
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
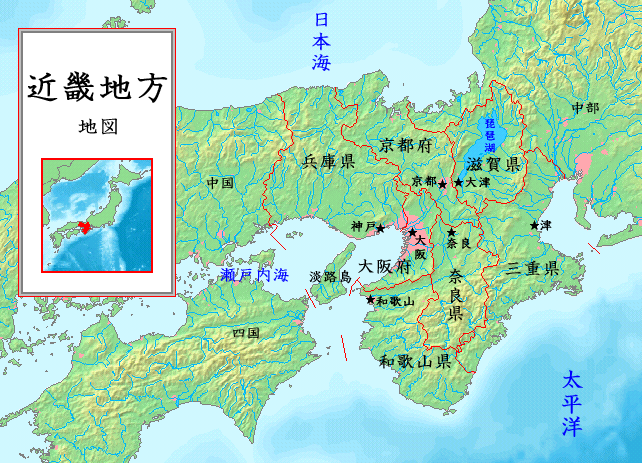
 Kinki
Kinki
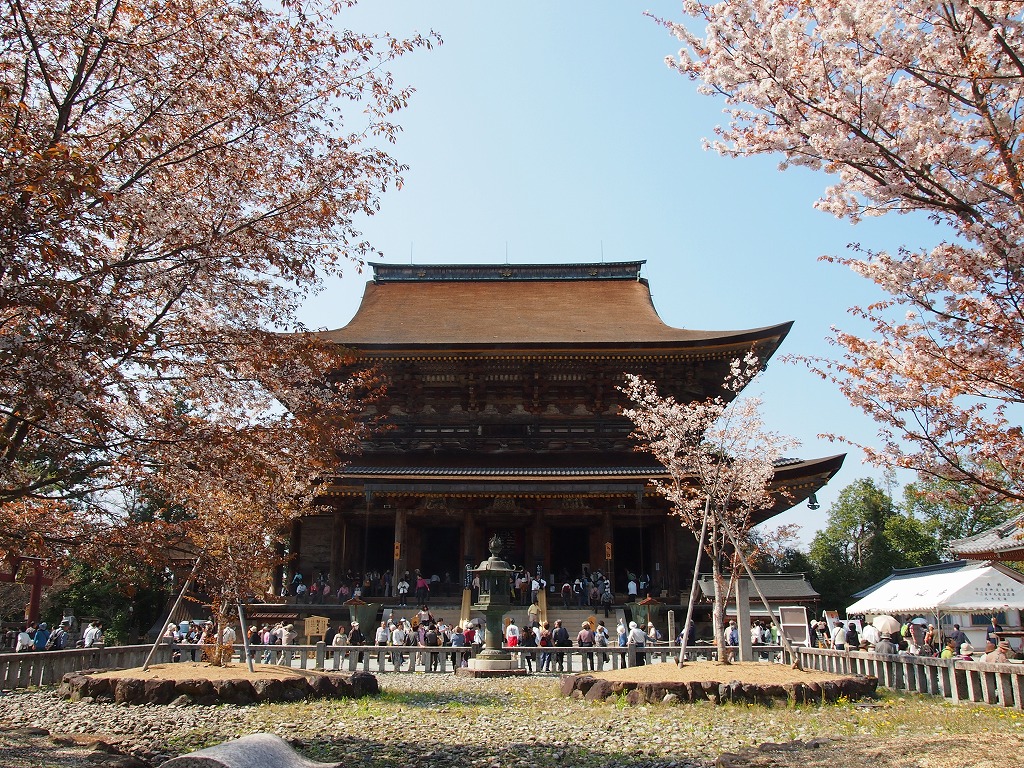



Kinkaku-ji (jap. 金閣寺, dt. „Goldener-Pavillon-Tempel“), eigentlich Rokuon-ji (鹿苑寺, dt. „Rehgarten-Tempel“), ist ein buddhistischer Tempel im Nordwesten der japanischen Stadt Kyōto.Bekannt ist die Tempelanlage für die Shariden (舎利殿, „Reliquienhalle“), deren obere Stockwerke vollständig mit Blattgold überzogen sind und die daher als Kinkaku (金閣), „Goldener Pavillon“, bezeichnet wird. Wegen der Bekanntheit des Pavillons wird heutzutage für die gesamte Anlage der Name Kinkaku-ji verwendet.
