
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Poland
Poland
 China
China
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Legend
Legend
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
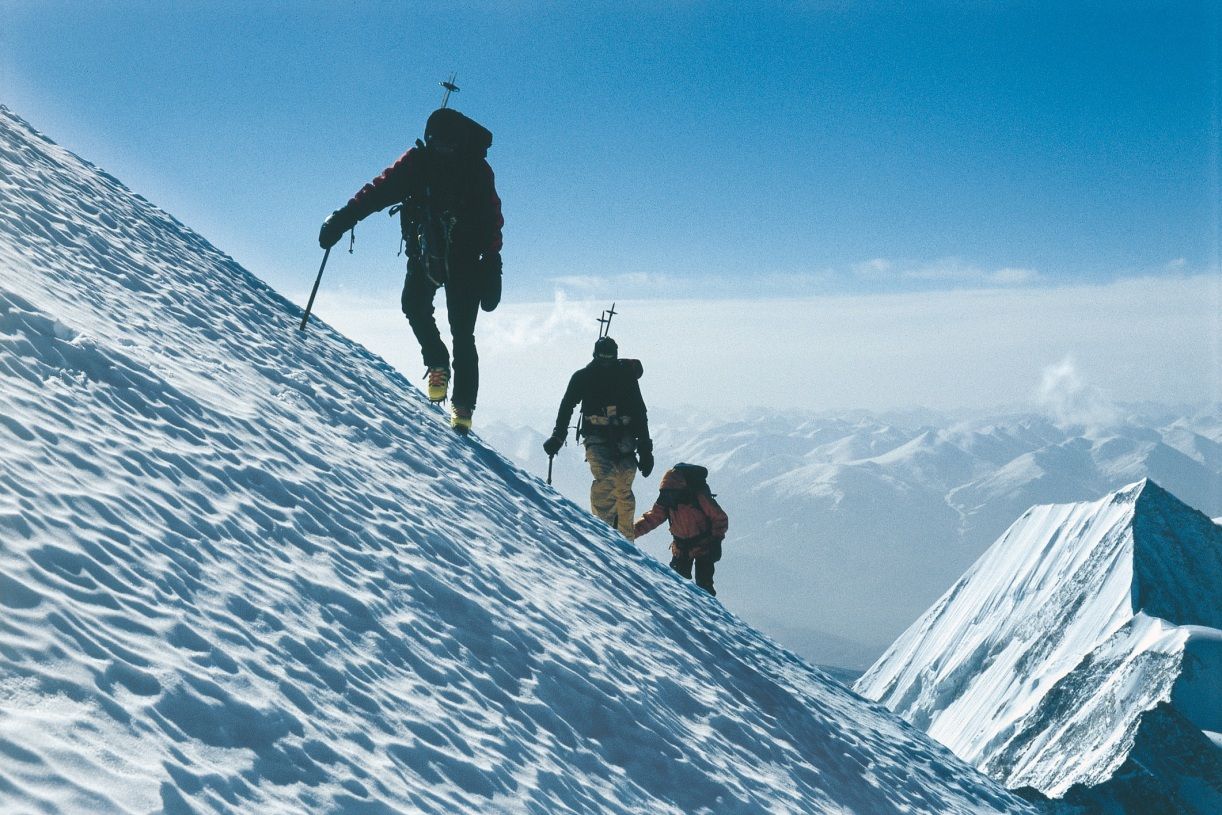



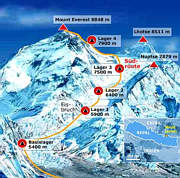


珠穆朗玛峰山体呈巨型金字塔状,威武雄壮昂首天外,地形极端险峻,环境异常复杂。雪线高度:北坡为5800—6200米,南坡为5500—6100米。东北山脊、 东南山脊和西山山脊中间夹着三大陡壁(北壁、东壁和西南壁),在这些山脊 和峭壁之间又分布着548条大陆型冰川,总面积达1457.07平方公里,平均厚度达7260米。冰川的补给主要靠印度洋季风带两大降水带积雪变质形成。冰川上 有千姿百态、瑰丽罕见的冰塔林,又有高达数十米的冰陡崖和步步陷井的明暗 冰裂隙,还有险象环生的冰崩雪崩区。(Quelle:http://news.xinhuanet.com)
珠穆朗玛峰(藏文:ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ;藏语拼音:qomolangma;威利:jo mo glang ma,香港称珠穆朗玛峰,台湾称圣母峰),中文简称珠峰,尼泊尔名萨加玛塔峰(尼泊尔语:सगरमाथा),英国名埃佛勒斯峰(英语:Mount Everest),为地球第一高峰,属于喜马拉雅山脉,位于中国西藏自治区与尼泊尔萨加玛塔专区边界上。2005年中国国家测绘局测量的岩面高为8,844.43米(29,017.2英尺),尼泊尔则使用传统的雪盖高8,848米(29,029英尺),BBC报道称2010年起两国官方互相承认对方的测量数据[5],中国国家测绘地理信息局则在2018年2月声明否认此说法,仍采用8,844.43米数据至今[6]。它除了是海拔最高的山峰之外,也是距离地心第五远的高峰。[7]它附近的高峰包括8,516米(27,940英尺)的洛子峰、7,855米(25,771英尺)的努子峰和7,580米(24,870英尺)的章子峰。
清朝经过测绘于1719年出版的全国地图上称此峰为“朱姆朗马阿林”,但没有标出高度或用经纬度标出其位置。1856年英属印度测量局首次公布此峰的经纬度及海拔高度,主张此峰8,840米(29,000英尺)是世界第一高峰。1865年英国皇家地理学会接受印度测量局局长安德鲁·史考特·华欧的建议,将此峰命名为“埃佛勒斯峰”,以纪念前任局长乔治·埃佛勒斯。1952年,中国采用“珠穆朗玛峰”为官方名称。
珠穆朗玛峰吸引了许多登山者。主要的攀登路线有两条,一条从尼泊尔东南部出发,经过与洛子峰之间的南坳登顶,称为“标准路线”;另一条则从西藏的北部出发,经过与章子峰之间的北坳登顶。从标准路线登顶对登山技术的挑战不算高,但这条路线的风险包括雪崩、摔落山谷、高山症、冻伤和通过昆布冰瀑的危险。到2016年为止,山上有超过200具尸体,其中一些成为地标。[8][9]
据气象记载,珠穆朗玛峰山顶最低温度为-60°C,最低月平均温度为-35°C,全年平均温度为-29°C,参照北极、南极,因此也被称为“世界第三极”。[10]
Der Mount Everest ist ein Berg im Himalaya und mit einer Höhe von 8848 m der höchste Berg der Erde. Er gehört zu den 14 Achttausendern und zu den Seven Summits. Der Mount Everest ist seit 1856 nach dem britischen Landvermesser George Everest benannt. Auf Nepali heißt der Berg Sagarmatha, auf Tibetisch Qomolangma (deutsche Aussprache „Tschomolangma“; englische Umschrift Chomolungma).
