
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 England
England
 France
France
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
 Kiel Canal
Kiel Canal
 Norwegen
Norwegen

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

Die Nordsee (veraltet Westsee, Deutsches Meer[2]) ist ein Randmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans. Sie ist ein Schelfmeer und liegt im nordwestlichen Europa. Bis auf die Meerengen beim Ärmelkanal und beim Skagerrak ist sie auf drei Seiten von Land begrenzt und öffnet sich trichterförmig zum nordöstlichen Atlantik. In einem 150-Kilometer-Bereich an der Küste leben rund 80 Millionen Menschen.
Die Nordsee selbst ist ein wichtiger Handelsweg und dient als Weg Mittel- und Nordeuropas zu den Weltmärkten. Die südliche Nordsee ist zusammen mit dem angrenzenden Ärmelkanal die am dichtesten befahrene Schifffahrtsregion der Welt. Unter dem Meeresboden befinden sich größere Erdöl- und Erdgasreserven, die seit den 1970er Jahren gefördert werden. Kommerzielle Fischerei hat den Fischbestand des Meeres in den letzten Jahrzehnten vermindert. Umweltveränderungen entstehen auch dadurch, dass die Abwässer aus Nordeuropa und Teilen Mitteleuropas direkt oder über die angrenzende Ostsee in das Meer fließen.
北海(挪威语:Nordsjøen;瑞典语:Nordsjön;丹麦语:Nordsøen或Vesterhavet;德语:Nordsee;荷兰语:Noordzee;法语:Mer du Nord;英语:North Sea)是北大西洋的一部分,位于大不列颠岛以东,斯堪的纳维亚半岛西南和欧洲大陆以北。北海海底有丰富的石油储藏,作为布兰特原油指数的基础。
北海向西南通过多佛尔海峡(法国称加来海峡)和英吉利海峡(法国称拉芒什海峡)与凯尔特海相通,向东通过斯卡格拉克海峡和卡特加特海峡与波罗的海相连,向北是挪威海。
斯凯尔特河、默兹河、莱茵河、威悉河、易北河和泰晤士河是注入北海的主要河流。重要的岛屿或群岛有北弗里西亚群岛、黑尔戈兰岛、东弗里西亚群岛和西弗里西亚群岛。
北海周边的国家有英国、挪威、瑞典、丹麦、德国、荷兰、比利时和法国。重要城市有阿伯丁、爱丁堡、加来、奥斯坦、鹿特丹、海牙、哈勒姆、威廉港、不来梅哈芬、库克斯港、埃斯比约、卑尔根、哥德堡等等。此外伦敦、不来梅哈芬和汉堡是北海重要的内陆港城。
北海(ほっかい、英語 North Sea、ドイツ語 Nordsee、フランス語 Mer du Nord、オランダ語 Noordzee、デンマーク語 Nordsøen、ノルウェー語 Nordsjøen)は、大西洋の付属海。古名はゲルマン海(ラテン語 Mare Germanicum、英語 German Ocean)。
東はノルウェー、デンマーク、南はドイツ、オランダ、ベルギー、フランス、西はイギリス、北はオークニー諸島・シェトランド諸島に囲まれている。東はスカゲラク海峡・カテガット海峡およびキール運河でバルト海に、北はノルウェー海に、南はドーバー海峡・イギリス海峡で大西洋に繋がっている。南北の長さは970km、東西は580km、面積は75万km2、水量は94000km3である[1]。
北海に流れ込む主な川はエルベ川、ヴェーザー川、エムス川、ライン川などがある。なかでも、最も北海に影響を及ぼす河川はエルベ川とライン川・ムーズ川である[2]。北海の集水域にはおよそ1億8500万人が暮らしており、また世界で最も工業化された地方のうちのひとつが含まれている[3]。
北海油田と総称される油田・ガス田が多数あり、ヨーロッパの貴重なエネルギー源である。
The North Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located between Great Britain (England and Scotland), Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France. An epeiric (or "shelf") sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than 970 kilometres (600 mi) long and 580 kilometres (360 mi) wide, with an area of 570,000 square kilometres (220,000 sq mi).
The North Sea has long been the site of important European shipping lanes as well as a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and more recently the sea has developed into a rich source of energy resources, including fossil fuels, wind, and early efforts in wave power.
Historically, the North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. Subsequently, the Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and thus access to the world's markets and resources. As Germany's only outlet to the ocean, the North Sea continued to be strategically important through both World Wars.
The coast of the North Sea presents a diversity of geological and geographical features. In the north, deep fjords and sheer cliffs mark the Norwegian and Scottish coastlines, whereas in the south, the coast consists primarily of sandy beaches and wide mudflats. Due to the dense population, heavy industrialization, and intense use of the sea and area surrounding it, there have been various environmental issues affecting the sea's ecosystems. Adverse environmental issues – commonly including overfishing, industrial and agricultural runoff, dredging, and dumping, among others – have led to a number of efforts to prevent degradation of the sea while still making use of its economic potential.
La mer du Nord est une mer épicontinentale de l'océan Atlantique, située au nord-ouest de l'Europe, et qui s'étend sur une superficie d'environ 575 000 km2.
Les pays qui bordent la mer du Nord sont le Royaume-Uni (île de Grande-Bretagne) à l'ouest ; les îles Shetland et Orcades au nord-ouest ; la Norvège au nord-est; le Danemark à l'est ; l'Allemagne au sud-est ; enfin les Pays-Bas, la Belgique et la France (pour 50 km de littoral entre Calais et la frontière belge) au sud. Elle communique avec la Manche par le pas de Calais au sud-sud-ouest ; avec l'océan Atlantique au nord-ouest et la mer de Norvège au nord ; avec le Skagerrak à l'est. Le canal de Kiel permet aux navires de rejoindre la mer Baltique.
Elle constitue une zone de fort transit maritime, d'exploitation pétrolière et de pêche. La mer du Nord et son littoral forment un milieu naturel très riche, mais la pollution marine, la surpêche, l'industrie pétrolière (plates-formes offshore) et le tourisme sont sources de menaces pour l'avenir. Elle est en aval du centre de l'Europe industrielle, de l'estuaire du Rhin aux fjords norvégiens et aux falaises du nord de la Grande-Bretagne. Le secteur Manche/Sud-mer du Nord, incluant le pas de Calais est considéré comme représentatif de mers mégatidales peu profondes, caractérisées par un fort courant et une eau très turbide (en raison des courants et phénomènes de renversement de marées), ce qui en fait une zone écologiquement particulière, mais également vulnérable au risque maritime en raison d'un intense trafic maritime (marchand et passager).
Il mare del Nord (in danese Nordsøen; in francese Mer du Nord; in inglese North Sea; in norvegese Nordsjøen;in olandese Noordzee; in svedese Nordsjön; in tedesco Nordsee) è un mare epicontinentale dell'Europa nord-occidentale che comunica con l'oceano Atlantico tramite il mare di Norvegia a nord e la Manica a sud; suo tributario è il Mar Baltico, ad esso collegato tramite gli stretti scandinavi di Skagerrak e Kattegat. Si estende per circa 970 km di lunghezza in direzione nord-sud e 560 km di larghezza in direzione est-ovest, e ha una superficie totale di circa 570000 km²[1]. Accoglie una considerevole parte dei bacini idrografici dell'Unione europea.
El mar del Norte es un mar marginal del océano Atlántico, situado entre las costas de Noruega y Dinamarca en el este, las de las islas británicas al oeste y las de Alemania, los Países Bajos, Bélgica y Francia al sur. El Skagerrak constituye una especie de bahía al este del mar, la cual lo conecta con el Báltico a través del Kattegat; también está conectado con el Báltico mediante el canal de Kiel. El canal de la Mancha lo conecta al resto del Atlántico por el sur, mientras que por el norte conecta en través del mar de Noruega, que es el nombre que adopta el mar al norte de las islas Shetland.
Las mareas son bastante irregulares ya que confluyen en él una corriente proveniente del norte y otra del sur. Hay mucha lluvia y niebla durante todo el año, y del noroeste vienen violentas tormentas que hacen la navegación peligrosa.
Tiene una superficie de unos 750 000 km²,1 una longitud aproximada de 960 km y una anchura máxima de 480 km. Es un mar muy poco profundo, con una profundidad media de 95 metros: el hecho que en el banco Dogger, en medio del mar y a una profundidad de unos 25 metros, se hayan encontrado restos de mamuts prueba que durante la última glaciación o bien estaba cubierto de hielo o bien estaba emergido. Con el deshielo, el banco se convirtió en una especie de último reducto en forma de isla.
Durante la Edad Antigua este mar se conocía como Oceanum o Mare Germanicum. El nombre actual se cree que surgió desde el punto de vista de las islas Frisias, desde donde quedaba totalmente al norte, y por oposición al mar del Sur (el mar de Frisia y el Zuiderzee, en los Países Bajos). A la larga, el nombre actual se acabó imponiendo, de manera que ya era predominante durante la Edad Moderna. En la citada Edad Moderna fue común llamar Mar del Norte o Mar del Nord a todo el océano Atlántico, siendo por contrapartida llamado «Mar del Sur» o «Mar del Sud» todo el océano Pacífico.
Según las lenguas oficiales de los estados que lo rodean, se denomina Mer du Nord, en francés; Noordzee, en neerlandés; Nordsee, en alemán; Nordsjön, en sueco; Nordsøen, en danés; Nordsjøen, en noruego; y North Sea en inglés. En frisón se dice Noardsee y en gaélico escocés A' Mhuir en Tuath.
Tiene importantes yacimientos de petróleo y gas natural, los cuales comenzaron a explotarse en los años 1970.
Се́верное мо́ре (ранее также Немецкое море[3]; фр. Mer du Nord, нем. Nordsee, нидерл. Noordzee, з.-фриз. Noardsee, англ. North Sea, норв. Nordsjøen, дат. Nordsøen или Vesterhavet) — мелководное шельфовое море Атлантического океана, омывающее берега северной Европы. Расположено между Британскими островами на западе, Ютландским, Скандинавским полуостровами на востоке и континентальной Европой на юге. Омывает берега Норвегии, Дании, Германии, Нидерландов, Бельгии, Франции и Великобритании.
Площадь — 750 тыс. км²[1]. Наибольшая глубина 725 м[2]. Более 2/3 моря имеет глубину менее 100 м; в южной части — отмели (банка Доггер и др.). Впадают крупные реки: Эльба, Везер, Рейн, Темза. Основные порты: Роттердам, Амстердам, Антверпен, Лондон, Гамбург, Осло, Берген[2].