鹿苑寺(日语:鹿苑寺/ろくおんじ Rokuonji),又名金阁寺(日语:金閣寺/きんかくじ kinkakuji)[1],正式名称为北山鹿苑禅寺(日语:北山鹿苑禅寺/ほくざんろくおんぜんじ hokuzanrokuonzenji)[2][3],是一座最早完成于1397年(应永四年)的日本佛寺,位于京都府京都市北区,是一座临济宗相国寺派的寺院,其名称源自于日本室町时代著名的足利氏第三代幕府将军足利义满之法名,又因为寺内核心建筑“舍利殿”的外墙全是以金箔装饰,所以又被称为“金阁”。
事实上,为人所知的“金阁寺”这个名称并不准确地代表整个寺庙。寺方强调,“鹿苑寺”是整个庙寺的名称,而“金阁”是当中的一个殿堂。金阁本身也是一个简称,其真正名称是“舍利殿”(日语:舎利殿/しゃりでん sharidono)。[4]
鹿苑寺除了是知名的观光旅游景点之外,并于1994年以“古都京都的文化财”的一部分被联合国教科文组织指定为世界文化遗产的重要历史建筑。
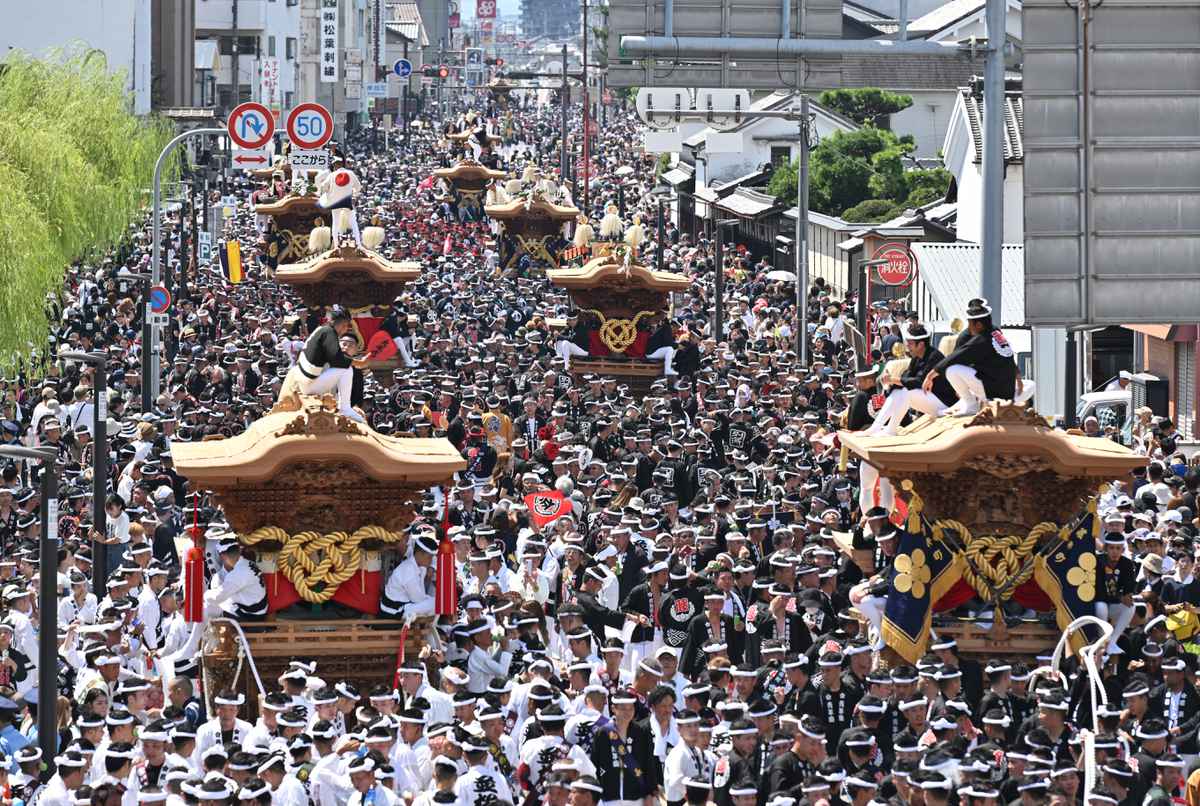


岸和田彩车祭拥有 300 年历史,由岸和田的民众代代相传至今,成为当地自豪的传统。融合静与动的活泼彩车拖曳游行,不仅在日本远近驰名,更以世界级祭典之姿名闻遐迩。而彩车会馆则是不限祭典期间,全年皆可让旅客亲身体验彩车祭活动的博物馆。本馆采用震撼力十足的影像和音响还原现场,还有精致的雕刻品和祭典体验区等众多精彩项目等着旅客探索。

清水寺是一座位于日本京都府京都市东山区清水的寺院,于778年(宝龟9年)前后由延镇上人起造。清水寺的山号为音羽山,主要供奉千手观音,原本属于法相宗这一宗派但目前已独立,成为北法相宗的大本山。
清水寺与鹿苑寺(金阁寺)、岚山等同为京都境内最著名的名胜古迹,一年四季前来朝拜的香客或来访的观光客是络驿不绝。除此之外,清水寺也与石山寺(滋贺县大津市),长谷寺(奈良县樱井市)等寺庙并列,自古以来就一直以嗣奉观音的庙宇而为人所熟知,也是西国三十三个所(在关西地区参拜33所观音庙的巡访活动)中第16所寺庙。自平安时代以来,就经常出现于日本文学作品当中。1994年,清水寺以身为古都京都的文化财之一部分,列名至世界文化遗产中。




神户市(日语:神戸市/こうべし Kōbe shi */?)是位于日本兵库县东南部的都市,为兵库县首府,也是政令指定都市之一[1],下辖有9个区。神户市的面积为552.83平方公里。2016年6月,神户市有人口1,538,053人[2],是日本人口第七多的都市。神户市与大阪市、京都市并为京阪神都会区的核心都市[3],同时也和其附近的卫星都市组成神户都市圈[4]。
“神户”这一地名是起源于现在神户市中心的三宫、元町地区在古代曾是生田神社的领地,并居住有生田神社的神封户[5]。神户地处大阪湾沿岸,风浪平缓且沿岸水深较深,地形极为适宜建设港口[6]。在古代时期,神户就是京都及大阪的外港之一[7]。1868年,神户成为日本最早开放对外国通商的五个港口之一,之后神户迅速发展为日本最重要的港湾都市之一[8]。也正因其是日本最早的通商港口,神户以开放和国际化的气氛而闻名。1995年的阪神淡路大震灾虽然给神户带来巨大的打击,然而经过多年的重建,神户的都市建设和人口都已超过地震之前的水准[9]。神户也是一座宜居都市,并曾在2007年入选福布斯杂志评出的“世界最清洁的25座城市”[10],其后也于2012年在瑞士的咨询公司ECA国际评选出的世界宜居都市排名中排名第五位,是唯一入选前10位的日本都市[11]。
Kōbe (jap. 神戸市, -shi) ist eine Großstadt in Japan auf der Insel Honshū. Die Stadt ist Sitz der Präfekturverwaltung von Hyōgo und hat einen der größten Seehäfen Japans. Die moderne, internationale Stadt bildet mit Osaka und Kyōto (Keihanshin) und kleineren Städten das Herz der Kansai-Gegend. Kōbe ist eine der ersten designierten Großstädte von 1956.
