
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur


 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Australia
Australia

 California-CA
California-CA
 China
China

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 England
England
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kyūshū
Kyūshū
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 Russia
Russia

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA

美洲杯帆船赛(英语:America's Cup)是赛艇运动中保存的最著名也是最古老的一项体育比赛。
比赛奖杯是银质大口水罐,奖励给来自不同国家的两艘帆船之间举行的九局五胜制比赛的胜者。两艘帆船中,一艘代表卫冕冠军游艇俱乐部,另一艘则代表俱乐部挑战奖杯。
美洲杯帆船赛源于1851年8月22日,一艘由代表纽约游艇俱乐部(New York Yacht Club,NYYC)的财团拥有的30.86米长纵帆船“美洲号”(America),同15艘代表皇家快艇舰队(Royal Yacht Squadron)的帆船在英国南部的怀特岛附近比赛。“美洲号”最终以领先20分钟胜出。拥有“美洲号”的财团后来将奖杯通过馈赠契约捐献给纽约游艇俱乐部。由此,奖杯被托管成为一项鼓励各国之间友谊竞赛的“挑战”奖品。
在当时公认无敌的英国海上霸权遭受如此打击后,一系列英国财团试图赢回奖杯。但纽约游艇俱乐部在超过132年的25次挑战中保持不败,成为体育运动史上最长的连胜纪录。1930年以前,这项赛事一直在纽约港附近举行,余下的NYYC全盛时期内则改在罗德岛的纽波特(Newport,Rhode Island)举行。
Der America’s Cup ist die älteste noch heute ausgetragene Segelregatta. Der Preis ist ein Wanderpokal und hat seinen Ursprung in einer Regatta rund um die britische Insel Isle of Wight im Jahre 1851.[1] Er ist benannt nach seiner erstmaligen Gewinnerin, der Yacht America des New York Yacht Club (NYYC).
Um den America’s Cup treten die Boote zweier Yachtclubs – Verteidiger und Herausforderer – in mehreren Wettfahrten gegeneinander an. Die Yacht, die eine vorher festgelegte Anzahl von Wettfahrten gewinnt, gewinnt den Cup. Laut der Stiftungsurkunde bestimmt der Verteidiger das Segelrevier. Die Stiftungsurkunde sieht vor, dass Verteidiger und Herausforderer innerhalb gewisser Grenzen Vereinbarungen über die Regeln treffen können, z. B. was die Anzahl der Wettfahrten betrifft.[2]
Von der ersten Verteidigung 1870 bis zur 20. Regatta im Jahr 1967 gab es jeweils nur einen Herausforderer. Im Jahr 1970 gab es erstmals mehrere Herausforderer, so dass der veranstaltende New York Yacht Club sich einverstanden erklärte, den offiziellen Herausforderer durch eine Vorausscheidung zu ermitteln. Zwischen 1983 und 2007 bis zum zeitweiligen Rückzug des Sponsors Louis Vuitton und ab 2013 erneut wurde der Herausforderer durch den Louis Vuitton Cup ermittelt. Schon die Teilnahme am Louis Vuitton Cup setzte großes finanzielles Engagement voraus: die Budgets der High-Tech-Yachten betrugen teilweise über 100 Mio. Dollar. Die Yachten mussten im Land des angemeldeten Teams gebaut werden. Wesentliche Neuerungen ergaben sich bei den letzten beiden ACs. 2010 segelten das erste Mal sowohl Verteidiger wie Herausforderer mit Mehrrumpfbooten. 2013 waren Katamarane vereinbart und die teilnehmenden Teams konstruierten „Tragflügelkatamarane“ die über 40 Knoten (75 km/h) schnell segelten. Für 2017 wurden die Boote „AC50F Katamaran“ von ehemals 72 Fuß (fast 22 m) auf 50 ft (gut 15 m) verkürzt, blieben 24 m hoch und wurden im Training erstmals 50 kn (92 km/h) schnell.[3]
アメリカスカップあるいはアメリカズカップ[1](英: America's Cup)は、1851年より現在まで続く国際ヨットレース。また、その優勝杯の名。その成立は近代オリンピックより45年、サッカーのワールドカップより79年、全英オープンよりも9年早く、継続して使用されている世界最古のスポーツトロフィーとして広く一般に認知されている。[2][3]
名称の由来は最初の優勝艇の『アメリカ号』の名を冠した『アメリカ号のカップ』であり、決して『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』という意味ではない。しかし、その後132年に亘ってアメリカ合衆国のヨットクラブがカップを防衛してきたため、事実上『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』と同じ定義で称される。
競技の本質は、カップの寄贈者が記した贈与証書の規定に基づき、アメリカズカップを掛けてマッチレース(1対1)形式で争われるヨットクラブ間の国際親善レースである。しかし、使用されるヨットは出場国で建造しなければならないため、参加各国の造船工学・建築工学・材料工学・流体力学・航空力学・気象学などの最先端技術や軍事からの応用技術が投入される等、参加国の威信を賭けた国別対抗レースとしての一面も持ち合わせている。またこれら最新ヨットにはオリンピックメダリストら多数のトップセーラーが乗り組むことあり、一般にヨットレース全般、或いはインショア(沿海)レースの最高峰として位置づけられており、別名「海のF1」とも称される。
The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
La Coupe de l'America (America's Cup) est une compétition nautique internationale à la voile, voulue par ses initiateurs comme un défi amical et perpétuel entre Yacht Clubs de différentes nations et définie sous cette dénomination en 1857 par les membres du New York Yacht Club (NYYC)2, vainqueurs, six ans plus tôt, en 1851, avec la goélette America, de la régate internationale originelle, organisée autour de l'île de Wight, par le Royal Yacht Squadron (RYS), en marge de l'exposition universelle de Londres.
Le trophée est une aiguière en argent, attribuée au Yacht Club vainqueur du défi jusqu'à sa remise en jeu. Fabriquée en 1848 pour le Royal Yacht Squadron par le bijoutier et orfèvre Robert Garrard de Londres comme trophée de la Coupe de Cent Souverains, elle est ramenée aux États-Unis, en septembre 1851 sous le nom de Coupe de Cent Guinées, pour prendre en juillet 1857 son nom actuel de Coupe de l'America, en hommage à la goélette victorieuse.
C'est une des plus anciennes compétitions sportives encore disputée de nos jours et se révèle être l'un des principaux théâtres de l'évolution de l'architecture navale en matière de voiliers de régates.
À la suite de la régate de 1851 et de la création de la course en 1857, la première édition de la coupe de l'America n'est disputée qu'après la guerre de Sécession, en août 1870. Après ces deux compétitions, lors desquelles un voilier challenger affronte une flotte de voiliers défendeurs, les adversaires se mesurent en duel (match-racing). La deuxième édition de 1871 se déroule en deux duels successifs avec deux défendeurs du NYYC contre l'unique challenger du Royal Thames Yacht Club.
C'est à partir de la troisième édition de 1876 que les régates opposent, le défender, tenant du titre, au challenger qui relève le défi. Ce dernier est désigné par des régates de sélection depuis la 21e édition de 1970, régates qui prennent le nom de Coupe Louis-Vuitton en 1983, lors de la 25e édition.
Chaque édition voit l'établissement d'un règlement particulier, appelé acte de donation, définissant entre autres les conditions de régates et le type de bateau utilisé basé sur une jauge de course, rédigé par le defender et le challenger de référence, c'est-à-dire le premier Yacht Club à défier le tenant du titre.
En 2002, une exposition intitulée L'America's Cup, 150 ans d'histoire racontée par Louis Vuitton est organisée au Musée national de la Marine à Paris.
Le trophée est détenu par Emirates Team New Zealand, représentant le Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron qui s'impose sept à un face au défi Oracle Team USA lors de la 35e édition disputée aux Bermudes. Grant Dalton, patron du défi néo-zélandais, annonce que le nouveau Challenger of Records est Circolo della Vela Sicilia (en) avec Luna Rossa.
L'America's Cup (Coppa America in italiano) è il più famoso trofeo nello sport della vela, nonché il più antico trofeo sportivo del mondo per cui si compete tuttora.
Si tratta di una serie di regate di match race, ovvero tra soli due yacht che gareggiano uno contro l'altro. Le due imbarcazioni appartengono a due Yacht Club differenti, una rappresentante lo yacht club che detiene la coppa e l'altra uno yacht club sfidante.
Nelle edizioni 1995, 2000, 2003 e 2007, la coppa, una brocca d'argento, è stata assegnata al vincitore di un incontro al meglio di nove regate. L'edizione 2010 della competizione è stata vinta dall'imbarcazione statunitense BMW Oracle Racing che ha avuto la meglio sul defender svizzero Alinghi con un risultato di 2-0. Oracle ha mantenuto la Coppa anche durante l'edizione 2013, battendo Emirates Team New Zealand 9-8. Nell'edizione numero 35, svoltasi nel 2017 nelle Isole Bermuda, Emirates Team New Zealand si aggiudica il trofeo sconfiggendo 7-1 il defender Oracle Team USA[1].
La Copa América (America's Cup en inglés y oficialmente) de vela es la competición más importante de ese deporte y algunas fuentes sostienen que es el tercer evento deportivo con mayor impacto económico para el país de acogida después de los Juegos Olímpicos y el Mundial de fútbol.1234
El actual defensor es el Real Escuadrón de Yates de Nueva Zelanda, que venció al Club de Yates Golden Gate en la última edición, celebrada en Hamilton (Bermudas).
El Challenger of Record para la próxima edición es el Círculo de Vela Sicilia.5
Der America’s Cup ist die älteste noch heute ausgetragene Segelregatta. Der Preis ist ein Wanderpokal und hat seinen Ursprung in einer Regatta rund um die britische Insel Isle of Wight im Jahre 1851.[1] Er ist benannt nach seiner erstmaligen Gewinnerin, der Yacht America des New York Yacht Club (NYYC).
