
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Kantō
Kantō



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Printer/Photocopier/Scanner
Printer/Photocopier/Scanner


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES
PLC/DCS/FCS/SCADA/MES


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 IC
IC


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Semiconductor technology
Semiconductor technology


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 MCU
MCU


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō

 Life and Style
Life and Style

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Global Innovators
Global Innovators


 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1964 Summer Olympics
1964 Summer Olympics
 2020 Summer Olympics
2020 Summer Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road

 Important port
Important port

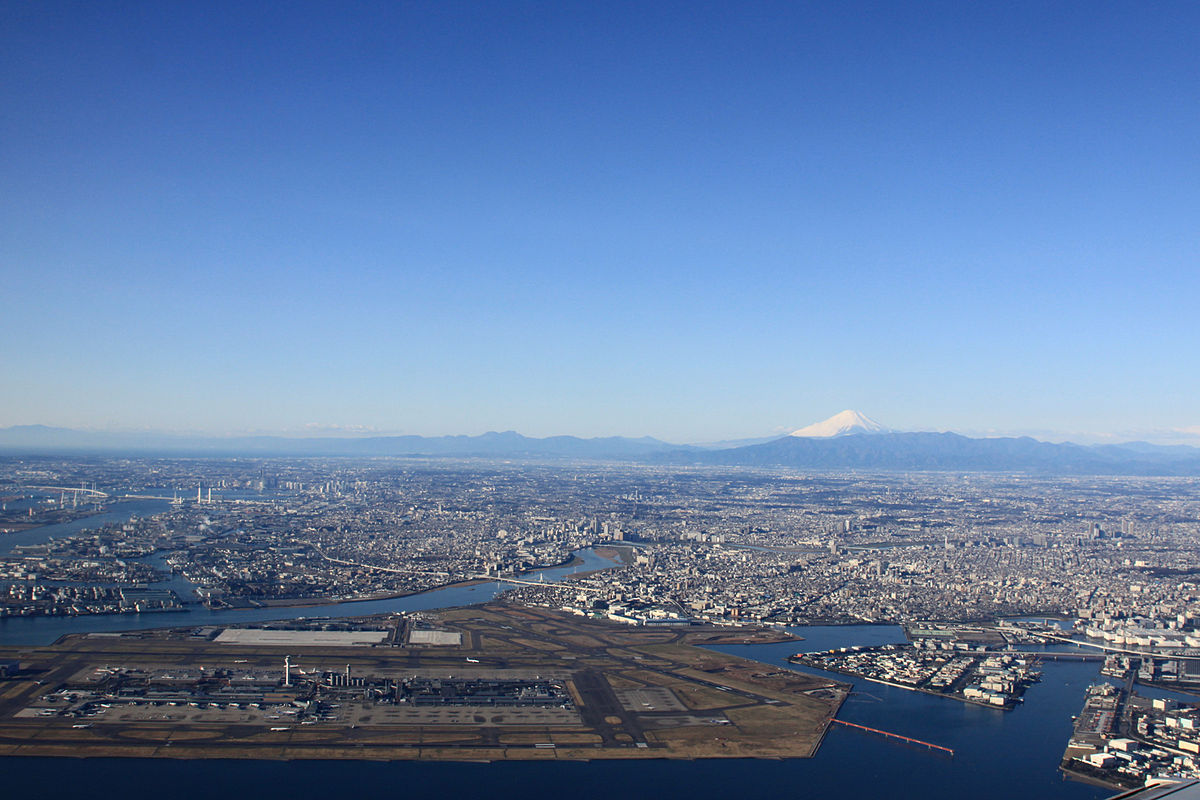
Tokio (auch Tokyo, japanisch 東京 Tōkyō  [to̞ːkjo̞ː]) ist eine Weltstadt[3] in der Kantō-Region im Osten der japanischen Hauptinsel Honshū. Mit 9.508.776 Einwohnern ist sie nicht nur die bevölkerungsreichste Metropole des Landes, sondern als Sitz der japanischen Regierung und des Tennō auch die Hauptstadt Japans. Sie umfasst die 23 Bezirke auf dem Gebiet der 1943 als Verwaltungseinheit abgeschafften Stadt Tokio und ist damit keine eigene Gebietskörperschaft mehr; stattdessen bilden die Bezirke zusammen mit den Städten und Gemeinden der westlich gelegenen Tama-Region und den südlichen Izu- und Ogasawara-Inseln die Präfektur Tokio. Diese bildet wiederum das Zentrum der Metropolregion Tokio-Yokohama, in der mehr als 37 Millionen Menschen leben (Stand 2014), was die Region zum größten Ballungsraum der Welt macht.
[to̞ːkjo̞ː]) ist eine Weltstadt[3] in der Kantō-Region im Osten der japanischen Hauptinsel Honshū. Mit 9.508.776 Einwohnern ist sie nicht nur die bevölkerungsreichste Metropole des Landes, sondern als Sitz der japanischen Regierung und des Tennō auch die Hauptstadt Japans. Sie umfasst die 23 Bezirke auf dem Gebiet der 1943 als Verwaltungseinheit abgeschafften Stadt Tokio und ist damit keine eigene Gebietskörperschaft mehr; stattdessen bilden die Bezirke zusammen mit den Städten und Gemeinden der westlich gelegenen Tama-Region und den südlichen Izu- und Ogasawara-Inseln die Präfektur Tokio. Diese bildet wiederum das Zentrum der Metropolregion Tokio-Yokohama, in der mehr als 37 Millionen Menschen leben (Stand 2014), was die Region zum größten Ballungsraum der Welt macht.