Прибрежная мелководная часть на юге иногда выделяется под названием Ваттового моря.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
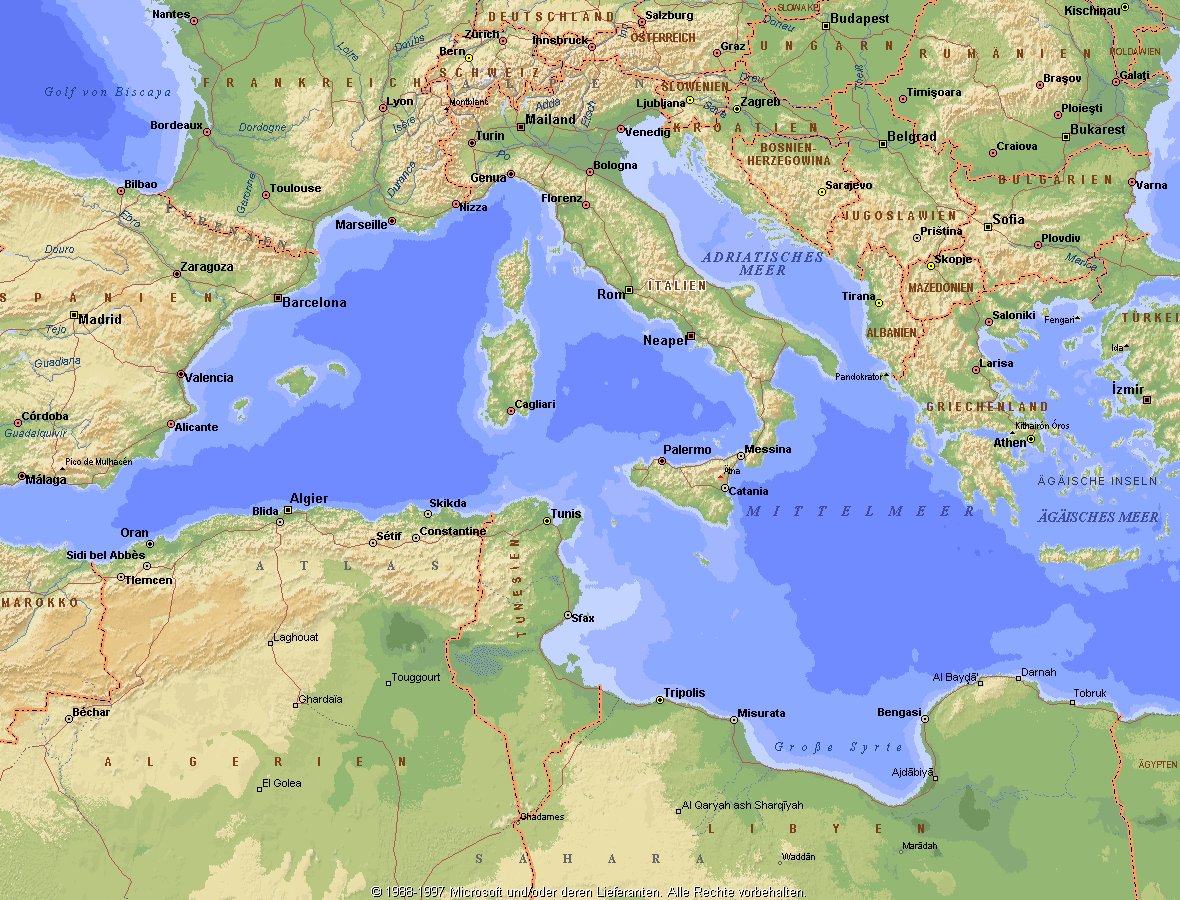
Das Mittelmeer (lateinisch Mare Mediterraneum,[1] deshalb deutsch auch Mittelländisches Meer, präzisierend Europäisches Mittelmeer, im Römischen Reich Mare Nostrum) ist ein Mittelmeer zwischen Europa, Afrika und Asien, ein Nebenmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans und, da es mit der Straße von Gibraltar nur eine sehr schmale Verbindung zum Atlantik besitzt, auch ein Binnenmeer. Im Arabischen und Türkischen wird es auch als „Weißes Meer“ (البحر الأبيض/al-baḥr al-abyaḍ bzw. türk. Akdeniz) bezeichnet.
Zusammen mit den darin liegenden Inseln und den küstennahen Regionen Südeuropas, Vorderasiens und Nordafrikas bildet das Mittelmeer den Mittelmeerraum, der ein eigenes Klima (mediterranes Klima) hat und von einer eigenen Flora und Fauna geprägt ist.
地中海(英文:Mediterranean),被北面的欧洲大陆、南面的非洲大陆以及东面的亚洲大陆包围着。东西长约4000千米,南北最宽处大约为1800千米,面积251.6万平方千米,是地球上最大的陆间海。地中海的平均深度是1500米,最深处为5267米。
地中海西部通过直布罗陀海峡与大西洋相接,东部通过土耳其海峡(达达尼尔海峡和博斯普鲁斯海峡、马尔马拉海)和黑海相连。19世纪时开通的苏伊士运河,接通了地中海与红海。地中海是世界上最古老的海之一[3],而其附属的大西洋却是年轻的海洋。地中海处在欧亚板块和非洲板块交界处,是世界最强地震带之一。地中海地区有维苏威火山、埃特纳火山。
地中海作为陆间海,风浪较小,加之沿岸海岸线曲折、岛屿众多,拥有许多天然良好的港口,成为沟通三个大陆的交通要道。这样的条件,使地中海从古代开始海上贸易就很繁盛,促进了古代古埃及文明、古希腊文明、罗马帝国等的发展。现在也是世界海上交通的重要地区之一。其沿岸的腓尼基人、克里特人、希腊人,以及后来的葡萄牙人和西班牙人都是航海业发达的民族。著名的航海家如哥伦布、达·伽马、麦哲伦等,都出自地中海沿岸的国家。
地中海沿岸夏季炎热干燥,冬季温暖湿润,被称作地中海性气候。植被,叶质坚硬,叶面有蜡质,根系深,有适应夏季干热气候的耐旱特征,属亚热带常绿硬叶林。这里光热充足,是欧洲主要的亚热带水果产区,盛产柑橘、无花果,和葡萄等,还有木本油料作物油橄榄。
地中海(ちちゅうかい、ラテン語: Mare Mediterraneum)は、北と東をユーラシア大陸、南をアフリカ大陸(両者で世界島)に囲まれた地中海盆地に位置する海である。面積は約3000平方キロメートル、平均水深は約1500メートル[2]。海洋学上の地中海の一つ。
地中海には、独立した呼称を持ついくつかの海域が含まれる(エーゲ海、アドリア海など)。地中海と接続する他の海としては、ジブラルタル海峡の西側に大西洋が、ダーダネルス海峡を経た北東にマルマラ海と黒海があり、南西はスエズ運河で紅海と結ばれている(「海域」「地理」で詳述)。
北岸の南ヨーロッパ、東岸の中近東、南岸の北アフリカは古代から往来が盛んで、「地中海世界」と総称されることもある[3]。
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa and on the east by the Levant. Although the sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually identified as a separate body of water. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years, the Messinian salinity crisis, before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.
It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km2 (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Gibraltar and Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.[2][3]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The sea is bordered on the north by Europe, the east by Asia, and in the south by Africa. It is located between latitudes 30° and 46° N and longitudes 6° W and 36° E. Its west-east length, from the Strait of Gibraltar to the Gulf of Iskenderun, on the southwestern coast of Turkey, is approximately 4,000 km (2,500 miles). The sea's average north-south length, from Croatia’s southern shore to Libya, is approximately 800 km (500 miles). The Mediterranean Sea, including the Sea of Marmara (connected by the Dardanelles to the Aegean Sea), has a surface area of approximately 2,510,000 square km (970,000 square miles).[4]
The sea was an important route for merchants and travellers of ancient times that allowed for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region. The history of the Mediterranean region is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
The countries surrounding the Mediterranean in clockwise order are Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco; Malta and Cyprus are island countries in the sea. In addition, the Gaza Strip and the British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia have coastlines on the sea.
La mer Méditerranée (prononcé [me.di.tɛ.ʁa.ne]) est une mer intercontinentale presque entièrement fermée, bordée par les côtes d'Europe du sud, d’Afrique du Nord et d’Asie, depuis le détroit de Gibraltar à l'ouest aux entrées des Dardanelles et du canal de Suez à l'est. Elle s’étend sur une superficie d’environ 2,5 millions de kilomètres carrés. Son ouverture vers l’océan Atlantique par le détroit de Gibraltar est large de 14 kilomètres.
Elle doit son nom au fait qu’elle est littéralement une « mer au milieu des terres », en latin « mare medi terra »1.
Durant l’Antiquité, la Méditerranée était une importante voie de transports maritimes permettant l’échange commercial et culturel entre les peuples de la région — les cultures mésopotamiennes, égyptienne, perse, phénicienne, carthaginoise, berbère, grecque, arabe (conquête musulmane), ottomane, byzantine et romaine. L’histoire de la Méditerranée est importante dans l’origine et le développement de la civilisation occidentale.
Il mar Mediterraneo, detto brevemente Mediterraneo, è un mare intercontinentale situato tra Europa, Nordafrica e Asia occidentale connesso all'Oceano Atlantico. La sua superficie approssimativa è di 2,51 milioni di km² e ha uno sviluppo massimo lungo i paralleli di circa 3 700 km. La lunghezza totale delle sue coste è di 46 000 km, la profondità media si aggira sui 1 500 m, mentre quella massima è di 5 270 m presso le coste del Peloponneso. La salinità media si aggira dal 36,2 al 39 ‰.[2] La popolazione presente negli stati bagnati dalle sue acque ammonta a circa 450 milioni di persone.[2].
El mar Mediterráneo es uno de los mares del Atlántico. Está rodeado por la región mediterránea, comprendida entre Europa meridional, Asia Occidental y África septentrional. Fue testigo de la evolución de varias civilizaciones como los egipcios, los fenicios, hebreos, griegos, cartagineses, romanos, etc. Con aproximadamente 2,5 millones de km² y 3.860 km de longitud, es el segundo mar interior más grande del mundo, después del Caribe.1 Sus aguas, que bañan las tres penínsulas del sur de Europa (Ibérica, Itálica, Balcánica) y una de Asia (Anatolia), comunican con el océano Atlántico a través del estrecho de Gibraltar, con el mar Negro por los estrechos del Bósforo y de los Dardanelos y con el mar Rojo por el canal de Suez.2 Es el mar con las tasas más elevadas de hidrocarburos y contaminación del mundo.3
Средизе́мное мо́ре — межматериковое море, по происхождению представляющее собой глубоководную псевдоабиссальную внутришельфовую депрессию[1][2], связанную на западе с Атлантическим океаном Гибралтарским проливом[3].