Der Mount Everest befindet sich im Mahalangur Himal in der Region Khumbu in Nepal an der Grenze zu China (Autonomes Gebiet Tibet); der westliche und südöstliche seiner drei Gipfelgrate bilden die Grenze. Auf nepalesischer Seite ist er Teil des Sagarmatha-Nationalparks, der zum UNESCO-Welterbe gehört. Auf der Nordseite gehört er zum Qomolangma National Nature Reserve, das mit dem von der UNESCO ausgewiesenen Qomolangma-Biosphärenreservat korrespondiert.[1]
Edmund Hillary und Tenzing Norgay gelang am 29. Mai 1953 die Erstbesteigung des „dritten Pols“. Am 8. Mai 1978 bestiegen Reinhold Messner und Peter Habeler den Gipfel erstmals ohne zusätzlichen Sauerstoff.
エベレスト、エヴェレスト(英: Everest)、またはチョモランマ(チベット語: ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ[1] Chomolungma, Qomolangma)、サガルマータ(ネパール語: सगरमाथा Sagarmāthā)は、ヒマラヤ山脈にある世界最高峰である。
エベレストはインド測量局(Survey of India)で長官を務めたジョージ・エベレストにちなんで命名された。
1920年代から長きにわたる挑戦の末、1953年にイギリス探検隊のメンバーでニュージーランド出身の登山家であるエドモンド・ヒラリーとネパール出身のシェルパであるテンジン・ノルゲイによって初登頂がなされた。
エベレストの標高については諸説あり、1954年にインド測量局が周辺12ヶ所で測定しその結果を平均して得られた8,848 mという数値が長年一般に認められてきた。1999年、全米地理学協会はGPSによる測定値が8,850mだったと発表した[2]。厳密には地殻変動などの影響によって標高は年々変動していると考えられている。
エベレストの南麓に位置するネパールのサガルマータ国立公園はユネスコの世界遺産に登録されている。
Mount Everest, known in Nepali as Sagarmatha (सगरमाथा) and in Tibetan as Chomolungma (ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ), is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The international border between Nepal (Province No. 1) and China (Tibet Autonomous Region) runs across its summit point.