Die Stadtgeschichte beginnt im Jahr 1446, als Ōta Dōkan in einem Sumpfgebiet am Nordufer der heutigen Bucht von Tokio mit dem Bau der Burg Edo begann, umgeben von einigen Fischerdörfern. 1590 ging diese Burg an Tokugawa Ieyasu, der hier nach seinem Sieg in der Schlacht von Sekigahara sein neues Shōgunat und damit die Edo-Zeit begründete. Edo wurde neben Kyōto zum politischen und kulturellen Zentrum des Landes. Mit der Meiji-Restauration 1868 wurde das Shōgunat abgeschafft und der Sitz des Tennō nach Edo verlegt, die Burg wurde zum Kaiserpalast und Edo bekam seinen neuen Namen Tokio, der „Östliche Hauptstadt“ bedeutet. Von da an wuchs auch die Bevölkerung der Stadt, die bereits um 1910 mit rund zwei Millionen Einwohnern zu den größten der Welt zählte. Im Zweiten Weltkrieg war Tokio zahlreichen Luftangriffen durch die USA ausgesetzt, bei denen rund die Hälfte der Stadtfläche zerstört wurde. Nach dem Ende der amerikanischen Besatzungszeit folgte ein rasanter wirtschaftlicher Aufschwung, einhergehend mit einem erneuten Bevölkerungszuwachs.
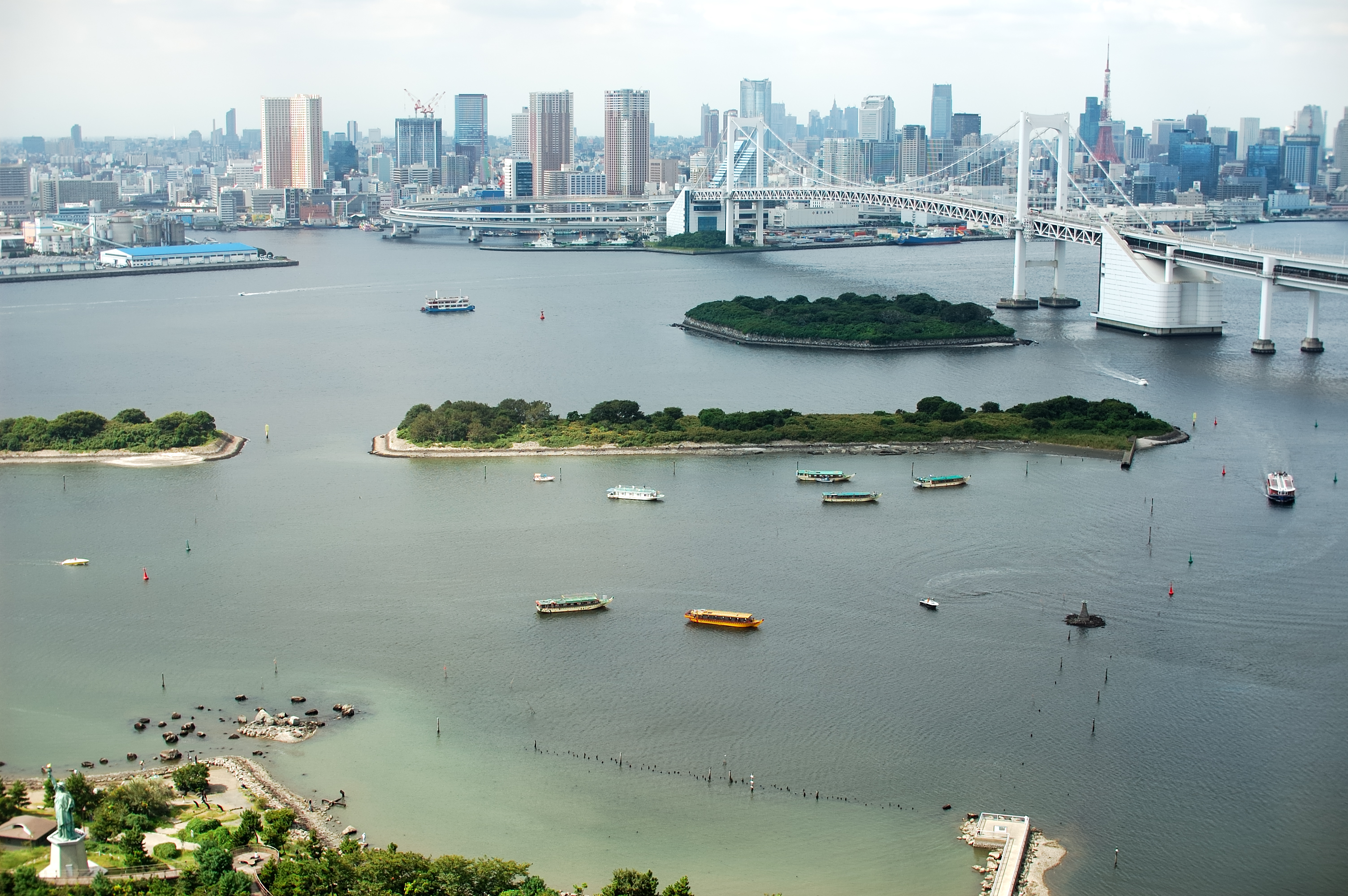
Tokio ist heute das Industrie-, Handels-, Bildungs- und Kulturzentrum Japans mit zahlreichen Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Mit den Flughäfen Narita und Haneda und als Ausgangspunkt der meisten Shinkansen-Linien ist es auch das Verkehrszentrum des Landes. Der Finanzplatz Tokio ist nicht nur der größte Japans, sondern zählt neben London, New York und Hongkong auch zu den fünf größten der Welt. Zudem weist die Stadt ein hohes Preisniveau auf und lag in einer Studie 2014 auf Platz 9 der teuersten Städte weltweit.[4][5] Neben modernen Sehenswürdigkeiten wie dem Tokyo Tower oder Tokyo Skytree bietet sie auch historische Anlagen wie die Kaiserlichen Gärten in Chiyoda, den Ueno-Park oder den Asakusa-Kannon-Tempel. In den vergangenen Jahren wurde Tokio zu einem zunehmend beliebten Tourismusziel und befindet sich mit jährlich bis zu acht Millionen Besuchern aus dem Ausland unter den 20 meistbesuchten Städten.[6] In einer Rangliste der Städte nach ihrer Lebensqualität belegte Tokio im Jahre 2018 den 50. Platz unter 231 untersuchten Städten weltweit.[7]
东京(日语:東京/とうきょう Tōkyō)是位于日本关东地方的都市,狭义上指东京都、或东京都区部(即东京市区),亦可泛指东京都及周边卫星都市群相连而成的“首都圈”(东京都会区)。目前(2017年8月)东京都区部人口数达946万,首都圈的人口数则达3千6百万,是目前全球规模最大的都会区[1],亦为亚洲最重要的世界级城市。东京是传统上的全球四大世界级城市[2]之一,在2016年GDP达9472.7亿美元,超越纽约(9006.8亿)成为全球第一,同时全球城市指数排名中排名第三。
东京古称江户,自德川幕府时代以来开始成为日本主要都市之一,明治维新时期改为现名后,更发展为日本政治、经济、文化、交通等众多领域的枢纽中心。经过二战后的继续发展,东京不仅成为世界商业金融、流行文化与时尚重镇,亦为世界经济发展度与富裕程度最高的都市之一。此外,东京还有目前全球最复杂、最密集的城市轨道交通系统,其中单就计算东京的地铁系统管辖区段每日平均运量达880万人次,繁忙程度居全球地铁第三位(如含地铁直通运转路线、私铁通勤路线及JR东日本通勤路线,则每日平均运量位居世界城市轨道交通运输系统第一位)。
在正式的行政区划定义上,东京仅限于东京都,与道、府、县同为日本的一级行政区,辖区包含东京都区部、多摩地方与伊豆群岛、小笠原群岛等离岛;其中,东京都区部为日本中央政府所在地。东京都同时也囊括了日本最南端(冲之鸟礁)和最东端(南鸟岛)等地理极点,拥有日本各都道府县中最多的人口数,同时也是日本人口密度最高的都道府县。
東京(とうきょう、英: Tokyo)は、日本の関東平野中央部に位置し、東京湾に面する都市。日本の首都である[1][注 1]。現在、その域内には23特別区・26市・5町・8村の基礎自治体がある[2]。
