
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Mexiko
Mexiko


 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 California-CA
California-CA

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA
 Kanada
Kanada

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA
 Mexiko
Mexiko

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 Vereinigte Staaten
Vereinigte Staaten

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA







Die Azteken (von Nahuatl aztecatl, deutsch etwa „jemand, der aus Aztlán kommt“) waren eine mesoamerikanische Kultur, die zwischen dem 14. und dem frühen 16. Jahrhundert existierte. Im Allgemeinen bezeichnet man mit dem Begriff „Azteken“ die ethnisch heterogene, mehrheitlich Nahuatl sprechende Bevölkerung des Tals von Mexiko; im engeren Sinne sind damit aber nur die Bewohner von Tenochtitlán und der beiden anderen Mitglieder des sogenannten „Aztekischen Dreibundes“, der Städte Texcoco und Tlacopán, gemeint.
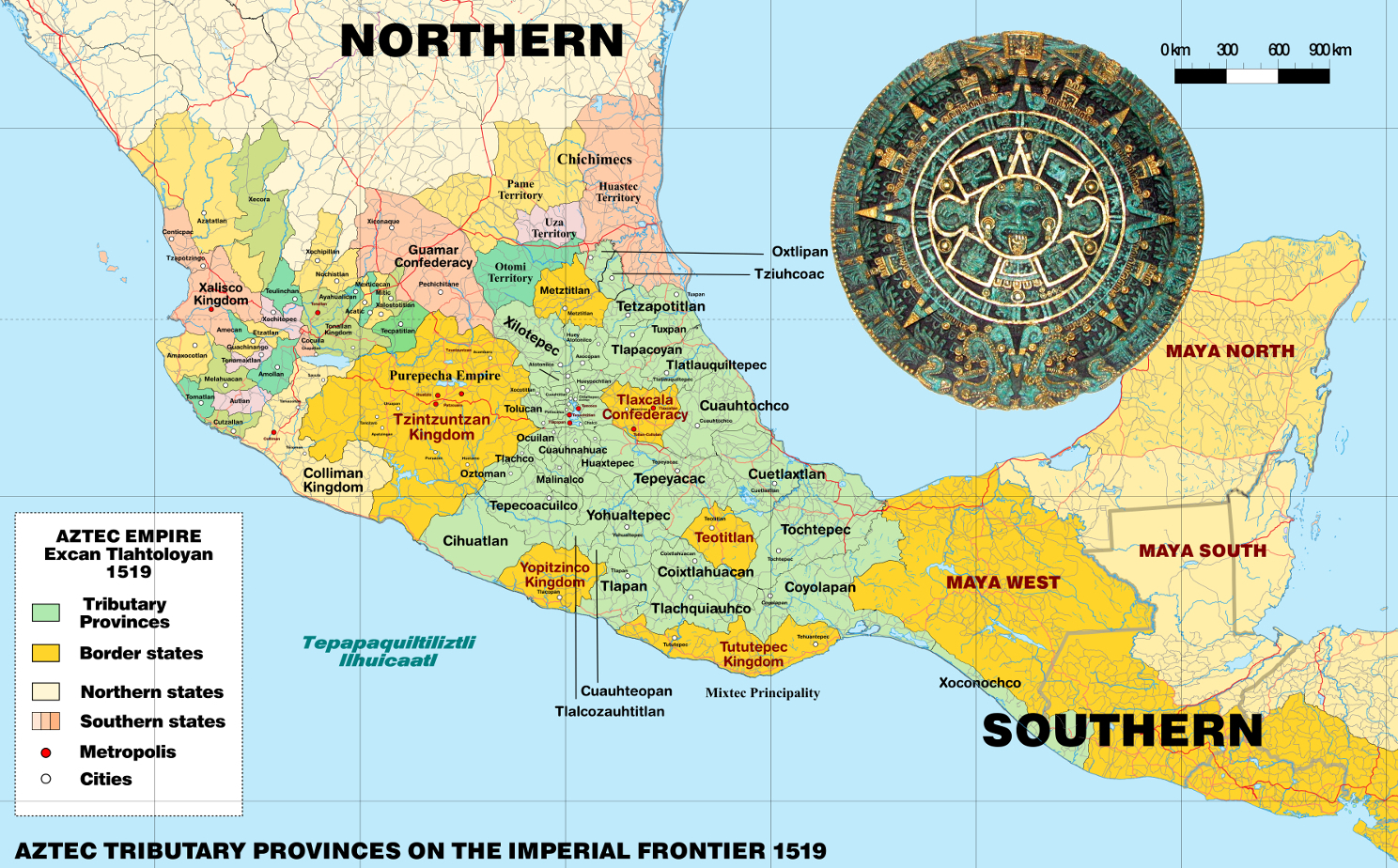
Ab dem späten 14. Jahrhundert weiteten die Azteken im Laufe der Jahre ihren politischen und militärischen Einfluss auf die umliegenden Städte und Völker aus, die nicht direkt dem Reich angegliedert, sondern zur Zahlung von Tributen gezwungen wurden. Auf dem Höhepunkt ihrer Macht kontrollierten sie weite Teile Zentralmexikos mit dem Tal von Mexiko als Zentrum. Zwischen 1519 und 1521 wurden die Azteken schließlich von den Spaniern unter Hernán Cortés unterworfen.
