
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO

 States of Europe
States of Europe
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
捷克共和国(捷克语:Česká republika),通称捷克(Česko),是一个位在于中欧的内陆国家。南面是奥地利,西面是德国,东北面是波兰,东面为斯洛伐克[7]。
捷克国家起源于波希米亚王国,是神圣罗马帝国的首都和三十年宗教战争的策源地,后成为奥地利帝国和奥匈帝国的工业中心。20世纪初,因一战结束而从奥匈帝国独立,和斯洛伐克合并为捷克斯洛伐克,名列世界七大工业国之一,二战时被纳粹德国吸收为保护国。冷战时代被苏联拉入东方集团,成为苏共的卫星国;1989年透过天鹅绒革命脱离共产体制转向民主,1993年经历天鹅绒分离与斯洛伐克以和平的方式分裂为独立国家,但两国关系依旧友好如初。捷克和德国、奥地利一样,在机械制造业、啤酒产业、观光旅游业领域都非常发达,也是所有斯拉夫民族的国家中教育程度最高及民主体制最稳定的国家,其福利政策在中欧国家中名列前茅。
Tschechien (tschechisch Česko, amtlich Tschechische Republik, veraltet auch Tschechei, tschechisch Česká republika ) ist ein Binnenstaat in Mitteleuropa mit rund 10,5 Millionen Einwohnern. Es setzt sich aus den historischen Ländern Böhmen (Čechy) und Mähren (Morava) sowie Teilen von Schlesien (Slezsko) zusammen. Das Land grenzt im Westen an Deutschland, im Norden an Polen, im Osten an die Slowakei und im Süden an Österreich. Hauptstadt und Millionenmetropole des Landes ist Prag (tschechisch Praha), weitere Großstädte sind Brünn (Brno), Ostrau (Ostrava), Pilsen (Plzeň), Reichenberg (Liberec) und Olmütz (Olomouc).
Im 6. Jahrhundert wanderten Slawen in das zuvor von Kelten und Germanen besiedelte Böhmen ein. Anfang des 9. Jahrhunderts bildete sich das Mährerreich als erstes slawisches Staatswesen heraus. Der geeinte tschechische Staat entstand unter der böhmischen Přemysliden-Dynastie, als im 11. Jahrhundert die Markgrafschaft Mähren Böhmen unterstellt und 1085 das Königreich Böhmen geformt wurde. Es hatte eine Sonderstellung im Heiligen Römischen Reich und beherrschte unter den Přemysliden und Luxemburgern große Gebiete Kontinentaleuropas. Im Zuge des Aufstiegs der Habsburger und des Dreißigjährigen Krieges wurde das Gebiet Teil der Habsburgermonarchie und blieb es bis zu deren Zerfall nach der Niederlage im Ersten Weltkrieg.
Im Jahre 1918 erfolgte die Gründung der demokratischen Tschechoslowakei. Im Jahre 1939 wurde der tschechische Landesteil durch das nationalsozialistische Deutschland besetzt und zum Protektorat Böhmen und Mähren erklärt. Im Jahre 1945 befreiten die Alliierten mit Unterstützung der Tschechoslowakischen Exilarmee das Land vom NS-Regime. Nach dem Krieg wurde die deutsche Minderheit vertrieben. Nachdem die Rote Armee den Großteil der Tschechoslowakei besetzt hatte, übernahm 1948 die Kommunistische Partei der Tschechoslowakei (KSČ) im sogenannten Februarumsturz die Macht im Land, das somit zum Satellitenstaat der Sowjetunion wurde. Die Reformbewegung des Prager Frühlings schlugen im Jahr 1968 Truppen des Warschauer Paktes nieder. Nach der Samtenen Revolution 1989 wurde unter Präsident Václav Havel die Demokratie wiedererrichtet. Die heutige Tschechische Republik entstand am 1. Januar 1993 mit der friedlichen Teilung der Tschechoslowakei. Sie ist seit 1999 Mitglied der NATO und seit 2004 Mitglied der Europäischen Union.
Tschechien ist ein Industriestaat. Sein Bruttoinlandsprodukt pro Einwohner ist das höchste der ehemaligen RGW-Mitglieder. Im Index der menschlichen Entwicklung belegte das Land 2019 weltweit Platz 26.[5] Sowohl im Bezug auf die politische als auch die wirtschaftliche Transformation belegt Tschechien Spitzenplätze.チェコ共和国(チェコきょうわこく、チェコ語: Česká republika、英: Czech Republic)、通称チェコは、中央ヨーロッパ[注釈 1]の共和制国家。首都はプラハである。国土は東西に細長い六角形に近い形をしており、北はポーランド、東はスロバキア、南はオーストリア、西はドイツと国境を接する。
1993年にチェコスロバキアがチェコとスロバキアに分離し成立した。NATO、EU、OECDの加盟国で、中欧4か国からなるヴィシェグラード・グループの一員でもある。
The Czech Republic,[a][11] also known by its short-form name Czechia[b][12] and formerly known as Bohemia,[13] is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the east.[14] The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of 78,871 square kilometers (30,452 sq mi) with a mostly temperate continental and oceanic climate.
The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial State of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became a kingdom in 1198.[15][16] Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the whole Crown of Bohemia was gradually integrated into the Habsburg Monarchy. The Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of the White Mountain, the Habsburgs consolidated their rule. With the dissolution of the Holy Empire in 1806, the Crown lands became part of the Austrian Empire.