В Средиземном море выделяют, как его составные части, моря: Адриатическое, Альборан, Балеарское, Ионическое, Кипрское, Критское, Левантийское, Ливийское, Лигурийское, Тирренское и Эгейское. В бассейн Средиземного моря также входят Мраморное, Чёрное и Азовское моря.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus

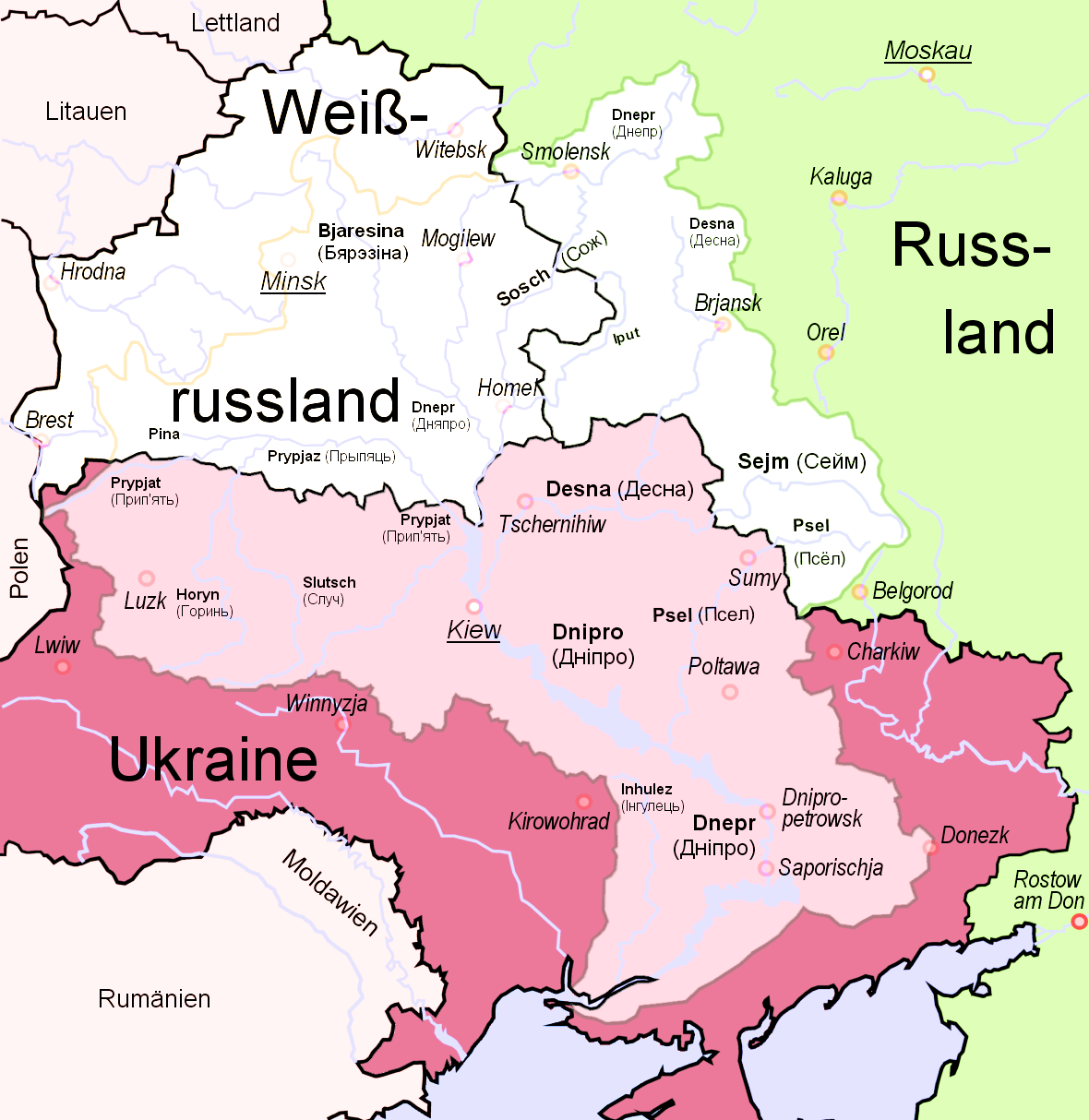
Der Dnepr (russisch Днепр, im Deutschen auch als Dnjepr transkribiert, belarussisch Дняпро Dnjapro, ukrainisch Дніпро Dnipro) ist ein 2201 km langer Strom, der durch Russland, Belarus und die Ukraine in das Schwarze Meer, fließt. Er ist nach der Wolga und der Donau der drittlängste Fluss Europas und seit der Anlage von fünf Schleusen auf rund 1700 km schiffbar.
第聂伯河,或称聂伯河(乌克兰语:Дніпро,罗马化:Dnipro、克里米亚鞑靼语:Özü、古希腊语:Βορυσθένης、拉丁语:Danapris、白俄罗斯语:Дняпро,罗马化:Dnjapro、俄语:Днепр,罗马化:Dnepr),全长2290公里,为欧洲第四长的河流(仅次于伏尔加河、多瑙河与乌拉尔河)。它发源于俄罗斯首都莫斯科以西的瓦尔代南部沼泽,流经白俄罗斯和乌克兰,出海口为黑海。在公元前5世纪,古希腊的历史学家希罗多德已经有记载这条河流。
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Kiel Canal
Kiel Canal
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden

Die Ostsee (auch Baltisches Meer, von lat. Mare Balticum, oder auch Baltische See genannt) ist ein 412.500 km²[2] großes und bis zu 459 m tiefes Binnenmeer in Europa und gilt als das größte Brackwassermeer der Erde, auch wenn in der westlichen Ostsee (Beltsee) aufgrund des Wasseraustausches mit der Nordsee zumeist ein höherer Salz- und Sauerstoffgehalt beobachtet werden kann. Der Rauminhalt des Meeres beträgt rund 20.000 km³. Im Ostseeraum leben, je nachdem, wie weit man diese Region eingrenzt, zwischen 50 und 85 Millionen Menschen.
波罗的海是中欧和北欧之间的陆间海,海域横贯北纬53度至北纬66度,东经10度至东经30度,介于斯堪的纳维亚半岛的瑞典部分、欧洲大陆和丹麦诸岛之间。
波罗的海由厄勒海峡、大贝尔特海峡和小贝尔特海峡注入卡特加特海峡,而后者则通过斯卡格拉克海峡注入北海,最后进入大西洋;此外它还通过白海运河同白海相连,通过基尔运河同北海相连。
波罗的海在北端与波的尼亚湾相邻,在东北端与芬兰湾相邻,在东端与里加湾相邻。这些海湾同样可以被看作是波罗的海的一部分。
バルト海(バルトかい、Baltic Sea)は、北ヨーロッパに位置する地中海。ヨーロッパ大陸とスカンディナビア半島に囲まれた海域である。ユーラシア大陸に囲まれた海域と説明されることもある[1]。
西岸にスウェーデン、東岸は、北から順にフィンランド、ロシア、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニア、南岸は、東から西にポーランド、ドイツ、デンマークが位置する。
The Baltic Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, enclosed by Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Russia, Poland, Germany and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A mediterranean sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish islands into the Kattegat by way of the straits of Øresund, the Great Belt, and the Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga, and the Bay of Gdańsk.
The Baltic Proper is bordered on its northern edge, at the latitude 60°N, by the Åland islands and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula.
The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the German Bight of the North Sea via the Kiel Canal.
La mer Baltique est une mer intracontinentale et intérieure de 364 800 km2 située dans le Nord de l'Europe et reliée à l'océan Atlantique par la mer du Nord. Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer du Nord par le Cattégat et le Skagerrak. Trois golfes principaux intègrent cet espace : le golfe de Botnie au nord, le golfe de Finlande à l'est et le golfe de Riga au sud-est.
Les pays riverains sont :
- la Suède à l'ouest et au nord ;
- la Finlande au nord-est ;
- la Russie (par le golfe de Finlande) et l'Estonie à l'est ;
- la Lettonie au sud-est ;
- la Lituanie, la Russie (à Kaliningrad) et la Pologne au sud;
- l'Allemagne et le Danemark au sud-ouest.
Ces pays riverains, ainsi que la mer proprement dite, font l'objet, depuis 2009, d'une « stratégie de la Commission européenne en faveur du développement de la région de la mer Baltique »1, incluant un effort de dépollution de la Baltique et un système commun de surveillance maritime.
Il mar Baltico è un mare interno dell'oceano Atlantico settentrionale e si trova nell'Europa nord-orientale, circondato dalla Penisola scandinàva (meno correttamente scandìnava)[1], dalla terraferma dell'Europa centrale e orientale e dalle Isole danesi. Sfocia nel Kattegat e nel mare del Nord passando attraverso le isole danesi in tre stretti, l'Øresund, il Piccolo Belt e il Grande Belt.
Sfociano nel mar Baltico cinque grandi fiumi: l'Oder, la Vistola, il Njemen, la Daugava (o Dvina Occidentale) e la Neva. Le coste del Baltico tendono a ghiacciare d'inverno specie in occasione di eventi meteorologici particolarmente freddi.
Viene indicato come "mare dell'Est" in diverse lingue dell'Europa continentale, precisamente in danese (Østersøen), tedesco (Ostsee), finlandese (Itämeri), olandese (Oostzee), norvegese (Østersjøen), e svedese (Östersjön). In estone viene invece chiamato "mare Occidentale" (Läänemeri). Oltre all'italiano, viene chiamato mar Baltico in francese (mer Baltique), inglese (Baltic Sea), polacco (Morze Bałtyckie), russo (Baltijskoe more, Балтийское море), lituano (Baltijos Jūra), lettone (Baltijas Jūra) e greco (Baltiké thálassa, Βαλτική Θάλασσα).
El mar Báltico (del latín: Mare Balticum) es un mar interior de agua salobre del norte de Europa abierto al mar del Norte y, finalmente, al océano Atlántico a través de los estrechos de Kattegat y Skagerrak. Los países que lo rodean son (empezando por la península Escandinava y siguiendo en sentido horario): Suecia, Finlandia, Rusia (óblast de Leningrado y Kaliningrado), Estonia, Letonia, Lituania, Polonia, Alemania y Dinamarca.
Su superficie es de 432 800 km² e incluye dos grandes golfos: el golfo de Finlandia, entre el sur de este país y Estonia, y el golfo de Botnia, entre la costa oriental de Suecia y el occidental de Finlandia. Geológicamente es muy joven: sólo existe desde el VI milenio a.C. Es muy poco profundo (la media es de 57 m; la profundidad máxima es de 459 m al norte de la isla sueca de Gotland), lo que, unida a la poca apertura al océano, hace la renovación de las aguas muy lenta y favorece los problemas de contaminación. Las mareas son de muy pequeña amplitud.
El mar Báltico es también, el mayor depósito de ámbar del mundo y, además, su calidad es de las mejores: de los veinte depósitos del mundo que hay de ámbar, se dice que el del mar báltico sólo es superado por los de México y la República Dominicana, siendo el que más ámbar de conífera produce y el de mejor calidad. De él se extraen de 500 a 800 millones de toneladas de ámbar.
La cuenca que drena al mar Báltico abarca la totalidad de algunos países ribereños como las repúblicas bálticas, Polonia y la región rusa de Kaliningrado. Además, estos ríos nacen en, o atraviesan territorios pertenecientes a otros países que, a pesar de no poseer costas, se comunican al mar por vía fluvial. Tal es el caso de la República Checa, Eslovaquia, Ucrania y Bielorrusia, quienes acaban aportando agua (indirectamente) al mar Báltico.