Die Azteken bezeichneten sich selbst meist als Mexica [meːˈʃiʔkaʔ], nach dem Namen des Ortes oder der Region Mexico – der Ursprung des heutigen Ländernamens Mexiko – bzw., nach ihren Siedlungsplätzen Tlatelolco und Tenochtitlán, auch Tlatelolca [tɬateˈloːlkaʔ] und Tenochca [teˈnoːtʃkaʔ]. In alten Quellen wird der Begriff „Azteken“ nur im Zusammenhang mit dem mythischen Herkunftsort Aztlán verwendet. Der erste, der ihn in moderner Zeit benutzte, war der Jesuit Francisco Javier Clavijero im 18. Jahrhundert; bekannt wurde er jedoch erst durch Alexander von Humboldt.
阿兹特克或阿兹台克是存在于14世纪至16世纪的墨西哥古文明,主要分布在墨西哥中部和南部,因阿兹特克人而得名。阿兹特克人包括墨西哥谷地的多个民族,以操纳瓦特尔语的族群为主。阿兹特克文明在政治上的基本单位是城邦,有些城邦组成政治联盟或政治邦联。其中,1427年建立的阿兹特克帝国最具影响力,帝国由墨西加城邦特诺奇蒂特兰、阿科尔瓦城邦特斯科科以及特帕内克城邦特拉科潘组成,政治影响力深远,领土范围极盛时东抵墨西哥湾,西至太平洋,南达恰帕斯和危地马拉。由于其强大的历史影响力,“阿兹特克”在狭义上常特指阿兹特克帝国;但广义来说,在殖民者入侵之前抑或是在西班牙殖民时代,中部美洲的所有纳瓦人政体和族群都可划作阿兹特克文明的一部分[1][2]。
阿兹特克人于约12世纪末由北方迁入墨西哥谷地,这里人口稠密,后来成为阿兹特克城邦崛起的中心。墨西加人是阿兹特克人的主要分支,他们在特斯科科湖中的岛礁建立起特诺奇蒂特兰城邦,并定居于此。1427年,特诺奇蒂特兰和特斯科科、特拉科潘结盟,联合击退了曾支配谷地的特帕内克城邦阿斯卡波察尔科。此三邦的联盟在后世被称为阿兹特克帝国,在随后的百余年内通过武力和贸易攻势展开扩张,成长为中部美洲势力范围最庞大的城邦联盟[3]。尽管被称为帝国,阿兹特克帝国事实上是一个以朝贡体系为基础的“朝贡帝国”,依托于扶植傀儡君主、政治联姻以及思想控制的方式间接控制其他城邦,强制其定期向宗主进贡,并不以军事驻防的方式实行直接统治[4]。帝国借此限制各邦同外部的贸易联系,使其属邦越发依赖帝国中央[5]。1519年,阿兹特克帝国的领土达到极盛,但一年后即迎来了欧洲人的历史性的访问。1520年,西班牙殖民者埃尔南·科尔特斯一行抵达中部美洲。科尔特斯利用中部美洲城邦间的矛盾,和阿兹特克的敌对城邦结盟,在1521年攻陷特诺奇蒂特兰,俘获并处决特拉托阿尼夸乌特莫克,并在特诺奇蒂特兰的废墟之上建起了现代墨西哥城。科尔特斯以此为中心实现对中部美洲全境的征服和殖民,将之纳入西班牙殖民帝国[6]。
近现代对阿兹特克文明的大规模研究始于19世纪,随着考古发掘和文献研究工作的进行,阿兹特克文明的文化、艺术和宗教逐渐为世人所了解。除了考古工作发现的古建筑和古物件外,既有的书面文献也起到重要作用,包括原住民手抄本、西班牙征服者的纪实文学,以及16世纪和17世纪由西班牙牧师或是有读写能力的阿兹特克人编撰的文化和历史文献等。十二卷手抄本佛罗伦萨手抄本是其中较为著名的文献,由方济各会修士贝尔纳迪诺·德萨阿贡结合一些阿兹特克人的描述写成,完整全面地记录了阿兹特克文明的文化、宗教、社会、经济和历史样貌。
德国地理学家冯·洪堡在19世纪早期率先用“阿兹特克”一词指代中部美洲纳瓦人以贸易、习俗、宗教、语言或政治联盟为纽带联系起来的文明集合体,“阿兹特克”一词就此被学界广泛接受和使用。不过,阿兹特克的具体界定也仍是一直以来学术讨论的主题之一[7]。根据中部美洲历史的断代法共识,900年至1521年的后古典时期内,中部美洲的绝大部分族群都拥有大体类似的文化烙印。因此,大部分普遍认为象征阿兹特克文明的文化元素并不是阿兹特克帝国的专属,因此对“阿兹特克文明”概念更贴切的理解是一种普遍存在的中部美洲文化体系[8],其农业以玉米栽培为主,社会形成皮尔利贵族和马塞瓦尔利平民的阶级分野,崇拜以特斯卡特利波卡、特拉洛克和克察尔科亚特尔为主的神系,历法系统由365天一周期的太阳历内嵌260天一周期的神圣历组成。与之相对应地,守护神祇维齐洛波奇特利、双子金字塔和阿兹特克陶制品则是阿兹特克人独有的文化符号[8]。现代墨西哥国家建立后,阿兹特克文化作为其国土上曾存在的重要文化而成为其现代国家认同的根基之一。特诺奇蒂特兰建城传说中雄鹰衔长蛇立于仙人掌之上的经典场面出现在墨西哥国旗和国徽上,为其重要的国家象征之一。
アステカ(Azteca、古典ナワトル語: Aztēcah)とは1428年頃から1521年までの約95年間北米のメキシコ中央部に栄えたメソアメリカ文明の国家。メシカ(古典ナワトル語: mēxihcah メーシッカッ)、アコルワ、テパネカの3集団の同盟によって支配され、時とともにメシカがその中心となった。言語は古典ナワトル語(ナワトル語)。
The Aztecs (/ˈæztɛks/) were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec peoples included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (altepetl), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427, Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era,[1] as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821).[2] The definitions of Aztec and Aztecs have long been the topic of scholarly discussion, ever since German scientist Alexander von Humboldt established its common usage in the early nineteenth century.[3]
Most ethnic groups of central Mexico in the post-classic period shared basic cultural traits of Mesoamerica, and so many of the traits that characterize Aztec culture cannot be said to be exclusive to the Aztecs. For the same reason, the notion of "Aztec civilization" is best understood as a particular horizon of a general Mesoamerican civilization.[4] The culture of central Mexico includes maize cultivation, the social division between nobility (pipiltin) and commoners (macehualtin), a pantheon (featuring Tezcatlipoca, Tlaloc and Quetzalcoatl), and the calendric system of a xiuhpohualli of 365 days intercalated with a tonalpohualli of 260 days. Particular to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan was the patron God Huitzilopochtli, twin pyramids, and the ceramic ware known as Aztec I to IV.[5]