日本における政治・経済・文化の中心である。政治面では、日本政府が本拠地としている。立法府である国会の議事堂、司法府の頂点である最高裁判所、行政府の長である内閣総理大臣の官邸、中央省庁街(「霞が関」)などは、いずれも東京の中心部である東京23区にある。経済面では、日本の株式上場企業の本社のほとんどが東京に集中し、(東京圏では)購買力平価(PPP)を基にしても東京都市圏のGDPは1兆5369億ドル(2014年)であり[3]、世界的な経済都市であり、大消費地でもある。文化面では、たとえば現在では(東京都内に)千数百におよぶ劇場・ホール・ライブハウス類があり[4]多数のアーティストたちが活動する場であり、ポップカルチャーなどの新しい文化の発信地でもあり、ミシュランガイドの星つきの飲食店の数は世界最多で[5]食文化が華開いている場所でもある。
東京には、日本国内からだけでなく近隣の様々な国や世界各国から外国人が観光に訪れるようになった他、東京に移住した外国人が移民街を形成している。関東大震災や東京大空襲で焼け野原となったが、戦後の発展により現在は世界最大級のメトロポリス・世界都市となっている。東京は明治期にも課題が山積みの都市であったが(#明治維新後の課題と都市政策を参照)、現在もさまざまな課題を抱えている都市である(#近年の東京が都市としてかかえる課題を参照)。 東京都(とうきょうと、英: Tokyo Metropolis)は、日本の首都[注 1]。関東地方に位置する広域地方公共団体(都道府県)のひとつ。都庁所在地は新宿区[注 2]。最大の都市は世田谷区[注 3]。 管轄する領域は東京都区部(東京23区)、多摩地域(26市[注 4]と西多摩郡3町1村)および東京都島嶼部(大島、三宅、八丈、小笠原)の4支庁(2町7村)からなっている。東京都区部(東京23区)は、一つの都市として「東京」とも呼ばれる。沖ノ鳥島、南鳥島を含む小笠原諸島を含むため、日本最南端および最東端に位置する都道府県でもある。都公認の「東京都」の英語表記はTokyo Metropolis(Tokyo Met.)。他には Tokyo Prefecture と Tokyo Metropolitan Prefecture がある。
Tokyo (東京 Tōkyō, /ˈtoʊkioʊ/;[7] Japanese: [toːkʲoː] ( listen)), officially Tokyo Metropolis (東京都 Tōkyō-to), is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan and has been the capital since 1869.[8][9] The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world.[10] It is the seat of the Emperor of Japan, the Japanese government and the National Diet. Tokyo is in the Kantō region on the southeastern side of the main island Honshu and includes the Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands.[11] Tokyo was formerly named Edo when Shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu made the city as his headquarters in 1603. It became the capital after Emperor Meiji moved his seat to the city from Kyoto in 1868; at that time Edo was renamed Tokyo. Tokyo Metropolis was formed in 1943 from the merger of the former Tokyo Prefecture (東京府 Tōkyō-fu) and the city of Tokyo (東京市 Tōkyō-shi).
listen)), officially Tokyo Metropolis (東京都 Tōkyō-to), is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan and has been the capital since 1869.[8][9] The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world.[10] It is the seat of the Emperor of Japan, the Japanese government and the National Diet. Tokyo is in the Kantō region on the southeastern side of the main island Honshu and includes the Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands.[11] Tokyo was formerly named Edo when Shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu made the city as his headquarters in 1603. It became the capital after Emperor Meiji moved his seat to the city from Kyoto in 1868; at that time Edo was renamed Tokyo. Tokyo Metropolis was formed in 1943 from the merger of the former Tokyo Prefecture (東京府 Tōkyō-fu) and the city of Tokyo (東京市 Tōkyō-shi).
