́ты (араб. الإمارات العربية المتحدة [аль-Имара́т аль-Араби́я аль-Мутта́хида], англ. United Arab Emirates), аббр. ОАЭ (сокращённо — Арабские Эмираты или просто Эмираты) — федеративное государство на Ближнем Востоке, состоящее из семи эмиратов (араб. إمارات [имара́т], ед.ч. إمارة [има́ра]), каждый из которых представляет собой государство — абсолютную монархию: Абу-Даби, Аджман, Дубай, Рас-аль-Хайма, Умм-эль-Кайвайн, Фуджейра и Шарджа. Некоторые из перечисленных эмиратов попадают под определение карликового государства.
Государство возглавляется президентом Объединённых Арабских Эмиратов, которым является эмир крупнейшего эмирата Абу-Даби. Столицей Объединённых Арабских Эмиратов также является одноимённая столица этого эмирата.
Такая ключевая роль эмирата Абу-Даби, крупнейшего и наиболее богатого из эмиратов, во многом связана с тем, что административное устройство ОАЭ опирается на право каждого эмирата распоряжаться запасами углеводородов на своей территории. Таким образом, фактически, в соответствии с запасами нефти распределяется влияние тех или иных эмиратов в определении общей политики страны. Например, эмир Дубая является главой правительства ОАЭ.
Государство ОАЭ расположено в юго-западной части Азии, восточной части Аравийского полуострова. Граничит с Саудовской Аравией на западе и юге, с Оманом — на юго-востоке и на северо-востоке (оманский полуанклав губернаторство Мусандам и его полный анклав, вилайет Мусандама Мадха). Омывается водами Персидского и Оманского заливов.

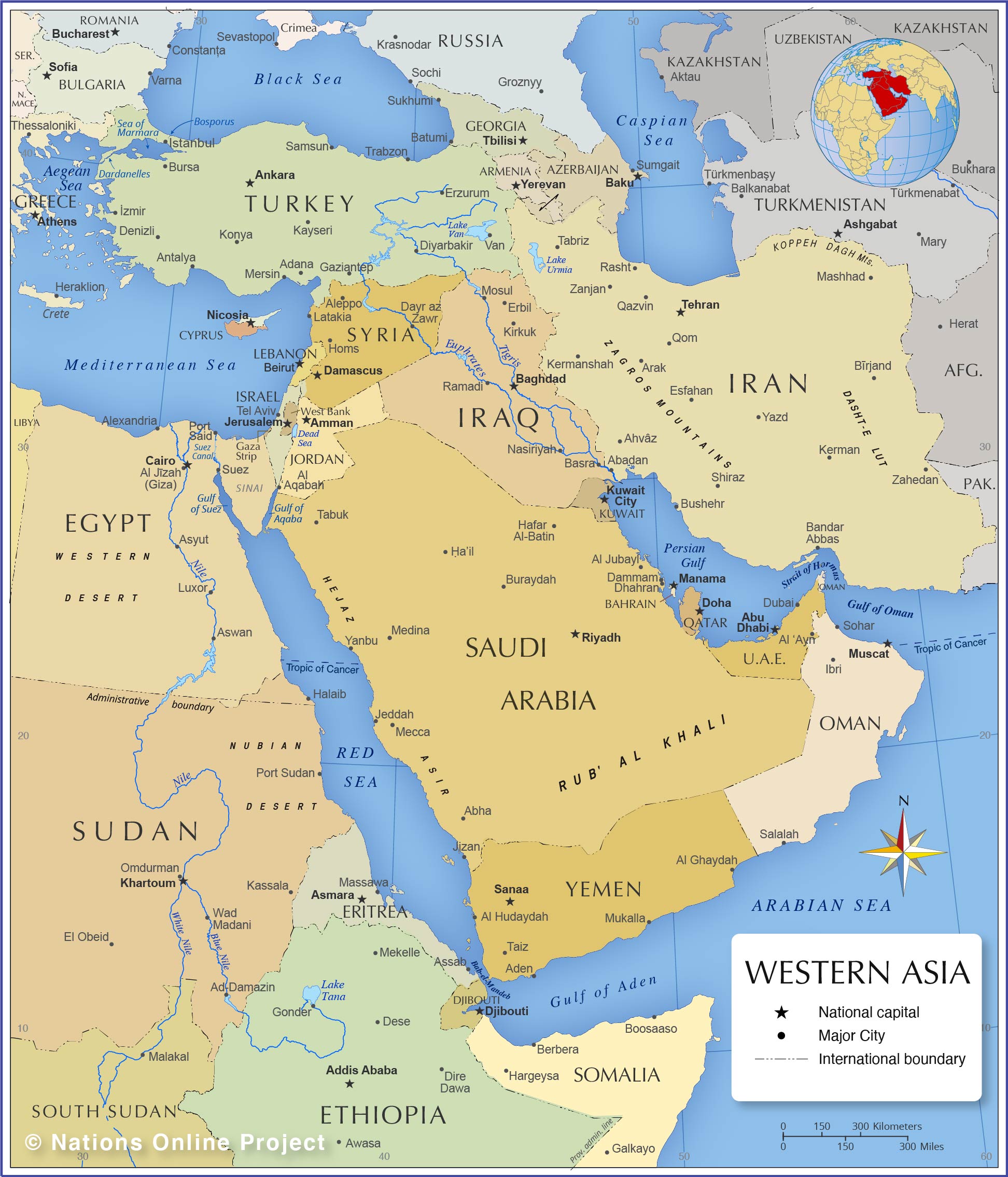
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Georgia
Georgia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Katar
Katar
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libanon
Libanon
 Oman
Oman
 Palestine
Palestine
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Syria
Syria
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Cyprus
Cyprus



 Sport
Sport
 Climate
Climate
 Companies
Companies
 Financial
Financial
 Geography
Geography
 Party and government
Party and government
 Architecture
Architecture
 Theme park
Theme park