From the 13th century, the Valley of Mexico was the heart of dense population and the rise of city-states. The Mexica were late-comers to the Valley of Mexico, and founded the city-state of Tenochtitlan on unpromising islets in Lake Texcoco, later becoming the dominant power of the Aztec Triple Alliance or Aztec Empire. It was a tributary empire that expanded its political hegemony far beyond the Valley of Mexico, conquering other city states throughout Mesoamerica in the late post-classic period. It originated in 1427 as an alliance between the city-states Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan; these allied to defeat the Tepanec state of Azcapotzalco, which had previously dominated the Basin of Mexico. Soon Texcoco and Tlacopan were relegated to junior partnership in the alliance, with Tenochtitlan the dominant power. The empire extended its reach by a combination of trade and military conquest. It was never a true territorial empire controlling a territory by large military garrisons in conquered provinces, but rather dominated its client city-states primarily by installing friendly rulers in conquered territories, by constructing marriage alliances between the ruling dynasties, and by extending an imperial ideology to its client city-states.[6] Client city-states paid tribute to the Aztec emperor, the Huey Tlatoani, in an economic strategy limiting communication and trade between outlying polities, making them dependent on the imperial center for the acquisition of luxury goods.[7] The political clout of the empire reached far south into Mesoamerica conquering polities as far south as Chiapas and Guatemala and spanning Mesoamerica from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans.
The empire reached its maximal extent in 1519, just prior to the arrival of a small group of Spanish conquistadors led by Hernán Cortés. Cortés allied with city-states opposed to the Mexica, particularly the Nahuatl-speaking Tlaxcalteca as well as other central Mexican polities, including Texcoco, its former ally in the Triple Alliance. After the fall of Tenochtitlan on August 13, 1521 and the capture of the emperor Cuauhtemoc, the Spanish founded Mexico City on the ruins of Tenochtitlan. From there they proceeded with the process of conquest and incorporation of Mesoamerican peoples into the Spanish Empire. With the destruction of the superstructure of the Aztec Empire in 1521, the Spanish utilized the city-states on which the Aztec Empire had been built, to rule the indigenous populations via their local nobles. Those nobles pledged loyalty to the Spanish crown and converted, at least nominally, to Christianity, and in return were recognized as nobles by the Spanish crown. Nobles acted as intermediaries to convey tribute and mobilize labor for their new overlords, facilitating the establishment of Spanish colonial rule.[8]
Aztec culture and history is primarily known through archaeological evidence found in excavations such as that of the renowned Templo Mayor in Mexico City; from indigenous writings; from eyewitness accounts by Spanish conquistadors such as Cortés and Bernal Díaz del Castillo; and especially from 16th- and 17th-century descriptions of Aztec culture and history written by Spanish clergymen and literate Aztecs in the Spanish or Nahuatl language, such as the famous illustrated, bilingual (Spanish and Nahuatl), twelve-volume Florentine Codex created by the Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún, in collaboration with indigenous Aztec informants. Important for knowledge of post-conquest Nahuas was the training of indigenous scribes to write alphabetic texts in Nahuatl, mainly for local purposes under Spanish colonial rule. At its height, Aztec culture had rich and complex mythological and religious traditions, as well as achieving remarkable architectural and artistic accomplishments.