神戸市(こうべし)は、兵庫県の南部に位置する同県の県庁所在地。垂水区・須磨区・長田区・兵庫区・中央区・灘区・東灘区・北区・西区から構成される政令指定都市。日本の市で6番目の人口を有する。
海と山の迫る東西に細長い市街地を持ち、十分な水深のある扇状の入り江部に発展した理想的な港湾・神戸港を有する日本を代表する港町である。
「神戸」という地名は、現在の三宮・元町周辺が古くから生田神社の神封戸の集落(神戸「かんべ」)であったことに由来する。西国街道の宿場町であり北前船の出発地の一つでもあった兵庫津(ひょうごのつ)に近く、廻船問屋が軒を並べていた神戸村を指していた。神戸三社(神戸三大神社)をはじめとする市内・国内にある神社の神事に使うお神酒の生産にも係わり、前述の有馬温泉や神封戸の形成も市名の由来に関係している。
海運においても古くから盛んで、近代には世界の市場にその名を知られるほどに隆盛していった。以降も貿易・鉄鋼・造船・機械・製造・ゴム・真珠加工・観光等の産業を中心に発展、ファッション・医療・食料品などの産業も近年は盛んである。
1995年1月17日に発生した兵庫県南部地震による阪神・淡路大震災では市内のほぼ全域で震度7を観測。市街地と港、道路、インフラは甚大な被害を受けたが急速に復興を遂げ、2005年には国内3番目の市営空港として神戸空港が開港した。
2008年、アジアの都市で初めて「デザイン都市」としてユネスコに認定された。
2012年、スイスのECAインターナショナルが世界400余りの都市の、気候、医療サービス、インフラ、安全性、大気品質などの生活水準を調査し発表した「世界で最も住みやすい都市」で、日本の都市で唯一トップ10に入り、世界全体で5位、アジア圏ではシンガポールに次ぐ2位に選ばれている。
Kobe (神戸市 Kōbe-shi, Japanese: [koːꜜbe]) is the sixth-largest city in Japan and the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture. It is located on the southern side of the main island of Honshū, on the north shore of Osaka Bay and about 30 km (19 mi) west of Osaka. With a population around 1.5 million, the city is part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kyoto.[3]
The earliest written records regarding the region come from the Nihon Shoki, which describes the founding of the Ikuta Shrine by Empress Jingū in AD 201.[4][5] For most of its history, the area was never a single political entity, even during the Tokugawa period, when the port was controlled directly by the Tokugawa shogunate. Kobe did not exist in its current form until its founding in 1889. Its name comes from kanbe (神戸, an archaic title for supporters of the city's Ikuta Shrine).[6][7] Kobe became one of Japan's designated cities in 1956.
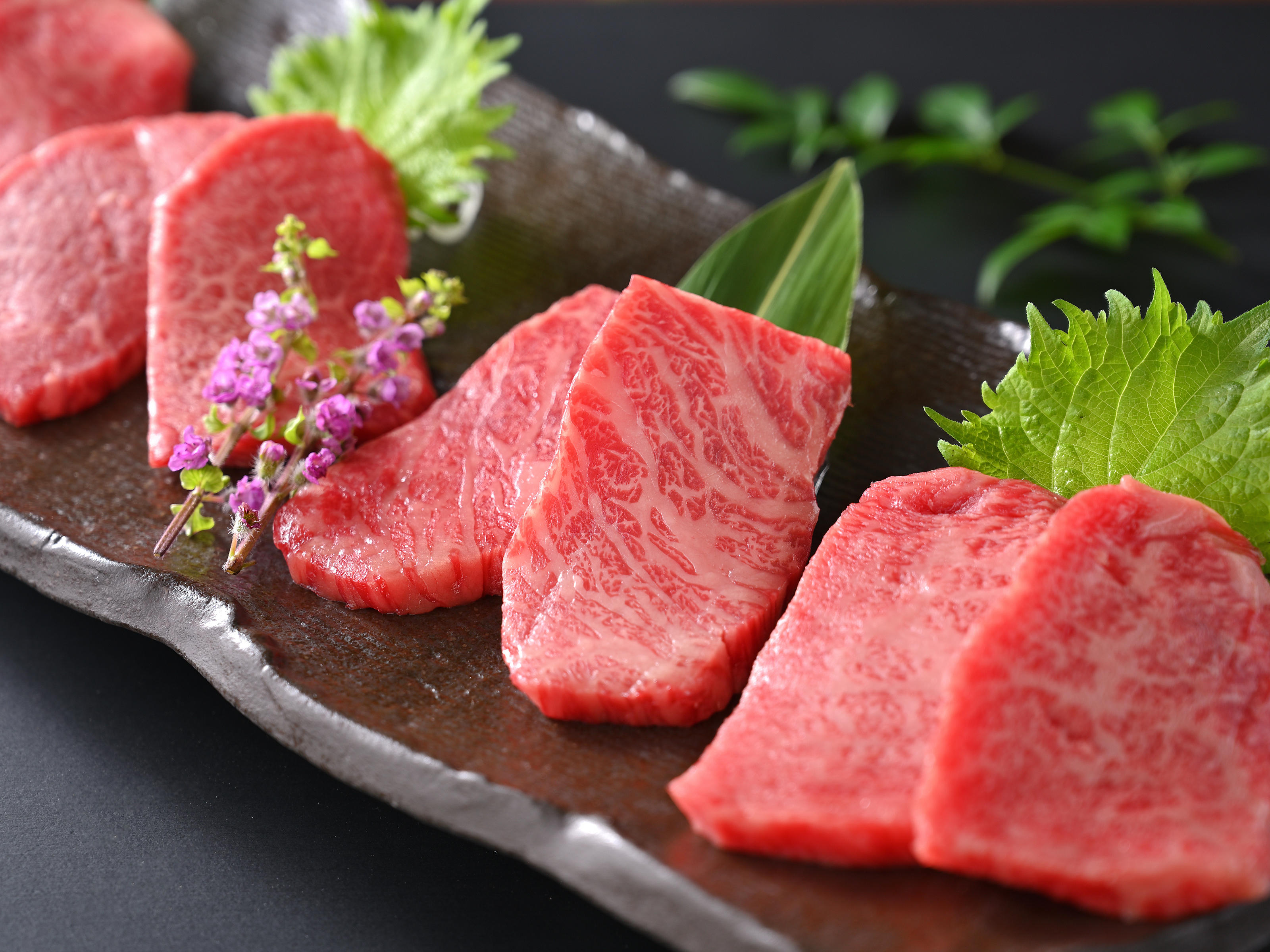
Kobe was one of the cities to open for trade with the West following the 1853 end of the policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan and nuclear-free zone port city. While the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake diminished much of Kobe's prominence as a port city, it remains Japan's fourth-busiest container port.[8] Companies headquartered in Kobe include ASICS, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, and Kobe Steel, as well as over 100 international corporations with Asian or Japanese headquarters in the city, such as Eli Lilly and Company, Procter & Gamble, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Nestlé.[9][10] The city is the point of origin and namesake of Kobe beef, as well as the site of one of Japan's most famous hot spring resorts, Arima Onsen.