The current official elevation of 8,848 m (29,029 ft), recognized by China and Nepal, was established by a 1955 Indian survey and subsequently confirmed by a Chinese survey in 1975.[1] In 2005, China remeasured the rock height of the mountain, with a result of 8844.43 m. There followed an argument between China and Nepal as to whether the official height should be the rock height (8,844 m., China) or the snow height (8,848 m., Nepal). In 2010, an agreement was reached by both sides that the height of Everest is 8,848 m, and Nepal recognizes China's claim that the rock height of Everest is 8,844 m.[5]
In 1865, Everest was given its official English name by the Royal Geographical Society, upon a recommendation by Andrew Waugh, the British Surveyor General of India. As there appeared to be several different local names, Waugh chose to name the mountain after his predecessor in the post, Sir George Everest, despite George Everest's objections.[6]
Mount Everest attracts many climbers, some of them highly experienced mountaineers. There are two main climbing routes, one approaching the summit from the southeast in Nepal (known as the "standard route") and the other from the north in Tibet. While not posing substantial technical climbing challenges on the standard route, Everest presents dangers such as altitude sickness, weather, and wind, as well as significant hazards from avalanches and the Khumbu Icefall. As of 2017, nearly 300 people have died on Everest, many of whose bodies remain on the mountain.[7]
The first recorded efforts to reach Everest's summit were made by British mountaineers. As Nepal did not allow foreigners into the country at the time, the British made several attempts on the north ridge route from the Tibetan side. After the first reconnaissance expedition by the British in 1921 reached 7,000 m (22,970 ft) on the North Col, the 1922 expedition pushed the north ridge route up to 8,320 m (27,300 ft), marking the first time a human had climbed above 8,000 m (26,247 ft). Seven porters were killed in an avalanche on the descent from the North Col. The 1924 expedition resulted in one of the greatest mysteries on Everest to this day: George Mallory and Andrew Irvine made a final summit attempt on 8 June but never returned, sparking debate as to whether or not they were the first to reach the top. They had been spotted high on the mountain that day but disappeared in the clouds, never to be seen again, until Mallory's body was found in 1999 at 8,155 m (26,755 ft) on the north face. Tenzing Norgay and Edmund Hillary made the first official ascent of Everest in 1953, using the southeast ridge route. Norgay had reached 8,595 m (28,199 ft) the previous year as a member of the 1952 Swiss expedition. The Chinese mountaineering team of Wang Fuzhou, Gonpo, and Qu Yinhua made the first reported ascent of the peak from the north ridge on 25 May 1960.[8][9]
L’Everest, en tibétain ཇོ་མོ་གླང་མ, Qomolangma ou encore Chomolungma, en népalais सगरमाथा, Sagarmāthā, aussi appelé mont Everest, est une montagne située dans la chaîne de l'Himalaya, à la frontière entre le Népal (province no 1 (en)) et la Chine (Tibet).
Il est aperçu par des Européens pour la première fois en 1847 puis, après quelques années d'observations et de calculs, son altitude est établie à 8 848 mètres et il est identifié comme le plus haut sommet du monde. Cette caractéristique lui vaut d'être baptisé de son nom actuel par les Occidentaux en 1865 et, dès les années 1920, de lui attirer l'intérêt des alpinistes qui se lancent à l'assaut de ses pentes. Plusieurs expéditions, en particulier britanniques, se succèdent depuis le versant nord au Tibet. Toutefois, les conditions climatiques extrêmes font leurs premières victimes, parmi lesquelles George Mallory et Andrew Irvine, en 1924, dont on ne saura probablement jamais avec certitude s'ils ont atteint le sommet. En 1950, le Népal autorise l'accès à la montagne depuis le sud offrant des possibilités d'ascension par l'arête Sud-Est, moins périlleuse. Finalement, trois ans plus tard, Edmund Hillary et Tensing Norgay réussissent à vaincre l'Everest. Dès lors, les exploits en tous genres s'enchaînent, alimentant les fantasmes populaires ; mais, en 1996, une série d'accidents mortels vient rappeler les dangers liés à la montagne, portant de nos jours à plus de 200 le nombre de victimes. Pourtant, le tourisme de masse se popularise, fragilisant le milieu naturel malgré les créations du parc national de Sagarmatha en 1976 et de la réserve naturelle du Qomolangma en 1988. Ainsi, plus de 14 000 alpinistes ont tenté l'ascension depuis 1922 et plus de 4 000 l'ont réussie, bien aidés, pour la majorité d'entre eux, par les porteurs sherpas.
Il monte Everest (pron. /ˈɛverest/[1]) è la vetta più alta del continente asiatico e della Terra con i suoi 8 848 m di altitudine s.l.m., situato nella catena dell'Himalaya assieme ad altri ottomila, al confine fra Cina e Nepal. Rientra dunque nelle cosiddette Sette Vette del Pianeta.
El monte Everest es la montaña más alta del planeta Tierra, con una altitud de 8.848 metros (29 029 pies) sobre el nivel del mar.1 Está localizada en el continente asiático, en la cordillera del Himalaya, concretamente en la subcordillera de Mahalangur Himal; marca la frontera entre China y Nepal, considerada como la frontera más alta del mundo.[cita requerida] El macizo incluye los picos vecinos Lhotse, 8516 m (27 940 pies); Nuptse, 7855 m (25 771 pies) y Changtse, 7580 m (24 870 pies).