Les Aztèques, ou Mexicas (du nom de leur capitale, Mexico-Tenochtitlan), étaient un peuple amérindien du groupe nahua, c'est-à-dire de langue nahuatl.
Ils s'étaient définitivement sédentarisés dans le plateau central du Mexique, dans la vallée de Mexico, sur une île du lac Texcoco, vers le début du XIVe siècle. Au début du XVIe siècle, ils avaient atteint un niveau de civilisation parmi les plus avancés d'Amérique et dominaient, avec les autres membres de leur Triple alliance, le plus vaste empire de la Mésoamérique postclassique. Leur seul vrai rival était le royaume tarasque.
L'arrivée, en 1519, des conquistadors menés par Hernán Cortés scella la fin de leur règne. Le 13 août 1521, les Espagnols, aidés par un grand nombre d’alliés autochtones, finirent par remporter le siège de Tenochtitlan et par capturer le dernier dirigeant aztèque, Cuauhtémoc. La civilisation aztèque s'est alors rapidement acculturée à l'époque coloniale ; il en résulte un profond syncrétisme dans le Mexique actuel entre les héritages aztèques (et, plus largement, mésoaméricains) et espagnols.
Les études de cette civilisation précolombienne se fondent sur les codex mésoaméricains, livres écrits par les autochtones sur papier d'amate, les témoignages des conquistadors, comme Hernán Cortés et Bernal Díaz del Castillo, les travaux des chroniqueurs du XVIe et XVIIe siècles, comme le codex de Florence compilé par le moine franciscain Bernardino de Sahagún avec l'aide de collaborateurs aztèques, ainsi que, depuis la fin du XVIIIe siècle, les recherches archéologiques, grâce aux fouilles comme celles du Templo Mayor de la ville de Mexico.
I Mexica (pron. mescìca; Nahuatl: Mēxihcah [meːˈʃiʔkaʔ], singolare Mēxihcatl) o Mexicas — meglio noti come Aztechi nella storiografia occidentale - furono una delle grandi civiltà precolombiane, la più florida e viva al momento del contatto con gli Spagnoli. Provenienti dalla California settentrionale, si svilupparono nella regione mesoamericana dell'attuale Messico dal secolo XIV al XVI.
Il nome con cui essi stessi si indicavano è "Mexica" o "Tenochca", e non Aztechi, non a caso Mexica è tuttora il termine usato per definire i loro discendenti; il termine Azteco è invece stato coniato solo molti secoli dopo dal geografo tedesco Alexander von Humboldt per distinguere queste popolazioni precolombiane dall'insieme dei Messicani moderni. Spesso con il termine "azteco" ci si riferisce esclusivamente al popolo residente a Tenochtitlán (dove oggi si trova Città del Messico), situata su un'isola del lago Texcoco, che faceva riferimento a se stessa come Mēxihcah Tenochcah [meːˈʃiʔkaʔ teˈnot͡ʃkaʔ] o Cōlhuah Mēxihcah [ˈkoːlwaʔ meːˈʃiʔkaʔ].
Talvolta il termine comprende anche gli abitanti delle due principali città-stato alleate di Tenochtitlan, gli Acolhua di Texcoco e i Tepanechi di Tlacopan, che insieme con i Mexica formavano la Triplice alleanza azteca spesso conosciuta come "impero azteco". In altri contesti, "azteco" può riferirsi a tutti i vari stati della città e dei loro popoli che hanno condiviso gran parte della loro storia etnica e tratti culturali con i Mexica, con gli Acolhua e con i Tepanechi e che spesso utilizzavano la lingua nahuatl come lingua franca. In questo senso si può parlare di una civiltà azteca comprensiva di tutti i modelli culturali comuni per la maggior parte dei popoli che abitarono il Messico centrale nel periodo tardo post-Classico.
A partire dal XIII secolo, la Valle del Messico è stata il cuore della civiltà azteca; qui la capitale della Triplice alleanza azteca, la città di Tenochtitlan, fu costruita su isole nel lago Texcoco. La Triplice Alleanza formò un impero tributario che espanse la propria egemonia politica ben oltre la Valle del Messico, conquistando altre città di tutto il Mesoamerica. Al suo apice, la cultura azteca vantava ricche e complesse tradizioni mitologiche e religiose, oltre ad aver raggiunto la capacità di realizzare notevoli manufatti architettonici e artistici. Nel 1521 Hernán Cortés, conquistò Tenochtitlan e sconfisse la Triplice alleanza azteca che al momento si trovava sotto la guida di Montezuma II (vedi Conquista dell'impero azteco). Successivamente, gli spagnoli fondarono il nuovo insediamento di Città del Messico sul sito della capitale azteca in rovina; da qui poi procedettero con il processo di colonizzazione dell'America Centrale.