Tokyo has 39 million residents, 50% more people than any other urban area, with a $2.5 trillion economy larger than that of any other city; if it were a country, Tokyo would be the 8th largest economy in the world. Tokyo is often referred to as a city, but is officially known and governed as a "metropolitan prefecture", which differs from and combines elements of a city and a prefecture, a characteristic unique to Tokyo. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers the 23 Special Wards of Tokyo (each governed as an individual city), which cover the area that was the city of Tokyo before it merged and became the metropolitan prefecture in 1943, the 30 municipalities in the western part of the prefecture, and the two outlying island chains. The population of the special wards is over 9 million people, with the total population of the prefecture exceeding 13 million. The prefecture is part of the world's most populous metropolitan area with upwards of 37.8 million people and the world's largest urban agglomeration economy. In 2011, the city hosted 51 of the Fortune Global 500 companies, the highest number of any city in the world at that time.[12] Tokyo ranked third (twice) in the International Financial Centres Development Index. The city is also home to various television networks such as Fuji TV, Tokyo MX, TV Tokyo, TV Asahi, Nippon Television, NHK and the Tokyo Broadcasting System.
Tokyo is ranked first in the Global Economic Power Index and third in the Global Cities Index. The city is considered an alpha+ world city – as listed by the GaWC's 2008 inventory[13] – and in 2014, Tokyo was ranked first in the "Best overall experience" category of TripAdvisor's World City Survey (the city also ranked first in the following categories: "helpfulness of locals", "nightlife", "shopping", "local public transportation" and "cleanliness of streets").[14] In 2015, Tokyo was ranked as the 11th most expensive city for expatriates, according to the Mercer consulting firm,[15] and also the world's 11th most expensive city, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit's cost-of-living survey.[16] In 2015, Tokyo was named the Most Liveable City in the world by the magazine Monocle.[17] The Michelin Guide has awarded Tokyo by far the most Michelin stars of any city in the world.[18][19] Tokyo was ranked first out of all sixty cities in the 2017 Safe Cities Index.[20] The QS Best Student Cities ranked Tokyo as the 3rd-best city in the world to be a university student in 2016[21] and 2nd in 2018.[22] Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympics, the 1979 G-7 summit, the 1986 G-7 summit, and the 1993 G-7 summit, and will host the 2019 Rugby World Cup, the 2020 Summer Olympics and the 2020 Summer Paralympics.
Tokyo (東京(とうきょう), Tōkyō?, littéralement « Capitale de l'est »), anciennement Edo (江戸(えど)?), officiellement la préfecture métropolitaine de Tokyo (東京都(とうきょうと), Tōkyō-to?), est la capitale actuelle du Japon. Elle est la plus peuplée des préfectures du Japon, avec plus de 13 831 421 habitants intra-muros en 2018 et 42 794 714 dans l'agglomération2, et forme l'aire urbaine la plus peuplée au monde. Située sur la côte est de l'île principale de l'archipel japonais, Honshū, Tokyo est l'une des quarante-sept préfectures du Japon. Principal centre politique de l'archipel depuis le XVIIe siècle, la ville accueille la plupart des institutions du pays : la résidence de l'empereur du Japon, du Premier ministre, le siège de la Diète (le parlement japonais), du Cabinet, les ministères qui le constituent ainsi que toutes les ambassades étrangères.
À l'origine, Tokyo était un petit village de pêcheurs nommé Edo (« l'estuaire »). Fortifié au XVe siècle, Edo devient la base militaire du shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu à la fin du XVIe siècle, puis la capitale de son gouvernement. Durant l’époque d'Edo (1603-1868), la ville se développe et devient l'une des plus peuplées au monde à la fin du XVIIIe siècle, avec une population de près d'un million d'habitants. Avec la restauration de l'Empire en 1868, elle est confortée dans son rôle de cœur politique du Japon : le château d'Edo devient la résidence de l'empereur Meiji (Kōkyo), et la ville acquiert son nom actuel par opposition à Kyoto, l'ancienne capitale. Elle est ravagée en 1923 par un séisme de magnitude 7,9 qui fait plus de 100 000 morts. Durant la Seconde Guerre mondiale, elle est détruite pour moitié par des bombardements aériens américains, mais est rapidement reconstruite. Dans la seconde moitié du XXe siècle, Tokyo devient une métropole de rang mondial grâce à un fort développement industriel — notamment dans l'électronique —, et voit sa population multipliée par dix en cinquante ans.
Principal centre économique et financier du Japon, Tokyo est l'une des principales places financières asiatiques et mondiales. Elle est la première ville mondiale en termes de produits urbains bruts. Le dynamique arrondissement de Shinjuku comporte de nombreux gratte-ciels, dont la mairie de la ville, et plusieurs grands magasins du Japon. Minato-ku accueille les sièges sociaux de nombreuses entreprises japonaises et étrangères, ainsi qu'une cinquantaine d'ambassades. Chiyoda concentre quant à lui les institutions politiques japonaises. Enfin, Shibuya est réputé être l'un des quartiers les plus animés de la ville, grâce à la présence de grands centres commerciaux comme le 109. Malgré la modernité de son architecture, dont témoigne la tour Tokyo Skytree, de nombreux sanctuaires shinto et temples bouddhistes ont été préservés ou reconstruits après les bombardements, comme le Sensō-ji, le sanctuaire Yasukuni, le Zōjō-ji ou les portes Hōzōmon.