Балти́йское мо́ре (Варяжское[1], польск. Morze Bałtyckie, нем. Ostsee, н.-нем. Oostsee, швед. Östersjön, дат. Østersøen, фин. Itämeri, эст. Läänemeri, латыш. Baltijas jūra, лит. Baltijos jūra) — внутриматериковое море Евразии, расположенное в Северной Европе (частично омывает также берега Западной и Восточной Европы). Относится к бассейну Атлантического океана.
Крайняя северная точка Балтийского моря находится вблизи Северного полярного круга (65°40' с. ш.), крайняя южная — около города Висмара (53°45' с. ш.).
Крайняя западная точка расположена в районе Фленсбурга (9°10' в. д.), крайняя восточная — в районе Санкт-Петербурга (30°15' в. д.)
Площадь поверхности моря (без островов) — 415 тыс. км². Объём воды — 21,5 тыс. км³. Из-за огромного стока рек вода имеет низкую солёность и потому море является солоноватоводным. Является крупнейшим в мире морем с такой особенностью[2].
Участок континентальной коры, на котором лежит современное Балтийское море, является частью устойчивой Русской тектонической плиты (Фенносарматия). Как единый массив он сложился около 1,8 миллиарда лет назад и с тех пор пребывал в относительной стабильности. Бо́льшая часть территории, соответствующей дну современной Балтики, бо́льшую часть времени находилась выше уровня моря, хотя южная и восточная части этого пространства продолжительное время были покрыты мелководными шельфовыми морями, о чём свидетельствует мощный слой донных осадков в этих областях. Балтийский кратон образовался в южном полушарии, дрейфовал на запад, находясь в эдиакарии в районе Южного Полярного круга, а далее на север, пересёк экватор около 375 млн л. н., и около 30 миллионов лет назад уже приблизился к современному положению. В разное время он был составной частью различных материков (Нуна, Нена, Родиния, Протолавразия, Паннотия, Лавруссия, Пангея, Лавразия, Евразия), а некоторое время также отдельным материком Балтикой.
Примерно 40 миллионов лет назад, когда контуры северной, центральной и восточной Европы уже сложились на близких к современным широтах, на месте будущего Балтийского моря возникла долина реки Эридан, протекавшей в юго-западном направлении параллельно Скандинавским горам — то есть приблизительно так же, как будет расположено Балтийское море: исток брала в Лапландии, а сильно ветвистая дельта в районе современных Нидерландов впадала в древнее Северное море, и в области нынешнего Финского залива располагался крупный приток. С наступлением четвертичного оледенения, примерно 700 тыс. л. н. Эридан прекратил существование, поскольку его долина, как и вся северная Европа, скрылась под ледниковым щитом. По берегам Эридана росла тайга. После образования ледника смола хвойных деревьев превратилась в янтарь.
ности и другие параметры Литоринового моря стали близки к современным — начинается около 4 тысяч лет назад. Примерно в это же время возникает и Нева.

Das Schwarze Meer ist ein zwischen Südosteuropa, Osteuropa und Vorderasien gelegenes Binnenmeer, das über den Bosporus und die Dardanellen mit dem östlichen Mittelmeer verbunden ist. Es ist bis 2212 m tief[1] und hat (ohne das Asowsche Meer) eine Fläche von etwa 436.400 km².[2] Der Rauminhalt des Schwarzen Meeres beträgt 547.000 km³. Die durchschnittliche Wassertiefe beträgt 1253 Meter.
黑海是欧亚大陆的一个陆间海,被欧洲、高加索和安那托利亚半岛所包围[4]。黑海通过土耳其海峡与地中海的爱琴海区域相联。西亚和东欧被这一系列水体分隔开来。黑海在北面通过刻赤海峡与亚速海相连。流入黑海的主要河流有多瑙河和第聂伯河。沿海国家有土耳其、保加利亚、罗马尼亚、乌克兰、俄罗斯和格鲁吉亚。沿海重要城市有伊斯坦布尔、布尔加斯、瓦尔纳、康斯坦察、图尔恰、敖德萨、塞瓦斯托波尔、巴统等。
黑海的面积有436,400平方千米(168,500平方英里)(不包括亚速海)[1],最大深度为2,212米(7,257英尺)[2],体积为547,000立方千米(131,200立方英里)。[3]黑海形成一个东西向的椭圆形凹陷。[5]黑海的南面是本廷山脉,东面是高加索山脉,西北面是宽阔的低地。黑海东西向最宽有大约1,175千米(730英里)。
黒海(こっかい)は、ヨーロッパとアジアの間にある内海で、大西洋の縁海(地中海 (海洋学))の一つである。マルマラ海を経てエーゲ海、地中海に繋がる。
バルカン半島、アナトリア半島、コーカサスと南ウクライナ・クリミア半島に囲まれており、ドナウ川、ドニエストル川、ドニエプル川などの東ヨーロッパの大河が注ぐ。アナトリアとバルカンの間のボスポラス海峡、マルマラ海、ダーダネルス海峡を通じて地中海に繋がっており、クリミアの東にはケルチ海峡を隔ててアゾフ海がある。
黒海に面する国は、南岸がトルコで、そこから時計回りにブルガリア、ルーマニア、ウクライナ、ロシア、ジョージアである。
黒海に面する有名な港湾には、イスタンブール(ビュザンティオン、コンスタンティノープル)から時計回りにブルガス、ヴァルナ、コンスタンツァ、オデッサ、セヴァストポリ、ヤルタ、ガグラ、バトゥミ、トラブゾン、サムスンなどがある。
The Black Sea is a body of water and marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean between the Balkans, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, and Western Asia.[1] It is supplied by a number of major rivers, such as the Danube, Dnieper, Southern Bug, Dniester, Don, and the Rioni. About a third of Europe drains into the Black Sea,[2] including the countries of Austria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Turkey and Ukraine.
The Black Sea has an area of 436,400 km2 (168,500 sq mi) (not including the Sea of Azov),[3] a maximum depth of 2,212 m (7,257 ft),[4] and a volume of 547,000 km3 (131,000 cu mi).[5] It is constrained by the Pontic Mountains to the south, Caucasus Mountains to the east, Crimean Mountains to the north, Strandzha to the southwest, Dobrogea Plateau to the northwest, and features a wide shelf to the northwest.
The longest East-West extent is about 1,175 km (730 mi).[6]
Important cities along the coast include Batumi, Burgas, Constanța, Giresun, Istanbul, Kerch, Novorossiysk, Odessa, Ordu, Poti, Rize, Samsun, Sevastopol, Sochi, Sukhumi, Trabzon, Varna, Yalta, and Zonguldak.
The Black Sea has a positive water balance; that is, a net outflow of water 300 km3 (72 cu mi) per year through the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles into the Aegean Sea. Mediterranean water flows into the Black Sea as part of a two-way hydrological exchange. The Black Sea outflow is cooler and less saline, and floats over the warm, more saline Mediterranean inflow – as a result of differences in density caused by differences in salinity – leading to a significant anoxic layer well below the surface waters. The Black Sea drains into the Mediterranean Sea, via the Aegean Sea and various straits, and is navigable to the Atlantic Ocean. The Bosphorus Strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the Strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean Sea region of the Mediterranean. These waters separate Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Western Asia. The Black Sea is also connected, to the North, to the Sea of Azov by the Strait of Kerch.
The water level has varied significantly. Due to these variations in the water level in the basin, the surrounding shelf and associated aprons have sometimes been land. At certain critical water levels it is possible for connections with surrounding water bodies to become established. It is through the most active of these connective routes, the Turkish Straits, that the Black Sea joins the world ocean. When this hydrological link is not present, the Black Sea is an endorheic basin, operating independently of the global ocean system, like the Caspian Sea for example. Currently the Black Sea water level is relatively high, thus water is being exchanged with the Mediterranean. The Turkish Straits connect the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea, and comprise the Bosphorus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles.
La mer Noire est située entre l’Europe, le Caucase et l’Anatolie. Large d'environ 1 150 km d’ouest en est et de 600 km du nord au sud, elle s’étend sur une superficie de 413 000 km2. L'adjectif correspondant est « pontique », qui vient du nom antique de cette mer, le Pont Euxin.
Le terme océanographique d'« euxinisme » y fait également référence, il désigne une anoxie des eaux profondes, plus salées qu'en surface et provenant de la Méditerranée via la mer de Marmara par un courant de fond inverse de celui des eaux plus douces de la surface alimentées par les fleuves se jetant dans la mer Noire.
Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer Méditerranée par le Bosphore, la mer de Marmara et le détroit des Dardanelles. Sur ses côtes ouest et nord, elle communique avec de nombreux limans (lagunes navigables dont la salinité et la turbidité varient avec la saison, et qui servaient de frayères pour le poisson). Au nord-est, la mer d'Azov, reliée par le détroit de Kertch, est considérée comme le plus grand des limans. Son climat spécifique doux et humide, aux épais brouillards aux saisons intermédiaires, subit des influences méditerranéennes au sud-ouest et en été (chaud, sec et ensoleillé), continentales au nord et en hiver (froid glacial, la mer peut geler, les chutes de neige sont fréquentes), et subtropicales au sud-est. Pendant les tempêtes, surtout hivernales, les vagues sont courtes, mais hautes, et peuvent venir de plusieurs directions à la fois, rendant la navigation difficile.
Depuis 1996, le 31 octobre est la « journée internationale pour la protection de la mer Noire »1.
Il Mar Nero (in ucraino: Чорне море? Čorne more; in russo: Чёрное море? Čiornoje morie; in bulgaro: Черно море? Černo more; in rumeno: Marea Neagră; in turco: Karadeniz, in georgiano: შავი ზღვა, Shavi zghva, in greco moderno: Μαύρη Θάλασσα, Mávri Thálassa) è un mare situato tra l'Europa sud-orientale e l'Asia minore. È collegato al Mar d'Azov tramite lo stretto di Kerč e, tramite il Bosforo, al Mare di Marmara, che a sua volta, tramite lo stretto dei Dardanelli, è collegato con il mare Egeo che fa parte del Mediterraneo.
I flussi di acqua in ingresso, attraverso il Bosforo, sono di circa 200 km³ (200 miliardi di metri cubi) all'anno. Il suo bacino imbrifero è molto ampio (2 milioni di km²); dalle aree circostanti riceve acque dolci per un totale di circa 320 km³ all'anno. I fiumi più importanti che vi sfociano sono il Danubio, il Dnepr e il Buh Meridionale.