La cultura e la storia azteca sono conosciute principalmente attraverso le testimonianze archeologiche rinvenute negli scavi, come quello del famoso Templo Mayor a Città del Messico; da codici scritti su corteccia; da testimonianze oculari dei conquistadores spagnoli come Hernán Cortés e Bernal Díaz del Castillo; e soprattutto dalle descrizioni del XVI e XVII secolo della cultura e della storia scritti da ecclesiastici spagnoli e da letterati Aztechi, come il famoso Codice Fiorentino compilato dal frate francescano Bernardino de Sahagún con l'aiuto di informatori originari aztechi.
Los mexicas (del náhuatl mēxihcah ![]() [meː'ʃiʔkaʔ] (?·i), «mexicas»1) —llamados en la historiografía tradicional aztecas2— fueron un pueblo mesoamericano de filiación nahua que fundó México-Tenochtitlan y hacia el siglo XV en el periodo posclásico tardío se convirtió en el centro de uno de los Estados más extensos que se conoció en Mesoamérica, asentado en un islote al poniente del lago de Texcoco, sobre los márgenes centro y el sur de los lagos, como en Huexotla, Coatlinchan, Culhuacan, Iztapalapa, Chalco, Xico, Xochimilco, Tacuba, Azcapotzalco, Tenayuca y Xaltocan, hacia finales del Posclásico Temprano (900-1200),3 hoy prácticamente desecado. Sobre el islote se asienta la actual Ciudad de México, y que corresponde a la misma ubicación geográfica. Aliados con otros pueblos de la cuenca lacustre del valle de México —Tlacopan y Texcoco—, los mexicas sometieron a varias poblaciones indígenas que se asentaron en el centro y sur del territorio actual de México agrupados territorialmente en altépetl.
[meː'ʃiʔkaʔ] (?·i), «mexicas»1) —llamados en la historiografía tradicional aztecas2— fueron un pueblo mesoamericano de filiación nahua que fundó México-Tenochtitlan y hacia el siglo XV en el periodo posclásico tardío se convirtió en el centro de uno de los Estados más extensos que se conoció en Mesoamérica, asentado en un islote al poniente del lago de Texcoco, sobre los márgenes centro y el sur de los lagos, como en Huexotla, Coatlinchan, Culhuacan, Iztapalapa, Chalco, Xico, Xochimilco, Tacuba, Azcapotzalco, Tenayuca y Xaltocan, hacia finales del Posclásico Temprano (900-1200),3 hoy prácticamente desecado. Sobre el islote se asienta la actual Ciudad de México, y que corresponde a la misma ubicación geográfica. Aliados con otros pueblos de la cuenca lacustre del valle de México —Tlacopan y Texcoco—, los mexicas sometieron a varias poblaciones indígenas que se asentaron en el centro y sur del territorio actual de México agrupados territorialmente en altépetl.
Los mexicas se caracterizaban por la explotación de cultivos altamente simbióticos (dependencia a la manipulación humana,4556 como maíz, chile, calabaza, frijol, etc.), el uso extensivo de plumas para la confección de vestimentas, el uso de calendarios astronómicos (uno ritual de 260 días y un civil de 365), una sofisticada metalurgia prehispánica ornamental y militar basada principalmente en el bronce, oro y plata;7 una escritura en forma de pictogramas el cual era usado para la documentación de hechos y el cálculo de obras arquitectónicas el cual estaba basado en un sistema métrico propio,8 que para mediciones de terrenos es comparable con otros sistemas de medida de la Edad Moderna,9 el uso extensivo de productos derivados de las cactáceas y agaves, y el uso de cerámico ígneo (obsidiana) para fines quirúrgicos y bélicos.
Ацте́ки, или асте́ки[1] (самоназв. mēxihcah [meː'ʃiʔkaʔ]), — индейский народ в центральной Мексике. Численность современных науа, как ещё называют ацтеков, — свыше 1,5 млн человек. Цивилизация ацтеков (XIV—XVI века) обладала богатой мифологией и культурным наследием. Столицей империи ацтеков был город Теночтитлан, расположенный на озере Тескоко, там, где сейчас располагается город Мехико.


 Geschichte
Geschichte
 H 1000 - 500 vor Christus
H 1000 - 500 vor Christus

 Geschichte
Geschichte
 I 500 - 0 vor Christus
I 500 - 0 vor Christus
 Mexiko
Mexiko

 Weltkulturerbe
Weltkulturerbe

 Zivilisation
Zivilisation
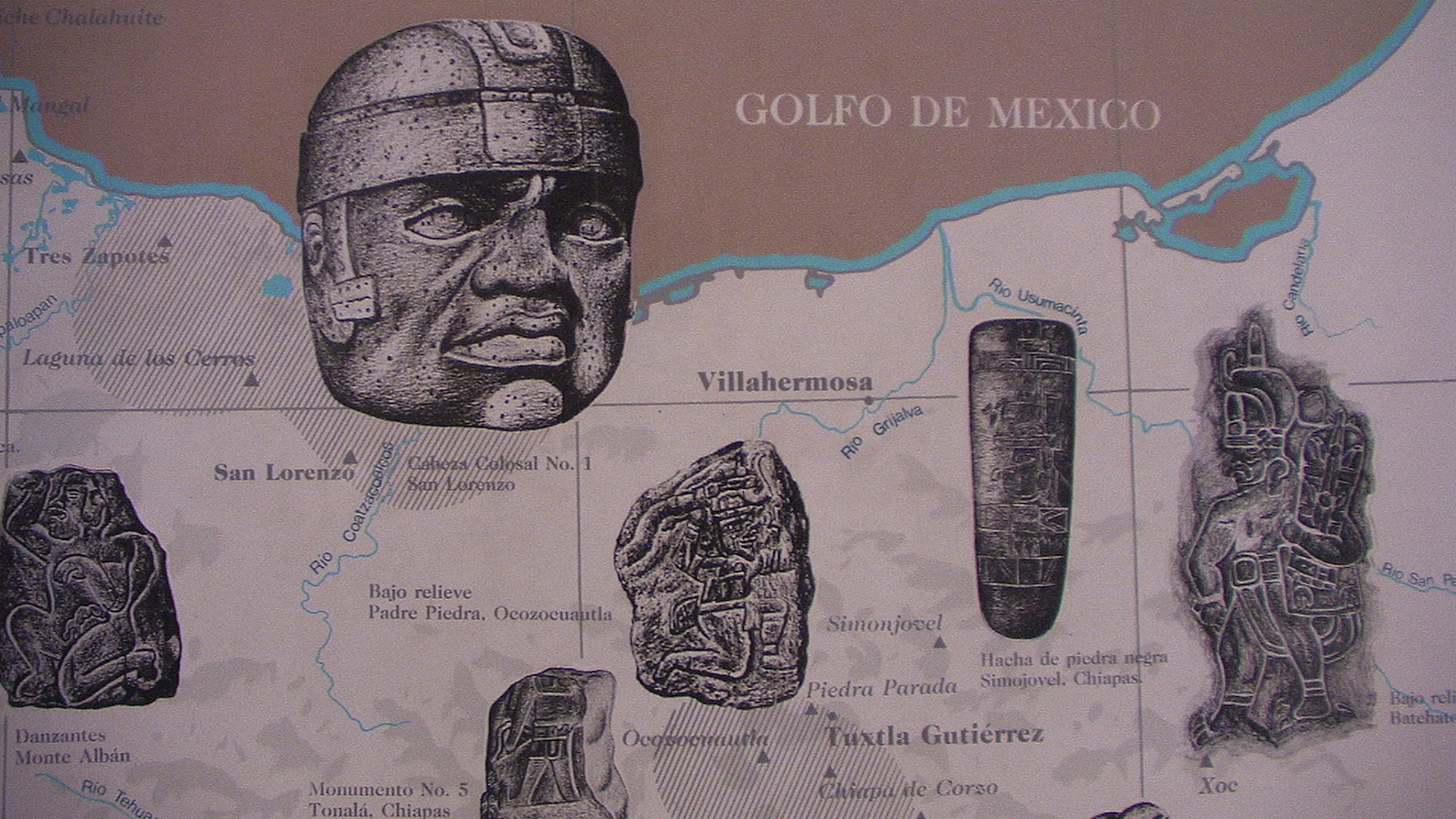
Als Olmeken (von Nahuatl Singular Ōlmēcatl beziehungsweise Plural Ōlmēcah für „Leute aus dem Kautschukland“) wurden von Archäologen die Träger der mittelamerikanischen La-Venta-Kultur bezeichnet. Ihre tatsächliche ethnische Zugehörigkeit ist unbekannt. Die Kultur der Olmeken ist von etwa 1500 bis um 400 v. Chr. entlang der Küste des Golfs von Mexiko nachweisbar. Ihre bekanntesten kulturellen Hinterlassenschaften sind mehrere Kolossalköpfe. Ob die Kultur der Olmeken als Proto-Maya-Kultur angesehen werden kann, wurde vielfach diskutiert, ist aber wegen des großen zeitlichen und räumlichen Abstands eher unwahrscheinlich.
奥尔梅克文明(Olmec)是已知的最古老的美洲文明之一。它存在和繁盛于公元前1200年到公元前400年的中美洲(现在的墨西哥中南部)。
“奥尔梅克”一词源自纳瓦特尔语中用以指奥尔梅克人的单词Ōlmēcatl(发音:/oːlˈmeːkat͡ɬ/,此词在纳瓦特尔语中之众数形为Ōlmēcah,发音/oːlˈmeːkaʔ/),而在纳瓦特尔语中,此词为ōlli(意即“橡胶”,发音/ˈoːlːi/)和mēcatl(意即“人”,发音/ˈmeːkat͡ɬ/)的合成词,故Ōlmēcatl在纳瓦特尔语中的意思可解作“胶人”。
オルメカ(Olmeca)は、紀元前1200年頃から紀元前後にかけ、先古典期のメソアメリカで栄えた文化・文明である[1]。アメリカ大陸で最も初期に生まれた文明であり、その後のメソアメリカ文明の母体となったことから、「母なる文明」と呼ばれる[2]。
オルメカとは、ナワトル語で「ゴムの国の人」を意味し、スペイン植民地時代にメキシコ湾岸の住民を指した言葉である。巨石や宝石を加工する技術を持ち、ジャガー信仰などの宗教性も有していた。その美術様式や宗教体系は、マヤ文明などの古典期メソアメリカ文明と共通するものがある。
オルメカの影響は中央アメリカの中部から南部に広がっていたが、支配下にあったのは中心地であるメキシコ湾岸地域に限られた[4]。その領域はベラクルス州南部からタバスコ州北部にかけての低地で、雨の多い熱帯気候のため、たびたび洪水が起こった。しかし、河川によって肥沃な土地が形成され、神殿を中心とした都市が築かれた[2]。
オルメカの文化は、出土するさまざまな石像に現れている。人間とジャガーを融合させた神像は、彼らにジャガーを信仰する風習があったことを物語っている[2]。祭祀場では儀式としての球技が行われ、その際には人間が生贄として捧げられた[4]。また、絵文字や数字を用い、ゼロの概念を持つなど、数学や暦が発達していた[2]。
The Olmecs (/ˈɒlmɛks, ˈoʊl-/) were the earliest known major civilization in Mesoamerica following a progressive development in Soconusco. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the present-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that the Olmecs derive in part from neighboring Mokaya or Mixe–Zoque.
The Olmecs flourished during Mesoamerica's formative period, dating roughly from as early as 1500 BCE to about 400 BCE. Pre-Olmec cultures had flourished in the area since about 2500 BCE, but by 1600–1500 BCE, early Olmec culture had emerged, centered on the San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán site near the coast in southeast Veracruz.[1] They were the first Mesoamerican civilization, and laid many of the foundations for the civilizations that followed.[2] Among other "firsts", the Olmec appeared to practice ritual bloodletting and played the Mesoamerican ballgame, hallmarks of nearly all subsequent Mesoamerican societies. The aspect of the Olmecs most familiar now is their artwork, particularly the aptly named "colossal heads".[3] The Olmec civilization was first defined through artifacts which collectors purchased on the pre-Columbian art market in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Olmec artworks are considered among ancient America's most striking.[4]
Les Olmèques sont un ancien peuple précolombien de Mésoamérique s'étant épanoui de 1200 av. J.-C. jusqu'à 500 av. J.-C. sur la côte du golfe du Mexique, dans le bassin de Mexico, et le long de la côte Pacifique (États du Guerrero, Oaxaca et Chiapas). Issu du terme nahuatl olmeca, qui signifie « les gens du pays du caoutchouc », ce mot est lié à la découverte de la première tête colossale olmèque, en 1862. Le terme « olmèque » a été officialisé en 1942 par les olmécologues.
Gli Olmechi erano un'antica civiltà precolombiana che viveva nell'area tropicale dell'odierno Messico centro-meridionale, approssimativamente negli stati messicani di Veracruz e Tabasco sull'Istmo di Tehuantepec. La civiltà olmeca fiorì durante il periodo formativo (pre-classico) mesoamericano (vedi Cronologie mesoamericane), estendentesi approssimativamente dal 1400 a.C. al 400 a.C. Gli Olmechi costituirono la prima civiltà mesoamericana e stabilirono le fondamenta delle culture successive. Esistono prove che gli Olmechi praticassero il sacrificio umano e praticassero un primitivo gioco con la palla (Giochi con la palla mesoamericani), caratteristiche di tutte le successive culture. L'influenza culturale olmeca fu molto ampia, tanto che opere d'arte di questa civiltà sono state trovate anche a El Salvador. Questo popolo ebbe il predominio nella sua area da circa il 1200 a circa il 400 a.C. e da molti è considerata la cultura madre di tutte le successive civiltà mesoamericane.
Il cuore del territorio olmeco (la cosiddetta area nucleare olmeca) è caratterizzato da pianure alluvionali, costellate da creste di basse colline e da vulcani. Le Montagne Tuxtlas vanno a nord, lungo la baia di Campeche. E fu proprio qui che gli olmechi costruirono complessi templari, fra cui San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán, La Venta, Tres Zapotes, Laguna de los Cerros e La Mojarra. La loro influenza si estese dagli altopiani alla costa del Pacifico, vicino all'odierno Guatemala (come dimostrano i ritrovamenti di divinità olmeche).