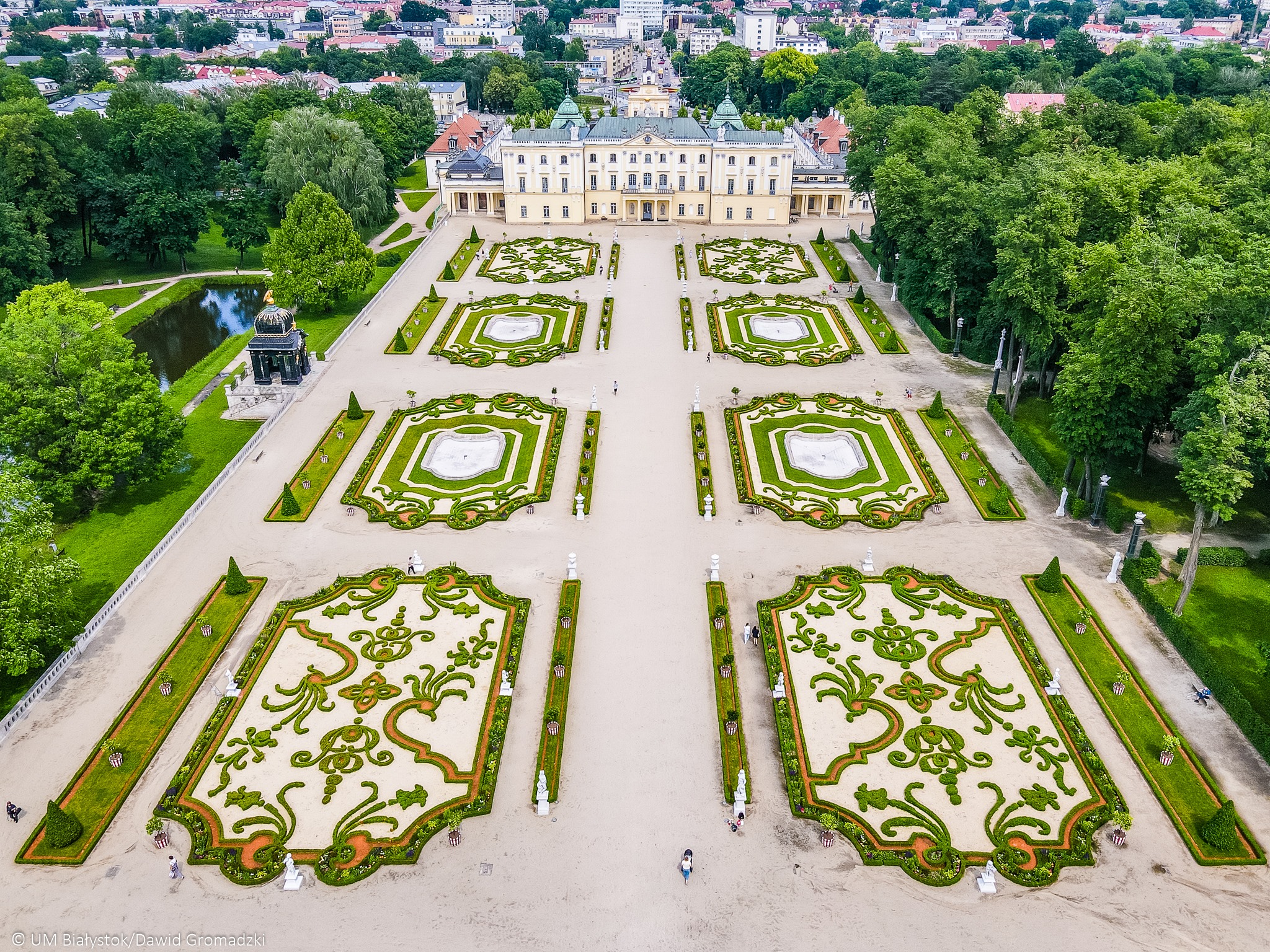






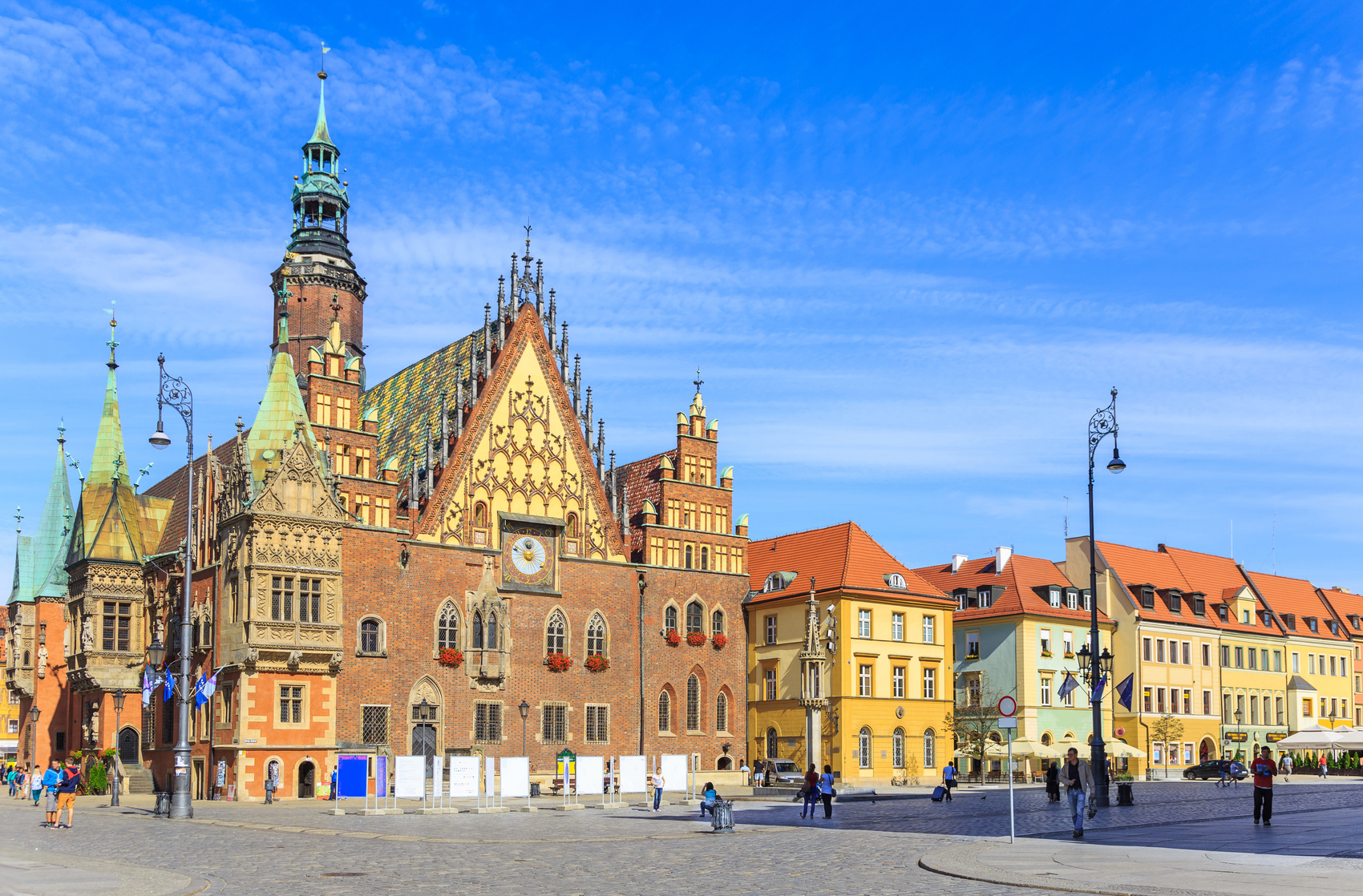
弗罗茨瓦夫(波兰语:Wrocław;德语:Breslau,中文譯為布雷斯勞、布列斯勞、洛克勞;捷克语:Vratislav;拉丁语:Wratislavia 或 Vratislavia),是波兰城市,位于波兰西南部的奥得河畔,自1999年起是下西里西亚省的省会。该市人口约为637,075人(2016年),列波兰第四大城(次于华沙、克拉科夫和罗兹),同时也是波兰仅次于华沙的第二大金融中心,在经济、文化、交通等诸多方面都在波兰具有相当重要的地位。
弗罗茨瓦夫在其城市发展史上的大部分时期内,一直是一个以多民族、多元文化为特色的城市,德意志、波兰、捷克、犹太等民族均扮演过重要角色。而德语曾长期是占有优势地位的语言,该市的德语名称布雷斯勞(Breslau)的知名度一直很高,二战以前该市曾是德国重要的工商业与文化名城之一,城市规模居全德国第六位,那時人口已达60多万。在第二次世界大战以后的领土调整和民族大迁徙中,该市是德国在战后失去的最大城市,原有的德国居民被迫西迁,而波兰东部因為割让给苏联,大批波蘭人湧入這座城市導致弗罗茨瓦夫在人口构成上基本上成为一个纯粹的波兰城市,但由于保留下来的以及战后重建的大量普鲁士、奥地利乃至波希米亚风格的建筑,该市在波兰境内仍是一个颇为独特的城市。
Breslau (polnisch  Wrocław?/i [ˈvrɔtswaf], schlesisch Brassel,[3] lateinisch Vratislavia oder Wratislavia), im Südwesten von Polen gelegen, ist mit über 630.000 Einwohnern nach Warschau, Krakau und Łódź die viertgrößte Stadt des Landes, Verwaltungssitz des gleichnamigen Landkreises (Powiat) sowie Hauptstadt der Woiwodschaft Niederschlesien.
Wrocław?/i [ˈvrɔtswaf], schlesisch Brassel,[3] lateinisch Vratislavia oder Wratislavia), im Südwesten von Polen gelegen, ist mit über 630.000 Einwohnern nach Warschau, Krakau und Łódź die viertgrößte Stadt des Landes, Verwaltungssitz des gleichnamigen Landkreises (Powiat) sowie Hauptstadt der Woiwodschaft Niederschlesien.