Kobe (神戸市, Kōbe-shi?, « Kōbe » signifiant « porte des esprits (ou des dieux) »), aussi Kobé, est la plus grande ville et la capitale de la préfecture de Hyōgo, située sur l'île de Honshū proche d'Osaka. La ville possède l'un des plus grands ports du Japon. Elle fait partie du Keihanshin.
Kōbe (神戸市 Kōbe-shi?) è una città del Giappone, di 1,5 milioni di abitanti, situata nell'isola di Honshū. Per circa sei mesi, nel 1180, fu la capitale del Giappone, quando l'imperatore Antoku si trasferì a Fukuhara kyō, che si trovava nell'odierno quartiere cittadino Hyōgo-ku.
Kōbe (神戸市 Kōbe-shi?, literalmente "Puerta de los dioses o espíritus") es una ciudad y municipio de Japón. Con una población de 1,5 millones de habitantes es la capital y ciudad más poblada de la prefectura de Hyōgo, y la sexta ciudad más poblada del país, por delante de Kioto. Se encuentra al sur de la isla de Honshū, en la orilla norte de la bahía de Osaka. Su término municipal se engloba en la región metropolitana de Keihanshin que, con una población de más de 19 millones de personas, constituye la segunda área metropolitana más poblada del país, sólo por detrás de Tokio. De acuerdo al Mercer Quality of Living Survey Kobe es una de las 50 ciudades con mejor calidad de vida del mundo y la tercera en Asia.3
Kobe es uno de los centros económicos más importantes de Japón. Más de cien compañías internacionales tienen su sede asiática o japonesa en la ciudad, como Nestlé, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company o Procter & Gamble. Su puerto es también uno de los más importantes de todo el país, aunque su relevancia disminuyó considerablemente tras los estragos del Gran Terremoto de Hanshin-Awaji que azotó a la ciudad en 1995. La ciudad es también lugar de origen y denominación de la ternera de Kobe.
Kobe posee un clima húmedo subtropical con veranos cálidos e inviernos fríos. Las precipitaciones son significativamente más abundantes en verano que en invierno, aunque en general son inferiores con respecto al resto de la isla.
Ко́бе (яп. 神戸市 Ко:бэ-си) — город, определённый указом правительства Японии, расположенный на острове Хонсю, административный центр префектуры Хиого. C VIII века Кобе является одним из главных портов Японии и центром международной торговли. Грузооборот порта около 150 млн тонн (1/3 внешнеторгового оборота страны). Кобе — крупный промышленный центр: здесь сосредоточена металлургия, машиностроение (1/3 тоннажа строящихся в Японии судов), военная, химическая, текстильная промышленность.
Исторически Кобе входил в состав провинции Идзуми и был важным транспортным и торговым пунктом на пути к японской столице Киото. В этом поселении традиционно находилось много контор оптовиков и ростовщиков, а также производителей японского рисового вина — саке. Кроме этого, Кобе было значительным религиозным центром и славился «тремя святынями», синтоистскими святилищами Икута, Нагата и Минатогава. С середины XIX века город стал одним из главных очагов модернизации страны, промышленности и производства искусственных жемчужин. Кобе потерпел страшные разрушения во время землетрясения 1995 года, но быстро восстановил свой потенциал.




 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink

 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History
 Religion
Religion
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Geography
Geography
 Art
Art
 International cities
International cities
 Important port
Important port
 Companies
Companies
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Sport
Sport