La sua superficie è pari a circa 436 400 km² (escludendo il Mar d'Azov)[1] con una salinità pari a circa il 17‰ (poco meno della metà della salinità media del Mare Mediterraneo). In profondità, oltre i 150 m, questo valore aumenta drasticamente. Il punto più profondo si trova a 2 212 m, mentre nel centro la profondità è di circa 1 830 m. [2]
El mar Negro es un mar interior ubicado entre Europa oriental y Asia occidental. Se encuentra encerrado entre los Balcanes, la estepa póntica, Crimea, el Cáucaso y la península de Anatolia. El estrecho del Bósforo lo conecta con el pequeño mar de Mármara, y el estrecho de los Dardanelos conecta al anterior mar con el mar Egeo, que es una división del mar Mediterráneo. También está conectado con el mar de Azov, situado al noreste, por el estrecho de Kerch. El mar Negro forma una depresión elíptica con una pendiente de este a oeste, y tiene una superficie de 436 400 km2 (sin incluir el mar de Azov),1 una profundidad máxima de 2212 m2 y un volumen de 547 000 km3.3 Los países ribereños del mar Negro son, empezando por el sur y en sentido horario, Turquía, Bulgaria, Rumania, Ucrania, Rusia y Georgia.4
Está delimitado por los montes Pónticos al sur y por las montañas del Cáucaso al este, y cuenta con una amplia meseta al noreste. Su mayor longitud de este a oeste es de 1 175 km. Entre las ciudades importantes de sus costas están: Batumi, Burgas, Constanza, Giresun, Hopa, Estambul, Kerch, Mangalia, Năvodari, Novorossiysk, Odesa, Ordu, Poti, Rize, Sinope, Samsun, Sevastopol, Sochi, Sozopol, Sujumi, Trabzon, Varna, Yalta y Zonguldak.
Existe una salida neta de agua de 300 km3 al año a través del Bósforo y del estrecho de Dardanelos hacia el mar Egeo, mientras que el agua del Mediterráneo discurre hacia el mar Negro como parte de un camino de ida y vuelta de intercambio hidrológico. El flujo que sale del mar Negro es más frío y menos salino, y el flujo que entra desde el Mediterráneo es más cálido y salino, por lo que este flujo es el resultado de los cambios de densidad causados por la diferente salinidad, lo que da lugar a una gran cantidad de agua anóxica a 150 m bajo la superficie, que tienen la particularidad de descomponer los barcos hundidos fabricados en hierro pero no así los barcos de madera.5 El mar Negro también recibe agua del gran sistema fluvial de Eurasia por el norte del mar. Los ríos que le aportan más agua son el Danubio, el Dniéster, el Dniéper y el Don.
Los niveles de agua de este mar han variado significativamente a lo largo de la historia. Debido a estas variaciones del nivel del agua en la cuenca, los límites actuales de este mar han sido a veces terrazas geológicas secas. Cuando se dan determinados niveles de agua elevados es posible que el mar se conecte con otras aguas cercanas para estabilizarse. Es a través de una de estas rutas de conexión más activas, el estrecho turco, donde este mar se conecta con los océanos del mundo. Cuando este enlace hidrológico no está presente, el mar Negro se transforma en una cuenca endorreica que opera de forma independiente del sistema global de los océanos, como es el caso del mar Caspio. El estrecho turco conecta el mar Negro con el Egeo, y abarca el Bósforo, el mar de Mármara y el estrecho de Dardanelos.
Чёрное мо́ре — внутреннее море бассейна Атлантического океана. Проливом Босфор соединяется с Мраморным морем, далее, через пролив Дарданеллы (эти проливы зачастую называют Черноморскими проливами) — с Эгейским и Средиземным морями. Керченским проливом соединяется с Азовским морем. С севера в море глубоко врезается Крымский полуостров. По поверхности Чёрного моря проходит водная граница между Европой и Азией.
Площадь Чёрного моря — 422 000 км²[1] (по другим данным — 436 400 км²[2]). Очертания Чёрного моря напоминают овал с наибольшей осью около 1150 км. Наибольшая протяжённость моря с севера на юг — 580 км. Наибольшая глубина — 2210 м[1], средняя — 1240 м. Объём воды в море составляет 555 тыс. км³[3]. Характерной особенностью Чёрного моря является полное (за исключением ряда анаэробных бактерий) отсутствие жизни на глубинах более 150—200 м из-за насыщенности глубинных слоёв воды сероводородом.
Море омывает берега России, Украины, Румынии, Болгарии, Турции, Грузии, Абхазии[4] (территории, расположенные вокруг моря, традиционно именуют термином «Причерноморье»).
Чёрное море — важный район транспортных перевозок. Помимо этого, Чёрное море сохраняет важное стратегическое и военное значение. В Севастополе и Новороссийске находятся основные военные базы российского Черноморского флота, в Синопе и Самсуне базируются корабли черноморской группировки ВМФ Турции, в Варне — ВМС Болгарии, в Поти и Батуми — корабельный состав департамента береговой охраны Пограничной полиции Грузии[5], в Констанце и Мангалии — ВМС Румынии. До марта 2014 года в Севастополе и Новоозёрном базировались части Военно-морских сил Украины, после присоединения Крыма к России переместившиеся в Одессу.
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary

琥珀之路(英语:Amber Road)是一条古代运输琥珀的贸易道路,这条水路和陆路结合而成的通商道路,从欧洲北部的北海和波罗的海通往欧洲南部的地中海,连结了欧洲的多个重要城市,维持了多个世纪。
在公元前后的很长一段时间,琥珀作为装饰品中的重要组成部分,被从北海和波罗的海海岸的产地,经由维斯瓦河和第聂伯河运输到意大利、希腊、黑海和埃及。琥珀之路连结了琥珀的产地和在欧洲、中东地区和远东地区的消费地,并经由另一条通商道路丝绸之路继续通往亚洲。
Als Bernsteinstraße werden verschiedene Handelswege des Altertums (Altstraßen) bezeichnet, auf denen (unter anderem) Bernstein von der Nord- und Ostsee nach Süden in den Mittelmeerraum gelangte. Genau genommen handelt es sich nicht um eine Straße, sondern um unabhängige Handelswege, die für verschiedene Handelsgüter genutzt wurden. Die Bezeichnung „Bernsteinstraße“ tritt etwa ab dem Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts auf und hat in antiken Quellen keine Entsprechung.

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Belarus
Belarus
 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Germany
Germany
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data
 France
France
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Georgia
Georgia
 Greece
Greece
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Hainan Sheng-HI
Hainan Sheng-HI

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Nepal
Nepal
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Russia
Russia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Silk road
Silk road
 Serbia
Serbia
 Serbia
Serbia
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Somalia
Somalia
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

Als Seidenstraße (chinesisch 絲綢之路 / 丝绸之路, Pinyin Sīchóu zhī Lù ‚die Route / Straße der Seide‘; mongolisch ᠲᠣᠷᠭᠠᠨ ᠵᠠᠮ Tôrgan Jam; kurz: 絲路 / 丝路, Sīlù) bezeichnet man ein altes Netz von Karawanenstraßen, dessen Hauptroute den Mittelmeerraum auf dem Landweg über Zentralasien mit Ostasien verband. Die Bezeichnung geht auf den im 19. Jahrhundert lebenden deutschen Geografen Ferdinand von Richthofen zurück, der den Begriff 1877 erstmals verwendet hat.
Auf der antiken Seidenstraße wurde in westliche Richtung hauptsächlich Seide, gen Osten vor allem Wolle, Gold und Silber gehandelt.[1] Nicht nur Kaufleute, Gelehrte und Armeen nutzten ihr Netz, sondern auch Ideen, Religionen und ganze Kulturkreise diffundierten und migrierten auf den Routen von Ost nach West und umgekehrt: hierüber kamen z. B. der Nestorianismus (aus dem spätantiken Römischen Reich) und der Buddhismus (von Indien) nach China.[1]
Die 6.400 Kilometer[1] lange Route begann in Xi’an und folgte dem Verlauf der Chinesischen Mauer in Richtung Nordwesten, passierte die Taklamakan-Wüste, überwand das Pamirgebirge und führte über Afghanistan in die Levante; von hier wurden die Handelsgüter dann über das Mittelmeer verschifft. Nur wenige Kaufleute reisten auf der gesamten Route, die Waren wurden eher gestaffelt über Zwischenhändler transportiert.
Ihre größte Bedeutung erreichte das Handels- und Wegenetz zwischen 115 v. Chr. und dem 13. Jahrhundert n. Chr. Mit dem allmählichen Verlust römischen Territoriums in Asien und dem Aufstieg Arabiens in der Levante wurde die Seidenstraße zunehmend unsicher und kaum noch bereist. Im 13. und 14. Jahrhundert wurde die Strecke unter den Mongolen wiederbelebt, u. a. benutzte sie zu der Zeit der Venezianer Marco Polo um nach Cathay (China) zu reisen. Nach weit verbreiteter Ansicht war die Route einer der Hauptwege, über die Mitte des 14. Jahrhunderts Pestbakterien von Asien nach Europa gelangten und dort den Schwarzen Tod verursachten.[1]
Teile der Seidenstraße sind zwischen Pakistan und dem autonomen Gebiet Xinjiang in China heute noch als asphaltierte Fernstraße vorhanden (-> Karakorum Highway). Die alte Straße inspirierte die Vereinten Nationen zu einem Plan für eine transasiatische Fernstraße. Von der UN-Wirtschafts- und Sozialkommission für Asien und den Pazifik (UNESCAP) wird die Einrichtung einer durchgehenden Eisenbahnverbindung entlang der Route vorangetrieben, der Trans-Asian Railway.[1]
Die "Neue Seidenstraße", das "One Belt, One Road"-Projekt der Volksrepublik China unter ihrem Staatspräsident Xi Jinping umfasst landgestützte (Silk Road Economic Belt) und maritime (Maritime Silk Road) Infrastruktur- und Handelsrouten, Wirtschaftskorridore und Transportlinien von China über Zentralasien und Russland bzw. über Afrika nach Europa, dazu werden verschiedenste Einrichtungen (z. B. Tiefsee- oder Containerterminals) und Verbindungen (wie Bahnlinien oder Gaspipelines) entwickelt bzw. ausgebaut. Bestehende Korridore sind einerseits Landverbindungen über die Türkei oder Russland und andererseits Anknüpfungen zum Hafen von Shanghai, über Hongkong und Singapur nach Indien und Ostafrika, Dubai, den Suez-Kanal, den griechischen Hafen Piräus nach Venedig.[2]
Das Projekt One Belt, One Road (OBOR, chinesisch 一帶一路 / 一带一路, Pinyin Yídài Yílù ‚Ein Band, Eine Straße‘, neuerdings Belt and Road, da „One“ zu negativ besetzt war) bündelt seit 2013 die Interessen und Ziele der Volksrepublik China unter Staatspräsident Xi Jinping zum Auf- und Ausbau interkontinentaler Handels- und Infrastruktur-Netze zwischen der Volksrepublik und zusammen 64 weiteren Ländern Afrikas, Asiens und Europas. Die Initiative bzw. das Gesamtprojekt betrifft u. A. rund 62 % der Weltbevölkerung und ca. 35 % der Weltwirtschaft.[1][2]
Umgangssprachlich wird das Vorhaben auch „Belt and Road Initiative“ (B&R, BRI) bzw. ebenso wie das Projekt Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA) auch „Neue Seidenstraße“ (新絲綢之路 / 新丝绸之路, Xīn Sīchóuzhīlù) genannt. Es bezieht sich auf den geografischen Raum des historischen, bereits in der Antike genutzten internationalen Handelskorridors „Seidenstraße“; zusammengefasst handelt es sich um zwei Bereiche, einen nördlich gelegenen zu Land mit sechs Bereichen unter dem Titel Silk Road Economic Belt und einen südlich gelegenen Seeweg namens Maritime Silk Road.