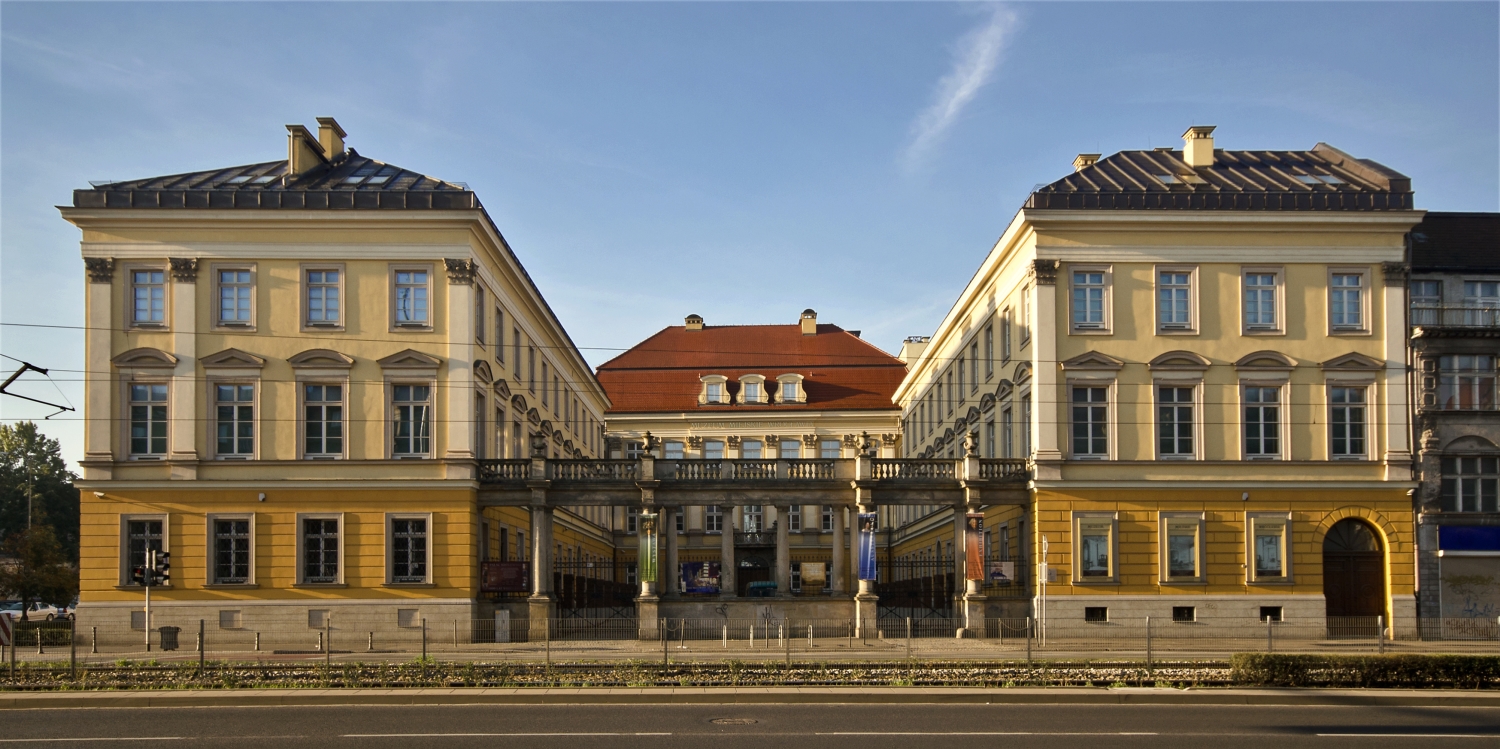
Als Hauptstadt der historischen Region Schlesien ist die kreisfreie Großstadt an der Oder (Odra) Sitz eines römisch-katholischen Erzbischofs und eines evangelischen Diözesanbischofs. Mit zahlreichen Unternehmen, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen bildet Breslau das wirtschaftliche, kulturelle und wissenschaftliche Zentrum Niederschlesiens.
Mit ihrer wechselvollen Geschichte zwischen Deutschen und Polen, den zahlreichen historischen Bauten, Parkanlagen und Plätzen ist die Stadt heute Anziehungspunkt für Besucher aus aller Welt. Breslau war 2012 einer der Austragungsorte der Fußball-Europameisterschaft und 2016 Kulturhauptstadt Europas sowie Verleihungsort des Europäischen Filmpreises.
ヴロツワフ(ポーランド語:  Wrocław[ヘルプ/ファイル]、ドイツ語: Breslau ブレスラウ、ハンガリー語: Boroszló ボロスロー)は、ポーランド西部にある第4の都市で、ドルヌィ・シロンスク県の県都。歴史的にシロンスク地方の中心都市で[1]、ポーランドの中でも最も古い都市のひとつである。市内にはオドラ川とその支流が流れ、200以上の橋が架かっている。
Wrocław[ヘルプ/ファイル]、ドイツ語: Breslau ブレスラウ、ハンガリー語: Boroszló ボロスロー)は、ポーランド西部にある第4の都市で、ドルヌィ・シロンスク県の県都。歴史的にシロンスク地方の中心都市で[1]、ポーランドの中でも最も古い都市のひとつである。市内にはオドラ川とその支流が流れ、200以上の橋が架かっている。
ヴロツワフは歴史上、様々な国(ポーランド王国、オーストリア帝国、ドイツ、ハンガリー、プロイセン、ボヘミア)の一部となっていたが、1945年(第二次世界大戦後)にポーランド領となった。
ヴロツワフは、UEFA欧州選手権2012 のホストである。2016年の欧州文化首都になることが決まっており[2]、またワールドゲームズ2017の開催地にも決定した。
Wrocław (Polish: [ˈvrɔt͡swaf] ( listen); German: Breslau [ˈbʁɛslaʊ]; Czech: Vratislav; Latin: Vratislavia) is a city in western Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly 350 kilometres (220 mi) from the Baltic Sea to the north and 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Sudeten Mountains to the south. The population of Wrocław in 2017 was 638,364, making it the fourth-largest city in Poland and the main city of Wrocław agglomeration.
listen); German: Breslau [ˈbʁɛslaʊ]; Czech: Vratislav; Latin: Vratislavia) is a city in western Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly 350 kilometres (220 mi) from the Baltic Sea to the north and 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Sudeten Mountains to the south. The population of Wrocław in 2017 was 638,364, making it the fourth-largest city in Poland and the main city of Wrocław agglomeration.