Um den America’s Cup treten die Boote zweier Yachtclubs – Verteidiger und Herausforderer – in mehreren Wettfahrten gegeneinander an. Die Yacht, die eine vorher festgelegte Anzahl von Wettfahrten gewinnt, gewinnt den Cup. Laut der Stiftungsurkunde bestimmt der Verteidiger das Segelrevier. Die Stiftungsurkunde sieht vor, dass Verteidiger und Herausforderer innerhalb gewisser Grenzen Vereinbarungen über die Regeln treffen können, z. B. was die Anzahl der Wettfahrten betrifft.[2]
Von der ersten Verteidigung 1870 bis zur 20. Regatta im Jahr 1967 gab es jeweils nur einen Herausforderer. Im Jahr 1970 gab es erstmals mehrere Herausforderer, so dass der veranstaltende New York Yacht Club sich einverstanden erklärte, den offiziellen Herausforderer durch eine Vorausscheidung zu ermitteln. Zwischen 1983 und 2007 bis zum zeitweiligen Rückzug des Sponsors Louis Vuitton und ab 2013 erneut wurde der Herausforderer durch den Louis Vuitton Cup ermittelt. Schon die Teilnahme am Louis Vuitton Cup setzte großes finanzielles Engagement voraus: die Budgets der High-Tech-Yachten betrugen teilweise über 100 Mio. Dollar. Die Yachten mussten im Land des angemeldeten Teams gebaut werden. Wesentliche Neuerungen ergaben sich bei den letzten beiden ACs. 2010 segelten das erste Mal sowohl Verteidiger wie Herausforderer mit Mehrrumpfbooten. 2013 waren Katamarane vereinbart und die teilnehmenden Teams konstruierten „Tragflügelkatamarane“ die über 40 Knoten (75 km/h) schnell segelten. Für 2017 wurden die Boote „AC50F Katamaran“ von ehemals 72 Fuß (fast 22 m) auf 50 ft (gut 15 m) verkürzt, blieben 24 m hoch und wurden im Training erstmals 50 kn (92 km/h) schnell.[3]
美洲杯帆船赛(英语:America's Cup)是赛艇运动中保存的最著名也是最古老的一项体育比赛。
比赛奖杯是银质大口水罐,奖励给来自不同国家的两艘帆船之间举行的九局五胜制比赛的胜者。两艘帆船中,一艘代表卫冕冠军游艇俱乐部,另一艘则代表俱乐部挑战奖杯。
美洲杯帆船赛源于1851年8月22日,一艘由代表纽约游艇俱乐部(New York Yacht Club,NYYC)的财团拥有的30.86米长纵帆船“美洲号”(America),同15艘代表皇家快艇舰队(Royal Yacht Squadron)的帆船在英国南部的怀特岛附近比赛。“美洲号”最终以领先20分钟胜出。拥有“美洲号”的财团后来将奖杯通过馈赠契约捐献给纽约游艇俱乐部。由此,奖杯被托管成为一项鼓励各国之间友谊竞赛的“挑战”奖品。
在当时公认无敌的英国海上霸权遭受如此打击后,一系列英国财团试图赢回奖杯。但纽约游艇俱乐部在超过132年的25次挑战中保持不败,成为体育运动史上最长的连胜纪录。1930年以前,这项赛事一直在纽约港附近举行,余下的NYYC全盛时期内则改在罗德岛的纽波特(Newport,Rhode Island)举行。
アメリカスカップあるいはアメリカズカップ[1](英: America's Cup)は、1851年より現在まで続く国際ヨットレース。また、その優勝杯の名。その成立は近代オリンピックより45年、サッカーのワールドカップより79年、全英オープンよりも9年早く、継続して使用されている世界最古のスポーツトロフィーとして広く一般に認知されている。[2][3]
名称の由来は最初の優勝艇の『アメリカ号』の名を冠した『アメリカ号のカップ』であり、決して『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』という意味ではない。しかし、その後132年に亘ってアメリカ合衆国のヨットクラブがカップを防衛してきたため、事実上『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』と同じ定義で称される。
競技の本質は、カップの寄贈者が記した贈与証書の規定に基づき、アメリカズカップを掛けてマッチレース(1対1)形式で争われるヨットクラブ間の国際親善レースである。しかし、使用されるヨットは出場国で建造しなければならないため、参加各国の造船工学・建築工学・材料工学・流体力学・航空力学・気象学などの最先端技術や軍事からの応用技術が投入される等、参加国の威信を賭けた国別対抗レースとしての一面も持ち合わせている。またこれら最新ヨットにはオリンピックメダリストら多数のトップセーラーが乗り組むことあり、一般にヨットレース全般、或いはインショア(沿海)レースの最高峰として位置づけられており、別名「海のF1」とも称される。
The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
La Coupe de l'America (America's Cup) est une compétition nautique internationale à la voile, voulue par ses initiateurs comme un défi amical et perpétuel entre Yacht Clubs de différentes nations et définie sous cette dénomination en 1857 par les membres du New York Yacht Club (NYYC)2, vainqueurs, six ans plus tôt, en 1851, avec la goélette America, de la régate internationale originelle, organisée autour de l'île de Wight, par le Royal Yacht Squadron (RYS), en marge de l'exposition universelle de Londres.
Le trophée est une aiguière en argent, attribuée au Yacht Club vainqueur du défi jusqu'à sa remise en jeu. Fabriquée en 1848 pour le Royal Yacht Squadron par le bijoutier et orfèvre Robert Garrard de Londres comme trophée de la Coupe de Cent Souverains, elle est ramenée aux États-Unis, en septembre 1851 sous le nom de Coupe de Cent Guinées, pour prendre en juillet 1857 son nom actuel de Coupe de l'America, en hommage à la goélette victorieuse.
C'est une des plus anciennes compétitions sportives encore disputée de nos jours et se révèle être l'un des principaux théâtres de l'évolution de l'architecture navale en matière de voiliers de régates.
À la suite de la régate de 1851 et de la création de la course en 1857, la première édition de la coupe de l'America n'est disputée qu'après la guerre de Sécession, en août 1870. Après ces deux compétitions, lors desquelles un voilier challenger affronte une flotte de voiliers défendeurs, les adversaires se mesurent en duel (match-racing). La deuxième édition de 1871 se déroule en deux duels successifs avec deux défendeurs du NYYC contre l'unique challenger du Royal Thames Yacht Club.
C'est à partir de la troisième édition de 1876 que les régates opposent, le défender, tenant du titre, au challenger qui relève le défi. Ce dernier est désigné par des régates de sélection depuis la 21e édition de 1970, régates qui prennent le nom de Coupe Louis-Vuitton en 1983, lors de la 25e édition.
Chaque édition voit l'établissement d'un règlement particulier, appelé acte de donation, définissant entre autres les conditions de régates et le type de bateau utilisé basé sur une jauge de course, rédigé par le defender et le challenger de référence, c'est-à-dire le premier Yacht Club à défier le tenant du titre.
En 2002, une exposition intitulée L'America's Cup, 150 ans d'histoire racontée par Louis Vuitton est organisée au Musée national de la Marine à Paris.
Le trophée est détenu par Emirates Team New Zealand, représentant le Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron qui s'impose sept à un face au défi Oracle Team USA lors de la 35e édition disputée aux Bermudes. Grant Dalton, patron du défi néo-zélandais, annonce que le nouveau Challenger of Records est Circolo della Vela Sicilia (en) avec Luna Rossa.
L'America's Cup (Coppa America in italiano) è il più famoso trofeo nello sport della vela, nonché il più antico trofeo sportivo del mondo per cui si compete tuttora.
Si tratta di una serie di regate di match race, ovvero tra soli due yacht che gareggiano uno contro l'altro. Le due imbarcazioni appartengono a due Yacht Club differenti, una rappresentante lo yacht club che detiene la coppa e l'altra uno yacht club sfidante.
Nelle edizioni 1995, 2000, 2003 e 2007, la coppa, una brocca d'argento, è stata assegnata al vincitore di un incontro al meglio di nove regate. L'edizione 2010 della competizione è stata vinta dall'imbarcazione statunitense BMW Oracle Racing che ha avuto la meglio sul defender svizzero Alinghi con un risultato di 2-0. Oracle ha mantenuto la Coppa anche durante l'edizione 2013, battendo Emirates Team New Zealand 9-8. Nell'edizione numero 35, svoltasi nel 2017 nelle Isole Bermuda, Emirates Team New Zealand si aggiudica il trofeo sconfiggendo 7-1 il defender Oracle Team USA[1].
La Copa América (America's Cup en inglés y oficialmente) de vela es la competición más importante de ese deporte y algunas fuentes sostienen que es el tercer evento deportivo con mayor impacto económico para el país de acogida después de los Juegos Olímpicos y el Mundial de fútbol.1234
El actual defensor es el Real Escuadrón de Yates de Nueva Zelanda, que venció al Club de Yates Golden Gate en la última edición, celebrada en Hamilton (Bermudas).
El Challenger of Record para la próxima edición es el Círculo de Vela Sicilia.5
Кубок «Америки» (англ. America's Cup) — одна из самых известных и самых престижных регат в мире. Является старейшим в мире международным соревнованием во всех видах спорта, будучи основанным на два десятилетия ранее Кубка Англии по футболу и на 45 лет раньше первых современных Олимпийских игр.
Кубок Америки получил своё название в честь яхты «Америка» , которая выиграла его в престижной английской регате в 1851 году. Трофей остался в Нью-Йоркском яхт-клубе.
Кубок был изготовлен в 1848 году компанией «Гаррард и Ко». Он представляет собой кувшин без дна, на котором выгравированы названия всех яхт — обладателей кубка. По легенде, дно в кубке отсутствует по желанию английской королевы Виктории, не желавшей, чтобы из него пили[1]. Материал кубка — это так называемый британский металл — сплав олова, меди и сурьмы, покрытый серебром. В 1958 и 2003 годах кубок был дополнен основаниями, для размещения названий очередных победителей. В 1997 году вандал, проникший в здание Новозеландского яхт-клуба, изуродовал Кубок кувалдой. Кубок был бесплатно восстановлен английскими мастерами.
Кубок разыгрывается в серии матчевых гонок между представителем страны, победившим в прошлом цикле, и претендентом. Претендентом является победитель предварительных отборочных соревнований. В настоящее время отборочными соревнованиями служит Кубок Луи Виттона. Место поединка выбирает обладатель кубка.



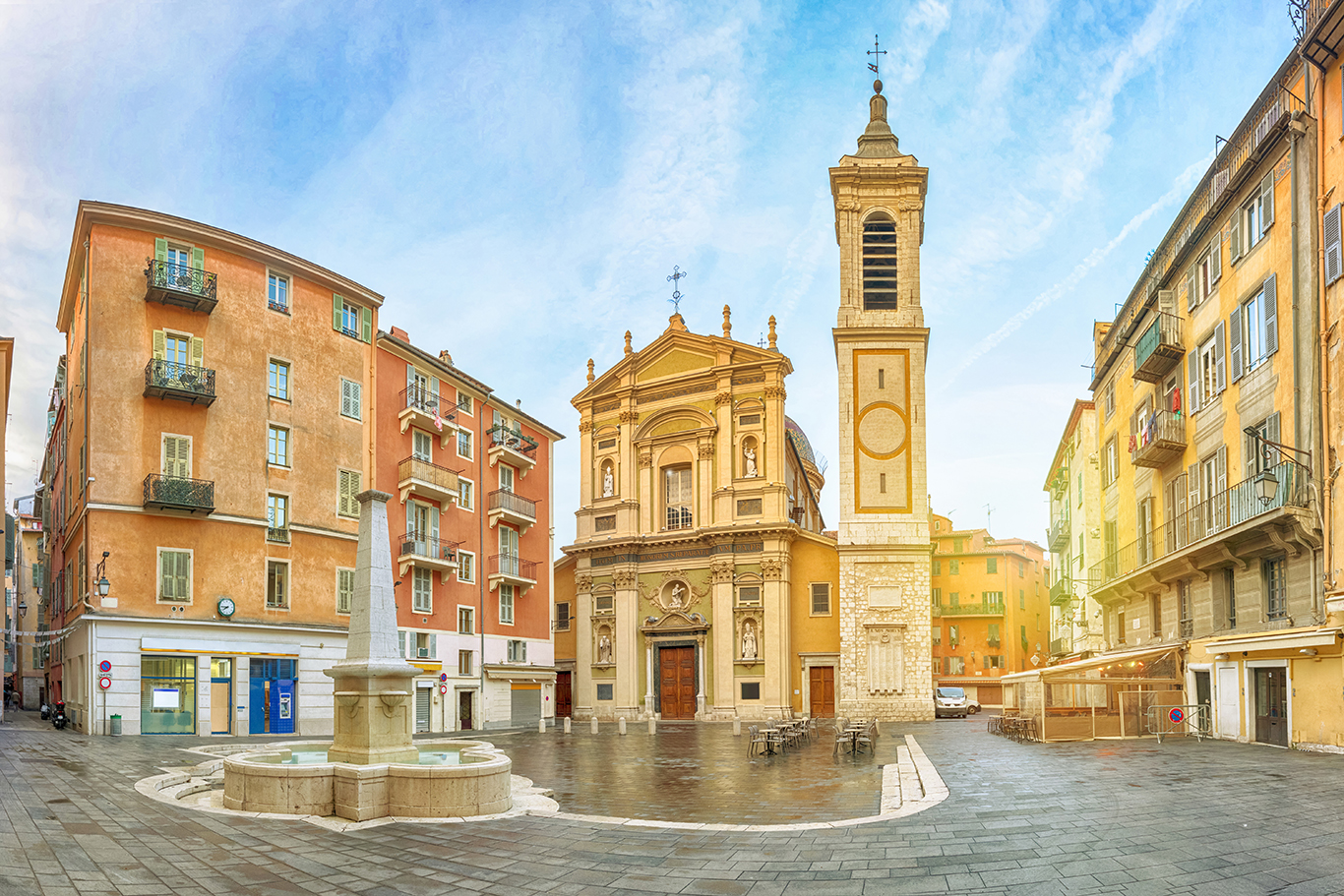
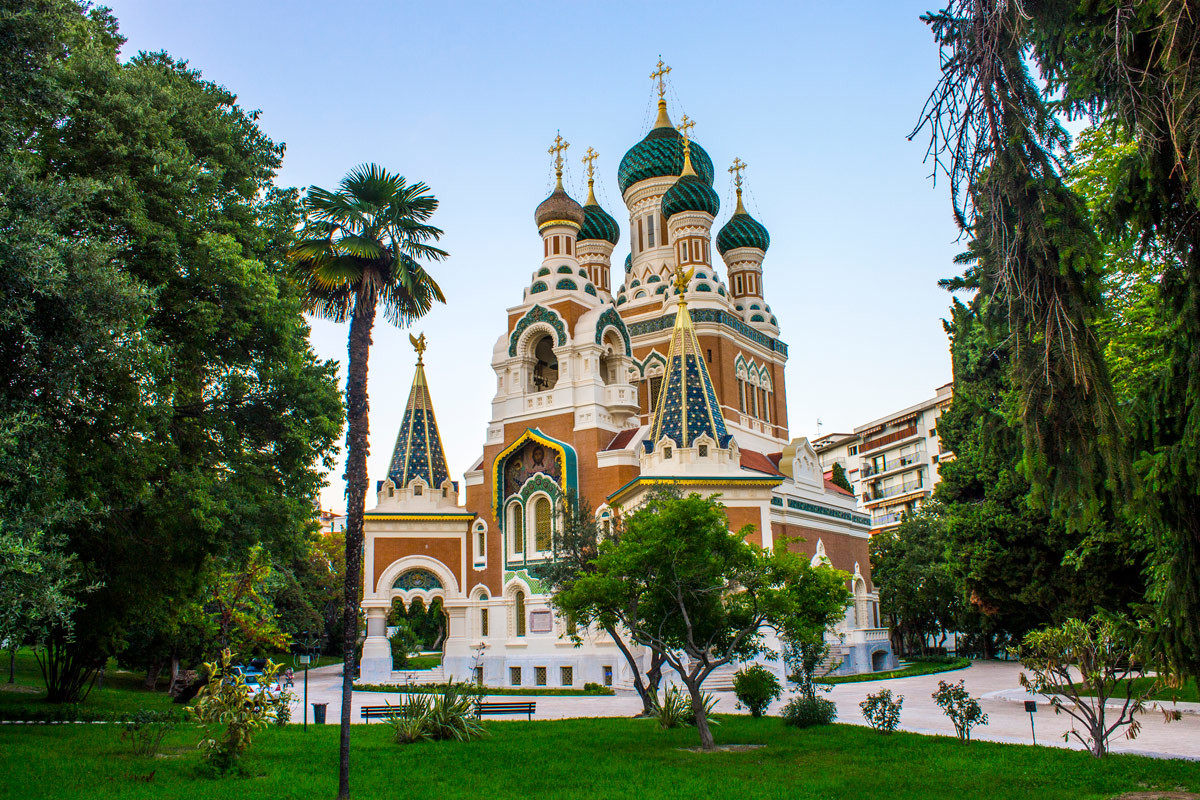
ニース(Nice)は、フランスの南東部に位置する都市で、アルプ=マリティーム県の県庁所在地である。プロバンス語(ニサール語)ではニッサ(Niça、Nissa)、イタリア語ではニッツァ(Nizza)という。
地中海・コート・ダジュールに面する、世界的に有名な保養地・観光都市である。現在はフランス領であるが、歴史的にイタリア文化圏に属した時代が長かったため、言語・文化の面ではフランスよりイタリアに近い特徴がある。
Nice (/niːs/, French pronunciation: [nis]; Niçard Occitan: Niça, classical norm, or Nissa, nonstandard, pronounced [ˈnisa]; Italian: Nizza [ˈnittsa]; Greek: Νίκαια; Latin: Nicaea) is the seventh most populous urban area in France and the capital of the Alpes-Maritimes département. The metropolitan area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of about 1 million[1][2] on an area of 721 km2 (278 sq mi).[1] Located in the French Riviera, on the south east coast of France on the Mediterranean Sea, at the foot of the Alps, Nice is the second-largest French city on the Mediterranean coast and the second-largest city in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region after Marseille. Nice is approximately 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) from the principality of Monaco and 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the French-Italian border. Nice's airport serves as a gateway to the region.
The city is nicknamed Nice la Belle (Nissa La Bella in Niçard), which means Nice the Beautiful, which is also the title of the unofficial anthem of Nice, written by Menica Rondelly in 1912.
The area of today's Nice contains Terra Amata, an archaeological site which displays evidence of a very early use of fire. Around 350 BC, Greeks of Marseille founded a permanent settlement and called it Nikaia, after Nike, the goddess of victory.[3] Through the ages, the town has changed hands many times. Its strategic location and port significantly contributed to its maritime strength. For centuries it was a dominion of Savoy, and was then part of France between 1792 and 1815, when it was returned to the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia until its re-annexation by France in 1860.
The natural environment of the Nice area and its mild Mediterranean climate came to the attention of the English upper classes in the second half of the 18th century, when an increasing number of aristocratic families took to spending their winters there. The city's main seaside promenade, the Promenade des Anglais ("Walkway of the English") owes its name to visitors to the resort.[4] The clear air and soft light have particularly appealed to notable painters, such as Marc Chagall, Henri Matisse, Niki de Saint Phalle and Arman. Their work is commemorated in many of the city's museums, including Musée Marc Chagall, Musée Matisse and Musée des Beaux-Arts.[5] Nice has the second largest hotel capacity in the country[6] and it is one of its most visited cities, receiving 4 million tourists every year.[7] It also has the third busiest airport in France, after the two main Parisian ones.[8] It is the historical capital city of the County of Nice (Comté de Nice).[9]
Nice — prononcé [nis] — (Nissa en nissart ; Nizza en italien) est une commune du Sud-Est de la France, préfecture du département des Alpes-Maritimes et deuxième ville de la région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur derrière Marseille. Située à l'extrémité sud-est de la France, à une trentaine de kilomètres de la frontière franco-italienne, elle est établie sur les bords de la mer Méditerranée, le long de la baie des Anges et à l'embouchure du Paillon.
Avec 342 637 habitants au dernier recensement de 2016, elle est la cinquième commune de France en population (après Paris, Marseille, Lyon et Toulouse). Elle est située au cœur de la septième aire urbaine de France, avec 1 004 914 habitants en 20121. La ville est le centre d'une métropole, Nice Côte d'Azur2, qui rassemble quarante-neuf communes et 537 769 habitants en 20123, 536 327 en 2013. La population du Scot de Nice (Schéma de cohérence territoriale), créé en 2003 et regroupant vingt-neuf communes, est estimée à 517 500 habitants en 20054.
Située entre mer et montagne, capitale économique et culturelle de la Côte d'Azur, Nice bénéficie d'importants atouts naturels. Le tourisme, le commerce et les administrations (publiques ou privées) occupent une place importante dans l'activité économique de la ville. Elle possède la troisième capacité hôtelière du pays5après Paris et Lourdes, et deuxième en nombre d'hôtels après Paris, en accueillant chaque année 4 millions de touristes6. Elle dispose également du troisième aéroport de France7,8 (le premier de province) et de deux palais des congrès consacrés au tourisme d'affaires. La ville possède aussi une université et plusieurs quartiers d'affaires. Nice est enfin dotée de certains équipements culturels importants. Elle possède ainsi de nombreux musées (il s'agit même de la ville qui en compte le plus en France, après Paris), un théâtre national, un opéra, une bibliothèque à vocation régionale, un conservatoire à rayonnement régional et des salles de concert.
Capitale de la Viguerie de Nice, elle faisait autrefois partie du Comté de Provence, avant de choisir la protection du Comté de Savoie à la suite de la guerre civile provençale de l'Union d'Aix gagnée par les pro-angevins (Marseille, Arles, Antibes, etc.) face aux pro-carlistes (Aix, Toulon, Nice, etc.). Son territoire et les autres vigueries sont renommées Terres Neuves de Provence par la Savoie en 1388 (Acte de Dédition) pour devenir en 1526 la capitale du Comté de Nice. En 1713, la Savoie obtient, par héritage, la Sicile qu'elle échange ensuite en 1720 avec la Sardaigne, donnant naissance au royaume de Sardaigne ou États-Sardes. Ce nouvel ensemble, installé des deux côtés des Alpes, forme ainsi l'un des États italiens pré-unitaires, dont la capitale est fixée à Turin. Nice ne devient définitivement française qu'en 1860, un an avant la réalisation de l'unité italienne. Ses habitants sont appelés les Niçoises et Niçois (Nissarda et Nissart en niçois).
Nizza (Nice in francese, Niça o Nissa in dialetto nizzardo)[2] è una città di 344.400 abitanti[3] della repubblica francese affacciata sulla Costa Azzurra, di cui è il maggior centro, vicino alla frontiera con l'Italia, nel dipartimento delle Alpi Marittime.
È il quinto comune della Francia per popolazione (dopo Parigi, Marsiglia, Lione e Tolosa) con 343.629 abitanti nel 2012. La sua area metropolitana (unité urbaine de Nice) tuttavia, raggiunge 943.695 abitanti (2012) ed è la settima di Francia dopo Parigi, Marsiglia, Lione, Tolosa, Bordeaux e Lilla. Il suo aeroporto intercontinentale Nice Côte d'Azur posto alla periferia occidentale della città, con i suoi 12.016.730 passeggeri (2015), è il terzo della Francia dopo i due aeroporti parigini. Si tratta di una città a vocazione turistica. È la seconda città francese per capacità alberghiera.
Niza (en francés Nice [nis], en occitano Niça, en nizardo Nissa, en italiano Nizza) es una ciudad francesa situada en el departamento de los Alpes Marítimos, en la región de Provenza-Alpes-Costa Azul.
Es uno de los centros de la turística Costa Azul, junto al mar Mediterráneo, próximo a la frontera con Italia (30 km) y Mónaco (20 km), encontrándose en las estribaciones de los Alpes, al este del río Var. Niza está situada a 960 km de París, 230 km de Marsella, la capital regional, 195 km de Génova y 215 km de Turín. Se trata de la ciudad más grande de la Costa Azul, extendida de Hyères a Menton. Sus balnearios y playas atraen a un turismo de alto nivel adquisitivo, al igual que sus paseos, sus museos, su vida nocturna y sus magníficas vistas del mar constituyen un atractivo para el turismo. Por su área urbana, es también la séptima ciudad de Francia.
Niza, capital histórica del Condado de Niza, estuvo ligada a Italia hasta su invasión y anexión francesa a finales del siglo XIX. Una parte de su población conserva el dialecto nizardo, una variedad de la lengua ligur fuertemente influida por la lengua occitana después de 1860. En zonas cercanas a la ciudad se hablan variantes del ligur, incluyendo la monegasca y la del valle del Roya. Es muy probable que en la Edad Media el ligur fuera la lengua vehicular de la ciudad.
Ни́цца (фр. Nice [nis], окс. Niça, итал. Nizza, лат. Nicaea, др.-греч. Νίκαια) — средиземноморский город, порт и коммуна на юго-востоке Франции в регионе Прованс — Альпы — Лазурный берег. Административный центр департамента Приморские Альпы, округа Ницца и 9 кантонов (Ницца-1 — Ницца-9)[2]. Более 352 тысяч жителей (2007). Крупный транспортный узел. Одно из главных курортных мест Лазурного Берега (или Французской Ривьеры).
 Ligue 1
Ligue 1
 Ligue 1 2016/17
Ligue 1 2016/17
 Ligue 1 2017/18
Ligue 1 2017/18
 Ligue 1 2018/19
Ligue 1 2018/19

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 UEFA Europa League 2017/18
UEFA Europa League 2017/18
 Group K
Group K
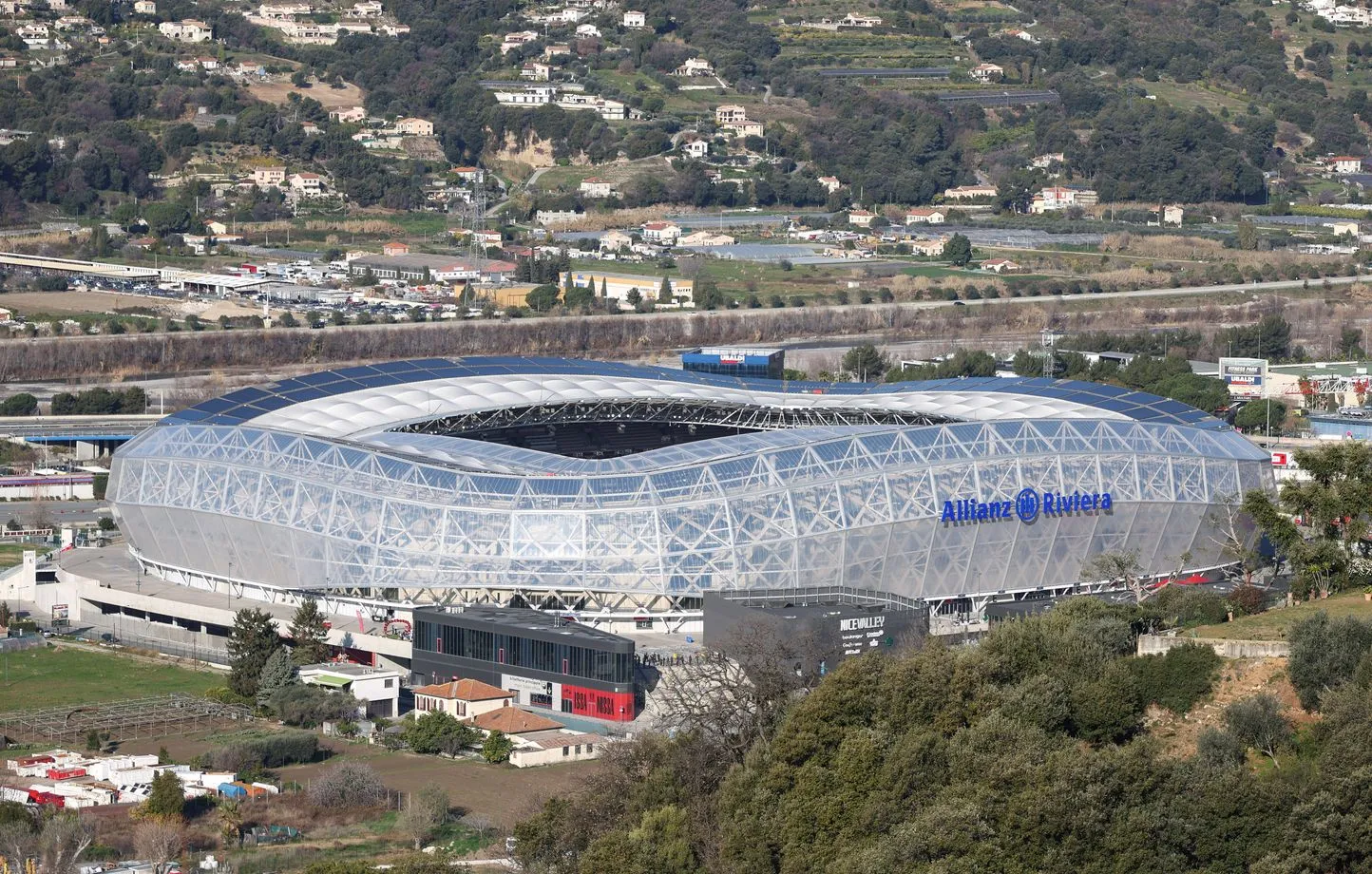







Heimspielbetrieb OGC Nizza RC Toulon (vereinzelt) Veranstaltungen Fußball-Europameisterschaft 2016 Fußball-Weltmeisterschaft der Frauen 2019 Rugby-Union-Weltmeisterschaft 2023 Olympische Sommerspiele 2024 (Fußball)
 Animal world
Animal world
 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Music
Music
 2024 Summer Olympics
2024 Summer Olympics