丝绸之路(德语:Seidenstraße;英语:Silk Road),常简称为丝路,此词最早来自于德意志帝国地理学家费迪南·冯·李希霍芬男爵于1877年出版的一套五卷本的地图集。[1]
丝绸之路通常是指欧亚北部的商路,与南方的茶马古道形成对比,西汉时张骞以长安为起点,经关中平原、河西走廊、塔里木盆地,到锡尔河与乌浒河之间的中亚河中地区、大伊朗,并联结地中海各国的陆上通道。这条道路也被称为“陆路丝绸之路”,以区别日后另外两条冠以“丝绸之路”名称的交通路线。因为由这条路西运的货物中以丝绸制品的影响最大,故得此名。其基本走向定于两汉时期,包括南道、中道、北道三条路线。但实际上,丝绸之路并非是一条 “路”,而是一个穿越山川沙漠且没有标识的道路网络,并且丝绸也只是货物中的一种。[1]:5
广义的丝绸之路指从上古开始陆续形成的,遍及欧亚大陆甚至包括北非和东非在内的长途商业贸易和文化交流线路的总称。除了上述的路线之外,还包括约于前5世纪形成的草原丝绸之路、中古初年形成,在宋代发挥巨大作用的海上丝绸之路和与西北丝绸之路同时出现,在宋初取代西北丝绸之路成为路上交流通道的南方丝绸之路。
虽然丝绸之路是沿线各君主制国家共同促进经贸发展的产物,但很多人认为,西汉的张骞在前138—前126年和前119年曾两次出使西域,开辟了中外交流的新纪元,并成功将东西方之间最后的珠帘掀开。司马迁在史记中说:“于是西北国始通于汉矣。然张骞凿空,其后使往者皆称博望侯,以为质与国外,外国由此信之”,称赞其开通西域的作用。从此,这条路线被作为“国道”踩了出来,各国使者、商人、传教士等沿着张骞开通的道路,来往络绎不绝。上至王公贵族,下至乞丐狱犯,都在这条路上留下了自己的足迹。这条东西通路,将中原、西域与大伊朗、累范特、阿拉伯紧密联系在一起。经过几个世纪的不断努力,丝绸之路向西伸展到了地中海。广义上丝路的东段已经到达了朝鲜、日本,西段至法国、荷兰。通过海路还可达意大利、埃及,成为亚洲和欧洲、非洲各国经济文化交流的友谊之路。
丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路(英语:The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road[1]),简称一带一路(英语:The Belt and Road Initiative,缩写B&R)[1],是中华人民共和国政府于2013年倡议[2]并主导的跨国经济带[3]。
一带一路范围涵盖历史上丝绸之路和海上丝绸之路行经的中国、中亚、北亚和西亚、印度洋沿岸、地中海沿岸的国家和地区。中国政府指出,“一带一路”倡议坚持共商、共建、共享的原则,努力实现沿线区域基础设施更加完善,更加安全高效,以形成更高水平的陆海空交流网络。同时使投资贸易的便利化水平更有效的提升,建立高品质、高标准的自由贸易区域网。以使沿线各国经济联系更加紧密,政治互信更加的深入,人文交流更加的广泛[4]。
シルクロード(絹の道、英語: Silk Road, ドイツ語: Seidenstraße, 繁体字:絲綢之路, 簡体字:丝绸之路)は、中国と地中海世界の間の歴史的な交易路を指す呼称である。絹が中国側の最も重要な交易品であったことから名付けられた。その一部は2014年に初めて「シルクロード:長安-天山回廊の交易路網」としてユネスコの世界遺産に登録された。
「シルクロード」という名称は、19世紀にドイツの地理学者リヒトホーフェンが、その著書『China(支那)』(1巻、1877年)においてザイデンシュトラーセン(ドイツ語:Seidenstraßen;「絹の道」の複数形)として使用したのが最初であるが、リヒトホーフェンは古来中国で「西域」と呼ばれていた東トルキスタン(現在の中国新疆ウイグル自治区)を東西に横断する交易路、いわゆる「オアシスの道(オアシスロード)」を経由するルートを指してシルクロードと呼んだのである。リヒトホーフェンの弟子で、1900年に楼蘭の遺跡を発見したスウェーデンの地理学者ヘディンが、自らの中央アジア旅行記の書名の一つとして用い、これが1938年に『The Silk Road』の題名で英訳されて広く知られるようになった。
シルクロードの中国側起点は長安(陝西省西安市)、欧州側起点はシリアのアンティオキアとする説があるが、中国側は洛陽、欧州側はローマと見る説などもある。日本がシルクロードの東端だったとするような考え方もあり、特定の国家や組織が経営していたわけではないのであるから、そもそもどこが起点などと明確に定められる性質のものではない。
現在の日本でこの言葉が使われるときは、特にローマ帝国と秦・漢帝国、あるいは大唐帝国の時代の東西交易が念頭に置かれることが多いが、広くは近代(大航海時代)以前のユーラシア世界の全域にわたって行われた国際交易を指し、南北の交易路や海上の交易路をも含める。つまり、北方の「草原の道(ステップロード)」から南方の「海の道(シーロード)」までを含めて「シルクロード」と呼ばれるようになっているわけである。
シルクロード経済ベルトと21世紀海洋シルクロード(シルクロードけいざいベルトと21せいきかいようシルクロード、拼音: 、英語: The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road)とは、2014年11月10日に中華人民共和国北京市で開催されたアジア太平洋経済協力首脳会議で、習近平総書記が提唱した経済圏構想である。
略称は一帯一路(いったいいちろ、拼音: 、英語: The Belt and Road Initiative, BRI; One Belt, One Road Initiative, OBOR)。
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West. It was central to cultural interaction between the regions for many centuries.[1][2][3] The Silk Road refers to both the terrestrial and the maritime routes connecting East Asia and Southeast Asia with East Africa, West Asia and Southern Europe.
The Silk Road derives its name from the lucrative trade in silk carried out along its length, beginning in the Han dynasty (207 BCE–220 CE). The Han dynasty expanded the Central Asian section of the trade routes around 114 BCE through the missions and explorations of the Chinese imperial envoy Zhang Qian.[4] The Chinese took great interest in the safety of their trade products and extended the Great Wall of China to ensure the protection of the trade route.[5]
Trade on the Road played a significant role in the development of the civilizations of China, Korea,[6] Japan,[2] India, Iran, Afghanistan, Europe, the Horn of Africa and Arabia, opening long-distance political and economic relations between the civilizations.[7] Though silk was the major trade item exported from China, many other goods were traded, as well as religions, syncretic philosophies, sciences, and technologies. Diseases, most notably plague, also spread along the Silk Road.[8] In addition to economic trade, the Silk Road was a route for cultural trade among the civilizations along its network.[9]
Traders in ancient history included the Bactrians, Sogdians, Syrians, Jews, Arabs, Iranians, Turkmens, Chinese, Malays, Indians, Somalis, Greeks, Romans, Georgians, Armenians, and Azerbaijanis.[10]
In June 2014, UNESCO designated the Chang'an-Tianshan corridor of the Silk Road as a World Heritage Site. The Indian portion is on the tentative site list.
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) or the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road is a development strategy adopted by the Chinese government. The 'belt' refers to the overland interconnecting infrastructure corridors; the Silk Road Economic Belt (SREB) component. The 'road' refers to the sea route corridors; the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (MSR) component.[2] The initiative focuses on connectivity and cooperation between Eurasian countries, primarily the People's Republic of China (PRC).
Until 2016 the initiative was known in English as the One Belt and One Road Initiative (OBOR) but the Chinese came to consider the emphasis on the word "one" as misleading.[3]
The Chinese government calls the initiative "a bid to enhance regional connectivity and embrace a brighter future".[4] Independent observers, however, see it as a push for Chinese dominance in global affairs with a China-centered trading network.[5][6]
La route de la soie est un réseau ancien de routes commerciales entre l'Asie et l'Europe, reliant la ville de Chang'an (actuelle Xi'an) en Chine à la ville d'Antioche, en Syrie médiévale (aujourd'hui en Turquie). Elle tire son nom de la plus précieuse marchandise qui y transitait : la soie.
La route de la soie était un faisceau de pistes par lesquelles transitaient de nombreuses marchandises, et qui monopolisa les échanges Est-Ouest pendant des siècles. Les plus anciennes traces connues de la route de la soie, comme voie de communication avec les populations de l'Ouest, remontent à « 2000 avant notre ère au moins ». Les Chinois en fixent l'ouverture au voyage de Zhang Qian en 138-1261. Mais la route de la soie s'est développée surtout sous la dynastie Han (221 av. J.-C. - 220 ap. J.-C.), en particulier Han Wudi.
Puis sous la dynastie Tang (618-907). À partir du XVe siècle, la route de la soie est progressivement abandonnée, l'instabilité des guerres turco-byzantines, puis la chute de Constantinople poussent en effet les Occidentaux à chercher une nouvelle route maritime vers les Indes. L'abandon de la route de la soie correspond ainsi au début de la période des « Grandes découvertes » durant laquelle les techniques de transport maritime deviennent de plus en plus performantes. Du côté chinois, les empereurs Ming Yongle, puis Ming Xuanzong chargent, à la même époque, l'amiral Zheng He d'expéditions maritimes similaires.
La nouvelle route de la soie ou la Ceinture et la Route2 (stratégie aussi appelée OBOR en anglais pour One Belt, One Road3) est à la fois un ensemble de liaisons maritimes et de voies ferroviaires entre la Chine et l'Europe passant par le Kazakhstan, la Russie, la Biélorussie, la Pologne, l'Allemagne, la France et le Royaume-Uni.
Le nouveau nom est Initiative route et ceinture (Belt and Road Initiative, B&R selon l’acronyme anglais) afin de marquer le fait que ce projet ne se limite pas à une seule route4.
Outre l'amélioration de la connectivité ferroviaire, il s'agit aussi d'une stratégie de développement pour promouvoir la coopération entre les pays sur une vaste bande s'étendant à travers l'Eurasie et pour renforcer la position de la Chine sur le plan mondial, par exemple en préservant la connexion de la Chine avec le reste du monde en cas de tensions militaires sur ses zones côtières5.
La Nouvelle route de la soie a été dévoilée à l'automne 2013 par le gouvernement chinois en tant que pendant terrestre du collier de perles6 ; elle est l'une des priorités de la diplomatie chinoise, sous la présidence de Xi Jinping7.