In the 19th century, the Czech lands became more industrialized, and in 1918 most of it became part of the First Czechoslovak Republic following the collapse of Austria-Hungary after World War I.[17] Czechoslovakia was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a parliamentary democracy during the entirety of the interwar period.[18] After the Munich Agreement in 1938, Nazi Germany systematically took control over the Czech lands. Czechoslovakia was restored in 1945 and became an Eastern Bloc communist state following a coup d'état in 1948. Attempts at a liberalisation of the government and economy were suppressed by a Soviet-led invasion of the country during the Prague Spring in 1968. In November 1989, the Velvet Revolution ended communist rule in the country, and on 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia was dissolved, with its constituent states becoming the independent states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic is a unitary parliamentary republic and developed country with an advanced, high-income social market economy. It is a welfare state with a European social model, universal health care and tuition-free university education. It ranks 12th in the UN inequality-adjusted human development and 24th in the World Bank Human Capital Index ahead of the United States. It ranks as the 9th safest and most peaceful country and 31st in democratic governance. The Czech Republic is a member of NATO, the EU, OECD, OSCE, and the CoE.
La Tchéquie, en forme longue la République tchèque4 (en tchèque : Česko /ˈt͡ʃɛskɔ/ Écouter et Česká republika /ˈt͡ʃɛskaː ˈrɛpublɪka/ Écouter), est un pays d'Europe centrale sans accès à la mer, entouré par la Pologne au nord-est, l’Allemagne au nord-ouest et à l’ouest, l’Autriche au sud et la Slovaquie à l'est-sud-est.
Regroupant les régions historiques de Bohême et de Moravie et une partie de la Silésie, la République tchèque5 naît formellement le 1er janvier 1969 de la fédéralisation de la Tchécoslovaquie.
Elle est indépendante depuis le 1er janvier 1993 à l'occasion de la scission de la République fédérale tchèque et slovaque, dernière forme de gouvernement de la Tchécoslovaquie6.
La Tchéquie est membre de l’OTAN depuis le 12 mars 1999 et fait partie de l’Union européenne depuis le 1er mai 2004.
La Repubblica Ceca[4][5] (in ceco: Česká republika, ), conosciuta anche come Cechia[6] (Česko), è uno Stato membro dell'Unione europea, situato nell'Europa centrale.
Confina a sud-est con la Slovacchia, a sud con l'Austria, a ovest con la Germania e a nord con la Polonia. È uno Stato senza sbocco al mare. La sua capitale è Praga. È formata storicamente da tre grandi regioni: Boemia (ovest), Moravia (est) e Slesia (divisa con la Polonia).
Nata il 1º gennaio 1993, assieme alla Slovacchia, dalla pacifica scissione della Cecoslovacchia, che già dal 1990 aveva assunto il nome di Repubblica Federale Ceca e Slovacca, la Repubblica Ceca fa parte dell'Unione europea e della NATO ed è uno degli Stati più sicuri al mondo, secondo il Global Peace Index 2019.[7] Non ha adottato l'euro come valuta.
La República Checa (en checo, Česká republika, pronunciado [ˈt͡ʃɛskaː ˈrɛpuˌblɪka] (![]() escuchar)), también conocida abreviadamente como Chequia (Česko, pronunciado [ˈt͡ʃɛsko]),nota 1 es un país soberano de Europa Central sin litoral. Limita con Alemania al oeste, con Austria al sur, con Eslovaquia al este y con Polonia al norte. Su capital y mayor ciudad es Praga. La República Checa está formada por los territorios históricos de Bohemia y Moravia, además de una pequeña parte de Silesia.
escuchar)), también conocida abreviadamente como Chequia (Česko, pronunciado [ˈt͡ʃɛsko]),nota 1 es un país soberano de Europa Central sin litoral. Limita con Alemania al oeste, con Austria al sur, con Eslovaquia al este y con Polonia al norte. Su capital y mayor ciudad es Praga. La República Checa está formada por los territorios históricos de Bohemia y Moravia, además de una pequeña parte de Silesia.