Wrocław is the historical capital of Silesia and Lower Silesia. Today, it is the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. The history of the city dates back over a thousand years, and its extensive heritage combines almost all religions and cultures of Europe.[2] At various times, it has been part of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Habsburg Monarchy, Kingdom of Prussia, German Empire, Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. Wrocław became part of Poland again in 1945, as a result of the border changes after the Second World War, which included a nearly complete exchange of population.
Wrocław is a university city with a student population of over 130,000, making it one of the most youthful cities in the country.[3] Since the beginning of the 20th century, the University of Wrocław, previously Breslau University, produced 9 Nobel Prize laureates[4] and is renowned for its high quality of teaching.[5]
Wrocław is classified as a Gamma- global city by GaWC.[6] It was placed among the top 100 cities in the world for the quality of life by the consulting company Mercer.[7]
The city hosted the Eucharistic Congress in 1997 and the Euro 2012 football championships. In 2016, the city was a European Capital of Culture and the World Book Capital. Also in this year, Wrocław hosted the Theatre Olympics, World Bridge Games and the European Film Awards. In 2017, the city was the host of the IFLA Annual Conference and the World Games.
Vratislavie1 ou localement Wrocław (prononcé [ˈvrɔt͡s.waf]Écouter ; en silésien : Brassel ; en allemand : Breslau) est la quatrième ville de Pologne par sa population (633 000 habitants), la cinquième par sa superficie (293 km2), et l'une des plus anciennement fondées (vers le IXe – Xe siècle). Aujourd’hui chef-lieu de la voïvodie de Basse-Silésie, elle est desservie par l’aéroport Nicolas Copernic de Wrocław, le cinquième plus important du pays en nombre de passagers.
Située au sud des « monts des Chats » (en polonais : Kocie Góry, et Wzgórza Trzebnickie), au nord des Sudètes, la ville est traversée par le fleuve Oder (en polonais : Odra), qui se divise ici en plusieurs bras, et quatre de ses affluents : la Bystrzyca, l’Oława, la Ślęza et la Widawa (en). Ces cours d'eau, avec les fosses municipales et les canaux d'évacuation qui s’y ajoutent, créent 12 îles et sont enjambés par plus de 120 ponts, ce qui vaut à Wrocław le surnom de « Venise polonaise » et Venise du Nord.
Vratislavie, capitale européenne de la culture 20161, après avoir été hôte de l'Euro 2012 de football, accueille les Prix du cinéma européen 2016 et Jeux mondiaux en 2017.
Breslavia (in polacco Wrocław[?·info] [ˈvrɔtswaf], in slesiano Wrocłow, in tedesco Breslau[1], in ceco Vratislav) è una città della Polonia di 640.000 abitanti, la quarta del paese per popolazione, capoluogo del voivodato della Bassa Slesia e capitale storica della Slesia. La città ha fatto parte del Regno di Prussia dal 1741 al 1918, in seguito della Repubblica di Weimar (dal 1919 al 1933) e dal 1933, della Germania nazista, che la controllerà fino al termine della seconda guerra mondiale, nel 1945.
Importante porto sul fiume Oder, sorge al centro di una ricca regione agricola. Sede di un'arcidiocesi, è il centro culturale ed economico della regione nonché polo importante nel settore della meccanica e dell'industria metallurgica. Dal 1945 al 1998 è stata capoluogo del Voivodato di Breslavia, oggi sostituito dal voivodato della Bassa Slesia. Breslavia è stata una delle città di UEFA EURO 2012. Nel 2016 è stata capitale europea della cultura e capitale mondiale del libro. Inoltre, ha ospitato i Giochi mondiali nel 2017.
Breslavia12 (en polaco, Wrocław  ˈvrɔt͡swaf (?·i), en alemán: Breslau; en checo: Vratislav; en latín: Vratislavia) es una ciudad con el estatus de distrito (o distrito urbano) situada en el voivodato de Baja Silesia, en el suroeste de Polonia, junto al río Óder y entre las colinas de Trzebnica y los Sudetes. En Breslavia, confluían dos importantes rutas comerciales: Vía Regia y Ruta del ámbar. La ciudad perteneció a la Liga Hanseática. En 2006 el Centro Centenario de Breslavia fue incluido en la lista de la Unesco del Patrimonio Mundial.
ˈvrɔt͡swaf (?·i), en alemán: Breslau; en checo: Vratislav; en latín: Vratislavia) es una ciudad con el estatus de distrito (o distrito urbano) situada en el voivodato de Baja Silesia, en el suroeste de Polonia, junto al río Óder y entre las colinas de Trzebnica y los Sudetes. En Breslavia, confluían dos importantes rutas comerciales: Vía Regia y Ruta del ámbar. La ciudad perteneció a la Liga Hanseática. En 2006 el Centro Centenario de Breslavia fue incluido en la lista de la Unesco del Patrimonio Mundial.