Selon CNN, ce projet englobera 68 pays représentant 4,4 milliards d’habitants et 62 % du PIB mondial8.
Per via della seta (in cinese: 絲綢之路T, 丝绸之路S, sī chóu zhī lùP; persiano: راه ابریشم, Râh-e Abrisham) s'intende il reticolo, che si sviluppava per circa 8.000 km, costituito da itinerari terrestri, marittimi e fluviali lungo i quali nell'antichità si erano snodati i commerci tra l'impero cinese e quello romano.
Le vie carovaniere attraversavano l'Asia centrale e il Medio Oriente, collegando Chang'an (oggi Xi'an), in Cina, all'Asia Minore e al Mediterraneo attraverso il Medio Oriente e il Vicino Oriente. Le diramazioni si estendevano poi a est alla Corea e al Giappone e, a Sud, all'India. Il nome apparve per la prima volta nel 1877, quando il geografo tedesco Ferdinand von Richthofen (1833-1905) pubblicò l'opera Tagebucher aus China. Nell'Introduzione von Richthofen nomina la Seidenstraße, la «via della seta».
La destinazione finale della seta che su di essa viaggiava (non certo da sola ma insieme a tante altre merci preziose) era Roma, dove per altro non si sapeva con precisione quale ne fosse l'origine (se animale o vegetale) e da dove provenisse. Altre merci altrettanto preziose viaggiavano in senso inverso, e insieme alle merci viaggiavano grandi idee e religioni (concetti fondamentali di matematica, geometria, astronomia) in entrambi i sensi, manicheismo, e nestorianesimo verso oriente. Sulla via della seta compì un complesso giro quasi in tondo anche il buddhismo, dall'India all'Asia Centrale alla Cina e infine al Tibet (il tutto per trovare itinerari che permettessero di evitare le quasi invalicabili montagne dell'Himalaya).
Questi scambi commerciali e culturali furono determinanti per lo sviluppo e il fiorire delle antiche civiltà dell'Egitto, della Cina, dell'India e di Roma, ma furono di grande importanza anche nel gettare le basi del mondo medievale e moderno.
La Nuova via della seta è un'iniziativa strategica della Cina per il miglioramento dei collegamenti e della cooperazione tra paesi nell'Eurasia. Comprende le direttrici terrestri della "zona economica della via della seta" e la "via della seta marittima del XXI secolo" (in cinese: 丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路S, Sīchóu zhī lù jīngjìdài hé èrshíyī shìjì hǎishàng sīchóu zhī lùP), ed è conosciuta anche come "iniziativa della zona e della via" (一带一路S, tradotta comunemente in inglese con Belt and Road Initiative, BRI) o "una cintura, una via" e col corrispondente iniziale acronimo inglese OBOR (One belt, one road), poi modificato in BRI per sottolineare l'estensione del progetto non esclusivo solo della Cina[1], nonostante la prospettiva sinocentrica, com'è stato illustrato in un recente studio italiano[2].
Partendo dallo sviluppo delle infrastrutture di trasporto e logistica, la strategia mira a promuovere il ruolo della Cina nelle relazioni globali, favorendo i flussi di investimenti internazionali e gli sbocchi commerciali per le produzioni cinesi. L'iniziativa di un piano organico per i collegamenti terrestri (la cintura) è stata annunciata pubblicamente dal presidente cinese Xi Jinping a settembre del 2013, e la via marittima ad ottobre dello stesso anno, contestualmente alla proposta di costituire la Banca asiatica d'investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), dotata di un capitale di 100 miliardi di dollari USA, di cui la Cina stessa sarebbe il principale socio, con un impegno pari a 29,8 miliardi e gli altri paesi asiatici (tra cui l'India e la Russia) e dell'Oceania avrebbero altri 45 miliardi (l'Italia si è impegnata a sottoscrivere una quota di 2,5 miliardi).
La Ruta de la Seda fue una red de rutas comerciales organizadas a partir del negocio de la seda china desde el siglo I a. C., que se extendía por todo el continente asiático, conectando a China con Mongolia, el subcontinente indio, Persia, Arabia, Siria, Turquía, Europa y África. Sus diversas rutas comenzaban en la ciudad de Chang'an (actualmente Xi'an) en China, pasando entre otras por Karakórum (Mongolia), el Paso de Khunjerab (China/Pakistán), Susa (Persia), el Valle de Fergana (Tayikistán), Samarcanda (Uzbekistán), Taxila (Pakistán), Antioquía en Siria, Alejandría (Egipto), Kazán (Rusia) y Constantinopla (actualmente Estambul, Turquía) a las puertas de Europa, llegando hasta los reinos hispánicos en el siglo XV, en los confines de Europa y a Somalia y Etiopía en el África oriental.
El término "Ruta de la Seda" fue creado por el geógrafo alemán Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen, quien lo introdujo en su obra Viejas y nuevas aproximaciones a la Ruta de la Seda, en 1877. Debe su nombre a la mercancía más prestigiosa que circulaba por ella, la seda, cuya elaboración era un secreto que solo los chinos conocían. Los romanos (especialmente las mujeres de la aristocracia) se convirtieron en grandes aficionados de este tejido, tras conocerlo antes del comienzo de nuestra era a través de los partos, quienes se dedicaban a su comercio. Muchos productos transitaban estas rutas: piedras y metales preciosos (diamantes de Golconda, rubíes de Birmania, jade de China, perlas del golfo Pérsico), telas de lana o de lino, ámbar, marfil, laca, especias, porcelana, vidrio, materiales manufacturados, coral, etc.
En junio de 2014, la Unesco eligió un tramo de la Ruta de la Seda como Patrimonio de la Humanidad con la denominación Rutas de la Seda: red viaria de la ruta del corredor Chang’an-Tian-shan. Se trata de un tramo de 5000 kilómetros de la gran red viaria de las Rutas de la Seda que va desde la zona central de China hasta la región de Zhetysu, situada en el Asia Central, incluyendo 33 nuevos sitios en China, Kazajistán y Kirguistán.1
La Iniciativa del Cinturón y Ruta de la Seda o Belt and Road Initiative, abreviada BRIZNA (también One Belt, One Road, abreviado OBOR y también la Nueva Ruta de la Seda) y NRS (Nueva Ruta de la Seda) por las siglas en español, es el nombre con que se conoce el proyecto político-económico del Secretario General del Partido Comunista de China, Xi Jinping, que propuso en septiembre de 2013 en sus respectivos viajes a Rusia, Kazajistán y Bielorrusia. Bajo el pretexto de que "hace más de dos milenios, las personas diligentes y valientes de Eurasia exploraron y abrieron nuevas vías de intercambio comercial y cultural que unían las principales civilizaciones de Asia, Europa y África, colectivamente llamadas ruta de la seda por generaciones posteriores", el proyecto quiere conectar Europa, Asia del Sur-Oriental, Asia Central y el Oriente Medio, mediante el modelo económico, e implícitamente político, chino.12
El proyecto parte de la reconstrucción de la antigua ruta de la seda y la creac
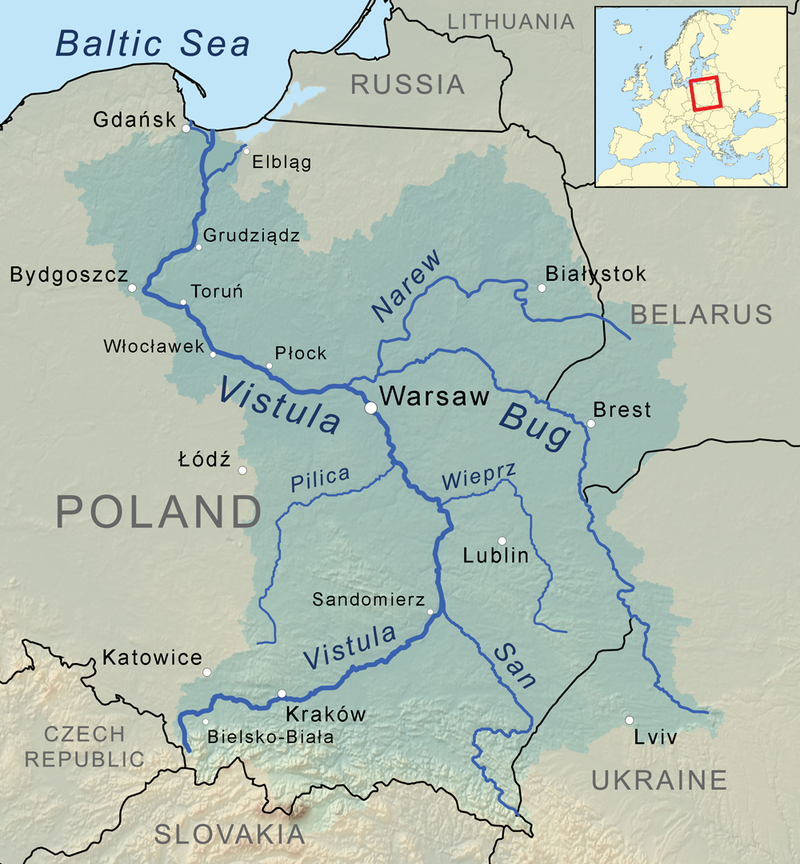
Die Weichsel (polnisch Wisła ([ˈvʲiswa] ![]()
![]() ), tschechisch Visla, lateinisch Vistula) ist ein 1048 Kilometer langer und für europäische Verhältnisse weitgehend unregulierter und naturbelassener Strom und der längste Fluss in Polen. Das Einzugsgebiet umfasst auch Teile der Slowakei, Belarus’ und der Ukraine. Der längste Gewässerlauf in ihrem Flusssystem sind die 1213 Flusskilometer von der Quelle des Westlichen Bug bis zur Ostsee.
), tschechisch Visla, lateinisch Vistula) ist ein 1048 Kilometer langer und für europäische Verhältnisse weitgehend unregulierter und naturbelassener Strom und der längste Fluss in Polen. Das Einzugsgebiet umfasst auch Teile der Slowakei, Belarus’ und der Ukraine. Der längste Gewässerlauf in ihrem Flusssystem sind die 1213 Flusskilometer von der Quelle des Westlichen Bug bis zur Ostsee.
Auf alten Landkarten findet man auch die Schreibweisen W(e)ixel oder Wissel.