El Estado checo, antes conocido como Bohemia, se formó en el siglo ix como un pequeño ducado en torno a Praga en el seno del entonces poderoso Imperio de Gran Moravia. Tras la disolución de este imperio en 907, el centro de poder pasó de Moravia a Bohemia bajo la dinastía Premislidas y desde 1002 el ducado fue formalmente reconocido como parte del Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico.1415 En 1212 el ducado alcanzó la categoría de reino y durante el gobierno de los reyes y duques Premislidas y sus sucesores, los Luxemburgo, el país alcanzó su mayor extensión territorial en los siglos xiii y xiv. Durante las guerras husitas el reino tuvo que sufrir embargos económicos y la llegada de caballeros cruzados de toda Europa.16
Tras la batalla de Mohács en 1526, el reino de Bohemia pasó a integrarse gradualmente a los dominios de los Habsburgo como uno de sus tres dominios principales, junto al archiducado de Austria y el reino de Hungría. La derrota de los bohemios en la batalla de la Montaña Blanca, que significó el fracaso de la revuelta de 1618-1620, llevó a la guerra de los Treinta Años y a una mayor centralización de la monarquía, además de a la imposición de la fe católica y la germanización. Con la disolución del Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico en 1806, el reino de Bohemia se integró en el Imperio austríaco.16 Durante el siglo xix las tierras checas se alzaron como centro industrial de la monarquía y después como núcleo de la República de Checoslovaquia que se creó en 1918, resultado del colapso del Imperio austrohúngaro en la Primera Guerra Mundial. Después de 1933, Checoslovaquia era la única democracia de toda la Europa central y del este.
Tras los Acuerdos de Múnich en 1938, la anexión polaca del área de Zaolzie y la ocupación alemana de Checoslovaquia y la consecuente desilusión de los checos con la pobre respuesta de Occidente, los comunistas se hicieron con su favor liberando el país del yugo nazi durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial. El Partido Comunista de Checoslovaquia ganó las elecciones de 1946 y en el Golpe de Praga de 1948 el país pasó a estar gobernado por el comunismo. Sin embargo, la creciente insatisfacción del pueblo llevó a intentar la reforma del régimen, que culminó en la conocida como Primavera de Praga de 1968 y provocó la invasión de las fuerzas armadas del Pacto de Varsovia, unas tropas que permanecieron en el país hasta la Revolución de Terciopelo de 1989, cuando colapsó el régimen comunista. El 1 de enero de 1993, Checoslovaquia se dividió pacíficamente en sus dos Estados constituyentes, la República Checa y la República Eslovaca.17
En 2006 la República Checa se convirtió en el primer exmiembro del Comecon en alcanzar el estatus pleno de país desarrollado según el Banco Mundial.18 Además, el país tiene el mayor índice de desarrollo humano de toda Europa Central y del Este19 y por ello está considerado un Estado con «Desarrollo humano muy alto». Es el noveno país más pacífico de Europa, el más democrático y el que registra menor mortalidad infantil de su región. La República Checa es una democracia representativa parlamentaria, miembro de la Unión Europea, la OTAN, la OCDE, la OSCE, el Consejo de Europa y el Grupo de Visegrado.
Че́хия (чеш. Česko, МФА (чешск.): [ˈʧɛskɔ], официально[7] — Че́шская Респу́блика (аббревиатура — ЧР); чеш. Česká republika (аббревиатура — ČR), МФА (чешск.): [ˈʧɛskaː ˈrɛpuˌblɪka]) — государство в Центральной Европе. Граничит с Польшей на севере (длина границы — 796 км), Германией — на северо-западе и западе (810 км), Австрией — на юге (466 км) и Словакией — на востоке (252 км)[8]. Общая протяжённость границы — 2324 км. Площадь — 78 866 км².
Современная Чехия образовалась в результате распада Чехословакии (Бархатный развод) 1 января 1993 года. Страна включает исторические области — Богемию, Моравию и часть Силезии. Унитарное государство. Относится к развитым странам. Столица Прага — туристическая достопримечательность и крупнейший город страны.
С 12 марта 1999 года Чехия — член НАТО, с 1 мая 2004 года — член Европейского союза.