Située au fond de la baie de Tokyo, la commune de Tokyo dispose d'un statut administratif particulier parmi les préfectures du Japon, la ville de Tokyo ayant été supprimée en tant qu'entité politique ou administrative en 1943. L'agglomération de Tokyo, qui s'étend bien au-delà des limites de la préfecture, s'étend sur une large frange de la baie de Tokyo ainsi que sur la région du Kantō. Elle constitue en outre un des pôles de la mégalopole japonaise, avec notamment Ōsaka et Nagoya. La préfecture a organisé les Jeux olympiques d'été de 1964, et les accueillera à nouveau en 2020.
Tokio (東京都 Tōkyō-to?, lit. ‘capital del este’; pronunciación japonesa:  [toːkʲoː] (?·i)) es la capital de facto6 de Japón, localizada en el centro-este de la isla de Honshu, concretamente en la región de Kanto. En conjunto forma una de las 47 prefecturas de Japón, aunque su denominación oficial es metrópolis o capital (都 -to). La ciudad es el centro de la política, economía, educación, comunicación y cultura popular del país. Cuenta también con la mayor concentración de sedes corporativas, instituciones financieras, universidades y colegios, museos, teatros, y establecimientos comerciales y de entretenimiento de todo Japón.
[toːkʲoː] (?·i)) es la capital de facto6 de Japón, localizada en el centro-este de la isla de Honshu, concretamente en la región de Kanto. En conjunto forma una de las 47 prefecturas de Japón, aunque su denominación oficial es metrópolis o capital (都 -to). La ciudad es el centro de la política, economía, educación, comunicación y cultura popular del país. Cuenta también con la mayor concentración de sedes corporativas, instituciones financieras, universidades y colegios, museos, teatros, y establecimientos comerciales y de entretenimiento de todo Japón.
Con una población que supera los 13 millones de habitantes, se subdivide en 23 barrios (区 -ku); 26 ciudades (市 -shi); un distrito (郡 -gun) subdividido en tres pueblos (町 -chō o -machi) y una villa (村 -son o -mura); y cuatro subprefecturas (支庁 -shichō) subdivididas en dos pueblos y siete villas, que representan a varias pequeñas islas al sur de Honshu que se extienden más allá de 1800 km de Shinjuku, capital de la metrópoli y sede de la gobernación. El centro de Tokio, con sus 23 barrios, ocupa un tercio de la metrópoli, con una población cercana a los 13,23 millones de habitantes; esta área es lo que se conoce internacionalmente como la ciudad de Tokio. En su área metropolitana viven más de 37 millones de habitantes, lo que la convierte en la mayor aglomeración urbana del mundo.
A pesar de que Tokyo es la romanización más común del nombre en japonés, el nombre de la ciudad es Tokio en español y otros idiomas —entre ellos el alemán y el neerlandés—. En inglés y otros idiomas se escribe Tokyo, aunque antiguamente también se escribía Tokio. En el pasado, la ciudad se denominaba como Tokei, Edo o Yedo. El gentilicio de Tokio es tokiota.
Tokio fue sede de los Juegos Olímpicos de 1964 y será sede de los Juegos Olímpicos de 2020.7
То́кио (яп. 東京 То:кё: (инф.), «Восточная столица»[4][5]) — столица Японии, её административный, финансовый, промышленный и политический центр. Крупнейшая городская экономика мира[6]. Расположен в юго-восточной части острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто в бухте Токийского залива Тихого океана.
Помимо столицы, Токио также является одной из сорока семи префектур страны. Площадь префектуры составляет 2188,67 км²[7], население — 13 742 906 человек (1 октября 2017)[8], плотность населения — 6279,11 чел./км². По состоянию на 1 мая 2020 года население Токио составляло 14 002 973 человека, что делает Токио префектурой с самым большим населением в Японии.[9] Большой Токио является городской территорией с самым большим населением в мире, с населением по состоянию на 2016 год в 38 140 000 человек.[2]
Токийский столичный округ — административная единица Японии, включающая в себя специальные районы Токио, область Тама и островные территории Токийского столичного округа (острова Идзу и Огасавара).
 Breakthrough Prize
Breakthrough Prize
 Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
 Breakthrough Prize
Breakthrough Prize
 New Horizons in Physics Prize
New Horizons in Physics Prize
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 Medical colleges/Research Institute
Medical colleges/Research Institute
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Literature
Nobel Prize in Literature
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Sinology
Sinology
 Top Global University Project
Top Global University Project
 National universities
National universities
 Top Global University Project
Top Global University Project
 Top Type
Top Type
 Universities in Japan
Universities in Japan

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 *World famous research institutions
*World famous research institutions







 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō

 Music
Music
 Music colleges/conservatoire
Music colleges/conservatoire
 Top Global University Project
Top Global University Project
 Global Traction Type
Global Traction Type
 Top Global University Project
Top Global University Project
 National universities
National universities
 Universities in Japan
Universities in Japan



 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō

 Companies
Companies
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Film & TV Produktion
Film & TV Produktion
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Architecture
Architecture


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Sport
Sport
 Art
Art