Questa civiltà emerse e dominò tra il 1200 e il 400 a.C. e sembra che sia stata anche la prima civiltà mesoamericana a sviluppare un sistema di scrittura, anche se non ne sono ancora stati trovati esempi. Attualmente si dibatte se i simboli trovati nel 2002 e datati 650 a.C. siano o meno una forma di scrittura olmeca precedente a quella zapoteca, datata intorno al 500 a.C.[1] Ci sono anche altri geroglifici successivi, conosciuti come Epi-Olmechi, cioè post-olmechi: e se alcuni ritengono che questo epi-olmeco potrebbe essere una traslitterazione scritta che si colloca tra un precedente e sconosciuto sistema di scrittura olmeca e la scrittura dei maya, la questione resta comunque irrisolta e aperta.
Gli Olmechi sarebbero anche gli inventori del gioco della palla, che si diffuse anche nelle altre culture della regione con scopi sia ricreativi sia cerimoniali.
Attorno all'anno 1000 a.C. gli Olmechi, primi conoscitori della pianta di cacao, chiamavano il cacao kakawa; in seguito, esso fu rinominato kakaw dai Maya. [2]
Le caratteristiche e le tematiche della loro religione si svilupparono anche in seguito nelle altre culture dell'area. Stessa cosa accadde per la struttura fortemente gerarchica e verticistica delle loro città-stato.
La cultura olmeca fue la civilización que se desarrolló durante el periodo Preclásico de Mesoamérica. Aunque se han encontrado vestigios de su presencia en amplias zonas de Mesoamérica, se considera que el área nuclear olmeca —zona metropolitana— abarca la parte sureste del estado de Veracruz y el oeste de Tabasco. En ese sentido, es necesario hacer la aclaración de que el etnónimo olmeca les fue impuesto por los arqueólogos del siglo XX, y no debe ser confundido con el de los olmeca-xicalancas, que fueron un grupo que floreció en el epiclásico en sitios del centro de México, como Cacaxtla.
Durante mucho tiempo se consideró que la olmeca era la cultura madre de la civilización mesoamericana.1 Sin embargo, no está claro el proceso que dio origen al estilo artístico identificado con esta sociedad, ni hasta qué punto los rasgos culturales que se revelan en la evidencia arqueológica son creación de los olmecas del área nuclear. Se sabe, por ejemplo, que algunos de los atributos propiamente olmecas pudiesen haber aparecido, primero en Chiapas o en los Valles Centrales de Oaxaca. Entre otras dudas que están pendientes de respuesta definitiva, está la cuestión de los numerosos sitios asociados a esta cultura en la Depresión del Balsas (centro de Guerrero). Sea cual haya sido el origen de la cultura olmeca, la red de intercambios comerciales entre distintas zonas de Mesoamérica contribuyó a la difusión de muchos elementos culturales que son identificados con la cultura olmeca, incluidos el culto a las montañas y a las cuevas; el culto a la Serpiente Emplumada, como deidad asociada a la agricultura, el simbolismo religioso del jade e, incluso, el propio estilo artístico, que fue reelaborado intensamente en los siglos posteriores a la declinación de los principales centros de estos tiempos.
Ольме́ки — название племени, упоминающееся в ацтекских исторических хрониках. Название дано условно, по одному из небольших племен, живших на указанной ниже территории[1]. Создатели первой «крупной» цивилизации в Мексике, которая была наследницей культур, последовательно развивавшихся в Соконуско (на юго-западе мексиканского штата Чьяпас)[2]. Ольмеки обитали в тропических долинах южной и центральной Мексики на территории современных штатов Веракрус и Табаско. Возможно, родственны создателям культуры Мокая из Соконуско и носителям языков михе-соке.
Цивилизация ольмеков процветала в течение периода становления Мезоамерики примерно с 1500 до н. э. до 400 до н. э. Доольмекская культура существовала примерно с 2500 до н. э. по 1600-1500 до н. э. Ранние формы культуры ольмеков появились в районе Сан-Лоренсо-Теночтитлана неподалёку от побережья океана в юго-восточной части современного мексиканского штата Веракрус[3]. Во многих отношениях эта мезоамериканская цивилизация стала пионерской, повлияв на все последующие[4]. Например, ольмеки первыми ввели практику ритуального кровопролития и игру в мяч.
О цивилизации ольмеков стало известно в конце XIX — начале XX века, когда собиратели артефактов доколумбовой эпохи обнаружили на рынке казавшиеся необычными изделия. Сегодня ольмеки известны широкой публике прежде всего своими произведениями искусства, особенно гигантскими головами[5].
 Sport
Sport
 Energieressource
Energieressource
 Film & TV Produktion
Film & TV Produktion
 Parteien und Regierung
Parteien und Regierung
 Freizeitpark
Freizeitpark
 Architektur
Architektur
 Geographie
Geographie