维斯瓦河(波兰语:Wisła,波兰语:[ˈvʲiswa](![]() 听)),又依英语译作维斯图拉河(英语:Vistula),是波兰最长的河流。全长1,047公里;流域面积194,424平方公里,占波兰国土面积的三分之二。
听)),又依英语译作维斯图拉河(英语:Vistula),是波兰最长的河流。全长1,047公里;流域面积194,424平方公里,占波兰国土面积的三分之二。
发源于波兰南部的喀尔巴阡山脉,维斯瓦河曲向北流,流经克拉科夫、华沙、托伦,在河口形成三角洲,最后注入波罗的海格但斯克湾。
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea

 Abruzzo
Abruzzo
 Albania
Albania
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia

 Marche
Marche

 Molise
Molise
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 Puglia
Puglia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Veneto
Veneto
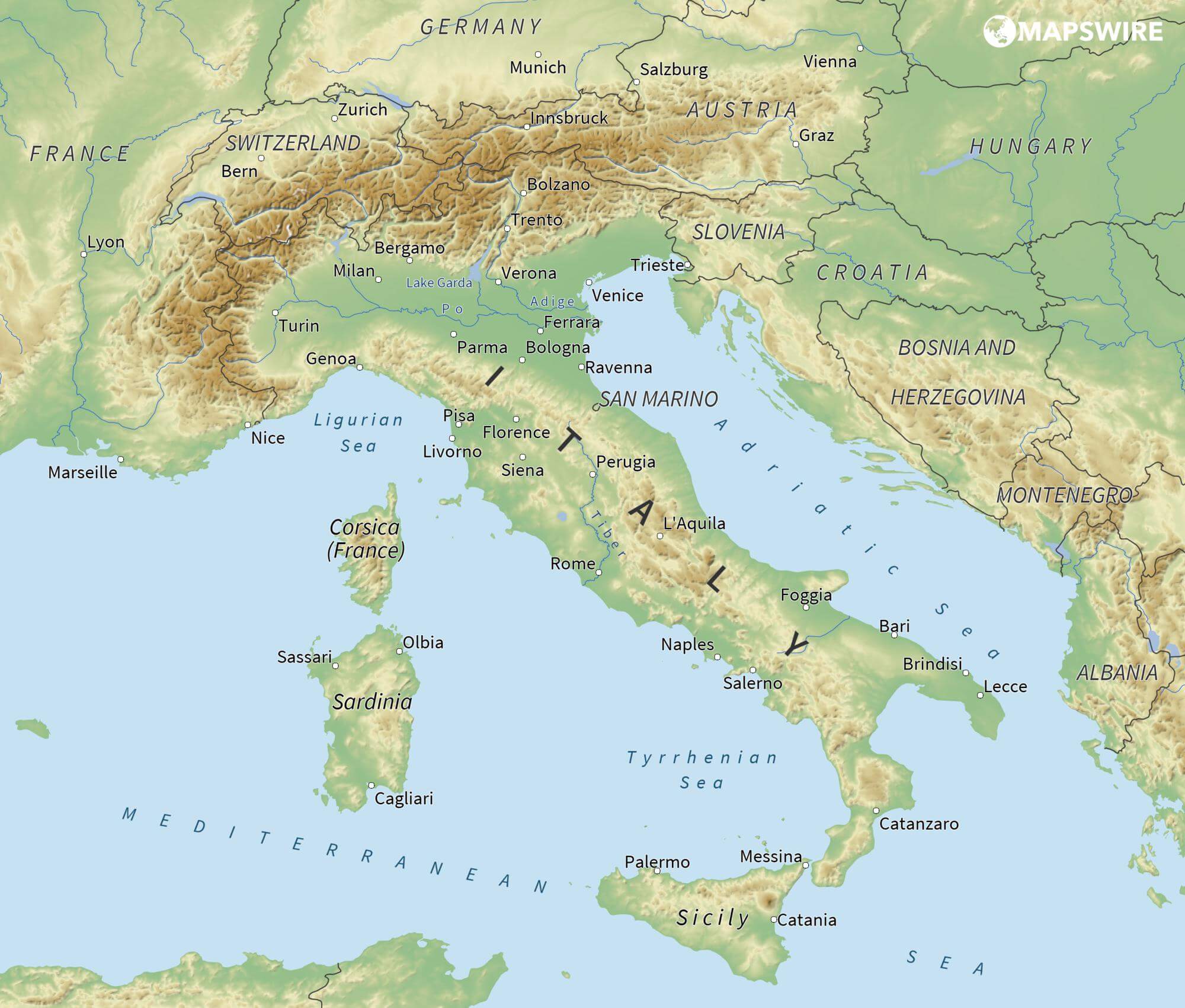
Das Adriatische Meer, kurz auch die Adria (lateinisch Mare Adriaticum; italienisch Mare Adriatico; bosnisch, kroatisch und serbisch Jadransko more oder kurz Jadran; slowenisch Jadransko morje; albanisch Deti Adriatik oder kurz Adriatiku), ist das lang gestreckte nördliche Seitenbecken des Mittelmeeres zwischen der Apenninhalbinsel und Balkanhalbinsel. Es ist nach der Stadt Adria in Italien (Provinz Rovigo) benannt. Zum Adriatischen Meer wird alles gerechnet, was nördlich der Straße von Otranto liegt.
亚得里亚海(意大利语:Mar Adriatico,斯洛文尼亚语:Jadransko morje,克罗地亚语:Jadransko more,阿尔巴尼亚语:Deti Adriatik),是地中海的一部分水域,分隔了意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)和巴尔干半岛,也分隔了亚平宁山脉与狄那里克阿尔卑斯山脉及其临近地区。亚得里亚海西岸属于意大利,东岸则分别属于斯洛文尼亚、克罗地亚、波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那、黑山和阿尔巴尼亚。亚得里亚海透过位于其南部的奥特朗托海峡与爱奥尼亚海相连。波河、阿迪杰河、奥凡托河等河流流入亚得里亚海;海中有近1200个岛屿,其中只有69个有人居住。
アドリア海(アドリアかい、英: Adriatic Sea ; イタリア語: Mar Adriatico ; クロアチア語: Jadransko more)は、地中海の海域の一つ。イタリア半島とバルカン半島に挟まれている。
The Adriatic Sea (/ˌeɪdriˈætɪk/) is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains over 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of 1,233 metres (4,045 ft). The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because the Adriatic collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures generally range from 30 °C (86 °F) in summer to 12 °C (54 °F) in winter, significantly moderating the Adriatic Basin's climate.
The Adriatic Sea sits on the Apulian or Adriatic Microplate, which separated from the African Plate in the Mesozoic era. The plate's movement contributed to the formation of the surrounding mountain chains and Apennine tectonic uplift after its collision with the Eurasian plate. In the Late Oligocene, the Apennine Peninsula first formed, separating the Adriatic Basin from the rest of the Mediterranean. All types of sediment are found in the Adriatic, with the bulk of the material transported by the Po and other rivers on the western coast. The western coast is alluvial or terraced, while the eastern coast is highly indented with pronounced karstification. There are dozens of marine protected areas in the Adriatic, designed to protect the sea's karst habitats and biodiversity. The sea is abundant in flora and fauna—more than 7,000 species are identified as native to the Adriatic, many of them endemic, rare and threatened ones.
The Adriatic's shores are populated by more than 3.5 million people; the largest cities are Bari, Venice, Trieste and Split. The earliest settlements on the Adriatic shores were Etruscan, Illyrian, and Greek. By the 2nd century BC, the shores were under Rome's control. In the Middle Ages, the Adriatic shores and the sea itself were controlled, to a varying extent, by a series of states—most notably the Byzantine Empire, the Croatian Kingdom, the Republic of Venice, the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The Napoleonic Wars resulted in the First French Empire gaining coastal control and the British effort to counter the French in the area, ultimately securing most of the eastern Adriatic shore and the Po Valley for Austria. Following Italian unification, the Kingdom of Italy started an eastward expansion that lasted until the 20th century. Following World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, the eastern coast's control passed to Yugoslavia and Albania. The former disintegrated during the 1990s, resulting in four new states on the Adriatic coast. Italy and Yugoslavia agreed on their maritime boundaries by 1975 and this boundary is recognised by Yugoslavia's successor states, but the maritime boundaries between Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Montenegro are still disputed. Italy and Albania agreed on their maritime boundary in 1992.
Fisheries and tourism are significant sources of income all along the Adriatic coast. Adriatic Croatia's tourism industry has grown faster economically than the rest of the Adriatic Basin's. Maritime transport is also a significant branch of the area's economy—there are 19 seaports in the Adriatic that each handle more than a million tonnes of cargo per year. The largest Adriatic seaport by annual cargo turnover is the Port of Trieste, while the Port of Split is the largest Adriatic seaport by passengers served per year.
La mer Adriatique (du latin : Mare Hadriaticum ou Mare Adriaticum) est une mer séparant la péninsule italienne de la péninsule balkanique. L'Adriatique est le bras de la Méditerranée situé le plus au nord en s'étendant du canal d'Otrante (où elle rejoint la mer Ionienne) jusqu'aux villes de Venise et de Trieste et à l'embouchure du Pô. Les pays côtiers sont l'Italie, la Slovénie, la Croatie, la Bosnie-Herzégovine, le Monténégro et l'Albanie, ainsi que la Grèce par l'île de Corfou.
Il mare Adriatico è l'articolazione del mar Mediterraneo orientale situata tra la penisola italiana e la penisola balcanica; suddiviso in Alto Adriatico, Medio Adriatico e Basso Adriatico, bagna sei Paesi: Italia, Slovenia, Croazia, Bosnia ed Erzegovina, Montenegro e Albania, confinando a sud-est con il Mar Ionio.
El mar Adriático (del latín, Mare Hadriaticum) es un golfo estrecho y alargado que forma parte del mar Mediterráneo. Se encuentra situado entre la península Itálica, al oeste, y la península de los Balcanes, al este, con una anchura máxima de unos 200 km, y una longitud de unos 800 km. Su extremo meridional limita con el mar Jónico, del que lo separa el canal de Otranto. Su superficie total es de, aproximadamente, 160 000 km².
Las costas occidental, septentrional, y parte de la oriental corresponden a Italia (60% de la longitud de costa del Adriático), mientras que el resto de la costa oriental corresponde a Croacia, Eslovenia, Bosnia y Herzegovina, Montenegro y Albania. Algunos de los ríos que desembocan en el Adriático son el Reno, el Po, el Adigio, el Brenta, el Piave y el Neretva.
La costa del Adriático concentra un gran número de centros turísticos, como Venecia, que recibe el nombre de «Reina del Adriático». Tras la división de Yugoslavia, la costa croata se ha convertido también en un destino turístico muy popular.
Sus aguas sostienen industria pesquera, y se llevan a cabo prospecciones petrolíferas en este mar. Durante los años 1990, varias investigaciones revelaron que sus niveles de contaminación son muy altos.
En las últimas décadas el gobierno de Italia ha intentado hacer de él una barrera contra la inmigración ilegal, en su mayor parte proveniente de Albania.
Адриати́ческое мо́ре (итал. mare Adriatico, эмил.-ром. Mèr Adriâtic, вен. Mar Adriàtico, неап. Mar Adriateco, словен. Jadransko morje, сербохорв. Jadransko more/Јадранско море, алб. Deti Adriatik, лат. mare Hadriaticum), также Адриатика — полузамкнутое море, часть Средиземного моря между Апеннинским и Балканским полуостровами. Омывает берега Италии (более 1000 км), Словении (47 км), Хорватии (1777 км), Боснии и Герцеговины (20 км), Черногории (200 км), Албании (472 км).
 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History