La población en 2011 era de 632 996 personas3 y es la principal ciudad de la región, aglomerando a más de un millón de habitantes en su área metropolitana además de ser la capital del voivodato de Baja Silesia.
Breslavia fue la sede de la Eurocopa 2012 y del Campeonato Mundial de Voleibol Masculino de 2014. Ha sido nombrada Capital Europea de la Cultura en 2016 junto con San Sebastián y ha sido sede de los Premios del Cine Europeo 2016 y Juegos Mundiales 2017.
Вро́цлав (польск. Wrocław [ˈvrɔt͡swaf]), старое русское название — Бреславль; нем. Бре́слау (нем. Breslau, сил. Wrocłow, сил.-нем. Brassel, лат. Vratislavia, Wratislavia) — столица Силезии, город на правах повята, один из самых крупных (четвёртый по населению в Польше после Варшавы, Кракова и Лодзи) и самых старых городов Польши, расположенный на обоих берегах среднего течения Одры, на Силезской низменности. Население — 634 404 чел. (по данным 2015 года)[1].






 Sport
Sport
 Animal world
Animal world

 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Financial
Financial
 Companies
Companies
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History


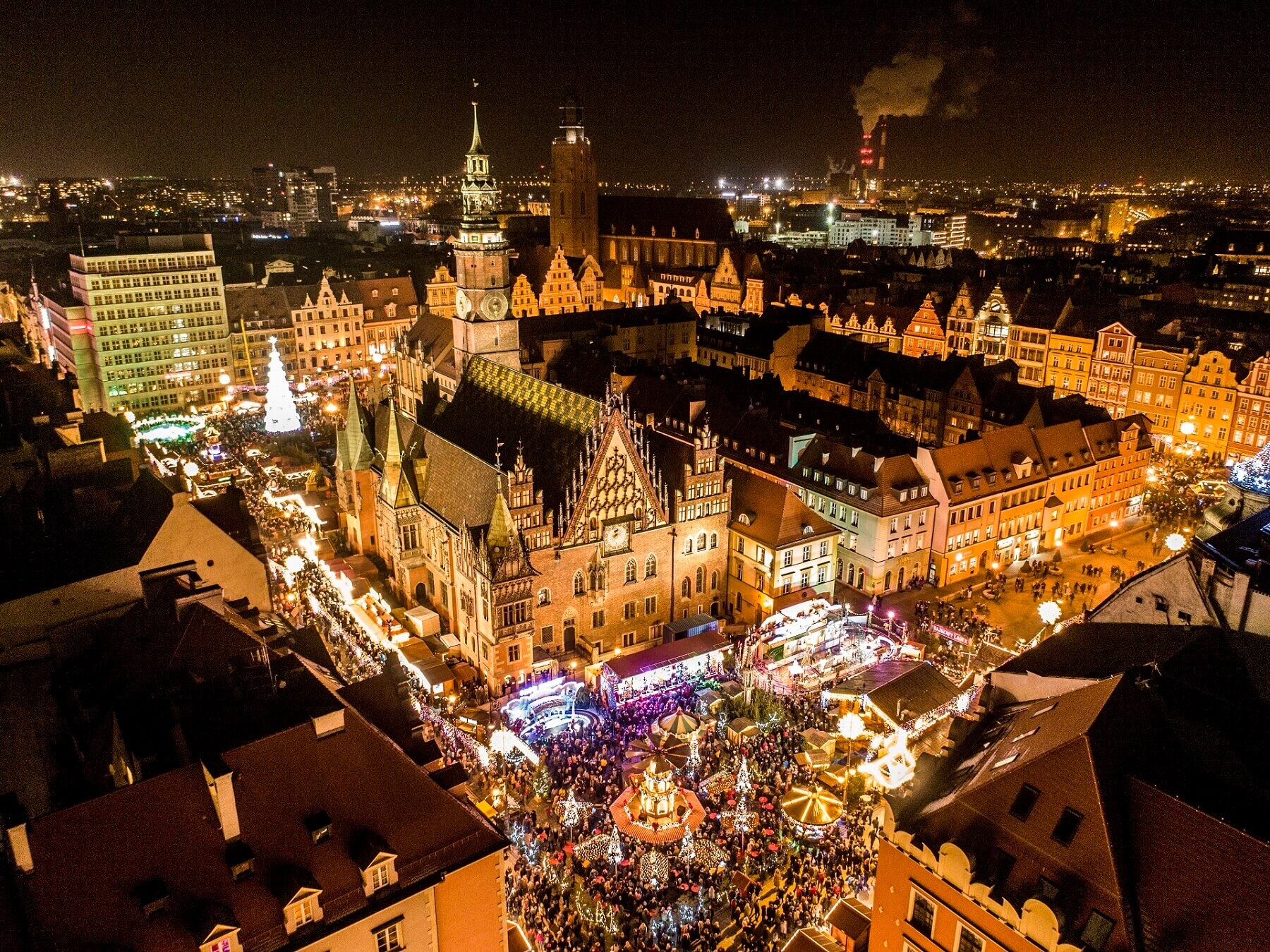
 Christmas Market
Christmas Market
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink