
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Australia
Australia
 Bahamas
Bahamas
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belize
Belize
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
 Dominica
Dominica
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Guyana
Guyana
 India
India
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kiribati
Kiribati
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nauru
Nauru
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tuvalu
Tuvalu
 Uganda
Uganda
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 Cyprus
Cyprus

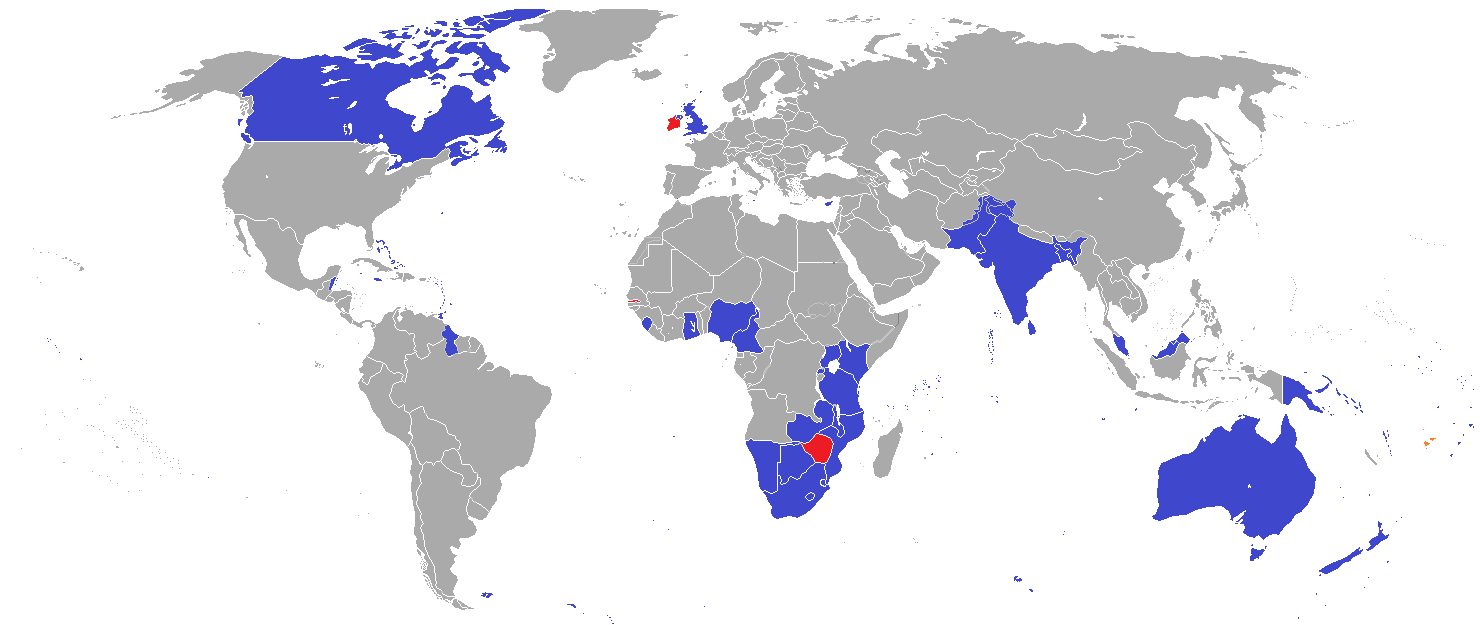
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Gujarat
Gujarat
 India
India
 Karnataka
Karnataka
 Maharashtra
Maharashtra
 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Punjab
Punjab
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
 West Bengal
West Bengal

Sri Lanka
ist offiziell eine Demokratische Sozialistische Republik, vor 1972 unter den Namen Ceylon bekannt. Von Norden nach Süden ca. 440 km lang und an der breitesten Stelle ca. 220 km breit, gesamt ca. 65.500 km². Der Regierungssitz ist Sri Jayawardenepura (Kotte), Hauptstadt und auch die größte Stadt ist Colombo.

孟加拉湾(印地语:बंगाल की खाड़ी、孟加拉语:বঙ্গোপসাগর、缅甸语:ဘင်္ဂလားပင်လယ်အော်)是印度洋北部的一个海湾,西临印度半岛,东临中南半岛,北临缅甸和孟加拉国,南在斯里兰卡至苏门达腊岛一线与印度洋本体相交,经马六甲海峡与暹罗湾和南海相连。宽约1600公里,面积217万平方公里;水深2000-4000米,南部较深;盐度30-34‰。
沿岸国家有印度、孟加拉国、缅甸、泰国、斯里兰卡、马来西亚和印度尼西亚。
印度和缅甸的一些主要河流均流入孟加拉湾,著名的大河有:恒河、布拉马普特拉河、伊洛瓦底江、萨尔温江、克里希纳河等等。孟加拉湾中著名的岛屿包括斯里兰卡岛、安达曼群岛、尼科巴群岛、普吉岛等。
孟加拉湾沿岸贸易发达,主要港口有:印度的加尔各答、金奈、本地治里、孟加拉国的吉大港、缅甸的仰光、毛淡棉、泰国的普吉、马来西亚的槟榔屿、印度尼西亚的班达亚齐、斯里兰卡的贾夫纳等等。
Der Golf von Bengalen (bengalisch বঙ্গোপসাগর baṅgopasāgar; indonesisch Teluk Benggala;malaiisch Teluk Bengal; thailändisch อ่าวเบงกอล; seltene deutsche Bezeichnungen: Bengalischer Golf, Bengalischer Meerbusen, Bai von Bengalen[1][2][3][4]) ist ein nordöstliches Randmeer des Indischen Ozeans mit einer Fläche von rund 2.171.000 km². Er ist 2090 km lang und bis zu 1610 km breit und hat grob gesehen die Form eines Dreiecks. Der Golf ist durchschnittlich 2600 Meter und maximal 4694 Meter tief. Er trennt die Landmasse des indischen Subkontinents von der Halbinsel Hinterindien. Das Klima ist vom Monsun geprägt. Besonderheiten der Region sind insbesondere eine Reihe von Schlammvulkanen sowie die größten Mangrovenwälder der Erde, wie die Sundarbans.
Der Golf von Bengalen wird im Westen von Sri Lanka und Indien, im Norden von der namensgebenden Region Bengalen, bestehend aus dem Staat Bangladesch und dem indischen Bundesstaat Westbengalen sowie im Osten von Myanmar, Thailand und Indonesien begrenzt. Im Süden ist er mit dem Indischen Ozean verbunden. Als ungefähre Abgrenzung des Golfes kann eine gedachte Linie zwischen der Südspitze Sri Lankas und der Nordspitze der zu Indonesien gehörenden Insel Sumatra angenommen werden.
ベンガル湾(ベンガルわん、Bay of Bengal)は、インド洋の北東部分の湾。湾はほぼ三角形で、南方に開けた形となっている。東にマレー半島、西にインド亜大陸、北に名前の元となったインドの西ベンガル州およびバングラデシュに面している。南端はスリランカとアンダマン・ニコバル諸島連邦直轄地に面している。同諸島の東側の海域はアンダマン海と呼ばれる。
インドやバングラデシュの多くの川がベンガル湾に流れ込んでいる。北からはガンジス川、メグナ川とブラマプトラ川が流れ込み、南西の沿岸であるオリッサ州からはマハナディ川、ゴータヴァリー川、クリシュナ川、カヴェリ川が流れ込んでいる。湾の北端のインド領には、スンダルバンス国立公園があり、豊かなマングローブの林がある。ミャンマーのエーヤワディー川もベンガル湾に流れ込んでいる。
チェンナイ(旧名マドラス)やコルカタ(旧名カルカッタ)といった大都市がベンガル湾に接しており、古くから交易拠点として栄えてきた。
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka and the north westernmost point of Sumatra (Indonesia). It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. In ancient India, Bay of Bengal was known as Kalinga Sagar. Later during the British India, it came forth as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region, as the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay.
The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of 2,600,000 square kilometres (1,000,000 sq mi). A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges–Hooghly, the Padma, the Brahmaputra–Jamuna, the Barak–Surma–Meghna, the Irrawaddy, the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Brahmani, the Baitarani, the Krishna and the Kaveri. Among the important ports are Chennai, Ennore, Chittagong, Colombo, Kolkata-Haldia, Mongla, Paradip, Port Blair, Thoothukudi, Visakhapatnam and Dhamra. Among the smaller ports are Gopalpur Port, Kakinada and Payra.
Le golfe du Bengale (bengali : বঙ্গপসাগর, anglais : Bay of Bengal) est une mer qui forme la partie du nord-est de l'océan Indien. Elle a la forme d'un triangle encadré à l'est par les côtes birmanes jusqu'au cap Negrais puis par les archipels Andaman et Nicobar, et à l'ouest par le sous-continent indien. Au nord du golfe, on trouve l'état indien du Bengale-Occidental et le Bangladesh, d'où provient son nom. Ses limites méridionales sont le pont d'Adam puis une ligne ouest-est ayant son origine à la pointe sud de l'île de Sri Lanka, et finissant à la pointe nord de l'île indonésienne de Breueh (Pulau Breueh), non loin de Sumatra.
Il golfo del Bengala (বঙ্গোপসাগর in bengalese, ဘင်္ဂလားပင်လယ်အော် in birmano, बंगाल की खाड़ी in hindi e බෙංගාල බොක්ක in singalese) è l'insenatura più ampia del mondo e, per le sue dimensioni (2.172.000 km² di superficie), al punto che può essere considerato un mare vero e proprio. Di forma approssimativamente triangolare, costituisce la parte nordorientale dell'Oceano Indiano ed è collocato fra il Subcontinente indiano a ovest e l'Indocina ad est.
El Golfo de Bengala es un mar en el área noreste del océano Índico. Su forma se parece a un triángulo. Limita al este con la península de Malaca, al oeste con el subcontinente indio. El extremo norte del golfo limita con el estado indio de Bengala Occidental y con Bangladés. Los extremos del sur están limitados por la isla de Sri Lanka y el territorio indio de las Islas Andamán y Nicobar. Estas últimas islas separan el golfo de Bengala del mar de Andamán (también mar de Birmania).
Muchos de los ríos principales de la India desembocan desde el oeste en la bahía de Bengala: en el norte el río Ganges (o Ganga), el río Meghna y el río Brahmaputra. Al sur el Mahanadi, el Godavari, el Krishna y el Kaveri (también escrito Cauvery). El bosque de mangle llamado los Sundarbans está situado en el delta que forman los ríos Ganges, Brahmaputra y Meghna en el golfo de Bengala.
Los puertos indios más importantes del golfo son Madrás, Vishakhapatnam, Calcuta y Pondicherry.
Бенга́льский зали́в (бенг. বঙ্গোপসাগর, там. வங்காள விரிகுடா, хинди बंगाल की खाड़ी, англ. Bay of Bengal[1]) — морской залив, расположенный в северо-восточной части Индийского океана, омывает берега Индии, Бангладеш, Мьянмы и Шри-Ланки. На западе ограничен полуостровом Индостан, на востоке — побережьем Мьянмы и островными дугами Андаманских и Никобарских островов. У северной оконечности залива располагается историческая область Бенгалия (включающая современную Бангладеш и индийский штат Западная Бенгалия), давшая ему название. Является самым большим заливом в мире, его площадь — 2191 тысяча км²[2] (по другим данным 2173 тысячи км²[1]). Наибольшая глубина — 4519 м[2], средняя — 2600 м[1].
В Бенгальский залив впадают многие крупные реки — Ганг, Брахмапутра и Мегхна (общий эстуарий), Кришна, Годавари, Кавери, Маханади, Иравади.
На северо-восточном побережье залива, у города Кокс-Базар (Бангладеш) расположен самый протяжённый в мире пляж (120 км).
По гидрологическому, гидрохимическому и прочим параметрам Бенгальский залив относится к морям.
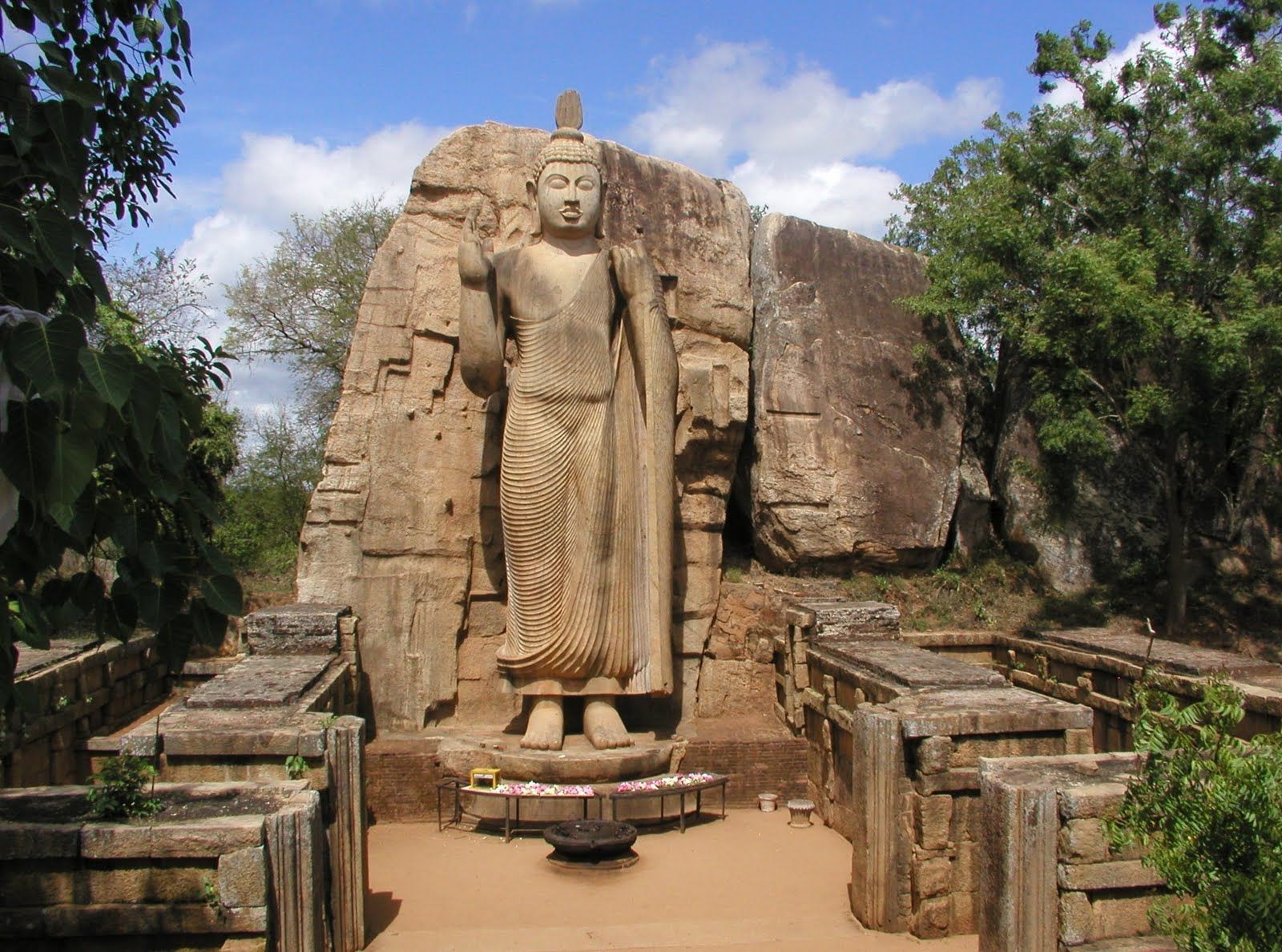





Das erste, was Sie sehen, wenn Sie sich dem Kande Viharaya nähern, ist eine dominierende Buddha-Statue. Diese 160 Fuß hohe Statue des im Schneidersitz sitzenden Buddha, die sich auf einem Tempel aus dem 18. Jahrhundert befindet, gilt als eine der höchsten der Welt. Kande Viharaya liegt in der Stadt Bentota, etwa 1 Stunde und 30 Minuten von Mirissa entfernt und ist ideal für einen schnellen Tagesausflug. Bentota ist vor allem als Wassersportzentrum Sri Lankas bekannt, und wer in der Gegend ist, kann nach einem Besuch des Tempels an einer Reihe von Aktivitäten teilnehmen.
Der Tempel wurde ursprünglich im Jahr 1734 entdeckt und ist seitdem eine wichtige Stätte für Gläubige und gilt als einer der heiligsten Tempel der Insel.

 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport

 Religion
Religion
 World Heritage
World Heritage

 States of Asia
States of Asia


 Important port
Important port
 History
History
 Civilization
Civilization
 Animal world
Animal world
 Architecture
Architecture