 CESAER
CESAER

 Colleges and Universities in Europe
Colleges and Universities in Europe
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry





 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 San Marino
San Marino
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic


 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Belgium
Belgium

 Bretagne
Bretagne
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 Germany
Germany

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 England
England
 France
France

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia

 Lombardia
Lombardia

 Madrid
Madrid
 Monaco
Monaco
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Austria
Austria

 Piemonte
Piemonte
 Portugal
Portugal

 Saxony
Saxony

 Salzburg
Salzburg
 Schottland
Schottland
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Spain
Spain

 Styria
Styria
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 UEFA Champions League 2024/25
UEFA Champions League 2024/25
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Germany
Germany
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 France
France
 UEFA European Championship 2016
UEFA European Championship 2016
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024
 Greece
Greece
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Russia
Russia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Spain
Spain
 Spain
Spain
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 (F)European football championship
(F)European football championship
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Union of European Football Associations
Union of European Football Associations

Der Henri-Delaunay-Pokal (französisch Coupe Henri Delaunay) ist die Gewinntrophäe der Fußball-Europameisterschaft, die seit 1960 verliehen wird.
Der versilberte EM-Pokal wurde 1960 in Paris von Pierre Delaunay entworfen und vom Goldschmied Adrien Chobillon angefertigt,[1] der seinerseits für den französischen Pokal verantwortlich zeichnete. Er ist etwa zehn Kilogramm schwer und hat eine Höhe von 42,5 Zentimetern. Benannt wurde er nach dem Franzosen Henri Delaunay, dem ersten UEFA-Generalsekretär und „geistigem Vater“ der Fußball-Europameisterschaft.
Die EM-Trophäe bleibt als Wanderpokal in ständigem Eigentum der UEFA. Sollte eine Mannschaft dreimal in Folge oder fünfmal insgesamt Europameister werden, erhält der entsprechende Verband eine originalgetreue Nachbildung der Trophäe vom europäischen Fußballverband.

 European Union
European Union
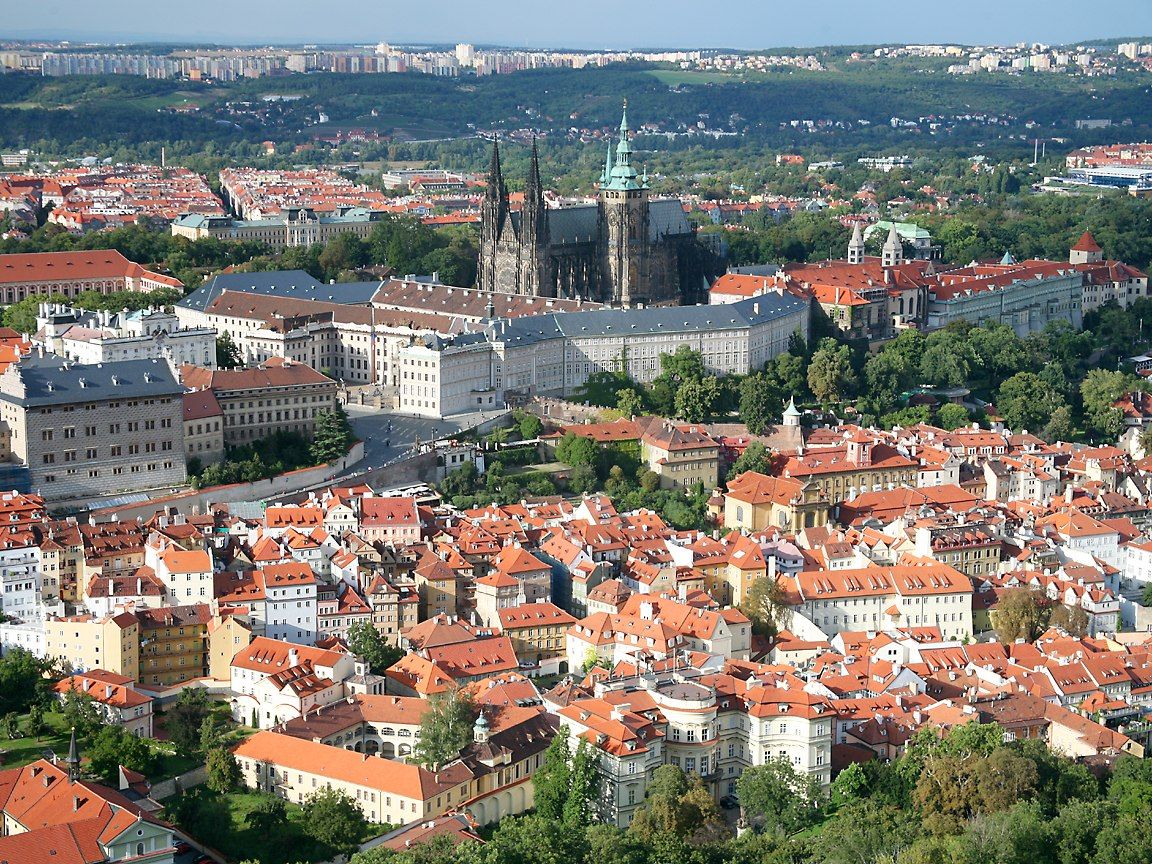

 Party and government
Party and government
 Literature
Literature
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 History
History
 Companies
Companies
 Energy resource
Energy resource